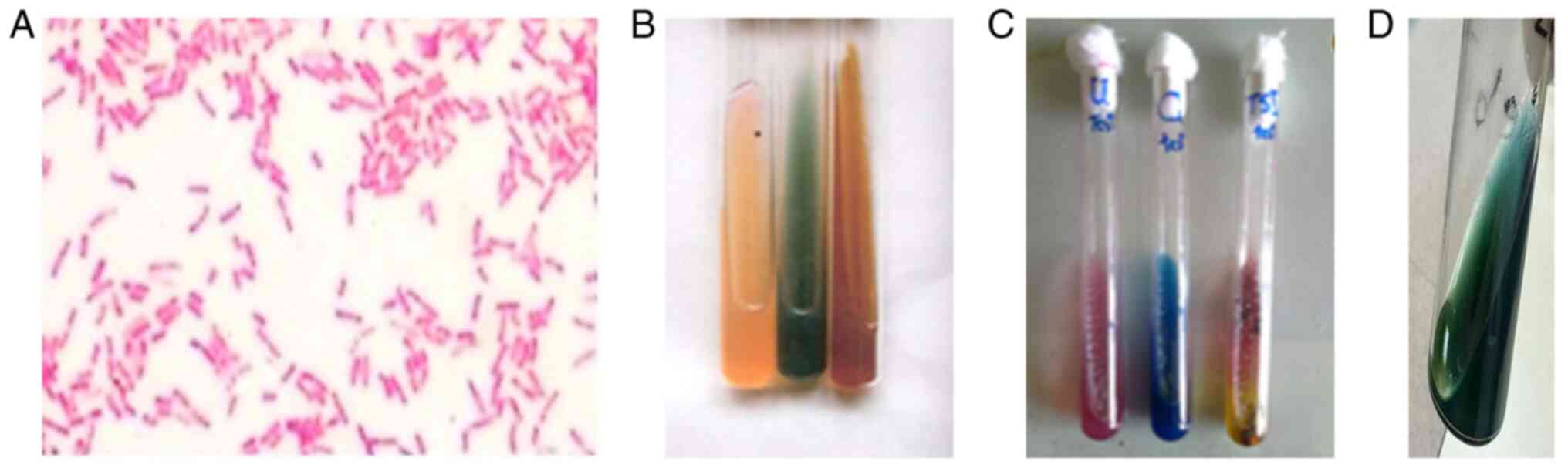
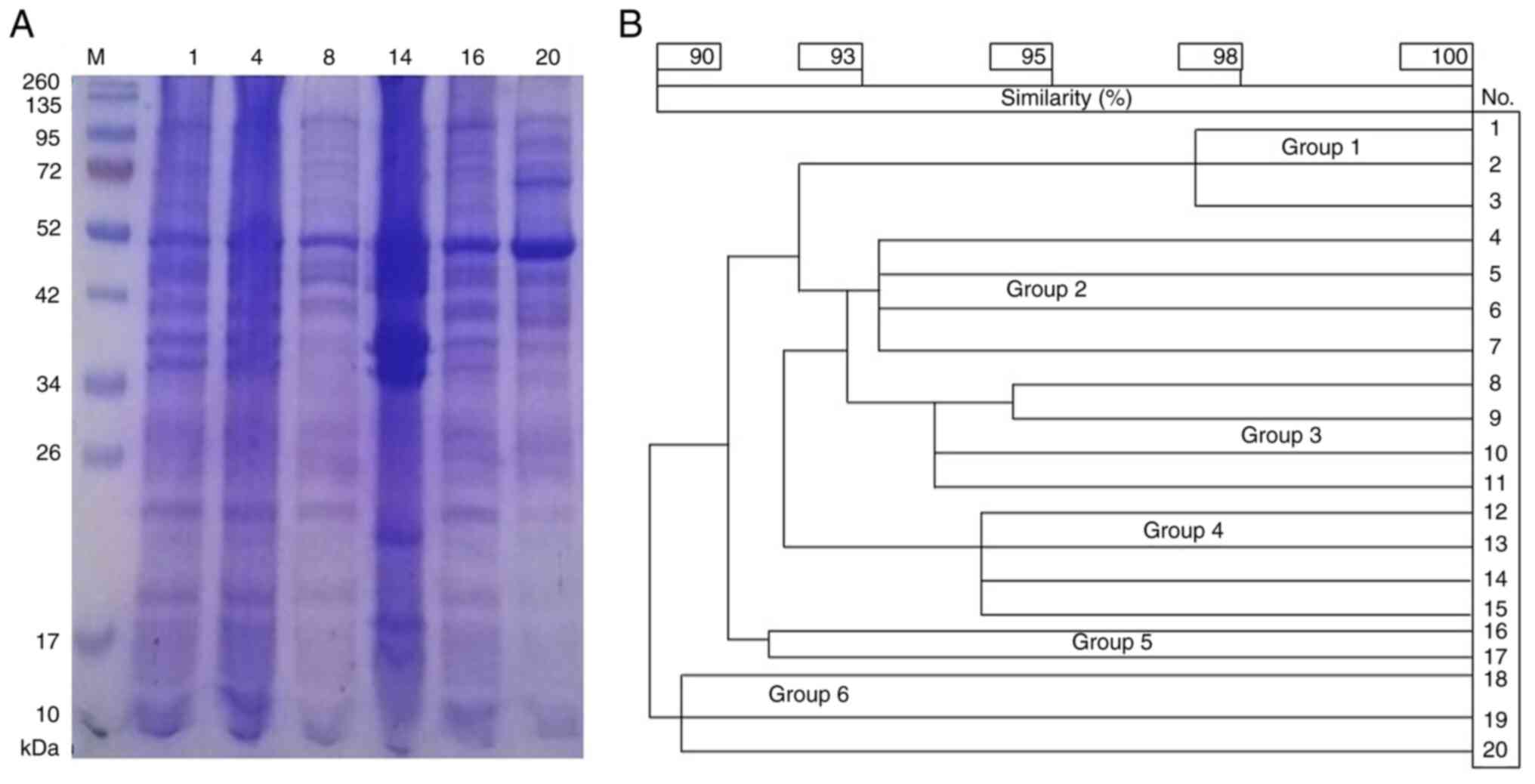
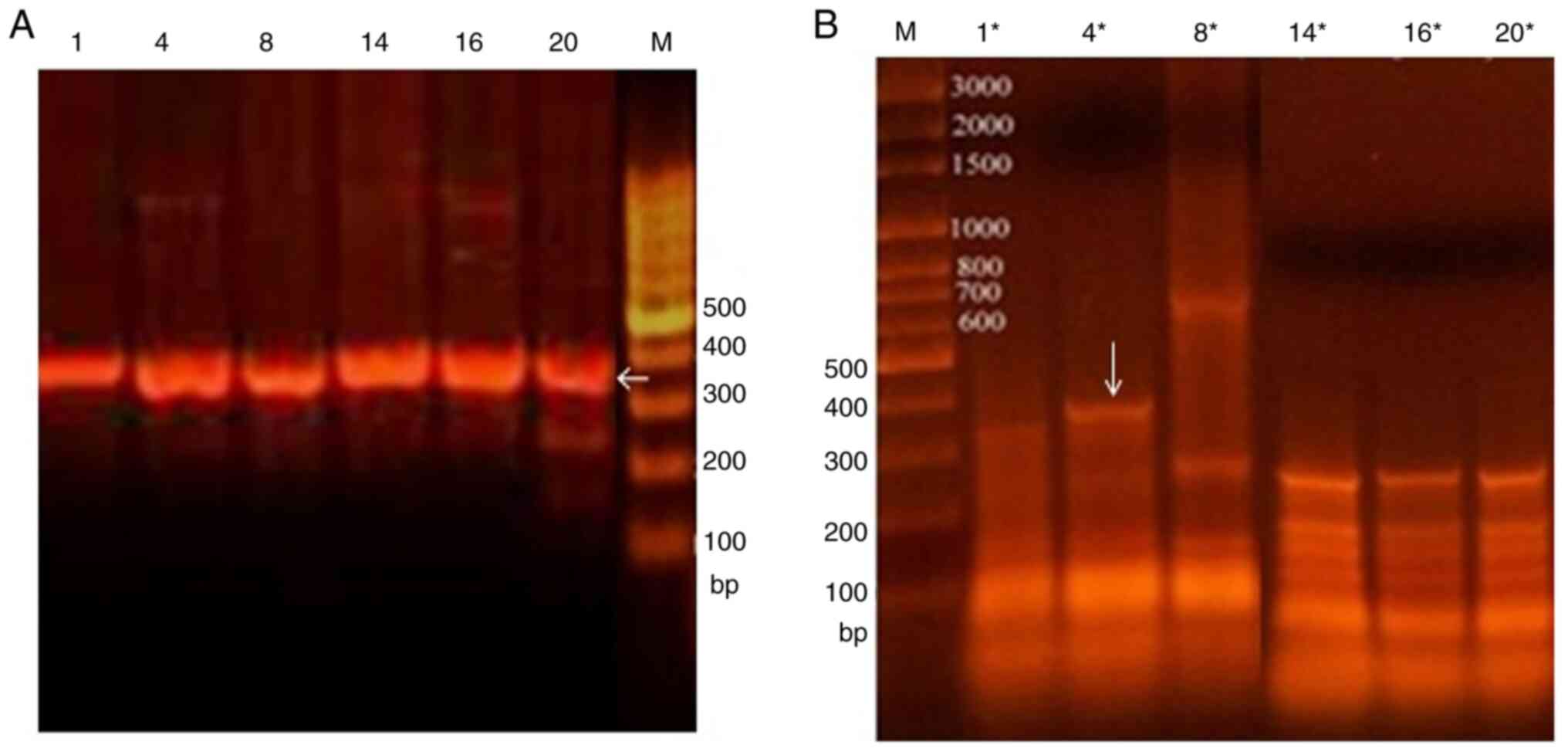
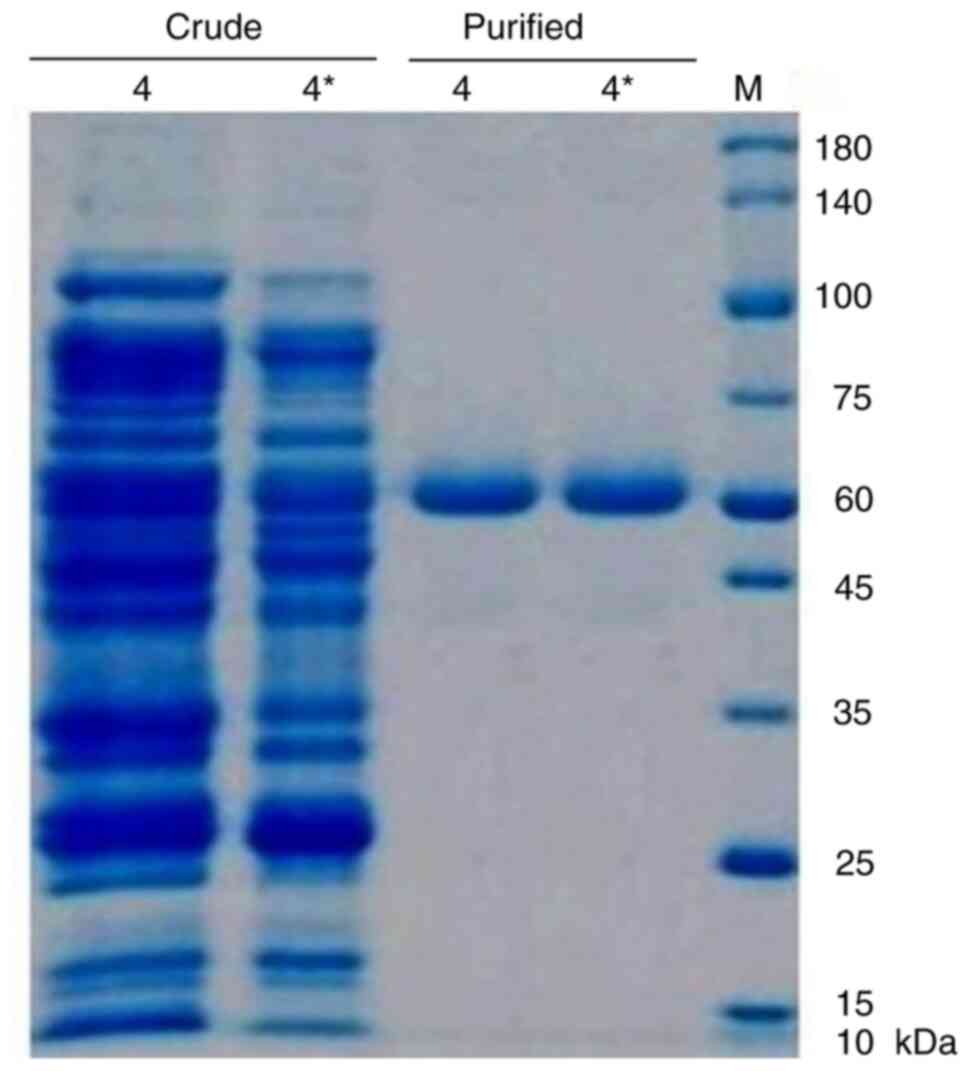
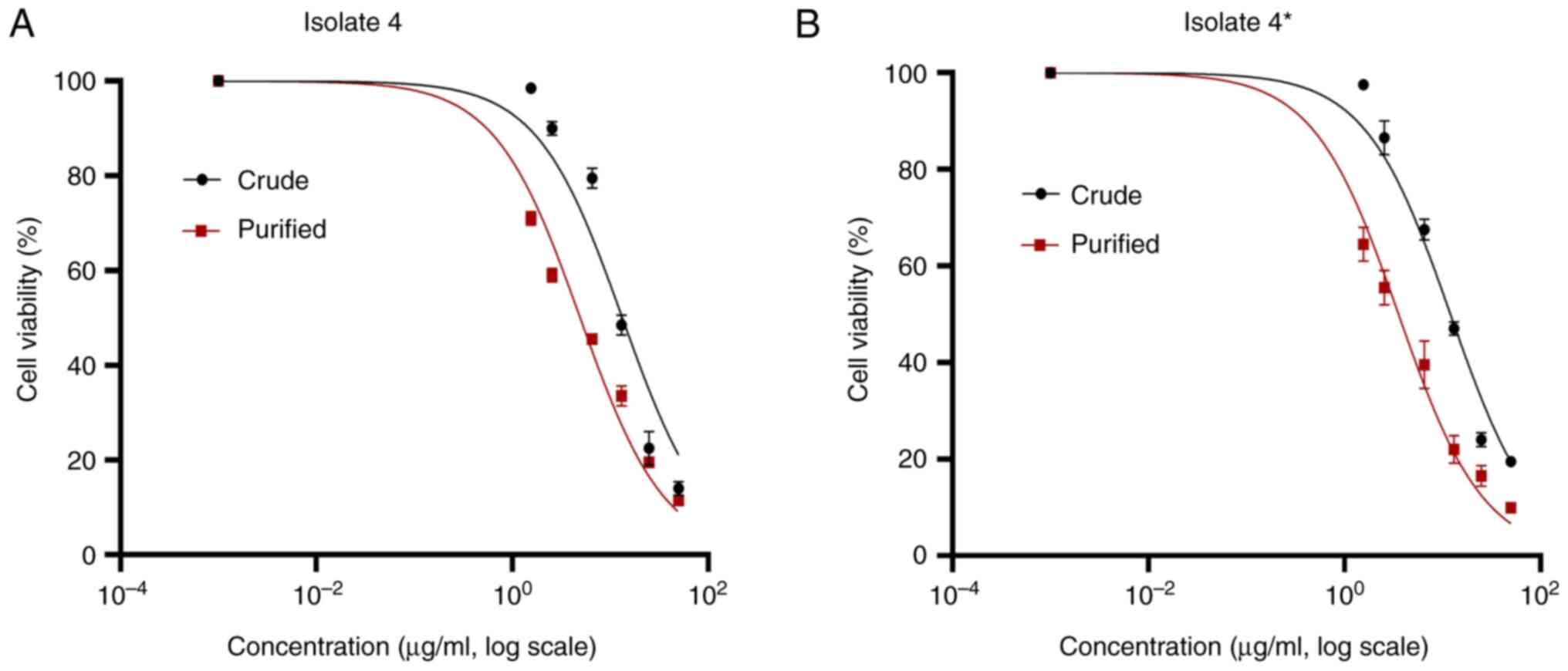
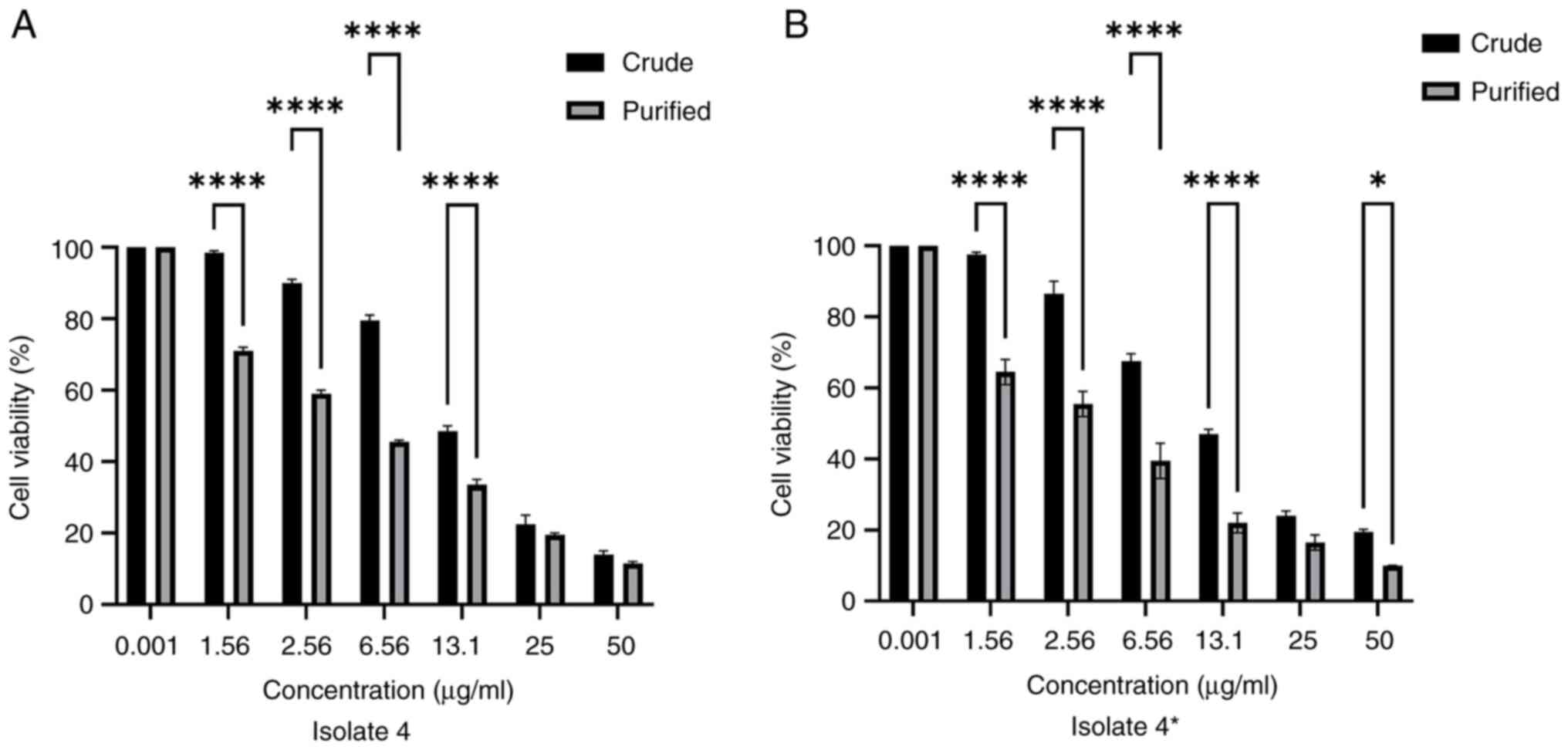
|
1
|
Washington JA: Principles of Diagnosis in
Baron's Medical Microbiology (Baron S), 4th Edition, Chapter 10,
1996. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK8014/.
|
|
2
|
Palleroni NJ and Moore ERB: Taxonomy of
pseudomonads: Experimental approaches. In: Pseudomonas, 2004.
|
|
3
|
Qin S, Xiao W, Zhou C, Pu Q, Deng X, Lan
L, Liang H, Song X and Wu M: Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Pathogenesis,
virulence factors, antibiotic resistance, interaction with host,
technology advances and emerging therapeutics. Signal Transduct
Target Ther. 7(199)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lu S, Chen K, Song K, Pilewski JM, Gunn
BM, Poch KR, Rysavy NM, Vestal BE, Saavedra MT and Kolls JK:
Systems serology in cystic fibrosis: Anti-Pseudomonas IgG1
responses and reduced lung function. Cell Rep Med.
4(101210)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Do Rego H and Timsit JF: Management
strategies for severe Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Curr Opin
Infect Dis. 36:585–595. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ren Y, Zhu R, You X, Li D, Guo M, Fei B,
Liu Y, Yang X, Liu X and Li Y: Quercetin: A promising virulence
inhibitor of pseudomonas aeruginosa LasB in vitro. Appl Microbiol
Biotechnol. 108(57)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ryan KJ, Ray CG, Ahmad N, et al: Sherris
Medical Microbiology 6th edition, 2014.
|
|
8
|
Liao C, Huang X, Wang Q, Yao D and Lu W:
Virulence factors of pseudomonas aeruginosa and antivirulence
strategies to combat its drug resistance. Front Cell Infect
Microbiol. 12(926758)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Casas V and Maloy S: Role of
bacteriophage-encoded exotoxins in the evolution of bacterial
pathogens. Future Microbiol. 6:1461–1473. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Gellatly SL and Hancock REW: Pseudomonas
aeruginosa: New insights into pathogenesis and host defenses.
Pathog Dis. 67:159–173. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Balasubramanian D, Schneper L, Kumari H
and Mathee K: A dynamic and intricate regulatory network determines
Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence. Nucleic Acids Res. 41:1–20.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Gholami A, Minai-Tehrani D, Mahdizadeh SJ,
Saenz-Mendez P and Eriksson LA: Structural insights into
pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A-elongation factor 2 interactions:
A molecular dynamics study. J Chem Inf Model. 63:1578–1591.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Yarahmadi A, Zare M, Aghayari M, Afkhami H
and Jafari GA: Therapeutic bacteria and viruses to combat cancer:
double-edged sword in cancer therapy: New insights for future. Cell
Commun Signal. 22(239)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Guo L, Ding J and Zhou W: Harnessing
bacteria for tumor therapy: Current advances and challenges.
Chinese Chemical Letters. 35(108557)2024.
|
|
15
|
Morgan RN, Saleh SE, Farrag HA and
Aboshanab KM: New insights on Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
exotoxin A-based immunotoxins in targeted cancer therapeutic
delivery. Ther Deliv. 14:31–60. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Gao M, Zhou J, Su Z and Huang Y: Bacterial
cupredoxin azurin hijacks cellular signaling networks:
Protein-protein interactions and cancer therapy. Protein Science.
26:2334–2341. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chakrabarty AM: Microbial pathogenicity: A
new approach to drug development. Adv Exp Med Biol. 808:41–49.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Benson RF, Tang PW and Fields BS:
Evaluation of the Binax and Biotest urinary antigen kits for
detection of Legionnaires' disease due to multiple serogroups and
species of Legionella. J Clin Microbiol. 38:2763–2765.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Bannoehr J, Franco A, Iurescia M, Battisti
A and Fitzgerald JR: Koneman. Koneman's color atlas and textbook of
diagnostic microbiology. J Clin Microbiol. 47:469–471. 2009.
|
|
20
|
Greenwood D, Slack R and Peutherer JF: A
guide to microbial infections, pathogenesis, immunity, laboratory
diagnosis and control. In: Medical Microbiology.
ThriftBooks-Phoenix, Tolleson, AZ, 2006.
|
|
21
|
Khan AA and Cerniglia CE: Detection of
pseudomonas aeruginosa from clinical and environmental samples by
amplification of the exotoxin A gene using PCR. Appl Environ
Microbiol. 60:3739–3745. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Trovão M, Schüler LM, Machado A, Bombo G,
Navalho S, Barros A, Pereira H, Silva J, Freitas F and Varela J:
Random mutagenesis as a promising tool for microalgal strain
improvement towards industrial production. Mar Drugs.
20(440)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bose JL: Chemical and UV mutagenesis.
Methods Mol Biol. 1373:111–115. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural
proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.
Nature. 227:680–685. 1970.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Mosmann T: Rapid colorimetric assay for
cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and
cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 65:55–63. 1983.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Vijayan P, Raghu C, Ashok G, Dhanaraj SA
and Suresh B: Antiviral activity of medicinal plants of Nilgiris.
Indian J Med Res. 120:24–29. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang Q, Wang B, Zheng Q, Li H, Meng X,
Zhou F and Zhang L: A review of gut microbiota-derived metabolites
in tumor progression and cancer therapy. Adv Sci (Weinh).
10(e2207366)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Masuyer G: Crystal structure of exotoxin A
from aeromonas pathogenic species. Toxins (Basel).
12(397)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Aljebory IS: PCR detection of some
virulence genes of pseudomonas aeruginosa in Kirkuk city, Iraq. J
Pharm Sci Res. 10:1068–1071. 2018.
|
|
30
|
Ismail YM, Fayed SM, Elesawy FM, El-Halim
NZA and El-Shimi OS: Phenotypic and molecular characteristics of
pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from burn unit. Egyptian Journal of
Medical Microbiology (Egypt). 30:19–28. 2021.
|
|
31
|
Bourdenet S, Doyonnas R, Vacheron MJ,
Guinand M, Fasciotto B, Ristic A, Michel G, Cozzone AJ, Durkin JP
and Whitfield JF: The cytotoxicity of Pseudomonas exotoxin A,
inactivated by modification of the cell-binding domain I, is
restored when conjugated to an erythroid cell-specific targeting
agent. Cancer Lett. 50:121–127. 1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Gallant CV, Raivio TL, Olson JC, Woods DE
and Storey DG: Pseudomonas aeruginosa cystic fibrosis clinical
isolates produce exotoxin A with altered ADP-ribosyltransferase
activity and cytotoxicity. Microbiology (NY). 146:1891–1899.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Prinsloo S, Pieters R and Bezuidenhout CC:
A cell viability assay to determine the cytotoxic effects of water
contaminated by microbes. S Afr J Sci. 109:1–4. 2013.
|
|
34
|
Wolf P, Alt K, Bühler P, Katzenwadel A,
Wetterauer U, Tacke M and Elsässer-Beile U: Anti-PSMA immunotoxin
as novel treatment for prostate cancer? High and specific antitumor
activity on human prostate xenograft tumors in SCID mice. Prostate.
68:129–138. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Panahi Z, Owrang M and Goli HR:
Significant role of pyocyanin and exotoxin A in the pathogenesis of
pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from hospitalized patients. Folia
Med (Plovdiv). 66:88–96. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|