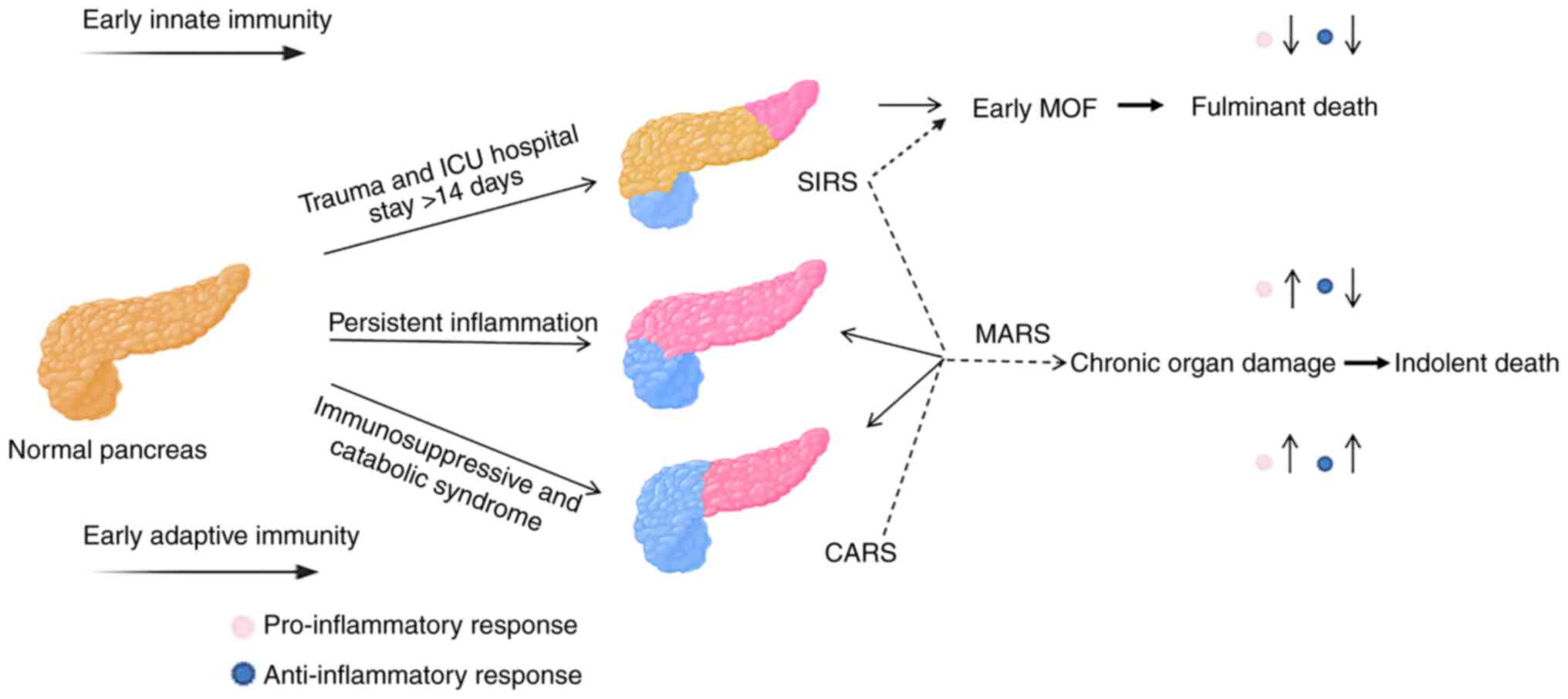
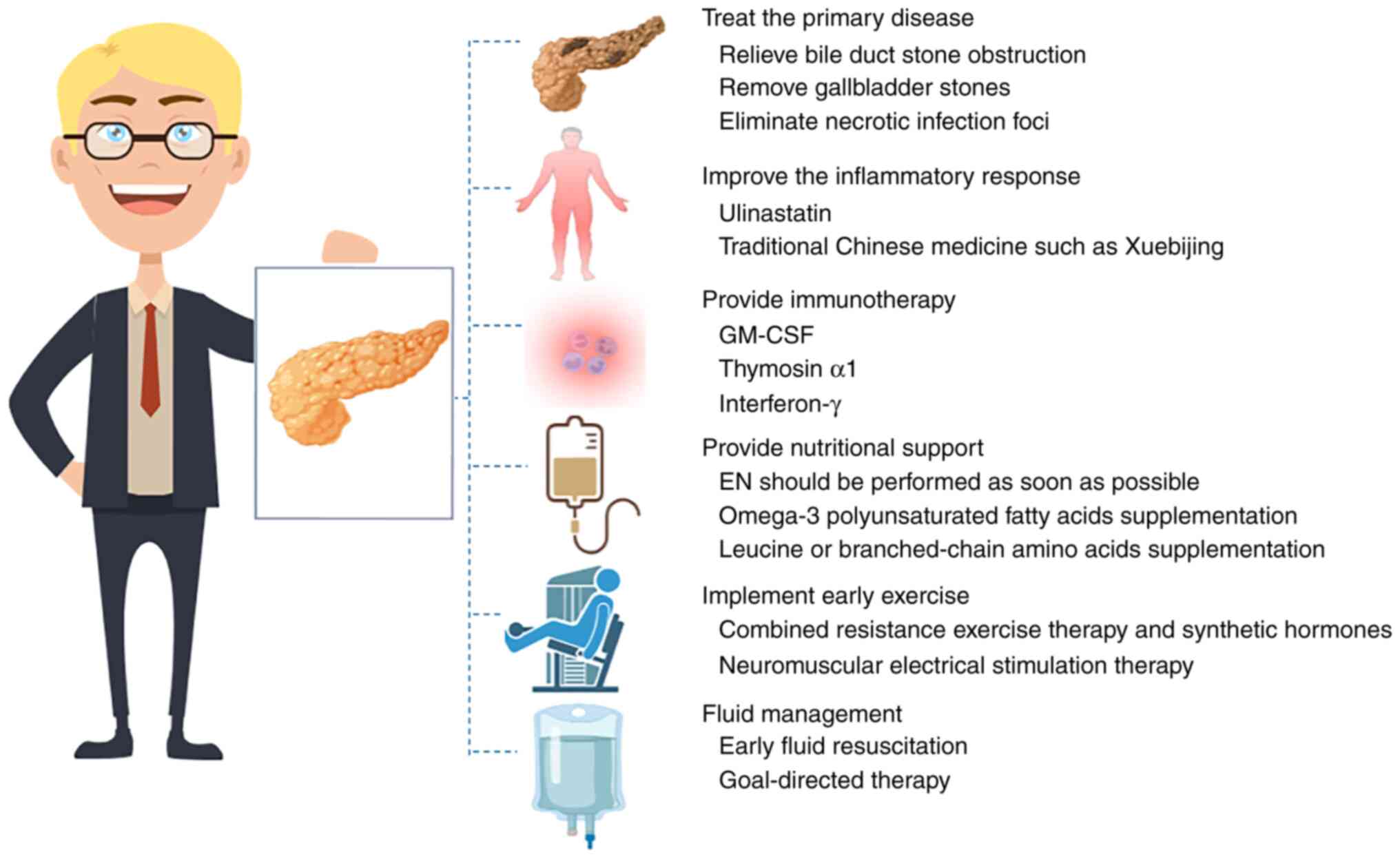
|
1
|
Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C, Gooszen
HG, Johnson CD, Sarr MG, Tsiotos GG and Vege SS: Acute Pancreatitis
Classification Working Group. Classification of acute
pancreatitis-2012: Revision of the Atlanta classification and
definitions by international consensus. Gut. 62:102–111.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wilkman E, Kaukonen KM, Pettila V,
Kuitunen A and Varpula M: Early hemodynamic variables and outcome
in severe acute pancreatitis: A retrospective single-center cohort
study. Pancreas. 42:272–278. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hawkins RB, Raymond SL, Stortz JA,
Horiguchi H, Brakenridge SC, Gardner A, Efron PA, Bihorac A, Segal
M, Moore FA and Moldawer LL: Chronic critical Illness and the
persistent inflammation, immunosuppression, and catabolism
Syndrome. Front Immunol. 9(1511)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Rosenthal MD and Moore FA: Persistent
inflammation, immunosuppression, and catabolism: Evolution of
multiple organ dysfunction. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 17:167–172.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Osuchowski MF, Craciun F, Weixelbaumer KM,
Duffy ER and Remick DG: Sepsis Chronically in MARS: Systemic
cytokine responses are always mixed regardless of the outcome,
magnitude, or phase of sepsis. J Immunol. 189:4648–4656.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Gentile LF, Cuenca AG, Efron PA, Ang D,
Bihorac A, McKinley BA, Moldawer LL and Moore FA: Persistent
inflammation and immunosuppression: A common syndrome and new
horizon for surgical intensive care. J Trauma Acute Care Surg.
72:1491–1501. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Rosenthal M, Gabrielli A and Moore F: The
evolution of nutritional support in long term ICU patients: From
multisystem organ failure to persistent inflammation
immunosuppression catabolism syndrome. Minerva Anestesiol.
82:84–96. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mira JC, Gentile LF, Mathias BJ, Efron PA,
Brakenridge SC, Mohr AM, Moore FA and Moldawer LL: Sepsis
pathophysiology, chronic critical Illness, and persistent
inflammation-immunosuppression and catabolism Syndrome. Crit Care
Med. 45:253–262. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Shepherd JM, Cole E and Brohi K:
Contemporary patterns of multiple organ dysfunction in trauma.
Shock. 47:429–435. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Moore FA, Phillips SM, McClain CJ, Patel
JJ and Martindale RG: Nutrition support for persistent
inflammation, immunosuppression, and catabolism Syndrome. Nutr Clin
Pract. 321 (1_suppl):121S–127S. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Mira JC, Brakenridge SC, Moldawer LL and
Moore FA: Persistent inflammation, immunosuppression and catabolism
Syndrome. Crit Care Clin. 33:245–258. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Oland GL and Hines OJ: New guidelines for
the treatment of severe acute pancreatitis. Hepatobiliary Surg
Nutr. 11:913–916. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Portelli M and Jones CD: Severe acute
pancreatitis: Pathogenesis, diagnosis and surgical management.
Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 16:155–159. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yang N, Li B, Ye B, Ke L, Chen F, Lu G,
Jiang F, Tong Z, Li J and Li W: The long-term quality of life in
patients with persistent inflammation-immunosuppression and
catabolism syndrome after severe acute pancreatitis: A
retrospective cohort study. J Crit Care. 42:101–106.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Koksal AR, Boga S, Alkim H, Sen I,
Neijmann ST and Alkim C: Chemerin: A new biomarker to predict
postendoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis.
Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 28:714–721. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Li J, Yang J, Huang J, Jiang DL, Zhang F,
Liu MF, Qiang Y and Gu YL: Immunosuppression and the infection
caused by gut mucosal barrier dysfunction in patients with early
severe acute pancreatitis. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 18:892–900.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Glaubitz J, Wilden A, Frost F, Ameling S,
Homuth G, Mazloum H, Rühlemann MC, Bang C, Aghdassi AA, Budde C, et
al: Activated regulatory T-cells promote duodenal bacterial
translocation into necrotic areas in severe acute pancreatitis.
Gut. 72:1355–1369. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Glaubitz J, Wilden A, van den Brandt C,
Weiss FU, Bröker BM, Mayerle J, Lerch MM and Sendler M:
Experimental pancreatitis is characterized by rapid T cell
activation, Th2 differentiation that parallels disease severity,
and improvement after CD4+ T cell depletion.
Pancreatology. 20:1637–1647. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Joshi I, Carney WP and Rock EP: Utility of
monocyte HLA-DR and rationale for therapeutic GM-CSF in sepsis
immunoparalysis. Front Immunol. 14(1130214)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wen W, Zheng H, Jiang Y, Huang L, Li D,
Zhang J and Zhang D: Effect of intestinal epithelial autophagy on
bacterial translocation in severe acute pancreatitis. Clin Res
Hepatol Gastroenterol. 41:703–710. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Liu J, Huang L, Luo M and Xia X: Bacterial
translocation in acute pancreatitis. Crit Rev Microbiol.
45:539–547. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Efron PA, Mohr AM, Bihorac A, Horiguchi H,
Hollen MK, Segal MS, Baker HV, Leeuwenburgh C, Moldawer LL, Moore
FA and Brakenridge SC: Persistent inflammation, immunosuppression,
and catabolism and the development of chronic critical illness
after surgery. Surgery. 164:178–184. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Fattahi F and Ward PA: Understanding
immunosuppression after sepsis. Immunity. 47:3–5. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Horiguchi H, Loftus TJ, Hawkins RB,
Raymond SL, Stortz JA, Hollen MK, Weiss BP, Miller ES, Bihorac A,
Larson SD, et al: Innate immunity in the persistent inflammation,
immunosuppression, and catabolism Syndrome and its implications for
therapy. Front Immunol. 9(595)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Veglia F, Perego M and Gabrilovich D:
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells coming of age. Nat Immunol.
19:108–119. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Haimovich B, Zhang Z, Calvano JE, Calvano
SE, Kumar A, Macor MA, Corbett S, Coyle SM and Lowry SF: Cellular
metabolic regulators: Novel indicators of low-grade inflammation in
humans. Ann Surg. 259:999–1006. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Eyenga P, Roussel D, Morel J, Rey B,
Romestaing C, Gueguen-Chaignon V, Sheu SS and Viale JP: Time course
of liver mitochondrial function and intrinsic changes in oxidative
phosphorylation in a rat model of sepsis. Intensive Care Med Exp.
6(31)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Asehnoune K, Hotchkiss RS and Monneret G:
Understanding why clinicians should care about danger-associated
molecular patterns. Intensive Care Med. 42:611–614. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhao H, Kilgas S, Alam A, Eguchi S and Ma
D: The role of extracellular adenosine triphosphate in ischemic
organ injury. Crit Care Med. 44:1000–1012. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kugelberg E: Immunometabolism: Complex
metabolic responses to microbial stimuli. Nat Rev Immunol.
17:78–79. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Cheng SC, Scicluna BP, Arts RJ, Gresnigt
MS, Lachmandas E, Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ, Kox M, Manjeri GR,
Wagenaars JA, Cremer OL, et al: Broad defects in the energy
metabolism of leukocytes underlie immunoparalysis in sepsis. Nat
Immunol. 17:406–413. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kau AL, Ahern PP, Griffin NW, Goodman AL
and Gordon JI: Human nutrition, the gut microbiome and the immune
system. Nature. 474:327–336. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Li WQ, Tong ZH, Quan ZF, Zhao RZ, Yu WK,
Ye XH, Wang ZM, Wang XY, Wang ZQ, Ji DX, et al: Treatment
experience of severe acute pancreatitis on 1033 cases. Zhonghua Wai
Ke Za Zhi. 47:1472–1482. 2009.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
34
|
Kim YJ, Kim DB, Chung WC, Lee JM, Youn GJ,
Jung YD, Choi S and Oh JH: Analysis of factors influencing survival
in patients with severe acute pancreatitis. Scand J Gastroenterol.
52:904–908. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Vanzant EL, Lopez CM, Ozrazgat-Baslanti T,
Ungaro R, Davis R, Cuenca AG, Gentile LF, Nacionales DC, Cuenca AL,
Bihorac A, et al: Persistent inflammation, immunosuppression, and
catabolism syndrome after severe blunt trauma. J Trauma Acute Care
Surg. 76:21–29; discussion 29-30. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Sadighi Akha AA: Aging and the immune
system: An overview. J Immunol Methods. 463:21–26. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Leppaniemi A, Tolonen M, Tarasconi A,
Segovia-Lohse H, Gamberini E, Kirkpatrick AW, Ball CG, Parry N,
Sartelli M, Wolbrink D, et al: 2019 WSES guidelines for the
management of severe acute pancreatitis. World J Emerg Surg.
14(27)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Lane-Fall MB, Kuza CM, Fakhry S and Kaplan
LJ: The lifetime effects of injury: Postintensive care syndrome and
posttraumatic stress disorder. Anesthesiol Clin. 37:135–150.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Nakamura K, Ogura K, Nakano H, Naraba H,
Takahashi Y, Sonoo T, Hashimoto H and Morimura N: C-reactive
protein clustering to clarify persistent inflammation,
immunosuppression and catabolism syndrome. Intensive Care Med.
46:437–443. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Hu D, Ren J, Wang G, Gu G, Chen J, Zhou B,
Liu S, Wu X and Li J: Persistent inflammation-immunosuppression
catabolism syndrome, a common manifestation of patients with
enterocutaneous fistula in intensive care unit. J Trauma Acute Care
Surg. 76:725–729. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Ding RY and Ma XC: Persistent inflammatory
response-immunosuppressed catabolic syndrome: A special type of
chronic severe disease. Chin J Gastrointestinal Surgery.
19:734–736. 2016.(In Chinese).
|
|
42
|
Whitfield JB: Genetics and molecular
biology in laboratory medicine, 1963-2013. Clin Chem Lab Med.
51:113–117. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Lai Y, Feldman KL and Clark RS:
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs). Crit Care Med. 33 (12
Suppl):S433–S434. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Manohar SM, Shah P and Nair A: Flow
cytometry: Principles, applications and recent advances.
Bioanalysis. 13:181–198. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Xu D and Xun J: Research progress of
severe acute pancreatitis with persistent
inflammatory-immunosuppressive-catabolic syndrome. Chin J Practical
Diagnosis and Therapy. 32:725–728. 2018.(In Chinese).
|
|
46
|
Antonini F, De Minicis S, Macarri G and
Pezzilli R: . Are we ready for early discharge of patients with
mild non-alcoholic acute interstitial pancreatitis? Pancreatology.
16:322–3. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Subbe CP, Kruger M, Rutherford P and
Gemmel L: Validation of a modified Early Warning Score in medical
admissions. QJM. 94:521–526. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Alaa AM, Yoon J, Hu S and van der Schaar
M: Personalized risk scoring for critical care prognosis using
mixtures of gaussian processes. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 65:207–218.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Kramer AA, Sebat F and Lissauer M: A
review of early warning systems for prompt detection of patients at
risk for clinical decline. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 87 (1S Suppl
1):S67–S73. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Wolbrink DRJ, Kolwijck E, Ten Oever J,
Horvath KD, Bouwense SAW and Schouten JA: Management of infected
pancreatic necrosis in the intensive care unit: A narrative review.
Clin Microbiol Infect. 26:18–25. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Karjula H, Nordblad Schmidt P, Makela J,
Liisanantti JH, Ohtonen P and Saarela A: Prophylactic pancreatic
duct stenting in severe acute necrotizing pancreatitis: A
prospective randomized study. Endoscopy. 51:1027–1034.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Su HY, Mo ZX, Chen Z, et al: Severe immune
imbalance in ICU: persistent
inflammatory-immunosuppressive-catabolic syndrome. Chin Critical
Care Emerg Med. 29:760–764. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
53
|
Wang X, Zhuang X, Wei R, Wang C, Xue X and
Mao L: Protective effects of Acanthopanax vs. Ulinastatin against
severe acute pancreatitis-induced brain injury in rats. Int
Immunopharmacol. 24:285–298. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Pan Y, Fang H, Lu F, Pan M, Chen F, Xiong
P, Yao Y and Huang H: Ulinastatin ameliorates tissue damage of
severe acute pancreatitis through modulating regulatory T cells. J
Inflamm (Lond). 14(7)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Zhu F, Yin S, Zhou L, Li Z, Yan H, Zhong
Y, Wu X, Luo B, Yang L, Gan D, et al: Chinese herbal medicine
xuebijing injection for acute pancreatitis: An overview of
systematic reviews. Front Pharmacol. 13(883729)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Li C, Wang P, Zhang L, Li M, Lei X, Liu S,
Feng Z, Yao Y, Chang B, Liu B and Shang H: Efficacy and safety of
Xuebijing injection (a Chinese patent) for sepsis: A meta-analysis
of randomized controlled trials. J Ethnopharmacol. 224:512–521.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Munir F, Jamshed MB, Shahid N, Hussain HM,
Muhammad SA, Mamun AA and Zhang Q: . Advances in immunomodulatory
therapy for severe acute pancreatitis. Immunol Letters. 217:72–76.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Hotchkiss RS, Monneret G and Payen D:
Immunosuppression in sepsis: A novel understanding of the disorder
and a new Therapeutic approach. Lancet Infect Dis. 13:260–268.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Wan J, Shan Y, Shan H, Li G, Wang T, Guan
J, Liu X, Chen D, Li W and Lin Z: Thymosin-alpha1 promotes the
apoptosis of regulatory T cells and survival rate in septic mice.
Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 16:3004–3013. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Hamilton JA: GM-CSF in inflammation. J Exp
Med. 217(e20190945)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Lee KMC, Achuthan AA and Hamilton JA:
GM-CSF: A promising target in inflammation and autoimmunity.
Immunotargets Ther. 9:225–240. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Fu XZ and Wang Y: Interferon-gamma
regulates immunosuppression in septic mice by promoting the Warburg
effect through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Mol Med.
29(95)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Hu Y, Xiong W, Li C and Cui Y: Continuous
blood purification for severe acute pancreatitis: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore).
98(e14873)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Gong D, Zhang P, Ji D, Chen Z, Li W, Li J,
Li L and Liu Z: Improvement of immune dysfunction in patients with
severe acute pancreatitis by high-volume hemofiltration: A
preliminary report. Int J Artif Organs. 33:22–29. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Clark E, Molnar AO, Joannes-Boyau O,
Honoré PM, Sikora L and Bagshaw SM: High-volume hemofiltration for
septic acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Crit Care. 18(R7)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Almeida BM, Moreno DH, Vasconcelos V and
Cacione DG: Interventions for treating catheter-related bloodstream
infections in people receiving maintenance haemodialysis. Cochrane
Database Syst Rev. 4(CD013554)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Gorski LA, Hadaway L, Hagle ME, Broadhurst
D, Clare S, Kleidon T, Meyer BM, Nickel B, Rowley S, Sharpe E and
Alexander M: Infusion therapy standards of practice, 8th Edition. J
Infus Nurs. 44 (1S Suppl 1):S1–224. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Legrand M and Tolwani A: Anticoagulation
strategies in continuous renal replacement therapy. Semin Dial.
34:416–422. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Lubbers T, Kox M, de Haan JJ, Greve JW,
Pompe JC, Ramakers BP, Pickkers P and Buurman WA: Continuous
administration of enteral lipid- and protein-rich nutrition limits
inflammation in a human endotoxemia model. Crit Care Med.
41:1258–1265. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Plauth M, Bernal W, Dasarathy S, Merli M,
Plank LD, Schütz T and Bischoff SC: ESPEN guideline on clinical
nutrition in liver disease. Clin Nutr. 38:485–521. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Wang CY, Huang CT, Chen CH, Chen MF, Ching
SL and Huang YC: Optimal energy delivery, rather than the
implementation of a feeding protocol, may benefit clinical outcomes
in critically Ill patients. Nutrients. 9(527)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
McClave SA, Taylor BE, Martindale RG,
Warren MM, Johnson DR, Braunschweig C, McCarthy MS, Davanos E, Rice
TW, Cresci GA, et al: Guidelines for the provision and assessment
of nutrition support therapy in the adult critically ill patient:
Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM) and American Society for
Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (A.S.P.E.N.). JPEN J Parenter
Enteral Nutr. 40:159–211. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Bozzetti F, Arends J, Lundholm K,
Micklewright A, Zurcher G and Muscaritoli M: ESPEN. ESPEN
guidelines on parenteral nutrition: Non-surgical oncology. Clin
Nutr. 28:445–454. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Wolfe RR: Perspective: Optimal protein
intake in the elderly. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 14:65–66.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Lu C, Sharma S, McIntyre L, Rhodes A,
Evans L, Almenawer S, Leduc L, Angus DC and Alhazzani W: Omega-3
supplementation in patients with sepsis: A systematic review and
meta-analysis of randomized trials. Ann Intensive Care.
7(58)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Wang M, Veeraperumal S, Zhong S and Cheong
KL: Fucoidan-Derived functional oligosaccharides: Recent
developments, preparation, and potential applications. Foods.
12(878)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Lin J, Lv C, Wu C, Zhang H, Liu Z, Ke L,
Li G, Tong Z, Tu J, et al: Incidence and risk factors of
nasogastric feeding intolerance in moderately-severe to severe
acute pancreatitis. BMC Gastroenterol. 22(327)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Sun JK, Li WQ, Ke L, Tong ZH, Ni HB, Li G,
Zhang LY, Nie Y, Wang XY, et al: Early enteral nutrition prevents
intra-abdominal hypertension and reduces the severity of severe
acute pancreatitis compared with delayed enteral nutrition: a
prospective pilot study. World J Surg. 37:2053–2060.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Heyland DK, Ortiz A, Stoppe C, Patel JJ,
Yeh DD, Dukes G, Chen YJ, Almansa C and Day AG: Incidence, risk
factors, and clinical consequence of enteral feeding intolerance in
the mechanically ventilated critically Ill: An analysis of a
multicenter, multiyear database. Crit Care Med. 49:49–59.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Gungabissoon U, Hacquoil K, Bains C,
Irizarry M, Dukes G, Williamson R, Deane AM and Heyland DK:
Prevalence, risk factors, clinical consequences, and treatment of
enteral feed intolerance during critical illness. JPEN J Parenter
Enteral Nutr. 39:441–448. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Wischmeyer PE, Puthucheary Z, San Millán
I, Butz D and Grocott MPW: Muscle mass and physical recovery in
ICU: Innovations for targeting of nutrition and exercise. Curr Opin
Crit Care. 23:269–278. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Fuke R, Hifumi T, Kondo Y, Hatakeyama J,
Takei T, Yamakawa K, Inoue S and Nishida O: Early rehabilitation to
prevent postintensive care syndrome in patients with critical
illness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open.
8(e019998)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Patel BK, Pohlman AS, Hall JB and Kress
JP: Impact of early mobilization on glycemic control and
ICU-acquired weakness in critically ill patients who are
mechanically ventilated. Chest. 146:583–589. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Wang CH, Qin JM and Ben YL: Effect of
early rehabilitation training on ICU acquired myasthenia in
patients with mechanical ventilation. Chin Nurs Manag. 19:457–461.
2019.(In Chinese).
|
|
85
|
Maffiuletti NA, Roig M, Karatzanos E and
Nanas S: Neuromuscular electrical stimulation for preventing
skeletal-muscle weakness and wasting in critically ill patients: A
systematic review. BMC Med. 11(137)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Dirks ML, Hansen D, Van Assche A, Dendale
P and Van Loon LJ: Neuromuscular electrical stimulation prevents
muscle wasting in critically ill comatose patients. Clin Sci
(Lond). 128:357–365. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Yang YJ, Liu GY, Li RY and Liu H: Research
progress of inspiratory muscle training in ICU patients with
mechanical ventilation. Chin Nurs Manag. 20:1436–1440. 2020.(In
Chinese).
|
|
88
|
Page VJ and McAuley DF: Sedation/drugs
used in intensive care sedation. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol.
28:139–144. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Tenner S, Baillie J, DeWitt J and Vege SS:
American College of Gastroenterology. American College of
Gastroenterology guideline: Management of acute pancreatitis. Am J
Gastroenterol. 108:1400–1415, 1416. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Working Group IAP/APA Acute Pancreatitis
Guidelines. IAP/APA evidence-based guidelines for the management of
acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 13 (4 Suppl 2):e1–e15.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Zhu Y, Cui Y, Zhang YC, Miao HJ, Wang F,
Chen RX and Rong QF: Efficacy of continuous blood purification in
treatment of severe acute pancreatitis in children. Zhonghua Er Ke
Za Zhi. 55:338–342. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
92
|
Crockett SD, Wani S, Gardner TB,
Falck-Ytter Y and Barkun AN: American Gastroenterological
Association Institute Clinical Guidelines Committee. American
gastroenterological association institute guideline on initial
management of acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 154:1096–1101.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Mouncey PR, Osborn TM, Power GS, Harrison
DA, Sadique MZ, Grieve RD, Jahan R, Harvey SE, Bell D, Bion JF, et
al: Trial of early, goal-directed resuscitation for septic shock. N
Engl J Med. 372:1301–1311. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Cooper ES and Silverstein DC: Fluid
therapy and the microcirculation in health and critical Illness.
Front Vet Sci. 8(625708)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Kara A, Akin S and Ince C: Monitoring
microcirculation in critical illness. Curr Opin Crit Care.
22:444–452. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
De-Madaria E, Herrera-Marante I,
Gonzalez-Camacho V, Bonjoch L, Quesada-Vázquez N, Almenta-Saavedra
I, Miralles-Maciá C, Acevedo-Piedra NG, Roger-Ibáñez M,
Sánchez-Marin C, et al: Fluid resuscitation with lactated Ringer's
solution vs. normal saline in acute pancreatitis: A triple-blind,
randomized, controlled trial. United European Gastroenterol J.
6:63–72. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Cordemans C, De Laet I, Van Regenmortel N,
Schoonheydt K, Dits H, Huber W and Malbrain ML: Fluid management in
critically ill patients: The role of extravascular lung water,
abdominal hypertension, capillary leak, and fluid balance. Ann
Intensive Care. 2 (Suppl 1 Diagnosis and management of
intra-abdominal hyperten)(S1)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|