Introduction
Lumbar disc herniation (LDH) is a prevalent spinal
disorder and a major cause of global disability, as evidenced by
its marked associated healthcare expenditures and economic burden
(1). When conservative management
proves ineffective, surgical intervention becomes necessary
(2,3). The advent of minimally invasive spine
surgery (MISS) has notably transformed treatment paradigms, with
endoscopic techniques gaining prominence for their ability to
minimize tissue trauma and enable precise decompression (4).
Selecting the optimal MISS approach for LDH remains
a subject of debate (5).
Transforaminal endoscopic lumbar discectomy, pioneered by Kambin
and Sampson (6) and based on the
anatomical concept of Kambin's triangle, has demonstrated
effectiveness but is typically limited at the L5-S1 level due to
high iliac crest obstruction and the restricted working corridor
within the safe zone (7).
Consequently, the interlaminar approach has emerged as a valuable
alternative, using the natural anatomical window of the
interlaminar space to overcome osseous restrictions. This method
provides improved access for central and L5-S1 herniations and has
facilitated the development of techniques such as percutaneous
endoscopic interlaminar discectomy (PEID) and unilateral biportal
endoscopic discectomy (UBE) (8,9).
Although both PEID and UBE employ the interlaminar
approach and have yielded favorable outcomes, direct comparative
evidence regarding their efficacy and safety profiles within this
shared surgical corridor remains limited (10). Therefore, the present meta-analysis
aimed to compare UBE and PEID regarding surgical efficiency,
including operative time, intraoperative blood loss, hospital stay
length and fluoroscopy frequency, functional outcomes including
MacNab excellent/good rate (11),
back and leg visual analog scale (VAS) scores (12) and Oswestry Disability Index (ODI)
(13), and safety-complication
rates. The present study aimed to provide evidence-based guidance
for clinical decision-making in selecting the most appropriate
surgical technique.
Materials and methods
Search strategy
A comprehensive systematic literature search was
conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for
Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines (14). The search encompassed four major
electronic databases: PubMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine,
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/), Web
of Science (Clarivate Analytics platform, https://www.webofscience.com/), Embase (Elsevier,
https://www.embase.com) and the Cochrane Library
(Wiley, https://www.cochranelibrary.com/). The search period
spanned from the inception of each database to June 10, 2025. The
strategy combined Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) and free-text
terms using Boolean operators (AND/OR). For example, the PubMed
search syntax was as follows: (‘Unilateral Biportal
Endoscopy’[MeSH] OR ‘Biportal Endoscopic’[tiab] OR UBE[tiab] OR
UBED[tiab]) AND (‘Percutaneous Endoscopy’[MeSH] OR ‘Percutaneous
Endoscopic Interlaminar Discectomy’[tiab] OR PEID[tiab] OR
PELD[tiab]) AND (‘Lumbar Disc Herniation’[MeSH] OR ‘Lumbar
Intervertebral Disc’[tiab] OR LDH[tiab]). Additionally, the
reference lists of relevant reviews were screened to identify
potentially eligible studies.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria were as follows: i) Comparative
studies of UBE vs. PEID performed exclusively using the
interlaminar approach for single-level LDH; ii) retrospective or
prospective cohort studies or randomized controlled trials and iii)
publications in English. Exclusion criteria were as follows: i)
Prior lumbar surgery or multi-level LDH; ii) comorbidity, such as
infection, tuberculosis, psychiatric disorders or neoplasms; iii)
non-primary literature (reviews, case reports or conference
abstracts); iv) studies with inaccessible outcome data and v)
procedures not utilizing the interlaminar approach.
Data extraction and quality
assessment
Data were extracted by two independent investigators
regarding study characteristics (first author, study design,
country, sample size, sex, age, BMI and operative levels) and
outcome parameters (operative time, blood loss, fluoroscopy
frequency, hospital stay duration, VAS for back and leg pain, ODI,
modified MacNab criteria with excellent rate and complication
rates). Study quality was evaluated using the Newcastle-Ottawa
Scale (NOS) (15) with
discrepancies resolved through discussion or arbitration by a third
author.
Statistical analysis
Meta-analyses were conducted using Review Manager
(RevMan; version 5.4; The Cochrane Collaboration). Dichotomous
variables (MacNab excellent/good rate and complication rates) were
analyzed using odds ratios (ORs) with 95% CIs. Continuous variables
(operative time, VAS and ODI) were analyzed using mean difference
(MD) or standardized MD (SMD) with 95% CIs. MDs were preferred when
outcomes were measured on identical scales across studies, whereas
SMDs were applied when outcomes were reported on different scales.
P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant
difference and heterogeneity was quantified using the I2
statistic. In accordance with the recommendations of the Cochrane
Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (16), a random-effects model was applied
to all meta-analyses to incorporate the expected heterogeneity of
intervention effects across studies from different settings.
Sensitivity or subgroup analyses were conducted to explore
potential sources of heterogeneity sources. Publication bias was
assessed using funnel plots and Egger's regression test.
Results
Search results
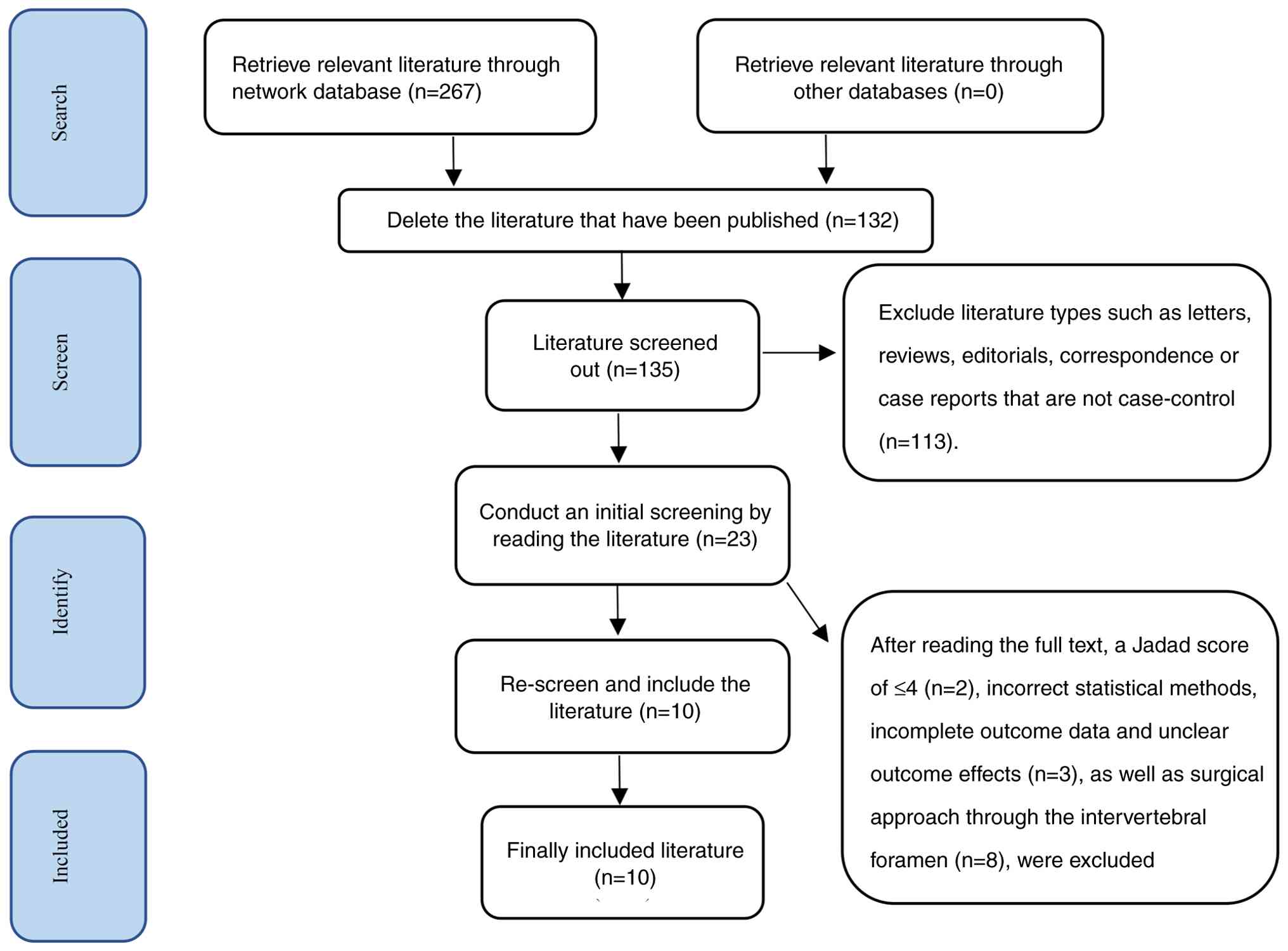
According to the predefined search strategy, a total
of 267 records were retrieved from Embase, the Cochrane Library,
PubMed and Web of Science databases. After removing 132 duplicate
entries, 135 unique records remained. Following a review of titles
and abstracts, 112 records were excluded. The remaining 23 studies
underwent full-text evaluation, of which 13 were excluded based on
the eligibility criteria. Ultimately, 10 studies were included in
the present meta-analysis (Fig. 1)
(17-26).
Basic characteristics of included
studies
Within the 10 included studies, the following
outcomes were reported; i) Operative time (n=10) (17-26);
ii) blood loss (n=5) (17-20,22);
iii) hospital stay duration (n=5) (17,18,20,21,23);
iv) fluoroscopy frequency (n=5) (18,19,23-25)
v) back and leg VAS score (n=10) (17-26);
vi) MacNab criteria with excellent/good rate (n=7) (17-22,24)
and vii) complication rates (n=6) (18-20,23-25).
In total, the studies encompassed 1,003 patients (514 male and 489
female). Detailed study characteristics are presented in Tables I and II.
 | Table IBasic information on included
retrospective studies. |
Table I
Basic information on included
retrospective studies.
| First author,
year | Country | Group | Sample size
(M/F) | Mean age,
years | BMI,
kg/m2 | Operation level
(n) | Mean fluoroscopy
frequency, n | (Refs.) |
|---|
| Wang et al,
2025 | China | UBE | 18 (10/8) | 40.94±13.73 | 24.51±3.12 | L2-3(1); L4-5(12);
L5-S1(11) | NR | (17) |
| | | PEID | 21 (14/7) | 42.33±11.63 | 23.14±3.83 | L2-3 (0); L4-5(6);
L5-S1(15) | NR | |
| Xiao et al,
2025 | China | UBE | 84 (45/39) | 53.46±15.60 | 24.17±2.94 | L3-4(4); L4-5(52);
L5-S1(28) | 4.06±4.63 | (18) |
| | | PEID | 62 (23/39) | 55.61±15.52 | 23.90±2.61 | L3-4(3); L4-5(37);
L5-S1(21) | 7.72±3.35 | |
| Guo et al,
2025 | China | UBE | 79 (43/36) | 47.35±14.07 | 22.51±2.38 | L4-5(38);
L5-S1(38); other (3) | 3.28±1.67 | (19) |
| | | PEID | 94 (52/42) | 44.03±14.19 | 22.99±2.06 | L4-5(44);
L5-S1(44); other (6) | 2.99±1.04 | |
| Yin et al,
2025 | China | UBE | 46 (29/17) | 43.85±11.41 | 24.83±3.92 | L5-S1(50) | NR | (20) |
| | | PEID | 50 (27/23) | 45.64±13.60 | 24.70±4.24 | L5-S1(46) | NR | |
| Qian et al,
2024 | China | UBE | 15 (8/7) | 36.27±11.11 | 21.93±2.12 | L4-5(4);
L5-S1(11) | NR | (21) |
| | | PEID | 26 (18/8) | 35.15±9.30 | 22.38±1.75 | L4-5(12);
L5-S1(14) | NR | |
| Yang et al,
2024 | China | UBE | 33 (18/15) | 43.60±15.80 | NR | L4-5(11);
L5-S1(22) | NR | (22) |
| | | PEID | 66 (36/30) | 44.70±12.90 | NR | L4-5(22);
L5-S1(44) | NR | |
| Wei et al,
2024 | China | UBE | 55 (19/36) | 56.89±15.01 | 26.88±4.13 | L4-5 (NR); L5-S1
(NR) | 3.51±0.63 | (23) |
| | | PEID | 60 (23/37) | 57.19±14.25 | 27.06±4.93 | L4-5 (NR); L5-S1
(NR) | 3.28±0.66 | |
| Wu et al,
2024 | China | UBE | 31 (16/15) | 58.50±13.20 | 24.10±3.00 | L4-5(17);
L5-S1(14) | 3.40±0.90 | (24) |
| | | PEID | 65 (29/36) | 57.60±16.80 | 25.00±2.90 | L4-5(35);
L5-S1(30) | 4.80±1.00 | |
| Wang et al,
2023 | China | UBE | 51 (22/29) | 43.80±14.20 | 25.40±3.70 | L5-S1(51) | 2.50±0.60 | (25) |
| | | PEID | 55 (28/27) | 42.30±3.80 | 25.80±3.60 | L5-S1(55) | 2.40±0.50 | |
| Zuo et al,
2022 | China | UBE | 42 (23/19) | 45.57±11.15 | NR | L5-S1(42) | NR | (26) |
| | | PEID | 50 (31/19) | 46.68±12.09 | NR | L5-S1(50) | NR | |
 | Table IIIntraoperative data and postoperative
recovery indices. |
Table II
Intraoperative data and postoperative
recovery indices.
| First author,
year | Group | Mean operative
time, min | Mean blood loss,
ml | Mean hospital stay,
days | Back VAS score | Leg VAS score | ODI score | MacNab score
excellence rate, % | Complic ations,
n | (Refs.) |
|---|
| Wang et al,
2025 | UBE | 136.44±32.11 | 18.89±6.54 | 9.17±2.81 | Pre-op; postop day
1; | Pre-op; postop | Pre-op; postop day
1; | 94.44 | NR | (17) |
| | PEID | 104.86±35.74 | 7.14±2.99 | 6.95±1.69 | 1 and 3 month
postop | day 1; 1 and 3
month postop | 1 and 3 month
postop | 95.24 | NR | |
| Xiao et al,
2025 | UBE | 66.67±15.83 | 76.81±26.74 | 5.39±1.83 | Pre-op; 1, 6
and | NR | Pre-op; 1, 6
and | 91.70 | 5 | (18) |
| | PEID | 69.11±25.84 | 69.44±25.74 | 5.11±3.42 | 24 month
postop | NR | 24 month
postop | 87.10 | 20 | |
| Guo et al,
2025 | UBE | 116.52±47.20 | 80.19±22.81 | 7.34±2.36
(post) | Pre-op; postop | Pre-op; postop | Pre-op; postop day
1; | 96.20 | 7 | (19) |
| | PEID | 99.96±34.74 | 20.85±11.06 | 3.47±1.23
(post) | day 1; 3 and 6
month postop | day 1; 3 and 6
month postop | 3 and 6 month
postop | 94.68 | 8 | |
| Yin et al,
2025 | UBE | 80.98±33.61 | 394.16±227.96 | 5.54±1.92 | Pre-op; postop day
1; | Pre-op; postop day
1; | Pre-op; final | 97.80 | 2 | (20) |
| | PEID | 89.42±32.16 | 273.83±158.53 | 5.24±1.89 | final
follow-up | final
follow-up | follow-up | 96.00 | 2 | |
| Qian et al,
2024 | UBE | 133.07±10.46 | NR | 4.24±1.44 | Pre -op; 1, 3
and | Pre -op; 1, 3
and | Pre -op; 1, 3
and | 86.70 | NR | (21) |
| | PEID | 110.81±11.48 | NR | 2.73±1.28 | 6 month postop | 6 month postop | 6 month postop | 92.30 | NR | |
| Yang et al,
2024 | UBE | 100.80±36.10 | 9.90±3.40 | NR | Pre-op; postop | NR | Pre-op;
post-op | 97.00 | NR | (22) |
| | PEID | 86.00±19.40 | 5.50±2.30 | NR | | NR | | 95.50 | NR | |
| Wei et al,
2024 | UBE | 56.74±10.57 | NR | 7.50±2.12 | Pre-op; postop day
1; | Pre-op; postop day
1; | Pre-op; postopday
1; | NR | 1 | (23) |
| | PEID | 54.34±10.15 | NR | 7.18±2.30 | 1, 3, 6 and 12
month postop | 1, 3, 6 and 12
month postop | 1, 3, 6 and 12
month postop | NR | 1 | |
| Wu et al,
2024 | UBE | 77.30±20.40 | NR | 4.50±2.60
(post) | Pre-op; postop day
1; | Pre-op; postop day
1; | Pre-op; postop day
1; | 90.30 | 1 | (24) |
| | PEID | 65.80±15.90 | NR | 3.10±1.80
(post) | 1 and 6 month
postop; final follow-up | 1 and 6 month
postop; final follow-up | 1 and 6 month
postop; final follow-up | 84.60 | 2 | |
| Wang et al,
2023 | UBE | 83.60±10.80 | NR | 2.10±0.80
(post) | Pre-op; postop day
1; | Pre-op; postop day
1; | Pre-op; postop day
1; | NR | 3 | (25) |
| | PEID | 80.20±8.40 | NR | 2.00±0.80
(post) | 3 month postop;
final follow-up | 3 month postop;
final follow-up | 3-month postop;
final follow-up | NR | 2 | |
| Zuo et al,
2022 | UBE | 68.57±10.87 | NR | 6.88±1.85
(post) | Pre-op; postop day
3; | Pre-op; postop day
3; | Pre-op; postop day
3; | NR | NR | (26) |
| | | | | 7.36±4.62
(post) | 3, 6 and 12 month
postop | 3, 6 and 12 month
postop | 3, 6 and 12 month
postop | | | |
| | PEID | 65.6±15.24 | NR | | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
Quality evaluation of the included
studies
All 10 included studies were retrospective in
design, with no prospective studies identified. Study quality was
assessed using the NOS, whereby three studies scored 8 points and
seven scored 7 points. All studies met the high-quality threshold
(NOS score ≥7; Table III).
 | Table IIIStudy evaluation using modified
Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. |
Table III
Study evaluation using modified
Newcastle-Ottawa Scale.
| First author,
year | Selection | Comparability | Exposure | Total score | (Refs.) |
|---|
| Wang et al,
2025 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 7 | (17) |
| Xiao et al,
2025 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 7 | (18) |
| Guo et al,
2025 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 7 | (19) |
| Yin et al,
2025 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 8 | (20) |
| Qian et al,
2024 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 7 | (21) |
| Yang et al,
2024 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 7 | (22) |
| Wei et al,
2024 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 7 | (23) |
| Wu et al,
2024 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 7 | (24) |
| Wang et al,
2023 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 8 | (25) |
| Zuo et al,
2022 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 8 | (26) |
Analysis of clinical outcomes.
Meta-analysis results of surgical efficiency
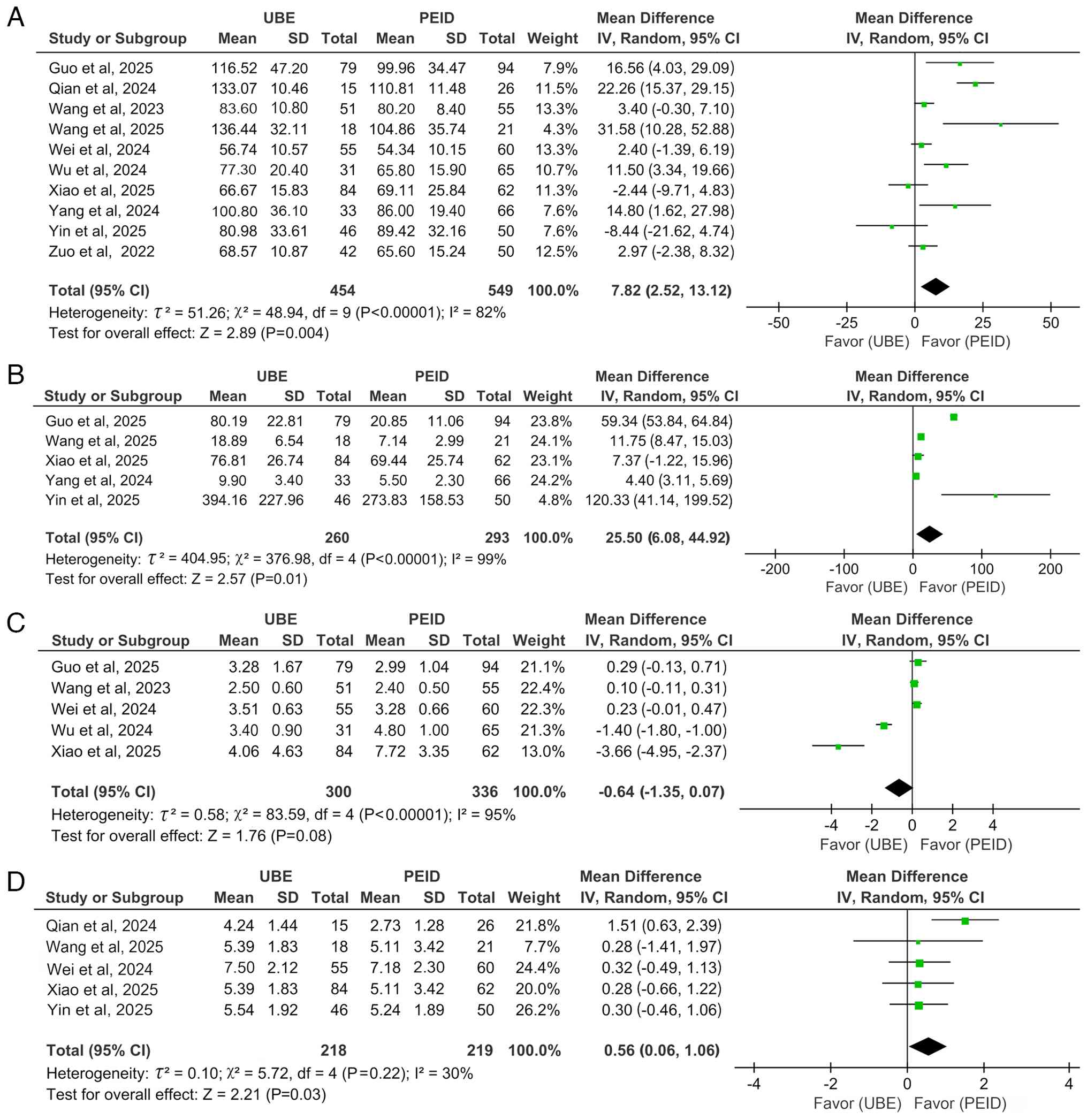
A pooled analysis of 10 studies (17-26)
comparing operative time demonstrated that PEID required a
significantly shorter operative time compared with UBE in the
treatment of LDH (MD=7.82; 95% CI: 2.52-13.12; P=0.004;
I2=82%; Fig. 2A).
Similarly, analysis of five studies (17-19,22,24)
on intraoperative blood loss showed that PEID was associated with a
significantly decreased blood loss (MD=25.50; 95% CI: 6.08-44.92;
P=0.01; I2=99%; Fig.
2B), also demonstrated through a random-effects model.
Furthermore, five studies (18,19,23-25)
comparing fluoroscopy frequency revealed no significant difference
between PEID and UBE (MD=-0.64; 95% CI: -1.35-0.07; P=0.08;
I2=95%), analyzed using a random-effects model (Fig. 2C).
In the comparison of hospital stay duration of UBE
and PEID, five studies (17,18,20,21,23)
demonstrated significantly shorter hospitalization with PEID
(MD=0.56; 95% CI: 0.06-1.06; P=0.03; I2=30%; Fig. 2D), analyzed using a random-effects
model.
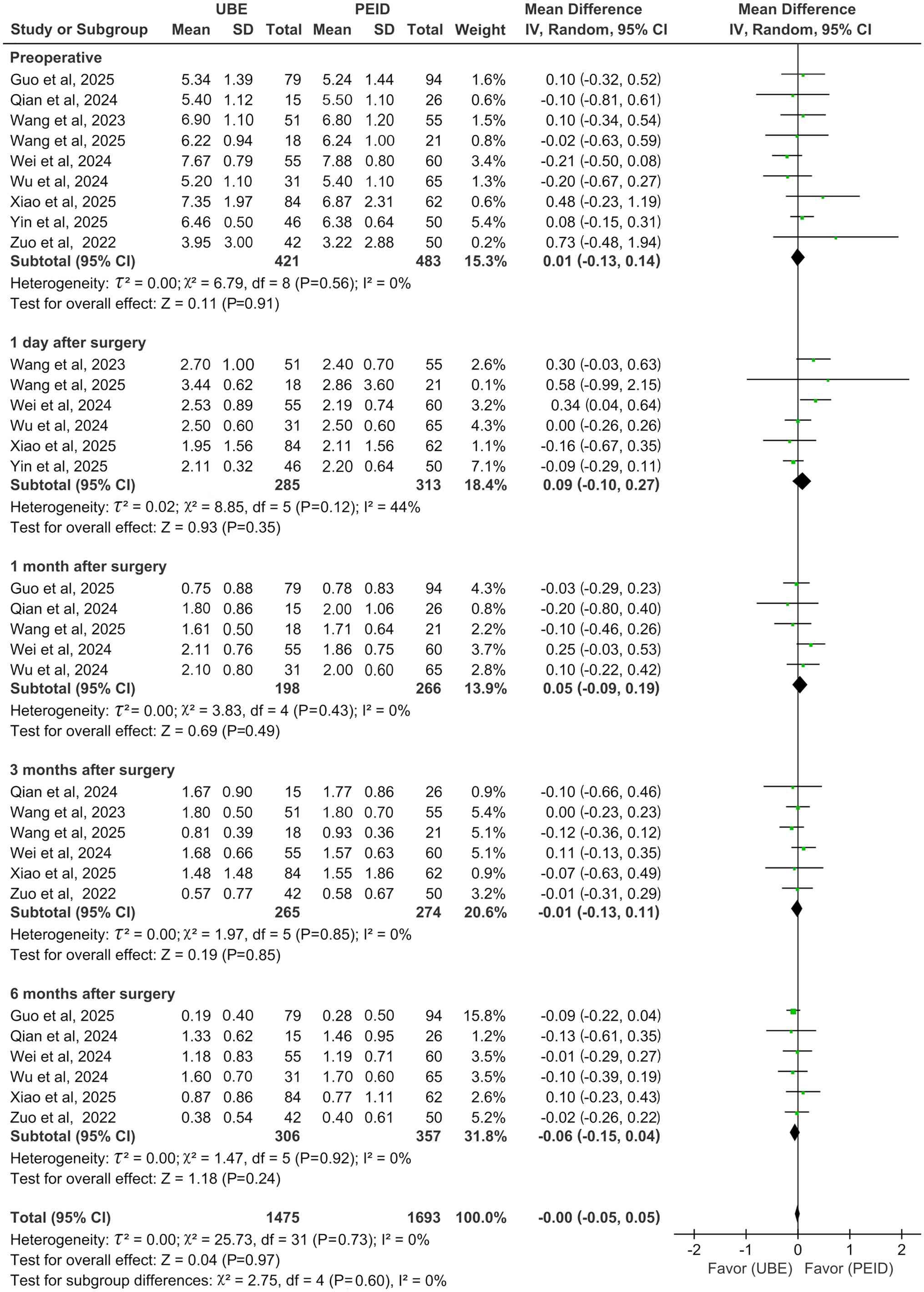
Meta-analysis results of functional outcomes.
Back VAS score showed no significant differences between UBE and
PEID at preoperative (MD=0.01; 95% CI: -0.13-0.14; P=0.91;
I2=0%) and postoperative day 1 (MD=0.09; 95% CI:
-0.10-0.27; P=0.35; I2=44%) and month 1 (MD=0.05; 95%
CI: -0.09-0.19; P=0.49; I2=0%), 3 (MD=-0.01; 95% CI:
-0.13-0.11; P=0.85; I2=0%) and 6 (MD=-0.06; 95% CI:
-0.15-0.04; P=0.24; I2=0%; Fig. 3), all analysed using a
random-effects model.
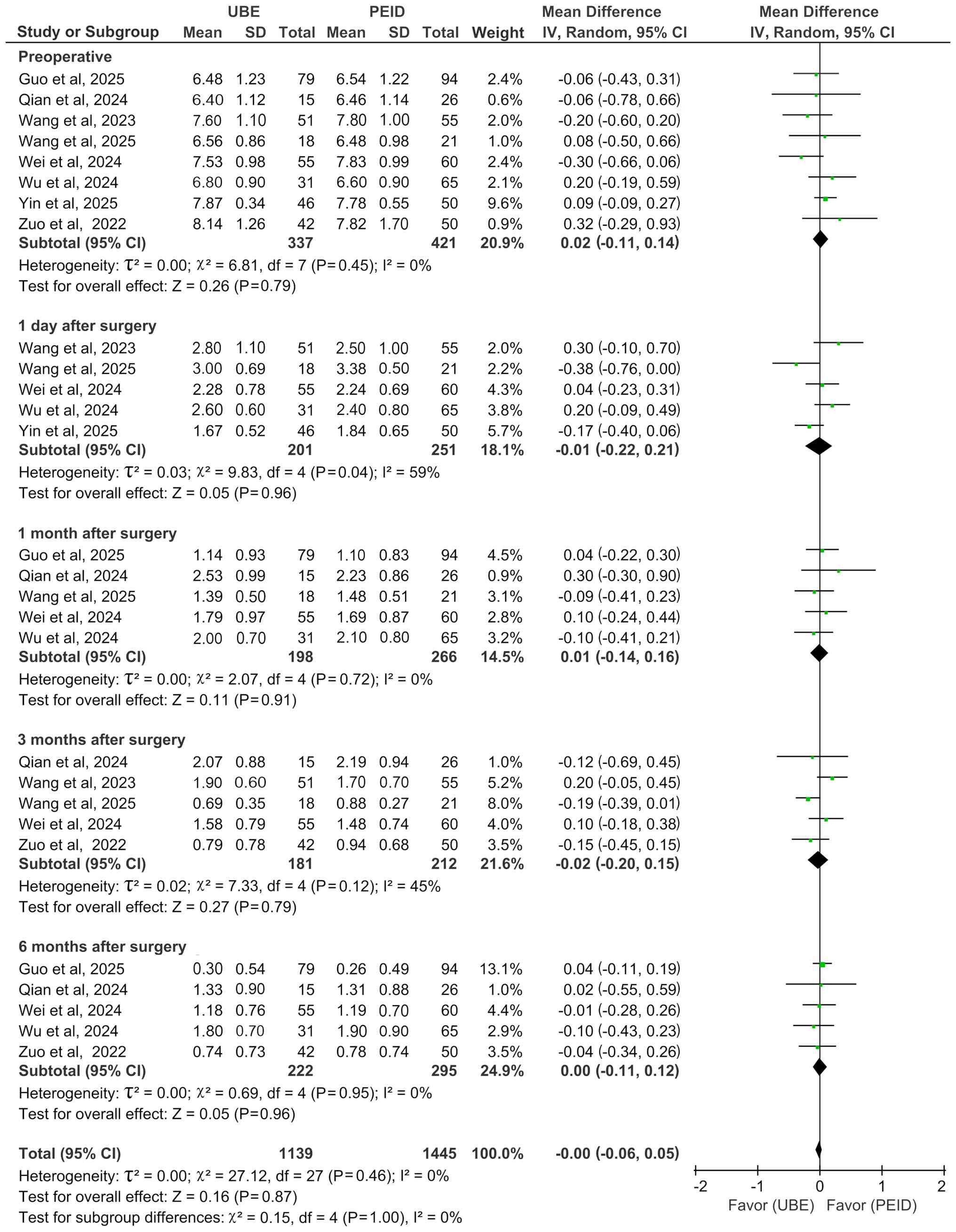
With regard to leg VAS score, no statistically
significant differences were observed between UBE and PEID at
preoperative (MD=0.02; 95% CI: -0.11-0.14; P=0.79;
I2=0%] and postoperative day 1 (MD=-0.01; 95% CI:
-0.22-0.21; P=0.96; I2=59%) and month 1 (MD=0.01; 95%
CI: -0.14-0.16; P=0.91; I2=0%), 3 (MD=-0.02; 95% CI:
-0.20-0.15; P=0.79; I2=45%) and 6 (MD=0.00; 95% CI:
-0.11-0.12; P=0.96; I2=0%; Fig. 4), with all analyses performed using
a random-effects model.
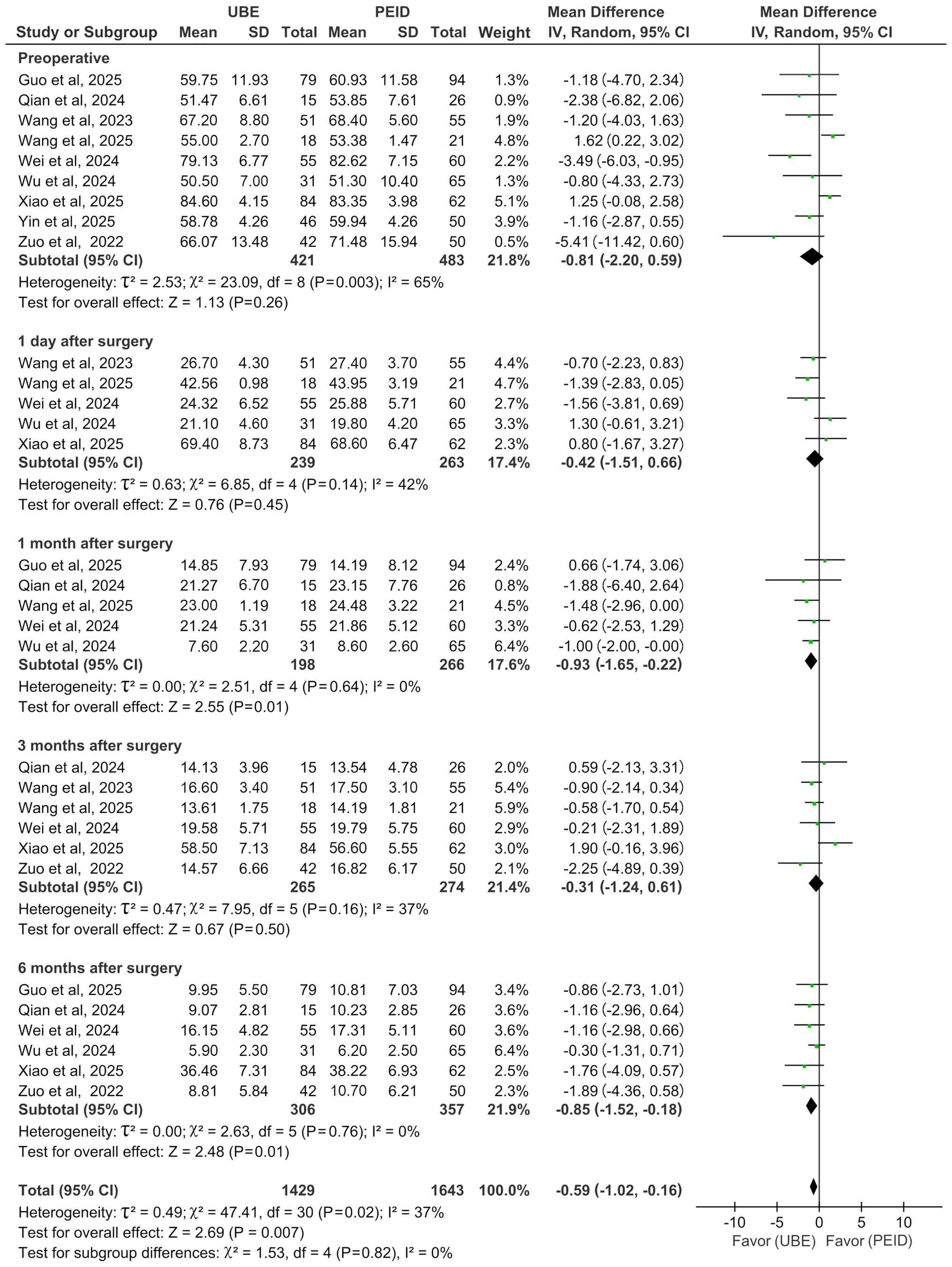
Preoperative ODI comparisons across nine studies
(17-21,23-26)
revealed no significant differences (MD=-0.81; 95% CI: -2.20-0.59;
P=0.26; I2=65%). Postoperative ODI analysis results were
as follows: Day 1 (17,18,23-25)
(MD=-0.42; 95% CI: -1.51-0.66; P=0.45; I2=42%) and month
1 (17,19,21,23,24)
(MD=-0.93; 95% CI: -1.65-0.22; P=0.01; I2=0%), 3
(17,18,21,23,25,26)
(MD=-0.31; 95% CI: -1.24-0.61; P=0.50; I2=37%) and 6
(18,19,21,23,24,26)
(MD=-0.85; 95% CI: -1.52-0.18; P=0.01; I2=0%; Fig. 5). UBE showed significant
superiority at 1 and 6 months (both P≤0.01) but not at
preoperative, postoperative day 1 or month 3. All analyses were
performed using a random-effects model (Fig. 5).
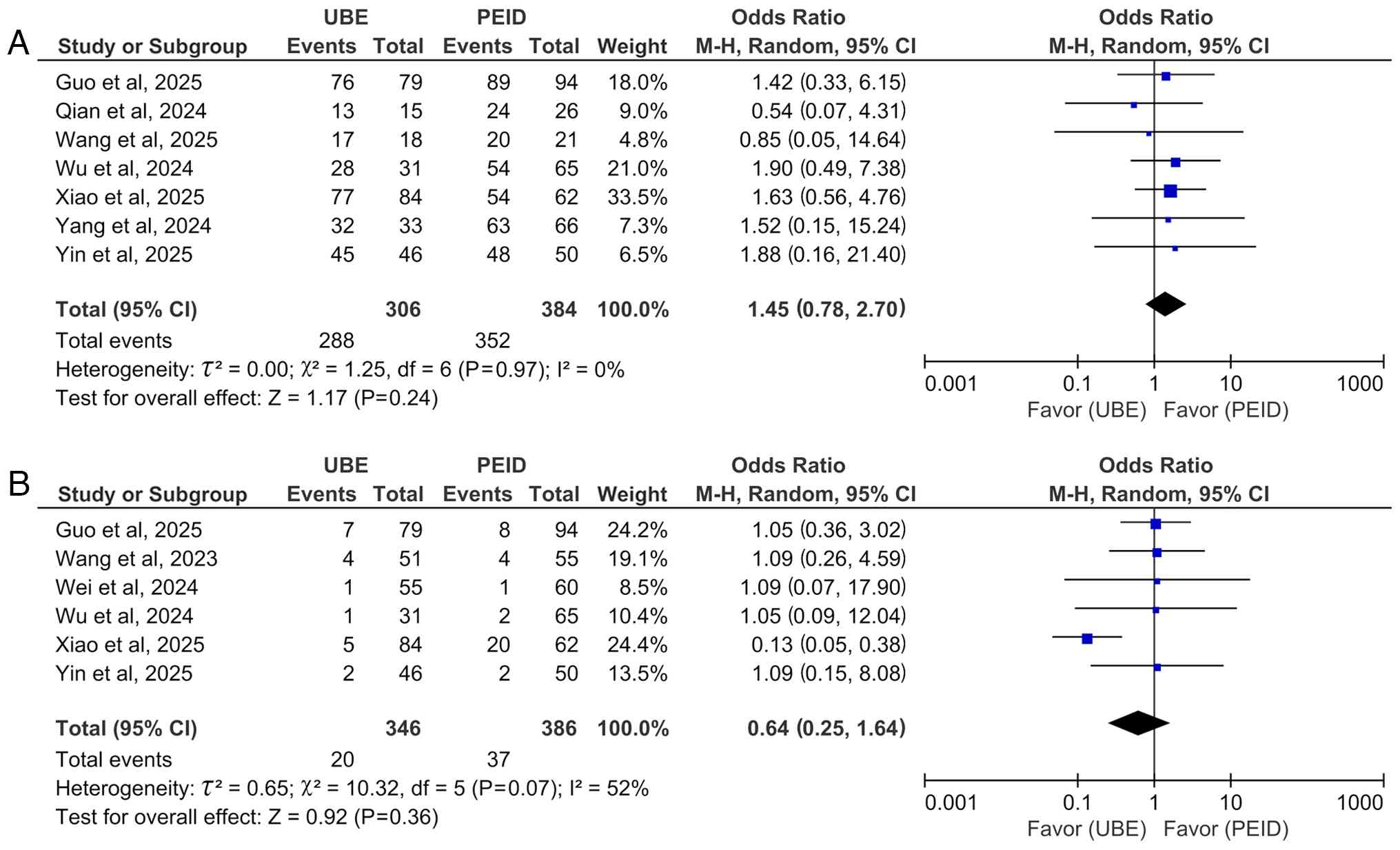
A total of seven studies (17-22,24)
comparing MacNab excellent/good rates showed no significant
difference between UBE and PEID groups (OR=1.45; 95% CI: 0.78-2.70;
P=0.24; I2=0%; Fig.
6A).
Meta-analysis of safety. A pooled analysis of
postoperative complications from six studies (18-20,23-25)
showed no significant difference between UBE and PEID (OR=0.64; 95%
CI: 0.25-1.64; P=0.36; I2=52%; Fig. 6B), using a random-effects
model.
Publication bias. Publication bias evaluation
for the nine primary outcomes including surgical efficiency
(operative time, blood loss, hospital stay and fluoroscopy
frequency), functional outcomes (MacNab excellent/good rate, back
and leg VAS and ODI) and safety (complications), was assessed using
funnel plots in RevMan 5.4. Visual inspection combined with Egger's
test (P>0.05 threshold) confirmed symmetrical funnel plots
across all outcomes (Fig. 7),
indicating no significant publication bias.
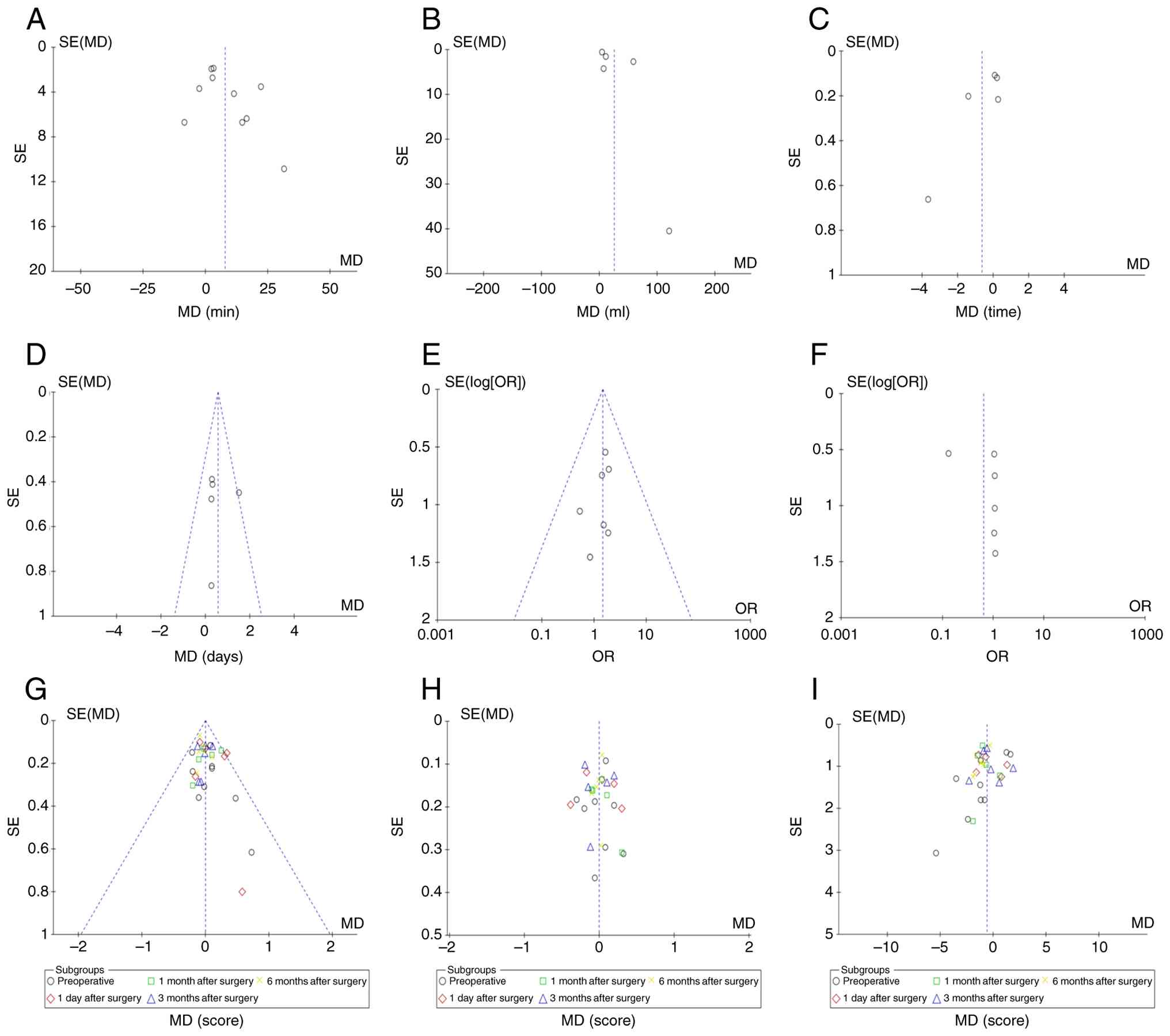 | Figure 7Funnel plots assessing publication
bias across (A) operative time, (B) blood loss, (C) fluoroscopy
frequency, (D) hospital stay, (E) MacNab excellent/good rate, (F)
complications, (G) back VAS score, (H) leg VAS score and (I) ODI
score outcomes. SE, standard error; MD, mean difference; OR, odds
ratio; VAS, Visual Analog Scale; ODI, Oswestry Disability
Index. |
Sensitivity and subgroup analyses. Notable
heterogeneity (I2>50%) was identified for operative
time, blood loss and fluoroscopy frequency (Fig. 2). Sensitivity analyses, performed
by sequentially excluding each individual study, demonstrated that
the overall results and the substantial heterogeneity remained
largely unchanged (I² consistently >50%) (data not shown). This
indicates that the observed heterogeneity is robust and not driven
by any single outlier study. Instead, the sources of heterogeneity
are likely multifactorial, potentially stemming from variations in
surgical techniques, patient selection criteria, case complexity
and surgeon experience across the included studies.
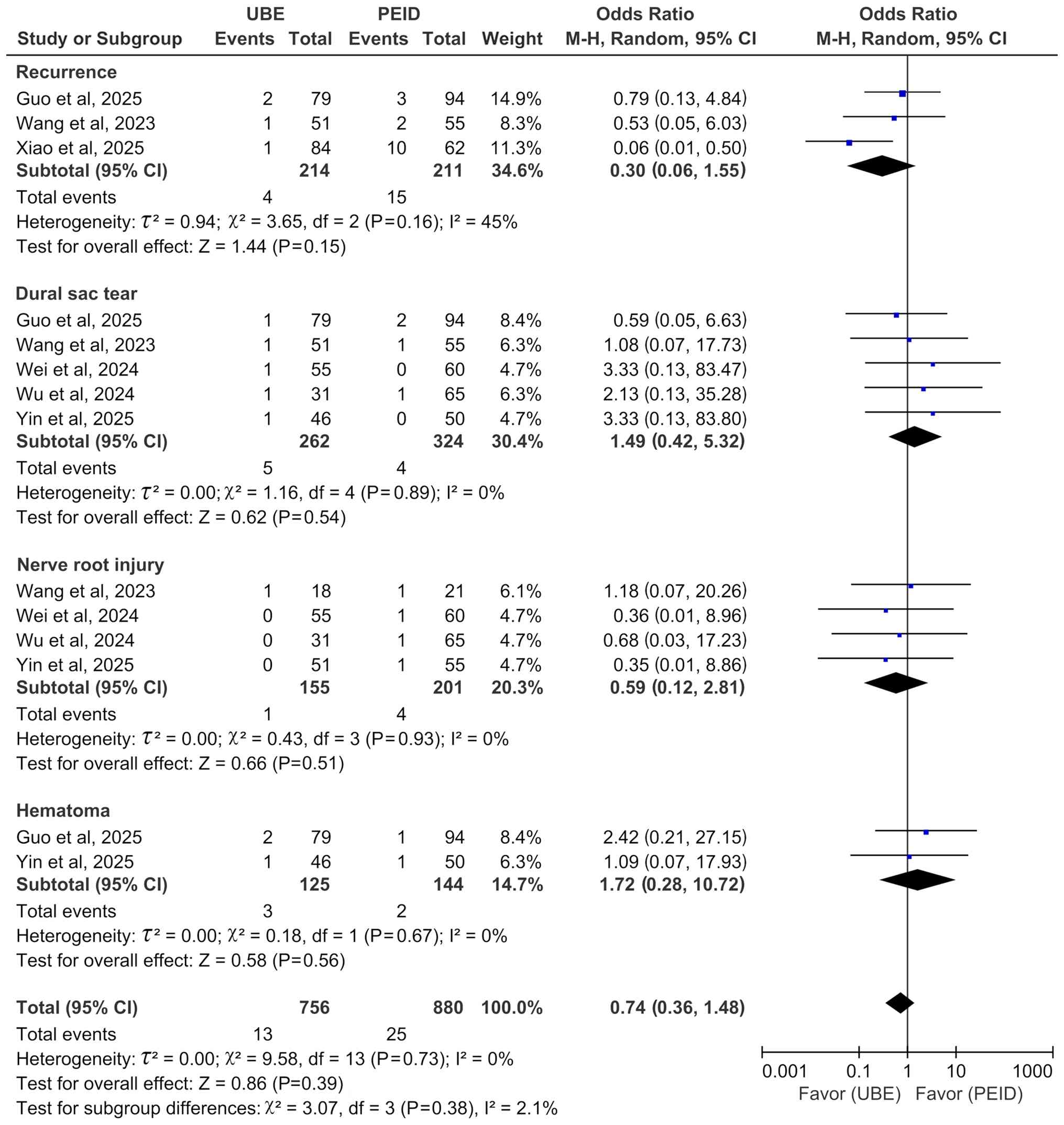
Subgroup analysis of complications was performed to
delineate the safety profiles of the two techniques beyond the
pooled overall rate. While the overall complication rates did not
differ significantly between UBE and PEID, the subgroup analysis
revealed distinct patterns. Notably, the recurrence subgroup
exhibited moderate heterogeneity (I²=45%), whereas heterogeneity
was negligible (I²=0%) in subgroups for dural tear, nerve root
injury and hematoma (Fig. 8).
For the recurrence outcome, subgroup analysis
revealed moderate heterogeneity (I²=45%). To investigate its
source, a sensitivity analysis was performed by sequentially
excluding each study. The exclusion of Xiao et al (18) eliminated the between-study
heterogeneity (I²=0%), identifying it as the primary source of
variance. This study (18)
reported an exceptionally high recurrence rate in the PEID group
(16.13%; 10/62) compared with that in the UBED group (1.19%; 1/84),
yielding an extreme effect size (OR, 0.06) that diverged markedly
from the other trials (Fig. 8).
This disparity was attributed to the technical and anatomical
limitations of the interlaminar PEID approach, particularly at the
L5-S1 level, such as a high iliac crest or a narrow interlaminar
space, which may restrict visual field and lead to incomplete
fragment removal. By contrast, the dual-portal design and wider
laminar exposure in UBED were described as enabling a broader
operative field and more complete decompression. Thus, the
sensitivity analysis confirms that the heterogeneity in recurrence
rates was largely driven by the distinct findings reported by Xiao
et al (18).
Discussion
Efficacy and safety of UBE and PEID in the treatment
of single-level LDH were compared using the interlaminar approach.
By focusing exclusively on this specific surgical corridor, the
present study offered a more precise comparison by minimizing
confounding variables associated with anatomical variations. The
main findings indicate a nuanced balance, whereby EID demonstrated
superior surgical efficiency, reflected by shorter operative time,
lower intraoperative blood loss and decreased hospital stay
durations. Conversely, UBE was associated with improved
intermediate-term functional recovery, evidenced by greater ODI
improvement at 1 and 6 months postoperatively. No significant
differences were found in pain relief (VAS score), MacNab
excellent/good rates or overall complication rates.
Observed advantages of PEID in operative time and
blood loss align with its minimally invasive, single-portal design,
which facilitates direct access and minimizes osseous disruption
(27). However, the notable
heterogeneity (I2>80%) in these outcomes warrants
cautious interpretation. Sensitivity analyses indicated that the
heterogeneity was not random but primarily driven by specific
studies (17-26),
suggesting both clinical and methodological variability. This
variability may be attributable to two primary factors: Case
selection bias, as the more versatile UBE technique may be
preferentially used for complex cases (such as those involving
migrated fragments or spinal stenosis) that inherently require
longer operative times and involve more vascularized tissue
(28) and variations in surgeon
experience and learning curves among the included studies. The
technically demanding spatial orientation required for PEID and the
steep learning curve associated with UBE both affect procedural
efficiency (19,29). Therefore, although PEID exhibits
higher efficiency in controlled analyses, the notable heterogeneity
indicates that real-world outcomes are influenced by
patient-specific characteristics and surgeon proficiency.
Consequently, the efficiency differences may partially reflect
variations in clinical application rather than inherent procedural
superiority.
Comparable VAS scores demonstrated that both
techniques are highly effective in relieving pain. The key finding,
however, is the sustained superiority of UBE in ODI improvement. As
the ODI represents a multifactorial index reflecting ability to
perform daily activities, this outcome suggests that UBE may
promote a more favorable quality of functional recovery. This
advantage may be attributed to the biportal configuration of the
UBE technique (30). The
separation of the endoscope from the surgical instruments provides
a panoramic, fluid-maintained visual field. Enhanced visualization,
together with the capacity for bimanual instrument triangulation,
enables meticulous dissection of herniated fragments and adhesions
and facilitates more comprehensive decompression of neural
structures, particularly in cases with concomitant pathological
changes such as ligamentum flavum hypertrophy or lateral recess
stenosis (31). Such complete
decompression may contribute to improved medium-term functional
restoration. By contrast, the single-channel design of PEID,
although minimally invasive, restricts instrument maneuverability
and limits the ability to adequately address coexisting pathology,
thereby increasing the likelihood of residual compression that may
hinder postoperative functional recovery (32,33).
Although the overall complication rates did not
differ significantly between UBE and PEID, the specific patterns of
complications and recurrence rates varied notably, reflecting their
technical characteristics.
The higher recurrence rate associated with PEID in
one study may be explained by anatomical and procedural factors
(18). At the L5-S1 level,
constraints such as a high iliac crest and a narrow interlaminar
window may restrict the working angle and motion range of the
single portal (34). These
limitations may impede the ability of the surgeon to adequately
access and remove migrated or sequestered disc fragments located
ventrally to the thecal sac or nerve root, thereby increasing the
likelihood of residual fragments and subsequent recurrence
(35). By contrast, the
configuration and broader operative field of the UBE dual-port
mitigate these constraints, enabling more extensive visualization
and thorough decompression (36).
Conversely, UBE exhibits a distinct risk profile,
primarily involving dural tears and epidural hematoma (37,38).
The use of multiple instruments, such as burrs and rongeurs, within
a confined space under continuous irrigation heightens the risk of
inadvertent dural injury (39,40).
Moreover, the greater degree of soft tissue dissection and bone
removal creates a larger potential dead space, predisposing
patients to postoperative epidural hematoma formation (41,42).
By contrast, the primary procedure-specific complications of PEID
include iatrogenic nerve root injury and dural tears, typically
occurring during working cannula insertion, instrument manipulation
or contact within the limited endoscopic field of view (43,44).
Selection between UBE and PEID should be
individualized based on a comprehensive evaluation of patient
anatomy, pathology and surgeon expertise (22,23).
PEID, utilizing a single-portal system, is optimally indicated for
contained central or paracentral disc herniations at the L5-S1
level (45). This approach
leverages the relatively larger anatomical interlaminar window at
this level, facilitating direct access with minimal tissue
disruption (46). Consequently,
PEID is typically associated with accelerated postoperative
recovery, making it a favorable option for patients seeking a rapid
return to daily activity (47).
By contrast, UBE, characterized by separate
endoscopic and instrumental channels, provides a panoramic field of
view and triangulated bimanual maneuverability (48). These technical advantages make it
suited for managing complex pathologies, including foraminal or
extraforaminal herniation, highly migrated disc fragments and cases
complicated by notable central or lateral recess stenosis (49). Furthermore, UBE is advantageous at
higher lumbar levels (L1-L4), where the narrower interlaminar space
poses a challenge for single-portal techniques (50). From a surgical ergonomics
perspective, the operational principles of UBE resemble those of
conventional microdiscectomy, which may flatten the learning curve
for surgeons transitioning from open procedures to endoscopic spine
surgery (30,36).
Within the present meta-analysis, several
limitations must be noted. i) All included studies were
retrospective cohorts, which inherently carry selection bias. The
notable variation in follow-up duration (range, 3-24 months)
limited long-term outcome evaluation. Inadequate reporting of disc
herniation subtypes (such as protrusion and extrusion) in the
primary studies precluded stratified subgroup analyses by pathology
severity. The relatively small number of studies/outcome metric
(4-10 studies) may have increased methodological heterogeneity.
Inclusion of only English language publications introduced
potential language bias and omission of parameters such as hidden
blood loss may have led to underestimation of total procedural
trauma. Consequently, these limitations may restrict the
generalizability of the findings to broader clinical settings.
Future validation should involve large-scale, multicenter,
prospective randomized controlled trials with standardized outcome
assessment protocols to demonstrate long-term efficacy and
safety.
In conclusion, the present meta-analysis
demonstrated that, for the treatment of single-level lumbar disc
herniation using the interlaminar approach, PEID is associated with
greater surgical efficiency, characterized by shorter operative
time, decreased intraoperative blood loss and shorter hospital
stay. Conversely, UBE provides improved intermediate-term
functional recovery, evidenced by markedly improved ODI scores at
1- and 6-month follow-ups. The notable heterogeneity in
efficiency-related outcomes highlights the influence of case
selection and surgeon proficiency. Therefore, the choice between
techniques should be individualized. PEID is most appropriate for
less complex cases in which rapid recovery is a clinical priority,
whereas UBE is preferable for complex scenarios requiring extensive
decompression. Ultimately, surgical decision-making should be
guided by the specific pathological features of the patient,
familiarity with the technique and the available institutional
resources.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding: The present study was supported by the Hospital-level
Scientific Research Fund of Changzhi Key Laboratory of
Biomechanical Research and Application of Spinal Degenerative
Diseases (grant no. 2022-008). This study was also facilitated by
the research platform of the Changzhi Key Laboratory of
Biomechanical Research and Application of Spinal Degenerative
Diseases.
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study are included
in the figures and/or tables of this article.
Authors' contributions
YG and FH conceived and designed the study. FH, JW
and SQ performed the literature search, data extraction and
meta-analysis. PH and YX conducted the statistical analysis and
interpreted the data. PH and YX drafted the manuscript. All authors
critically reviewed and revised the manuscript for important
intellectual content. All authors have read and approved the final
version of the manuscript. YG and FH confirm the authenticity of
all the raw data.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Dieleman JL, Cao J, Chapin A, Chen C, Li
Z, Liu A, Horst C, Kaldjian A, Matyasz T, Scott KW, et al: US
Health Care Spending by Payer and Health Condition, 1996-2016.
JAMA. 323:863–884. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Benzakour T, Igoumenou V, Mavrogenis AF
and Benzakour A: Current concepts for lumbar disc herniation. Int
Orthop. 43:841–851. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Martin BI, Deyo RA, Mirza SK, Turner JA,
Comstock BA, Hollingworth W and Sullivan SD: Expenditures and
health status among adults with back and neck problems. JAMA.
299:656–664. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kwon H and Park JY: The role and future of
endoscopic spine surgery: A narrative review. Neurospine. 20:43–55.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Penchev P, Ilyov IG, Todorov T, Petrov PP
and Traykov P: Comprehensive analysis of treatment approaches for
lumbar disc herniation: A systematic review. Cureus.
16(e67899)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kambin P and Sampson S: Posterolateral
percutaneous suction-excision of herniated lumbar intervertebral
discs. Report of interim results. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 207:37–43.
1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sakti YM, Khadafi RN, Tarsan AK, Putro AC,
Sakadewa GP, Susanto DB and Sukotjo KK: Transforaminal endoscopic
lumbar discectomy for L5-S1 disc herniation: A case series. Int J
Surg Case Rep. 83(105967)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Chen J, Jing X, Li C, Jiang Y, Cheng S and
Ma J: Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy for L5S1 lumbar
disc herniation using a transforaminal approach versus an
interlaminar approach: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World
Neurosurg. 116:412–420.e2. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Chen KT, Tseng C, Sun LW, Chang KS and
Chen CM: Technical considerations of interlaminar approach for
lumbar disc herniation. World Neurosurg. 145:612–620.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
He Y, Wang H, Yu Z, Yin J, Jiang Y and
Zhou D: Unilateral biportal endoscopic versus uniportal
full-endoscopic for lumbar degenerative disease: A meta-analysis. J
Orthop Sci. 29:49–58. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Burke SM, Safain MG, Kryzanski J and
Riesenburger RI: Nerve root anomalies: Implications for
transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion surgery and a review of the
Neidre and Macnab classification system. Neurosurg Focus.
35(E9)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Price DD, McGrath PA, Rafii A and
Buckingham B: The validation of visual analogue scales as ratio
scale measures for chronic and experimental pain. Pain. 17:45–56.
1983.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Fairbank JC and Pynsent PB: The oswestry
disability index. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 25:2940–2952; discussion
2952. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron
I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan
SE, et al: The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for
reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 372(n71)2021.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Cook DA and Reed DA: Appraising the
quality of medical education research methods: The medical
education research study quality instrument and the
newcastle-ottawa scale-education. Acad Med. 90:1067–1076.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Nasser M: New Standards for Systematic
Reviews Incorporate Population Health Sciences. Am J Public Health.
110:753–754. 2020.
|
|
17
|
Wang D, Yang J, Liu C, Lin W, Chen Y, Lei
S, Cheng P, Huang Y, Gu S, Lin Y, et al: Comparative analysis of
endoscopic discectomy for demanding lumbar disc herniation. Sci
Rep. 15(9098)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Xiao L, Zhou J, Zhong Q, Zhang X and Cao
X: Clinical comparison of percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar vs.
unilateral biportal endoscopic discectomy for lumbar disc
herniation: A retrospective study. Sci Rep.
15(15347)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Guo W, Guo S, Zhang X, Zhang W, Xia G and
Liao B: Comparative study of the learning curves for percutaneous
endoscopic interlaminar lumbar discectomy and unilateral biportal
endoscopy techniques. BMC Surg. 25(210)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yin J, Gao G, Chen S, Ma T and Nong L:
comparative study between unilateral biportal endoscopic discectomy
and percutaneous interlaminar endoscopic discectomy for the
treatment of L5/S1 disc herniation. World Neurosurg.
194(123526)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Qian J, Lv X, Luo Y, Liu Y and Jiang W:
Unilateral biportal endoscopic discectomy versus percutaneous
endoscopic lumbar discectomy in the treatment of lumbar disc
herniation linked with posterior ring apophysis separation: A
retrospective study. World Neurosurg. 193:957–963. 2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Yang YF, Yu JC, Zhu ZW, Li YW, Xiao Z, Zhi
CG, Xie Z, Kang YJ, Li J and Zhou B: Comparison of clinical
outcomes and cost-utility between unilateral biportal endoscopic
discectomy and percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar discectomy for
single-level lumbar disc herniation: A retrospective matched
controlled study. J Orthop Surg Res. 19(755)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wei WB, Dang SJ, Liu HZ, Duan DP and Wei
L: Unilateral biportal endoscopic discectomy versus percutaneous
endoscopic interlaminar discectomy for lumbar disc herniation. J
Pain Res. 17:1737–1744. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wu S, Zhong D, Zhao G, Liu Y and Wang Y:
Comparison of clinical outcomes between unilateral biportal
endoscopic discectomy and percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar
discectomy for migrated lumbar disc herniation at lower lumbar
spine: A retrospective controlled study. J Orthop Surg Res.
19(21)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wang L, Li C, Han K, Chen Y, Qi L and Liu
X: Comparison of clinical outcomes and muscle invasiveness between
unilateral biportal endoscopic discectomy and percutaneous
endoscopic interlaminar discectomy for lumbar disc herniation at
L5/S1 Level. Orthop Surg. 15:695–703. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zuo R, Jiang Y, Ma M, Yuan S, Li J, Liu C
and Zhang J: The clinical efficacy of biportal endoscopy is
comparable to that of uniportal endoscopy via the interlaminar
approach for the treatment of L5/S1 lumbar disc herniation. Front
Surg. 9(1014033)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wu TL, Yuan JH, Jia JY, He DW, Miao XX,
Deng JJ and Cheng XG: Percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar
discectomy via laminoplasty technique for L5 -S1 lumbar disc
herniation with a narrow interlaminar window. Orthop Surg.
13:825–832. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Feng F, Li G, Meng H, Chen H, Li X and Fei
Q: Clinical efficacy of unilateral biportal endoscopic technique
for adjacent segment pathology following lumbar fusion. J Orthop
Surg Res. 20(628)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Demirtaş OK and Özer Mİ: Unilateral
biportal endoscopic discectomy for lumbar disc herniation: Learning
curve analysis with CUSUM analysis and clinical outcomes. Clin
Neurol Neurosurg. 249(108755)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Yu Z, Ye C, Alhendi MA and Zhang H:
Unilateral biportal endoscopy for the treatment of lumbar disc
herniation. J Vis Exp. 15:2023.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kwon O, Yoo SJ and Park JY: Comparison of
unilateral biportal endoscopic discectomy with other surgical
technics: A systemic review of indications and outcomes of
unilateral biportal endoscopic discectomy from the current
literature. World Neurosurg. 168:349–358. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Fang N, Yan S and Yang A: Research
advances in unilateral endoscopic spinal surgery for the treatment
of lumbar disc herniation: A review. J Orthop Surg Res.
20(643)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Fukuhara D, Ono K, Kenji T and Majima T: A
narrative review of full-endoscopic lumbar discectomy using
interlaminar approach. World Neurosurg. 168:324–332.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Choi G, Lee SH, Raiturker PP, Lee S and
Chae YS: Percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar discectomy for
intracanalicular disc herniations at L5-S1 using a rigid working
channel endoscope. Neurosurgery. 58 (1 Suppl):ONS59–68; discussion
ONS59-68. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kim HS and Park JY: Comparative assessment
of different percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar lumbar discectomy
(PEID) techniques. Pain Physician. 16:359–367. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kim SK, Kang SS, Hong YH, Park SW and Lee
SC: Clinical comparison of unilateral biportal endoscopic technique
versus open microdiscectomy for single-level lumbar discectomy: A
multicenter, retrospective analysis. J Orthop Surg Res.
13(22)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Bai TY, Meng H, Lin JS, Fan ZH and Fei Q:
Application of intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring in
unilateral biportal endoscopic lumbar spine surgery. J Orthop Surg
Res. 20(334)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Lee SY, Shin DA, Yi S, Ha Y, Kim KN and
Lee CK: Overview and prevention of complications during biportal
endoscopic lumbar spine surgery. J Minim Invasive Spine Surg Tech.
8:145–152. 2023.
|
|
39
|
Deng C, Li X, Wu C, Xie W and Chen M:
One-hole split endoscopy versus unilateral biportal endoscopy for
lumbar degenerative disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis
of clinical outcomes and complications. J Orthop Surg Res.
20(187)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Matsukawa K, Fujiyoshi K, Kobayashi Y,
Kitagawa T and Yato Y: Delayed herniation of cauda equina root
through occult dural tear following unilateral biportal endoscopic
decompression: Illustrative case. J Neurosurg Case Lessons.
10(CASE25438)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Lou X, Chen P, Shen J, Chen J, Ge Y and Ji
W: Why does such a cyst appear after unilateral biportal endoscopy
surgery: A case report and literature review. Medicine (Baltimore).
102(e36665)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Xu J, Wang D, Liu J, Zhu C, Bao J, Gao W,
Zhang W and Pan H: Learning curve and complications of unilateral
biportal endoscopy: Cumulative sum and risk-adjusted cumulative sum
analysis. Neurospine. 19:792–804. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zhou C, Zhang G, Panchal RR, Ren X, Xiang
H, Xuexiao M, Chen X, Tongtong G, Hong W and Dixson AD: Unique
complications of percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy and
percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar discectomy. Pain physician.
21:E105–E112. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Xie TH, Zeng JC, Li ZH, Wang L, Nie HF,
Jiang HS, Song YM and Kong QQ: Complications of lumbar disc
herniation following full-endoscopic interlaminar lumbar
discectomy: A large, single-center, retrospective study. Pain
Physician. 20:E379–E387. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Pan M, Li Q, Li S, Mao H, Meng B, Zhou F
and Yang H: percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy: Indications
and complications. Pain Physician. 23:49–56. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li T, Yang G, Zhong W, Liu J, Ding Z and
Ding Y: Percutaneous endoscopic transforaminal vs. interlaminar
discectomy for L5-S1 lumbar disc herniation: A retrospective
propensity score matching study. J Orthop Surg Res.
19(64)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Liu W, Liu L, Pan Z and Gu E: Percutaneous
endoscopic interlaminar discectomy with patients' participation :
Better postoperative rehabilitation and satisfaction. J Orthop Surg
Res. 19(547)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Liu L, Zhang X and Kang N: Application
status and considerations of unilateral biportal endoscopy
technique. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 38:1510–1516.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
49
|
Reis JPG, Pinto EM, Teixeira A, Frada R,
Rodrigues D, Cunha R and Miranda A: Unilateral biportal endoscopy:
Review and detailed surgical approach to extraforaminal approach.
EFORT Open Rev. 10:151–155. 2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Shao R, Du W, Zhang W, Cheng W, Zhu C,
Liang J, Yue J and Pan H: Unilateral biportal endoscopy via two
different approaches for upper lumbar disc herniation: A technical
note. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 25(367)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|