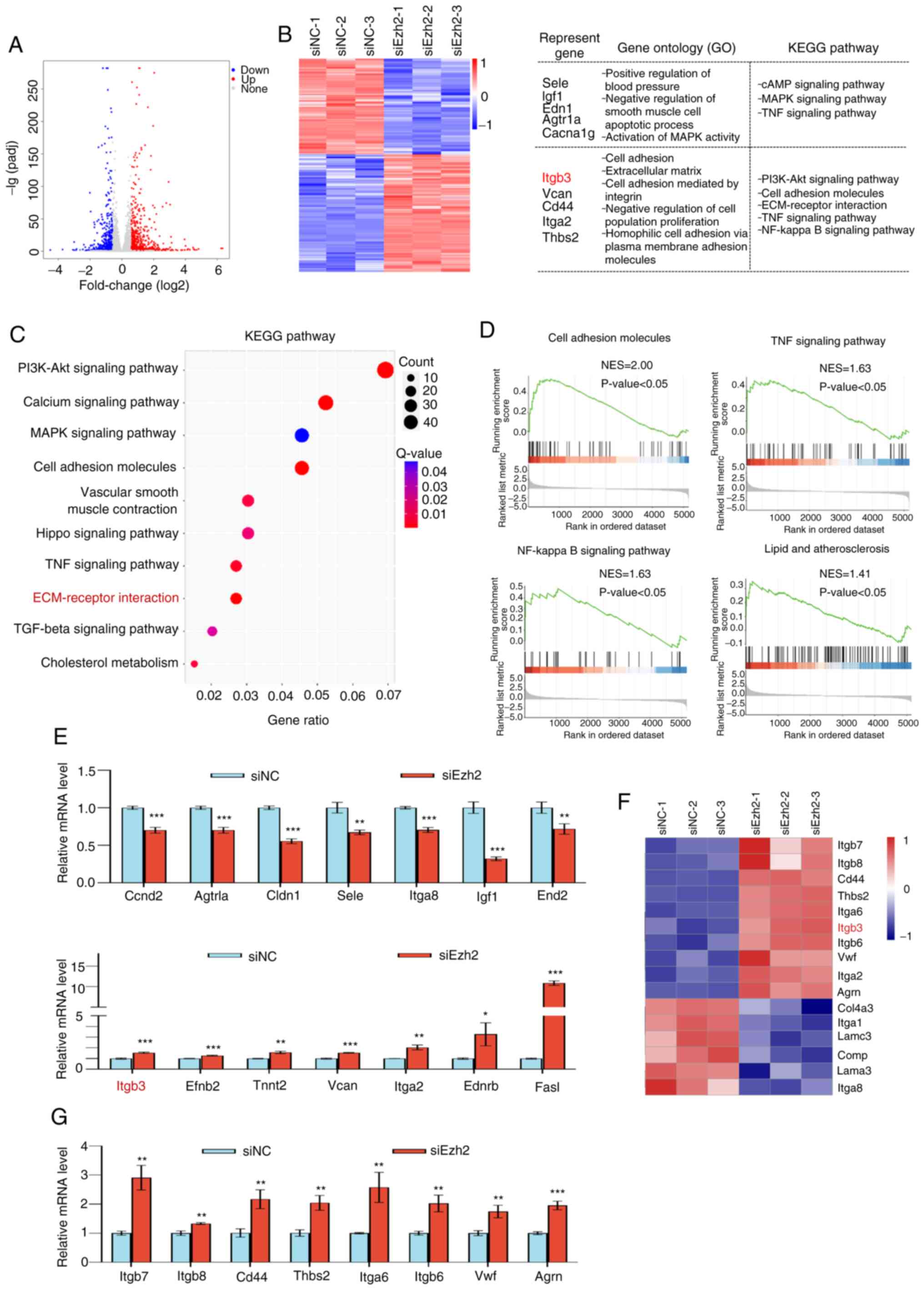
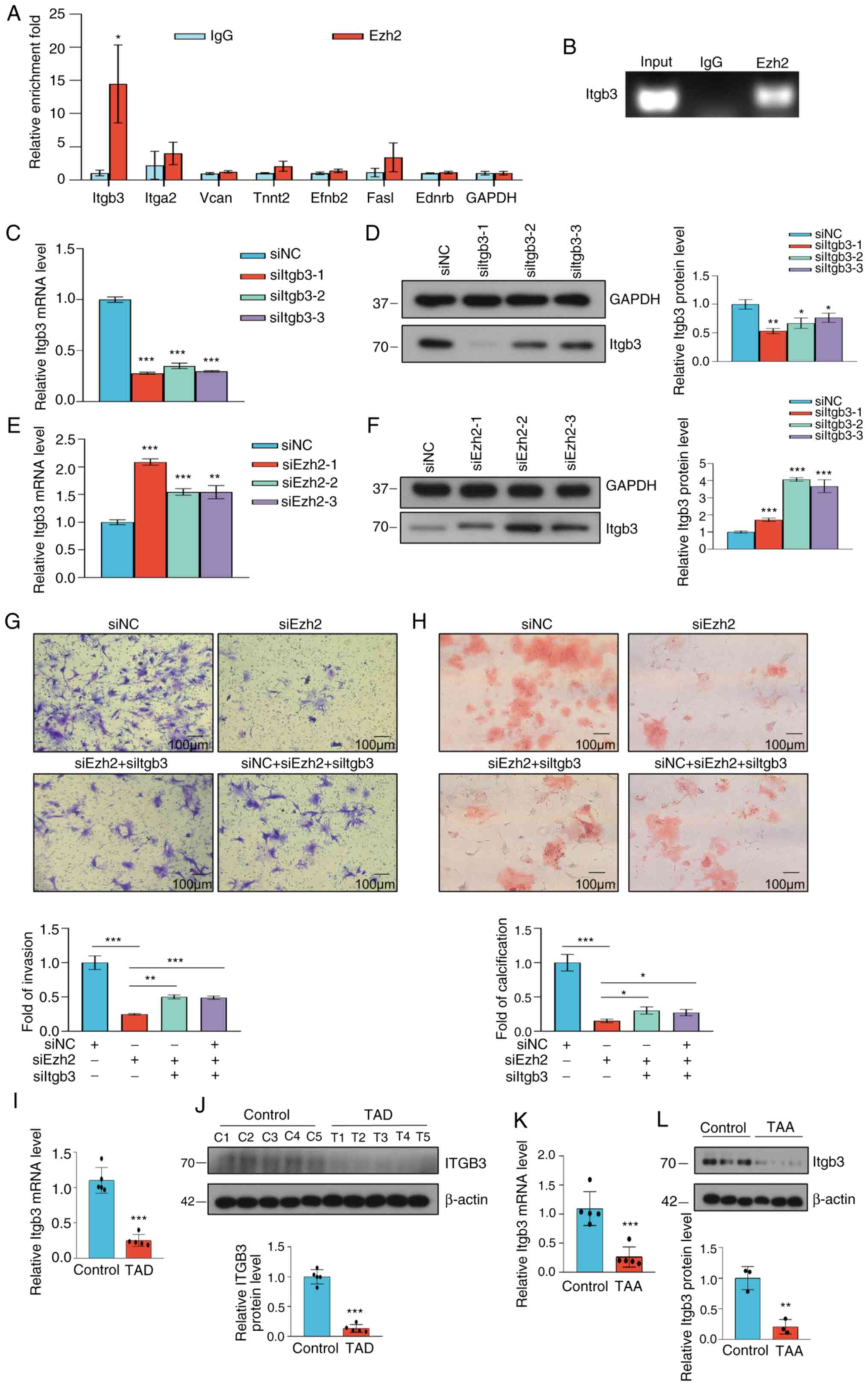
|
1
|
Bossone E and Eagle KA: Epidemiology and
management of aortic disease: Aortic aneurysms and acute aortic
syndromes. Nat Rev Cardiol. 18:331–348. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bento JR, Meester J, Luyckx I, Peeters S,
Verstraeten A and Loeys B: The genetics and typical traits of
thoracic aortic aneurysm and dissection. Annu Rev Genomics Hum
Genet. 23:223–253. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lu H, Du W, Ren L, Hamblin MH, Becker RC,
Chen YE and Fan Y: Vascular smooth muscle cells in aortic aneurysm:
From genetics to mechanisms. J Am Heart Assoc.
10(e023601)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Bossone E, LaBounty TM and Eagle KA: Acute
aortic syndromes: Diagnosis and management, an update. Eur Heart J.
39:739–749d. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Heiss C, Pitcher A, Belch JJF, De Carlo M,
Reinecke H, Baumgartner I, Mazzolai L and Aboyans V: The year in
cardiology: Aorta and peripheral circulation. Eur Heart J.
41:501–508b. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Jana S, Hu M, Shen M and Kassiri Z:
Extracellular matrix, regional heterogeneity of the aorta, and
aortic aneurysm. Exp Mol Med. 51:1–15. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Li C, Qiu S, Liu X, Guo F, Zhai J, Li Z,
Deng L, Ge L, Qian H, Yang L and Xu B: Extracellular matrix-derived
mechanical force governs breast cancer cell stemness and quiescence
transition through integrin-DDR signaling. Signal Transduct Target
Ther. 8(247)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Cescon M, Rampazzo E, Bresolin S, Da Ros
F, Manfreda L, Cani A, Della Puppa A, Braghetta P, Bonaldo P and
Persano L: Collagen VI sustains cell stemness and chemotherapy
resistance in glioblastoma. Cell Mol Life Sci.
80(233)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Golledge J: Abdominal aortic aneurysm:
Update on pathogenesis and medical treatments. Nat Rev Cardiol.
16:225–242. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Sorokin V, Vickneson K, Kofidis T, Woo CC,
Lin XY, Foo R and Shanahan CM: Role of vascular smooth muscle cell
plasticity and interactions in vessel wall inflammation. Front
Immunol. 11(599415)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Inamoto S, Kwartler CS, Lafont AL, Liang
YY, Fadulu VT, Duraisamy S, Willing M, Estrera A, Safi H, Hannibal
MC, et al: TGFBR2 mutations alter smooth muscle cell phenotype and
predispose to thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections. Cardiovasc
Res. 88:520–529. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Han DG, Ahn CB, Lee JH, Hwang Y, Kim JH,
Park KY, Lee JW and Son KH: Optimization of electrospun
poly(caprolactone) fiber diameter for vascular scaffolds to
maximize smooth muscle cell infiltration and phenotype modulation.
Polymers (Basel). 11(643)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Michel JB, Jondeau G and Milewicz DM: From
genetics to response to injury: Vascular smooth muscle cells in
aneurysms and dissections of the ascending aorta. Cardiovasc Res.
114:578–589. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Aherrahrou R, Baig F, Theofilatos K, Lue
D, Beele A, Örd T, Kaikkonen MU, Aherrahrou Z, Cheng Q, Ghosh S, et
al: Secreted protein profiling of human aortic smooth muscle cells
identifies vascular disease associations. medRxiv.
10(23298351)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhang L, Xia C, Yang Y, Sun F, Zhang Y,
Wang H, Liu R and Yuan M: DNA methylation and histone
post-translational modifications in atherosclerosis and a novel
perspective for epigenetic therapy. Cell Commun Signal.
21(344)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ibarrola J, Kim SK, Lu Q, DuPont JJ,
Creech A, Sun Z, Hill MA, Jaffe JD and Jaffe IZ: Smooth muscle
mineralocorticoid receptor as an epigenetic regulator of vascular
ageing. Cardiovasc Res. 118:3386–3400. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Le T, He X, Huang J, Liu S, Bai Y and Wu
K: Knockdown of long noncoding RNA GAS5 reduces vascular smooth
muscle cell apoptosis by inactivating EZH2-mediated RIG-I signaling
pathway in abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Transl Med.
19(466)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Delgado-Olguín P, Dang LT, He D, Thomas S,
Chi L, Sukonnik T, Khyzha N, Dobenecker MW, Fish JE and Bruneau BG:
Ezh2-mediated repression of a transcriptional pathway upstream of
Mmp9 maintains integrity of the developing vasculature.
Development. 141:4610–4617. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wang Y, Huang XX, Leng D, Li JF, Liang Y
and Jiang T: Effect of EZH2 on pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell
migration in pulmonary hypertension. Mol Med Rep.
23(129)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Li Y, Guo S, Zhao Y, Li R, Li Y, Qiu C,
Xiao L and Gong K: EZH2 regulates ANXA6 expression via H3K27me3 and
is involved in angiotensin II-induced vascular smooth muscle cell
senescence. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022(4838760)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhuang T, Liu J, Chen X, Pi J, Kuang Y,
Wang Y, Tomlinson B, Chan P, Zhang Q, Li Y, et al: Cell-specific
effects of GATA (GATA Zinc Finger Transcription Factor Family)-6 in
vascular smooth muscle and endothelial cells on vascular injury
neointimal formation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 39:888–901.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene
Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
The Gene Ontology Consortium. The gene
ontology resource: 20 years and still GOing strong. Nucleic Acids
Res. 47:D330–D338. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Minoru Kanehisa: Post-genome informatics.
Oxford University Press, 2000.
|
|
26
|
Wu T, Hu E, Xu S, Chen M, Guo P, Dai Z,
Feng T, Zhou L, Tang W, Zhan L, et al: clusterProfiler 4.0: A
universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation
(Camb). 2(100141)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Pan L, Bai P, Weng X, Liu J, Chen Y, Chen
S, Ma X, Hu K, Sun A and Ge J: Legumain is an endogenous modulator
of integrin αvβ3 triggering vascular degeneration, dissection, and
rupture. Circulation. 145:659–674. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhou Y, Wang T, Fan H, Liu S, Teng X, Shao
L and Shen Z: Research progress on the pathogenesis of aortic
aneurysm and dissection in metabolism. Curr Probl Cardiol.
49(102040)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Chakraborty A, Li Y, Zhang C, Li Y,
Rebello KR, Li S, Xu S, Vasquez HG, Zhang L, Luo W, et al:
Epigenetic induction of smooth muscle cell phenotypic alterations
in aortic aneurysms and dissections. Circulation. 148:959–977.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Pinard A, Jones GT and Milewicz DM:
Genetics of thoracic and abdominal aortic diseases. Circ Res.
124:588–606. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chang CJ and Hung MC: The role of EZH2 in
tumour progression. Br J Cancer. 106:243–247. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Rao ZY, Cai MY, Yang GF, He LR, Mai SJ,
Hua WF, Liao YJ, Deng HX, Chen YC, Guan XY, et al: EZH2 supports
ovarian carcinoma cell invasion and/or metastasis via regulation of
TGF-beta1 and is a predictor of outcome in ovarian carcinoma
patients. Carcinogenesis. 31:1576–1583. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Mitić T, Caporali A, Floris I, Meloni M,
Marchetti M, Urrutia R, Angelini GD and Emanueli C: EZH2 modulates
angiogenesis in vitro and in a mouse model of limb ischemia. Mol
Ther. 23:32–42. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Liu Y, Dai C, Lei Y, Wu W and Liu W:
Inhibition of EZH2 attenuates coronary heart disease by interacting
with microRNA-22 to regulate the TXNIP/nuclear factor-κB pathway.
Exp Physiol. 105:2038–2050. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Aljubran SA, Cox R Jr, Parthasarathy PT,
Ramanathan GK, Rajanbabu V, Bao H, Mohapatra SS, Lockey R and
Kolliputi N: Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 induces pulmonary artery
smooth muscle cell proliferation. PLoS One.
7(e37712)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Yuan Y, Wang C, Xu J, Tao J, Xu Z and
Huang S: BRG1 overexpression in smooth muscle cells promotes the
development of thoracic aortic dissection. BMC Cardiovasc Disord.
14(144)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
He D, Mao A, Zheng CB, Kan H, Zhang K,
Zhang Z, Feng L and Ma X: Aortic heterogeneity across segments and
under high fat/salt/glucose conditions at the single-cell level.
Natl Sci Rev. 7:881–896. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Owens GK, Kumar MS and Wamhoff BR:
Molecular regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation
in development and disease. Physiol Rev. 84:767–801.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Cardenas CL, Kessinger CW, MacDonald C,
Jassar AS, Isselbacher EM, Jaffer FA and Lindsay ME: Inhibition of
the methyltranferase EZH2 improves aortic performance in
experimental thoracic aortic aneurysm. JCI insight.
3(e97493)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
McDonald RA, Hata A, MacLean MR, Morrell
NW and Baker AH: MicroRNA and vascular remodelling in acute
vascular injury and pulmonary vascular remodelling. Cardiovasc Res.
93:594–604. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zhu C, Kong Z, Wang B, Cheng W, Wu A and
Meng X: ITGB3/CD61: A hub modulator and target in the tumor
microenvironment. Am J Transl Res. 11:7195–7208. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang X, Xu C, Yao F, Ding Q, Liu H, Luo C,
Wang D, Huang J, Li Z, Shen Y, et al: Targeting endothelial tight
junctions to predict and protect thoracic aortic aneurysm and
dissection. Eur Heart J. 44:1248–1261. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Desgrosellier JS and Cheresh DA: Integrins
in cancer: Biological implications and therapeutic opportunities.
Nat Rev Cancer. 10:9–22. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|