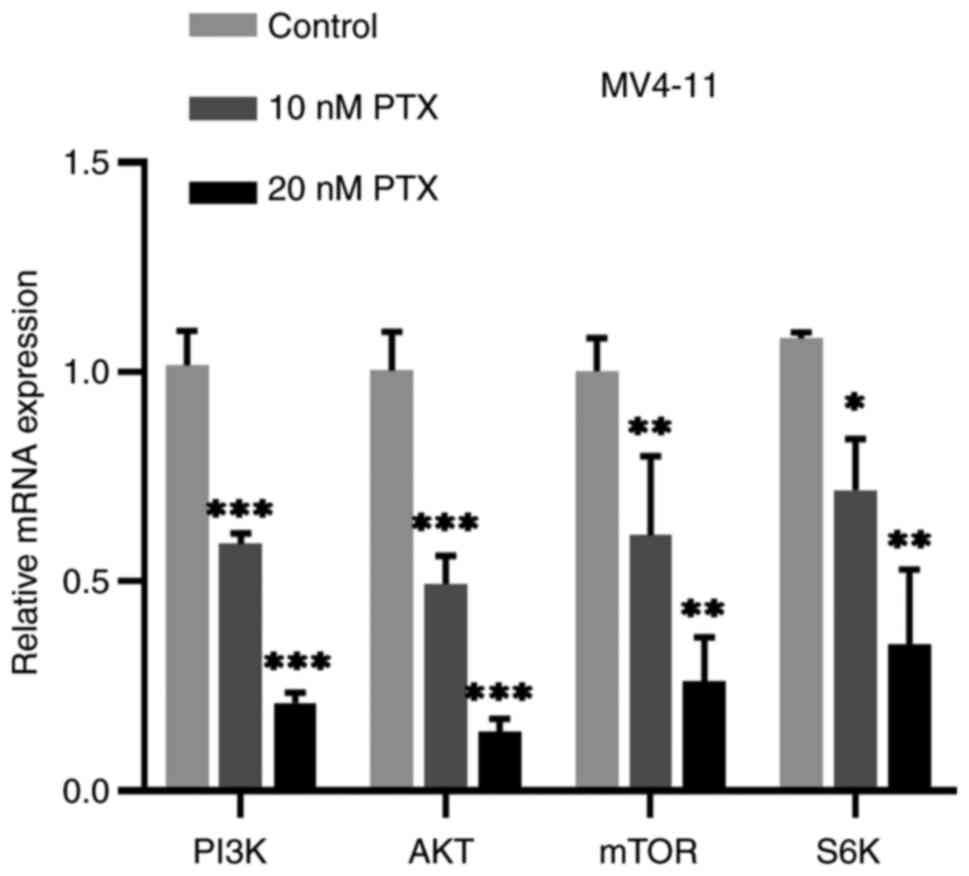
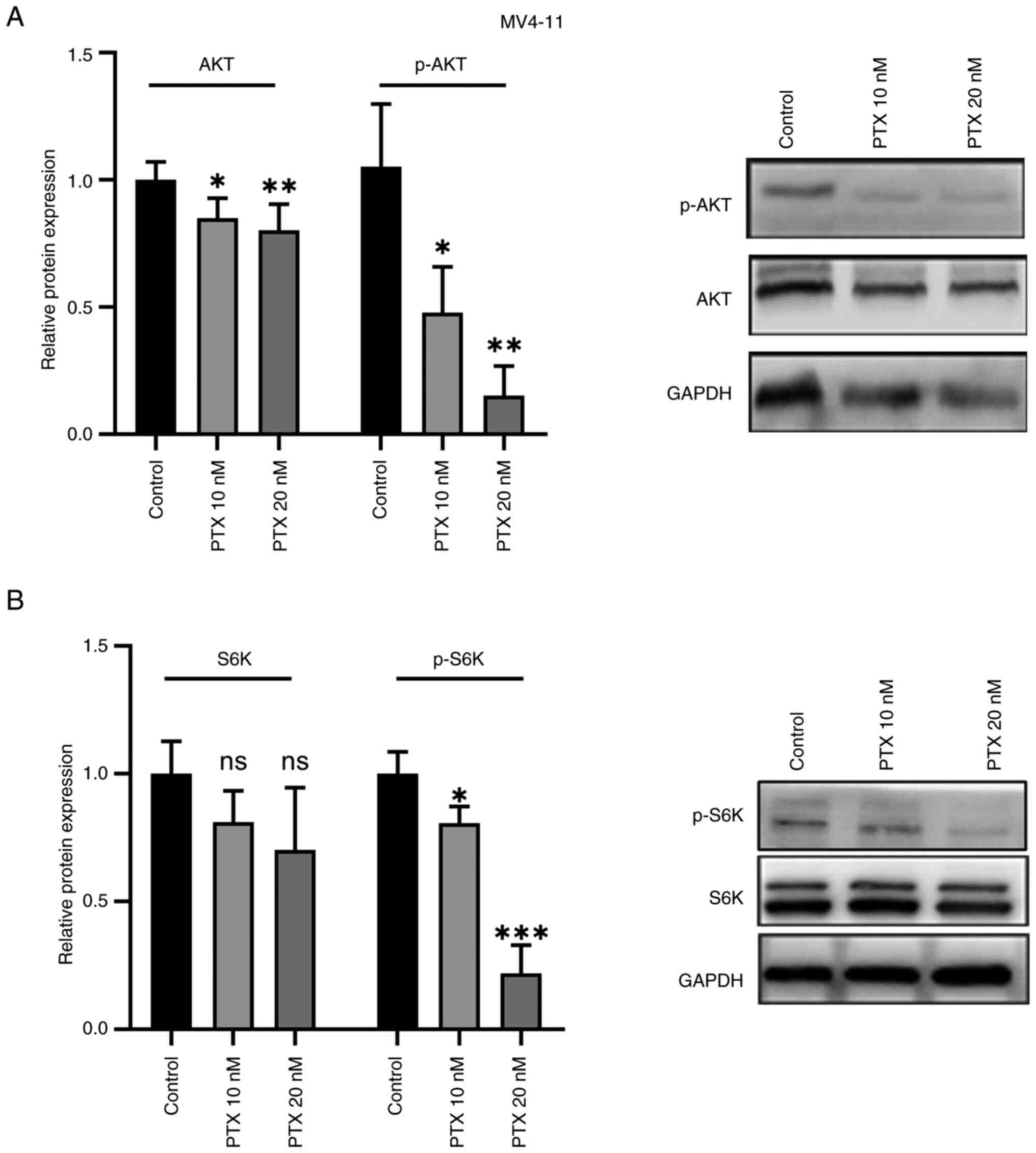
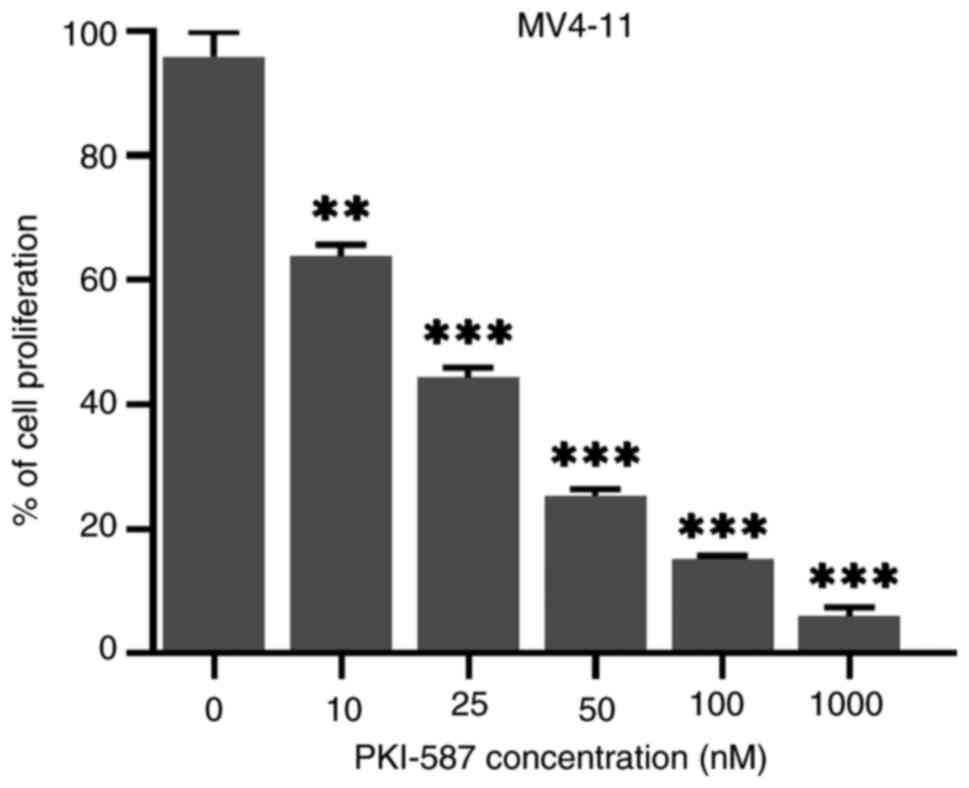
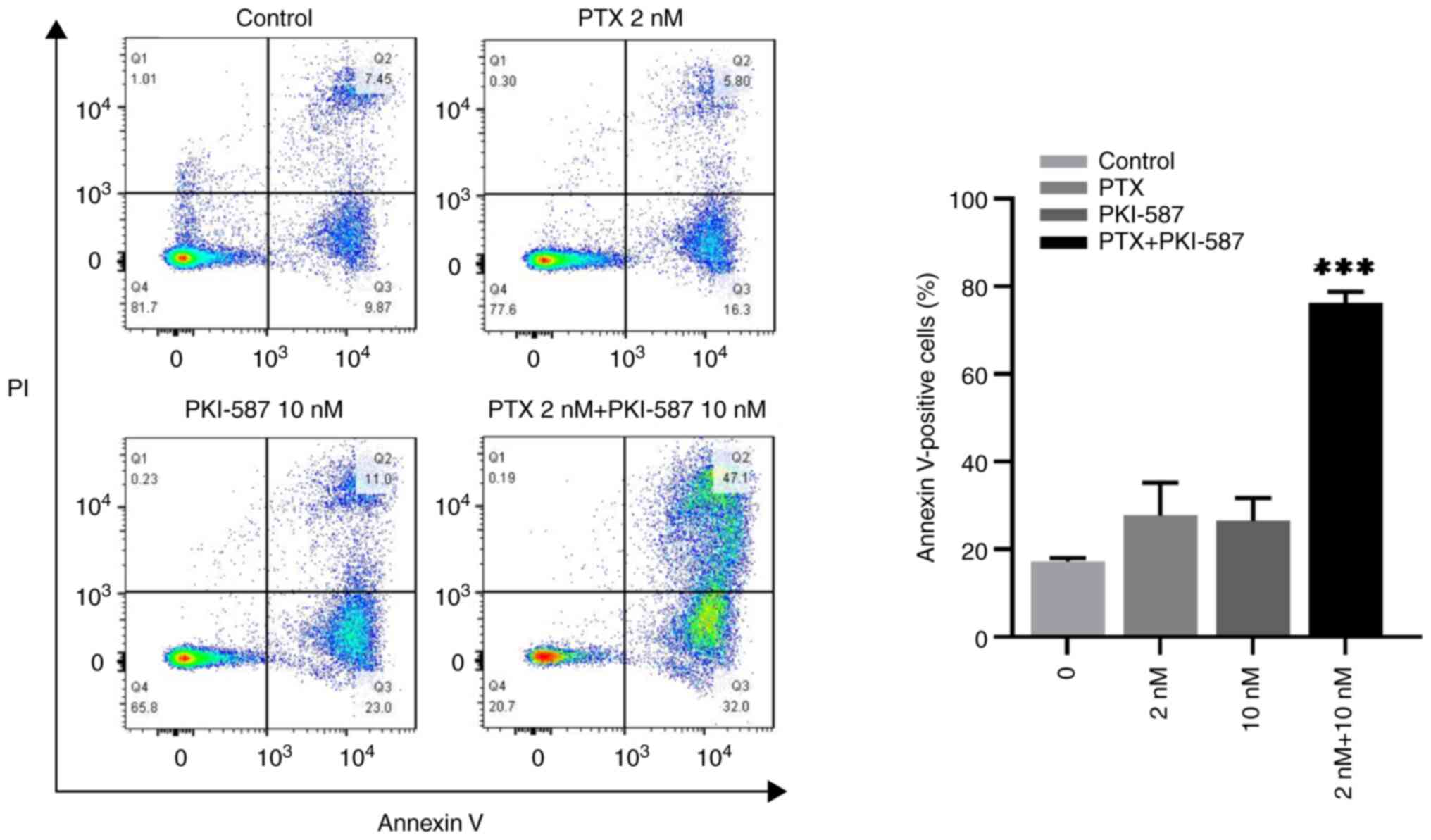
|
1
|
Estey E and Döhner H: Acute myeloid
leukaemia. Lancet. 368:1894–1907. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Yang F, Anekpuritanang T and Press RD:
Clinical utility of next-generation sequencing in acute myeloid
leukemia. Mol Diagn Ther. 24:1–13. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ley TJ, Miller C, Ding L, Raphael BJ,
Mungall AJ, Robertson A, Hoadley K, Triche TJ Jr, Laird PW, Baty
JD, et al: Genomic and epigenomic landscapes of adult de novo acute
myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 368:2059–2074. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Daver N, Schlenk RF, Russell NH and Levis
MJ: Targeting FLT3 mutations in AML: Review of current knowledge
and evidence. Leukemia. 33:299–312. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Döhner H, Estey E, Grimwade D, Amadori S,
Appelbaum FR, Büchner T, Dombret H, Ebert BL, Fenaux P, Larson RA,
et al: Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2017 ELN
recommendations from an international expert panel. Blood.
129:424–447. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sun YM, Wang WT, Zeng ZC, Chen TQ, Han C,
Pan Q, Huang W, Fang K, Sun LY, Zhou YF, et al: CircMYBL2, a
circRNA from MYBL2, regulates FLT3 translation by recruiting PTBP1
to promote FLT3-ITD AML progression. Blood. 134:1533–1546.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
De Kouchkovsky I and Abdul-Hay M: ‘Acute
myeloid leukemia: A comprehensive review and 2016 update’. Blood
Cancer J. 6(e441)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Whitman SP, Ruppert AS, Radmacher MD,
Mrózek K, Paschka P, Langer C, Baldus CD, Wen J, Racke F, Powell
BL, et al: FLT3 D835/I836 mutations are associated with poor
disease-free survival and a distinct gene-expression signature
among younger adults with de novo cytogenetically normal acute
myeloid leukemia lacking FLT3 internal tandem duplications. Blood.
111:1552–1559. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Whitman SP, Archer KJ, Feng L, Baldus C,
Becknell B, Carlson BD, Carroll AJ, Mrózek K, Vardiman JW, George
SL, et al: Absence of the wild-type allele predicts poor prognosis
in adult de novo acute myeloid leukemia with normal cytogenetics
and the internal tandem duplication of FLT3: A cancer and leukemia
group b study. Cancer Res. 61:7233–7239. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Almatani MF, Ali A, Onyemaechi S, Zhao Y,
Gutierrez L, Vaikari VP and Alachkar H: Strategies targeting FLT3
beyond the kinase inhibitors. Pharmacol Ther.
225(107844)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Levis M and Small D: FLT3: It does matter
in leukemia. Leukemia. 17:1738–1752. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Takahashi S: Downstream molecular pathways
of FLT3 in the pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia: Biology and
therapeutic implications. J Hematol Oncol. 4(13)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Brandts CH, Sargin B, Rode M, Biermann C,
Lindtner B, Schwäble J, Buerger H, Müller-Tidow C, Choudhary C,
McMahon M, et al: Constitutive activation of Akt by FLT3 internal
tandem duplications is necessary for increased survival,
proliferation, and myeloid transformation. Cancer Res.
65:9643–9650. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Rocnik JL, Okabe R, Yu JC, Lee BH, Giese
N, Schenkein DP and Gilliland DG: Roles of tyrosine 589 and 591 in
STAT5 activation and transformation mediated by FLT3-ITD. Blood.
108:1339–1345. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Döhner H, Weisdorf DJ and Bloomfield CD:
Acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 373:1136–1152.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Smith CC, Wang Q, Chin CS, Salerno S,
Damon LE, Levis MJ, Perl AE, Travers KJ, Wang S, Hunt JP, et al:
Validation of ITD mutations in FLT3 as a therapeutic target in
human acute myeloid leukaemia. Nature. 485:260–263. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Piloto O, Levis M, Huso D, Li Y, Li H,
Wang MN, Bassi R, Balderes P, Ludwig DL, Witte L, et al: Inhibitory
anti-FLT3 antibodies are capable of mediating antibody-dependent
cell-mediated cytotoxicity and reducing engraftment of acute
myelogenous leukemia blasts in nonobese diabetic/severe combined
immunodeficient mice. Cancer Res. 65:1514–1522. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Alvarado Y, Kantarjian HM, Luthra R,
Ravandi F, Borthakur G, Garcia-Manero G, Konopleva M, Estrov Z,
Andreeff M and Cortes JE: Treatment with FLT3 inhibitor in patients
with FLT3-mutated acute myeloid leukemia is associated with
development of secondary FLT3-tyrosine kinase domain mutations.
Cancer. 120:2142–2149. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Weisberg E, Barrett R, Liu Q, Stone R,
Gray N and Griffin JD: FLT3 inhibition and mechanisms of drug
resistance in mutant FLT3-positive AML. Drug Resist Updat.
12:81–89. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Alotaibi AS, Yilmaz M, Kanagal-Shamanna R,
Loghavi S, Kadia TM, DiNardo CD, Borthakur G, Konopleva M, Pierce
SA, Wang SA, et al: Patterns of resistance differ in patients with
acute myeloid leukemia treated with type I versus type II FLT3
inhibitors. Blood Cancer Discov. 2:125–134. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhu L and Chen L: Progress in research on
paclitaxel and tumor immunotherapy. Cell Mol Biol Lett.
24(40)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Tamburin S, Park SB, Alberti P, Demichelis
C, Schenone A and Argyriou AA: Taxane and epothilone-induced
peripheral neurotoxicity: From pathogenesis to treatment. J
Peripher Nerv Syst. 24 (Suppl 2):S40–S51. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Leung JC and Cassimeris L: Reorganization
of paclitaxel-stabilized microtubule arrays at mitotic entry: Roles
of depolymerizing kinesins and severing proteins. Cancer Biol Ther.
20:1337–1347. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Vassileva V, Allen CJ and Piquette-Miller
M: Effects of sustained and intermittent paclitaxel therapy on
tumor repopulation in ovarian cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:630–637.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Al-Mahayri ZN, AlAhmad MM and Ali BR:
Current opinion on the pharmacogenomics of paclitaxel-induced
toxicity. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 17:785–801.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Li T: Pacilitaxel induces human
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line CNE2 apoptosis and growth
inhibition by suppressing PI3K/AKT/P53 signaling pathway. Lin Chung
Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 29:2147–2150. 2015.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
27
|
Guertin DA and Sabatini DM: Defining the
role of mTOR in cancer. Cancer Cell. 12:9–22. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ma D, Li S, Cui Y, Li L, Liu H, Chen Y and
Zhou X: Paclitaxel increases the sensitivity of lung cancer cells
to lobaplatin via PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncol Lett. 15:6211–6216.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Moschetta M, Pretto F, Berndt A, Galler K,
Richter P, Bassi A, Oliva P, Micotti E, Valbusa G, Schwager K, et
al: Paclitaxel enhances therapeutic efficacy of the F8-IL2
immunocytokine to EDA-fibronectin-positive metastatic human
melanoma xenografts. Cancer Res. 72:1814–1824. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ying J, Yang W, Xie CY, Ni QC, Pan XD,
Dong JH, Liu ZM and Wang XS: Induction of caspase-3-dependent
apoptosis in human leukemia HL-60 cells by δ-elemene. Yakugaku
Zasshi. 131:1383–1394. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Xia RL, Lu Y, Zhu LN, Zhang SF, Zhao FK
and Fu CY: Different regulatory pathways are involved in the
proliferative inhibition of two types of leukemia cell lines
induced by paclitaxel. Oncol Rep. 30:1853–1859. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Meshkini A and Yazdanparast R: Involvement
of oxidative stress in taxol-induced apoptosis in chronic
myelogenous leukemia K562 cells. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 64:357–365.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Bai ZW, Wu MQ, Zhou BW, Shi ZY, Yao YB,
Liu ZF, Pang RL and Zhao WH: Effects of paclitaxel and quizartinib
alone and in combination on aml cell line MV4-11 and Its STAT5
signal pathway. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 30:671–676.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
34
|
Jin ZJ and Zhang XW: Equal probability and
curve with ‘q50’-A new method to estimate the effect of drug
combination. Journal of Shanghai Second Medical College.
(01)(15-18+86)1981.(In Chinese).
|
|
35
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Nepstad I, Hatfield KJ, Grønningsæter IS
and Reikvam H: The PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling pathway in human acute
myeloid leukemia (AML) cells. Int J Mol Sci.
21(2907)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Martelli AM, Evangelisti C, Chappell W,
Abrams SL, Bäsecke J, Stivala F, Donia M, Fagone P, Nicoletti F,
Libra M, et al: Targeting the translational apparatus to improve
leukemia therapy: Roles of the PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR pathway.
Leukemia. 25:1064–1079. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Lindblad O, Cordero E, Puissant A,
Macaulay L, Ramos A, Kabir NN, Sun J, Vallon-Christersson J,
Haraldsson K, Hemann MT, et al: Aberrant activation of the
PI3K/mTOR pathway promotes resistance to sorafenib in AML.
Oncogene. 35:5119–5131. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Port M, Böttcher M, Thol F, Ganser A,
Schlenk R, Wasem J, Neumann A and Pouryamout L: Prognostic
significance of FLT3 internal tandem duplication, nucleophosmin 1,
and cebpa gene mutations for acute myeloid leukemia patients with
normal karyotype and younger than 60 years: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Ann Hematol. 93:1279–1286. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Almond LM, Charalampakis M, Ford SJ,
Gourevitch D and Desai A: Myeloid sarcoma: Presentation, diagnosis,
and treatment. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 17:263–267.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Ganzel C and Douer D: Extramedullary
disease in APL: A real phenomenon to contend with or not? Best
Pract Res Clin Haematol. 27:63–68. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Levis M: Midostaurin approved for
FLT3-mutated AML. Blood. 129:3403–3406. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Pulte ED, Norsworthy KJ, Wang Y, Xu Q,
Qosa H, Gudi R, Przepiorka D, Fu W, Okusanya OO, Goldberg KB, et
al: FDA approval summary: Gilteritinib for relapsed or refractory
acute myeloid leukemia with a FLT3 mutation. Clin Cancer Res.
27:3515–3521. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Antar A, Otrock ZK, El-Cheikh J,
Kharfan-Dabaja MA, Battipaglia G, Mahfouz R, Mohty M and Bazarbachi
A: Inhibition of FLT3 in AML: A focus on sorafenib. Bone Marrow
Transplant. 52:344–351. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Cucchi DGJ, Denys B, Kaspers GJL, Janssen
J, Ossenkoppele GJ, de Haas V, Zwaan CM, van den Heuvel-Eibrink MM,
Philippé J, Csikós T, et al: RNA-based FLT3-ITD allelic ratio is
associated with outcome and ex vivo response to FLT3 inhibitors in
pediatric AML. Blood. 131:2485–2489. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Mrózek K, Marcucci G, Paschka P, Whitman
SP and Bloomfield CD: Clinical relevance of mutations and
gene-expression changes in adult acute myeloid leukemia with normal
cytogenetics: Are we ready for a prognostically prioritized
molecular classification? Blood. 109:431–448. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Min YH, Eom JI, Cheong JW, Maeng HO, Kim
JY, Jeung HK, Lee ST, Lee MH, Hahn JS and Ko YW: Constitutive
phosphorylation of Akt/PKB protein in acute myeloid leukemia: Its
significance as a prognostic variable. Leukemia. 17:995–997.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Chen W, Drakos E, Grammatikakis I,
Schlette EJ, Li J, Leventaki V, Staikou-Drakopoulou E, Patsouris E,
Panayiotidis P, Medeiros LJ and Rassidakis HZ: Mtor signaling is
activated by FLT3 kinase and promotes survival of FLT3-mutated
acute myeloid leukemia cells. Mol Cancer. 9(292)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Nepstad I, Hatfield KJ, Grønningsæter IS,
Aasebø E, Hernandez-Valladares M, Hagen KM, Rye KP, Berven FS,
Selheim F, Reikvam H and Bruserud Ø: Effects of insulin and pathway
inhibitors on the PI3K-Akt-mTOR phosphorylation profile in acute
myeloid leukemia cells. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
4(20)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Watanabe D, Nogami A, Okada K, Akiyama H,
Umezawa Y and Miura O: FLT3-ITD activates RSK1 to enhance
proliferation and survival of AML cells by activating mTORC1 and
eIF4B cooperatively with PIM or PI3K and by inhibiting BAD and BIM.
Cancers (Basel). 11(1827)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Dong P, Hao F, Dai S and Tian L:
Combination therapy eve and pac to induce apoptosis in cervical
cancer cells by targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways. J Recept Signal
Transduct Res. 38:83–88. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Ding Z, Xu F, Li G, Tang J, Tang Z, Jiang
P and Wu H: Knockdown of Akt2 expression by shRNA inhibits
proliferation, enhances apoptosis, and increases chemosensitivity
to paclitaxel in human colorectal cancer cells. Cell Biochem
Biophys. 71:383–388. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Lin YH, Chen BY, Lai WT, Wu SF, Guh JH,
Cheng AL and Hsu LC: The Akt inhibitor MK-2206 enhances the
cytotoxicity of paclitaxel (Taxol) and cisplatin in ovarian cancer
cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 388:19–31.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Liu X, Xie C, Li A, Zhang Y, Liu X, Zhou
S, Shen J, Huo Z, Cao W, Ma Y, et al: BEZ235 enhances
chemosensitivity of paclitaxel in hepatocellular carcinoma through
inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Am J Transl Res.
11:7255–7271. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Hacıhanefioglu A, Gonullu E, Mehtap O,
Keski H, Yavuz M and Ercin C: Effect of heat shock protein-90
(HSP90) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) on survival
in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: An immunohistochemical study. Med
Oncol. 28:846–851. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Han SY: Small molecule induced FLT3
degradation. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 15(320)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Yao Q, Nishiuchi R, Li Q, Kumar AR, Hudson
WA and Kersey JH: FLT3 expressing leukemias are selectively
sensitive to inhibitors of the molecular chaperone heat shock
protein 90 through destabilization of signal
transduction-associated kinases. Clin Cancer Res. 9:4483–4493.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ly BT, Chi HT, Yamagishi M, Kano Y, Hara
Y, Nakano K, Sato Y and Watanabe T: Inhibition of FLT3 expression
by green tea catechins in FLT3 mutated-AML cells. PLoS One.
8(e66378)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Al Shaer L, Walsby E, Gilkes A, Tonks A,
Walsh V, Mills K, Burnett A and Rowntree C: Heat shock protein 90
inhibition is cytotoxic to primary AML cells expressing mutant FLT3
and results in altered downstream signalling. Br J Haematol.
141:483–493. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Hieronymus H, Lamb J, Ross KN, Peng XP,
Clement C, Rodina A, Nieto M, Du J, Stegmaier K, Raj SM, et al:
Gene expression signature-based chemical genomic prediction
identifies a novel class of HSP90 pathway modulators. Cancer Cell.
10:321–330. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Peng B, Xu L, Cao F, Wei T, Yang C, Uzan G
and Zhang D: HSP90 inhibitor, celastrol, arrests human monocytic
leukemia cell U937 at G0/G1 in thiol-containing agents reversible
way. Mol Cancer. 9(79)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Lu Z, Jin Y, Qiu L, Lai Y and Pan J:
Celastrol, a novel HSP90 inhibitor, depletes Bcr-Abl and induces
apoptosis in imatinib-resistant chronic myelogenous leukemia cells
harboring T315I mutation. Cancer Lett. 290:182–191. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Zhang FZ, Ho DH and Wong RH: Triptolide, a
HSP90 middle domain inhibitor, induces apoptosis in triple manner.
Oncotarget. 9:22301–22315. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|