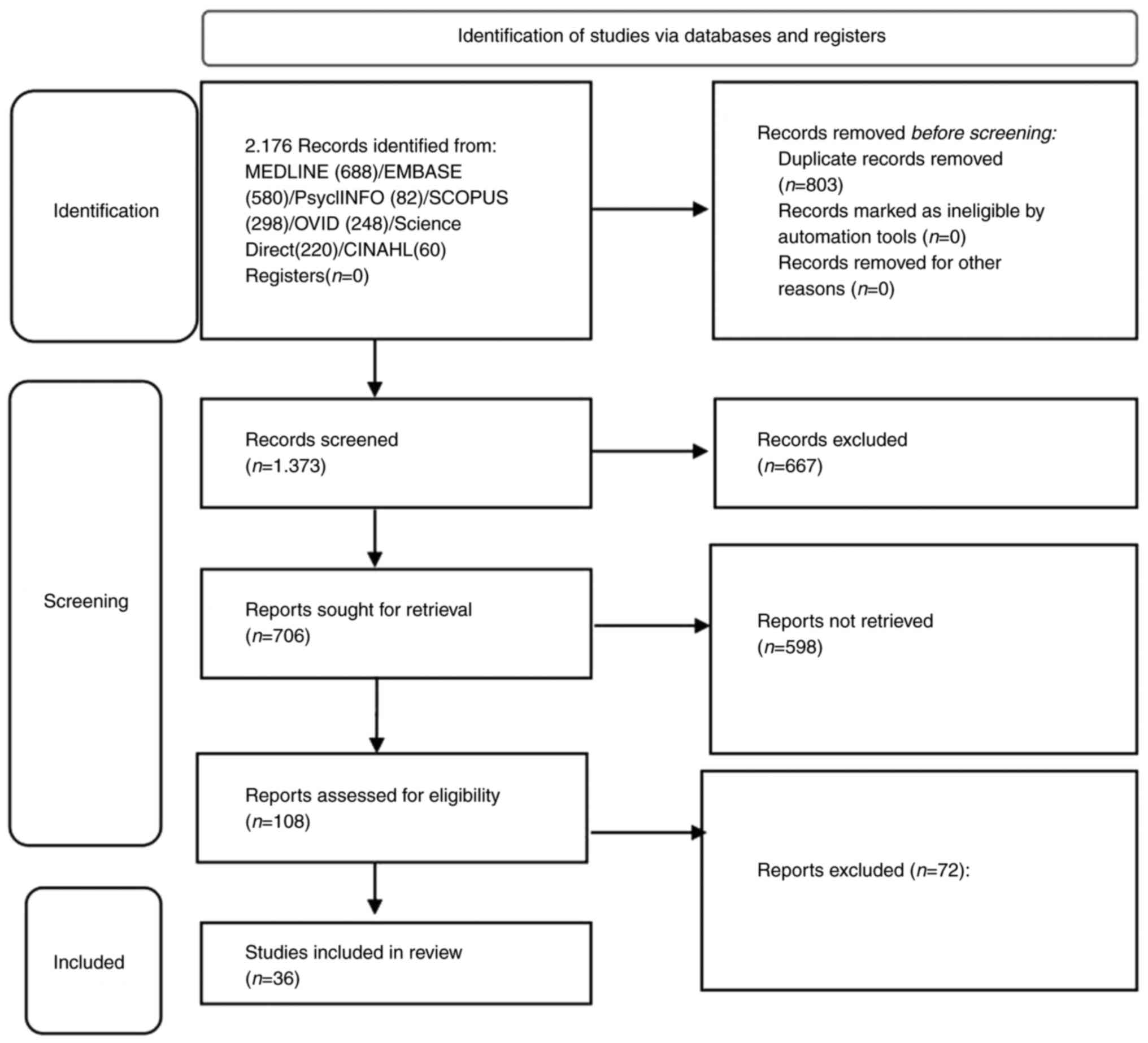
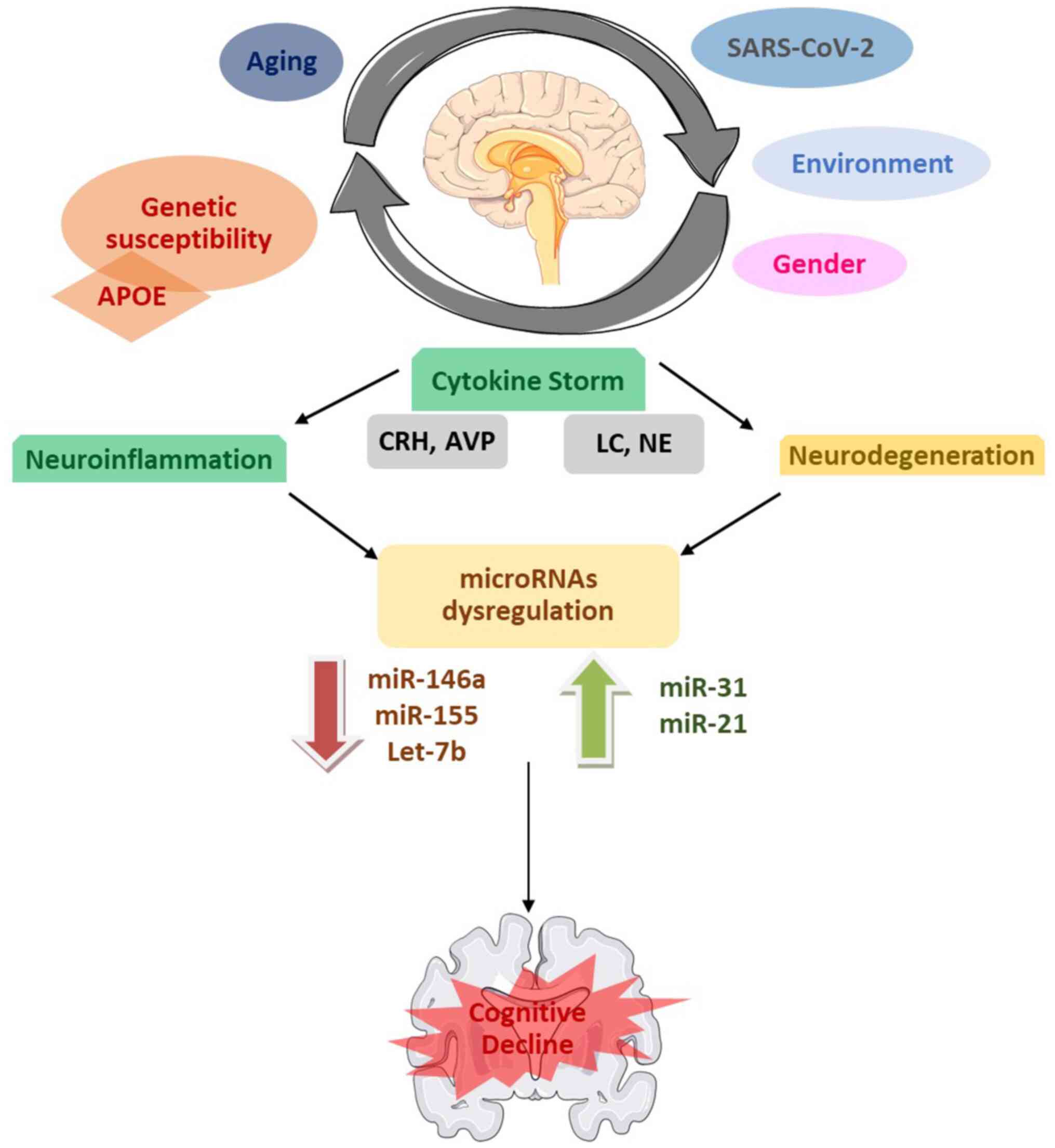
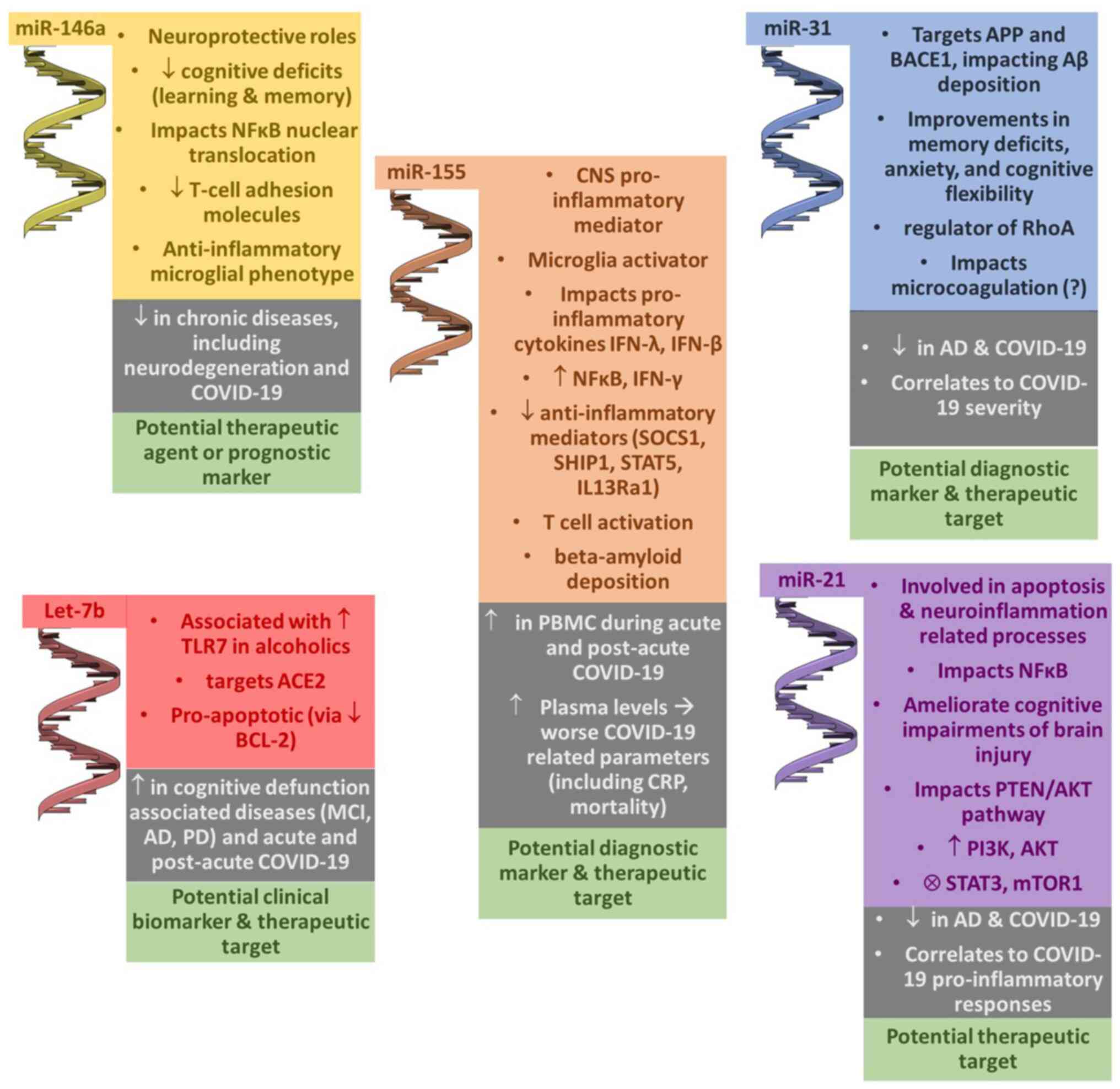
|
1
|
Georgakopoulou VE, Gkoufa A, Damaskos C,
Papalexis P, Pierrakou A, Makrodimitri S, Sypsa G, Apostolou A,
Asimakopoulou S, Chlapoutakis S, et al: COVID-19-associated acute
appendicitis in adults. A report of five cases and a review of the
literature. Exp Ther Med. 24(482)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Khatoon F, Prasad K and Kumar V: COVID-19
associated nervous system manifestations. Sleep Med. 91:231–236.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Gordon MN, Heneka MT, Le Page LM,
Limberger C, Morgan D, Tenner AJ, Terrando N, Willette AA and
Willette SA: Impact of COVID-19 on the onset and progression of
Alzheimer's disease and related dementias: A roadmap for future
research. Alzheimers Dement. 18:1038–1046. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Graham EL, Clark JR, Orban ZS, Lim PH,
Szymanski AL, Taylor C, DiBiase RM, Jia DT, Balabanov R, Ho SU, et
al: Persistent neurologic symptoms and cognitive dysfunction in
non-hospitalized Covid-19 ‘long haulers’. Ann Clin Transl Neurol.
8:1073–1085. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
de Erausquin GA, Snyder H, Carrillo M,
Hosseini AA, Brugha TS and Seshadri S: CNS SARS-CoV-2 Consortium.
The chronic neuropsychiatric sequelae of COVID-19: The need for a
prospective study of viral impact on brain functioning. Alzheimers
Dement. 17:1056–1065. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Manzo C, Serra-Mestres J, Isetta M and
Castagna A: Could COVID-19 anosmia and olfactory dysfunction
trigger an increased risk of future dementia in patients with
ApoE4? Med Hypotheses. 147(110479)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Li Z, Zhang Z, Zhang Z, Wang Z and Li H:
Cognitive impairment after long COVID-19: Current evidence and
perspectives. Front Neurol. 14(1239182)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Biomarkers Definitions Working Group.
Biomarkers and surrogate endpoints: Preferred definitions and
conceptual framework. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 69:89–95.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Bougea A: MicroRNA as candidate biomarkers
in atypical parkinsonian syndromes: Systematic literature review.
Medicina (Kaunas). 58(483)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Parnetti L, Farotti L, Eusebi P,
Chiasserini D, De Carlo C, Giannandrea D, Salvadori N, Lisetti V,
Tambasco N, Rossi A, et al: Differential role of CSF
alpha-synuclein species, tau, and Aβ42 in Parkinson's disease.
Front Aging Neurosci. 6(53)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Vivacqua G, Latorre A, Suppa A, Nardi M,
Pietracupa S, Mancinelli R, Fabbrini G, Colosimo C, Gaudio E and
Berardelli A: Abnormal Salivary Total and Oligomeric
Alpha-Synuclein in Parkinson's Disease. PLoS One.
11(e0151156)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Eusebi P, Giannandrea D, Biscetti L,
Abraha I, Chiasserini D, Orso M, Calabresi P and Parnetti L:
Diagnostic utility of cerebrospinal fluid α-synuclein in
Parkinson's disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mov
Disord. 32:1389–1400. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Bougea A: New markers in Parkinson's
disease. Adv Clin Chem. 96:137–178. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bougea A, Koros C and Stefanis L: Salivary
alpha-synuclein as a biomarker for Parkinson's disease: A
systematic review. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 126:1373–1382.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kuo MC, Liu SC, Hsu YF and Wu RM: The role
of noncoding RNAs in Parkinson's disease: Biomarkers and
associations with pathogenic pathways. J Biomed Sci.
28(78)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Gebert LFR and MacRae IJ: Regulation of
microRNA function in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 20:21–37.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kozomara A, Birgaoanu M and
Griffiths-Jones S: miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function.
Nucleic Acids Res. 47(D1):D155–D162. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Barbagallo C, Mostile G, Baglieri G,
Giunta F, Luca A, Raciti L, Zappia M, Purrello M, Ragusa M and
Nicoletti A: Specific signatures of serum miRNAs as potential
biomarkers to discriminate clinically similar neurodegenerative and
vascular-related diseases. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 40:531–546.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Candido S, Lupo G, Pennisi M, Basile MS,
Anfuso CD, Petralia MC, Gattuso G, Vivarelli S, Spandidos DA, Libra
M and Falzone L: The analysis of miRNA expression profiling
datasets reveals inverse microRNA patterns in glioblastoma and
Alzheimer's disease. Oncol Rep. 42:911–922. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Pierouli K, Papakonstantinou E,
Papageorgiou L, Diakou I, Mitsis T, Dragoumani K, Spandidos DA,
Bacopoulou F, Chrousos GP, Goulielmos GΝ, et al: Role of non-coding
RNAs as biomarkers and the application of omics technologies in
Alzheimer's disease (Review). Int J Mol Med. 51(5)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Conti I, Varano G, Simioni C, Laface I,
Milani D, Rimondi E and Neri LM: miRNAs as influencers of cell-cell
communication in tumor microenvironment. Cells.
9(220)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Ramaswamy P, Yadav R, Pal PK and
Christopher R: Clinical application of circulating MicroRNAs in
Parkinson's Disease: The challenges and opportunities as diagnostic
biomarker. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 23:84–97. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ravanidis S, Bougea A, Papagiannakis N,
Koros C, Simitsi AM, Pachi I, Breza M, Stefanis L and Doxakis E:
Validation of differentially expressed brain-enriched microRNAs in
the plasma of PD patients. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 7:1594–1607.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Roser AE, Caldi Gomes L, Schünemann J,
Maass F and Lingor P: Circulating miRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers
for Parkinson's disease. Front Neurosci. 12(625)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ravanidis S, Bougea A, Papagiannakis N,
Maniati M, Koros C, Simitsi AM, Bozi M, Pachi I, Stamelou M,
Paraskevas GP, et al: Circulating Brain-enriched MicroRNAs for
detection and discrimination of idiopathic and genetic Parkinson's
disease. Mov Disord. 35:457–467. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Schulz J, Takousis P, Wohlers I, Itua IOG,
Dobricic V, Rücker G, Binder H, Middleton L, Ioannidis JPA,
Perneczky R, et al: Meta-analyses identify differentially expressed
micrornas in Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol. 85:835–851.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron
I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan
SE, et al: The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for
reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 372(n71)2021.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Atkins D, Best D, Briss PA, Eccles M,
Falck-Ytter Y, Flottorp S, Guyatt GH, Harbour RT, Haugh MC, Henry
D, et al: Grading quality of evidence and strength of
recommendations. BMJ. 328(1490)2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kong H, Yin F, He F, Omran A, Li L, Wu T,
Wang Y and Peng J: The Effect of miR-132, miR-146a, and miR-155 on
MRP8/TLR4-Induced astrocyte-related inflammation. J Mol Neurosci.
57:28–37. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Lukiw WJ: microRNA-146a Signaling in
Alzheimer's Disease (AD) and Prion Disease (PrD). Front Neurol.
11(462)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Liang C, Zou T, Zhang M, Fan W, Zhang T,
Jiang Y, Cai Y, Chen F, Chen X, Sun Y, et al: MicroRNA-146a
switches microglial phenotypes to resist the pathological processes
and cognitive degradation of Alzheimer's disease. Theranostics.
11:4103–4121. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kumar S and Reddy PH: Are circulating
microRNAs peripheral biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease? Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1862:1617–1627. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Maffioletti E, Milanesi E, Ansari A,
Zanetti O, Galluzzi S, Geroldi C, Gennarelli M and
Bocchio-Chiavetto L: miR-146a Plasma Levels Are Not Altered in
Alzheimer's Disease but Correlate With Age and Illness Severity.
Front Aging Neurosci. 11(366)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Roganović J: Downregulation of
microRNA-146a in diabetes, obesity and hypertension may contribute
to severe COVID-19. Med Hypotheses. 146(110448)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Sabbatinelli J, Giuliani A, Matacchione G,
Latini S, Laprovitera N, Pomponio G, Ferrarini A, Svegliati Baroni
S, Pavani M, Moretti M, et al: Decreased serum levels of the
inflammaging marker miR-146a are associated with clinical
non-response to tocilizumab in COVID-19 patients. Mech Ageing Dev.
193(111413)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Tili E, Mezache L, Michaille JJ, Amann V,
Williams J, Vandiver P, Quinonez M, Fadda P, Mikhail A and Nuovo G:
microRNA 155 up regulation in the CNS is strongly correlated to
Down's syndrome dementia. Ann Diagn Pathol. 34:103–109.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zingale VD, Gugliandolo A and Mazzon E:
MiR-155: An important regulator of neuroinflammation. Int J Mol
Sci. 23(90)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Song J and Lee JE: miR-155 is involved in
Alzheimer's disease by regulating T lymphocyte function. Front
Aging Neurosci. 7(61)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Henry RJ, Doran SJ, Barrett JP, Meadows
VE, Sabirzhanov B, Stoica BA, Loane DJ and Faden AI: Inhibition of
miR-155 limits neuroinflammation and improves functional recovery
after experimental traumatic brain injury in mice.
Neurotherapeutics. 16:216–230. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Guedes JR, Santana I, Cunha C, Duro D,
Almeida MR, Cardoso AM, de Lima MC and Cardoso AL: MicroRNA
deregulation and chemotaxis and phagocytosis impairment in
Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 3:7–17.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Varma-Doyle AV, Lukiw WJ, Zhao Y, Lovera J
and Devier D: A hypothesis-generating scoping review of miRs
identified in both multiple sclerosis and dementia, their protein
targets, and miR signaling pathways. J Neurol Sci.
420(117202)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Abbasi-Kolli M, Sadri Nahand J, Kiani SJ,
Khanaliha K, Khatami A, Taghizadieh M, Torkamani AR, Babakhaniyan K
and Bokharaei-Salim F: The expression patterns of MALAT-1, NEAT-1,
THRIL, and miR-155-5p in the acute to the post-acute phase of
COVID-19 disease. Braz J Infect Dis. 26(102354)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Donyavi T, Bokharaei-Salim F, Baghi HB,
Khanaliha K, Alaei Janat-Makan M, Karimi B, Sadri Nahand J, Mirzaei
H, Khatami A, Garshasbi S, et al: Acute and post-acute phase of
COVID-19: Analyzing expression patterns of miRNA-29a-3p, 146a-3p,
155-5p, and let-7b-3p in PBMC. Int Immunopharmacol.
97(107641)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Haroun RA, Osman WH, Amin RE, Hassan AK,
Abo-Shanab WS and Eessa AM: Circulating plasma miR-155 is a
potential biomarker for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Pathology. 54:104–110. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Kenny A, McArdle H, Calero M, Rabano A,
Madden SF, Adamson K, Forster R, Spain E, Prehn JHM, Henshall DC,
et al: Elevated Plasma microRNA-206 levels predict cognitive
decline and progression to dementia from mild cognitive impairment.
Biomolecules. 9(734)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Leidinger P, Backes C, Deutscher S,
Schmitt K, Mueller SC, Frese K, Haas J, Ruprecht K, Paul F, Stähler
C, et al: A blood based 12-miRNA signature of Alzheimer disease
patients. Genome Biol. 14(R78)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Huang Y, Liu Y, Huang J, Gao L, Wu Z, Wang
L and Fan L: Let-7b-5p promotes cell apoptosis in Parkinson's
disease by targeting HMGA2. Mol Med Rep. 24(820)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Coleman LG Jr, Zou J and Crews FT:
Microglial-derived miRNA let-7 and HMGB1 contribute to
ethanol-induced neurotoxicity via TLR7. J Neuroinflammation.
14(22)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Bellae Papannarao J, Schwenke DO, Manning
P and Katare R: Upregulated miR-200c is associated with
downregulation of the functional receptor for severe acute
respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 ACE2 in individuals with
obesity. Int J Obes (Lond). 46:238–241. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Islam MB, Chowdhury UN, Nain Z, Uddin S,
Ahmed MB and Moni MA: Identifying molecular insight of synergistic
complexities for SARS-CoV-2 infection with pre-existing type 2
diabetes. Comput Biol Med. 136(104668)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Dong H, Li J, Huang L, Chen X, Li D, Wang
T, Hu C, Xu J, Zhang C, Zen K, et al: Serum MicroRNA profiles serve
as novel biomarkers for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Dis
Markers. 2015(625659)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Barros-Viegas AT, Carmona V, Ferreiro E,
Guedes J, Cardoso AM, Cunha P, Pereira de Almeida L, Resende de
Oliveira C, Pedro de Magalhães J, Peça J and Cardoso AL: miRNA-31
improves cognition and abolishes amyloid-β pathology by targeting
APP and BACE1 in an animal model of Alzheimer's disease. Mol Ther
Nucleic Acids. 19:1219–1236. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Pearn ML, Schilling JM, Jian M, Egawa J,
Wu C, Mandyam CD, Fannon-Pavlich MJ, Nguyen U, Bertoglio J, Kodama
M, et al: Inhibition of RhoA reduces propofol-mediated growth cone
collapse, axonal transport impairment, loss of synaptic
connectivity, and behavioural deficits. Br J Anaesth. 120:745–760.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Qian H, Shang Q, Liang M, Gao B, Xiao J,
Wang J, Li A, Yang C, Yin J, Chen G, et al: MicroRNA-31-3p/RhoA
signaling in the dorsal hippocampus modulates
methamphetamine-induced conditioned place preference in mice.
Psychopharmacology (Berl). 238:3207–3219. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Bautista-Becerril B, Pérez-Dimas G,
Sommerhalder-Nava PC, Hanono A, Martínez-Cisneros JA,
Zarate-Maldonado B, Muñoz-Soria E, Aquino-Gálvez A,
Castillejos-López M, Juárez-Cisneros A, et al: miRNAs, from
evolutionary junk to possible prognostic markers and therapeutic
targets in COVID-19. Viruses. 14(41)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Keikha R, Hashemi-Shahri SM and Jebali A:
The relative expression of miR-31, miR-29, miR-126, and miR-17 and
their mRNA targets in the serum of COVID-19 patients with different
grades during hospitalization. Eur J Med Res. 26(75)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Farr RJ, Rootes CL, Rowntree LC, Nguyen
THO, Hensen L, Kedzierski L, Cheng AC, Kedzierska K, Au GG, Marsh
GA, et al: Altered microRNA expression in COVID-19 patients enables
identification of SARS-CoV-2 infection. PLoS Pathog.
17(e1009759)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Bai X and Bian Z: MicroRNA-21 Is a
versatile regulator and potential treatment target in central
nervous system disorders. Front Mol Neurosci.
15(842288)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Gámez-Valero A, Campdelacreu J, Vilas D,
Ispierto L, Reñé R, Álvarez R, Armengol MP, Borràs FE and Beyer K:
Exploratory study on microRNA profiles from plasma-derived
extracellular vesicles in Alzheimer's disease and dementia with
Lewy bodies. Transl Neurodegener. 8(31)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Ma X, Becker Buscaglia LE, Barker JR and
Li Y: MicroRNAs in NF-kappaB signaling. J Mol Cell Biol. 3:159–166.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Gao X, Xiong Y, Li Q, Han M, Shan D, Yang
G, Zhang S, Xin D, Zhao R, Wang Z, et al: Extracellular
vesicle-mediated transfer of miR-21-5p from mesenchymal stromal
cells to neurons alleviates early brain injury to improve cognitive
function via the PTEN/Akt pathway after subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Cell Death Dis. 11(363)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Feng MG, Liu CF, Chen L, Feng WB, Liu M,
Hai H and Lu JM: MiR-21 attenuates apoptosis-triggered by amyloid-β
via modulating PDCD4/PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β pathway in SH-SY5Y cells.
Biomed Pharmacother. 101:1003–1007. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Wang Y and Chang Q: MicroRNA miR-212
regulates PDCD4 to attenuate Aβ25-35-induced
neurotoxicity via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in Alzheimer's
disease. Biotechnol Lett. 42:1789–1797. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Blount GS, Coursey L and Kocerha J:
MicroRNA networks in cognition and dementia. Cells.
11(1882)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Keikha R, Hashemi-Shahri SM and Jebali A:
The miRNA neuroinflammatory biomarkers in COVID-19 patients with
different severity of illness. Neurologia (Engl Ed). 38:e41–e51.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Tang H, Gao Y, Li Z, Miao Y, Huang Z, Liu
X, Xie L, Li H, Wen W, Zheng Y and Su W: The noncoding and coding
transcriptional landscape of the peripheral immune response in
patients with COVID-19. Clin Transl Med. 10(e200)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Nersisyan S, Shkurnikov M, Turchinovich A,
Knyazev E and Tonevitsky A: Integrative analysis of miRNA and mRNA
sequencing data reveals potential regulatory mechanisms of ACE2 and
TMPRSS2. PLoS One. 15(e0235987)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|