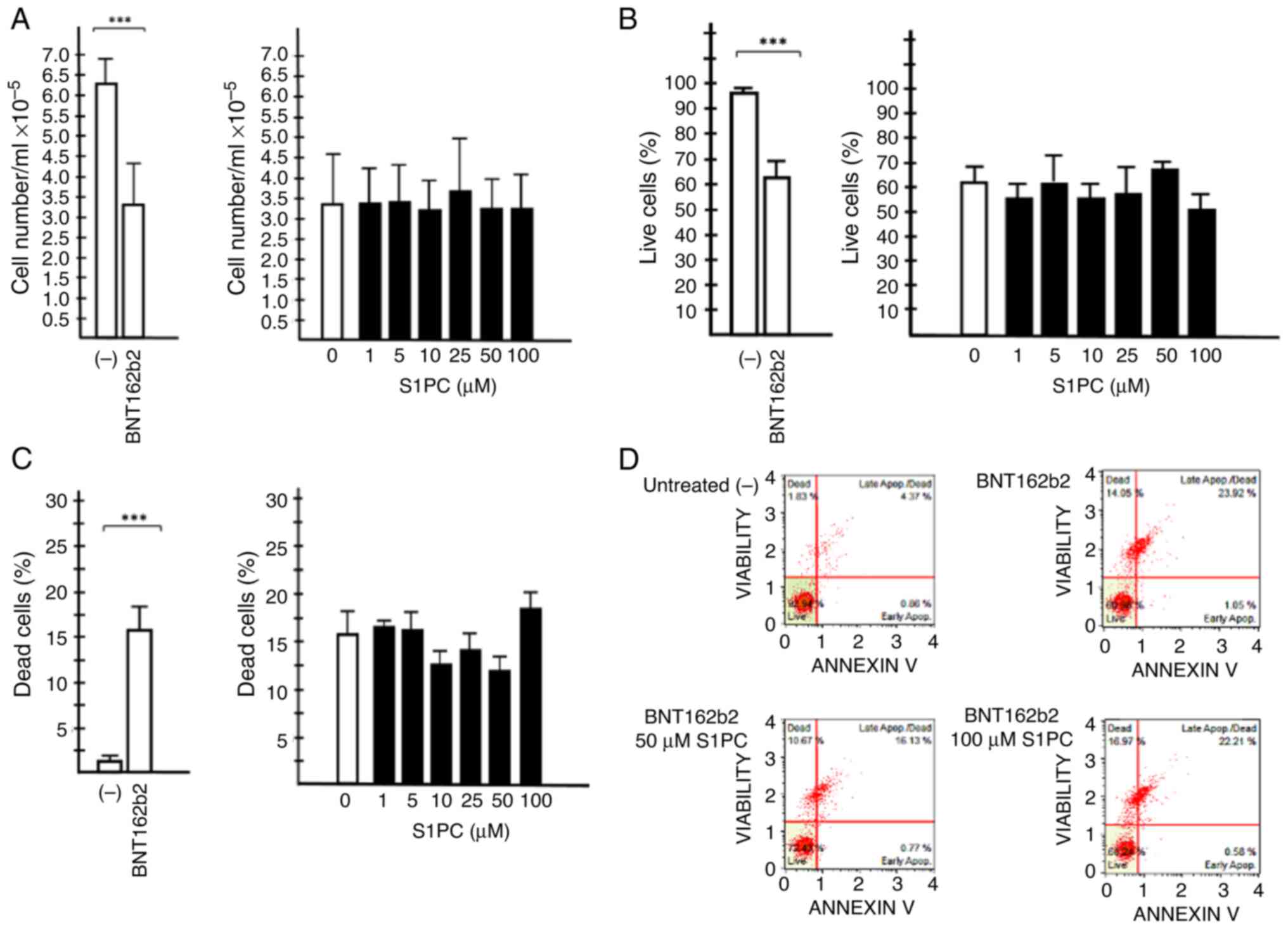
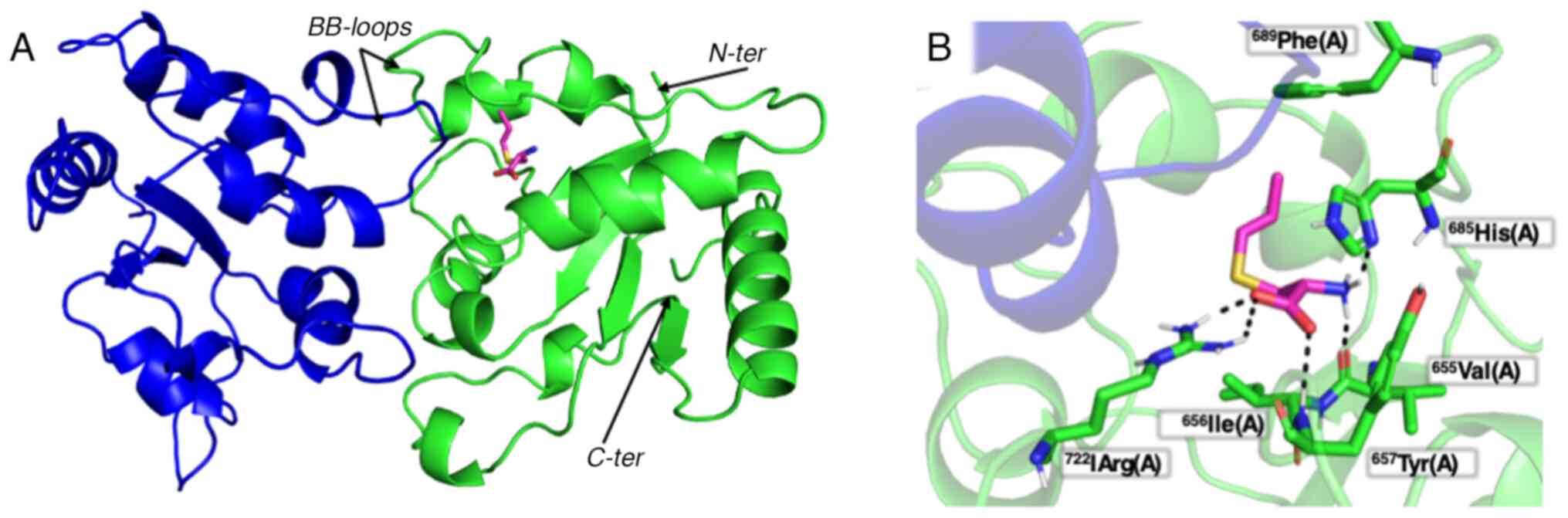
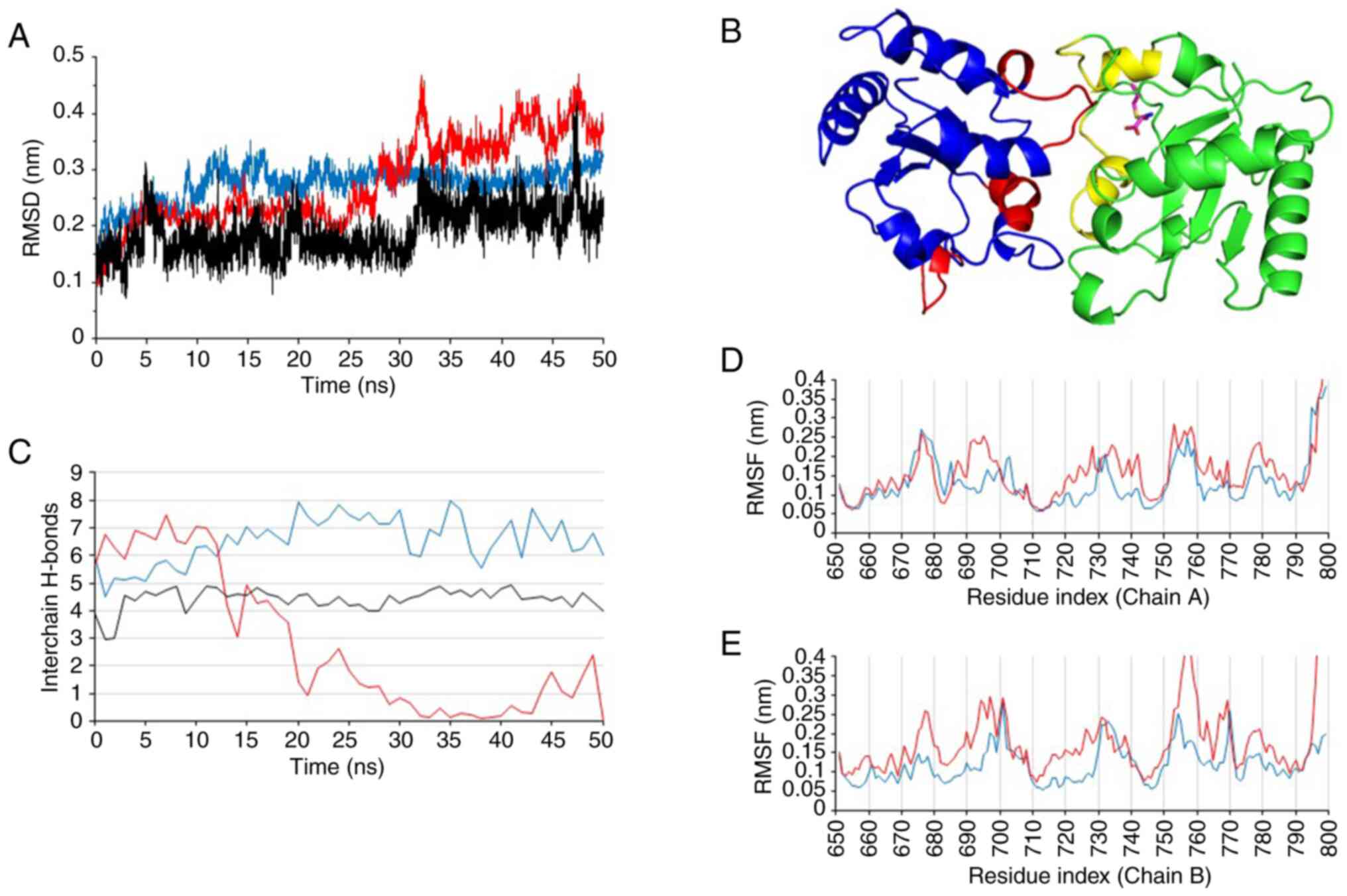
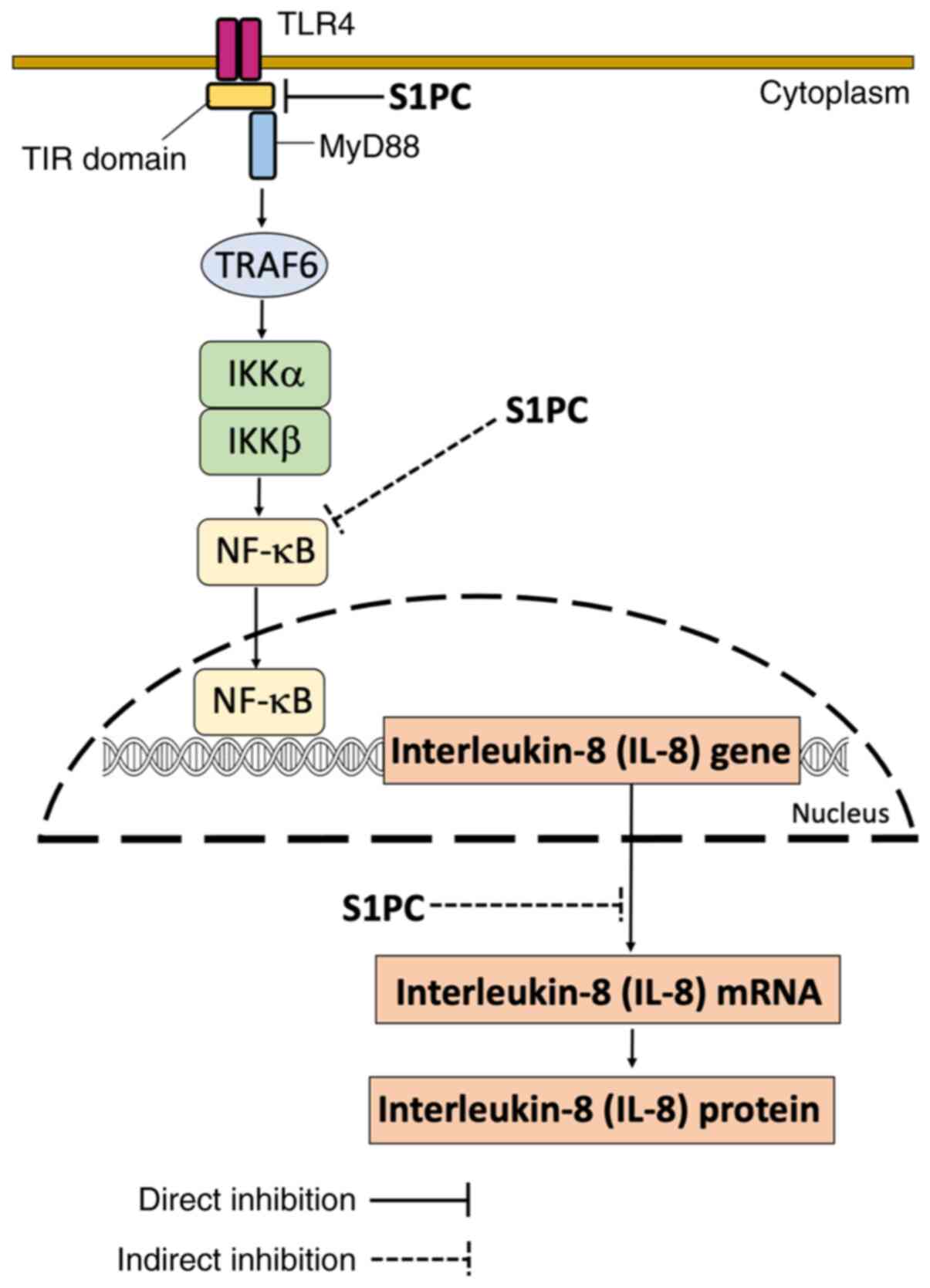
|
1
|
Pascarella G, Strumia A, Piliego C, Bruno
F, Del Buono R, Costa F, Scarlata S and Agrò FE: COVID-19 diagnosis
and management: A comprehensive review. J Intern Med. 288:192–206.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Pelaia C, Tinello C, Vatrella A, De Sarro
G and Pelaia G: Lung under attack by COVID-19-induced cytokine
storm: Pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Ther Adv
Respir Dis. 14(1753466620933508)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Fajgenbaum DC and June CH: Cytokine storm.
N Engl J Med. 383:2255–2273. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Mangalmurti N and Hunter CA: Cytokine
storms: Understanding COVID-19. Immunity. 53:19–25. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Fara A, Mitrev Z, Rosalia RA and Assas BM:
Cytokine storm and COVID-19: A chronicle of pro-inflammatory
cytokines. Open Biol. 10(200160)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ratajczak MZ, Bujko K, Ciechanowicz A,
Sielatycka K, Cymer M, Marlicz W and Kucia M: SARS-CoV-2 entry
receptor ACE2 is expressed on very small CD45-
precursors of hematopoietic and endothelial cells and in response
to virus spike protein activates the Nlrp3 inflammasome. Stem Cell
Rev Rep. 17:266–277. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Soumagne T, Winiszewski H, Besch G, Mahr
N, Senot T, Costa P, Grillet F, Behr J, Mouhat B, Mourey G, et al:
Pulmonary embolism among critically ill patients with ARDS due to
COVID-19. Respir Med Res. 78(100789)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Grasselli G, Tonetti T, Protti A, Langer
T, Girardis M, Bellani G, Laffey J, Carrafiello G, Carsana L,
Rizzuto C, et al: Pathophysiology of COVID-19-associated acute
respiratory distress syndrome: A multicentre prospective
observational study. Lancet Respir Med. 8:1201–1208.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Matthay MA, Leligdowicz A and Liu KD:
Biological mechanisms of COVID-19 acute respiratory distress
syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 202:1489–1491. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Nasonov E and Samsonov M: The role of
interleukin 6 inhibitors in therapy of severe COVID-19. Biomed
Pharmacother. 131(110698)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Andreakos E, Papadaki M and Serhan CN:
Dexamethasone, pro-resolving lipid mediators and resolution of
inflammation in COVID-19. Allergy. 76:626–628. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
de Simone G and Mancusi C: Finding the
right time for anti-inflammatory therapy in COVID-19. Int J Infect
Dis. 101:247–248. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Khalifa SAM, Yosri N, El-Mallah MF,
Ghonaim R, Guo Z, Musharraf SG, Du M, Khatib A, Xiao J, Saeed A, et
al: Screening for natural and derived bio-active compounds in
preclinical and clinical studies: One of the frontlines of fighting
the coronaviruses pandemic. Phytomedicine.
85(153311)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Matveeva T, Khafizova G and Sokornova S:
In search of herbal anti-SARS-Cov2 compounds. Front Plant Sci.
11(589998)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ohkubo S, Dalla Via L, Grancara S,
Kanamori Y, García-Argáez AN, Canettieri G, Arcari P, Toninello A
and Agostinelli E: The antioxidant, aged garlic extract, exerts
cytotoxic effects on wild-type and multidrug-resistant human cancer
cells by altering mitochondrial permeability. Int J Oncol.
53:1257–1268. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Lee J, Zhao N, Fu Z, Choi J, Lee HJ and
Chung M: Effects of garlic intake on cancer: A systematic review of
randomized clinical trials and cohort studies. Nutr Res Pract.
15:773–788. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kodera Y, Ushijima M, Amano H, Suzuki JI
and Matsutomo T: Chemical and biological properties of
S-1-propenyl-l-cysteine in aged garlic extract. Molecules.
22(570)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yeh YY and Liu L: Cholesterol-lowering
effect of garlic extracts and organosulfur compounds: Human and
animal studies. J Nutr. 131 (3S):989S–993S. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Nango H and Ohtani M:
S-1-propenyl-L-cysteine suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced
expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1 through inhibition of
tumor necrosis factor-α converting enzyme-epidermal growth factor
receptor axis in human gingival fibroblasts. PLoS One.
18(e0284713)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ushijima M, Takashima M, Kunimura K,
Kodera Y, Morihara N and Tamura K: Effects of S-1-propenylcysteine,
a sulfur compound in aged garlic extract, on blood pressure and
peripheral circulation in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Pharm
Pharmacol. 70:559–565. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Gasparello J, d'Aversa E, Breveglieri G,
Borgatti M, Finotti A and Gambari R: In vitro induction of
interleukin-8 by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein is inhibited in bronchial
epithelial IB3-1 cells by a miR-93-5p agomiR. Int Immunopharmacol.
101(108201)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zurlo M, Gasparello J, Verona M, Papi C,
Cosenza LC, Finotti A, Marzaro G and Gambari R: The anti-SARS-CoV-2
BNT162b2 vaccine suppresses mithramycin-induced erythroid
differentiation and expression of embryo-fetal globin genes in
human erythroleukemia K562 cells. Exp Cell Res.
433(113853)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Jiménez-Martín E, Ruiz J, Pérez-Palacios
T, Silva A and Antequera T: Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
method for the determination of free amino acids as their
dimethyl-tert-butylsilyl (TBDMS) derivatives in animal source food.
J Agric Food Chem. 60:2456–2463. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Gasparello J, Lomazzi M, Papi C, D'Aversa
E, Sansone F, Casnati A, Donofrio G, Gambari R and Finotti A:
Efficient delivery of MicroRNA and AntimiRNA molecules using an
argininocalix[4]arene macrocycle. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids.
18:748–763. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Aldén M, Olofsson Falla F, Yang D,
Barghouth M, Luan C, Rasmussen M and De Marinis Y: Intracellular
reverse transcription of pfizer BioNTech COVID-19 mRNA vaccine
bnt162b2 in vitro in human liver cell line. Curr Issues Mol Biol.
44:1115–1126. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Patra MC, Kwon HK, Batool M and Choi S:
Computational insight into the structural organization of
full-length Toll-like receptor 4 dimer in a model phospholipid
bilayer. Front Immunol. 9(489)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Hanwell MD, Curtis DE, Lonie DC,
Vandermeersch T, Zurek E and Hutchison GR: Avogadro: An advanced
semantic chemical editor, visualization, and analysis platform. J
Cheminform. 4(17)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Eberhardt J, Santos-Martins D, Tillack AF
and Forli S: AutoDock Vina 1.2.0: New docking methods, expanded
force field, and python bindings. J Chem Inf Model. 61:3891–3898.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Abraham MJ, Murtola T, Schulz R, Páll S,
Smith JC, Hess B and Lindahl E: GROMACS: High performance molecular
simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to
supercomputers. SoftwareX. 1-2:19–25. 2015.
|
|
31
|
Bonomi M, Branduardi D, Bussi G, Camilloni
C, Provasi D, Raiteri P, Donadio D, Marinelli F, Pietrucci F,
Broglia RA and Parrinello M: PLUMED: A portable plugin for
free-energy calculations with molecular dynamics. Comput Phys
Commun. 180:1961–1972. 2009.
|
|
32
|
Huang J and MacKerell AD Jr: CHARMM36
all-atom additive protein force field: Validation based on
comparison to NMR data. J Comput Chem. 34:2135–2145.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Darden T, York D and Pedersen L: Particle
mesh Ewald: An N·log(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J
Chem Phys. 98:10089–10092. 1993.
|
|
34
|
Hess B: P-LINCS: A parallel linear
constraint solver for molecular simulation. J Chem Theory Comput.
4:116–122. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Evans D and Holian B: The nose-hoover
thermostat. J Chem Phys. 83:4069–4074. 1985.
|
|
36
|
Parrinello M and Rahman A: Polymorphic
transitions in single crystals: A new molecular dynamics method. J
Appl Phys. 52:7182–7190. 1981.
|
|
37
|
Tupini C, Zurlo M, Gasparello J, Lodi I,
Finotti A, Scattolin T, Visentin F, Gambari R and Lampronti I:
Combined treatment of cancer cells using allyl palladium complexes
bearing purine-based NHC ligands and molecules targeting MicroRNAs
miR-221-3p and miR-222-3p: Synergistic effects on apoptosis.
Pharmaceutics. 15(1332)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Cari L, Naghavi Alhosseini M, Mencacci A,
Migliorati G and Nocentini G: Differences in the expression levels
of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in cells treated with mRNA-based
COVID-19 vaccines: A study on vaccines from the real world.
Vaccines (Basel). 11(879)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Bansal S, Perincheri S, Fleming T, Poulson
C, Tiffany B, Bremner RM and Mohanakumar T: Cutting edge:
Circulating exosomes with COVID spike protein are induced by
BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) Vaccination prior to Development of
Antibodies: A novel mechanism for immune activation by mRNA
vaccines. J Immunol. 207:2405–2410. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Gambari R, Papi C, Gasparello J,
Agostinelli E and Finotti A: Preliminary results and a theoretical
perspective of co-treatment using a miR-93-5p mimic and aged garlic
extract to inhibit the expression of the pro-inflammatory
interleukin-8 gene. Exp Ther Med. 29(85)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Kodera Y, Matsutomo T and Itoh K: The
evidence for the production mechanism of cis-S-1-propenylcysteine
in aged garlic extract based on a model reaction approach using its
isomers and deuterated solvents. Planta Med Lett. 2:e69–e72.
2015.
|
|
42
|
Kircheis R and Planz O: Could a lower
Toll-like receptor (TLR) and NF-κB activation due to a changed
charge distribution in the spike protein be the reason for the
lower pathogenicity of omicron? Int J Mol Sci.
23(5966)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Robles JP, Zamora M, Adan-Castro E,
Siqueiros-Marquez L, Martinez de la Escalera G and Clapp C: The
spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 induces endothelial inflammation
through integrin α5β1 and NF-κB signaling. J Biol Chem.
298(101695)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Forsyth CB, Zhang L, Bhushan A, Swanson B,
Zhang L, Mamede JI, Voigt RM, Shaikh M, Engen PA and Keshavarzian
A: The SARS-CoV-2 S1 spike protein promotes MAPK and NF-κB
activation in human lung cells and inflammatory cytokine production
in human lung and intestinal epithelial cells. Microorganisms.
10(1996)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Gasparello J, D'Aversa E, Papi C, Gambari
L, Grigolo B, Borgatti M, Finotti A and Gambari R: Sulforaphane
inhibits the expression of interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 induced
in bronchial epithelial IB3-1 cells by exposure to the SARS-CoV-2
spike protein. Phytomedicine. 87(153583)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Múnera-Rodríguez AM, Leiva-Castro C,
Sobrino F, López-Enríquez S and Palomares F: Sulforaphane-mediated
immune regulation through inhibition of NF-κB and MAPK signaling
pathways in human dendritic cells. Biomed Pharmacother.
177(117056)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Gasparello J, Marzaro G, Papi C, Gentili
V, Rizzo R, Zurlo M, Scapoli C, Finotti A and Gambari R: Effects of
sulforaphane on SARS-CoV-2 infection and NF-κB dependent expression
of genes involved in the COVID-19 ‘cytokine storm’. Int J Mol Med.
52(76)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Dharra R, Kumar Sharma A and Datta S:
Emerging aspects of cytokine storm in COVID-19: The role of
proinflammatory cytokines and therapeutic prospects. Cytokine.
169(156287)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Leavis HL, van de Veerdonk FL and Murthy
S: Stimulating severe COVID-19: The potential role of GM-CSF
antagonism. Lancet Respir Med. 10:223–224. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Cherubini A, Rusconi F and Lazzari L:
Identification of the best housekeeping gene for RT-qPCR analysis
of human pancreatic organoids. PLoS One.
16(e0260902)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Gentile AM, Lhamyani S, Coín-Aragüez L,
Oliva-Olivera W, Zayed H, Vega-Rioja A, Monteseirin J, Romero-Zerbo
SY, Tinahones FJ, Bermúdez-Silva FJ and El Bekay R: RPL13A and
EEF1A1 are suitable reference genes for qPCR during adipocyte
differentiation of vascular stromal cells from patients with
different BMI and HOMA-IR. PLoS One. 11(e0157002)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Pease JE and Sabroe I: The role of
interleukin-8 and its receptors in inflammatory lung disease:
Implications for therapy. Am J Respir Med. 1:19–25. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Molnar V, Matišić V, Kodvanj I, Bjelica R,
Jeleč Ž, Hudetz D, Rod E, Čukelj F, Vrdoljak T, Vidović D, et al:
Cytokines and chemokines involved in osteoarthritis pathogenesis.
Int J Mol Sci. 22(9208)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Marzaro G, Lampronti I, D'Aversa E,
Sacchetti G, Miolo G, Vaccarin C, Cabrini G, Dechecchi MC, Gambari
R and Chilin A: Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of
novel trimethylangelicin analogues targeting nuclear factor kB
(NF-κB). Eur J Med Chem. 151:285–293. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Gambari R, Borgatti M, Lampronti I, Fabbri
E, Brognara E, Bianchi N, Piccagli L, Yuen MCW, Kan CW, Hau DKP, et
al: Corilagin is a potent inhibitor of NF-kappaB activity and
downregulates TNF-alpha induced expression of IL-8 gene in cystic
fibrosis IB3-1 cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 13:308–315.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Doyle SL and O'Neill LAJ: Toll-like
receptors: From the discovery of NFkappaB to new insights into
transcriptional regulations in innate immunity. Biochem Pharmacol.
72:1102–1113. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Carmody RJ and Chen YH: Nuclear
factor-kappaB: Activation and regulation during Toll-like receptor
signaling. Cell Mol Immunol. 4:31–41. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Verstrepen L, Bekaert T, Chau TL,
Tavernier J, Chariot A and Beyaert R: TLR-4, IL-1R and TNF-R
signaling to NF-kappaB: Variations on a common theme. Cell Mol Life
Sci. 65:2964–2978. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Zeng Z, Yu H, Chen H, Qi W, Chen L, Chen
G, Yan W, Chen T, Ning Q, Han M and Wu D: Longitudinal changes of
inflammatory parameters and their correlation with disease severity
and outcomes in patients with COVID-19 from Wuhan, China. Crit
Care. 24(525)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Del Valle DM, Kim-Schulze S, Huang HH,
Beckmann ND, Nirenberg S, Wang B, Lavin Y, Swartz TH, Madduri D,
Stock A, et al: An inflammatory cytokine signature predicts
COVID-19 severity and survival. Nat Med. 26:1636–1643.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Burke H, Freeman A, Cellura DC, Stuart BL,
Brendish NJ, Poole S, Borca F, Phan HTT, Sheard N, Williams S, et
al: Inflammatory phenotyping predicts clinical outcome in COVID-19.
Respir Res. 21(245)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Aldallal N, McNaughton EE, Manzel LJ,
Richards AM, Zabner J, Ferkol TW and Look DC: Inflammatory response
in airway epithelial cells isolated from patients with cystic
fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 166:1248–1256. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Maiuri L, Luciani A, Giardino I, Raia V,
Villella VR, D'Apolito M, Pettoello-Mantovani M, Guido S, Ciacci C,
Cimmino M, et al: Tissue transglutaminase activation modulates
inflammation in cystic fibrosis via PPARgamma down-regulation. J
Immunol. 180:7697–7705. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Bhattacharyya S, Balakathiresan NS,
Dalgard C, Gutti U, Armistead D, Jozwik C, Srivastava M, Pollard HB
and Biswas R: Elevated miR-155 promotes inflammation in cystic
fibrosis by driving hyperexpression of interleukin-8. J Biol Chem.
286:11604–11615. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Balakathiresan NS, Bhattacharyya S, Gutti
U, Long RP, Jozwik C, Huang W, Srivastava M, Pollard HB and Biswas
R: Tristetraprolin regulates IL-8 mRNA stability in cystic fibrosis
lung epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
296:L1012–L1018. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Kanamori Y, Via LD, Macone A, Canettieri
G, Greco A, Toninello A and Agostinelli E: Aged garlic extract and
its constituent, S-allyl-L-cysteine, induce the apoptosis of
neuroblastoma cancer cells due to mitochondrial membrane
depolarization. Exp Ther Med. 19:1511–1521. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Amano H, Kazamori D and Itoh K:
Pharmacokinetics and N-acetylation metabolism of
S-methyl-l-cysteine and trans-S-1-propenyl-l-cysteine in rats and
dogs. Xenobiotica. 46:1017–1025. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Amano H, Kazamori D and Itoh K: Evaluation
of the effects of S-allyl-L-cysteine, S-methyl-L-cysteine,
trans-S-1-propenyl-L-cysteine, and their N-acetylated and
S-oxidized metabolites on human CYP activities. Biol Pharm Bull.
39:1701–1707. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Soy M, Keser G, Atagündüz P, Tabak F,
Atagündüz I and Kayhan S: Cytokine storm in COVID-19: Pathogenesis
and overview of anti-inflammatory agents used in treatment. Clin
Rheumatol. 39:2085–2094. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Mustafa MI, Abdelmoneim AH, Mahmoud EM and
Makhawi AM: Cytokine storm in COVID-19 patients, its impact on
organs and potential treatment by QTY code-designed detergent-free
chemokine receptors. Mediators Inflamm.
2020(8198963)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Gasparello J, Papi C, Marzaro G, Macone A,
Zurlo M, Finotti A, Agostinelli E and Gambari R: Aged garlic
extract (AGE) and its constituent S-allyl-cysteine (SAC) inhibit
the expression of pro-inflammatory genes induced in bronchial
epithelial IB3-1 cells by exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein
and the BNT162b2 vaccine. Molecules. 29(5938)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Choudhury A and Mukherjee S: In silico
studies on the comparative characterization of the interactions of
SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein with ACE-2 receptor homologs and
human TLRs. J Med Virol. 92:2105–2113. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Shirato K and Kizaki T: SARS-CoV-2 spike
protein S1 subunit induces pro-inflammatory responses via Toll-like
receptor 4 signaling in murine and human macrophages. Heliyon.
7(e06187)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Zhao Y, Kuang M, Li J, Zhu L, Jia Z, Guo
X, Hu Y, Kong J, Yin H, Wang X and You F: SARS-CoV-2 spike protein
interacts with and activates TLR41. Cell Res. 31:818–820.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Chakraborty C, Mallick B, Bhattacharya M
and Byrareddy SN: SARS-CoV-2 omicron spike shows strong binding
affinity and favourable interaction landscape with the TLR4/MD2
compared to other variants. J Genet Eng Biotechnol.
22(100347)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Aboudounya MM and Heads RJ: COVID-19 and
Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4): SARS-CoV-2 may bind and activate TLR4
to increase ACE2 expression, facilitating entry and causing
hyperinflammation. Mediators Inflamm. 2021(8874339)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Kawai T and Akira S: Signaling to
NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptors. Trends Mol Med. 13:460–469.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Tang S, Liang Y, Wang M, Lei J, Peng Y,
Tao Q, Ming T, Yang W, Zhang C, Guo J and Xu H: Qinhuo Shanggan
oral solution resolves acute lung injury by down-regulating
TLR4/NF-κB signaling cascade and inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome
activation. Front Immunol. 14(1285550)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Kaushik D, Bhandari R and Kuhad A: TLR4 as
a therapeutic target for respiratory and neurological complications
of SARS-CoV-2. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 25:491–508.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Yang G, Zhang S, Wang Y, Li L, Li Y, Yuan
D, Luo F, Zhao J, Song X and Zhao Y: Aptamer blocking S-TLR4
interaction selectively inhibits SARS-CoV-2 induced inflammation.
Signal Transduct Target Ther. 7(120)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Asaba CN, Ekabe CJ, Ayuk HS, Gwanyama BN,
Bitazar R and Bukong TN: Interplay of TLR4 and SARS-CoV-2:
Unveiling the complex mechanisms of inflammation and severity in
COVID-19 infections. J Inflamm Res. 17:5077–5091. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Verbeke R, Hogan MJ, Loré K and Pardi N:
Innate immune mechanisms of mRNA vaccines. Immunity. 55:1993–2005.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Sartorius R, Trovato M, Manco R, D'Apice L
and De Berardinis P: Exploiting viral sensing mediated by Toll-like
receptors to design innovative vaccines. NPJ Vaccines.
6(127)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Delehedde C, Even L, Midoux P, Pichon C
and Perche F: Intracellular routing and recognition of lipid-based
mRNA nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics. 13(945)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Da Costa CBP, Cruz ACM, Penha JCQ, Castro
HC, Da Cunha LER, Ratcliffe NA, Cisne R and Martins FJ: Using in
vivo animal models for studying SARS-CoV-2. Expert Opin Drug
Discov. 17:121–137. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Wlosinska M, Nilsson AC, Hlebowicz J,
Fakhro M, Malmsjö M and Lindstedt S: Aged garlic extract reduces
IL-6: A double-blind placebo-controlled trial in females with a low
risk of cardiovascular disease. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2021(6636875)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Xu C, Mathews AE, Rodrigues C, Eudy BJ,
Rowe CA, O'Donoughue A and Percival SS: Aged garlic extract
supplementation modifies inflammation and immunity of adults with
obesity: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical
trial. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 24:148–155. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Fabbri E, Borgatti M, Montagner G, Bianchi
N, Finotti A, Lampronti I, Bezzerri V, Dechecchi MC, Cabrini G and
Gambari R: Expression of microRNA-93 and interleukin-8 during
Pseudomonas aeruginosa-mediated induction of proinflammatory
responses. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 50:1144–1155. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
De Stefano D, Ungaro F, Giovino C,
Polimeno A, Quaglia F and Carnuccio R: Sustained inhibition of IL-6
and IL-8 expression by decoy ODN to NF-κB delivered through
respirable large porous particles in LPS-stimulated cystic fibrosis
bronchial cells. J Gene Med. 13:200–208. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Lampronti I, Dechecchi MC, Rimessi A,
Bezzerri V, Nicolis E, Guerrini A, Tacchini M, Tamanini A, Munari
S, D'Aversa E, et al: β-Sitosterol reduces the expression of
chemotactic cytokine genes in cystic fibrosis bronchial epithelial
cells. Front Pharmacol. 8(236)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Hawdon NA, Aval PS, Barnes RJ, Gravelle
SK, Rosengren J, Khan S, Ciofu O, Johansen HK, Høiby N and Ulanova
M: Cellular responses of A549 alveolar epithelial cells to serially
collected Pseudomonas aeruginosa from cystic fibrosis
patients at different stages of pulmonary infection. FEMS Immunol
Med Microbiol. 59:207–220. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Demonbreun AR, Velez MP, Saber R, Ryan DT,
Sancilio A, McDade TW and McNally EM: mRNA intramuscular
vaccination produces a robust IgG antibody response in advanced
neuromuscular disease. Neuromuscul Disord. 32:33–35.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Elmazoglu Z, Aydın Bek Z, Sarıbaş SG,
Özoğul C, Goker B, Bitik B, Aktekin CN and Karasu Ç:
S-allylcysteine inhibits chondrocyte inflammation to reduce human
osteoarthritis via targeting RAGE, TLR4, JNK, and Nrf2 signaling:
Comparison with colchicine. Biochem Cell Biol. 99:645–654.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Shao Z, Pan Z, Lin J, Zhao Q, Wang Y, Ni
L, Feng S, Tian N, Wu Y, Sun L, et al: S-allyl cysteine reduces
osteoarthritis pathology in the tert-butyl hydroperoxide-treated
chondrocytes and the destabilization of the medial meniscus model
mice via the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Aging (Albany NY).
12:19254–19272. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Cantin AM, Hartl D, Konstan MW and Chmiel
JF: Inflammation in cystic fibrosis lung disease: Pathogenesis and
therapy. J Cyst Fibros. 14:419–430. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Lemanske RF Jr: Inflammatory events in
asthma: An expanding equation. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
105:S633–S636. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Xu J, Zeng Q, Li S, Su Q and Fan H:
Inflammation mechanism and research progress of COPD. Front
Immunol. 15(1404615)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Degan D, Ornello R, Tiseo C, Carolei A,
Sacco S and Pistoia F: The role of inflammation in neurological
disorders. Curr Pharm Des. 24:1485–1501. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Ji Y, Li M, Chang M, Liu R, Qiu J, Wang K,
Deng C, Shen Y, Zhu J, Wang W, et al: Inflammation: Roles in
skeletal muscle atrophy. Antioxidants (Basel).
11(1686)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Henein MY, Vancheri S, Longo G and
Vancheri F: The role of inflammation in cardiovascular disease. Int
J Mol Sci. 23(12906)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Tsalamandris S, Antonopoulos AS, Oikonomou
E, Papamikroulis GA, Vogiatzi G, Papaioannou S, Deftereos S and
Tousoulis D: The role of inflammation in diabetes: Current concepts
and future perspectives. Eur Cardiol. 14:50–59. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Coussens LM and Werb Z: Inflammation and
cancer. Nature. 420:860–867. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Zhao H, Wu L, Yan G, Chen Y, Zhou M, Wu Y
and Li Y: Inflammation and tumor progression: Signaling pathways
and targeted intervention. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
6(263)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|