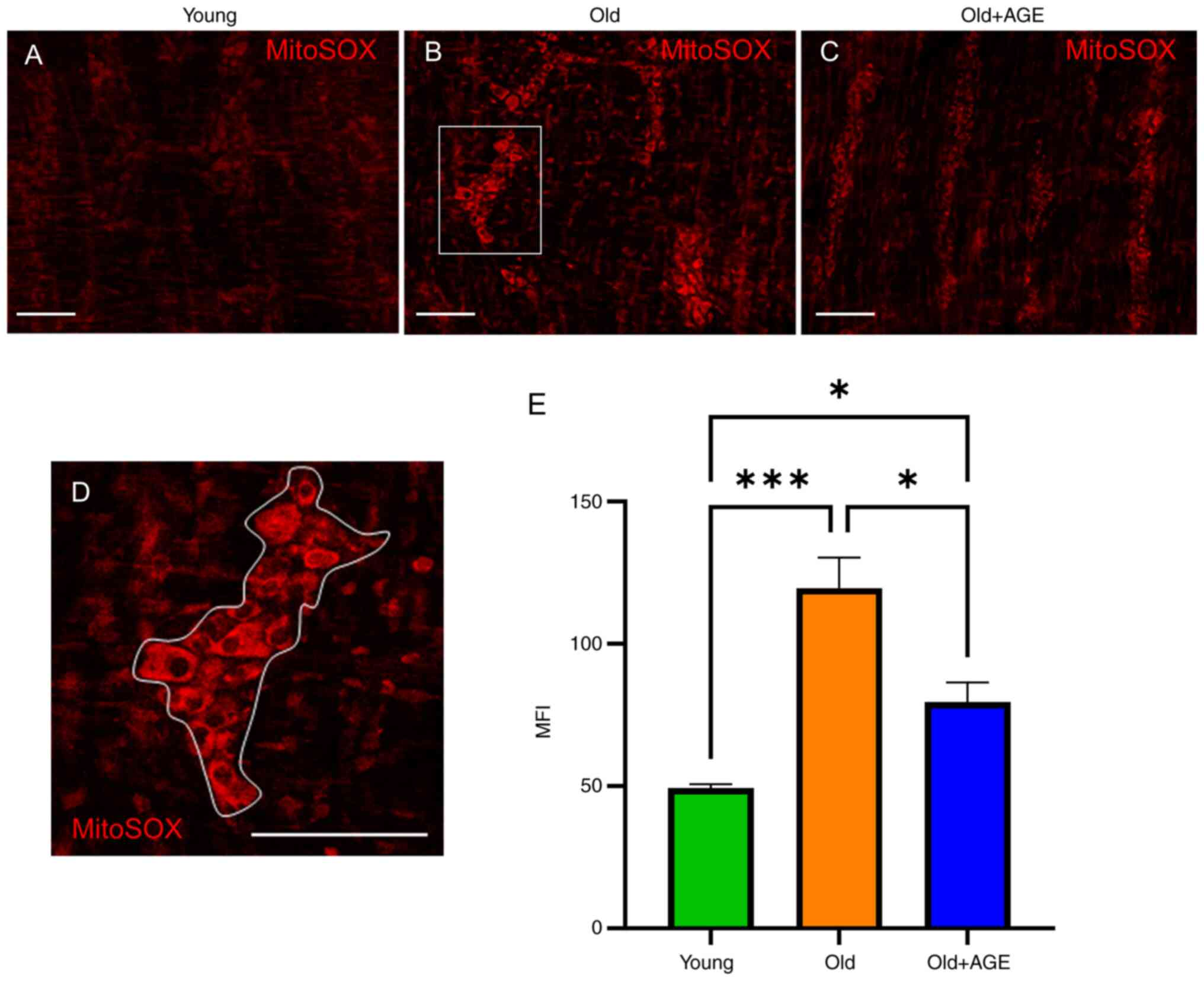
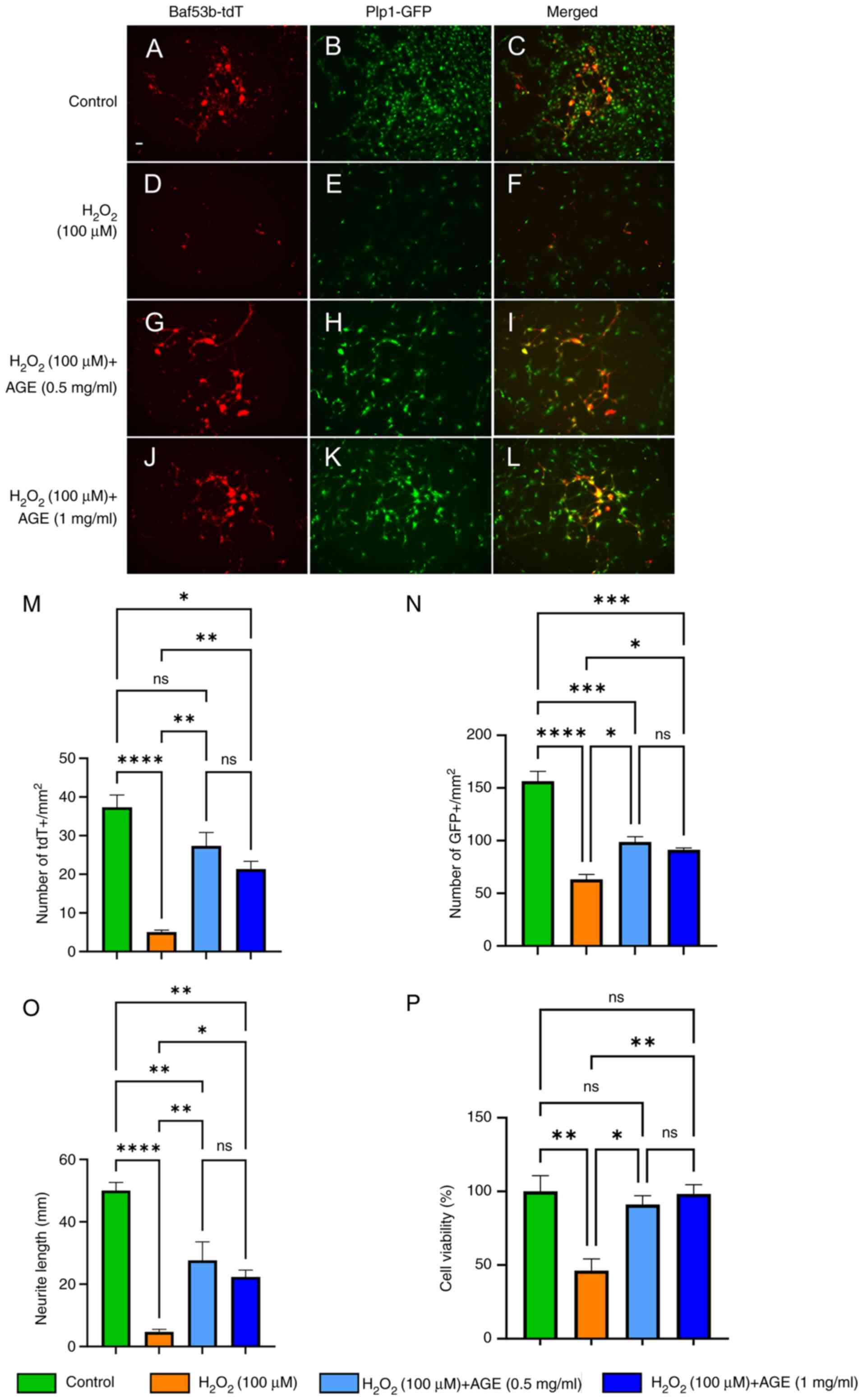
|
1
|
Kennedy BK, Berger SL, Brunet A, Campisi
J, Cuervo AM, Epel ES, Franceschi C, Lithgow GJ, Morimoto RI,
Pessin JE, et al: Geroscience: Linking aging to chronic disease.
Cell. 159:709–713. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Campisi J: Aging, cellular senescence, and
cancer. Annu Rev Physiol. 75:685–705. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Saffrey MJ: Aging of the mammalian
gastrointestinal tract: A complex organ system. Age (Dordr).
36(9603)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Cox NJ, Ibrahim K, Sayer AA, Robinson SM
and Roberts HC: Assessment and treatment of the anorexia of aging:
A systematic review. Nutrients. 11(144)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Parker BA and Chapman IM: Food intake and
ageing-the role of the gut. Mech Ageing Dev. 125:859–866.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Siddappa PK and Birk JW: Gastrointestinal
health and healthy aging. In: Healthy Aging: A Complete Guide to
Clinical Management. Coll PP (ed). Springer International
Publishing, Cham, pp67-79, 2019.
|
|
7
|
Doan TN, Ho WC, Wang LH, Chang FC, Nhu NT
and Chou LW: Prevalence and methods for assessment of oropharyngeal
dysphagia in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J
Clin Med. 11(2605)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Mounsey A, Raleigh M and Wilson A:
Management of constipation in older adults. Am Fam Physician.
92:500–504. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chang L, Toner BB, Fukudo S, Guthrie E,
Locke GR, Norton NJ and Sperber AD: Gender, age, society, culture,
and the patient's perspective in the functional gastrointestinal
disorders. Gastroenterology. 130:1435–1446. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kim YS and Kim N: Sex-gender differences
in irritable bowel syndrome. J Neurogastroenterol Motil.
24:544–558. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Alqudah M, Al-Shboul O, Al Dwairi A,
Al-U´Datt DG and Alqudah A: Progesterone inhibitory role on
gastrointestinal motility. Physiol Res. 71:193–198. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Oh JE, Kim YW, Park SY and Kim JY:
Estrogen rather than progesterone cause constipation in both female
and male mice. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 17:423–426.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Shah E, Rezaie A, Riddle M and Pimentel M:
Psychological disorders in gastrointestinal disease: Epiphenomenon,
cause or consequence? Ann Gastroenterol. 27:224–230.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Haug TT, Mykletun A and Dahl AA: Are
anxiety and depression related to gastrointestinal symptoms in the
general population? Scand J Gastroenterol. 37:294–298.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Salk RH, Hyde JS and Abramson LY: Gender
differences in depression in representative national samples:
Meta-analyses of diagnoses and symptoms. Psychol Bull. 143:783–822.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Furness JB: The enteric nervous system and
neurogastroenterology. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 9:286–294.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Rao M and Gershon MD: Enteric nervous
system development: What could possibly go wrong? Nat Rev Neurosci.
19:552–565. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Camilleri M, Cowen T and Koch TR: Enteric
neurodegeneration in ageing. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 20:418–429.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Saffrey MJ: Cellular changes in the
enteric nervous system during ageing. Dev Biol. 382:344–355.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
El-Salhy M, Sandström O and Holmlund F:
Age-induced changes in the enteric nervous system in the mouse.
Mech Ageing Dev. 107:93–103. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Bernard CE, Gibbons SJ, Gomez-Pinilla PJ,
Lurken MS, Schmalz PF, Roeder JL, Linden D, Cima RR, Dozois EJ,
Larson DW, et al: Effect of age on the enteric nervous system of
the human colon. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 21:746–e46.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Colín-González AL, Santana RA, Silva-Islas
CA, Chánez-Cárdenas ME, Santamaría A and Maldonado PD: The
antioxidant mechanisms underlying the aged garlic extract- and
S-allylcysteine-induced protection. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2012(907162)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Matsutomo T and Kodera Y: Development of
an analytic method for sulfur compounds in aged garlic extract with
the use of a postcolumn high performance liquid chromatography
method with sulfur-specific detection. J Nutr. 146:450S–455S.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ried K, Frank OR and Stocks NP: Aged
garlic extract lowers blood pressure in patients with treated but
uncontrolled hypertension: A randomised controlled trial.
Maturitas. 67:144–150. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ried K, Frank OR and Stocks NP: Aged
garlic extract reduces blood pressure in hypertensives: A
dose-response trial. Eur J Clin Nutr. 67:64–70. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ried K, Travica N and Sali A: The effect
of aged garlic extract on blood pressure and other cardiovascular
risk factors in uncontrolled hypertensives: The AGE at Heart trial.
Integr Blood Press Control. 9:9–21. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ried K, Travica N and Sali A: The effect
of kyolic aged garlic extract on gut microbiota, inflammation, and
cardiovascular markers in hypertensives: The GarGIC trial. Front
Nutr. 5(122)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zini A, Mann J, Mazor S and Vered Y: The
efficacy of aged garlic extract on gingivitis-A randomized clinical
trial. J Clin Dent. 29:52–56. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Takahashi K, Nango H, Ushijima M,
Takashima M, Nakamoto M, Matsutomo T, Jikihara H, Arakawa N, Maki
S, Yabuki A, et al: Therapeutic effect of aged garlic extract on
gingivitis in dogs. Front Vet Sci. 10(1277272)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Harauma A and Moriguchi T: Aged garlic
extract improves blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats
more safely than raw garlic. J Nutr. 136 (3 Suppl):769S–773S.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Matsutomo T, Ushijima M, Kodera Y,
Nakamoto M, Takashima M, Morihara N and Tamura K: Metabolomic study
on the antihypertensive effect of S-1-propenylcysteine in
spontaneously hypertensive rats using liquid chromatography coupled
with quadrupole-Orbitrap mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt
Technol Biomed Life Sci. 1046:147–155. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Matsutomo T, Ushijima M, Kunimura K and
Ohtani M: Metabolomic study reveals the acute hypotensive effect of
S-1-propenylcysteine accompanied by alteration of the plasma
histidine level in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Pharm Biomed
Anal. 168:148–154. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Ushijima M, Takashima M, Kunimura K,
Kodera Y, Morihara N and Tamura K: Effects of S-1-propenylcysteine,
a sulfur compound in aged garlic extract, on blood pressure and
peripheral circulation in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Pharm
Pharmacol. 70:559–565. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Matsutomo T: Potential benefits of garlic
and other dietary supplements for the management of hypertension.
Exp Ther Med. 19:1479–1484. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Borek C: Antioxidant health effects of
aged garlic extract. J Nutr. 131 (3S):1010S–1015S. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Yamato O, Tsuneyoshi T, Ushijima M,
Jikihara H and Yabuki A: Safety and efficacy of aged garlic extract
in dogs: Upregulation of the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related
factor 2 (Nrf2) signaling pathway and Nrf2-regulated phase II
antioxidant enzymes. BMC Vet Res. 14(373)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Tsuneyoshi T: BACH1 mediates the
antioxidant properties of aged garlic extract. Exp Ther Med.
19:1500–1503. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Moriguchi T, Saito H and Nishiyama N: Aged
garlic extract prolongs longevity and improves spatial memory
deficit in senescence-accelerated mouse. Biol Pharm Bull.
19:305–307. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ogawa T, Kodera Y, Hirata D, Blackwell TK
and Mizunuma M: Natural thioallyl compounds increase oxidative
stress resistance and lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans by
modulating SKN-1/Nrf. Sci Rep. 6(21611)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Morihara N, Hino A, Miki S, Takashima M
and Suzuki JI: Aged garlic extract suppresses inflammation in
apolipoprotein E-knockout mice. Mol Nutr Food Res.
61:2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Suzuki JI, Kodera Y, Miki S, Ushijima M,
Takashima M, Matsutomo T and Morihara N: Anti-inflammatory action
of cysteine derivative S-1-propenylcysteine by inducing MyD88
degradation. Sci Rep. 8(14148)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Ohtani M and Nishimura T:
Sulfur-containing amino acids in aged garlic extract inhibit
inflammation in human gingival epithelial cells by suppressing
intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression and IL-6 secretion.
Biomed Rep. 12:99–108. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Miki S, Suzuki JI, Kunimura K and Morihara
N: Mechanisms underlying the attenuation of chronic inflammatory
diseases by aged garlic extract: Involvement of the activation of
AMP-activated protein kinase. Exp Ther Med. 19:1462–1467.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Liu J: Aged garlic therapeutic
intervention targeting inflammatory pathways in pathogenesis of
bowel disorders. Heliyon. 10(e33986)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Maeda T, Miki S, Morihara N and Kagawa Y:
Aged garlic extract ameliorates fatty liver and insulin resistance
and improves the gut microbiota profile in a mouse model of insulin
resistance. Exp Ther Med. 18:857–866. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Ried K: Garlic lowers blood pressure in
hypertensive subjects, improves arterial stiffness and gut
microbiota: A review and meta-analysis. Exp Ther Med. 19:1472–1478.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Horie T, Li T, Ito K, Sumi S and Fuwa T:
Aged garlic extract protects against methotrexate-induced apoptotic
cell injury of IEC-6 cells. J Nutr. 136 (3 Suppl):861S–863S.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Kang YK, Min B, Eom J and Park JS:
Different phases of aging in mouse old skeletal muscle. Aging
(Albany NY). 14:143–160. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Jackson SJ, Andrews N, Ball D, Bellantuono
I, Gray J, Hachoumi L, Holmes A, Latcham J, Petrie A, Potter P, et
al: Does age matter? The impact of rodent age on study outcomes.
Lab Anim. 51:160–169. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Mallon BS and Macklin WB: Overexpression
of the 3'-untranslated region of myelin proteolipid protein mRNA
leads to reduced expression of endogenous proteolipid mRNA.
Neurochem Res. 27:1349–1360. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Guyer RA, Stavely R, Robertson K, Bhave S,
Mueller JL, Picard NM, Hotta R, Kaltschmidt JA and Goldstein AM:
Single-cell multiome sequencing clarifies enteric glial diversity
and identifies an intraganglionic population poised for
neurogenesis. Cell Rep. 42(112194)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Kodera Y, Kurita M, Nakamoto M and
Matsutomo T: Chemistry of aged garlic: Diversity of constituents in
aged garlic extract and their production mechanisms via the
combination of chemical and enzymatic reactions. Exp Ther Med.
19:1574–1584. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Bradham KD, Scheckel KG, Nelson CM, Seales
PE, Lee GE, Hughes MF, Miller BW, Yeow A, Gilmore T, Serda SM, et
al: Relative bioavailability and bioaccessibility and speciation of
arsenic in contaminated soils. Environ Health Perspect.
119:1629–1634. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Sasselli V, Boesmans W, Vanden Berghe P,
Tissir F, Goffinet AM and Pachnis V: Planar cell polarity genes
control the connectivity of enteric neurons. J Clin Invest.
123:1763–1772. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Natale G, Kastsiushenka O, Fulceri F,
Ruggieri S, Paparelli A and Fornai F: MPTP-induced parkinsonism
extends to a subclass of TH-positive neurons in the gut. Brain Res.
1355:195–206. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Patel BA, Patel N, Fidalgo S, Wang C,
Ranson RN, Saffrey MJ and Yeoman MS: Impaired colonic motility and
reduction in tachykinin signalling in the aged mouse. Exp Gerontol.
53:24–30. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Jeong D, Kim DH, Kang IB, Kim H, Song KY,
Kim HS and Seo KH: Modulation of gut microbiota and increase in
fecal water content in mice induced by administration of
Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens DN1. Food Funct. 8:680–686.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Rahman AA, Ohkura T, Bhave S, Pan W,
Ohishi K, Ott L, Han C, Leavitt A, Stavely R, Burns AJ, et al:
Enteric neural stem cell transplant restores gut motility in mice
with Hirschsprung disease. JCI Insight. 9(e179755)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Rahman AA, Stavely R, Pan W, Ott L, Ohishi
K, Ohkura T, Han C, Hotta R and Goldstein AM: Optogenetic
activation of cholinergic enteric neurons reduces inflammation in
experimental colitis. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 17:907–921.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
McCann CJ, Cooper JE, Natarajan D, Jevans
B, Burnett LE, Burns AJ and Thapar N: Transplantation of enteric
nervous system stem cells rescues nitric oxide synthase deficient
mouse colon. Nat Commun. 8(15937)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Fried DE, Watson RE, Robson SC and
Gulbransen BD: Ammonia modifies enteric neuromuscular transmission
through glial γ-aminobutyric acid signaling. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 313:G570–G580. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Stavely R, Bhave S, Ho WLN, Ahmed M, Pan
W, Rahman AA, Ulloa J, Bousquet N, Omer M, Guyer R, et al: Enteric
mesenchymal cells support the growth of postnatal enteric neural
stem cells. Stem Cells. 39:1236–1252. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Bhave S, Arciero E, Baker C, Ho WL,
Stavely R, Goldstein AM and Hotta R: Enteric neuronal cell therapy
reverses architectural changes in a novel diphtheria toxin-mediated
model of colonic aganglionosis. Sci Rep. 9(18756)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Hotta R, Rahman A, Bhave S, Stavely R, Pan
W, Srinivasan S, de Couto G, Rodriguez-Borlado L, Myers R, Burns AJ
and Goldstein AM: Transplanted ENSCs form functional connections
with intestinal smooth muscle and restore colonic motility in
nNOS-deficient mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 14(232)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Sahakian L, Filippone RT, Stavely R,
Robinson AM, Yan XS, Abalo R, Eri R, Bornstein JC, Kelley MR and
Nurgali K: Inhibition of APE1/Ref-1 redox signaling alleviates
intestinal dysfunction and damage to myenteric neurons in a mouse
model of spontaneous chronic colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis.
27:388–406. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Mueller JL, Leavitt AR, Rahman AA, Han CY,
Ott LC, Mahdavian NS, Carbone SE, King SK, Burns AJ, Poole DP, et
al: Highly neurogenic glia from human and mouse myenteric ganglia
generate functional neurons following culture and transplantation
into the gut. Cell Rep. 43(114919)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Jonscher R and Belkind-Gerson J: Concise
review: Cellular and molecular mechanisms of postnatal
injury-induced enteric neurogenesis. Stem Cells. 37:1136–1143.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Sohal RS and Weindruch R: Oxidative
stress, caloric restriction, and aging. Science. 273:59–63.
1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Thrasivoulou C, Soubeyre V, Ridha H,
Giuliani D, Giaroni C, Michael GJ, Saffrey MJ and Cowen T: Reactive
oxygen species, dietary restriction and neurotrophic factors in
age-related loss of myenteric neurons. Aging Cell. 5:247–257.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Li J, O W, Li W, Jiang ZG and Ghanbari HA:
Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative disorders. Int J Mol Sci.
14:24438–24475. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Liu Z, Zhou T, Ziegler AC, Dimitrion P and
Zuo L: Oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases: From
molecular mechanisms to clinical applications. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2017(2525967)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Morén C, deSouza RM, Giraldo DM and Uff C:
Antioxidant therapeutic strategies in neurodegenerative diseases.
Int J Mol Sci. 23(9328)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Fukui K: Reactive oxygen species induce
neurite degeneration before induction of cell death. J Clin Biochem
Nutr. 59:155–159. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Zhao X, Fang J, Li S, Gaur U, Xing X, Wang
H and Zheng W: Artemisinin attenuated hydrogen peroxide
(H2O2)-induced oxidative injury in sh-sy5y
and hippocampal neurons via the activation of AMPK pathway. Int J
Mol Sci. 20(2680)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Becker L, Nguyen L, Gill J, Kulkarni S,
Pasricha PJ and Habtezion A: Age-dependent shift in macrophage
polarisation causes inflammation-mediated degeneration of enteric
nervous system. Gut. 67:827–836. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Sun T, Li D, Hu S, Huang L, Sun H, Yang S,
Wu B, Ji F and Zhou D: Aging-dependent decrease in the numbers of
enteric neurons, interstitial cells of Cajal and expression of
connexin43 in various regions of gastrointestinal tract. Aging
(Albany NY). 10:3851–3865. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Kruger GM, Mosher JT, Bixby S, Joseph N,
Iwashita T and Morrison SJ: Neural crest stem cells persist in the
adult gut but undergo changes in self-renewal, neuronal subtype
potential, and factor responsiveness. Neuron. 35:657–669.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Laszczyk AM, Fox-Quick S, Vo HT, Nettles
D, Pugh PC, Overstreet-Wadiche L and King GD: Klotho regulates
postnatal neurogenesis and protects against age-related spatial
memory loss. Neurobiol Aging. 59:41–54. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Song H, Lu Y, Qu Z, Mossine VV, Martin MB,
Hou J, Cui J, Peculis BA, Mawhinney TP, Cheng J, et al: Effects of
aged garlic extract and FruArg on gene expression and signaling
pathways in lipopolysaccharide-activated microglial cells. Sci Rep.
6(35323)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Wlosinska M, Nilsson AC, Hlebowicz J,
Hauggaard A, Kjellin M, Fakhro M and Lindstedt S: The effect of
aged garlic extract on the atherosclerotic process-a randomized
double-blind placebo-controlled trial. BMC Complement Med Ther.
20(132)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Lindstedt S, Wlosinska M, Nilsson AC,
Hlebowicz J, Fakhro M and Sheikh R: Successful improved peripheral
tissue perfusion was seen in patients with atherosclerosis after 12
months of treatment with aged garlic extract. Int Wound J.
18:681–691. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Yang J, Luo J, Tian X, Zhao Y, Li Y and Wu
X: Progress in understanding oxidative stress, aging, and
aging-related diseases. Antioxidants (Basel).
13(394)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Chen X, Guo C and Kong J: Oxidative stress
in neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regen Res. 7:376–385.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Sienes Bailo P, Llorente Martín E,
Calmarza P, Montolio Breva S, Bravo Gómez A, Pozo Giráldez A,
Sánchez-Pascuala Callau JJ, Vaquer Santamaría JM, Dayaldasani
Khialani A, Cerdá Micó C, et al: The role of oxidative stress in
neurodegenerative diseases and potential antioxidant therapies. Adv
Lab Med. 3:342–360. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In English,
Spanish).
|
|
85
|
Smith AN, Shaughness M, Collier S, Hopkins
D and Byrnes KR: Therapeutic targeting of microglia mediated
oxidative stress after neurotrauma. Front Med (Lausanne).
9(1034692)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Pan W, Rahman AA, Ohkura T, Stavely R,
Ohishi K, Han CY, Leavitt A, Kashiwagi A, Burns AJ, Goldstein AM
and Hotta R: Autologous cell transplantation for treatment of
colorectal aganglionosis in mice. Nat Commun.
15(2479)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Imai J, Ide N, Nagae S, Moriguchi T,
Matsuura H and Itakura Y: Antioxidant and radical scavenging
effects of aged garlic extract and its constituents. Planta Med.
60:417–420. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Shi H, Jing X, Wei X, Perez RG, Ren M,
Zhang X and Lou H: S-allyl cysteine activates the Nrf2-dependent
antioxidant response and protects neurons against ischemic injury
in vitro and in vivo. J Neurochem. 133:298–308. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Wu W, Liu BH, Xie CL, Xia XD and Zhang YM:
Neuroprotective effects of N-acetyl cysteine on primary hippocampus
neurons against hydrogen peroxide-induced injury are mediated via
inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinases signal transduction
and antioxidative action. Mol Med Rep. 17:6647–6654.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Shah SA, Yoon GH, Kim HO and Kim MO:
Vitamin C neuroprotection against dose-dependent glutamate-induced
neurodegeneration in the postnatal brain. Neurochem Res.
40:875–884. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Hui Y, Chengyong T, Cheng L, Haixia H,
Yuanda Z and Weihua Y: Resveratrol attenuates the cytotoxicity
induced by amyloid-β1-42 in PC12 cells by upregulating
heme oxygenase-1 via the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway. Neurochem Res.
43:297–305. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Tonelli C, Chio IIC and Tuveson DA:
Transcriptional regulation by Nrf2. Antioxid Redox Signal.
29:1727–1745. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Moratilla-Rivera I, Sánchez M,
Valdés-González JA and Gómez-Serranillos MP: Natural products as
modulators of Nrf2 signaling pathway in neuroprotection. Int J Mol
Sci. 24(3748)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Nagy N and Goldstein AM: Enteric nervous
system development: A crest cell's journey from neural tube to
colon. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 66:94–106. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Belkind-Gerson J, Graham HK, Reynolds J,
Hotta R, Nagy N, Cheng L, Kamionek M, Shi HN, Aherne CM and
Goldstein AM: Colitis promotes neuronal differentiation of Sox2+
and PLP1+ enteric cells. Sci Rep. 7(2525)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Hotta R, Stamp LA, Foong JP, McConnell SN,
Bergner AJ, Anderson RB, Enomoto H, Newgreen DF, Obermayr F,
Furness JB and Young HM: Transplanted progenitors generate
functional enteric neurons in the postnatal colon. J Clin Invest.
123:1182–1191. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Stamp LA, Gwynne RM, Foong JPP, Lomax AE,
Hao MM, Kaplan DI, Reid CA, Petrou S, Allen AM, Bornstein JC and
Young HM: Optogenetic demonstration of functional innervation of
mouse colon by neurons derived from transplanted neural cells.
Gastroenterology. 152:1407–1418. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Hotta R, Pan W, Bhave S, Nagy N, Stavely
R, Ohkura T, Krishnan K, de Couto G, Myers R, Rodriguez-Borlado L,
et al: Isolation, expansion, and endoscopic delivery of autologous
enteric neuronal stem cells in swine. Cell Transplant.
32(9636897231215233)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Lindley RM, Hawcutt DB, Connell MG, Almond
SL, Vannucchi MG, Faussone-Pellegrini MS, Edgar DH and Kenny SE:
Human and mouse enteric nervous system neurosphere transplants
regulate the function of aganglionic embryonic distal colon.
Gastroenterology. 135:205–216.e6. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Cheng LS, Hotta R, Graham HK,
Belkind-Gerson J, Nagy N and Goldstein AM: Postnatal human enteric
neuronal progenitors can migrate, differentiate, and proliferate in
embryonic and postnatal aganglionic gut environments. Pediatr Res.
81:838–846. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Metzger M, Bareiss PM, Danker T, Wagner S,
Hennenlotter J, Guenther E, Obermayr F, Stenzl A, Koenigsrainer A,
Skutella T and Just L: Expansion and differentiation of neural
progenitors derived from the human adult enteric nervous system.
Gastroenterology. 137:2063–2073.e4. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Rollo BN, Zhang D, Stamp LA, Menheniott
TR, Stathopoulos L, Denham M, Dottori M, King SK, Hutson JM and
Newgreen DF: Enteric neural cells from hirschsprung disease
patients form ganglia in autologous aneuronal colon. Cell Mol
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2:92–109. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Lin L, Wu Q, Lu F, Lei J, Zhou Y, Liu Y,
Zhu N, Yu Y, Ning Z, She T and Hu M: Nrf2 signaling pathway:
Current status and potential therapeutic targetable role in human
cancers. Front Oncol. 13(1184079)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Kärkkäinen V, Pomeshchik Y, Savchenko E,
Dhungana H, Kurronen A, Lehtonen S, Naumenko N, Tavi P, Levonen AL,
Yamamoto M, et al: Nrf2 regulates neurogenesis and protects neural
progenitor cells against Aβ toxicity. Stem Cells. 32:1904–1916.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Mittal RK: Integrated Systems Physiology:
From Molecule to Function to Disease. In: Motor Function of the
Pharynx, Esophagus, and its Sphincters. Morgan & Claypool Life
Sciences. Copyright © 2011 by Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences,
San Rafael (CA), 2011.
|
|
106
|
Takashima M, Kanamori Y, Kodera Y,
Morihara N and Tamura K: Aged garlic extract exerts
endothelium-dependent vasorelaxant effect on rat aorta by
increasing nitric oxide production. Phytomedicine. 24:56–61.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Sanders KM: Regulation of smooth muscle
excitation and contraction. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 20 (Suppl
1):S39–S53. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Sarna SK: Integrated Systems Physiology:
From Molecule to Function to Disease. In: Colonic Motility: From
Bench Side to Bedside. Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences.
Copyright © 2010 by Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences, San Rafael
(CA), 2010.
|
|
109
|
Mori M and Gotoh T: Regulation of nitric
oxide production by arginine metabolic enzymes. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 275:715–719. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Bayer S, Jellali A, Crenner F, Aunis D and
Angel F: Functional evidence for a role of GABA receptors in
modulating nerve activities of circular smooth muscle from rat
colon in vitro. Life Sci. 72:1481–1493. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Ghia JE, Pradaud I, Crenner F,
Metz-Boutigue MH, Aunis D and Angel F: Effect of acetic acid or
trypsin application on rat colonic motility in vitro and modulation
by two synthetic fragments of chromogranin A. Regul Pept.
124:27–35. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Tepavcević SN, Isenović ER, Varagić VM and
Milovanović SR: Sodium nitroprusside regulates the relaxation of
the longitudinal muscle in the gut. Pharmazie. 63:151–155.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Shah V, Lyford G, Gores G and Farrugia G:
Nitric oxide in gastrointestinal health and disease.
Gastroenterology. 126:903–913. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Dunn WR, Alexander SP, Ralevic V and
Roberts RE: Effects of hydrogen sulphide in smooth muscle.
Pharmacol Ther. 158:101–113. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Rose P, Moore PK and Zhu YZ: Garlic and
gaseous mediators. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 39:624–634.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Benavides GA, Squadrito GL, Mills RW,
Patel HD, Isbell TS, Patel RP, Darley-Usmar VM, Doeller JE and
Kraus DW: Hydrogen sulfide mediates the vasoactivity of garlic.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:17977–17982. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Abe K, Hori Y and Myoda T: Volatile
compounds of fresh and processed garlic. Exp Ther Med.
19:1585–1593. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Gallego D, Clavé P, Donovan J, Rahmati R,
Grundy D, Jiménez M and Beyak MJ: The gaseous mediator, hydrogen
sulphide, inhibits in vitro motor patterns in the human, rat and
mouse colon and jejunum. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 20:1306–1316.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Gil V, Parsons S, Gallego D, Huizinga J
and Jimenez M: Effects of hydrogen sulphide on motility patterns in
the rat colon. Br J Pharmacol. 169:34–50. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Kerfoot WW, Park HY, Schwartz LB, Hagen PO
and Carson CC III: Characterization of calcium channel blocker
induced smooth muscle relaxation using a model of isolated corpus
cavernosum. J Urol. 150:249–252. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Zheng Z, Tang J, Hu Y and Zhang W: Role of
gut microbiota-derived signals in the regulation of
gastrointestinal motility. Front Med (Lausanne).
9(961703)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Carabotti M, Scirocco A, Maselli MA and
Severi C: The gut-brain axis: Interactions between enteric
microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann Gastroenterol.
28:203–209. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Panyod S, Wu WK, Chen PC, Chong KV, Yang
YT, Chuang HL, Chen CC, Chen RA, Liu PY, Chung CH, et al:
Atherosclerosis amelioration by allicin in raw garlic through gut
microbiota and trimethylamine-N-oxide modulation. NPJ Biofilms
Microbiomes. 8(4)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Li M, Yun W, Wang G, Li A, Gao J and He Q:
Roles and mechanisms of garlic and its extracts on atherosclerosis:
A review. Front Pharmacol. 13(954938)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|