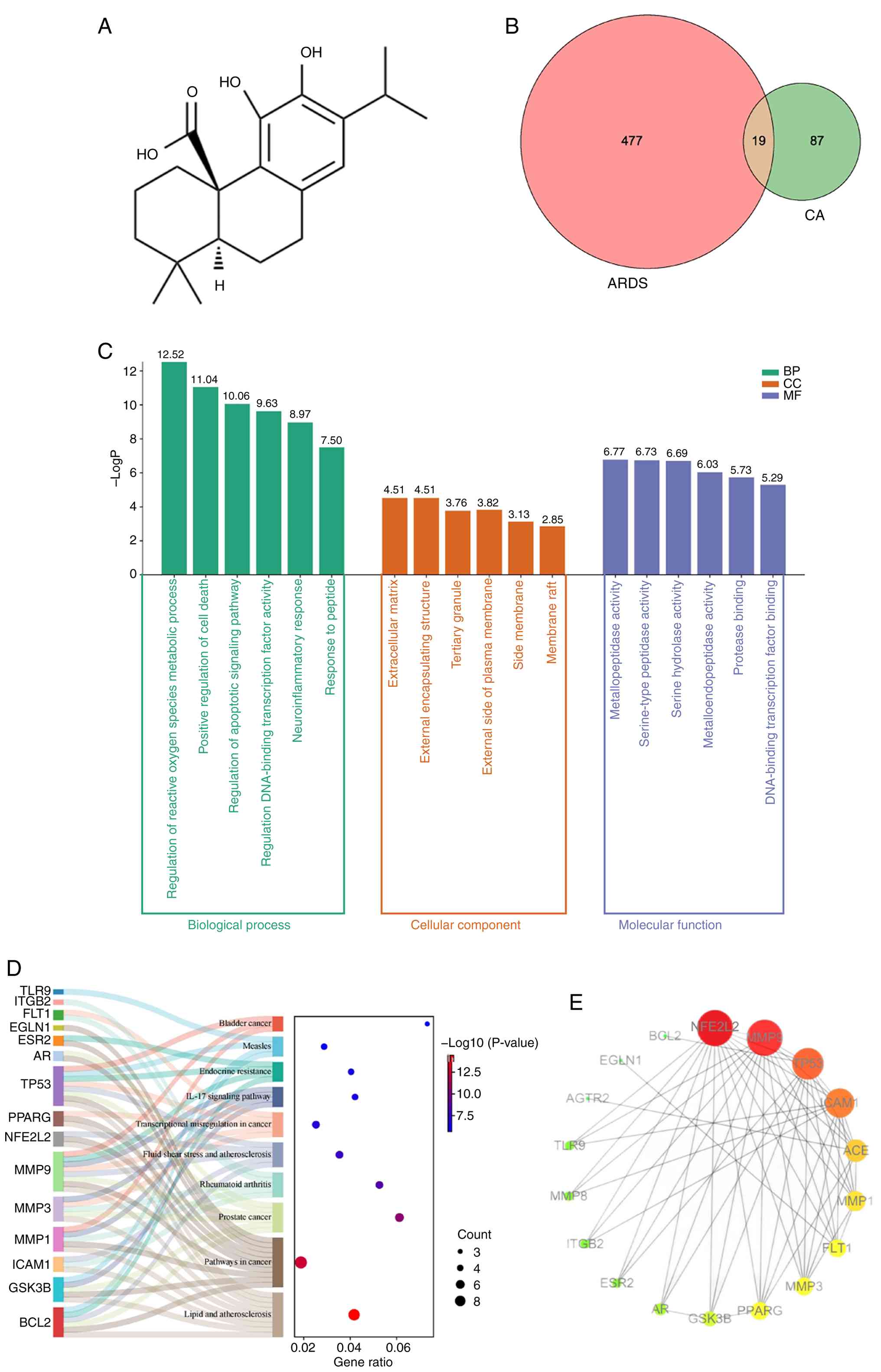
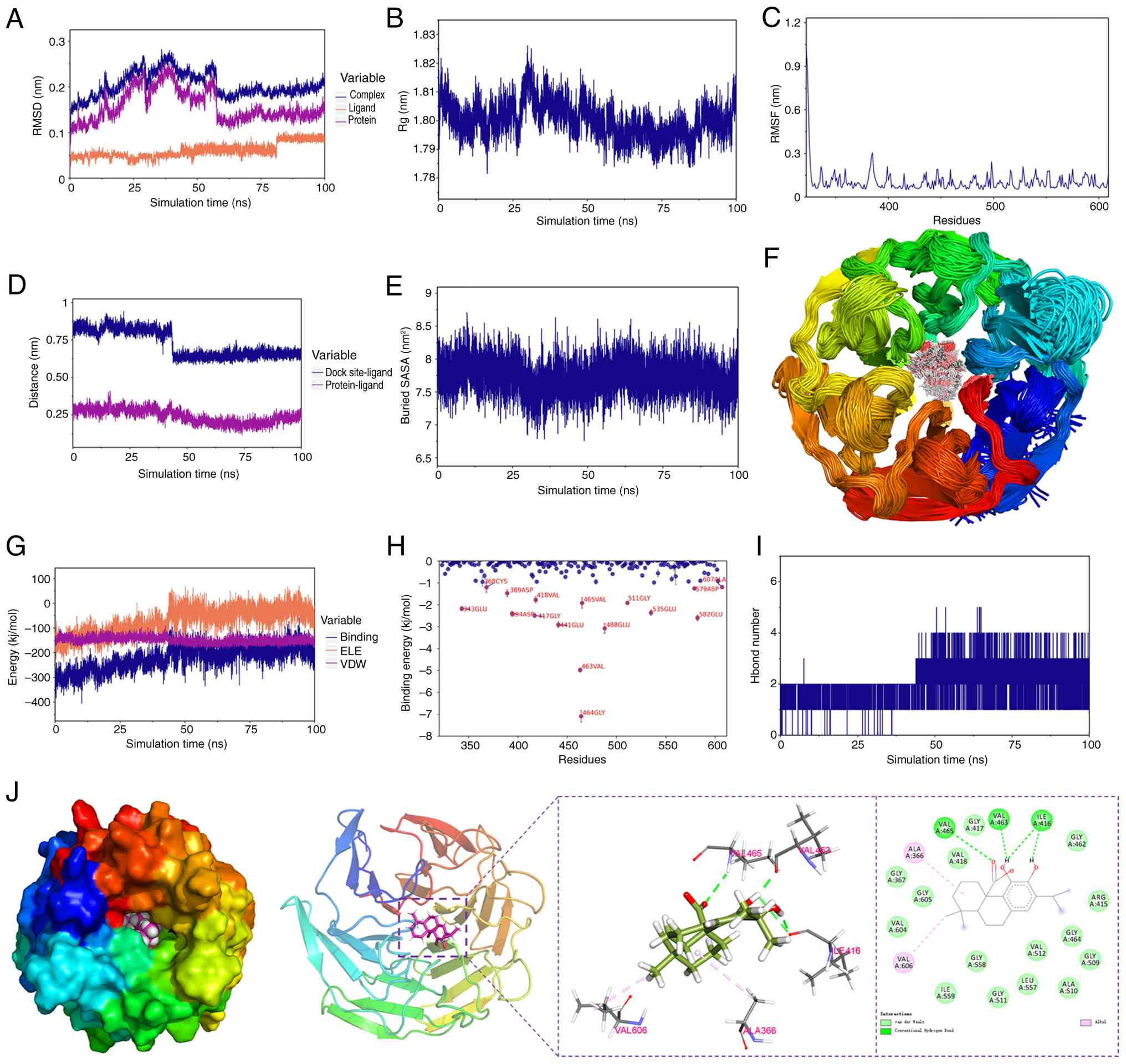
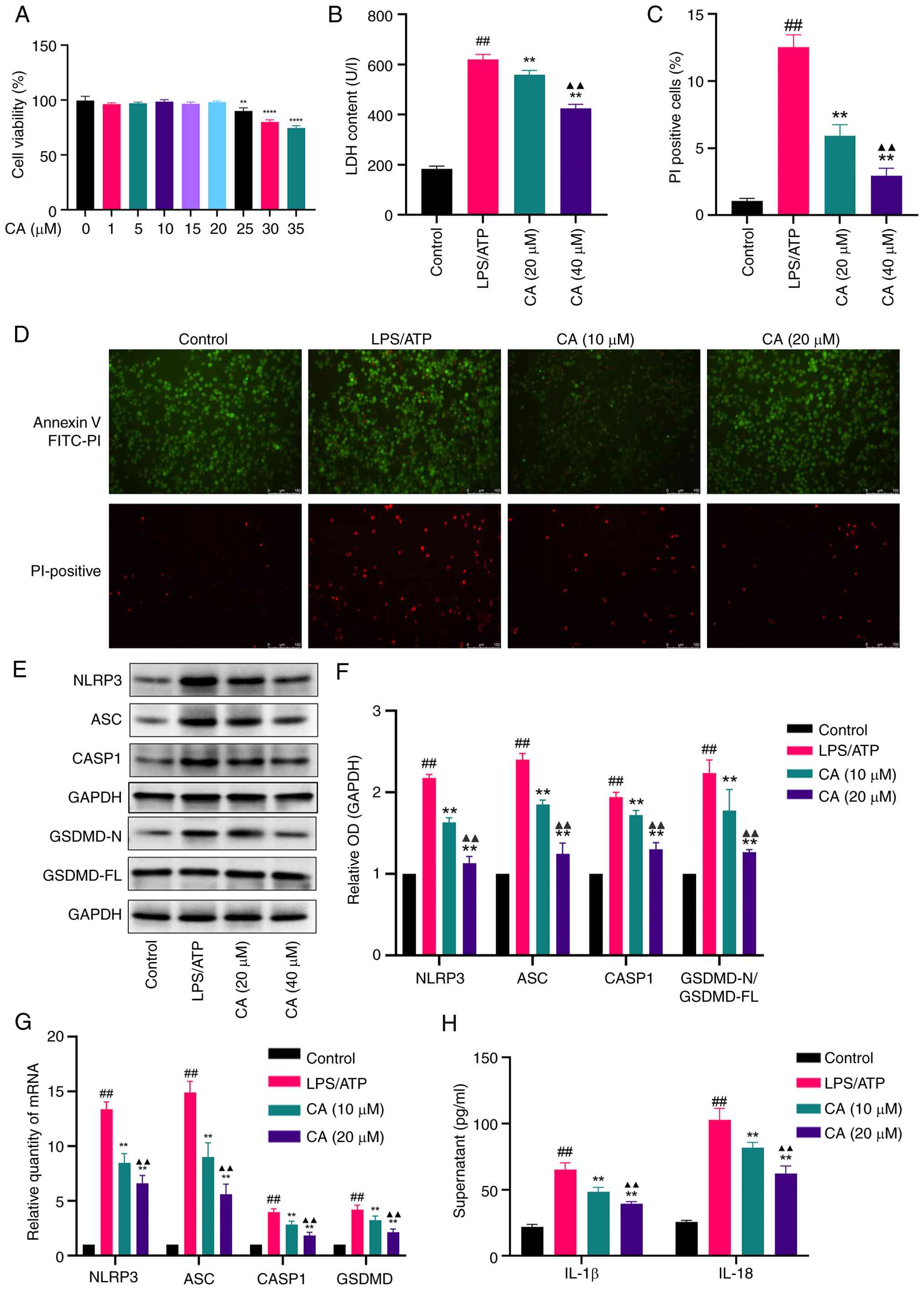
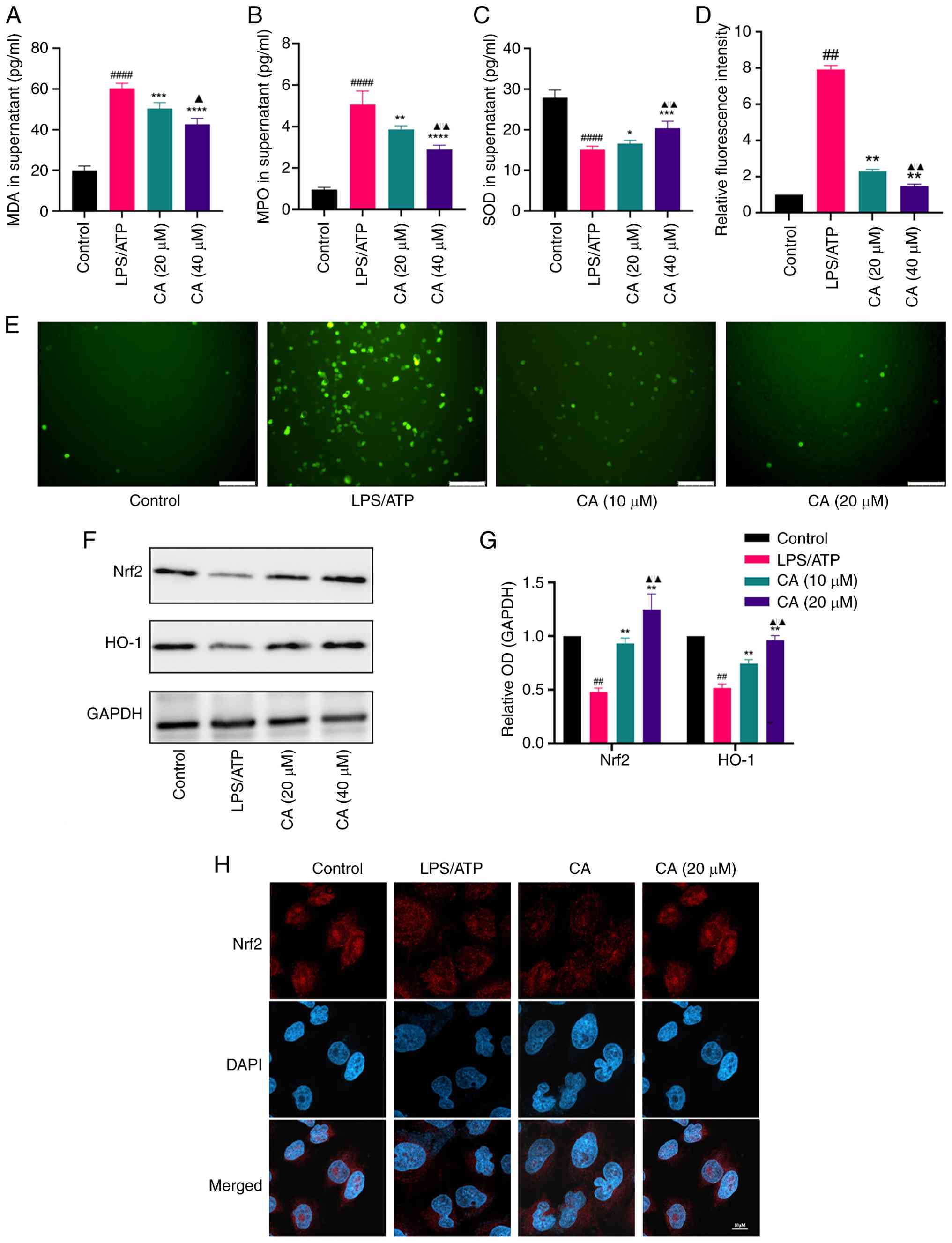
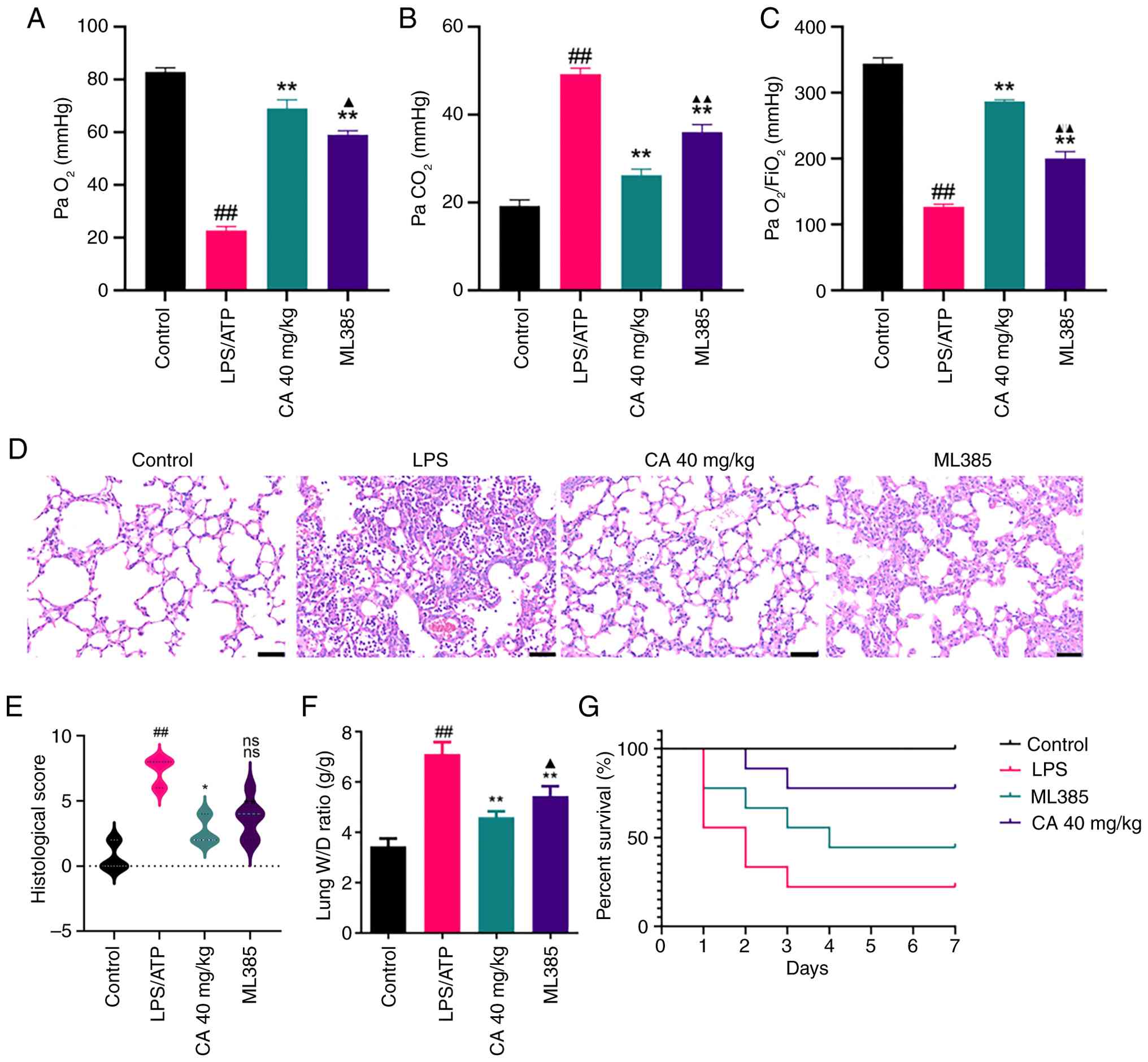
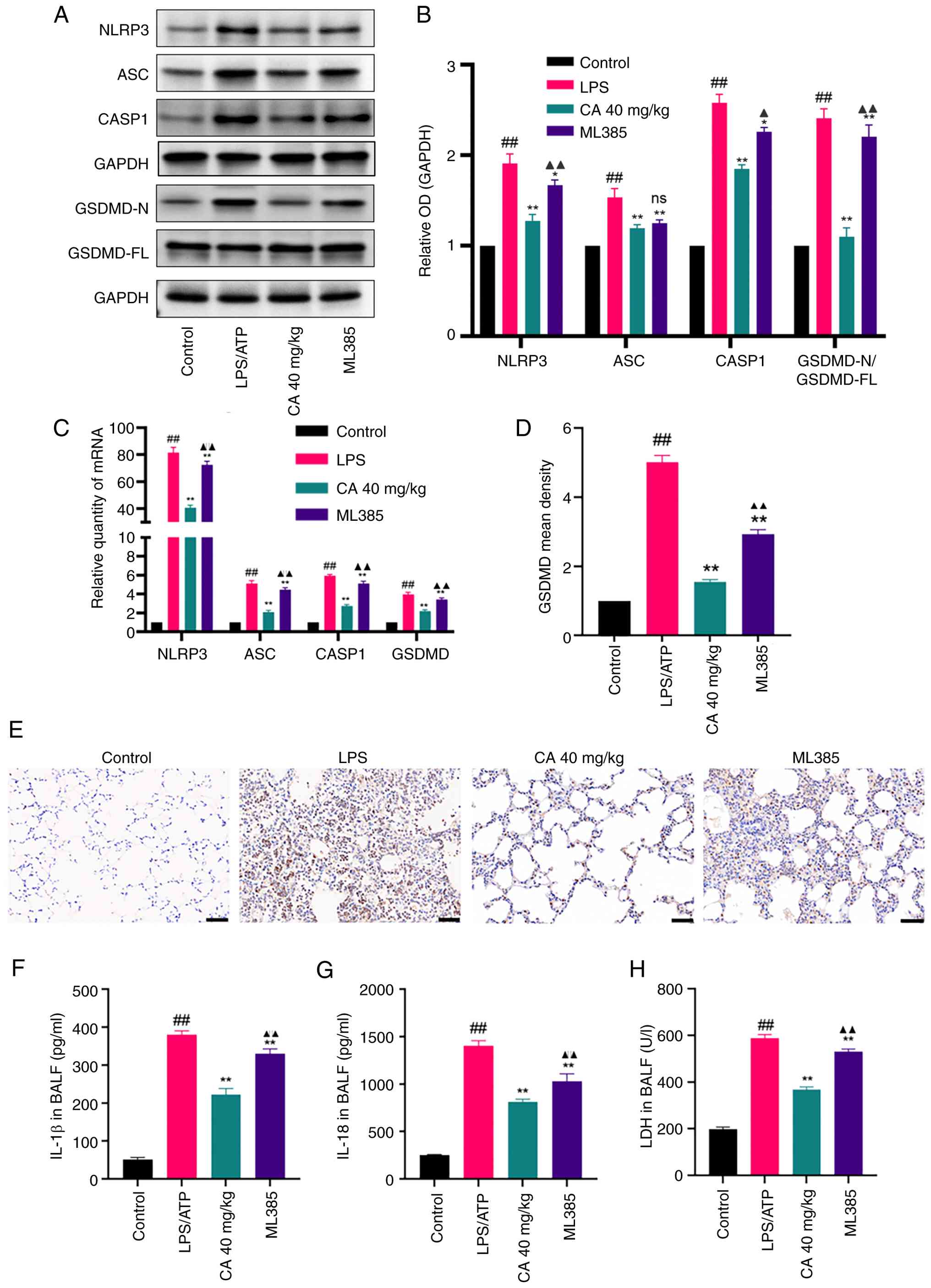
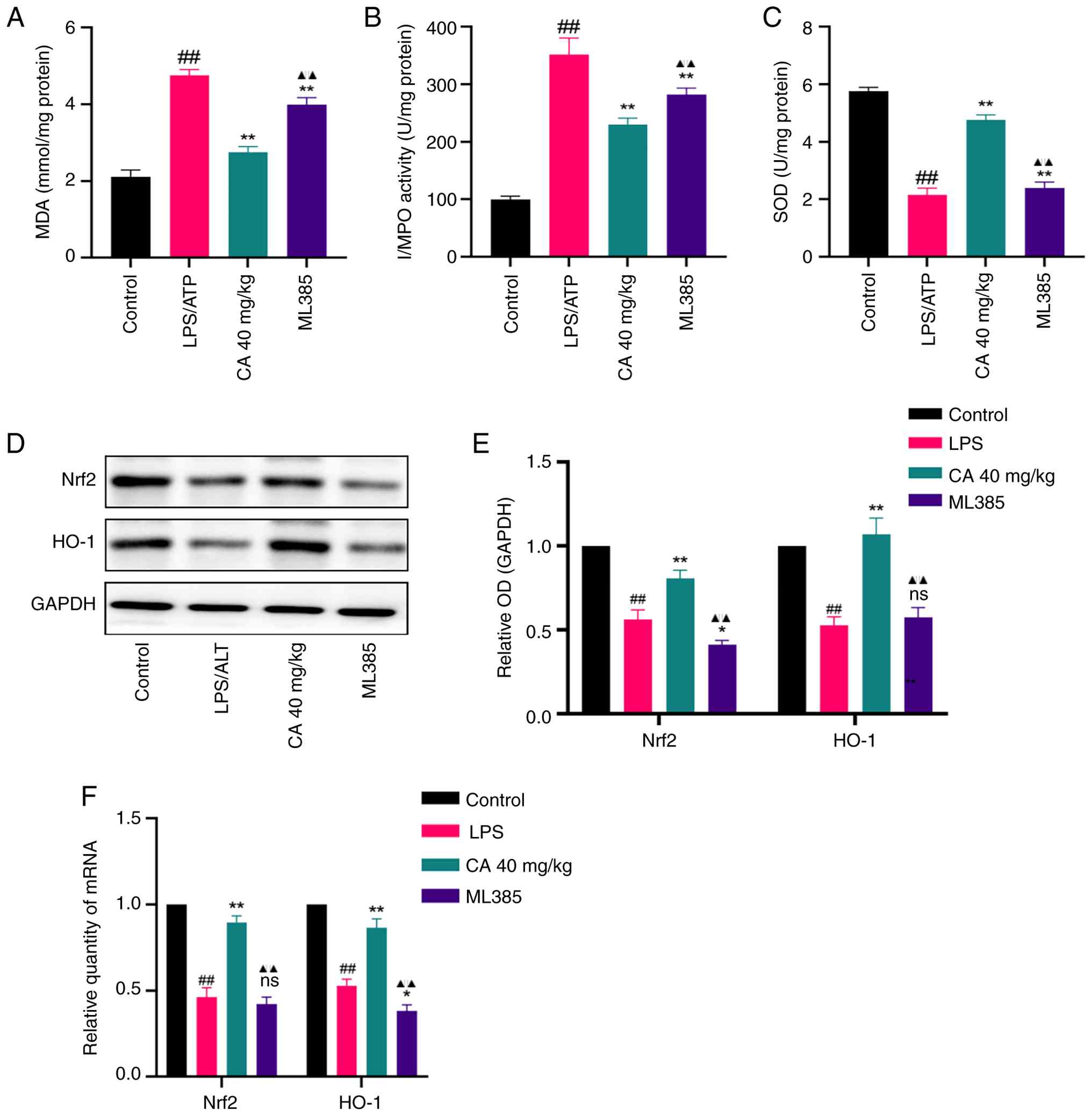
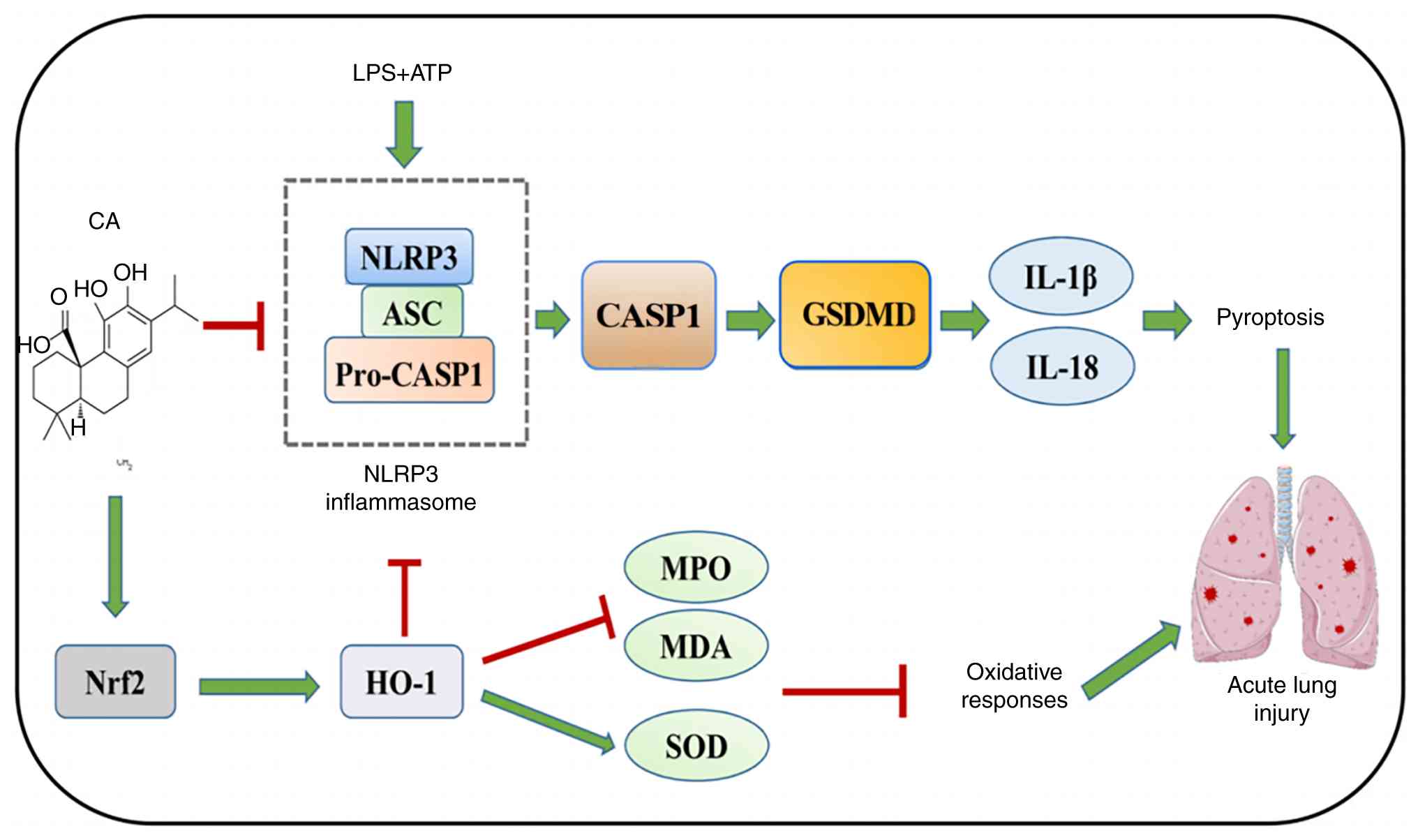
|
1
|
Gorman EA, O'Kane CM and McAuley DF: Acute
respiratory distress syndrome in adults: diagnosis, outcomes,
long-term sequelae, and management. Lancet. 400:1157–1170.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wick KD, Ware LB and Matthay MA: Acute
respiratory distress syndrome. BMJ. 387(e76612)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Matthay MA, Arabi Y, Arroliga AC, Bernard
G, Bersten AD, Brochard LJ, Calfee CS, Combes A, Daniel BM,
Ferguson ND, et al: A new global definition of acute respiratory
distress syndrome. Am J Resp Crit Care. 209:37–47. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
He YQ, Zhou CC, Yu LY, Wang L, Deng JL,
Tao YL, Zhang F and Chen WS: Natural product derived phytochemicals
in managing acute lung injury by multiple mechanisms. Pharmacol
Res. 163(105224)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Farhadi F, Baradaran Rahimi V, Mohamadi N
and Askari VR: Effects of rosmarinic acid, carnosic acid, rosmanol,
carnosol, and ursolic acid on the pathogenesis of respiratory
diseases. Biofactors. 49:478–501. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
McCord JM, Hybertson BM, Cota-Gomez A and
Gao B: Nrf2 activator PB125® as a carnosic acid-based therapeutic
agent against respiratory viral diseases, including COVID-19. Free
Radical Bio Med. 175:56–64. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zhang D, Lee B, Nutter A, Song P,
Dolatabadi N, Parker J, Sanz-Blasco S, Newmeyer T, Ambasudhan R,
McKercher SR, et al: Protection from cyanide-induced brain injury
by the Nrf2 transcriptional activator carnosic acid. J Neurochem.
133:898–908. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhang C, Zhao M, Wang B, Su Z, Guo B, Qin
L, Zhang W and Zheng R: The Nrf2-NLRP3-caspase-1 axis mediates the
neuroprotective effects of Celastrol in Parkinson's disease. Redox
Biol. 47(102134)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Arioz BI, Tastan B, Tarakcioglu E, Tufekci
KU, Olcum M, Ersoy N, Bagriyanik A, Genc K and Genc S: Melatonin
attenuates LPS-Induced acute depressive-like behaviors and
microglial NLRP3 inflammasome activation through the SIRT1/Nrf2
pathway. Front Immunol. 10(1511)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Xu L, Zhu Y, Li C, Wang Q, Ma L, Wang J
and Zhang S: Small extracellular vesicles derived from
Nrf2-overexpressing human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells protect
against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting
NLRP3. Biol Direct. 17(35)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Dhar R, Rana MN, Zhang L, Li Y, Li N, Hu
Z, Yan C, Wang X, Zheng X, Liu H, et al: Phosphodiesterase 4B is
required for NLRP3 inflammasome activation by positive feedback
with Nrf2 in the early phase of LPS-induced acute lung injury. Free
Radical Bio Med. 176:378–391. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhou Y, Zhou B, Pache L, Chang M,
Khodabakhshi AH, Tanaseichuk O, Benner C and Chanda SK: Metascape
provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of
systems-level datasets. Nat Commun. 10(1523)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Gene Ontology Consortium. Gene Ontology
Consortium: Going forward. Nucleic Acids Res. 43(Database
issue):D1049–D1056. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Paggi JM, Pandit A and Dror RO: The art
and science of molecular docking. Annu Rev Biochem. 93:389–410.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kaiyun T, Xiaotong X, Min L, Yongrong W,
Xuyi T, Fu S, Jinwen G and Gaoyan K: Jiawei duhuo jisheng mixture
mitigates osteoarthritis progression in rabbits by inhibiting
inflammation: A network pharmacology and experimental approach.
Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 28:2107–2131. 2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ding Z, Lu Y, Zhao J, Zhang D and Gao B:
Network pharmacology and molecular dynamics identified potential
androgen receptor-targeted metabolites in crocus alatavicus. Int J
Mol Sci. 26(3533)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kumari R and Kumar R: Open Source Drug
Discovery Consortium. Lynn A: g_mmpbsa-a GROMACS tool for
high-throughput MM-PBSA calculations. J Chem Inf Model.
54:1951–1962. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Xuan W, Wu X, Zheng L, Jia H, Zhang X,
Zhang X and Cao B: Gut microbiota-derived acetic acids promoted
sepsis-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome by delaying
neutrophil apoptosis through FABP4. Cell Mol Life Sci.
81(438)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Huang X, Zhu W, Zhang H, Qiu S and Shao H:
SARS-CoV-2 N protein induces alveolar epithelial apoptosis via
NLRP3 pathway in ARDS. Int Immunopharmacol.
144(113503)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Jeong EJ, Choi JJ, Lee SY and Kim YS: The
effects of ML385 on head and neck squamous cell carcinoma:
implications for NRF2 inhibition as a therapeutic strategy. Int J
Mol Sci. 25(7011)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Chen J, Ding W, Zhang Z, Li Q, Wang M,
Feng J, Zhang W, Cao L, Ji X, Nie S and Sun Z: Shenfu injection
targets the PI3K-AKT pathway to regulate autophagy and apoptosis in
acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by sepsis.
Phytomedicine. 129(155627)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
McGinn R, Fergusson DA, Stewart DJ,
Kristof AS, Barron CC, Thebaud B, McIntyre L, Stacey D, Liepmann M,
Dodelet-Devillers A, et al: Surrogate humane endpoints in small
animal models of acute lung injury: A modified delphi consensus
study of researchers and laboratory animal veterinarians. Crit Care
Med. 49:311–323. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zingarelli B: First do no harm: A proposal
of an expert-guided framework of surrogate humane endpoints in
preclinical models of acute lung injury. Crit Care Med. 49:373–375.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kang JY, Xu MM, Sun Y, Ding ZX, Wei YY,
Zhang DW, Wang YG, Shen JL, Wu HM and Fei GH: Melatonin attenuates
LPS-induced pyroptosis in acute lung injury by inhibiting
NLRP3-GSDMD pathway via activating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling axis. INT
Immunopharmacol. 109(108782)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Bahri S, Jameleddine S and Shlyonsky V:
Relevance of carnosic acid to the treatment of several health
disorders: Molecular targets and mechanisms. Biomed Pharmacother.
84:569–582. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
He F, Ru X and Wen T: NRF2, a
transcription factor for stress response and beyond. Int J Mol Sci.
21(4777)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Pinela J, Dias MI, Pereira C and
Alonso-Esteban JI: Antioxidant activity of foods and natural
products. Molecules. 29(1814)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Cardoso SM and Fassio A: The antioxidant
capacities of natural products 2019. Molecules.
25(5676)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Qiu Y, Chen S, Yu M, Shi J, Liu J, Li X,
Chen J, Sun X, Huang G and Zheng C: Natural products from
marine-derived fungi with anti-inflammatory activity. Mar Drugs.
22(433)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Moudgil KD and Venkatesha SH: The
anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory activities of natural
products to control autoimmune inflammation. Int J Mol Sci.
24(95)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Heard SC, Wu G and Winter JM: Antifungal
natural products. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 69:232–241. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lewis K, Lee RE, Brötz-Oesterhelt H,
Hiller S, Rodnina MV, Schneider T, Weingarth M and Wohlgemuth I:
Sophisticated natural products as antibiotics. Nature. 632:39–49.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Amaral-Machado L, Oliveira WN, Rodrigues
VM, Albuquerque NA, Alencar ÉN and Egito EST: Could natural
products modulate early inflammatory responses, preventing acute
respiratory distress syndrome in COVID-19-confirmed patients?
Biomed Pharmacother. 134(111143)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Maione F, Cantone V, Pace S, Chini MG,
Bisio A, Romussi G, Pieretti S, Werz O, Koeberle A, Mascolo N and
Bifulco G: Anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity of carnosol and
carnosic acid in vivo and in vitro and in silico analysis of their
target interactions. Br J Pharmacol. 174:1497–1508. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Albadrani GM, Altyar AE, Kensara OA,
Haridy MAM, Zaazouee MS, Elshanbary AA, Sayed AA and Abdel-Daim MM:
Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-DNA damage effects of
carnosic acid against aflatoxin B1-induced hepatic, renal, and
cardiac toxicities in rats. Toxicol Res (Camb).
13(tfae083)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Dhlamini Q, Wang W, Feng G, Chen A, Chong
L, Li X, Li Q, Wu J, Zhou D, Wang J, et al: FGF1 alleviates
LPS-induced acute lung injury via suppression of inflammation and
oxidative stress. Mol Med. 28(73)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Gong L, Shen Y, Wang S, Wang X, Ji H, Wu
X, Hu L and Zhu L: Nuclear SPHK2/S1P induces oxidative stress and
NLRP3 inflammasome activation via promoting p53 acetylation in
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Cell Death Discov.
9(12)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zhu YS, Shah SAA, Yang BY, Fan SS, He L,
Sun YR, Shang WB, Qian Y and Zhang X: Gen-17, a beta-methyl
derivative of Genipin, attenuates LPS-induced ALI by regulating
Keap1-Nrf2/HO-1 and suppressing NF-κB and MAPK-dependent signaling
pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis.
1871(167770)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Huang J, Zhu Y, Li S, Jiang H, Chen N,
Xiao H, Liu J, Liang D, Zheng Q, Tang J and Meng X: Licochalcone B
confers protective effects against LPS-Induced acute lung injury in
cells and mice through the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway. Redox Rep.
28(2243423)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Song Y, Gou Y, Gao J, Chen D, Zhang H,
Zhao W, Qian F, Xu A and Shen Y: Lomerizine attenuates LPS-induced
acute lung injury by inhibiting the macrophage activation through
reducing Ca(2+) influx. Front Pharmacol. 14(1236469)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Sayson SG, Ashbaugh A, Porollo A, Smulian
G and Cushion MT: Pneumocystis murina promotes inflammasome
formation and NETosis during Pneumocystis pneumonia. mBio.
15(e140924)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Che J, Wang H, Dong J, Wu Y, Zhang H, Fu L
and Zhang J: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived
exosomes attenuate neuroinflammation and oxidative stress through
the NRF2/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther.
30(e14454)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Rajan S, Tryphena KP, Khan S, Vora L,
Srivastava S, Singh SB and Khatri DK: Understanding the involvement
of innate immunity and the Nrf2-NLRP3 axis on mitochondrial health
in Parkinson's disease. Ageing Res Rev. 87(101915)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Sun YY, Zhu HJ, Zhao RY, Zhou SY, Wang MQ,
Yang Y and Guo ZN: Remote ischemic conditioning attenuates
oxidative stress and inflammation via the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in MCAO
mice. Redox Biol. 66(102852)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Han QQ and Le W: NLRP3
inflammasome-mediated neuroinflammation and related mitochondrial
impairment in Parkinson's disease. Neurosci Bull. 39:832–844.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Qiu WQ, Ai W, Zhu FD, Zhang Y, Guo MS, Law
BY, Wu JM, Wong VK, Tang Y, Yu L, et al: Polygala saponins inhibit
NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neuroinflammation via SHP-2-Mediated
mitophagy. Free Radical Bio Med. 179:76–94. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|