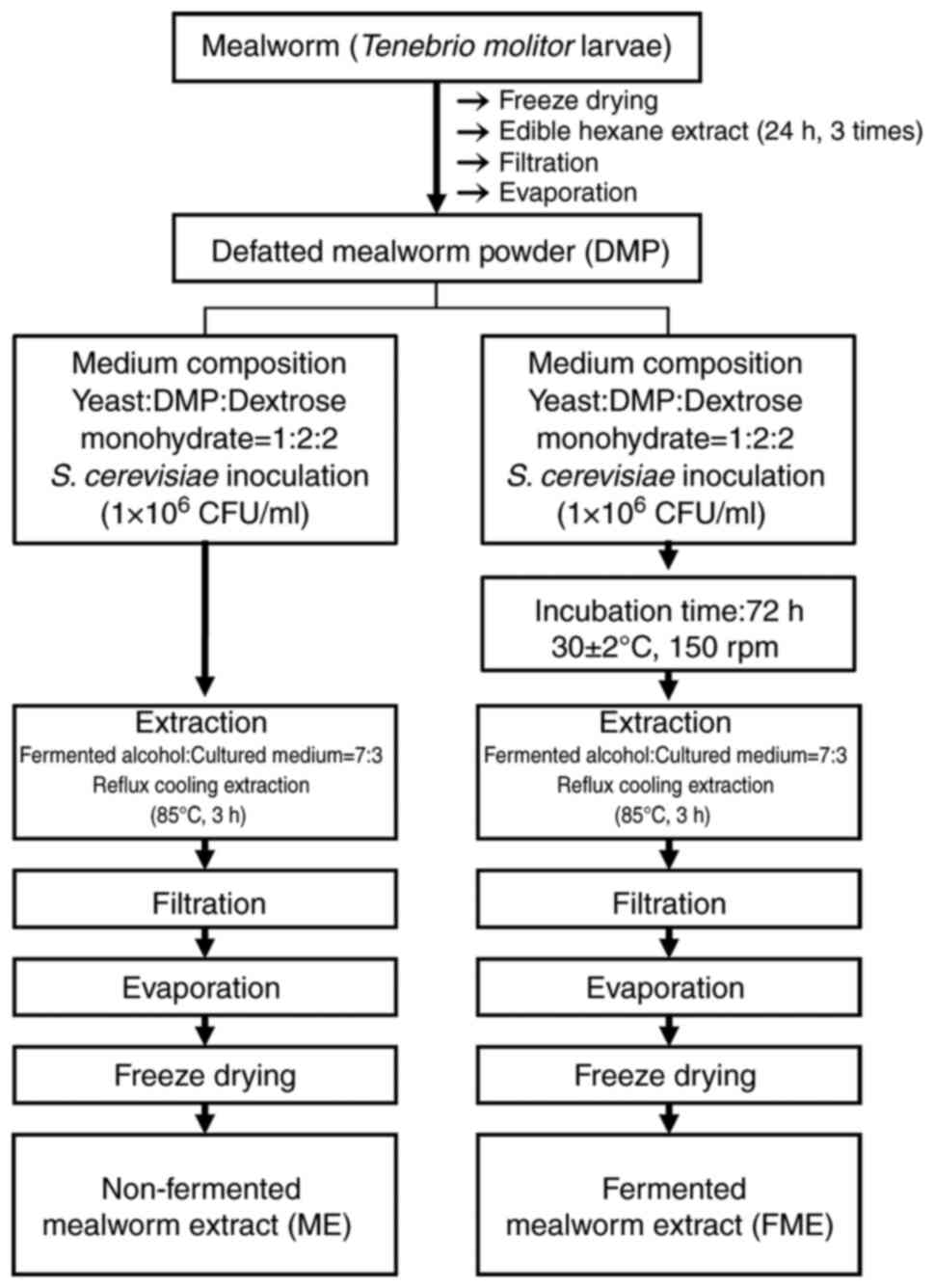
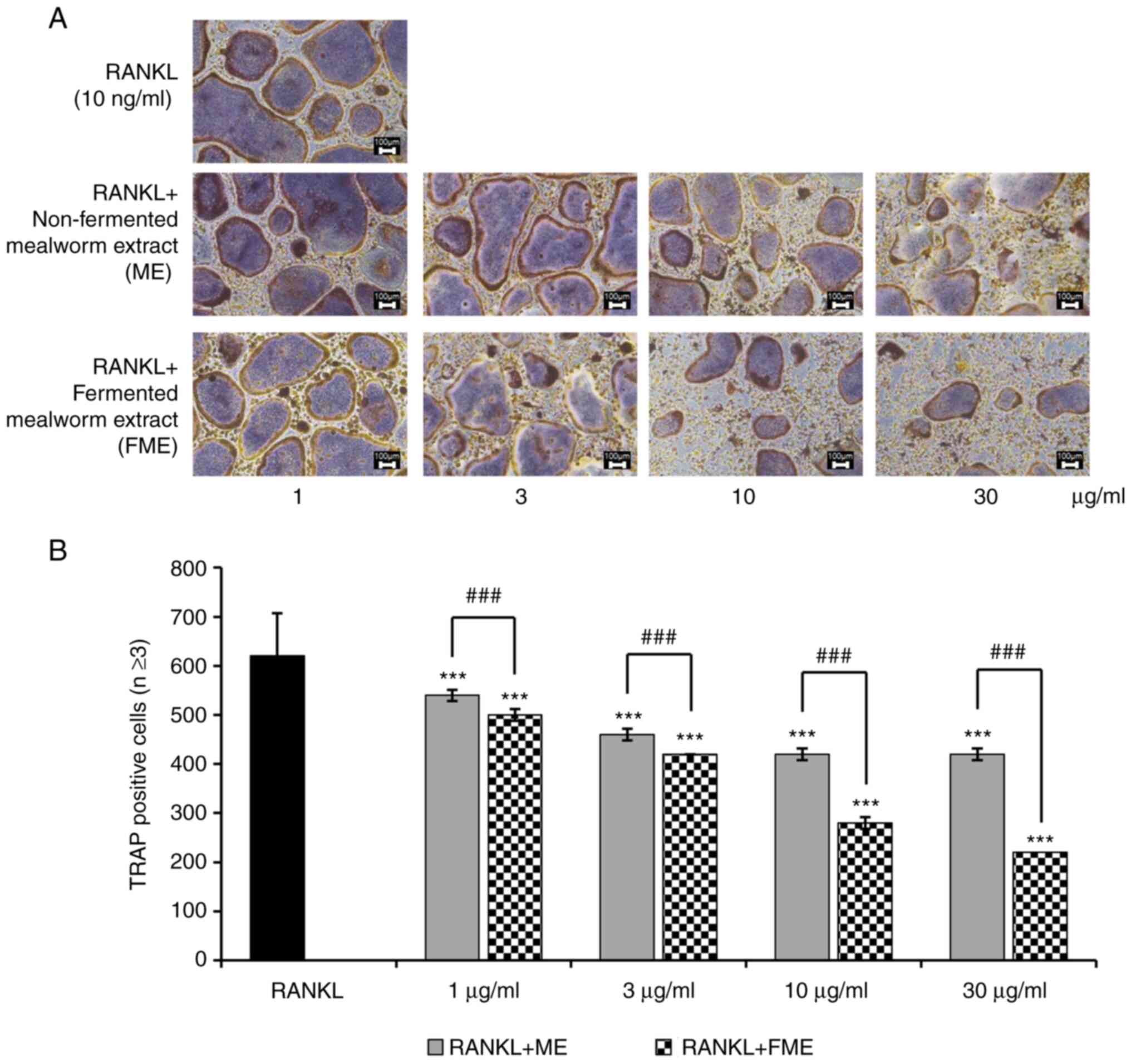
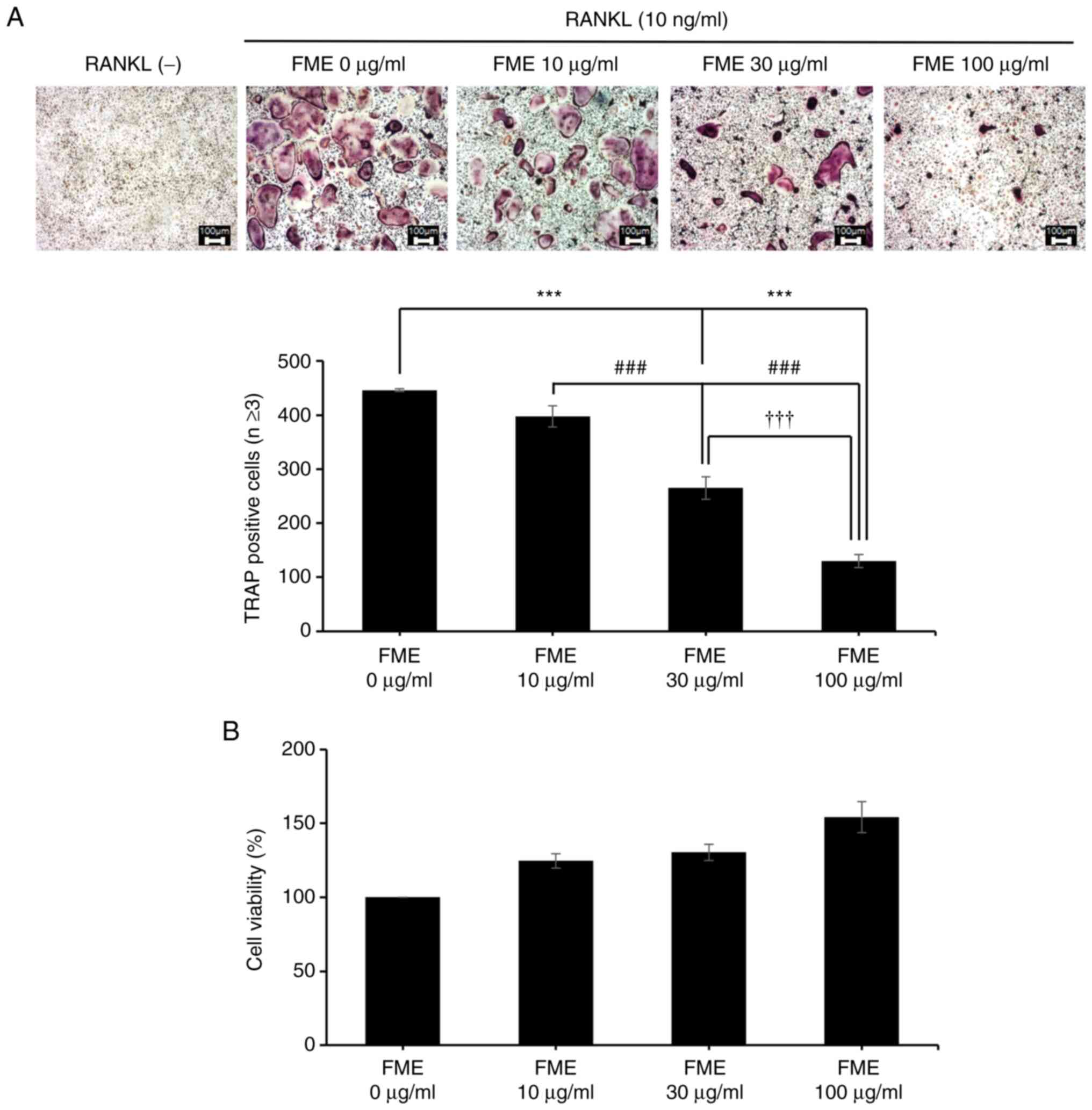
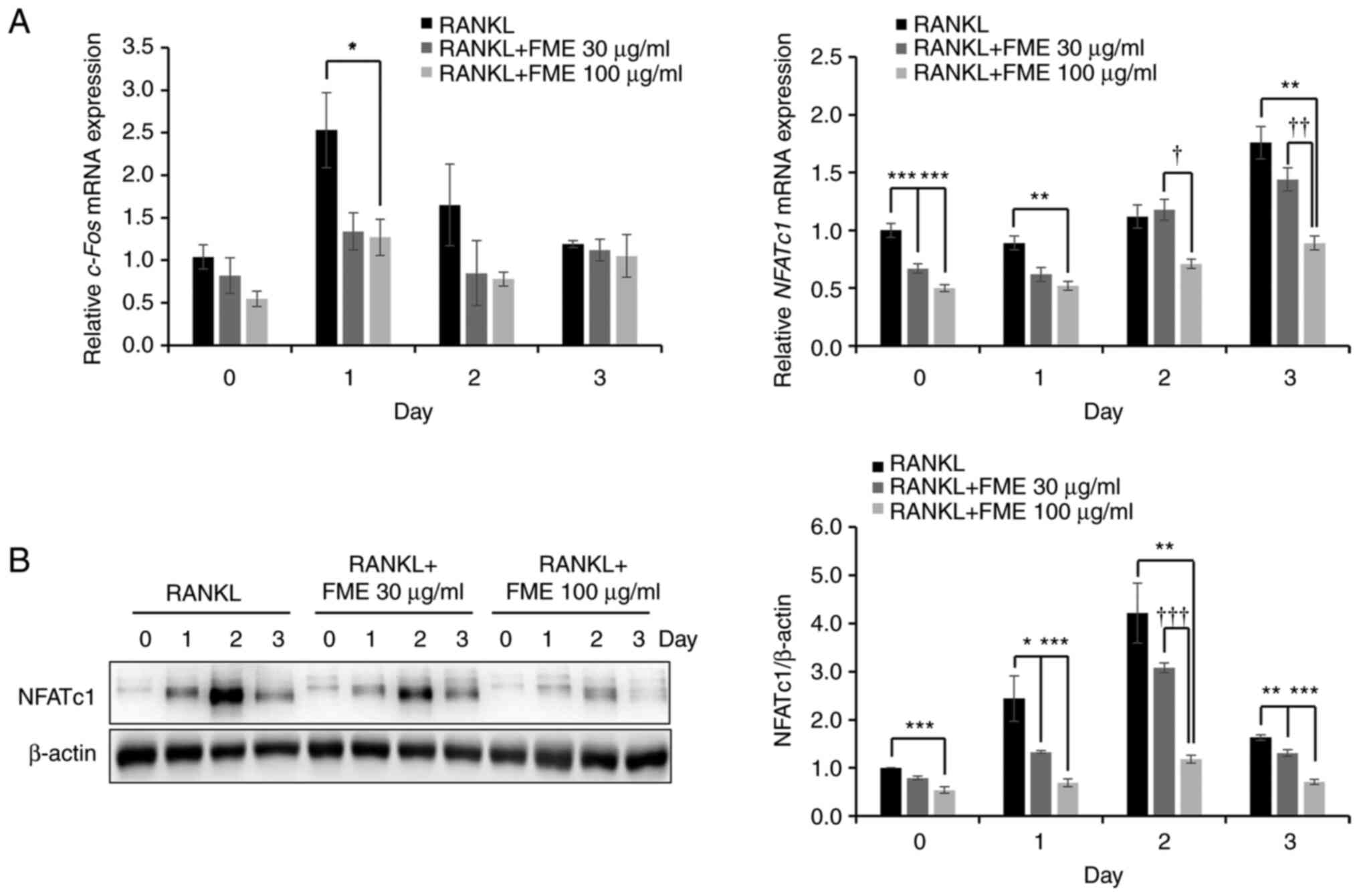
|
1
|
Baron R and Kneissel M: WNT signaling in
bone homeostasis and disease: From human mutations to treatments.
Nat Med. 19:179–192. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Salari N, Ghasemi H, Mohammadi L, Behzadi
MH, Rabieenia E, Shohaimi S and Mohammadi M: The global prevalence
of osteoporosis in the world: A comprehensive systematic review and
meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 16(609)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Chen X, Wang C, Qiu H, Yuan Y, Chen K, Cao
Z, Xiang Tan R, Tickner J, Xu J and Zou J: Asperpyrone A attenuates
RANKL-induced osteoclast formation through inhibiting NFATc1,
Ca2+ signalling and oxidative stress. J Cell Mol Med.
23:8269–8279. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
He J, Chen K, Deng T, Xie J, Zhong K, Yuan
J, Wang Z, Xiao Z, Gu R, Chen D, et al: Inhibitory effects of
rhaponticin on osteoclast formation and resorption by targeting
RANKL-induced NFATc1 and ROS activity. Front Pharmacol.
12(645140)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Tu KN, Lie JD, Wan CKV, Cameron M, Austel
AG, Nguyen JK, Van K and Hyun D: Osteoporosis: A review of
treatment options. P T. 43:92–104. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee Y, Lee HJ, Shin HB, Ham JR, Lee MK,
Lee MJ and Son YJ: Triphenyl hexene, an active substance of Betaone
barley water extract, inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast
differentiation and LPS-induced osteoporosis. J Funct Foods.
92(105037)2022.
|
|
7
|
Ham JR, Choi RY, Yee ST, Hwang YH, Kim MJ
and Lee MK: Methoxsalen supplementation attenuates bone loss and
inflammatory response in ovariectomized mice. Chem Biol Interact.
278:135–140. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hong J, Han T and Kim YY: Mealworm
(Tenebrio molitor larvae) as an alternative protein source
for monogastric animal: A review. Animals (Basel).
10(2068)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Veldkamp T and Bosch G: Insects: A
protein-rich feed ingredient in pig and poultry diets. Anim Front.
5:45–50. 2015.
|
|
10
|
Seo M, Goo T, Chung MY, Baek M, Hwang J,
Kim M and Yun E: Tenebrio molitor larvae inhibit
adipogenesis through AMPK and MAPKs signaling in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
and obesity in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Int J Mol Sci.
18(518)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kim SY, Park JE and Han JS: Tenebrio
molitor (mealworm) extract improves insulin sensitivity and
alleviates hyperglycemia in C57BL/Ksj-db/db mice. Kor J Life Sci.
29:570–579. 2019.
|
|
12
|
Baek M, Kim M, Kwon Y, Hwang J, Goo T, Jun
M and Yun E: Effects of processing methods on nutritional
composition and antioxidant activity of mealworm (Tenebrio
molitor) larvae. Entomol Res. 49:284–293. 2019.
|
|
13
|
Ham JR, Choi RY, Lee Y and Lee MK: Effects
of edible insect Tenebrio molitor larva fermentation extract
as a substitute protein on hepatosteatogenesis and proteomic
changes in obese mice induced by high-fat diet. Int J Mol Sci.
22(3615)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Choi RY, Ham JR, Ryu HS, Lee SS, Michelle
AM, Paik MJ, Ji M, Park KW, Kang KY, Lee HI, et al: Defatted
Tenebrio molitor larva fermentation extract modifies
steatosis, inflammation and intestinal microflora in chronic
alcohol-fed rats. Nutrients. 12(1426)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Turkyilmaz A, Lee Y and Lee MK: Fermented
extract of mealworm (Tenebrio molitor larvae) as a dietary
protein source modulates hepatic proteomic profiles in
C57BLKS/J-db/db mice. J Insects Food Feed. 9:1199–1210. 2023.
|
|
16
|
Cui Z, Feng H, He B, He J and Tian Y:
Relationship between serum amino acid levels and bone mineral
density: A mendelian randomization study. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 12(763538)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhang X, Goncalves R and Mosser DM: The
isolation and characterization of murine macrophages. Curr Protoc
Immunol Chapter. 14:14.1.1–14.1.14. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Huang S, Xu L, Sun Y, Wu T, Wang K and Li
G: An improved protocol for isolation and culture of mesenchymal
stem cells from mouse bone marrow. J Orthop Transl. 3:26–33.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kim HJ, Kang WY, Seong SJ, Kim SY, Lim MS
and Yoon YR: Follistatin-like 1 promotes osteoclast formation via
RANKL-mediated NF-κB activation and M-CSF-induced precursor
proliferation. Cell Signal. 28:1137–1144. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kim KJ, Lee Y, Son SR, Lee H, Son YJ, Lee
MK and Lee M: Water extracts of hull-less waxy barley (Hordeum
vulgare L.) cultivar ‘Boseokchal’ inhibit RANKL-induced
osteoclastogenesis. Molecules. 24(3735)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Jeong DH, Kwak SC, Lee MS, Yoon KH, Kim JY
and Lee CH: Betulinic acid inhibits RANKL-induced
osteoclastogenesis via attenuating Akt, NF-κB, and
PLCγ2-Ca2+ signaling and prevents inflammatory bone
loss. J Nat Prod. 83:1174–1182. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Park GD, Cheon YH, Eun SY, Lee CH, Lee MS,
Kim JY and Cho HJ: β-Boswellic acid inhibits RANKL-induced
osteoclast differentiation and function by attenuating NF-κB and
PLCγ2 signaling pathways. Molecules. 26(2665)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Nam HH, Lee AY, Seo YS, Park I, Yang S,
Chun JM, Moon BC, Song JH and Kim JS: Three Scrophularia
species (Scrophularia buergeriana, S. koreaiensis,
and S. takesimensis) inhibit RANKL-induced osteoclast
differentiation in bone marrow-derived macrophages. Plants (Basel).
9(1656)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Stephens AS, Stephens SR and Morrison NA:
Internal control genes for quantitative RT-PCR expression analysis
in mouse osteoblasts, osteoclasts and macrophages. BMC Res Notes.
4(410)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zeng Xz, He L, Wang S, Wang K, Zhang YY,
Tao L, Li XJ and Liu SW: Aconine inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast
differentiation in RAW264.7 cells by suppressing NF-κB and NFATc1
activation and DC-STAMP expression. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 37:255–263.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Negishi-Koga T and Takayanagi H:
Ca2+-NFATc1 signaling is an essential axis of osteoclast
differentiation. Immunol Rev. 231:241–256. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wang J, Guan H, Liu H, Lei Z, Kang H, Guo
Q, Dong Y, Liu H, Sun Y, Fang Z and Li F: Inhibition of PFKFB3
suppresses osteoclastogenesis and prevents ovariectomy-induced bone
loss. J Cell Mol Med. 24:2294–2307. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhou Z, Immel D, Xi CX, Bierhaus A, Feng
X, Mei L, Naworth P, Stern DM and Xiong WC: Regulation of
osteoclase function and bone mass by RAGE. J Exp Med.
203:1067–1080. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Jin H, Yao L, Chen K, Liu Y, Wang Q, Wang
Z, Liu Q, Cao Z, Kenny J, Tickner J, et al: Evodiamine inhibits
RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and prevents ovariectomy-induced
bone loss in mice. J Cell Mol Med. 23:522–534. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kwak HB, Lee BK, Oh J, Yeon JT, Choi SW,
Cho HJ, Lee MS, Kim JJ, Bae JM, Kim SH and Kim HS: Inhibition of
osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption by rotenone, through
down-regulation of RANKL-induced c-Fos and NFATc1 expression. Bone.
46:724–731. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Jimi E and Ghosh S: Role of nuclear
factor-kappaB in the immune system and bone. Immunol Rev.
208:80–87. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kim JH, Kim K, Kim I, Seong S, Kim SW and
Kim N: Role of anoctamin 5, a gene associated with gnathodiaphyseal
dysplasia, in osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation. Bone.
120:432–438. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Xiao D, Zhou Q, Gao Y, Cao B, Zhang Q,
Zeng G and Zong S: PDK1 is important lipid kinase for RANKL-induced
osteoclast formation and function via the regulation of the
Akt-GSK3β-NFATc1 signaling cascade. J Cell Biochem. 121:4542–4557.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Takayanagi H, Sunhwa K, Koga T, Nishina H,
Isshiki M, Yoshida H, Saiura A, Isobe M, Yokochi T, Inoue J, et al:
Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2)
integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of
osteoclasts. Dev Cell. 3:889–901. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Kim JH and Kim N: Regulation of NFATc1 in
osteoclast differentiation. J Bone Metab. 21:233–241.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Kim JH, Kim K, Jin HM, Song I, Youn BU,
Lee SH, Choi Y and Kim N: Negative feedback control of osteoclast
formation through ubiquitin-mediated down-regulation of NFATc1. J
Biol Chem. 285:5224–5231. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Lee Y, Kantayos V, Kim JS, Rha ES, Son YJ
and Baek SH: Inhibitory effects of protopanaxadiol-producing
transgenic rice seed extracts on RANKL-induced osteoclast
differentiation. Life (Basel). 12(1886)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Suh KS, Chon S, Jung WW and Choi EM:
Effects of methylglyoxal on RANKL-induced osteoclast
differentiation in RAW264.7 cells. Chem Biol Interact. 296:18–25.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Hwang YH, Kim T, Kim R and Ha H: Magnolol
inhibits osteoclast differentiation via suppression of RANKL
expression. Molecules. 23(1598)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Song C, Yang X, Lei Y, Zhang Z, Smith W,
Yan J and Kong L: Evaluation of efficacy on RANKL induced
osteoclast from RAW264.7 cells. J Cell Physiol. 234:11969–11975.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zeng Z, Zhang C and Chen J:
Lentivirus-mediated RNA interference of DC-STAMP expression
inhibits the fusion and resorptive activity of human osteoclasts. J
Bone Miner Metab. 31:409–416. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Islam R, Bae HS, Yoon WJ, Woo KM, Baek JH,
Kim HH, Uchida T and Ryoo HM: Pin1 regulates osteoclast fusion
through suppression of the master regulator of cell fusion
DC-STAMP. J Cell Physiol. 229:2166–2174. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Zhang C, Dou CE, Xu J and Dong S:
DC-STAMP, the key fusion-mediating molecule in osteoclastogenesis.
J Cell Physiol. 229:1330–1335. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Panahi N, Fahimfar N, Roshani S, Arjmand
B, Gharibzadeh S, Shafiee G, Migliavacca E, Breuille D, Feige JN,
Grzywinski Y, et al: Association of amino acid metabolites with
osteoporosis, a metabolomic approach: Bushehr elderly health
program. Metabolomics. 18(63)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Go M, Shin E, Jang SY, Nam M, Hwang G and
Lee SY: BCAT1 promotes osteoclast maturation by regulating
branched-chain amino acid metabolism. Exp Mol Med. 54:825–833.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|