Introduction
Osimertinib is a third-generation irreversible
epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor
(TKI). It is widely used as treatment for EGFR mutation-positive
non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Cutaneous side effects of
EGFR-TKI are well known, and more commonly occur in female patients
(1). These include
acneiform and papulopustular eruption, pruritus, xerosis,
paronychia and fissure/cracks (2).
To the best of our knowledge, erythromelalgia has never been
reported as a skin-related adverse event of EGFR-TKI. Here, we
report the first case of osimertinib-induced erythromelalgia in a
77-year old woman diagnosed with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma.
Erythromelalgia is a rare and debilitating disorder characterized
by burning pain, redness and increased temperature of the
extremities. It is classified as primary and secondary
erythromelalgia. Primary erythromelalgia is a hereditary autosomal
dominant disorder due to a heterozygous mutation in SCN9A gene,
responsible for encoding a voltage-gated sodium channel expressed
by neurons. Secondary erythromelalgia is linked with a spectrum of
various underlying medical conditions. It may be a consequence of
myeloproliferative disorders, including polycythemia vera or
essential thrombocythemia, connective tissue disorders such as
lupus or rheumatoid arthritis, metabolic conditions such as
diabetes, infections, musculoskeletal issues and neurological
disorders like multiple sclerosis. Moreover, erythromelalgia can be
a paraneoplastic syndrome (3).
Case report
We present the case of a 77-year old woman diagnosed
with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR L858R mutation in
exon 21 treated with osimertinib, a third-generation irreversible
epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor
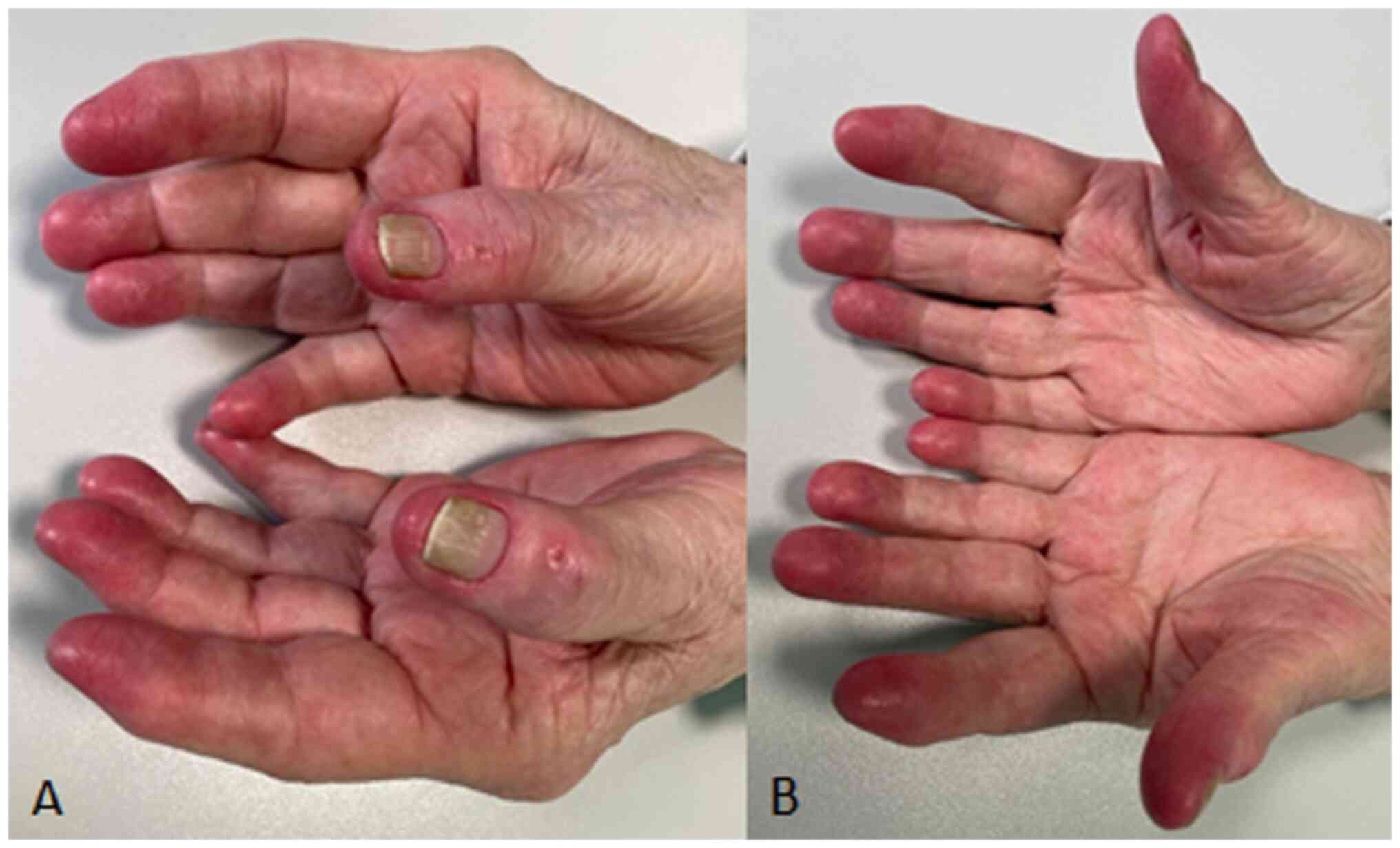
(TKI). She presented to the dermatology outpatient clinic due to
the onset of painful erythema and warmth in the distal phalanges of
all fingers on both hands (Fig.
1). This condition appeared after eight months of therapy with
osimertinib, worsened in response to heat and relieved with cold,
significantly impacting her quality of life. Additionally, the
patient had a history of MRGE, hypertension, diverticulosis of the
colon, and hypothyroidism. Moreover, she didn't report recent
infective episodes. Alongside osimertinib, she was concurrently
receiving bisoprolol, acetylsalicylic acid, ramipril, and
levothyroxine. Routine blood tests, encompassing complete blood
cell counts, hepatic and renal function assessments, and ion
levels, yielded normal results. Furthermore, contrast CT scans
showed no signs of cancer progression.
Based on clinical manifestations, erythromelalgia
was diagnosed. The patient was prescribed pain relief therapy with
a local anesthetic drug (lidocaine 1% cream) once a day as needed,
and reported reduction in symptoms. After a couple of months,
osimertinib was discontinued by oncologists because of a severe
infectious complication (hepatic abscess), with subsequent complete
remission of the cutaneous condition in a few weeks.
In this case a primary erythromelalgia, an inherited
autosomal dominant disorder due to a heterozygous mutation in SCN9A
gene encoding a sodium channel, has been excluded because of the
elderly age of onset. Extensive evaluation of the patient including
the recent history of the patient, in-range blood exams and CT with
contrast, which was negative for cancer progression, ruled out
other conditions associated with erythromelalgia, such as
myeloproliferative disorders, connective tissue disorders,
metabolic disorders, infections, musculoskeletal and neurological
conditions, and paraneoplastic erythromelalgia. Given the absence
of alternative explanations, the association with osimertinib was
considered the most probable diagnosis. Osimertinib, being a
life-saving therapy, has not been discontinued. Instead, topical
anesthetic was chosen to alleviate the patient's symptoms. During
follow-up, the remission of erythromelalgia after discontinuation
of osimertinib intake based on the oncologist's recommendation
supported the hypothesis of osimertinib-induced
erythromelalgia.
Discussion
Erythromelalgia is a rare distressing condition
characterized by burning pain of the extremities, erythema and
increased temperature of affected skin, exacerbated by warming and
relieved by cooling. The diagnosis is made upon clinical signs and
symptoms. It is categorized as primary (an inherited autosomal
dominant disorder associated with mutations in the SCN9A gene) and
secondary, which is linked to underlying medical conditions.
Secondary erythromelalgia's pathogenesis is not fully understood,
however it has been suggested that erythromelalgia is a disorder of
vascular dynamics, with a decrease in capillary perfusion that
creates tissue hypoxia, and a simultaneous microvascular
arteriovenous deviation within the skin, which then appears
erythematous and hot (3).
In the skin, EGFR is expressed by basal keratinocytes, sebocytes,
the outer root sheath and endothelial cells, and plays a role in
the differentiation of keratinocytes and vessels of the dermis. It
has been proposed that EFGR inhibition may contribute a vascular
impairment (4). We suggest that
this may be the primum movens of the vascular dynamics disorder
with both decreased perfusion and arteriovenous shunting in skin.
Cutaneous side effects of EGFR-TKI reported in literature include
acneiform and papulopustular eruption, pruritus, xerosis,
paronychia and fissure/cracks (2).
Less frequently described EGFR-TKI cutaneous side effects are
ashy-dermatosis like hyperpigmentation (5), cutaneous vasculitis (6) and acute onset life-threatening
conditions such as severe psoriasis and toxic epidermal necrolysis
(7). The dermatological adverse
event profile of osimertinib, a third-generation EGFR-TKI, appears
to be milder than that found for first and second-generation agents
(8). This case study reports the
first known instance of erythromelalgia in a patient treated with
an EGFR inhibitor, implying that EGFR inhibition may induce
vascular dysfunction, potentially leading to arteriovenous shunting
in the skin. Despite the significant impact of erythromelalgia on
patient's quality of life, discontinuing EGFR inhibitor therapy is
discouraged due to its life-saving nature. Instead, symptoms
management is recommended in order to avoid discontinuation of this
life-sparing therapy.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding: No funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be
requested from the corresponding author.
Authors' contributions
AB and AG were equally responsible for
conceptualization, writing the original draft, reviewing and
editing. MASA was responsible for conceptualization and
supervision. All authors have read and approved the final
manuscript. AB and AG confirm the authenticity of all the raw
data.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
The patient referred in this manuscript gave written
informed consent to the publication of the case details.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Barbieri MA, Sorbara EE, Cicala G, Santoro
V, Cutroneo PM, Franchina T, Santarpia M, Silvestris N and Spina E:
Safety profile of tyrosine kinase inhibitors used in non-small-cell
lung cancer: An analysis from the Italian pharmacovigilance
database. Front Oncol. 12(1005626)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kozuki T: Skin problems and EGFR-tyrosine
kinase inhibitor. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 46:291–298. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Mann N, King T and Murphy R: Review of
primary and secondary erythromelalgia. Clin Exp Dermatol.
44:477–482. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Iskandar AS, Hwang A and Dasanu CA: EGFR
inhibitor-induced cut-like skin lesions of the fingers. BMJ Case
Rep. 2018(bcr2017224144)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Funai K: Rare ashy dermatosis-like
hyperpigmentation associated with osimertinib. Thorac Cancer.
13:1436–1437. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Iriarte C, Young JH, Rabin MS and LeBoeuf
NR: Osimertinib-induced cutaneous vasculitis responsive to low-dose
dapsone without interruption of anticancer therapy: A case report
and review of the literature. JTO Clin Res Rep.
3(100415)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Rittberg R, Ho C and Wang Y: Acute onset
of a life-threatening skin toxicity due to osimertinib: Severe
psoriasis versus toxic epidermal necrolysis. Cureus.
14(e24513)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yang JC, Ahn MJ, Kim DW, Ramalingam SS,
Sequist LV, Su WC, Kim SW, Kim JH, Planchard D, Felip E, et al:
Osimertinib in pretreated T790M-positive advanced non-small-cell
lung cancer: AURA study phase II extension component. J Clin Oncol.
35:1288–1296. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|