Introduction
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a
life-threatening pulmonary disorder characterized by uncontrolled
inflammatory responses, diffuse alveolar damage and increased
pulmonary vascular permeability, leading to severe impairment of
gas exchange and potentially fatal respiratory failure (1). Despite significant advances in
supportive care, primarily involving lung-protective ventilation
strategies and refined fluid management, the mortality rate of ARDS
remains unacceptably high, ranging from 35 to 46% (2). The current therapeutic landscape
lacks effective pharmacological agents that directly target these
underlying pathological mechanisms, highlighting a critical unmet
need for novel therapeutic interventions (3).
In recent years, natural products derived from
medicinal plants have garnered significant attention as promising
sources for drug discovery due to their multi-target activities and
favorable safety profiles (4).
Carnosic acid (CA), a phenolic diterpene abundantly found in
rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis Linnaeus) and sage, has
been extensively documented for its potent anti-inflammatory,
antioxidant and antimicrobial properties (5). Previous studies have demonstrated
that CA can activate the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor
2 (Nrf2) pathway, a master regulator of cellular antioxidant
responses. Upon activation, Nrf2 translocates to the nucleus and
induces the expression of a battery of cytoprotective genes,
including heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), which collectively counteract
oxidative stress (6,7). Furthermore, evidence suggests that
Nrf2 activation can indirectly suppress the NLR family pyrin domain
containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome, a key component of innate
immunity whose hyperactivation drives pyroptosis, a highly
inflammatory form of programmed cell death, through
caspase-1-mediated cleavage of gasdermin D (GSDMD) and subsequent
release of IL-1β and IL-18 (8,9).
This Nrf2-NLRP3 axis has been implicated in various inflammatory
diseases but remains relatively unexplored in the context of
ARDS.
Given the central roles of oxidative stress and
NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis in the pathogenesis of ARDS
(10,11), we hypothesize that CA may confer
protective effects against this syndrome. However, a systematic
investigation into the therapeutic potential and precise molecular
mechanisms of CA in ARDS, particularly its potential to
simultaneously modulate the Nrf2 pathway and NLRP3-mediated
pyroptosis, is still lacking.
Therefore, the present study employed an integrative
approach combining network pharmacology prediction, molecular
docking, molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and experimental
verification to elucidate the protective mechanisms and therapeutic
benefits of CA against ARDS. The study aims to provide a solid
foundation for the further development of CA as a potential
therapeutic agent for ARDS.
Materials and methods
Network pharmacology analysis. Data
preparation
Potential targets for CA were predicted using the
SwissTargetPrediction database (http://www.swisstargetprediction.ch). ARDS-related
targets were identified using public databases, including the
GeneCards database (https://www.genecards.org/) and the DisGeNET database
(version 7.0; http://www.disgenet.org/). To identify relevant
targets, the search terms ‘ARDS’, ‘acute lung injury’, ‘acute
respiratory distress syndrome’, ‘adult respiratory distress
syndrome’ and ‘acute lung injury’ were used. In the GeneCards
database, target selection was carried out using the following
criteria: i) Ranking targets by their relevance score; ii)
retaining only those with a score >2 times the median value and
iii) identifying and presenting the common targets between CA and
ARDS using a Venn diagram.
Functional enrichment analysis. Metascape
(http://www.metascape.org) is an online tool for
functional annotation. This platform facilitates gene function
annotation analysis, empowering users to leverage contemporary,
prevalent bioinformatics methodologies in the examination of gene
and protein batches. By doing so, it enables the elucidation of
gene and protein functionalities (12). The tool was used to carry out a
functional enrichment analysis of the intersected target genes
using Gene Ontology (GO) (13) and
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analyses
(14). The GO analysis encompassed
three categories: i) Biological processes (BP); ii) molecular
functions (MF); and iii) cellular components (CC). The top 10 most
significantly enriched terms in both GO-BP and KEGG pathway
analyses were then visualized using the SRplot bioinformatics
platform (http://www.bioinformatics.com.cn/; last accessed on
April 1, 2025). P<0.05 was considered to indicate a
statistically significant difference.
Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network
construction. Overlapping targets were analyzed using Search
Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes/Proteins (STRING;
https://cn.string-db.org/; version 11.0) to
construct a PPI network. This network was constructed with a
specific focus on Homo sapiens and a high confidence score
of 0.950 to ensure the reliability of interactions. Following this,
the PPI network was visually rendered using Cytoscape software
(version 3.7.2) (15),
facilitating a comprehensive visualization and analysis of the
intricate protein interactions.
Molecular docking. Molecular docking has
emerged as a fundamental technique in modern drug discovery,
allowing researchers to predict binding affinities and molecular
interactions by analyzing the three-dimensional conformations of
protein-ligand complexes. In the present study, molecular docking
simulations were carried out between CA and its key target proteins
identified through the aforementioned analysis. The
three-dimensional structures of CA and the pivotal proteins were
sourced from PubChem (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) and the Research
Collaboratory for Structural Bioinformatics Protein Data Bank
database (http://www.rcsb.org/). All docking
procedures were executed using AutoDock Tools (version 1.5.6;
https://autodock.scripps.edu/), with
validation steps incorporated to verify the reliability of the
computational predictions. Analysis of molecular docking utilized
binding energy to assess protein-ligand interactions, with values
≤-5 kcal/mol indicating strong binding affinity (16). To assess structural alignment, root
mean square deviation (RMSD) calculations were employed. The RMSD
lower bound (RMSD l.b.) and the RMSD upper bound (RMSD u.b.) allow
the diversity of conformations in the molecular docking results,
and the deviation range from the target conformation to be
understood. This is useful for evaluating the reliability and
accuracy of the docking results. Generally, the smaller the RMSD
l.b., the more similar the conformation obtained from the docking
is to the target conformation, and the more reliable the docking
result is. Conversely, the RMSD u.b. can assist in determining
whether the docking algorithm is capable of searching a
sufficiently wide enough conformational space. To facilitate a
deeper understanding of the docking results, the molecular docking
patterns were visually represented using PyMOL software (version
2.4; https://www.pymol.com/pymol.html),
allowing for a detailed examination of the interactions at a
molecular level.
MD. Groningen Machine for Chemical
Simulations (GROMACS; version 2022.4; http://www.gromacs.org) was used to carry out MD
simulations, which were all executed under isothermal-isobaric
ensemble conditions simulating a system with a constant number of
particles, temperature and pressure (NPT) with periodic boundary
constraints. The linear constraint solver algorithm constrained
hydrogen bonds with a 2 fsec integration time step. Electrostatic
energy (ELE) interactions were calculated using the particle-mesh
Ewald method, with a 1.2-nm cutoff (17), while van der Waals (VDW)
interactions employed a 10 Å cutoff distance, updated every 10
steps. Temperature (298 K) and pressure (1 bar) were maintained
using the V-rescale thermostat and Berendsen barostat algorithms,
respectively (18). The system
underwent sequential equilibration under the protocol of 100 ps
(constant number of particles, volume and temperature) followed by
100 ps NPT, before a 100 ns production run, with trajectories saved
every 10 ps. Post-simulation analyses included trajectory
visualization using Visual Molecular Dynamics (https://www.ks.uiuc.edu/Research/vmd/)
and PyMOL, along with binding free energy calculations using the
GROMACS package ‘g_mmpbsa’ (19).
Key evaluation metrics comprised: i) System stability parameters
(RMSD of complex protein and ligand; radius of gyration of complex;
root mean square fluctuation of protein residues); ii) interaction
characteristics (binding site distance, buried solvent-accessible
surface area, VDW/ELE energies, hydrogen bond dynamics and
per-residue energy contributions); and iii) structural features
(conformational superposition and interaction fingerprints). This
comprehensive analysis protocol ensured rigorous assessment of the
protein-ligand complex dynamics.
Experimental design. Reagents and
antibodies
Most of the reagents and antibodies used in the
present study are shown in Table
I.
 | Table IReagents and antibodies. |
Table I
Reagents and antibodies.
| Name | Catalogue
number | Manufacturer |
|---|
| CA | B21175 | Shanghai Yuanye
Biotechnology Co., Ltd. |
| LPS (0111:B4) | L4391 | Sigma Aldrich;
Merck KGaA |
| ML385 | HY-100523 | MEDCHEMEXPRESS
LLC |
| DMEM | 12100 | Beijing Solarbio
Science & Technology Co., Ltd. |
| RIPA Buffer | R0010 | Beijing Solarbio
Science & Technology Co., Ltd. |
| ATP | A9310 | Beijing Solarbio
Science & Technology Co., Ltd. |
| NLRP3 antibody | 15101 | Cell Signaling
Technology, Inc. |
| ASC antibody | 67824 | Cell Signaling
Technology, Inc. |
| CASP1 antibody | 24232 | Cell Signaling
Technology, Inc. |
| GSDMD antibody | 39754 | Cell Signaling
Technology, Inc. |
| Nrf2 antibody | 12721 | Cell Signaling
Technology, Inc. |
| HO-1 antibody | 43966 | Cell Signaling
Technology, Inc. |
| GAPDH antibody | 2118 | Cell Signaling
Technology, Inc. |
| Secondary
antibody | 7074 | Cell Signaling
Technology, Inc. |
| Fluorescent
secondary antibody | 8889 | Cell Signaling
Technology, Inc. |
| IL-1β ELISA | E-EL-R0012c | Wuhan Elabscience
Biotechnology Co., Ltd. |
| IL-18 ELISA | SEA064Ra | Wuhan Elabscience
Biotechnology Co., Ltd. |
| MDA assay kit | A003-1-2 | Nanjing Jiancheng
Bioengineering Institute |
| MPO assay kit | A044-1-1 | Nanjing Jiancheng
Bioengineering Institute |
| SOD assay kit | A001-3-2 | Nanjing Jiancheng
Bioengineering Institute |
| LDH assay kit | C0016 | Beyotime
Biotechnology |
| Annexin
V-FITC/PI | APOAF | Sigma Aldrich;
Merck KGaA |
| DCFH-DA | S0033 | Beyotime
Biotechnology |
| Goat serum | C0265 | Beyotime
Biotechnology |
| BCA | PC0020 | Beijing Solarbio
Science & Technology Co., Ltd. |
| CCK-8 | C0037 | Beyotime
Biotechnology |
| RT-qPCR kit | D7268S | Beyotime
Biotechnology |
Animals and treatments. Male BALB/c mice
(n=48; age, 8 weeks; weight, 21-25 g), were obtained from the Model
Animal Research Center of Nanjing University. Mice were housed in a
standard laboratory environment maintained at a temperature range
of 20-26˚C, with a relative humidity of 40-70% and a 12-h
light/dark cycle. The mice were allowed to feed and drink ad
libitum throughout the present study. All animal experiments
were approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of Medical
School of Nanjing University Affiliated Jinling Hospital (Nanjing,
China; approval no. 2022DZGKJDWLS-00161) and complied with the
Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (https://olaw.nih.gov/policies-laws/guide-care-use-lab-animals).
The ARDS model was established through
intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS; 10
mg/kg), a well-established method documented in previous studies
(20,21). Mice were randomly allocated into
the following four experimental groups (n=6/group): i) Control
group (PBS; i.p.); ii) LPS group (10 mg/kg; i.p.); iii) CA group
(40 mg/kg; i.p.); and iv) ML385 group (40 mg/kg CA + 30 mg/kg
ML385; i.p.). All animals were anesthetized with 1% sodium
pentobarbital (40 mg/kg; i.p.) before administration. A total of 30
min post-LPS injection, treatment groups received either CA
(dissolved in 0.5% DMSO) or the combination of ML385 [nuclear
factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) inhibitor; dissolved in
0.5% DMSO; 30 mg/kg, i.p.] (22)
followed by CA, while controls received equivalent volumes of PBS.
Survival rates were recorded every 24 h for a 7-day observation
period following the LPS challenge. Animal deaths were checked for
twice daily (morning and evening) using a combination of criteria:
i) The absence of spontaneous movement for >5 min of
observation; ii) the lack of a response to gentle tactile stimuli
(e.g., a soft touch with a clean gloved finger); and iii) the
absence of visible respiration and signs of a heartbeat. For mice
reaching the predefined moribund state (severe lethargy, inability
to rise, dyspnea, etc.), euthanasia was performed promptly with an
overdose of sodium pentobarbital (100 mg/kg, i.p.), and the time of
euthanasia was recorded as the time of death for survival analysis.
Upon confirmation of death, a necropsy was immediately performed.
The thoracic cavity was exposed, and the lung tissues were
carefully excised en bloc. Subsequently, the lungs were perfused
via the trachea with ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) to
clear residual blood. After blotting the surface liquid with filter
paper, the tissues were processed according to downstream
experimental needs: The left lung lobe was fixed in 4%
paraformaldehyde at 4˚C for 24 h for histological analysis, while
the right lung lobe was snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen and then
transferred to a -80˚C freezer for storage, and reserved for
subsequent protein or RNA extraction. All tissue samples were
maintained at -80˚C until use.
Following euthanasia, 0.6-0.8 ml left ventricular
blood was immediately collected for blood gas analysis testing of
arterial oxygen partial pressure (PaO2) levels and
arterial carbon dioxide partial pressure (PaCO2),
FiO2 was measured during sampling using an oxygen
monitor. The PaO2/FiO2 ratio was then
calculated as PaO2 (mmHg) divided by FiO2.
Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) was obtained by carrying out
three cycles of instillation and withdrawal with 1-ml sterile PBS
through a tracheal cannula. The BALF samples were centrifuged at
1,500 x g for 15 min at 4˚C and the resulting supernatant was
aliquoted and stored at -80˚C for subsequent cytokine analysis. For
histological examination, the left lung lobes were perfused with
PBS and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at 4˚C for 24 h before
paraffin embedding. Tissue sections (4-µm thick) were prepared and
stained with H&E using standard protocols (hematoxylin: 0.1%,
5-8 min, room temperature; eosin: 0.5%, 1-3 min, room temperature).
Lung pathology was examined under a light microscope (Olympus BX53)
by an observer blinded to the groupings. Lung injury scores were
graded using the following scale: 0, no injury; 2, mild injury (up
to 25% injury of the field of view); 4, moderate injury (up to 50%
injury of the field of view); 6, severe injury (up to 75% injury of
the field of view); and 8, extremely severe injury (diffused
injury) (10). The upper right
lung lobes were excised and weighed to determine the wet/dry (W/D)
ratio by comparing fresh weight to weight after 72 h of desiccation
at 60˚C. Remaining lung tissues were quickly frozen in liquid
nitrogen and maintained at -80˚C for future protein
semi-quantification through ELISA and western blotting. This
comprehensive sample collection and processing protocol enabled
systematic evaluation of physiological parameters,
histopathological changes, and molecular markers through techniques
including ELISA, western blotting, RT-qPCR, and immunohistochemical
(IHC) analysis using commercial assay kits, thereby providing a
multi-faceted assessment of the ARDS model.
In the survival study (n=9 per group), mice received
the following treatments: The ARDS model was induced by a single
i.p. injection of LPS (10 mg/kg). After 30 min, the CA group
received CA (40 mg/kg, i.p.), while the CA + ML385 group received
ML385 (30 mg/kg, i.p.) followed by CA (40 mg/kg, i.p.), as
previously described (23).
Survival rates were recorded every 24 h for a 7-day observation
period following LPS challenge and euthanized at the moribund
stage. The humane endpoints were defined as the occurrence of
moribund animal characteristics in the mice, such as severe or
persistent lethargy, inability to rise from a recumbent position,
convulsions, tetraplegia and dyspnea (24,25).
Mortality was assessed through twice-daily monitoring (morning and
evening) to ensure accurate determination of survival time
points.
Cell culture. MH-S cells (murine alveolar
macrophage cells) were obtained from The Cell Bank of Type Culture
Collection of The Chinese Academy of Sciences. Cells were
maintained in a culture medium consisting of DMEM, supplemented
with 10% FBS and 1% penicillin and streptomycin. The cells were
incubated at 37˚C in an environment containing 5% CO2.
Following the respective treatments, cell culture supernatants were
collected for subsequent analysis by centrifugation of the culture
medium at 1,000 x g for 5 min at 4˚C to remove cellular debris.
For in vitro investigations, MH-S cells were
systematically allocated into the following four groups: i) Control
group; ii) LPS/ATP group; iii) CA-10 group; and iv) CA-20 group.
MH-S cells in the LPS/ATP, CA-10 and CA-20 groups were initially
exposed to LPS (1 µg/ml) for 4 h at 37˚C, followed by ATP
stimulation (5 mM) for 30 min at 37˚C (26). Subsequently, the CA-10 and CA-20
groups received either 10 or 20 µM CA and were further incubated
for 48 h at 37˚C, whereas the control groups received equivalent
volumes of culture medium.
Cell viability assay. A Cell Counting Kit-8
(CCK-8) assay was used to assess cell viability according to the
instructions of the manufacturer. MH-S cells were plated in 96-well
plates at a concentration of 5x103 cells/well and left
to adhere for 24 h under standard culture conditions. The cells
were then exposed to CA (0, 0.1, 1, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30 and 35 µM)
for 48 h at 37˚C. After treatment, each well received 10 µl CCK-8
solution (5 mg/ml) and the plates were incubated for 1 h at 37˚C in
an environment with 5% CO2. Absorbance was read at 450
nm with the model 680 microplate reader (Bio-Rad Laboratories,
Inc.).
Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
analysis. In accordance with a previous study (23), total RNA was extracted from lung
tissues and cultured cells using TRIzol® reagent
(Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.), strictly adhering to
the guidelines of the manufacturer. Subsequently, cDNA synthesis
was performed using the RT Kit (Vazyme Biotech Co., Ltd.) according
to the manufacturer's protocol. The qPCR amplification was then
conducted on the SmartCycler® II system (Cepheid) using the
following thermocycling conditions: Initial denaturation at 95˚C
for 30 sec, followed by 40 cycles of denaturation at 95˚C for 10
sec and annealing/extension at 60˚C for 30 sec. A melting curve
analysis was performed immediately after amplification to verify
the specificity of the PCR products. GAPDH as the endogenous
control. Relative gene expression levels were calculated using the
2-ΔΔCq method (27).
The specificity of the PCR amplification was confirmed by a single
peak in the melting curve analysis. The primer sequences used are
listed in Table II.
 | Table IIPrimer sequences. |
Table II
Primer sequences.
| Gene | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
|---|
| NLRP3 |
5'-GCTGCGATCAACAGGCGAGAC-3' |
5'-AAGGCTGTCCTCCTGGCATACC-3' |
| ASC |
5'-AACCCAAGCAAGATGCGGAAG-3' |
5'-TTAGGGCCTGGAGGAGCAAG-3' |
| CASP1 |
5'-ACAACCACTCGTACACGTCTTGC-3' |
5'-CCAGATCCTCCAGCAGCAACTTC-3' |
| GSDMD |
5'-ACTGAGGTCCACAGCCAAGAGG-3' |
5'-GCCACTCGGAATGCCAGGATG-3' |
| Nrf2 |
5'-TCTCCTCGCTGGAAAAAGAA-3' |
5'-AATGTGCTGGCTGTGCTTTA-3' |
| HO-1 |
5'-CAAGCCGAGAATGCTGAGTTCATG-3' |
5'-GCAAGGGATGATTTCCTGCCAG-3' |
| GAPDH |
5'-GCACCGTCAAGGCTGAGAAC-3' |
5'-TGGTGAAGACGCCAGTGGA-3' |
Western blotting. Protein lysates were
prepared from both treated MH-S cells and mouse lung tissues using
RIPA buffer supplemented with protease and phosphatase inhibitors.
Protein concentrations were evaluated through the BCA assay kit,
according to the manufacturer's protocol. Prior to electrophoresis,
protein samples were mixed with 5X Laemmli sample buffer containing
5% β-mercaptoethanol (or 100 mM DTT) as a reducing agent and
denatured by boiling at 95-100˚C for 5-10 min. For western
blotting, protein lysates were adjusted to a concentration of 0.75
µg/µl for lung tissues or 1.0 µg/µl for MH-S cells using RIPA
buffer. A total of 15 µg protein/lane was loaded for all samples,
corresponding to 20 µl for lung tissues and 15 µl for cell lysates.
Proteins were then separated by SDS-PAGE on 8-12% gels (depending
on target protein size) under reducing conditions. The resolved
proteins were then electrophoretically transferred onto PVDF
membranes (0.45-µm pore size; MilliporeSigma) using a semi-dry
transfer system.
Each target protein and its loading control, GAPDH,
were ultimately detected on the same physical membrane to ensure
direct comparability. This was achieved through sequential
detection (stripping and re-probing) on a single membrane: For
analysis of the inflammasome pathway, the membrane was first probed
for NLRP3, ASC, and caspase-1 (p20). After imaging, the antibodies
were stripped, and the same membrane was then re-probed for GAPDH.
For analysis of GSDMD cleavage, the membrane was first probed for
GSDMD-FL and GSDMD-N. After imaging, the antibodies were stripped,
and the same membrane was then re-probed for GAPDH. Electrophoresis
conditions were optimized to ensure sufficient separation between
the GAPDH (~36 kDa) and GSDMD-N (30-35 kDa) bands prior to
stripping and re-probing, allowing for accurate post hoc alignment
and densitometric analysis.
Following transfer, all membranes were stained with
Ponceau S to confirm uniform protein loading and transfer
efficiency. The membranes were then blocked with 5% skimmed milk in
Tris-buffered saline containing 0.1% Tween-20 (TBST) at 4˚C
overnight (or for 1 h at room temperature if applicable). After
washing three times with TBST (10 min each), the membranes were
incubated with corresponding HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies
diluted in 5% skimmed milk/TBST for 1 h at room temperature.
Immunoreactive bands were detected using the Enhanced ECL Kit (cat.
no. P0018; Beyotime Biotechnology) according to the manufacturer's
instructions, and visualized using a Tanon-5200 Imaging System
(Tanon Science & Technology Co., Ltd.). Between probing cycles,
the membranes were stripped using a mild stripping buffer. Complete
removal of previous antibodies was verified by incubating the
membrane with ECL substrate and confirming the absence of signal
prior to the next round of antibody incubation. Densitometric
analysis of the bands was performed using ImageJ software (V1.37;
National Institutes of Health). The signal intensity of each target
protein was normalized to that of GAPDH obtained from the same
membrane lane.
Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis. Firstly,
lung tissue samples were preserved in 4% paraformaldehyde at 4˚C
for 1 day, processed through a graded ethanol series and embedded
in paraffin blocks. Serial sections (5 µm) were then cut using the
RM2235 rotary microtome (Leica Biosystems). The staining procedure
involved: i) Deparaffinization in xylene (three changes, 5 min
each); ii) rehydration through a graded ethanol series (100-70%);
iii) antigen retrieval in citrate buffer (pH 6.0) at 95˚C for 20
min; iv) endogenous peroxidase blocking with 3%
H2O2 for 10 min at room temperature; and v)
non-specific site blocking with 5% goat serum for 30 min at room
temperature.
Sections were incubated with a primary antibody
against gasdermin D (GSDMD; 1:1,000) overnight at 4˚C in a
humidified environment. After three washes with PBS (5 min each),
the sections were exposed to an HRP-conjugated secondary antibody
(1:200) for 20 min at room temperature, followed by
3,3'-diaminobenzidine chromogen development (6 min) with
microscopic monitoring. Counterstaining was performed with
hematoxylin at room temperature for 30 sec, followed by dehydration
through graded ethanol and xylene clearing. Slides were examined
under the LSM700 confocal microscope (Zeiss GmbH).
Semi-quantitative analysis of IHC staining was performed using
ImageJ software.
For the co-detection of GSDMD-FL and GSDMD-N, the
same membrane was used. Due to the close molecular weights of
GSDMD-N and GAPDH, which could lead to overlapping bands and
imprecise semi-quantification, GAPDH was probed on a separate
membrane. Similarly, other target proteins (NLRP3, caspase-1 and
ASC) were detected on dedicated membranes to optimize antibody
conditions and avoid excessive stripping/re-probing cycles. To
ensure perfect comparability between different membranes, total
protein lysates for all samples were run on two identical SDS-PAGE
gels in parallel under the same electrophoretic conditions.
Proteins were then transferred in parallel onto separate PVDF
membranes under identical transfer conditions. To control for
loading and transfer variations, the membranes were stained with
Ponceau S (Sigma-Aldrich) after transfer. Densitometric analysis of
the total protein stain (Ponceau S) for each lane was performed
using ImageJ software, and the signal intensity of each target
protein was normalized to the total protein signal of its
corresponding lane.
Immunofluorescence analysis. Cells were
rinsed with PBS, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 min at room
temperature and then washed three times with TBST (5 min each).
Permeabilization with 0.1% Triton X for 20 min at room temperature
was carried out after another three TBST washes (5 min each).
Primary antibodies of Nrf2 (as aforementioned) diluted in blocking
buffer were then applied and incubated overnight at 4˚C in a
humidified chamber. Subsequently, the cells were washed, incubated
with secondary antibody for 1 h in the dark at room temperature and
rinsed three times with TBST. Each sample received 200 µl antifade
mounting medium with DAPI and visualization was performed using the
LSM700 confocal microscope. Semi-quantitative analysis of IF
staining was performed using ImageJ software.
ELISA. Concentrations of IL-1β and IL-18 in
MH-S cell culture supernatants and BALF were quantified using ELISA
kits following the manufacturer's protocols. Standards and samples
(100 µl/well) were loaded in duplicate onto 96-well plates and
incubated at 37˚C for 90 min. After washing, 100 µl biotinylated
detection antibody was added to each well and incubated for 60 min
at 37˚C. After three washes, 100 µl HRP-conjugated streptavidin was
added and incubated for 30 min at 37˚C in the dark. The enzymatic
reaction was terminated by adding 50 µl stop solution and the
absorbance was immediately measured at 450 nm (with 570 nm
correction) using the Bio-Rad Model 680 microplate reader (Bio-Rad
Laboratories, Inc.). Cytokine concentrations were interpolated from
a four-parameter logistic standard curve generated with reference
standards.
Annexin V-FITC staining. MH-S cells were
cultured in a 24-well plate. After treatment, the plates were
centrifuged at 1,000 x g for 5 min at room temperature, the
supernatant was removed and the cells were washed twice with PBS.
Subsequently, the cells were stained with 250 µl Annexin V-FITC/PI
solution for 15 min at room temperature in the dark. Images were
then acquired using an IX73 inverted fluorescence microscope
(Olympus Corporation).
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release assay.
Cytotoxicity was assessed by quantifying LDH activity in cell
culture supernatants and BALF using a commercial LDH detection kit
assay, following the product description. A total of 100 µl
cell-free supernatant from each sample was transferred to a 96-well
plate and incubated with the reaction mixture for 30 min at room
temperature in the dark. The enzymatic reaction was terminated by
adding stop solution and absorbance was immediately measured at 450
nm using the model 680 microplate reader (Bio-Rad Laboratories,
Inc.).
Assessment of intracellular reactive oxygen
species (ROS) levels. Intracellular ROS levels were quantified
using 2',7'-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) as a
fluorescent probe. Cells were seeded in 24-well plates
(5x104 cells/well) and treated as indicated for 48 h at
37˚C. Subsequently, the cells were incubated with 10 µM DCFH-DA in
serum-free medium at 37˚C for 20 min in the dark. After three
washes with warm DMEM to remove excess probe, ROS detection was
carried out using the IX73 inverted fluorescence microscope
(Olympus Corporation).
Measurement of oxidative stress markers.
Myeloperoxidase (MPO), malondialdehyde (MDA) and superoxide
dismutase (SOD) oxidative stress marker activity was quantitatively
analyzed in both cell culture supernatants and BALF using
commercial assay kits according to the manufacturer's protocols.
All spectrophotometric measurements were carried out in triplicate
using the model 680 microplate reader (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.),
with appropriate blank and standard controls included in each assay
plate.
Statistical analysis. All quantitative data,
except for survival data, are presented as the mean ± standard
deviation (SD) from at least three independent experiments, with
each experiment carried out in triplicate. Statistical analyses
were carried out using GraphPad Prism (version 6.0; Dotmatics). For
comparisons between multiple groups, one-way analysis of variance
(ANOVA) was performed: for data with homogeneous variances, Tukey's
post hoc test was used; for data with heterogeneous variances,
Welch's ANOVA followed by Games-Howell's post hoc test was
employed. For the survival study, Kaplan-Meier survival curves were
generated, and differences between groups were compared for
statistical significance using the log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. In
all analyses, a P-value of less than 0.05 (P<0.05) was
considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
Network pharmacology analysis. Target
screening of CA and ARDS
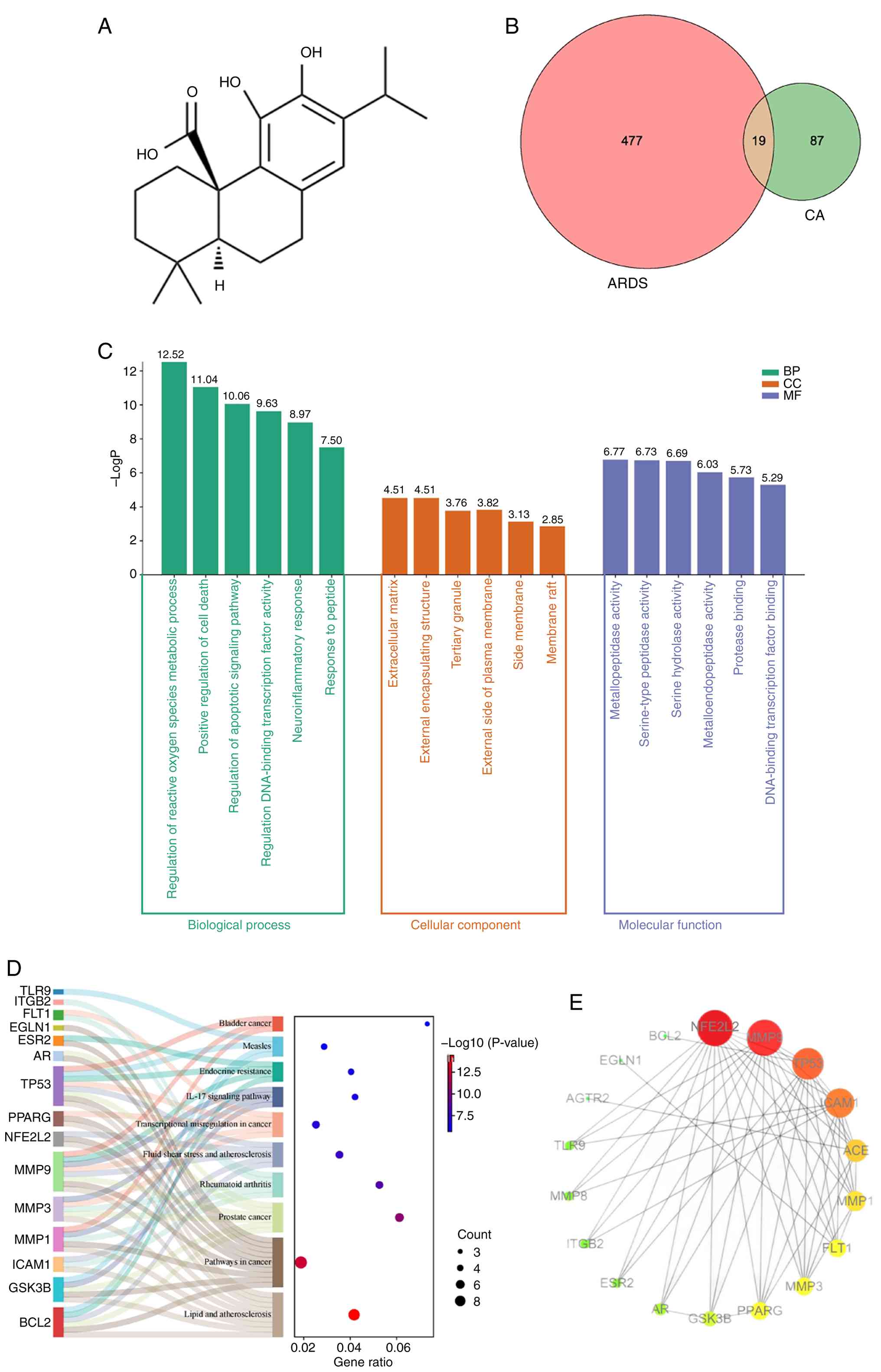
The two-dimensional structure of CA was retrieved
from the PubChem database (Fig.
1A). Target prediction analysis using the SwissTargetPrediction
platform identified 106 potential CA target genes (probability
score, >0.1). In addition, 496 ARDS-associated genes were
compiled from comprehensive disease databases (GeneCards, 387
targets; DisGeNET, 109 targets) after removing duplicates.
Comparative analysis through a Venn diagram revealed 19 overlapping
genes between CA targets and ARDS-related genes (Fig. 1B), representing potential
therapeutic targets through which CA may exert its pharmacological
effects against ARDS. These 19 candidate targets were subsequently
prioritized for further network pharmacology analysis.
Functional enrichment analysis.
Bioinformatics analysis using the Metascape platform revealed
significant functional enrichment among the 19 common targets,
identifying 466 GO BP, 22 GO CC, 56 GO MF and 37 KEGG pathways. BP
analysis demonstrated that these targets were predominantly
involved in ‘regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic
process’ (GO: 2000377), ‘positive regulation of cell death’,
‘regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway’ and ‘regulation of
DNA-binding transcription factor activity’, suggesting these BP may
mediate the therapeutic effects of CA in ARDS (Fig. 1C). MF analysis results demonstrated
that the common target genes were most involved in
‘metallopeptidase activity’, ‘serine-type peptidase activity’ and
‘serine hydrolase activity’. CC analysis results indicated that the
common target genes were the most predicated on the ‘extracellular
matrix’, ‘external encapsulating structure’ and ‘tertiary granule’.
Results of the KEGG analysis revealed that the 19 genes were mainly
enriched in ‘Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis’, ‘Pathways in
cancer’, ‘Lipid and atherosclerosis’ and the ‘IL-17 signaling
pathway’ (Fig. 1D).
PPI network construction. Among the 19 genes,
ADCY10 was excluded from PPI network construction as it exhibited
no association with the other genes. The finalized network
comprised 18 nodes and 80 edges, illustrating the complex web of
interactions among the remaining targets (Fig. 1E). Hub targets were subsequently
identified to uncover the core characteristics of the network.
These key nodes were pinpointed based on their degree values, which
effectively captured their relative importance and connectivity
within the network, providing insight into the functional
architecture of the network.
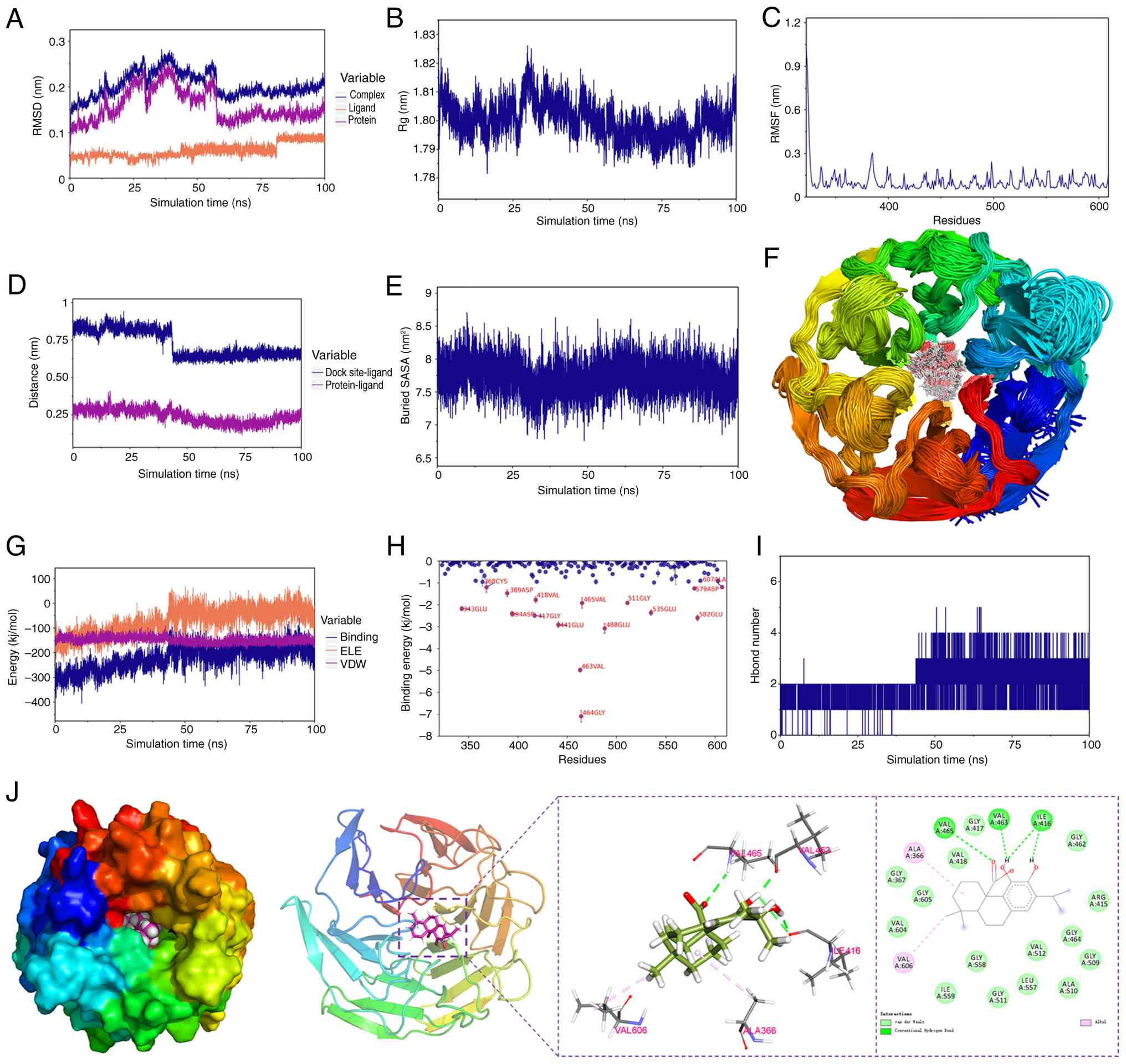
Molecular docking and MD. Following
comprehensive analysis of the PPI network, NFE2L2 (encoding the
Nrf2 protein) emerged as the pivotal target. Subsequently, to
explore the potential binding mode and interaction mechanism,
molecular docking experiments were conducted between NFE2L2 and CA.
A total of 10 different docking sites were assessed, with findings
indicating that the docking affinity was <-5 kcal/mol (Table III). Subsequently, the top-ranked
conformation from the molecular docking results, which demonstrated
the highest binding affinity, was subjected to MD simulations for
further validation. All results suggested that NFE2L2 and CA are
capable of stable binding (Fig.
2). As shown in Fig. 2A-C, the
RMSD of the complex, protein and ligand CA, the radius of gyration,
and the root-mean-square fluctuation of amino acid residues all
stabilized over the 100 nsec molecular dynamics simulation,
indicating that the complex system reached equilibrium and the
binding conformation remained stable. Further binding analysis
revealed that the distance between CA and the Nrf2 binding site, as
well as the buried solvent-accessible surface area, remained stable
during the later stages of the simulation (Fig. 2D-E). Moreover, superimposed
simulation conformations demonstrated that CA stably bound the
initial docking site (Fig. 2F).
Binding free energy calculations (molecular mechanics
Poisson-Boltzmann surface area) revealed that van der Waals
interactions served as the primary driving force for binding.
Additionally, residual energy decomposition analysis identified key
amino acids, such as GLY-464 and VAL-463, that contributed
significantly to the binding energy (Fig. 2H). These results confirm at the
atomic level that CA and Nrf2 can form a stable complex, providing
a theoretical foundation for subsequent experimental
validation.
 | Table IIIMolecular docking affinity between
carnosic acid and the target protein nuclear factor erythroid
2-related factor 2. |
Table III
Molecular docking affinity between
carnosic acid and the target protein nuclear factor erythroid
2-related factor 2.
| Dock poses | Affinity,
kcal/mol | RMSD l.b. | RMSD u.b. |
|---|
| 1 | -9.606 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | -9.508 | 1.605 | 6.209 |
| 3 | -9.473 | 1.861 | 6.457 |
| 4 | -8.859 | 4.454 | 7.007 |
| 5 | -8.743 | 4.177 | 6.832 |
| 6 | -8.615 | 4.637 | 7.487 |
| 7 | -8.588 | 3.847 | 6.335 |
| 8 | -8.396 | 2.010 | 3.009 |
| 9 | -8.266 | 1.572 | 2.136 |
| 10 | -7.930 | 6.649 | 10.900 |
Biological experiment results. Effect
of CA on MH-S cell viability
A CCK-8 assay was used to assess the cytotoxic
effects of CA on MH-S cells. The results demonstrated that low CA
concentrations (1-20 µM) did not significantly affect cell
viability. Based on these findings, 10 and 20 µM CA concentrations
were selected for subsequent experimental investigation (Fig. 3A).
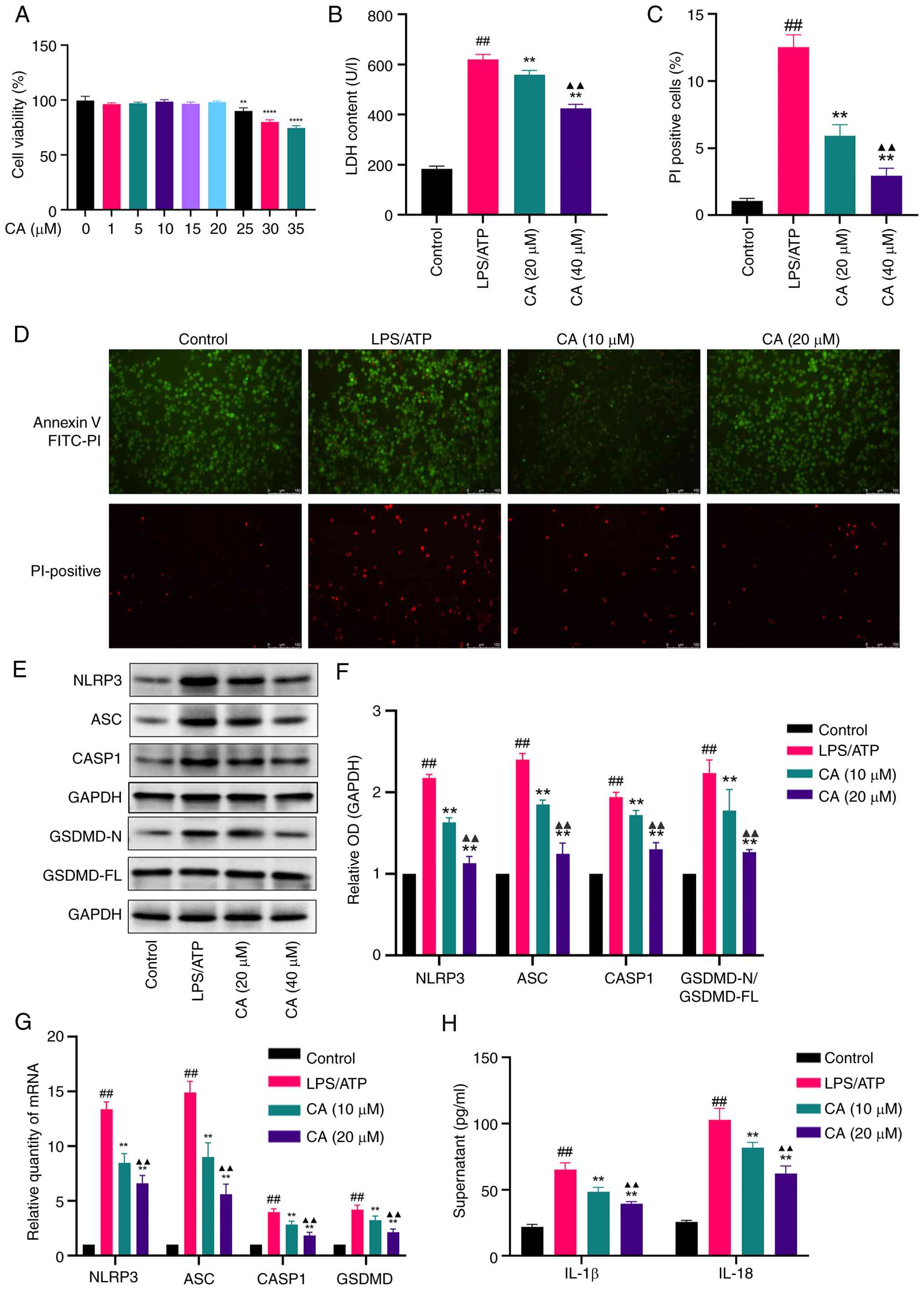 | Figure 3CA inhibits pyroptosis in
LPS/ATP-stimulated MH-S cells. (A) Cytotoxicity of CA evaluated by
a Cell Counting Kit-8 assay. (B) LDH release in the supernatant
following CA treatment. (C) Percentage of PI-positive cells
following CA treatment. (D) Annexin V-FITC (green)
double-fluorescent staining representing apoptosis levels and PI
(red) double-fluorescent staining representing cell necrosis
levels. Scale bar, 100 µm. PI-positive cell rate was calculated
using ImageJ software. (E) Representative bands and (F) analysis of
protein expression of NLRP3, ASC, CASP1 and GSDMD detected by
western blotting. (G) mRNA expression levels of NLRP3, ASC, CASP1
and GSDMD detected by reverse transcription-quantitative PCR. (H)
Production of IL-18 and IL-1β in the supernatant measured by ELISA.
Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three independent
experiments. ##P<0.01 vs. control;
**P<0.01, ****P<0.0001 vs. LPS/ATP;
▲▲P<0.01 vs. CA (10 µM). CA, carnosic acid; LPS,
lipopolysaccharide; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; NLRP3, NLR family
pyrin domain containing 3; ASC, apoptosis-associated speck-like
protein containing a CARD; CASP1, caspase-1; GSDMD, gasdermin D;
OD, optical density. |
CA inhibits pyroptosis in LPS/ATP-stimulated MH-S
cells. To assess the impact of CA on pyroptosis, MH-S cells
were treated with LPS and ATP. Pyroptosis was then quantified by
measuring the proportion of PI-positive cells (Annexin V-FITC and
PI double staining, a combination of methods evaluating membrane
integrity and inflammasome activation) and LDH levels in the cell
supernatant. The findings indicated a notable reduction in both LDH
release (Fig. 3B) and PI-positive
cells (Fig. 3C and D) following CA treatment. During the
early stages of apoptosis and pyroptosis, phosphatidylserine
becomes externalized on the cell membrane. However, pyroptosis
ultimately leads to complete membrane rupture. Consequently, a cell
population positive for Annexin V-FITC (green) and negative for PI
(red) indicates an early stage of cell death, while cells positive
for both Annexin V and PI represent a later stage characterized by
loss of membrane integrity. The results demonstrated that LPS/ATP
stimulation significantly increased the proportion of
double-positive cells, an effect that was effectively reversed by
CA treatment. To assess NLR family pyrin domain containing 3
(NLRP3) inflammasome activation, key markers were examined,
including apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD
(ASC), caspase-1 (CASP1), the N-terminal fragment of GSDMD and the
downstream cytokines IL-18 and IL-1β. CA treatment significantly
inhibited the protein expression of these key markers induced by
LPS/ATP and their corresponding mRNA upregulation (Fig. 3E-G). Furthermore, CA markedly
attenuated the release of IL-18 and IL-1β in the supernatant
compared with the LPS/ATP-stimulated group (Fig. 3H). Collectively, these outcomes
indicated that CA may effectively hinder LPS/ATP-induced pyroptosis
in MH-S cells by inhibiting NLRP3 activation and averting GSDMD
cleavage.
CA activates Nrf2 and alleviates oxidative stress
in LPS/ATP-stimulated MH-S cells. CA has previously been
documented to exhibit potent antioxidative properties (28); however, its protective effects
against oxidative stress in MH-S cells remain unclear. Thus, the
antioxidant effects and underlying mechanisms of CA in
LPS/ATP-challenged MH-S cells were investigated.
To assess the antioxidant properties of CA, the key
oxidative stress markers MDA, MPO and SOD were analyzed. CA
treatment significantly reduced MDA and MPO levels while enhancing
SOD activity in MH-S cells compared with the LPS/ATP group
(Fig. 4A-C). In addition, LPS/ATP
stimulation led to a notable increase in intracellular ROS
production in MH-S cells compared with that in the control group,
with CA treatment effectively mitigating this increase (Fig. 4D and E).
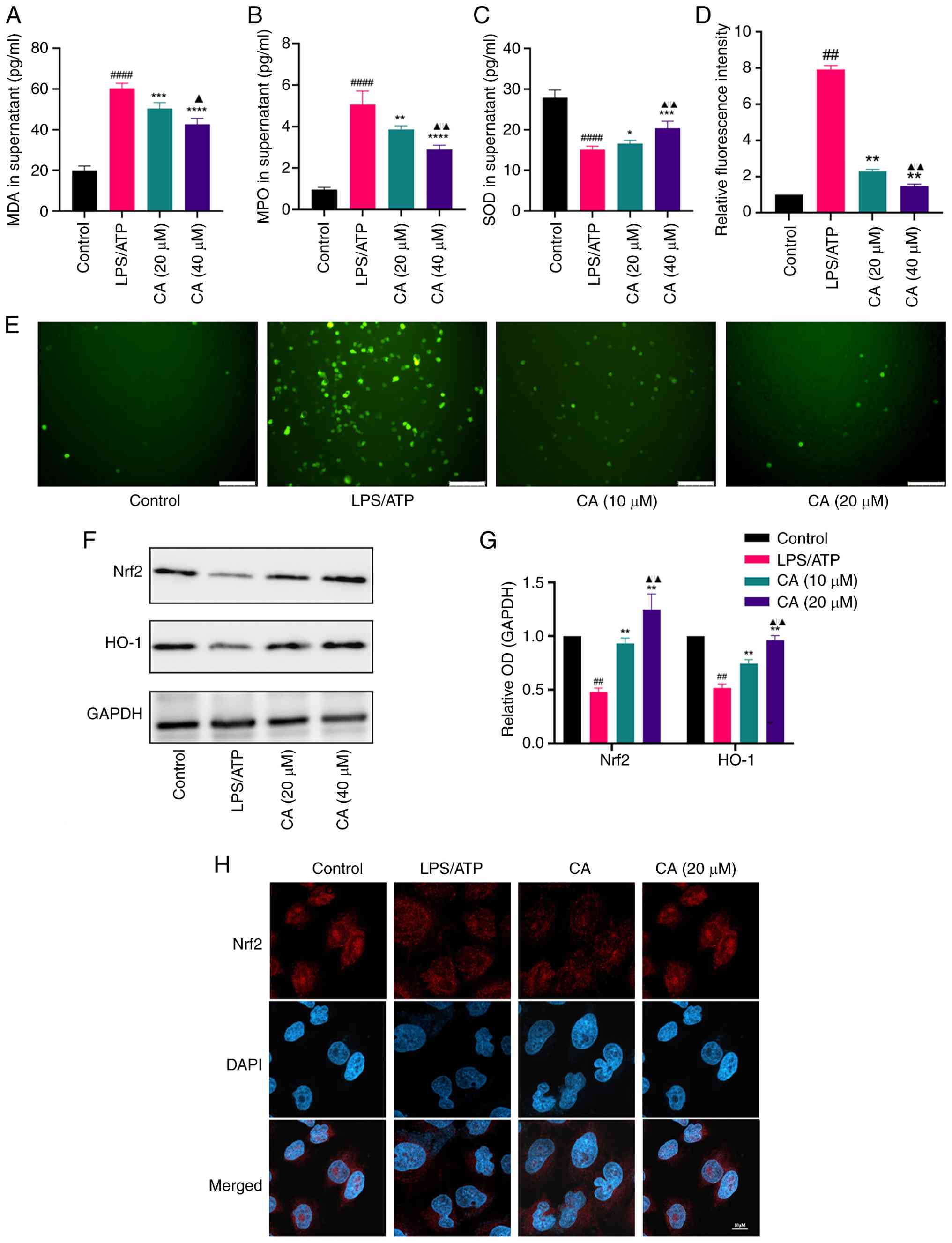 | Figure 4CA activates Nrf2 and improves the
oxidative stress in LPS/ATP-stimulated MH-S cells. Levels of (A)
MDA, (B) MPO and (C) SOD in the supernatant measured by ELISA. (D
and E) ROS generation of MH-S cells detected by
2',7'-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate cellular ROS detection
assay, with fluorescence intensity calculated using ImageJ
software. Scale bar, 100 µm. (F) Representative bands and (G)
analysis of protein expression of Nrf2 and HO-1 detected by western
blotting. (H) Nuclear translocation of the Nrf2 subunit determined
by an immunofluorescence assay. Scale bar, 20 µm. Data are
presented as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
##P<0.01, ####P<0.0001 vs. control;
*P<0.05, **P<0.01,
***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001 vs. LPS/ATP
group; ▲P<0.05, ▲▲P<0.01 vs. CA (10
µM). CA, carnosic acid; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related
factor 2; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MDA,
malondialdehyde; MPO, myeloperoxidase; SOD, superoxide dismutase;
ROS, reactive oxygen species; OD, optical density. |
Subsequently, the molecular mechanisms responsible
for the antioxidant properties of CA were explored. Nrf2, a
regulator of cellular antioxidant responses, was focused on to
determine its involvement in CA-mediated oxidative stress
protection (29). The findings
demonstrated that, compared to the LPS/ATP-stimulated group, CA
treatment significantly augmented the protein expression of both
total Nrf2 and heme oxygenase-1 (Fig.
4F and G) and facilitated the
nuclear translocation of Nrf2 (Fig.
4H). Collectively, these findings suggested that CA may
alleviate oxidative stress and activate Nrf2 in MH-S cells.
CA attenuates LPS-induced ARDS in mice.
Arterial blood gas analysis showed that, in comparison with the
control group, the LPS group exhibited a notable decrease in
PaO2 and PO2/FiO2 levels, and a
marked increase in PaCO2 levels (Fig. 5A-C). These characteristic
alterations in blood gas parameters confirm the successful
establishment of the ARDS mouse model (23). The mice that received treatment
with CA demonstrated an elevation in PaO2 levels and a
significant decrease in PaCO2 levels, indicating a
marked improvement in pulmonary gas exchange, thus supporting its
potential for clinical application.
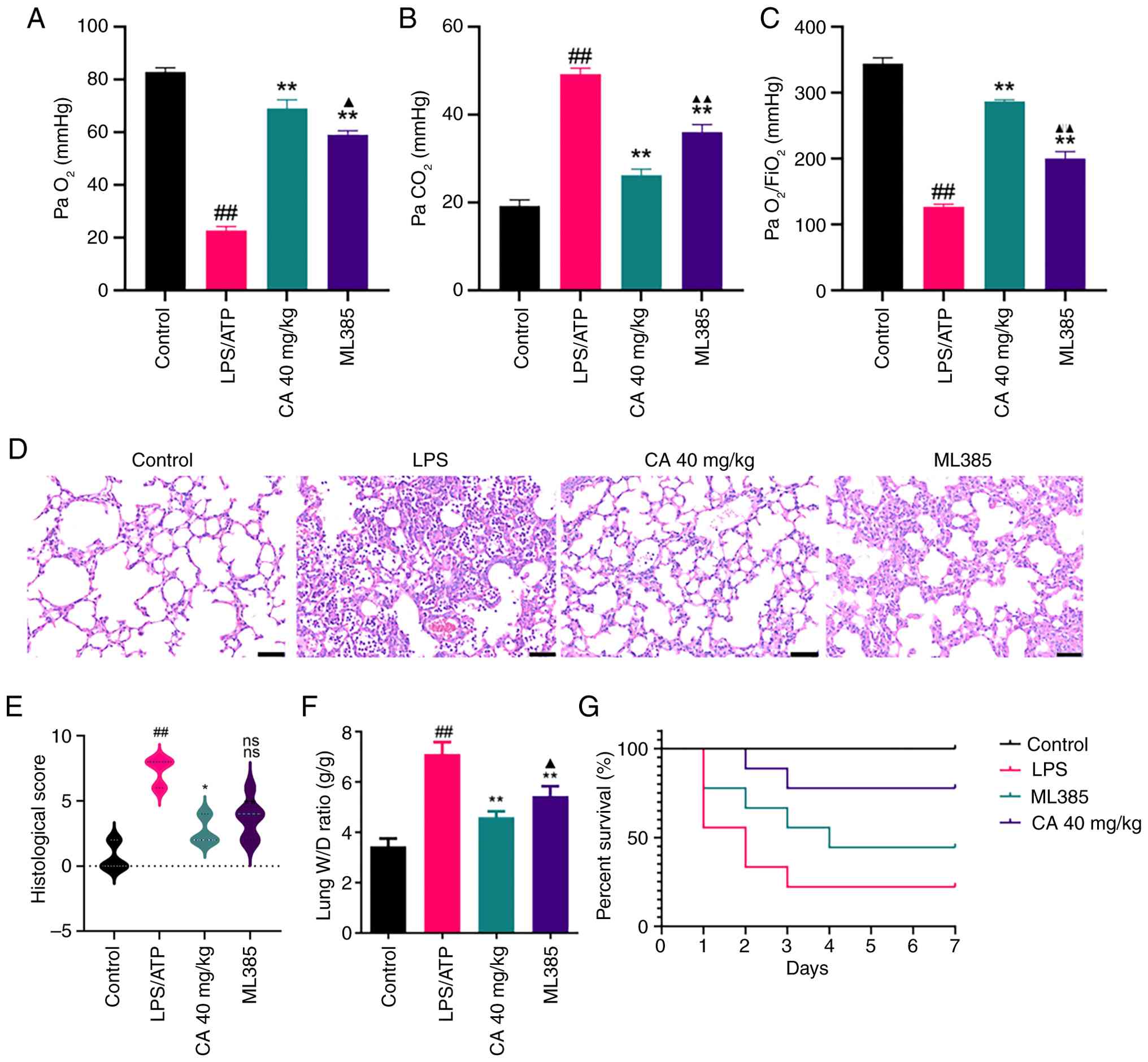 | Figure 5CA attenuates LPS-induced acute
respiratory distress syndrome in mice. (A) PaO2 and (B)
PaCO2 data of each group. (C)
PaO2/FiO2 ratio of each group. (D)
Histopathological variation in lung tissues determined using
H&E staining. Scale bar, 50 µm. (E) Lung injury score. (F) Lung
W/D ratio assessed using histological sections. (G) Survival rate
for mice observed twice daily for 7 days. Data are presented as the
mean ± SD of three independent experiments. ##P<0.01
vs. control; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs. LPS;
▲P<0.05, ▲▲P<0.01 vs. CA (40 mg/kg).
CA, carnosic acid; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; ns, not significant;
PaO2, partial pressure of oxygen; PaCO2,
partial pressure of carbon dioxide; FiO2, fraction of
inspired oxygen; W/D, wet dry. |
The effects of CA against LPS-induced ARDS were
subsequently evaluated by performing histopathological analysis of
lung tissues using H&E staining (Fig. 5D). Compared with in the control
group, LPS-challenged mice exhibited significantly elevated
histological scores, characterized by extensive inflammatory cell
infiltration, alveolar hemorrhage and interstitial edema (Fig. 5E). Notably, CA treatment markedly
attenuated these pathological alterations and significantly
improved histological scores. These findings provide histological
evidence for the protective role of CA in mitigating LPS-induced
acute lung injury.
To further assess pulmonary edema formation, lung
tissue water content was quantified by measuring the W/D weight
ratio. As shown in Fig. 5F, ARDS
mice exhibited a significantly elevated lung W/D ratio compared
with that in the control group, indicating severe pulmonary edema.
Notably, CA treatment effectively normalized this parameter.
Together with the histological findings, these results demonstrated
that CA could confer marked protection against ARDS by attenuating
pathological vascular permeability and edema formation.
Consistent with its reversal of CA-mediated
improvements in lung injury parameters (Fig. 5A-F), pharmacological inhibition of
Nrf2 with ML385 also significantly attenuated the survival benefit
conferred by CA. Survival analysis via the Kaplan-Meier method
revealed marked differences between groups (log-rank test, Fig. 5G). LPS-challenged mice only
exhibited a 20% survival rate, treatment with CA markedly improved
survival rates to >50%. Pharmacological inhibition of Nrf2 with
ML385 attenuated the protective effects of CA, thus reducing
survival rates. These findings suggested that CA may provide a
notable survival benefit in LPS-induced ARDS, mediated through Nrf2
pathway activation.
CA inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated
pyroptosis in mice with LPS-induced ARDS through activation of
Nrf2. To further explore the anti-pyroptotic effect of CA and
its protective role in LPS-induced ARDS, the impact of CA on NLRP3
inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis was investigated in vivo.
Quantitative analysis revealed that LPS challenge induced
pyroptotic activation, as evidenced by significant upregulation of
NLRP3 inflammasome components (NLRP3, ASC, CASP1 and GSDMD) at both
transcriptional and translational levels (Fig. 6A-E). This was associated with
elevated BALF concentrations of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β
(Fig. 6F) and IL-18 (Fig. 6G), and increased LDH release
(Fig. 6F). Notably, CA exerts its
effects by selectively inhibiting the activation of the NLRP3
inflammasome, reducing LDH release and decreasing IL-18 and IL-1β
secretion, thereby demonstrating the anti-pyroptotic effects
observed in vitro through suppression of the NLRP3
inflammasome pathway.
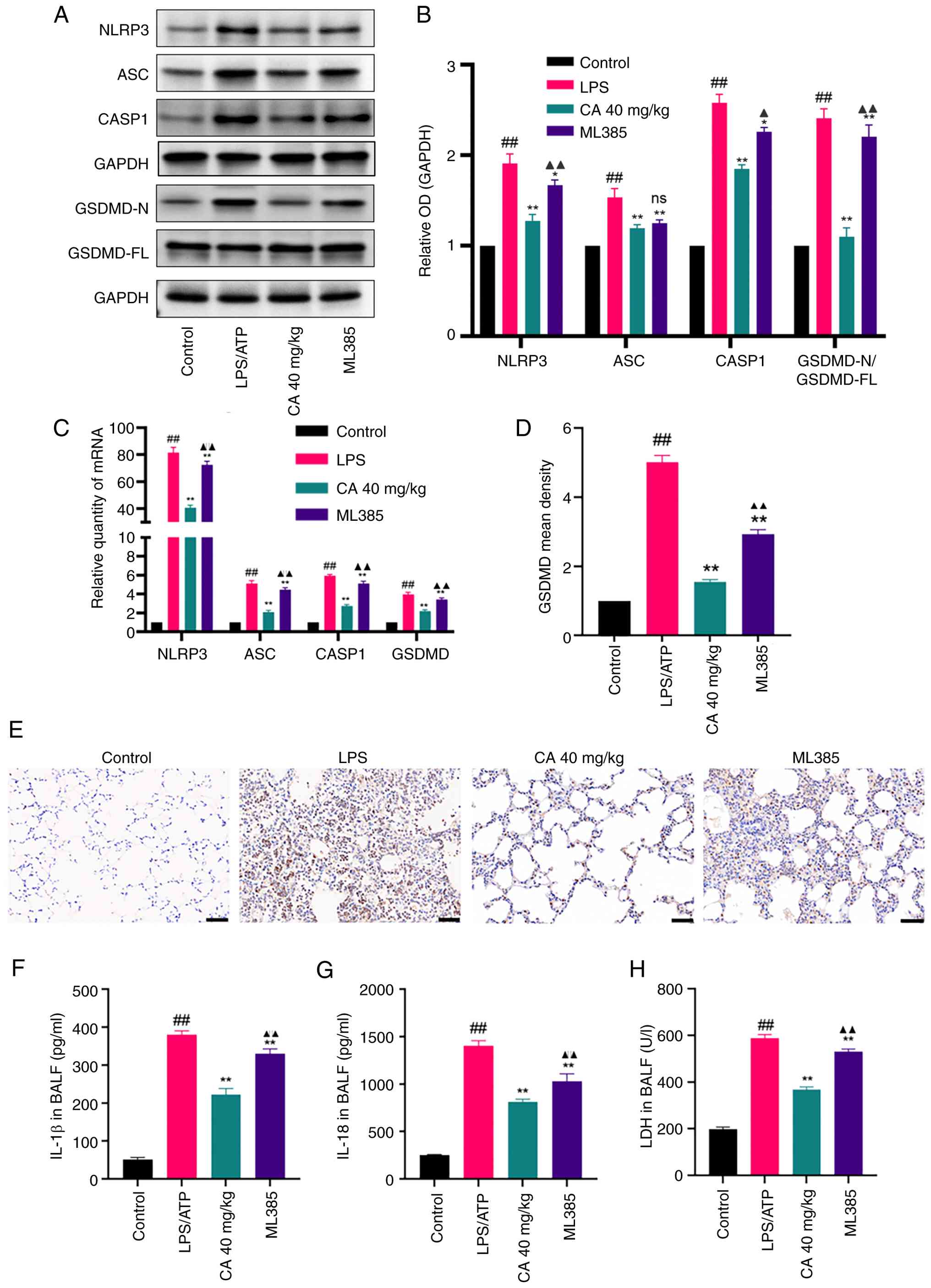 | Figure 6CA inhibits NLRP3
inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis in LPS-induced acute respiratory
distress syndrome in mice. (A) Representative bands and (B)
analysis of protein expression of NLRP3, ASC, CASP1 and GSDMD
detected by western blotting. (C) mRNA expression levels of NLRP3,
ASC, CASP1 and GSDMD detected by reverse transcription-quantitative
PCR. (D) Analysis and (E) immunohistochemical staining showing the
positive rate of GSDMD protein expression in lung tissues of mice
in each group. Scale bar, 50 µm. Production of (F) IL-18 and (G)
IL-1β in the BALF measured by ELISA. (H) LDH release in the BALF.
Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three independent
experiments. ##P<0.01 vs. control;
*P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs. LPS;
▲P<0.05, ▲▲P<0.01 vs. CA (40 mg/kg).
CA, carnosic acid; NLRP3, NLR family pyrin domain containing 3;
LPS, lipopolysaccharide; ASC, apoptosis-associated speck-like
protein containing a CARD; CASP1, caspase-1; GSDMD, gasdermin D;
LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; BALF, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; ns,
not significant; OD, optical density. |
To explore whether the effects of CA were
Nrf2-dependent, mice were pretreated with the Nrf2 inhibitor ML385.
This pretreatment eliminated the ability of CA to downregulate
NLRP3 inflammasome components and reduce inflammatory mediator
release (Fig. 6A-H). Therefore,
these findings suggested that CA could attenuate LPS-induced ARDS
by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis, a process
partially dependent on Nrf2 activation.
CA alleviates LPS-induced ARDS through
Nrf2-dependent antioxidant mechanisms. MPO, MDA and SOD
activity was assessed to evaluate whether CA exerted a protective
effect against LPS-induced ARDS through its antioxidant properties.
In addition, the protein and mRNA levels of Nrf2 and HO-1 were
measured. The findings revealed that LPS administration notably
elevated MPO and MDA activities, while suppressing SOD levels in
the BALF (Fig. 7A-C). However,
these changes were effectively prevented by pretreatment with CA.
Additionally, treatment with CA resulted in a notable upregulation
of both Nrf2 and HO-1 at both transcriptional and translational
levels in the lung tissue of mice (Fig. 7D-F).
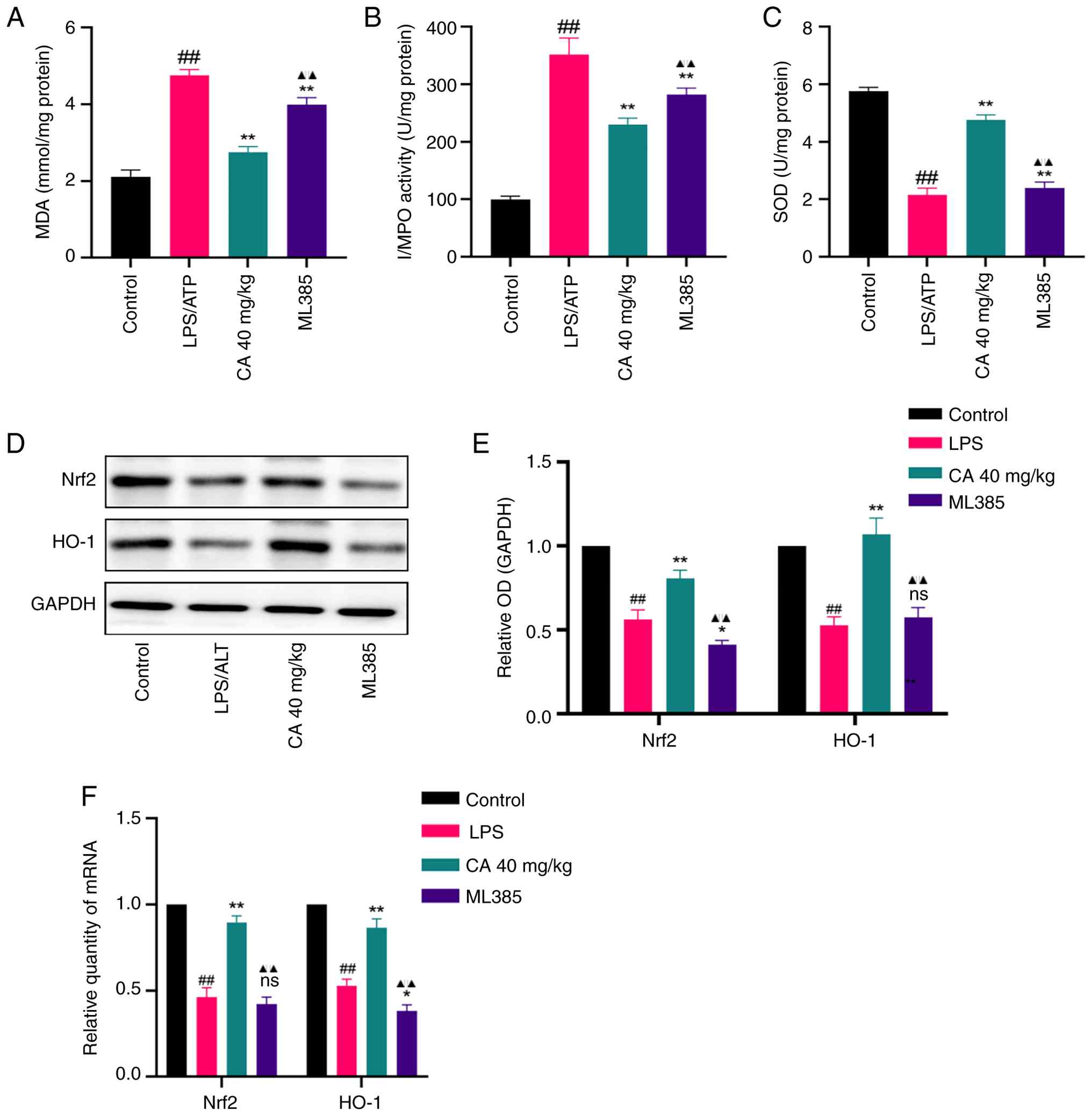 | Figure 7CA exerts an anti-oxidative effect in
LPS-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. Levels of (A) MDA,
(B) MPO and (C) SOD in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid measured by
ELISA. (D) Representative bands and (E) analysis of protein
expression of Nrf2 and HO-1 detected by western blotting. (F) mRNA
expression of Nrf2 and HO-1 detected by reverse
transcription-quantitative PCR. Data are presented as the mean ± SD
of three independent experiments. ##P<0.01 vs.
control; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs. LPS;
▲▲P<0.01 vs. CA (40 mg/kg). CA, carnosic acid; LPS,
lipopolysaccharide; MDA, malondialdehyde; MPO, myeloperoxidase;
SOD, superoxide dismutase; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related
factor 2; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; ns, not significant; OD, optical
density. |
To further substantiate whether the antioxidant
protection offered by CA against LPS-induced ARDS was dependent
upon Nrf2 activation, mice were pretreated with the aforementioned
ML385. ML385 not only abolished the CA-mediated reduction in MPO
and MDA levels and the restoration of SOD activity (Fig. 7A-C), but also attenuated the
CA-induced upregulation of both Nrf2 and HO-1 (Fig. 7D-F). These findings indicated that
Nrf2 activation constitutes an essential mechanism underlying the
antioxidant protection of CA in LPS-induced ARDS.
Discussion
ARDS is a severe respiratory disease marked by high
rates of mortality (30-50%). To the best of our knowledge, at the
present time, no treatment has been demonstrated as completely
effective and conclusive for managing ARDS (2). As phytochemistry and pharmacological
research have advanced, numerous natural products exhibiting
antioxidant (30,31), anti-inflammatory (32,33)
and antibacterial (34,35) properties have emerged.
Consequently, there is a growing interest in utilizing the
botanical constituents of traditional medicines as potential
preventative and therapeutic agents for ARDS (4,36).
CA, a naturally occurring compound derived from Rosmarinus
officinalis Linnaeus, has demonstrated promising antioxidant
and anti-inflammatory effects (37,38).
The present study systematically investigated the therapeutic
potential and molecular mechanisms of CA against LPS-induced ARDS,
employing an integrative approach combining network pharmacology,
molecular docking, MD simulations, and comprehensive in
vitro and in vivo validation experiments.
Network pharmacology identified 19 overlapping
targets between CA and ARDS, with NFE2L2 (Nrf2) emerging as the hub
target based on Venn and PPI network analysis. GO analysis
suggested that the regulation of the ROS metabolic process is an
important biological process in the mechanism of how CA treats
ARDS. Research has suggested that uncontrolled oxidative stress
markedly aggravates pulmonary inflammation, and accelerates the
development and progression of ARDS (39,40).
Central to this process is Nrf2, a key transcriptional factor that
governs cellular antioxidant defense systems and maintains redox
equilibria. Nrf2 activation induces the expression of
cytoprotective enzymes, including HO-1, creating a key defense
mechanism against oxidative damage. Emerging evidence has indicated
that Nrf2/HO-1 pathway activation is specifically associated with
ARDS mitigation through oxidative stress suppression (41,42).
Building on these findings and considering the documented
antioxidant properties of CA, it was hypothesized that CA could
ameliorate LPS-induced ARDS through Nrf2/HO-1 pathway activation.
Computational analyses, including molecular docking and MD
simulations, demonstrated that CA forms stable binding complexes
with the Nrf2 protein, perhaps indicating direct modulation of this
transcriptional regulator. This prediction was experimentally
validated in both cellular and animal models, whereby CA
upregulated the protein and mRNA expression levels of Nrf2 and
HO-1, decreased the levels of MPO and MDA, and increased the level
of SOD. CA was also found to exert its antioxidant effects by
reversing the LPS-induced downregulation of Nrf2, suggesting that
CA serves an antioxidant role in LPS-induced ARDS through
modulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway.
KEGG pathway enrichment analysis revealed that the
most significantly enriched pathways were primarily associated with
oxidative stress and inflammatory responses.. GO analysis suggested
that the BP term ‘positive regulation of cell death’ is also
important. Macrophages are important inflammatory response cells
and there is increasing evidence suggesting that macrophages are
involved in the pathogenesis of ARDS. Activated macrophages
exacerbate pulmonary edema in LPS-induced ARDS through excessive
production of pro-inflammatory mediators (43). Particularly, hyperactivation of the
NLRP3 inflammasome has been shown to amplify lung inflammation and
tissue injury (44).
Mechanistically, NLRP3 inflammasome activation triggers
CASP1-dependent cleavage of GSDMD, leading to the release of IL-1β
and IL-18, which ultimately drives pyroptotic cell death. Despite
these advances, the specific involvement of NLRP3
inflammasome-mediated macrophage pyroptosis in ARDS progression
remains poorly characterized, highlighting a key gap in
understanding the pathophysiology of ARDS.
In vitro experiments using LPS/ATP-stimulated
MH-S macrophages demonstrated characteristic pyroptotic changes,
including notable elevation of pyroptosis-related markers (NLRP3,
ASC, CASP1 and GSDMD) at both the protein and mRNA levels,
increased cell death indicators and the release of mature
inflammatory cytokines (IL-18 and IL-1β) into culture supernatants.
Notably, CA was revealed to prevent the changes observed in the
aforementioned indicators. These in vitro findings were
corroborated in vivo using a mouse model of ARDS. CA
administration reduced pulmonary expression of NLRP3 inflammasome
components, alveolar damage markers (LDH release), and BALF
concentrations of IL-18 and IL-1β. Collectively, these findings
suggested airway macrophage pyroptosis as a promising therapeutic
target for ARDS intervention, with CA representing a potential
NLRP3-targeted therapeutic candidate that warrants further clinical
investigation.
Emerging evidence has highlighted a key regulatory
relationship between Nrf2 activation and NLRP3 inflammasome
suppression across various cell types (45-47).
Notably, Nrf2 has been shown to negatively regulate NLRP3
inflammasome activation in primary microglia, attenuating
neuroinflammatory responses (48,49),
while in cardiomyocytes, Nrf2 similarly modulates ROS-induced NLRP3
activation. To the best of our knowledge, the Nrf-NLRP3 regulatory
axis had not been investigated in MH-S cells prior to the present
study. The findings of the present study demonstrated that CA
simultaneously activated Nrf2 signaling and inhibited NLRP3
inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis in MH-S cells. Through
pharmacological inhibition using ML385, a potentially causal
relationship was established whereby the Nrf2 blockade abrogated
the suppressive effects of CA on NLRP3 activation. These results
suggested that CA may exert its protective effects against ARDS
through Nrf2-dependent suppression of NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis in
alveolar macrophages, revealing a novel therapeutic mechanism for
this phytochemical compound.
In conclusion, the present study established that CA
exerts potent protective effects against ARDS through a novel
dual-mechanism action, activating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway to
alleviate oxidative stress, and inhibiting NLRP3
inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis by blocking CASP1 activation and
GSDMD cleavage (Fig. 8). The
findings suggested that CA may simultaneously target these two key
pathways in MH-S cells, revealing an important Nrf2-NLRP3
regulatory axis in the pathogenesis of ARDS. While the therapeutic
potential of CA was established through in vitro and in
vivo validation, further research is necessary to evaluate
dose-response relationships, long-term safety profiles, optimal
delivery methods and potential drug interactions before clinical
translation. The present study not only advances general
understanding of ARDS pathophysiology but also provides a
foundation for developing plant-derived multi-target therapies for
inflammatory lung diseases.
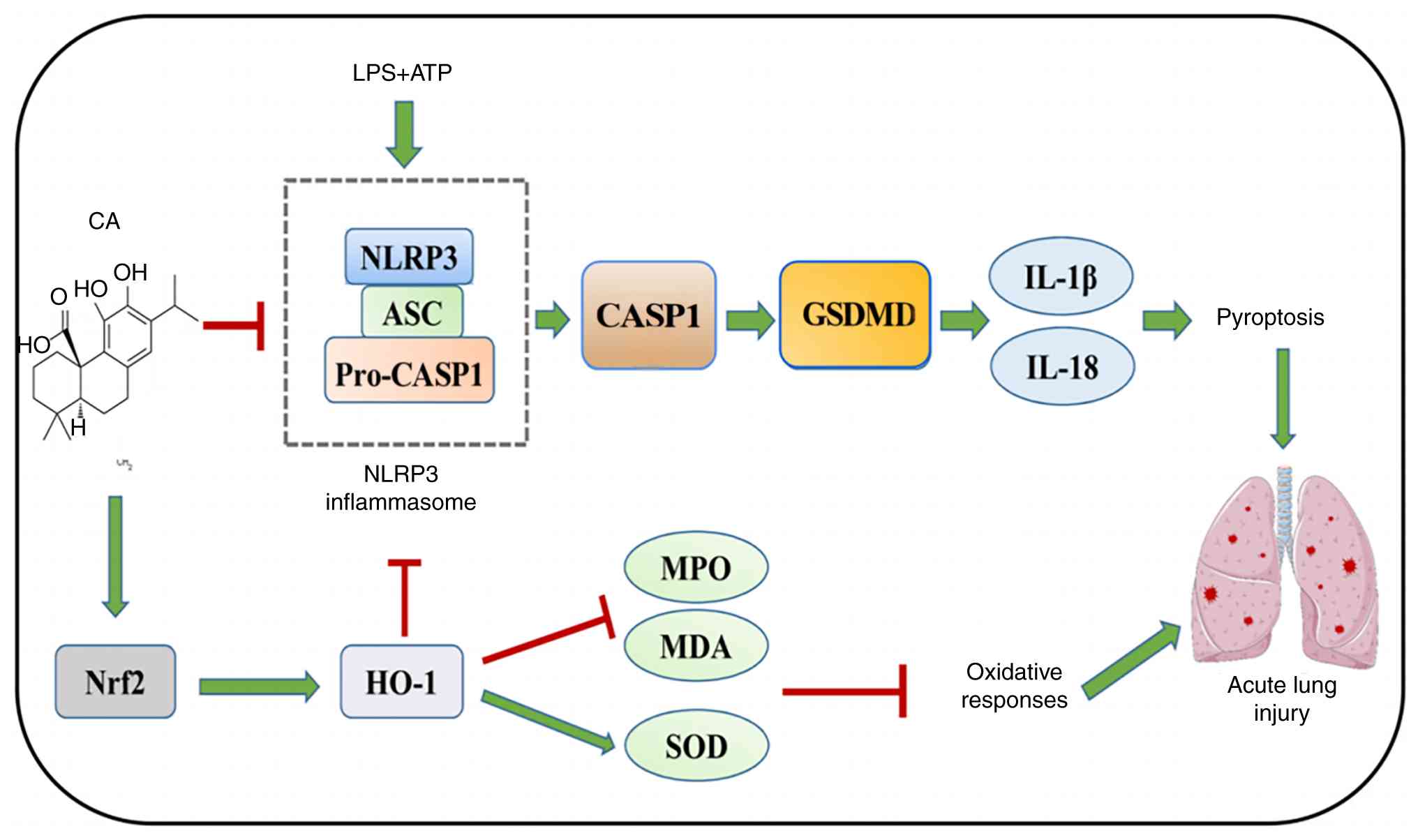 | Figure 8CA protects against acute respiratory
distress syndrome by targeting Nrf2, suppressing oxidative stress
and pyroptosis. LPS activates the NLRP3/CASP1/GSDMD signaling
pathway to induce pyroptosis. CA inhibits oxidative stress and
pyroptosis by activating Nrf2 to reduce lung injury. CA, carnosic
acid; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; NLRP3, NLR family pyrin domain
containing 3; ASC, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein
containing a CARD; CASP1, caspase-1; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1, MPO,
myeloperoxidase; MDA, malondialdehyde; SOD, superoxide dismutase;
GSDMD, gasdermin D; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor
2. |
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding: This work was financially supported by the Suqian
Science&Tech Program (grant no. KY202209), the General Project
of Science and Technology Development Fund of Nanjing Medical
University (grant no. NMUB20210295) and the Suqian City Traditional
Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Project (grant no.
YB202212).
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be
requested from the corresponding author.
Authors' contributions
QL contributed to writing the original draft,
project administration, methodology, investigation, funding
acquisition, formal analysis and data curation. LD contributed to
the software used, formal analysis, data curation and
visualization. HS contributed to data curation, formal analysis,
methodology and writing the original draft. WD contributed to the
methodology, data curation, formal analysis and investigation. MW
contributed to project administration and data curation. ZS
contributed to the study conception and design, data
interpretation, and critically revised the manuscript for important
intellectual content. CM contributed to the acquisition of funding,
project administration, data analysis and interpretation, and
critically revised the manuscript. QL and CM confirm the
authenticity of all the raw data. All authors have read and
approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
All experimental procedures involving animals were
conducted in strict adherence to the Guide for the Care and Use of
Laboratory Animals. Furthermore, the present study protocol was
approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of Jinling Hospital,
Medical School of Nanjing University (approval no.
2022DZGKJDWLS-00161).
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Gorman EA, O'Kane CM and McAuley DF: Acute
respiratory distress syndrome in adults: diagnosis, outcomes,
long-term sequelae, and management. Lancet. 400:1157–1170.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wick KD, Ware LB and Matthay MA: Acute
respiratory distress syndrome. BMJ. 387(e76612)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Matthay MA, Arabi Y, Arroliga AC, Bernard
G, Bersten AD, Brochard LJ, Calfee CS, Combes A, Daniel BM,
Ferguson ND, et al: A new global definition of acute respiratory
distress syndrome. Am J Resp Crit Care. 209:37–47. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
He YQ, Zhou CC, Yu LY, Wang L, Deng JL,
Tao YL, Zhang F and Chen WS: Natural product derived phytochemicals
in managing acute lung injury by multiple mechanisms. Pharmacol
Res. 163(105224)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Farhadi F, Baradaran Rahimi V, Mohamadi N
and Askari VR: Effects of rosmarinic acid, carnosic acid, rosmanol,
carnosol, and ursolic acid on the pathogenesis of respiratory
diseases. Biofactors. 49:478–501. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
McCord JM, Hybertson BM, Cota-Gomez A and
Gao B: Nrf2 activator PB125® as a carnosic acid-based therapeutic
agent against respiratory viral diseases, including COVID-19. Free
Radical Bio Med. 175:56–64. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zhang D, Lee B, Nutter A, Song P,
Dolatabadi N, Parker J, Sanz-Blasco S, Newmeyer T, Ambasudhan R,
McKercher SR, et al: Protection from cyanide-induced brain injury
by the Nrf2 transcriptional activator carnosic acid. J Neurochem.
133:898–908. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhang C, Zhao M, Wang B, Su Z, Guo B, Qin
L, Zhang W and Zheng R: The Nrf2-NLRP3-caspase-1 axis mediates the
neuroprotective effects of Celastrol in Parkinson's disease. Redox
Biol. 47(102134)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Arioz BI, Tastan B, Tarakcioglu E, Tufekci
KU, Olcum M, Ersoy N, Bagriyanik A, Genc K and Genc S: Melatonin
attenuates LPS-Induced acute depressive-like behaviors and
microglial NLRP3 inflammasome activation through the SIRT1/Nrf2
pathway. Front Immunol. 10(1511)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Xu L, Zhu Y, Li C, Wang Q, Ma L, Wang J
and Zhang S: Small extracellular vesicles derived from
Nrf2-overexpressing human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells protect
against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting
NLRP3. Biol Direct. 17(35)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Dhar R, Rana MN, Zhang L, Li Y, Li N, Hu
Z, Yan C, Wang X, Zheng X, Liu H, et al: Phosphodiesterase 4B is
required for NLRP3 inflammasome activation by positive feedback
with Nrf2 in the early phase of LPS-induced acute lung injury. Free
Radical Bio Med. 176:378–391. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhou Y, Zhou B, Pache L, Chang M,
Khodabakhshi AH, Tanaseichuk O, Benner C and Chanda SK: Metascape
provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of
systems-level datasets. Nat Commun. 10(1523)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Gene Ontology Consortium. Gene Ontology
Consortium: Going forward. Nucleic Acids Res. 43(Database
issue):D1049–D1056. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Paggi JM, Pandit A and Dror RO: The art
and science of molecular docking. Annu Rev Biochem. 93:389–410.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kaiyun T, Xiaotong X, Min L, Yongrong W,
Xuyi T, Fu S, Jinwen G and Gaoyan K: Jiawei duhuo jisheng mixture
mitigates osteoarthritis progression in rabbits by inhibiting
inflammation: A network pharmacology and experimental approach.
Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 28:2107–2131. 2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ding Z, Lu Y, Zhao J, Zhang D and Gao B:
Network pharmacology and molecular dynamics identified potential
androgen receptor-targeted metabolites in crocus alatavicus. Int J
Mol Sci. 26(3533)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kumari R and Kumar R: Open Source Drug
Discovery Consortium. Lynn A: g_mmpbsa-a GROMACS tool for
high-throughput MM-PBSA calculations. J Chem Inf Model.
54:1951–1962. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Xuan W, Wu X, Zheng L, Jia H, Zhang X,
Zhang X and Cao B: Gut microbiota-derived acetic acids promoted
sepsis-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome by delaying
neutrophil apoptosis through FABP4. Cell Mol Life Sci.
81(438)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Huang X, Zhu W, Zhang H, Qiu S and Shao H:
SARS-CoV-2 N protein induces alveolar epithelial apoptosis via
NLRP3 pathway in ARDS. Int Immunopharmacol.
144(113503)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Jeong EJ, Choi JJ, Lee SY and Kim YS: The
effects of ML385 on head and neck squamous cell carcinoma:
implications for NRF2 inhibition as a therapeutic strategy. Int J
Mol Sci. 25(7011)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Chen J, Ding W, Zhang Z, Li Q, Wang M,
Feng J, Zhang W, Cao L, Ji X, Nie S and Sun Z: Shenfu injection
targets the PI3K-AKT pathway to regulate autophagy and apoptosis in
acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by sepsis.
Phytomedicine. 129(155627)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
McGinn R, Fergusson DA, Stewart DJ,
Kristof AS, Barron CC, Thebaud B, McIntyre L, Stacey D, Liepmann M,
Dodelet-Devillers A, et al: Surrogate humane endpoints in small
animal models of acute lung injury: A modified delphi consensus
study of researchers and laboratory animal veterinarians. Crit Care
Med. 49:311–323. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zingarelli B: First do no harm: A proposal
of an expert-guided framework of surrogate humane endpoints in
preclinical models of acute lung injury. Crit Care Med. 49:373–375.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kang JY, Xu MM, Sun Y, Ding ZX, Wei YY,
Zhang DW, Wang YG, Shen JL, Wu HM and Fei GH: Melatonin attenuates
LPS-induced pyroptosis in acute lung injury by inhibiting
NLRP3-GSDMD pathway via activating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling axis. INT
Immunopharmacol. 109(108782)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Bahri S, Jameleddine S and Shlyonsky V:
Relevance of carnosic acid to the treatment of several health
disorders: Molecular targets and mechanisms. Biomed Pharmacother.
84:569–582. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
He F, Ru X and Wen T: NRF2, a
transcription factor for stress response and beyond. Int J Mol Sci.
21(4777)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Pinela J, Dias MI, Pereira C and
Alonso-Esteban JI: Antioxidant activity of foods and natural
products. Molecules. 29(1814)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Cardoso SM and Fassio A: The antioxidant
capacities of natural products 2019. Molecules.
25(5676)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Qiu Y, Chen S, Yu M, Shi J, Liu J, Li X,
Chen J, Sun X, Huang G and Zheng C: Natural products from
marine-derived fungi with anti-inflammatory activity. Mar Drugs.
22(433)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Moudgil KD and Venkatesha SH: The
anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory activities of natural
products to control autoimmune inflammation. Int J Mol Sci.
24(95)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Heard SC, Wu G and Winter JM: Antifungal
natural products. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 69:232–241. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lewis K, Lee RE, Brötz-Oesterhelt H,
Hiller S, Rodnina MV, Schneider T, Weingarth M and Wohlgemuth I:
Sophisticated natural products as antibiotics. Nature. 632:39–49.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Amaral-Machado L, Oliveira WN, Rodrigues
VM, Albuquerque NA, Alencar ÉN and Egito EST: Could natural
products modulate early inflammatory responses, preventing acute
respiratory distress syndrome in COVID-19-confirmed patients?
Biomed Pharmacother. 134(111143)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Maione F, Cantone V, Pace S, Chini MG,
Bisio A, Romussi G, Pieretti S, Werz O, Koeberle A, Mascolo N and
Bifulco G: Anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity of carnosol and
carnosic acid in vivo and in vitro and in silico analysis of their
target interactions. Br J Pharmacol. 174:1497–1508. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Albadrani GM, Altyar AE, Kensara OA,
Haridy MAM, Zaazouee MS, Elshanbary AA, Sayed AA and Abdel-Daim MM:
Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-DNA damage effects of
carnosic acid against aflatoxin B1-induced hepatic, renal, and
cardiac toxicities in rats. Toxicol Res (Camb).
13(tfae083)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Dhlamini Q, Wang W, Feng G, Chen A, Chong
L, Li X, Li Q, Wu J, Zhou D, Wang J, et al: FGF1 alleviates
LPS-induced acute lung injury via suppression of inflammation and
oxidative stress. Mol Med. 28(73)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Gong L, Shen Y, Wang S, Wang X, Ji H, Wu
X, Hu L and Zhu L: Nuclear SPHK2/S1P induces oxidative stress and
NLRP3 inflammasome activation via promoting p53 acetylation in
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Cell Death Discov.
9(12)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zhu YS, Shah SAA, Yang BY, Fan SS, He L,
Sun YR, Shang WB, Qian Y and Zhang X: Gen-17, a beta-methyl
derivative of Genipin, attenuates LPS-induced ALI by regulating
Keap1-Nrf2/HO-1 and suppressing NF-κB and MAPK-dependent signaling
pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis.
1871(167770)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Huang J, Zhu Y, Li S, Jiang H, Chen N,
Xiao H, Liu J, Liang D, Zheng Q, Tang J and Meng X: Licochalcone B
confers protective effects against LPS-Induced acute lung injury in
cells and mice through the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway. Redox Rep.
28(2243423)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Song Y, Gou Y, Gao J, Chen D, Zhang H,
Zhao W, Qian F, Xu A and Shen Y: Lomerizine attenuates LPS-induced
acute lung injury by inhibiting the macrophage activation through
reducing Ca(2+) influx. Front Pharmacol. 14(1236469)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Sayson SG, Ashbaugh A, Porollo A, Smulian
G and Cushion MT: Pneumocystis murina promotes inflammasome
formation and NETosis during Pneumocystis pneumonia. mBio.
15(e140924)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Che J, Wang H, Dong J, Wu Y, Zhang H, Fu L
and Zhang J: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived
exosomes attenuate neuroinflammation and oxidative stress through
the NRF2/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther.
30(e14454)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Rajan S, Tryphena KP, Khan S, Vora L,
Srivastava S, Singh SB and Khatri DK: Understanding the involvement
of innate immunity and the Nrf2-NLRP3 axis on mitochondrial health
in Parkinson's disease. Ageing Res Rev. 87(101915)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Sun YY, Zhu HJ, Zhao RY, Zhou SY, Wang MQ,
Yang Y and Guo ZN: Remote ischemic conditioning attenuates
oxidative stress and inflammation via the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in MCAO
mice. Redox Biol. 66(102852)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Han QQ and Le W: NLRP3
inflammasome-mediated neuroinflammation and related mitochondrial
impairment in Parkinson's disease. Neurosci Bull. 39:832–844.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Qiu WQ, Ai W, Zhu FD, Zhang Y, Guo MS, Law
BY, Wu JM, Wong VK, Tang Y, Yu L, et al: Polygala saponins inhibit
NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neuroinflammation via SHP-2-Mediated
mitophagy. Free Radical Bio Med. 179:76–94. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|