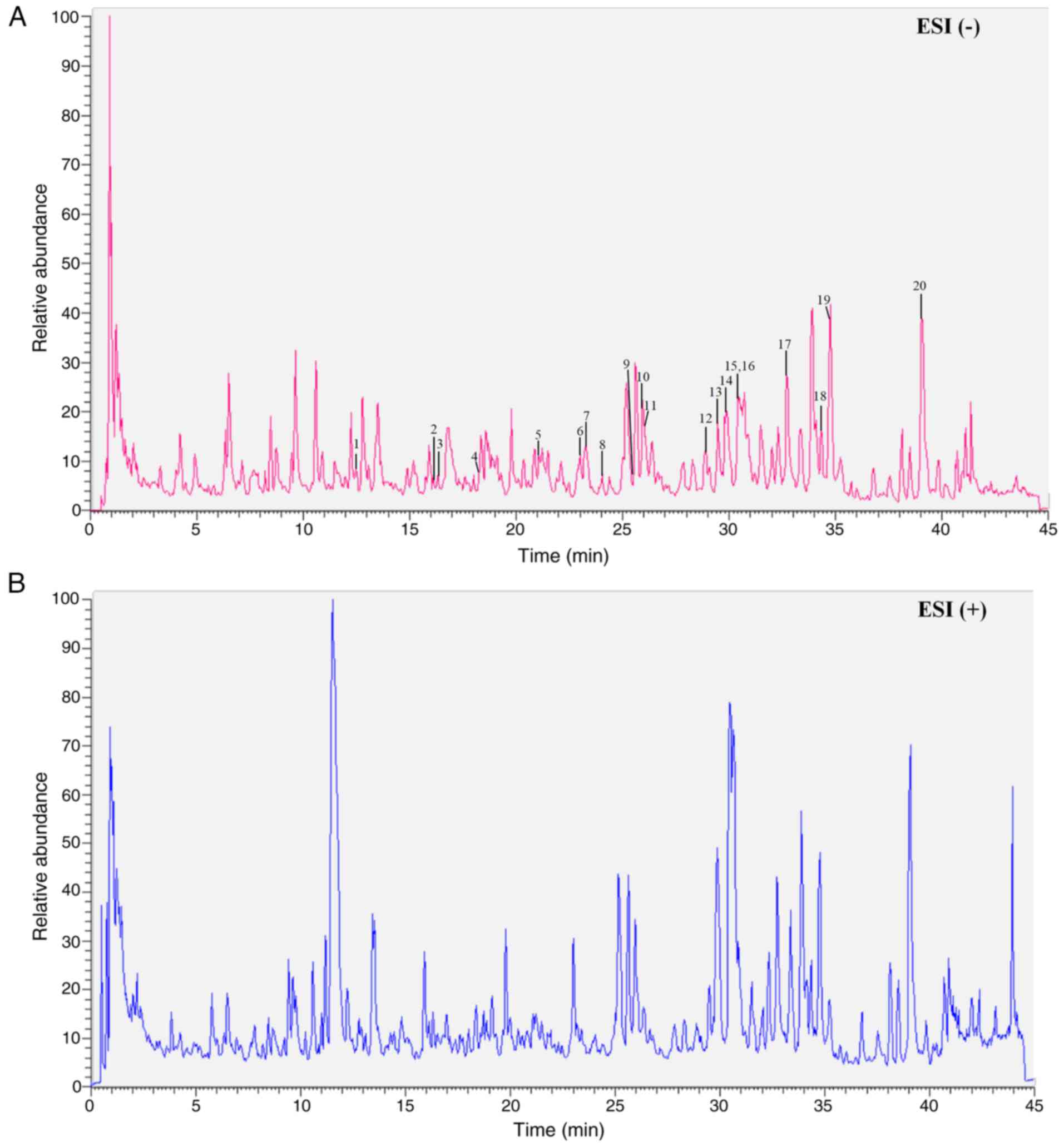
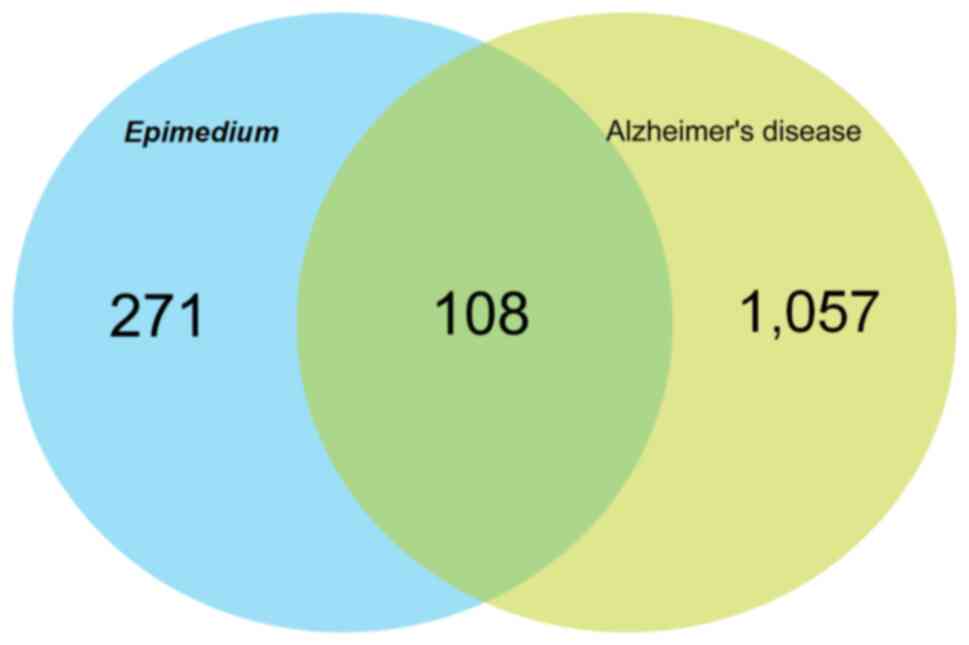
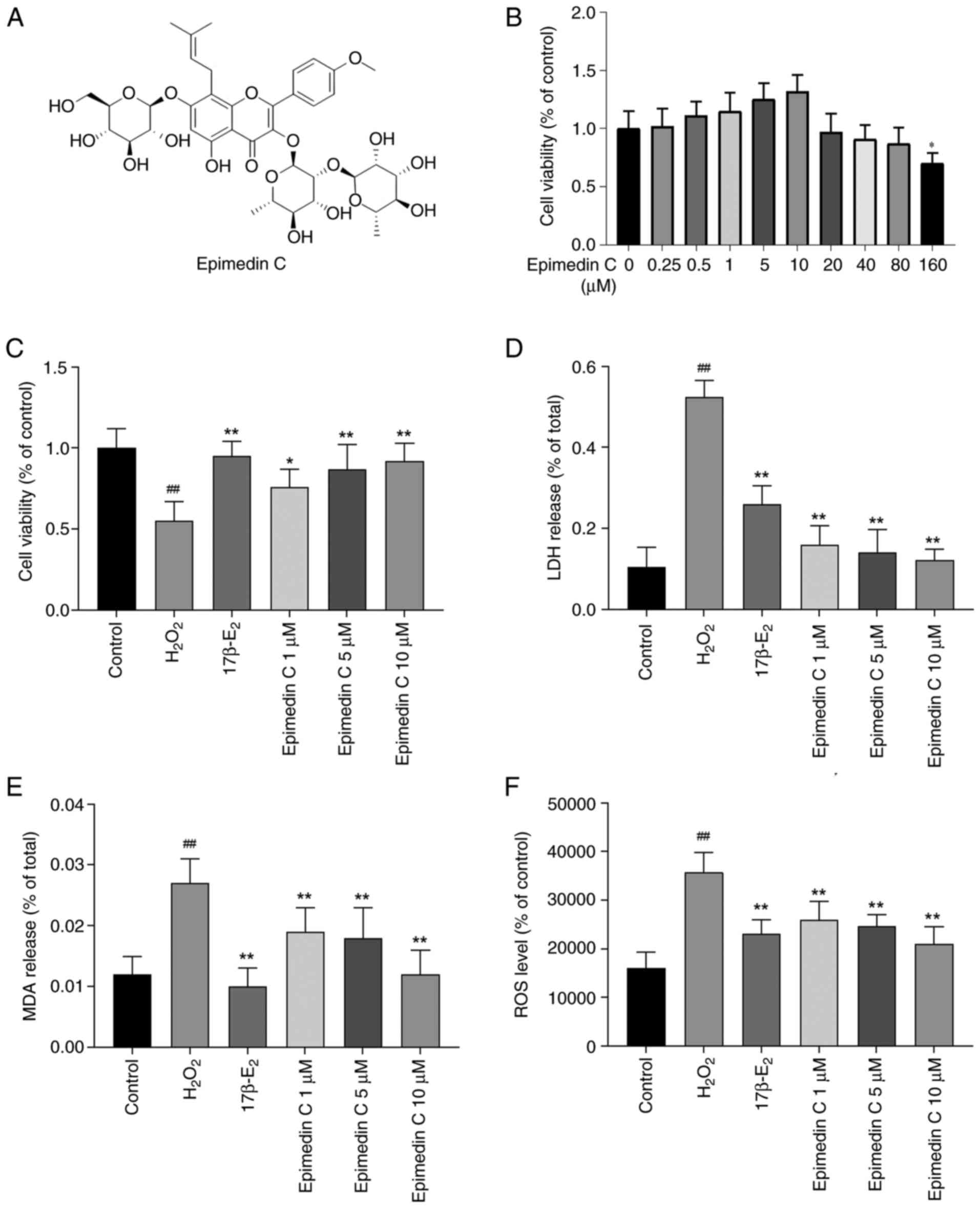
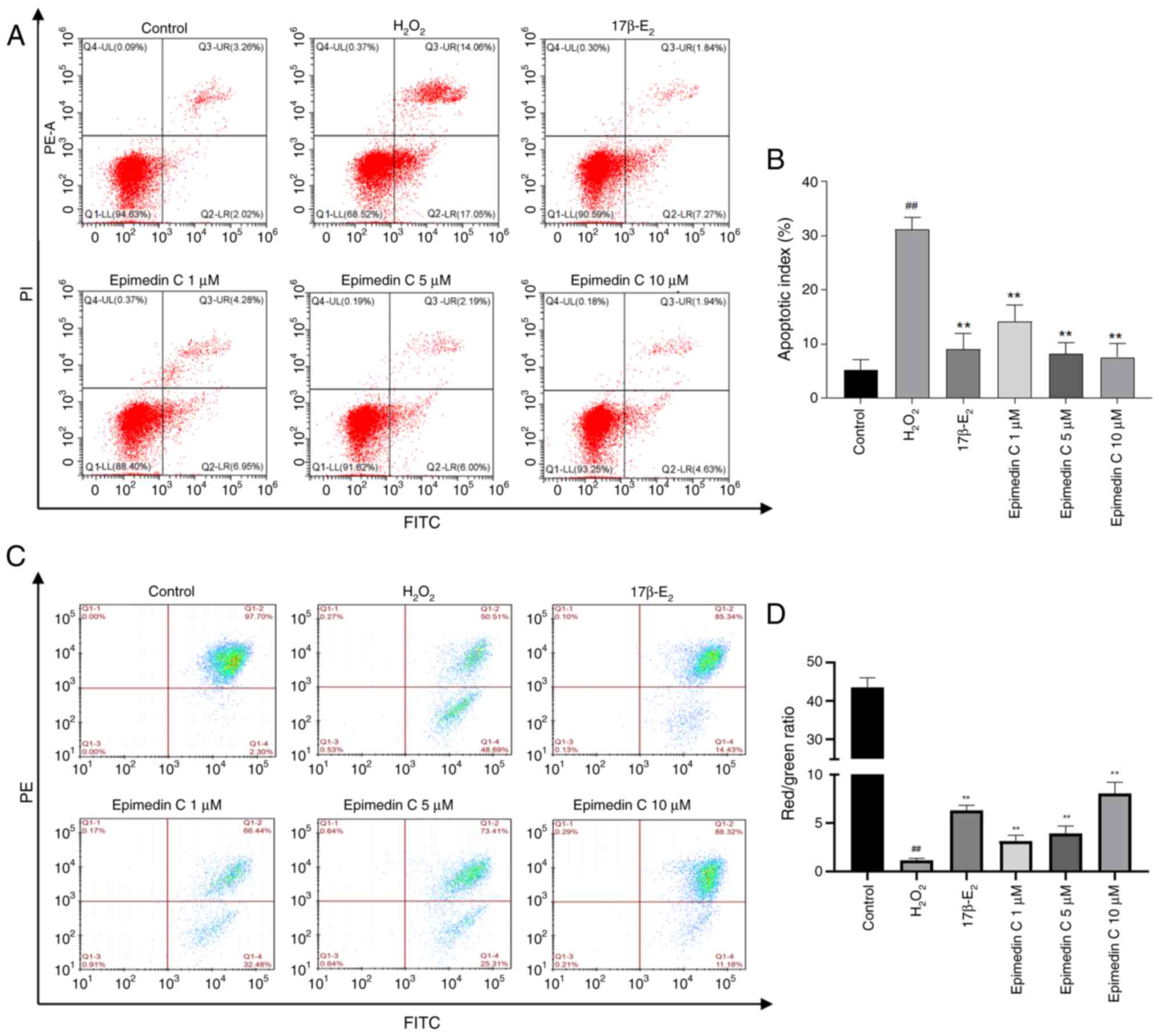
|
1
|
Li R, Robinson M, Ding X, Geetha T,
Al-Nakkash L, Broderick TL and Babu JR: Genistein: A focus on
several neurodegenerative diseases. J Food Biochem.
46(e14155)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bell SM, Burgess T, Lee J, Blackburn DJ,
Allen SP and Mortiboys H: Peripheral glycolysis in
neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 21(8924)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kovacs GG: Molecular pathology of
neurodegenerative diseases: Principles and practice. J Clin Pathol.
72:725–735. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Varela L and Garcia-Rendueles MER:
Oncogenic pathways in neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Mol Sci.
23(3223)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Orfali R, Alwatban AZ, Orfali RS, Lau L,
Chea N, Alotaibi AM, Nam YW and Zhang M: Oxidative stress and ion
channels in neurodegenerative diseases. Front Physiol.
15(1320086)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Chang KH, Cheng ML, Chiang MC and Chen CM:
Lipophilic antioxidants in neurodegenerative diseases. Clin Chim
Acta. 485:79–87. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Finkel T and Holbrook NJ: Oxidants,
oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature. 408:239–247.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Li Y, Li L and Hölscher C: Therapeutic
potential of genipin in central neurodegenerative diseases. CNS
Drugs. 30:889–897. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Chen Q, Chen G and Wang Q: Application of
network pharmacology in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases
with traditional Chinese medicine. Planta Med. 91:226–237.
2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wang SF, Wu MY, Cai CZ, Li M and Lu JH:
Autophagy modulators from traditional Chinese medicine: Mechanisms
and therapeutic potentials for cancer and neurodegenerative
diseases. J Ethnopharmacol. 194:861–876. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Li XL, Lin ZH, Chen SR, Ni S, Lin GY, Wang
W, Lin JY, Zhao Q, Cong C and Xu LW: Tiaogeng decoction improves
mild cognitive impairment in menopausal APP/PS1 mice through the
ERs/NF-κ b/AQP1 signaling pathway. Phytomedicine.
138(156391)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yang X, Chen J, Huang W, Zhang Y, Yan X,
Zhou Z and Wang Y: Synthesis of icariin in tobacco leaf by
overexpression of a glucosyltransferase gene from Epimedium
sagittatum. Ind Crop Prod. 156(112841)2020.
|
|
13
|
Li J, Yu Y, Zhang Y, Zhou Y, Ding S, Dong
S, Jin S and Li Q: Flavonoids derived from Chinese Medicine:
Potential neuroprotective agents. Am J Chin Med. 52:1613–1640.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zhou M, Zheng W, Sun X, Yuan M, Zhang J,
Chen X, Yu K, Guo B and Ma B: Comparative analysis of chemical
components in different parts of Epimedium Herb. J Pharm Biomed
Anal. 198(113984)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhang HF, Yang XH, Zhao LD and Wang Y:
Ultrasonic-assisted extraction of epimedin C from fresh leaves of
Epimedium and extraction mechanism. Innovative Food Science &
Emerging Technologies. 54-60:1466–8564. 2009.
|
|
16
|
Luo D, Shi D and Wen L: From epimedium to
neuroprotection: Exploring the potential of wushanicaritin. Foods.
13(1493)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Li XA, Ho YS, Chen L and Hsiao WL: The
protective effects of icariin against the homocysteine-induced
neurotoxicity in the primary embryonic cultures of rat cortical
neurons. Molecules. 21(1557)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission:
Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China. Vol 1. China
Medical Science Press, Beijing, 2020.
|
|
19
|
Wu L, Du ZR, Xu AL, Yan Z, Xiao HH, Wong
MS, Yao XS and Chen WF: Neuroprotective effects of total flavonoid
fraction of the Epimedium koreanum Nakai extract on dopaminergic
neurons: In vivo and in vitro. Biomed Pharmacother. 91:656–663.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhang HF, Yang TS, Li ZZ and Wang Y:
Simultaneous extraction of epimedin A, B, C and icariin from Herba
Epimedii by ultrasonic technique. Ultrason Sonochem. 15:376–385.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Huang X, Wang X, Zhang Y, Shen L, Wang N,
Xiong X, Zhang L, Cai X and Shou D: Absorption and utilisation of
epimedin C and icariin from Epimedii herba, and the regulatory
mechanism via the BMP2/Runx2 signalling pathway. Biomed
Pharmacother. 118(109345)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wei DH, Deng JL, Shi RZ, Ma L, Shen JM,
Hoffman R, Hu YH, Wang H and Gao JL: Epimedin C protects
H2O2-induced peroxidation injury by enhancing the function of
endothelial progenitor HUVEC populations. Biol Pharm Bull.
42:1491–1499. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ohnuma K, Hayashi Y, Furue M, Kaneko K and
Asashima M: Serum-free culture conditions for serial subculture of
undifferentiated PC12 cells. J Neurosci Methods. 151:250–261.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Cheng B, Lu H, Bai B and Chen J:
d-β-Hydroxybutyrate inhibited the apoptosis of PC12 cells induced
by H2O2 via inhibiting oxidative stress. Neurochem Int. 62:620–625.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Gao X, Li S, Liu X, Cong C, Zhao L, Liu H
and Xu L: Neuroprotective effects of Tiaogeng decoction against
H2O2-induced oxidative injury and apoptosis in PC12 cells via Nrf2
and JNK signaling pathways. J Ethnopharmacol.
279(114379)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhao Y, Kuca K, Wu W, Wang X, Nepovimova
E, Musilek K and Wu Q: Hypothesis: JNK signaling is a therapeutic
target of neurodegenerative diseases. Alzheimers Dement.
18:152–158. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Cho H and Hah JM: A perspective on the
development of c-Jun N-terminal Kinase inhibitors as therapeutics
for Alzheimer's disease: Investigating structure through docking
studies. Biomedicines. 9(1431)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Osama A, Zhang J, Yao J, Yao X and Fang J:
Nrf2: A dark horse in Alzheimer's disease treatment. Ageing Res
Rev. 64(101206)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wang M, Tong K, Chen Z and Wen Z:
Mechanisms of 15-Epi-LXA4-Mediated HO-1 in cytoprotection following
inflammatory injury. J Surg Res. 281:245–255. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Atabaki MM, Ghotbeddin Z, Rahimi K and
Tabandeh MR: The potential of alphapinene as a therapeutic agent
for maternal hypoxia-induced cognitive impairments: A study on HO-1
and Nrf2 gene expression in rats. Metab Brain Dis.
40(112)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Li J, Kuang G, Chen X and Zeng R:
Identification of chemical composition of leaves and flowers from
paeonia rockii by UHPLC-Q-exactive orbitrap HRMS. Molecules.
21(947)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Lozan E, Shinkaruk S, Al Abed SA, Lamothe
V, Potier M, Marighetto A, Schmitter JM, Bennetau-Pelissero C and
Buré C: Derivatization-free LC-MS/MS method for estrogen
quantification in mouse brain highlights a local metabolic
regulation after oral versus subcutaneous administration. Anal
Bioanal Chem. 409:5279–5289. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Guglielmotto M, Reineri S, Iannello A,
Ferrero G, Vanzan L, Miano V, Ricci L, Tamagno E, De Bortoli M and
Cutrupi S: E2 regulates epigenetic signature on neuroglobin
enhancer-promoter in neuronal cells. Front Cell Neurosci.
10(147)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Singh P and Paramanik V: Neuromodulating
roles of estrogen and phytoestrogens in cognitive therapeutics
through epigenetic modifications during aging. Front Aging
Neurosci. 14(945076)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lin J, Wu J, Xu Y, Zhao Y and Ye S:
RhFGF21 protected PC12 cells against mitochondrial apoptosis
triggered by H2O2 via the AKT-mediated ROS signaling pathway. Exp
Cell Res. 445(114417)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Li Y, Long J, Li L, Yu Z, Liang Y, Hou B,
Xiang L and Niu X: Pioglitazone protects PC12 cells against
oxidative stress injury: An in vitro study of its antiapoptotic
effects via the PPARγ pathway. Exp Ther Med. 26(522)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Cheng Y, Huang X, Tang Y, Li J, Tan Y and
Yuan Q: Effects of evodiamine on ROS/TXNIP/NLRP3 pathway against
gouty arthritis. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol.
397:1015–1023. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Abedi A, Ghobadi H, Sharghi A, Iranpour S,
Fazlzadeh M and Aslani MR: Effect of saffron supplementation on
oxidative stress markers (MDA, TAC, TOS, GPx, SOD, and
pro-oxidant/antioxidant balance): An updated systematic review and
meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Front Med
(Lausanne). 10(1071514)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Satoh T, Enokido Y, Aoshima H, Uchiyama Y
and Hatanaka H: Changes in mitochondrial membrane potential during
oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells. J Neurosci Res.
50:413–420. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Perelman A, Wachtel C, Cohen M, Haupt S,
Shapiro H and Tzur A: JC-1: Alternative excitation wavelengths
facilitate mitochondrial membrane potential cytometry. Cell Death
Dis. 3(e430)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Kyrylkova K, Kyryachenko S, Leid M and
Kioussi C: Detection of apoptosis by TUNEL assay. Methods Mol Biol.
887:41–47. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Protasoni M and Zeviani M: mitochondrial
structure and bioenergetics in normal and disease conditions. Int J
Mol Sci. 22(586)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Wang G, Zhao Z, Ren B, Yu W, Zhang X, Liu
J, Wang L, Si D and Yang M: Exenatide exerts a neuroprotective
effect against diabetic cognitive impairment in rats by inhibiting
apoptosis: Role of the JNK/c-JUN signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep.
25(111)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Kong R, Shi J, Xie K, Wu H, Wang X, Zhang
Y and Wang Y: A study of JUN's promoter region and its regulators
in chickens. Genes (Basel). 15(1351)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Huang HM and Liu JC: c-Jun blocks cell
differentiation but not growth inhibition or apoptosis of chronic
myelogenous leukemia cells induced by STI571 and by histone
deacetylase inhibitors. J Cell Physiol. 218:568–574.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Chen F, Xiao M, Hu S and Wang M:
Keap1-Nrf2 pathway: A key mechanism in the occurrence and
development of cancer. Front Oncol. 14(1381467)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Galan-Cobo A, Sitthideatphaiboon P, Qu X,
Poteete A, Pisegna MA, Tong P, Chen PH, Boroughs LK, Rodriguez MLM,
Zhang W, et al: LKB1 and KEAP1/NRF2 pathways cooperatively promote
metabolic reprogramming with enhanced glutamine dependence in
KRAS-mutant lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 79:3251–3267.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Buendia I, Michalska P, Navarro E, Gameiro
I, Egea J and León R: Nrf2-ARE pathway: An emerging target against
oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative
diseases. Pharmacol Ther. 157:84–104. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Xiao Q, Piao R, Wang H, Li C and Song L:
Orientin-mediated Nrf2/HO-1 signal alleviates H2O2-induced
oxidative damage via induction of JNK and PI3K/AKT activation. Int
J Biol Macromol. 118 (Pt A):747–755. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Feng L, Wu Y, Wang J, Han Y, Huang J and
Xu H: Neuroprotective effects of a novel tetrapeptide SGGY from
Walnut against H2O2-Stimulated oxidative stress in SH-SY5Y cells:
Possible involved JNK, p38 and Nrf2 signaling pathways. Foods.
12(1490)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Kuntić M, Hahad O, Münzel T and Daiber A:
Crosstalk between oxidative stress and inflammation caused by noise
and air pollution-implications for neurodegenerative diseases.
Antioxidants (Basel). 13(266)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Downs BW, Kushner S, Bagchi M, Blum K,
Badgaiyan RD, Chakraborty S and Bagchi D: Etiology of
neuroinflammatory pathologies in neurodegenerative diseases: A
treatise. Curr Psychopharmacol. 10:123–137. 2021.
|
|
53
|
Li Y, Zhang W, Zhang Q, Li Y, Xin C, Tu R
and Yan H: Oxidative stress of mitophagy in neurodegenerative
diseases: Mechanism and potential therapeutic targets. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 764(110283)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Pardillo-Díaz R, Pérez-García P, Castro C,
Nunez-Abades P and Carrascal L: Oxidative stress as a potential
mechanism underlying membrane hyperexcitability in
neurodegenerative diseases. Antioxidants (Basel).
11(1511)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Kim S, Jung UJ and Kim SR: Role of
oxidative stress in blood-brain barrier disruption and
neurodegenerative diseases. Antioxidants (Basel).
13(1462)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Tarozzi A: Oxidative stress in
neurodegenerative diseases: From preclinical studies to clinical
applications. J Clin Med. 9(1223)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Shams Ul Hassan S, Ishaq M, Zhang WD and
Jin HZ: An overview of the mechanisms of marine Fungi-derived
anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor agents and their novel role in
drug targeting. Curr Pharm Des. 27:2605–2614. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Cai Z, Liu M, Zeng L, Zhao K, Wang C, Sun
T, Li Z and Liu R: Role of traditional Chinese medicine in
ameliorating mitochondrial dysfunction via non-coding RNA
signaling: Implication in the treatment of neurodegenerative
diseases. Front Pharmacol. 14(1123188)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Mohd Sairazi NS and Sirajudeen KNS:
Natural products and their bioactive compounds: Neuroprotective
potentials against neurodegenerative diseases. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2020(6565396)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Chen L, Liu Y and Xie J: The beneficial
pharmacological effects of Uncaria rhynchophylla in
neurodegenerative diseases: Focus on alkaloids. Front Pharmacol.
15(1436481)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Wang ZY, Liu J, Zhu Z, Su CF,
Sreenivasmurthy SG, Iyaswamy A, Lu JH, Chen G, Song JX and Li M:
Traditional Chinese medicine compounds regulate autophagy for
treating neurodegenerative disease: A mechanism review. Biomed
Pharmacother. 133(110968)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Chen XL, Li SX, Ge T, Zhang DD, Wang HF,
Wang W, Li YZ and Song XM: Epimedium Linn: A comprehensive review
of phytochemistry, pharmacology, clinical applications and quality
control. Chem Biodivers. 21(e202400846)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Li C, Li Q, Mei Q and Lu T:
Pharmacological effects and pharmacokinetic properties of icariin,
the major bioactive component in Herba Epimedii. Life Sci.
126:57–68. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Zong N, Li F, Deng Y, Shi J, Jin F and
Gong Q: Icariin, a major constituent from Epimedium brevicornum,
attenuates ibotenic acid-induced excitotoxicity in rat hippocampus.
Behav Brain Res. 313:111–119. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Liu F, Wei B, Cheng L, Zhao Y, Liu X, Yuan
Q and Liang H: Co-Immobilizing two glycosidases based on
cross-linked enzyme aggregates to enhance enzymatic properties for
achieving high titer Icaritin biosynthesis. J Agric Food Chem.
70:11631–11642. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Yang J, Yang J, Liang SH, Xu Y, Moore A
and Ran C: Imaging hydrogen peroxide in Alzheimer's disease via
cascade signal amplification. Sci Rep. 6(35613)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Gharai PK, Khan J, Mallesh R, Garg S, Saha
A and Ghosh S and Ghosh S: Vanillin benzothiazole derivative
reduces cellular reactive oxygen species and detects amyloid
fibrillar aggregates in Alzheimer's disease brain. ACS Chem
Neurosci. 14:773–786. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Sajjad N, Wani A, Sharma A, Ali R, Hassan
S, Hamid R, Habib H and Ganai BA: Artemisia amygdalina Upregulates
Nrf2 and protects neurons against oxidative stress in Alzheimer
disease. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 39:387–399. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Zakharova IO, Sokolova TV, Furaev VV,
Rychkova MP and Avrova NF: (Effects of oxidative stress inducers,
neurotoxins, and ganglioside GM1 on Na+, K+-ATPase in PC12 and
brain synaptosomes). Zh Evol Biokhim Fiziol. 43:148–154.
2007.PubMed/NCBI(In Russian).
|
|
70
|
Demirci-Çekiç S, Özkan G, Avan AN, Uzunboy
S, Çapanoğlu E and Apak R: Biomarkers of oxidative stress and
antioxidant defense. J Pharm Biomed Anal.
209(114477)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Pisoschi AM and Pop A: The role of
antioxidants in the chemistry of oxidative stress: A review. Eur J
Med Chem. 97:55–74. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Zhang R, Guo X, Zhang Y and Tian C:
Influence of modified atmosphere treatment on post-harvest reactive
oxygen metabolism of pomegranate peels. Nat Prod Res. 34:740–744.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
González-Rubio G, Sellers-Moya Á, Martín H
and Molina M: A walk-through MAPK structure and functionality with
the 30-year-old yeast MAPK Slt2. Int Microbiol. 24:531–543.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Miloso M, Scuteri A, Foudah D and Tredici
G: MAPKs as mediators of cell fate determination: An approach to
neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Med Chem. 15:538–548.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Du J, Wang G, Luo H, Liu N and Xie J:
JNK-IN-8 treatment alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung
injury via suppression of inflammation and oxidative stress
regulated by JNK/NF-κB signaling. Mol Med Rep. 23(150)2021.
|
|
76
|
Li R, Yang W, Yan X, Zhou X, Song X, Liu
C, Zhang Y and Li J: Folic acid mitigates the developmental and
neurotoxic effects of bisphenol A in zebrafish by inhibiting the
oxidative stress/JNK signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf.
288(117363)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Shakya A, McKee NW, Dodson M, Chapman E
and Zhang DD: Anti-ferroptotic effects of Nrf2: Beyond the
antioxidant response. Mol Cells. 46:165–175. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Hallis SP, Kim JM and Kwak MK: Emerging
role of NRF2 signaling in cancer stem cell phenotype. Mol Cells.
46:153–164. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Huang SY, Chang SF, Chau SF and Chiu SC:
The protective effect of hispidin against hydrogen peroxide-induced
oxidative stress in ARPE-19 cells via Nrf2 signaling pathway.
Biomolecules. 9(380)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Li S, Cong C, Liu Y, Liu X, Liu H, Zhao L,
Gao X, Gui W and Xu L: Tiao Geng decoction inhibits tributyltin
chloride-induced GT1-7 neuronal apoptosis through ASK1/MKK7/JNK
signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 269(113669)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Li S, Cong C, Liu Y, Liu X, Kluwe L, Shan
X, Liu H, Gao M, Zhao L, Gao X and Xu L: Tiao Geng decoction for
treating menopausal syndrome exhibits anti-aging effects likely via
suppressing ASK1/MKK7/JNK mediated apoptosis in ovariectomized
rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 261(113061)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Ryan J, Scali J, Carriere I, Ritchie K and
Ancelin ML: Hormonal treatment, mild cognitive impairment and
Alzheimer's disease. Int Psychogeriatr. 20:47–56. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Li C, Jia WW, Yang JL, Cheng C and Olaleye
OE: Multi-compound and drug-combination pharmacokinetic research on
Chinese herbal medicines. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 43:3080–3095.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Chen L, Zhen Y, Wang X, Wang J and Zhu G:
Neurovascular glial unit: A target of phytotherapy for cognitive
impairments. Phytomedicine. 119(155009)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Sharma S, Mehan S, Khan Z, Tiwari A, Kumar
A, Gupta GD, Narula AS and Kalfin R: Exploring the neuroprotective
potential of icariin through modulation of neural pathways in the
treatment of neurological diseases. Curr Mol Med: Sep 26, 2024
(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
86
|
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Zhang X, Liu Y, Li J and
Wang J: Metabolic profiling of epimedin C in Rats: In vivo and in
vitro studies. Front. Pharmacol. 9(456)2018.
|
|
87
|
Wong SP, Shen P, Lee L, Li J and Yong EL:
Pharmacokinetics of prenylflavonoids and correlations with the
dynamics of estrogen action in sera following ingestion of a
standardized Epimedium extract. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 50:216–223.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Xie L, Zhao S, Zhang X, Huang W, Qiao L,
Zhan D, Ma C, Gong W, Dang H and Lu H: Wenshenyang recipe treats
infertility through hormonal regulation and inflammatory responses
revealed by transcriptome analysis and network pharmacology. Front
Pharmacol. 13(917544)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Hara Y, Waters EM, McEwen BS and Morrison
JH: estrogen effects on cognitive and synaptic health over the
lifecourse. Physiol Rev. 95:785–807. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Uddin MS, Rahman MM, Jakaria M, Rahman MS,
Hossain MS, Islam A, Ahmed M, Mathew B, Omar UM, Barreto GE and
Ashraf GM: Estrogen signaling in Alzheimer's disease: Molecular
Insights and therapeutic targets for Alzheimer's dementia. Mol
Neurobiol. 57:2654–2670. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Dubal DB, Zhu H, Yu J, Rau SW, Shughrue
PJ, Merchenthaler I, Kindy MS and Wise PM: Estrogen receptor alpha,
not beta, is a critical link in estradiol-mediated protection
against brain injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:1952–1957.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Li B, Lima MRM, Nie Y, Xu L, Liu X, Yuan
H, Chen C, Dias AC and Zhang X: HPLC-DAD fingerprints combined with
multivariate analysis of epimedii folium from major producing areas
in eastern Asia: Effect of geographical origin and species. Front
Pharmacol. 12(761551)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Lee D, Jeong HC, Kim SY, Chung JY, Cho SH,
Kim KA, Cho JH, Ko BS, Cha IJ, Chung CG, et al: A comparison study
of pathological features and drug efficacy between Drosophila
models of C9orf72 ALS/FTD. Mol Cells. 47(100005)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|