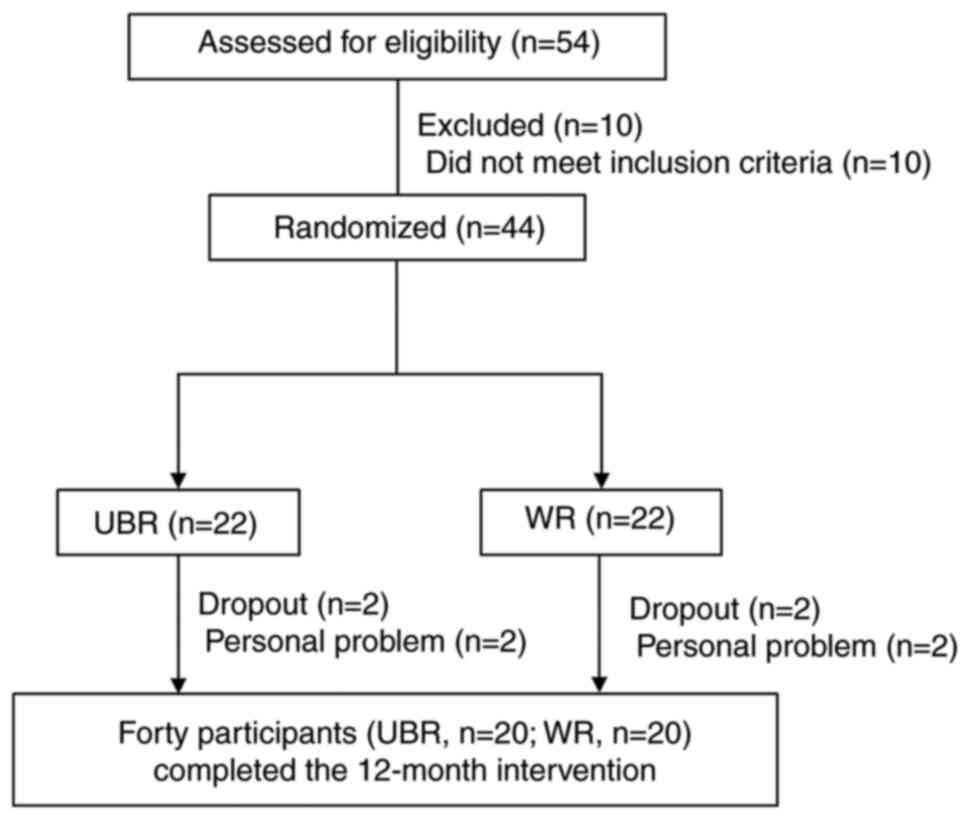
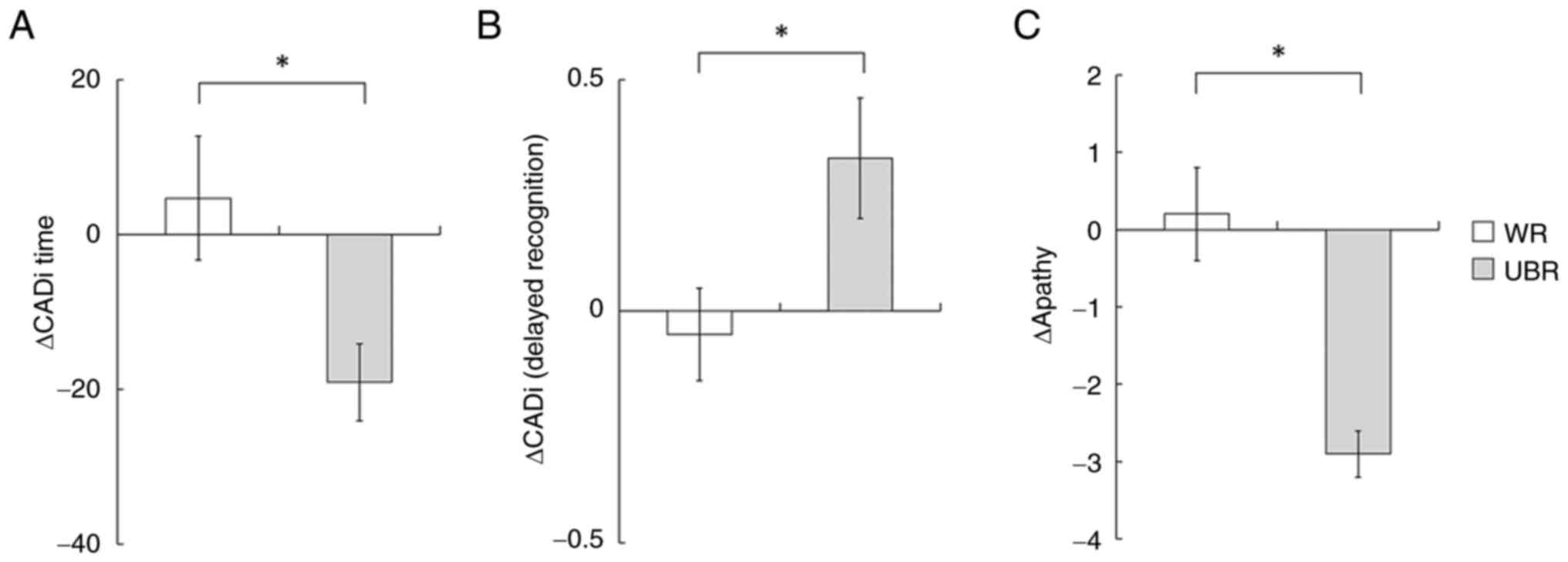
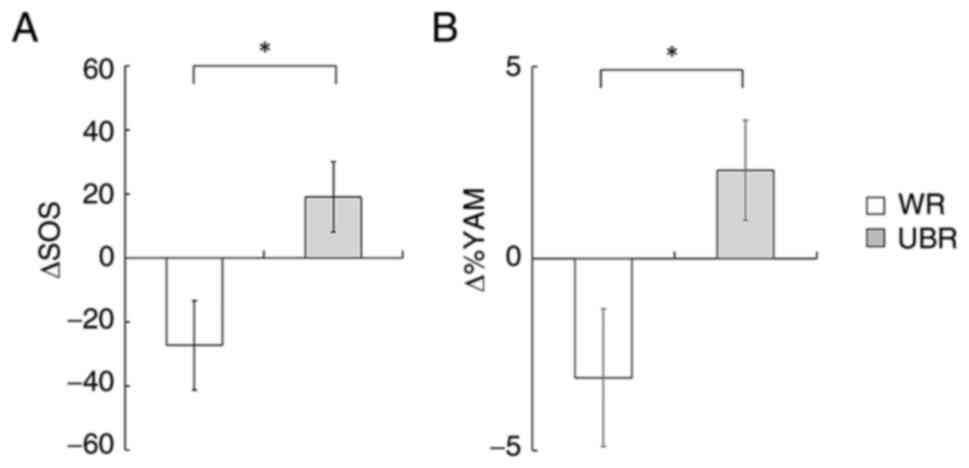
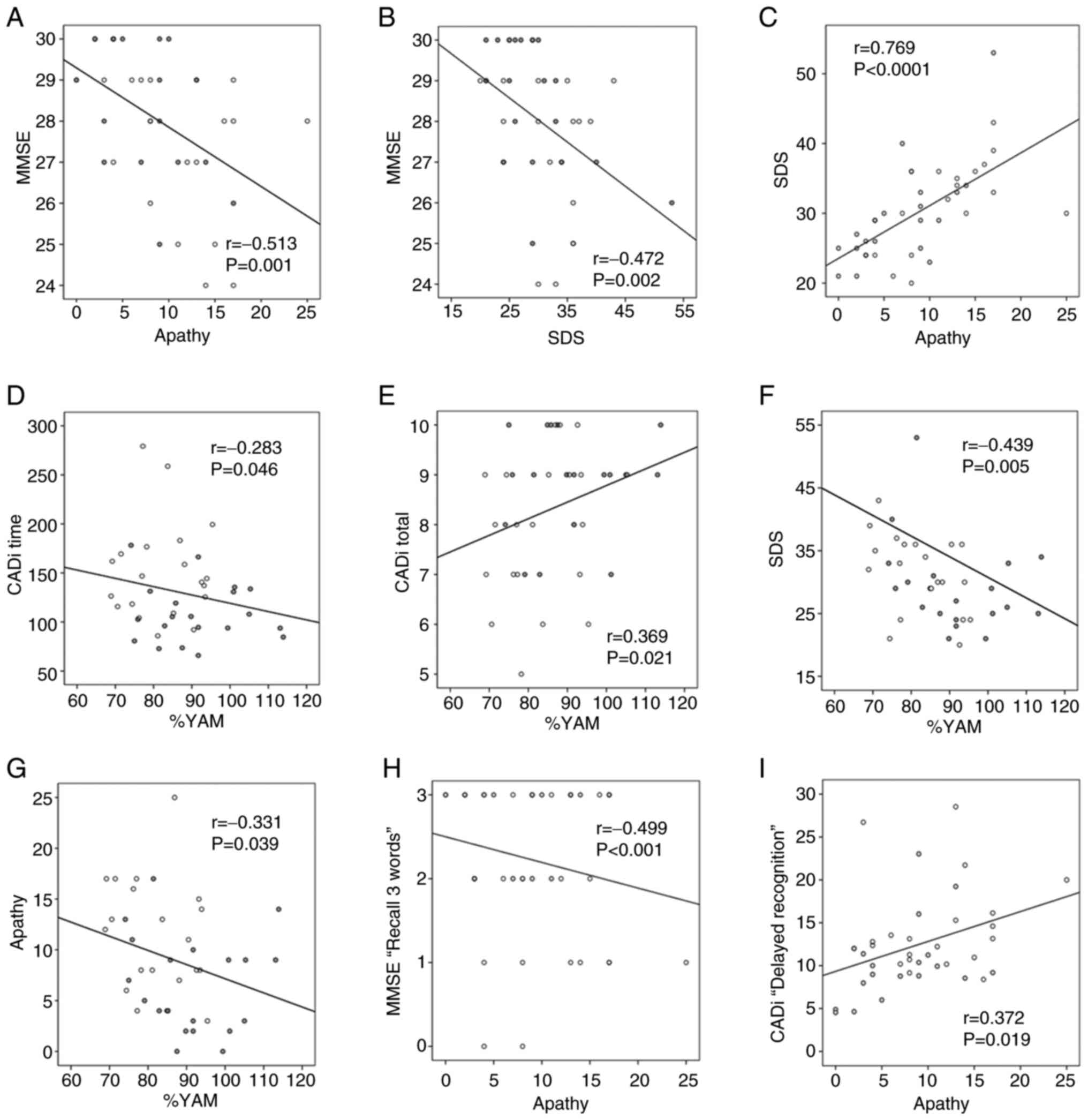
|
1
|
Loskutova N, Honea RA, Vidoni ED, Brooks
WM and Burns JM: Bone density and brain atrophy in early
Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 18:777–785. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Mehta K, Thandavan SP, Mohebbi M, Pasco
JA, Williams LJ, Walder K, Ng BL and Gupta VB: Depression and bone
loss as risk factors for cognitive decline: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Ageing Res Rev. 76(101575)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Xiao T, Ghatan S, Mooldijk SS, Trajanoska
K, Oei L, Gomez MM, Ikram MK, Rivadeneira F and Ikram MA:
Association of bone mineral density and dementia: The Rotterdam
study. Neurology. 100:e2125–e2133. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Filler J, Georgakis MK and Dichgans M:
Risk factors for cognitive impairment and dementia after stroke: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Healthy Longev.
5:e31–e44. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ruggiero C, Baroni M, Xenos D, Parretti L,
Macchione IG, Bubba V, Laudisio A, Pedone C, Ferracci M, Magierski
R, et al: Dementia, osteoporosis and fragility fractures: Intricate
epidemiological relationships, plausible biological connections,
and twisted clinical practices. Ageing Res Rev.
93(102130)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Mehta K, Mohebbi M, Pasco JA, Williams LJ,
Walder K, Ng BL and Gupta VB: Impact of mood disorder history and
bone health on cognitive function among men without dementia. J
Alzheimers Dis. 96:381–393. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ichinose T, Kato M, Matsuzaki K, Tanabe Y,
Tachibana N, Morikawa M, Kato S, Ohata S, Ohno M, Wakatsuki H, et
al: Beneficial effects of docosahexaenoic Acid-enriched milk
beverage intake on cognitive function in healthy elderly Japanese:
A 12-month randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J
Funct Foods. 74(104195)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lisco G, Disoteo OE, De Tullio A, De
Geronimo V, Giagulli VA, Monzani F, Jirillo E, Cozzi R,
Guastamacchia E, De Pergola G and Triggiani V: Sarcopenia and
diabetes: A detrimental liaison of advancing age. Nutrients.
16(63)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hashimoto M, Hossain S, Al Mamun A,
Matsuzaki K and Arai H: Docosahexaenoic acid: One molecule diverse
functions. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 37:579–597. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Hashimoto M, Hossain S, Matsuzaki K, Shido
O and Yoshino K: The journey from white rice to ultra-high
hydrostatic pressurized brown rice: An excellent endeavor for ideal
nutrition from staple food. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 62:1502–1520.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Matsuzaki K, Nakajima A, Guo Y and Ohizumi
Y: A narrative review of the effects of citrus peels and extracts
on human brain health and metabolism. Nutrients.
14(1847)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hashimoto M, Yamashita K, Kato S, Tamai T,
Tanabe Y, Mitarai M, Matsumoto I and Ohno M: Beneficial effects of
daily dietary omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation on
age-related cognitive decline in elderly Japanese with very mild
dementia: A 2-year randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled
trial. J Aging Res Clin Pract. 1:193–201. 2012.
|
|
13
|
Hashimoto M, Matsuzaki K, Maruyama K,
Hossain S, Sumiyoshi E, Wakatsuki H, Kato S, Ohno M, Tanabe Y,
Kuroda Y, et al: Perilla seed oil in combination with
nobiletin-rich ponkan powder enhances cognitive function in healthy
elderly Japanese individuals: A possible supplement for brain
health in the elderly. Food Funct. 13:2768–2781. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hashimoto M, Matsuzaki K, Maruyama K,
Sumiyoshi E, Hossain S, Wakatsuki H, Kato S, Ohno M, Tanabe Y,
Kuroda Y, et al: Perilla frutescens seed oil combined with Anredera
cordifolia leaf powder attenuates age-related cognitive decline by
reducing serum triglyceride and glucose levels in healthy elderly
Japanese individuals: A possible supplement for brain health. Food
Funct. 13:7226–7239. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ichinose T, Matsuzaki K, Kato M, Tanabe Y,
Tachibana N, Morikawa M, Kato S, Ohata S, Ohno M, Wakatsuki H, et
al: Intake of docosahexaenoic Acid-enriched milk beverage prevents
Age-related cognitive decline and decreases serum bone resorption
marker levels. J Oleo Sci. 70:1829–1838. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kaup RM, Khayyal MT and Verspohl EJ:
Antidiabetic effects of a standardized Egyptian rice bran extract.
Phytother Res. 27:264–271. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Savage K, Firth J, Stough C and Sarris J:
GABA-modulating phytomedicines for anxiety: A systematic review of
preclinical and clinical evidence. Phytother Res. 32:3–18.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kokumai T, Ito J, Kobayashi E, Shimizu N,
Hashimoto H, Eitsuka T, Miyazawa T and Nakagawa K: Comparison of
blood profiles of γ-oryzanol and ferulic acid in rats after oral
intake of γ-oryzanol. Nutrients. 11(1174)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Jalali A, Firouzabadi N and Zarshenas MM:
Pharmacogenetic-based management of depression: Role of traditional
Persian medicine. Phytother Res. 35:5031–5052. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Hayashi R: High pressure in bioscience and
biotechnology: pure science encompassed in pursuit of value.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1595:397–399. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yoshino K and Inoue T: Ultra high pressure
and food processing technology. J Highly Water Pressurized Food
Eng. 1:5–14. 2016.
|
|
22
|
Kuroda Y, Matsuzaki K, Wakatsuki H, Shido
O, Harauma A, Moriguchi T, Sugimoto H, Yamaguchi S, Yoshino K and
Hashimoto M: Influence of ultra-High hydrostatic pressurizing brown
rice on cognitive functions and mental health of elderly Japanese
individuals: A 2-year randomized and controlled trial. J Nutr Sci
Vitaminol (Tokyo). 65 (Suppl 1):S80–S87. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Matsuzaki K, Yano S, Sumiyoshi E, Shido O,
Katsube T, Tabata M, Okuda M, Sugimoto H, Yoshino K and Hashimoto
M: Long-term ultra-high hydrostatic pressurized brown rice intake
prevents bone mineral density decline in elderly Japanese
individuals. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 65 (Suppl 1):S88–S92.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sumiyoshi E, Matsuzaki K, Sugimoto N,
Tanabe Y, Hara T, Katakura M, Miyamoto M, Mishima S and Shido O:
Sub-chronic consumption of dark chocolate enhances cognitive
function and releases nerve growth factors: A parallel-group
randomized trial. Nutrients. 11(2800)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Hashimoto M, Matsuzaki K, Hossain S, Ito
T, Wakatsuki H, Tanabe Y, Ohno M, Kato S, Yamashita K and Shido O:
Perilla Seed oil enhances cognitive function and mental health in
healthy elderly Japanese individuals by enhancing the biological
antioxidant potential. Foods. 10(1130)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Hashimoto M, Matsuzaki K, Kato S, Hossain
S, Ohno M and Shido O: Twelve-month studies on perilla oil intake
in Japanese adults-possible supplement for mental health. Foods.
9(530)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Folstein MF, Folstein SE and McHugh PR:
‘Mini-mental state’. A practical method for grading the cognitive
state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 12:189–198.
1975.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Imai Y and Hasegawa K: The revised
Hasegawa's dementia scale (HDS-R)-evaluation of its usefulness as a
screening test for dementia. J.H.K.C Psych. 4:2–24. 1994.
|
|
29
|
Dubois B, Slachevsky A, Litvan I and
Pillon B: The FAB: A frontal assessment battery at bedside.
Neurology. 55:1621–1626. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Onoda K, Hamano T, Nabika Y, Aoyama A,
Takayoshi H, Nakagawa T, Ishihara M, Mitaki S, Yamaguchi T, Oguro
H, et al: Validation of a new mass screening tool for cognitive
impairment: Cognitive Assessment for Dementia, iPad version. Clin
Interv Aging. 8:353–360. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Okada K, Kobayashi S, Aoki K, Suyama N and
Yamaguchi S: Assessment of motivational loss in poststroke patients
using the Japanese version of Starkstein's Apathy Scale. Jpn J
Stroke. 20:318–327. 1998.
|
|
32
|
Zung WWK: A Self-rating depression scale.
Arch Gen Psychiatry. 12:63–70. 1965.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yamazaki K, Kushida K, Ohmura A, Sano M
and Inoue T: Ultrasound bone densitometry of the os calcis in
Japanese women. Osteoporosis Int. 4:220–225. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Soen S, Fukunaga M, Sugimoto T, Sone T,
Fujiwara S, Endo N, Gorai I, Shiraki M, Hagino H, Hosoi T, et al:
Diagnostic criteria for primary osteoporosis: Year 2012 revision. J
Bone Miner Metab. 31:247–257. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Matsuzaki K, Hossain S, Wakatsuki H,
Tanabe Y, Ohno M, Kato S, Shido O and Hashimoto M: Perilla seed oil
improves bone health by inhibiting bone resorption in healthy
Japanese adults: A 12-month, randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled trial. Phytother Res. 37:2230–2241.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zhao Y, Shen L and Ji HF: Alzheimer's
disease and risk of hip fracture: A meta-analysis study. Sci World
J. 2012:1–5. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Baker NL, Cook MN, Arrighi HM and Bullock
R: Hip fracture risk and subsequent mortality among Alzheimer's
disease patients in the United Kingdom, 1988-2007. Age Ageing.
40:49–54. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Lai SW, Chen YL, Lin CL and Liao KF:
Alzheimer's disease correlates with greater risk of hip fracture in
older people: A cohort in Taiwan. J Am Geriatr Soc. 61:1231–1232.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Wang HK, Hung CM, Lin SH, Tai YC, Lu K,
Liliang PC, Lin CW, Lee YC, Fang PH, Chang LC and Li YC: Increased
risk of hip fractures in patients with dementia: A nationwide
population-based study. BMC Neurol. 14(175)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Yaffe K, Krueger K, Cummings SR, Blackwell
T, Henderson VW, Sarkar S, Ensrud K and Grady D: Effect of
raloxifene on prevention of dementia and cognitive impairment in
older women: The Multiple Outcomes of Raloxifene Evaluation (MORE)
randomized trial. Am J Psychiatry. 162:683–690. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Jacobsen DE, Melis RJF, Verhaar HJJ and
Olde Rikkert MGM: Raloxifene and tibolone in elderly women: A
randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, placebo-controlled trial. J
Am Med Dir Assoc. 13:189.e1–e7. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Yang ZD, Yu J and Zhang Q: Effects of
raloxifene on cognition, mental health, sleep and sexual function
in menopausal women: A systematic review of randomized controlled
trials. Maturitas. 75:341–348. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Golomb J, de Leon MJ, Kluger A, George AE,
Tarshish C and Ferris SH: Hippocampal atrophy in normal aging. An
association with recent memory impairment. Arch Neurol. 50:967–973.
1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Jack CR Jr, Knopman DS, Jagust WJ,
Petersen RC, Weiner MW, Aisen PS, Shaw LM, Vemuri P, Wiste HJ,
Weigand SD, et al: Tracking pathophysiological processes in
Alzheimer's disease: An updated hypothetical model of dynamic
biomarkers. Lancet Neurol. 12:207–216. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Mori T, Shimada H, Shinotoh H, Hirano S,
Eguchi Y, Yamada M, Fukuhara R, Tanimukai S, Zhang MR, Kuwabara S,
et al: Apathy correlates with prefrontal amyloid β deposition in
Alzheimer's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 85:449–455.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Moriguchi S, Takahata K, Shimada H, Kubota
M, Kitamura S, Kimura Y, Tagai K, Tarumi R, Tabuchi H, Meyer JH, et
al: Excess tau PET ligand retention in elderly patients with major
depressive disorder. Mol Psychiatry. 26:5856–5863. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Parrotta I, Maltais M, Rolland Y,
Spampinato DA, Robert P, de Souto Barreto P and Vellas B: MAPT/DSA
group. The association between apathy and frailty in older adults:
A new investigation using data from the Mapt study. Aging Ment
Health. 24:1985–1989. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Voorend CGN, van Buren M, Berkhout-Byrne
NC, Kerckhoffs APM, van Oevelen M, Gussekloo J, Richard E, Bos WJW
and Mooijaart SP: Apathy symptoms, physical and cognitive function,
health-related quality of life, and mortality in older patients
with CKD: A longitudinal observational study. Am J Kidney Dis.
83:162–172.e1. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Okuda M, Fujita Y, Katsube T, Tabata H,
Yoshino K, Hashimoto M and Sugimoto H: Highly water pressurized
brown rice improves cognitive dysfunction in senescence-accelerated
mouse prone 8 and reduces amyloid beta in the brain. BMC Complement
Altern Med. 18(110)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Morris MC, Schneider JA and Tangney CC:
Thoughts on B-vitamins and dementia. J Alzheimers Dis. 9:429–433.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Gil Martínez V, Avedillo Salas A and
Santander Ballestín S: Vitamin supplementation and dementia: A
systematic review. Nutrients. 14(1033)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Fekete M, Lehoczki A, Tarantini S,
Fazekas-Pongor V, Csípő T, Csizmadia Z and Varga JT: Improving
cognitive function with nutritional supplements in aging: A
comprehensive narrative review of clinical studies investigating
the effects of vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and other dietary
supplements. Nutrients. 15(5116)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Dai Z and Koh WP: B-vitamins and bone
health-a review of the current evidence. Nutrients. 7:3322–3346.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Sassa S, Kikuchi T, Shinoda H, Suzuki S,
Kudo H and Sakamoto S: Preventive effect of ferulic acid on bone
loss in ovariectomized rats. In Vivo. 17:277–280. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Di Giacomo S, Percaccio E, Gullì M, Romano
A, Vitalone A, Mazzanti G, Gaetani S and Di Sotto A: Recent
advances in the neuroprotective properties of ferulic acid in
Alzheimer's disease: A narrative review. Nutrients.
14(3709)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Fujii K, Kajiwara T and Kurosu H: Effect
of vitamin B6 deficiency on the crosslink formation of collagen.
FEBS Lett. 97:193–195. 1979.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Murari G, Liang DR, Ali A, Chan F,
Mulder-Heijstra M, Verhoeff NPLG, Herrmann N, Chen JJ and Mah L:
Prefrontal GABA levels correlate with memory in older adults at
high risk for Alzheimer's disease. Cereb Cortex Commun.
1(tgaa022)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Inotsuka R, Uchimura K, Yamatsu A, Kim M
and Katakura Y: γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) activates neuronal cells
by inducing the secretion of exosomes from intestinal cells. Food
Funct. 11:9285–9290. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Meng N, Pan P, Hu S, Miao C, Hu Y, Wang F,
Zhang J and An L: The molecular mechanism of γ-aminobutyric acid
against AD: the role of CEBPα/circAPLP2/miR-671-5p in regulating
CNTN1/2 expression. Food Funct. 14:2082–2095. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Rungratanawanich W, Cenini G, Mastinu A,
Sylvester M, Wilkening A, Abate G, Bonini SA, Aria F, Marziano M,
Maccarinelli G, et al: γ-Oryzanol improves cognitive function and
modulates hippocampal proteome in mice. Nutrients.
11(753)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Muhammad SI, Maznah I, Mahmud R, Zuki AB
and Imam MU: Upregulation of genes related to bone formation by
γ-amino butyric acid and γ-oryzanol in germinated brown rice is via
the activation of GABAB-receptors and reduction of serum IL-6 in
rats. Clin Interv Aging. 8:1259–1271. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Welan R: Effect of vitamin B6 on
osteoporosis fracture. J Bone Metab. 30:141–147. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
van Meurs JBJ, Dhonukshe-Rutten RAM,
Pluijm SMF, van der Klift M, de Jonge R, Lindemans J, de Groot
LCPGM, Hofman A, Witteman JCM, van Leeuwen JPTM, et al:
Homocysteine levels and the risk of osteoporotic fracture. N Engl J
Med. 350:2033–2041. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Fratoni V and Brandi ML: B vitamins,
homocysteine and bone health. Nutrients. 7:2176–2192.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Seshadri S, Beiser A, Selhub J, Jacques
PF, Rosenberg IH, D'Agostino RB, Wilson PWF and Wolf PA: Plasma
homocysteine as a risk factor for dementia and Alzheimer's disease.
N Engl J Med. 346:476–483. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Tanaka K, Ao M and Kuwabara A:
Insufficiency of B vitamins with its possible clinical
implications. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 67:19–25. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Itoh M, Nishibori N, Sagara T, Horie Y,
Motojima A and Morita K: Extract of fermented brown rice induces
apoptosis of human colorectal tumor cells by activating
mitochondrial pathway. Phytother Res. 26:1661–1666. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Praengam K, Sahasakul Y, Kupradinun P,
Sakarin S, Sanitchua W, Rungsipipat A, Rattanapinyopituk K,
Angkasekwinai P, Changsri K, Mhuantong W, et al: Brown rice and
retrograded brown rice alleviate inflammatory response in dextran
sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis mice. Food Funct. 8:4630–4643.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Saleh ASM, Wang P, Wang N, Yang L and Xiao
Z: Brown rice versus white rice: nutritional quality, potential
health benefits, development of food products, and preservation
technologies. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 18:1070–1096.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|