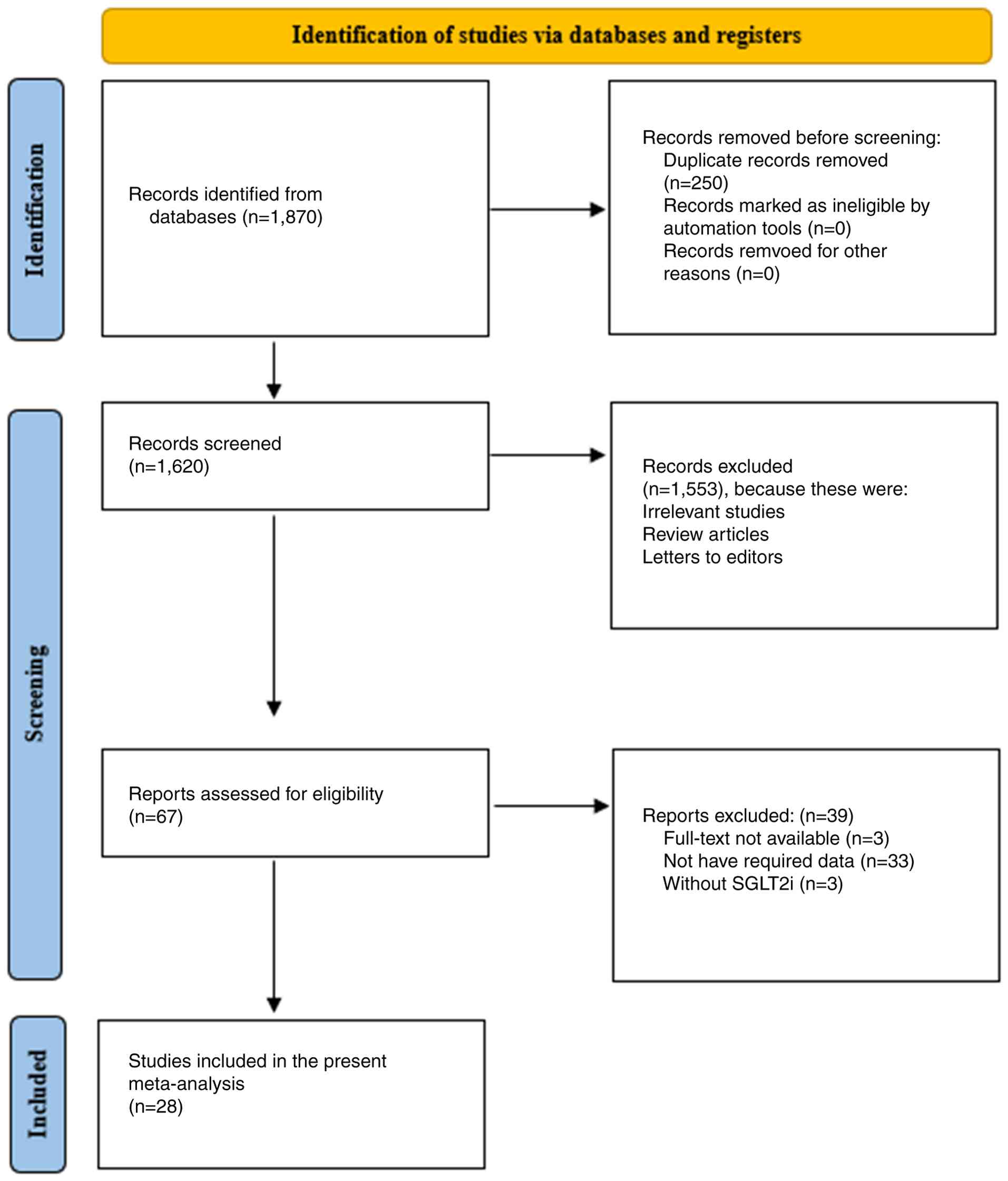
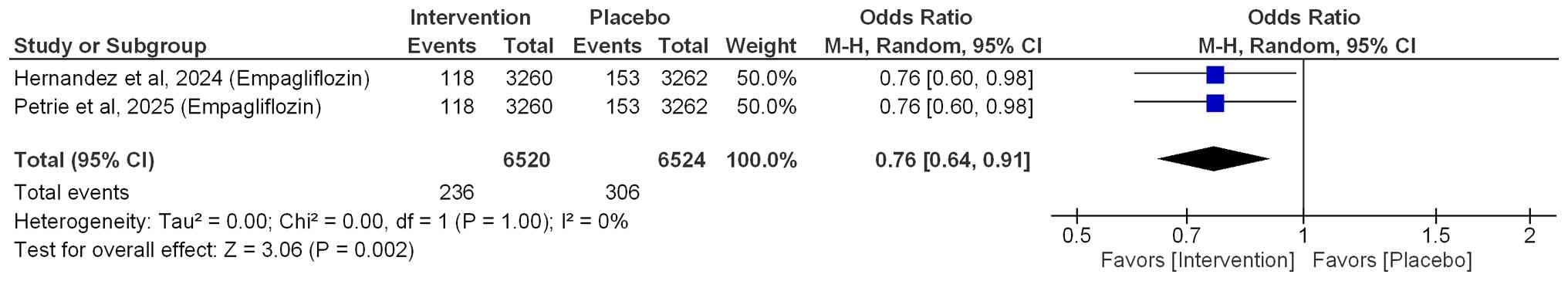
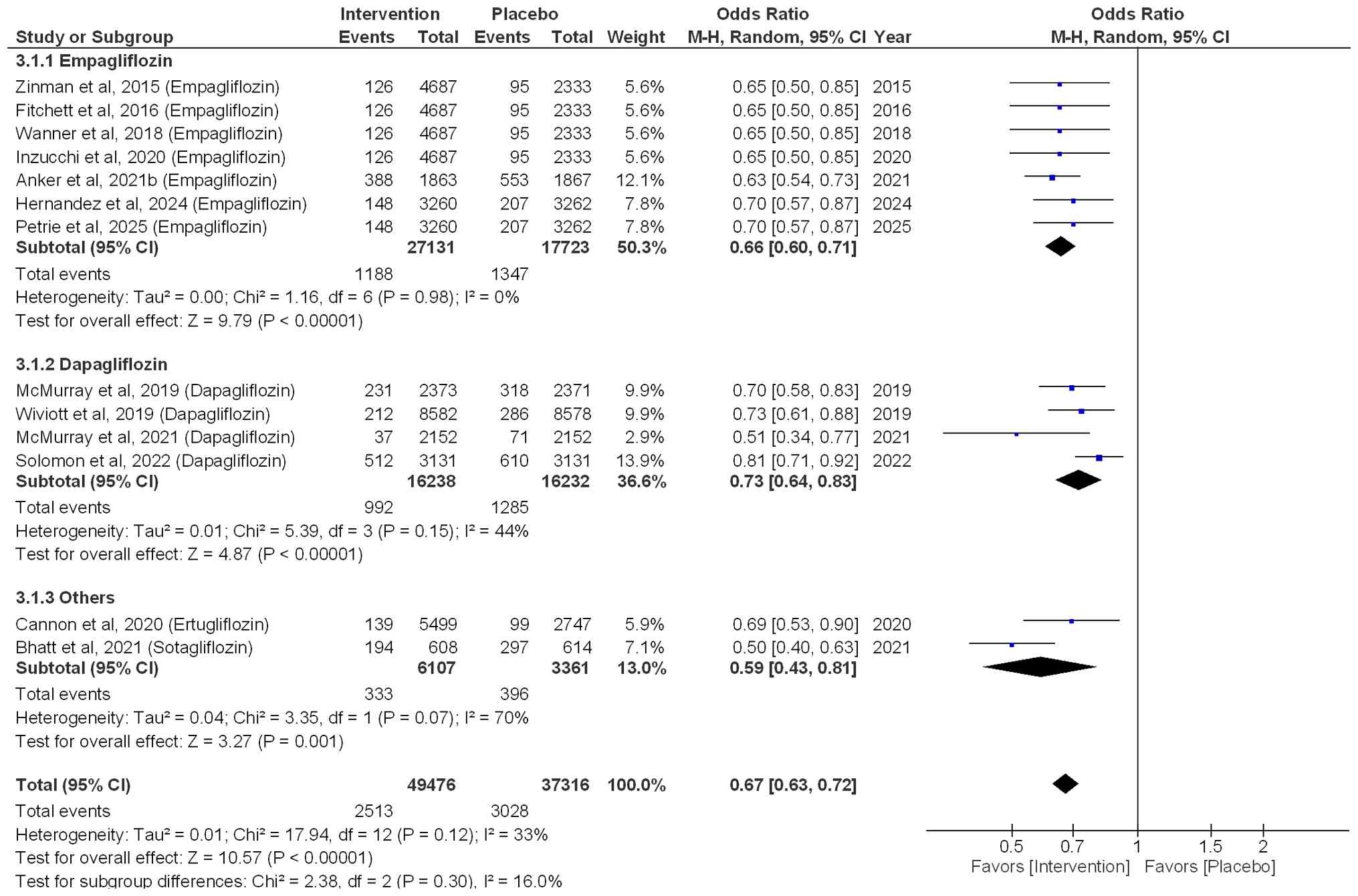
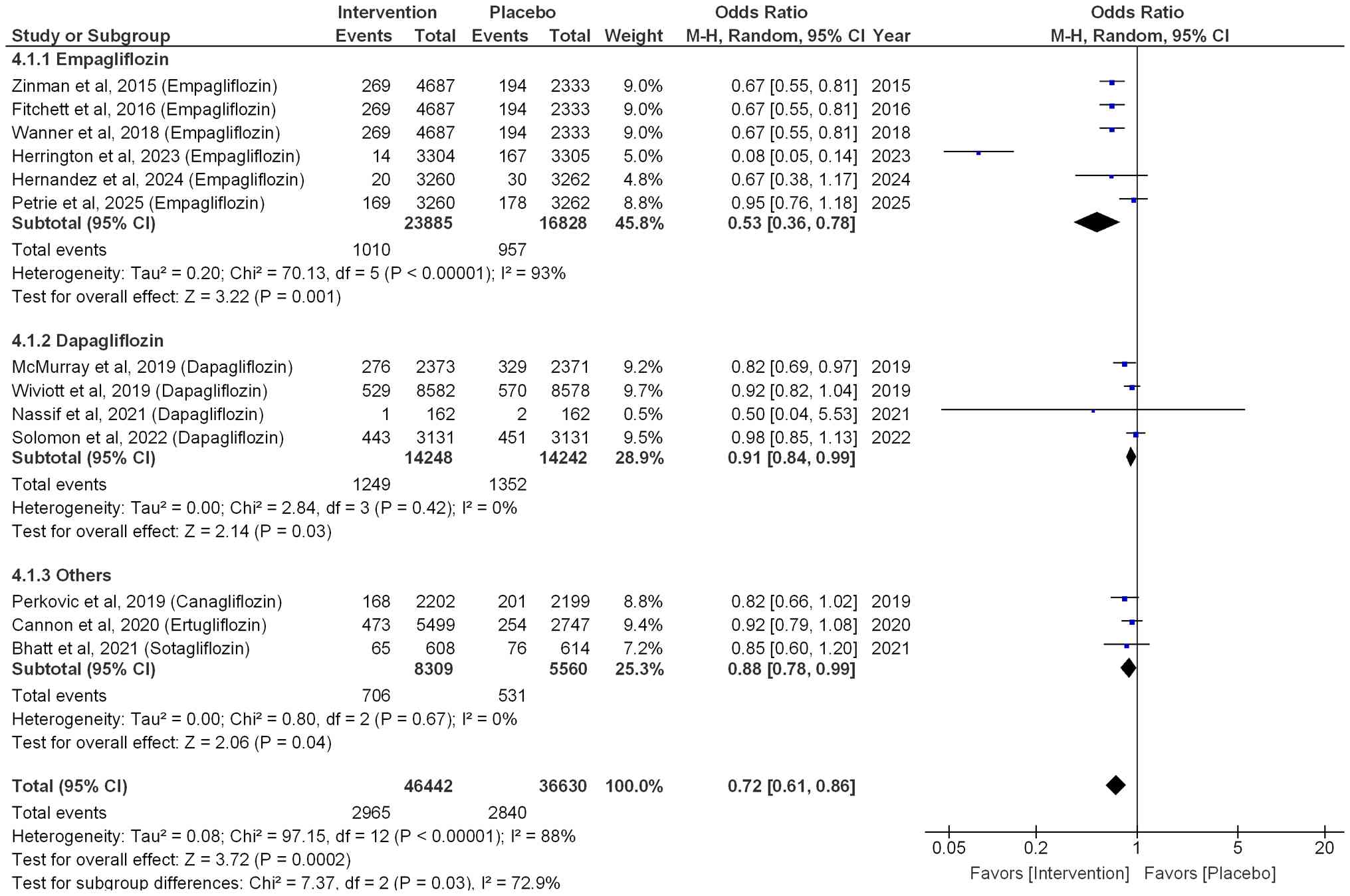
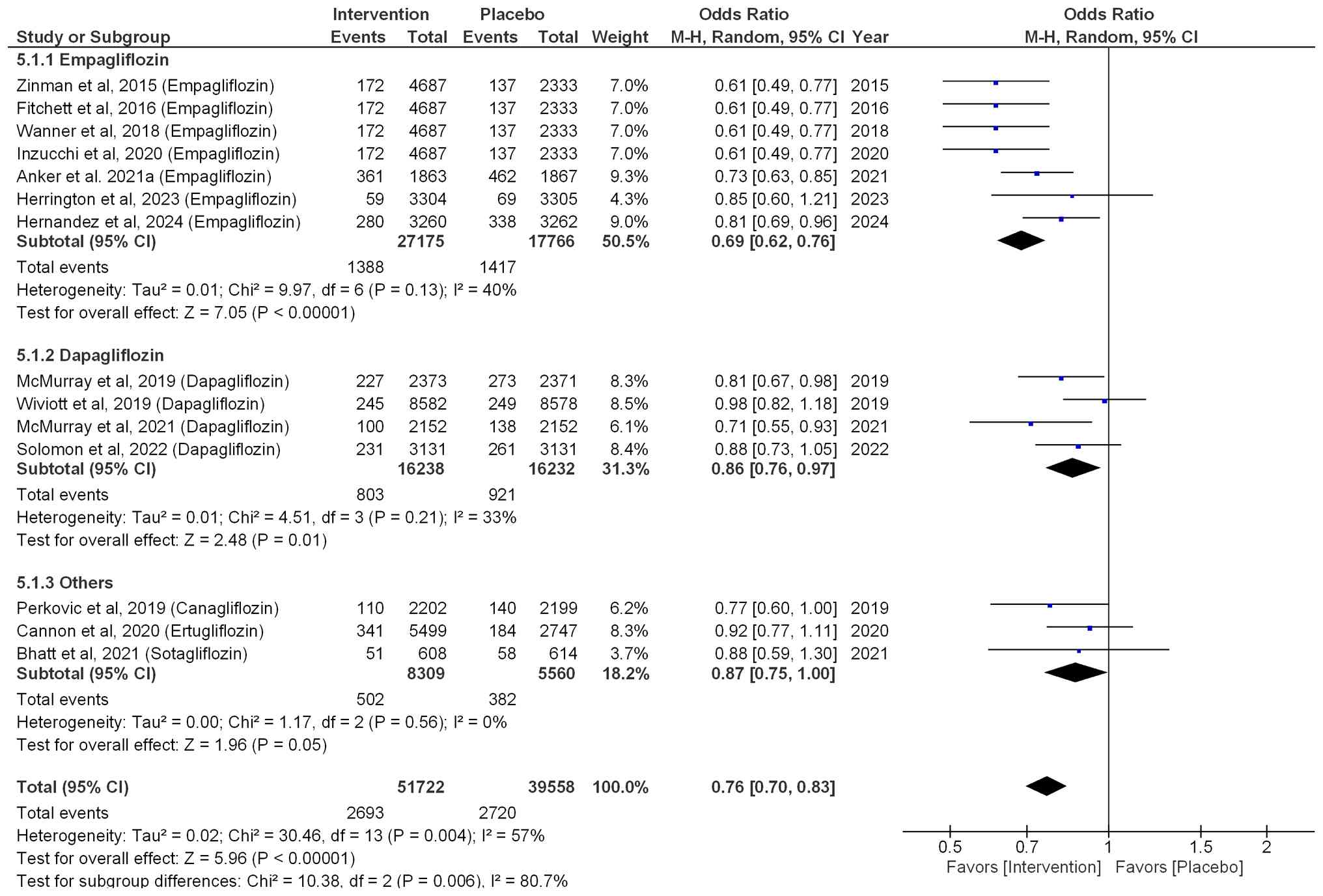
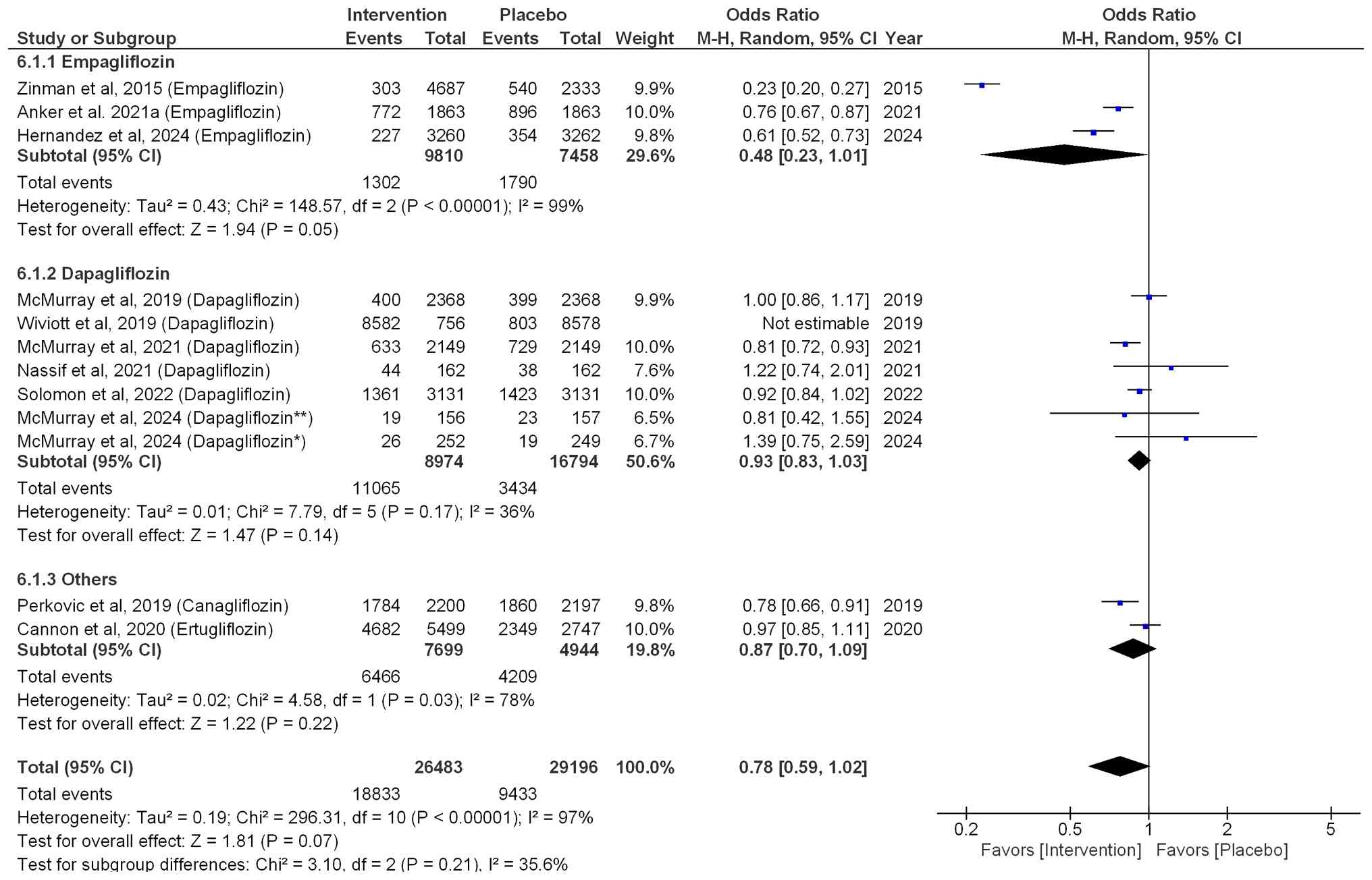
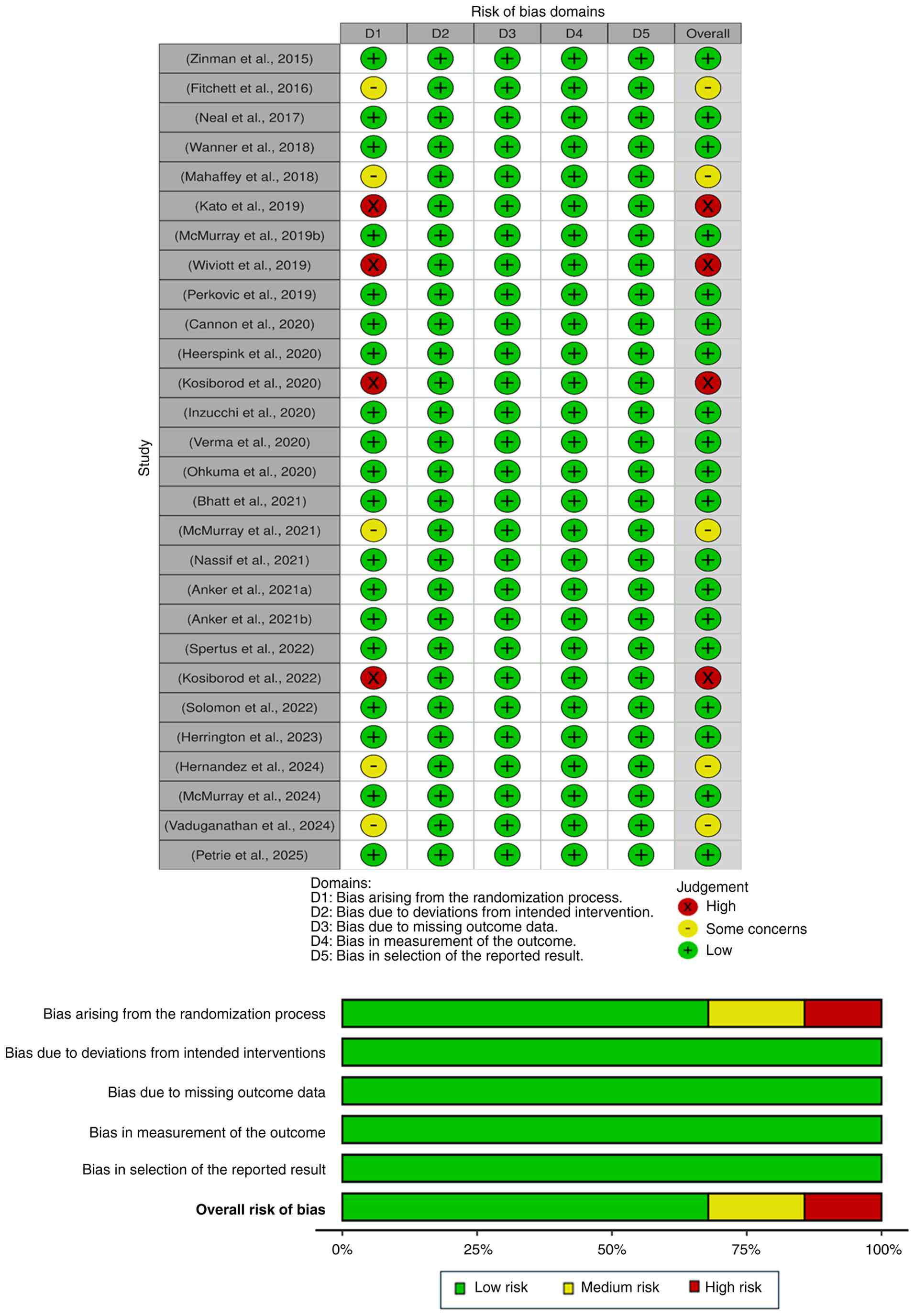
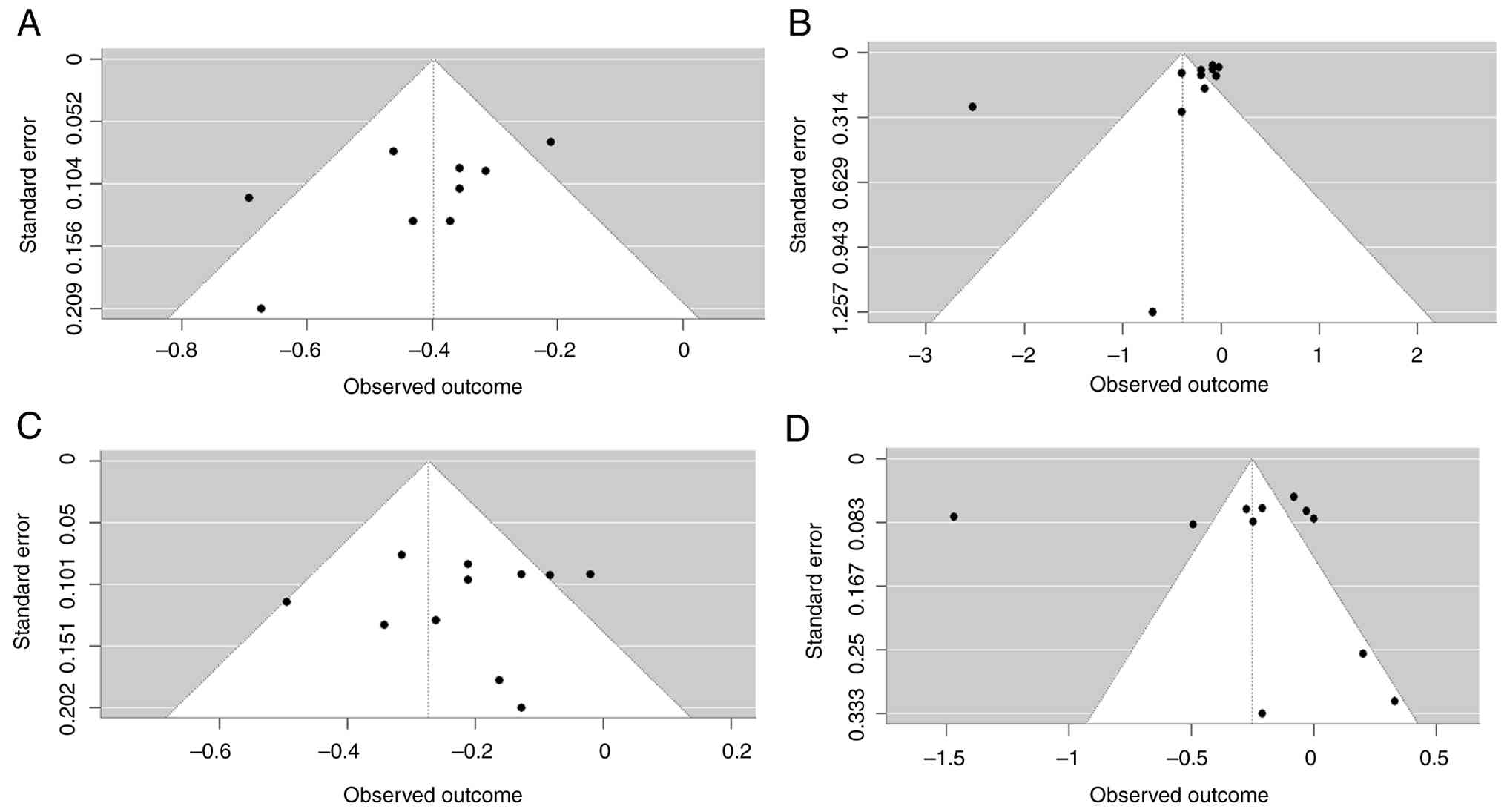
|
1
|
Savarese G, Becher PM, Lund LH, Seferovic
P, Rosano GMC and Coats AJS: Global burden of heart failure: A
comprehensive and updated review of epidemiology. Cardiovasc Res.
118:3272–3287. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sheraliev A: Pathophysiology of heart
failure, hemodynamic changes and their consequences. Mod Sci Res.
4:965–969. 2025.
|
|
3
|
Ran J, Zhou P, Wang J, Zhao X, Huang Y,
Zhou Q, Zhai M and Zhang Y: Global, regional, and national burden
of heart failure and its underlying causes, 1990-2021: Results from
the global burden of disease study 2021. Biomark Res.
13(16)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Dini FL, Pugliese NR, Ameri P, Attanasio
U, Badagliacca R, Correale M, Mercurio V, Tocchetti CG, Agostoni P
and Palazzuoli A: Heart Failure Study Group of the Italian Society
of Cardiology. Right ventricular failure in left heart disease:
From pathophysiology to clinical manifestations and prognosis.
Heart Fail Rev. 28:757–766. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Shah P, Pellicori P, Cuthbert J and Clark
AL: Pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatment for
decompensated heart failure: What is new? Curr Heart Fail Rep.
14:147–157. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Shahim B, Kapelios CJ, Savarese G and Lund
LH: Global public health burden of heart failure: An updated
review. Card Fail Rev. 9(e11)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Talha KM, Anker SD and Butler J: SGLT-2
inhibitors in heart failure: A review of current evidence. Int J
Heart Fail. 5(82)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Salvatore T, Pafundi PC, Galiero R,
Albanese G, Di Martino A, Caturano A, Vetrano E, Rinaldi L and
Sasso FC: The diabetic cardiomyopathy: The contributing
pathophysiological mechanisms. Front Med (Lausanne).
8(695792)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Chen J, Jiang C, Guo M, Zeng Y, Jiang Z,
Zhang D, Tu M, Tan X, Yan P, Xu X, et al: Effects of SGLT2
inhibitors on cardiac function and health status in chronic heart
failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiovasc
Diabetol. 23(2)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Vasquez-Rios G and Nadkarni GN: SGLT2
inhibitors: Emerging roles in the protection against cardiovascular
and kidney disease among diabetic patients. Int J Nephrol Renovasc
Dis. 13:281–296. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Singh J: A Comprehensive Analysis of
SGLT2-inhibition in Type 2 Diabetes and Heart Failure. University
of Dundee, 2019.
|
|
12
|
Fernandes GC, Fernandes A, Cardoso R,
Penalver J, Knijnik L, Mitrani RD, Myerburg RJ and Goldberger JJ:
Association of SGLT2 inhibitors with arrhythmias and sudden cardiac
death in patients with type 2 diabetes or heart failure: A
meta-analysis of 34 randomized controlled trials. Heart rhythm.
18:1098–1105. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Treewaree S, Kulthamrongsri N,
Owattanapanich W and Krittayaphong R: Is it time for class I
recommendation for sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in
heart failure with mildly reduced or preserved ejection fraction?:
An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Cardiovasc
Med. 10(1046194)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
McMurray JJV, DeMets DL, Inzucchi SE,
Køber L, Kosiborod MN, Langkilde AM, Martinez FA, Bengtsson O,
Ponikowski P, Sabatine MS, et al: The dapagliflozin and prevention
of Adverse-outcomes in heart failure (DAPA-HF) trial: Baseline
characteristics. Eur J Heart Fail. 21:1402–1411. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Packer M, Butler J, Zannad F, Filippatos
G, Ferreira JP, Pocock SJ, Carson P, Anand I, Doehner W, Haass M,
et al: Effect of empagliflozin on worsening heart failure events in
patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction:
EMPEROR-preserved trial. Circulation. 144:1284–1294.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Gao M, Bhatia K, Kapoor A, Badimon J,
Pinney SP, Mancini DM, Santos-Gallego CG and Lala A: SGLT2
inhibitors, functional capacity, and quality of life in patients
with heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA
Netw Open. 7(e245135)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Savarese G, Butler J, Lund LH, Bhatt DL
and Anker SD: Cardiovascular effects of non-insulin
glucose-lowering agents: A comprehensive review of trial evidence
and potential cardioprotective mechanisms. Cardiovasc Res.
118:2231–2252. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Banerjee M, Pal R, Nair K and Mukhopadhyay
S: SGLT2 inhibitors and cardiovascular outcomes in heart failure
with mildly reduced and preserved ejection fraction: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Indian Heart J. 75:122–127.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Minisy MM and Abdelaziz A: The role of
SGLT 2 inhibitors in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
(HFpEF): A systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized
controlled trials. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 25(765)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Parums DV: Review articles, systematic
reviews, meta-analysis, and the updated preferred reporting items
for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) 2020 guidelines.
Med Sci Monit. 27(e934475)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
McGuinness LA and Higgins JP: Risk-of-bias
VISualization (robvis): An R package and Shiny web app for
visualizing risk-of-bias assessments. Res Syn Methods. 12:55–61.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
González-Padilla DA and Dahm P: Evaluating
the certainty of evidence in Evidence-based medicine. Euro Urol
Focus. 9:708–710. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Nassif ME, Windsor SL, Borlaug BA, Kitzman
DW, Shah SJ, Tang F, Khariton Y, Malik AO, Khumri T, Umpierrez G,
et al: The SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin in heart failure with
preserved ejection fraction: A multicenter randomized trial. Nat
Med. 27:1954–1960. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Spertus JA, Birmingham MC, Nassif M,
Damaraju CV, Abbate A, Butler J, Lanfear DE, Lingvay I, Kosiborod
MN and Januzzi JL: The SGLT2 inhibitor canagliflozin in heart
failure: The CHIEF-HF remote, patient-centered randomized trial.
Nat Med. 28:809–813. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Vaduganathan M, Cannon CP, Jardine MJ,
Heerspink HJL, Arnott C, Neuen BL, Sarraju A, Gogate J, Seufert J,
Neal B, et al: Effects of canagliflozin on total heart failure
events across the kidney function spectrum: Participant-level
pooled analysis from the CANVAS Program and CREDENCE trial. Eur J
Heart Fail. 26:1967–1975. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
The EMPA-KIDNEY Collaborative Group.
Herrington WG, Staplin N, Wanner C, Green JB, Hauske SJ, Emberson
JR, Preiss D, Judge P, Mayne KJ, et al: Empagliflozin in patients
with chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 388:117–127.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Petrie MC, Udell JA, Anker SD, Harrington
J, Jones WS, Mattheus M, Gasior T, van der Meer P, Amir O, Bahit
MC, et al: Empagliflozin in acute myocardial infarction in patients
with and without type 2 diabetes: A pre-specified analysis of the
EMPACT-MI trial. Eur J Heart Fail. 27:577–588. 2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Perkovic V, Jardine MJ, Neal B, Bompoint
S, Heerspink HJL, Charytan DM, Edwards R, Agarwal R, Bakris G, Bull
S, et al: Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and
nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 380:2295–2306. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Verma S, Sharma A, Zinman B, Ofstad AP,
Fitchett D, Brueckmann M, Wanner C, Zwiener I, George JT, Inzucchi
SE, et al: Empagliflozin reduces the risk of mortality and
hospitalization for heart failure across Thrombolysis In Myocardial
Infarction Risk Score for Heart Failure in Diabetes categories:
Post hoc analysis of the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial. Diabetes Obes
Metab. 22:1141–1150. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Heerspink HJL, Stefánsson BV,
Correa-Rotter R, Chertow GM, Greene T, Hou FF, Mann JFE, McMurray
JJV, Lindberg M, Rossing P, et al: Dapagliflozin in patients with
chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 383:1436–1446.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wiviott SD, Raz I, Bonaca MP, Mosenzon O,
Kato ET, Cahn A, Silverman MG, Zelniker TA, Kuder JF and Murphy SA:
Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N
Engl J Med. 380:347–357. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Bhatt DL, Szarek M, Steg PG, Cannon CP,
Leiter LA, McGuire DK, Lewis JB, Riddle MC, Voors AA, Metra M, et
al: Sotagliflozin in patients with diabetes and recent worsening
heart failure. N Engl J Med. 384:117–128. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Cannon CP, Pratley R, Dagogo-Jack S,
Mancuso J, Huyck S, Masiukiewicz U, Charbonnel B, Frederich R,
Gallo S, Cosentino F, et al: Cardiovascular outcomes with
ertugliflozin in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 383:1425–1435.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Fitchett D, Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM,
Hantel S, Salsali A, Johansen OE, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC and Inzucchi
SE: EMPA-REG OUTCOME® trial investigators. Heart failure
outcomes with empagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes at
high cardiovascular risk: Results of the EMPA-REG
OUTCOME® trial. Eur Heart J. 37:1526–1534.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Inzucchi SE, Khunti K, Fitchett DH, Wanner
C, Mattheus M, George JT, Ofstad AP and Zinman B: Cardiovascular
benefit of empagliflozin across the spectrum of cardiovascular risk
factor control in the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 105:3025–3035. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Kato ET, Silverman MG, Mosenzon O,
Zelniker TA, Cahn A, Furtado RHM, Kuder J, Murphy SA, Bhatt DL,
Leiter LA, et al: Effect of dapagliflozin on heart failure and
mortality in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 139:2528–2536.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Mahaffey KW, Neal B, Perkovic V, de Zeeuw
D, Fulcher G, Erondu N, Shaw W, Fabbrini E, Sun T, Li Q, et al:
Canagliflozin for primary and secondary prevention of
cardiovascular events: Results from the CANVAS Program
(Canagliflozin Cardiovascular Assessment Study). Circulation.
137:323–334. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Neal B, Perkovic V, Mahaffey KW, De Zeeuw
D, Fulcher G, Erondu N, Shaw W, Law G, Desai M and Matthews DR:
CANVAS Program Collaborative Group. Canagliflozin and
cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med.
377:644–657. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ohkuma T, Van Gaal L, Shaw W, Mahaffey KW,
de Zeeuw D, Matthews DR, Perkovic V and Neal B: Clinical outcomes
with canagliflozin according to baseline body mass index: Results
from post hoc analyses of the CANVAS Program. Diabetes Obes Metab.
22:530–539. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Wanner C, Lachin JM, Inzucchi SE, Fitchett
D, Mattheus M, George J, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC, von Eynatten M and
Zinman B: EMPA-REG OUTCOME Investigators. Empagliflozin and
clinical outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus,
established cardiovascular disease, and chronic kidney disease.
Circulation. 137:119–129. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D,
Bluhmki E, Hantel S, Mattheus M, Devins T, Johansen OE, Woerle HJ,
et al: Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in
type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 373:2117–2128. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Anker SD, Butler J, Filippatos G, Ferreira
JP, Bocchi E, Böhm M, Brunner-La Rocca HP, Choi DJ, Chopra V,
Chuquiure-Valenzuela E, et al: Empagliflozin in heart failure with
a preserved ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 385:1451–161.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Anker SD, Butler J, Filippatos G, Khan MS,
Marx N, Lam CSP, Schnaidt S, Ofstad AP, Brueckmann M, Jamal W, et
al: Effect of empagliflozin on cardiovascular and renal outcomes in
patients with heart failure by baseline diabetes status: Results
from the EMPEROR-Reduced trial. Circulation. 143:337–349.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Hernandez AF, Udell JA, Jones WS, Anker
SD, Petrie MC, Harrington J, Mattheus M, Seide S, Zwiener I, Amir
O, et al: Effect of empagliflozin on heart failure outcomes after
acute myocardial infarction: Insights from the EMPACT-MI trial.
Circulation. 149:1627–1638. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Kosiborod MN, Angermann CE, Collins SP,
Teerlink JR, Ponikowski P, Biegus J, Comin-Colet J, Ferreira JP,
Mentz RJ, Nassif ME, et al: Effects of empagliflozin on symptoms,
physical limitations, and quality of life in patients hospitalized
for acute heart failure: Results From the EMPULSE trial.
Circulation. 146:279–288. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Kosiborod MN, Jhund PS, Docherty KF, Diez
M, Petrie MC, Verma S, Nicolau JC, Merkely B, Kitakaze M, DeMets
DL, et al: Effects of dapagliflozin on symptoms, function, and
quality of life in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection
fraction: Results from the DAPA-HF trial. Circulation. 141:90–99.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
McMurray JJV, Docherty KF, de Boer RA,
Hammarstedt A, Kitzman DW, Kosiborod MN, Maria Langkilde A, Reicher
B, Senni M, Shah SJ, et al: Effect of dapagliflozin versus placebo
on symptoms and 6-Minute walk distance in patients with heart
failure: The DETERMINE randomized clinical trials. Circulation.
149:825–838. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
McMurray JJV, Solomon SD, Inzucchi SE,
Køber L, Kosiborod MN, Martinez FA, Ponikowski P, Sabatine MS,
Anand IS, Bělohlávek J, et al: Dapagliflozin in patients with heart
failure and reduced ejection fraction. Eur Heart J. 381:1995–2008.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
McMurray JJV, Wheeler DC, Stefánsson BV,
Jongs N, Postmus D, Correa-Rotter R, Chertow GM, Hou FF, Rossing P,
Sjöström CD, et al: Effects of dapagliflozin in patients with
kidney disease, with and without heart failure. JACC Heart failure.
9:807–820. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Solomon SD, McMurray JJV, Claggett B, de
Boer RA, DeMets D, Hernandez AF, Inzucchi SE, Kosiborod MN, Lam
CSP, Martinez F, et al: Dapagliflozin in heart failure with mildly
reduced or preserved ejection fraction. N Engl J Med.
387:1089–1098. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Usman MS, Bhatt DL, Hameed I, Anker SD,
Cheng AYY, Hernandez AF, Jones WS, Khan MS, Petrie MC, Udell JA, et
al: Effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on heart failure outcomes and
cardiovascular death across the cardiometabolic disease spectrum: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.
12:447–461. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Teo YH, Teo YN, Syn NL, Kow CS, Yoong CSY,
Tan BYQ, Yeo TC, Lee CH, Lin W and Sia CH: Effects of
Sodium/Glucose Cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors on cardiovascular
and metabolic outcomes in patients without diabetes mellitus: A
systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized-controlled
trials. J Am Heart Assoc. 10(e019463)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Greene SJ, Butler J and Fonarow GC:
Contextualizing risk among patients with heart failure. JAMA.
326:2261–2262. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Kenny HC and Abel ED: Heart failure in
type 2 diabetes mellitus: Impact of glucose-lowering agents, heart
failure therapies, and novel therapeutic strategies. Circ Res.
124:121–141. 2019.
|
|
55
|
Kluger AY, Tecson KM, Lee AY, Lerma EV,
Rangaswami J, Lepor NE, Cobble ME and McCullough PA: Class effects
of SGLT2 inhibitors on cardiorenal outcomes. Cardiovasc Diabetol:
Aug 5, 2019 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
56
|
Tromp J, Lim SL, Tay WT, Teng THK,
Chandramouli C, Ouwerkerk W, Wander GS, Sawhney JPS, Yap J,
MacDonald MR, et al: Microvascular disease in patients with
diabetes with heart failure and reduced ejection versus preserved
ejection fraction. Diabetes Care. 42:1792–1799. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Nuffield Department of Population Health
Renal Studies Group; SGLT2 inhibitor Meta-Analysis Cardio-Renal
Trialists' Consortium. Impact of diabetes on the effects of sodium
glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors on kidney outcomes:
Collaborative meta-analysis of large placebo-controlled trials.
Lancet. 400:1788–1801. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Abdelgadir E, Rashid F, Bashier A and Ali
R: SGLT-2 inhibitors and cardiovascular protection: Lessons and
gaps in understanding the current outcome trials and possible
benefits of combining SGLT-2 Inhibitors With GLP-1 agonists. J Clin
Med Res. 10:615–625. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Packer M, Wilcox CS and Testani JM:
Critical analysis of the effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on renal
tubular sodium, water and chloride homeostasis and their role in
influencing heart failure outcomes. Circulation. 148:354–372.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Dyck JRB, Sossalla S, Hamdani N, Coronel
R, Weber NC, Light PE and Zuurbier CJ: Cardiac mechanisms of the
beneficial effects of SGLT2 inhibitors in heart failure: Evidence
for potential off-target effects. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 167:17–31.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Hanke J, Romejko K and Niemczyk S:
Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 inhibitors in diabetes and beyond:
Mechanisms, pleiotropic benefits, and clinical Use-Reviewing
protective effects exceeding glycemic control. Molecul.
30(4125)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
McLean P and Bennett J: ‘Trey’ Woods E.
Chandrasekhar S, Newman N, Mohammad Y, Khawaja M, Rizwan A,
Siddiqui R, Birnbaum Y, et al: SGLT2 inhibitors across various
patient populations in the era of precision medicine: The
multidisciplinary team approach. npj Metab Health Dis.
3(29)2025.
|
|
63
|
Rastogi T and Girerd N: SGLT2 inhibitors
in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: A paradigm shift
toward dual Cardio-renal protection. Heart Fail Clin. 18:561–577.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Siddiqui R, Obi Y, Dossabhoy NR and Shafi
T: Is there a role for SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with end-stage
kidney disease? Curr Hypertens Rep. 26:463–474. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|