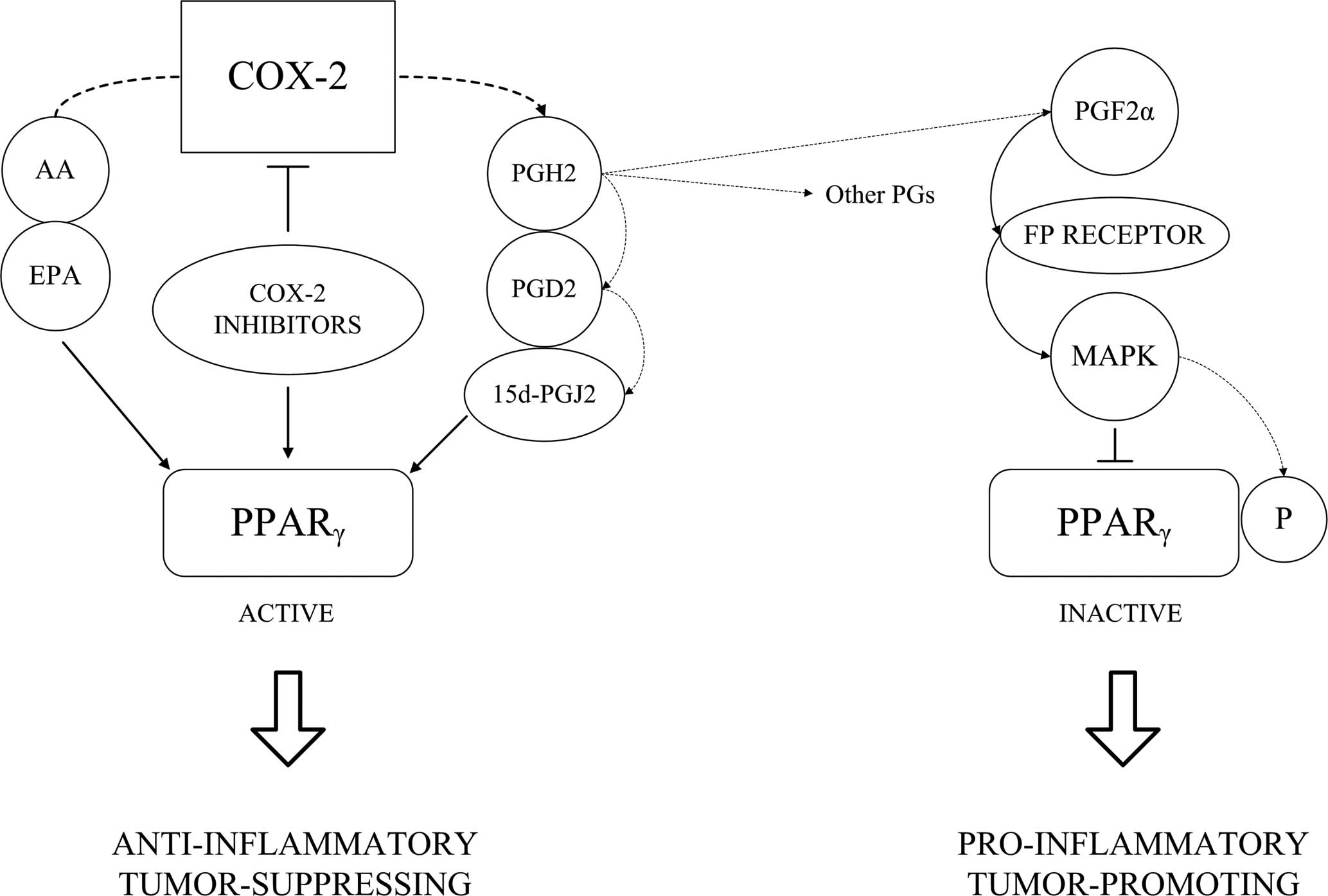
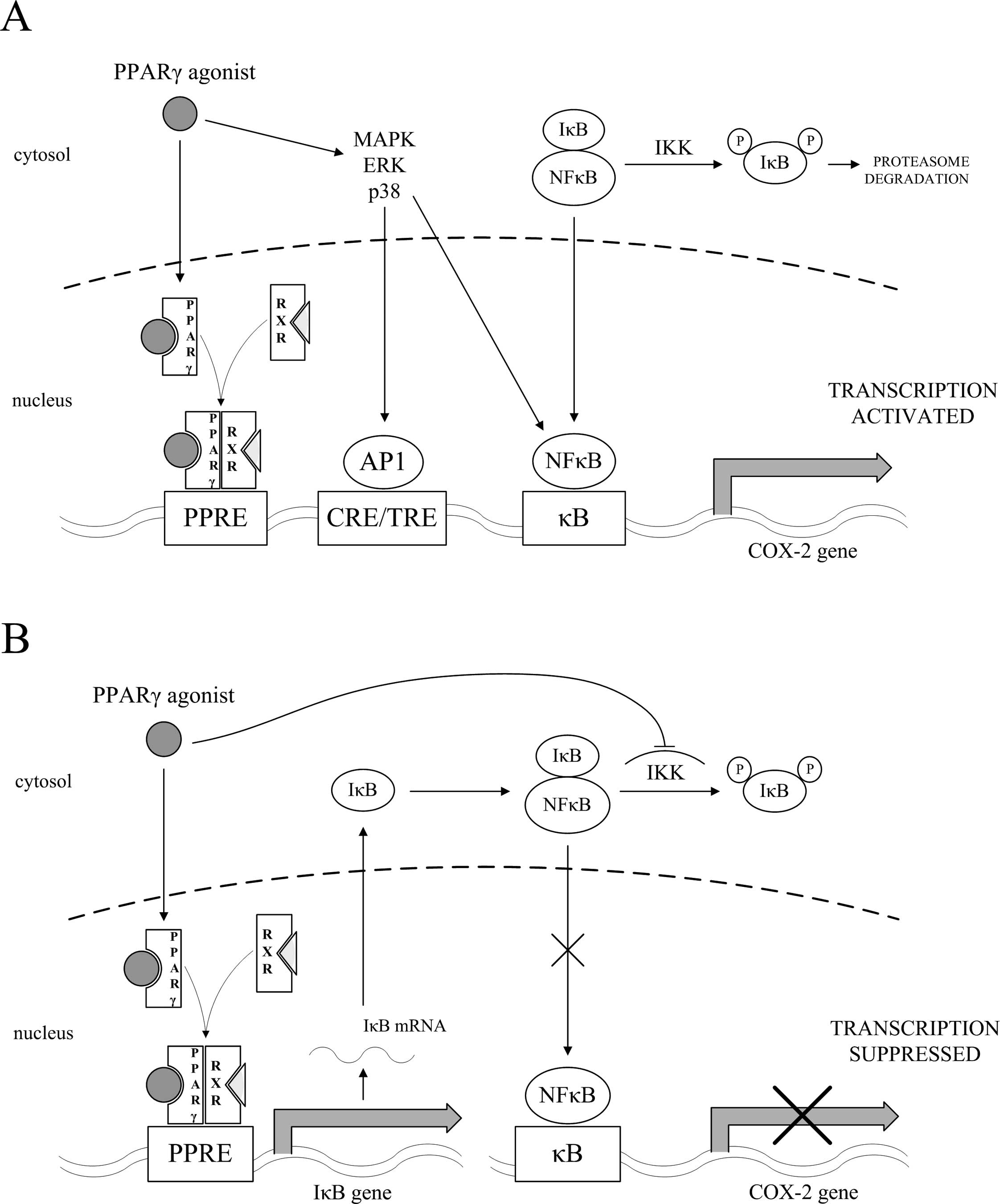
|
1.
|
Zha S, Yegnasubramanian V, Nelson WG,
Isaacs WB and De Marzo AM: Cyclooxygenases in cancer: progress and
perspective. Cancer Lett. 215:1–20. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Liao Z, Mason KA and Milas L:
Cyclo-oxygenase-2 and its inhibition in cancer: is there a role?
Drugs. 67:821–845. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Koehne CH and Dubois RN: COX-2 inhibition
and colorectal cancer. Semin Oncol. 31:12–21. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4.
|
Khuder SA and Mutgi AB: Breast cancer and
NSAID use: a meta-analysis. Br J Cancer. 84:1188–1192. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Castelao JE, Yuan JM, Gago-Dominguez M, Yu
MC and Ross RK: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and bladder
cancer prevention. Br J Cancer. 82:1364–1369. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Sooriakumaran P, Langley SE, Laing RW and
Coley HM: COX-2 inhibition: a possible role in the management of
prostate cancer? J Chemother. 19:21–32. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Muscat JE, Chen SQ, Richie JP Jr, Altorki
NK, Citron M, Olson S, Neugut AI and Stellman SD: Risk of lung
carcinoma among users of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs.
Cancer. 97:1732–1736. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Sandler AB and Dubinett SM: COX-2
inhibition and lung cancer. Semin Oncol. 31:45–52. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Steinbach G, Lynch PM, Phillips RK,
Wallace MH, Hawk E, Gordon GB, Wakabayashi N, Saunders B, Shen Y,
Fujimura T, Su LK and Levin B: The effect of celecoxib, a
cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, in familial adenomatous polyposis. N
Engl J Med. 342:1946–1952. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Suzuki R, Yamamoto M, Saka H, Taniguchi H,
Shindoh J, Tanikawa Y, Nomura F, Gonda H, Imaizumi K, Hasegawa Y
and Shimokata K: A phase II study of carboplatin and paclitacel
with meloxicam. Lung Cancer. 63:72–76. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Soriano F, Helfrich B, Chan DC, Heasley
LE, Bunn PA Jr and Chou TC: Synergistic effects of new
chemopreventive agents and conventional cytotoxic agents against
human lung cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 59:6178–6184.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Tuettenberg J, Grobholz R, Korn T, Wenz F,
Erber R and Vajkoczy P: Continuous low-dose chemotherapy plus
inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 as an antiangiogenic therapy of
glioblastoma multiforme. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 131:31–40. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Tachimori A, Yamada N, Amano R, Ohira M
and Hirakawa K: Combination therapy of S-1 with selective
cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor for liver metastasis of colorectal
carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 28:629–638. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Eichele K, Ramer R and Hinz B: Decisive
role of cyclooxygenase-2 and lipocalin-type prostaglandin D
synthase in chemotherapeutic-induced apoptosis of human cervical
carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 27:3032–3044. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Gilroy DW, Colville-Nash PR, Willis D,
Chivers J, Paul-Clark MJ and Willoughby DA: Inducible
cyclooxygenase may have anti-inflammatory properties. Nat Med.
5:698–701. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Issemann I and Green S: Activation of a
member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily by peroxisome
proliferators. Nature. 347:645–650. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Nosjean O and Boutin JA: Natural ligands
of PPARγ: Are prostaglandin J2 derivatives really playing the part?
Cell Signal. 14:573–583. 2002.
|
|
18.
|
Bull AW, Steffensen KR, Leers J and Rafter
JJ: Activation of PPAR gamma in colon tumor cell lines by oxidized
metabolites of linoleic acid, endogenous ligands for PPAR gamma.
Carcinogenesis. 24:1717–1722. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Kepez A, Oto A and Dagdelen S: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-gamma: novel therapeutic target
linking adiposity, insulin resistance and atherosclerosis.
BioDrugs. 20:121–135. 2006.
|
|
20.
|
Chiarelli F and Di Marzio D: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonists and diabetes:
current evidence and future perspectives. Vasc Health Risk Manag.
4:297–304. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Quinn CE, Hamilton PK, Lockhart CJ and
McVeigh GE: Thiazolidinediones: effects on insulin resistance and
the cardiovascular system. Br J Pharmacol. 153:636–645. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Konstantinopoulos PA, Vandoros GP,
Sotiropoulou-Bonikou G, Kominea A and Papavassiliou AG: NF-κB/PPARγ
and/or AP-1/PPARγ ‘on/off’ switches and induction of CBP in colon
adenocarcinomas: correlation with COX-2 expression. Int J
Colorectal Dis. 22:57–68. 2007.
|
|
23.
|
Badawi AF and Badr MZ: Expression of
cyclooxygenase-2 and peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor-gamma and levels of prostaglandin E2 and
15-deoxy-delta12,14-prostaglandin J2 in human breast cancer and
metastasis. Int J Cancer. 103:84–90. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24.
|
Nagata D, Yoshihiro H, Nakanishi M,
Naruyama H, Okada S, Ando R, Tozawa K and Kohri K: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-gamma and growth inhibition by its
ligands in prostate cancer. Cancer Detect Prev. 32:259–266. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Matsuyama M and Yoshimura R: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-gamma is a potent target for
prevention and treatment in human prostate and testicular cancer.
PPAR Res. 2008:2498492008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Segawa Y, Yoshimura R, Hase T, Nakatani T,
Wada S, Kawahito Y, Kishimoto T and Sano H: Expression of
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) in human prostate
cancer. Prostate. 51:108–116. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Sato H, Ishihara S, Kawashima K, Moriyama
N, Suetsugu H, Kazumori H, Okuyama T, Rumi MA, Fukuda R, Nagasue N
and Kinoshita Y: Expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor (PPAR)gamma in gastric cancer and inhibitory effects of
PPARgamma agonists. Br J Cancer. 83:1394–1400. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Inoue K, Kawahito Y, Tsubouchi Y, Yamada
R, Kohno M, Hosokawa Y, Katoh D, Bishop-Bailey D, Hla T and Sano H:
Expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
(PPAR)-gamma in human lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 21:2471–2476.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Kristiansen G, Jacob J, Buckendahl AC,
Grützmann R, Alldinger I, Sipos B, Klöppel G, Bahra M, Langrehr JM,
Neuhaus P, Dietel M and Pilarsky C: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma is highly expressed in
pancreatic cancer and is associated with shorter overall survival
times. Clin Cancer Res. 12:6444–6451. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30.
|
Vignati S, Albertini V, Rinaldi A, Kwee I,
Riva C, Oldrini R, Capella C, Bertoni F, Carbone GM and Catapano
CV: Cellular and molecular consequences of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-gamma activation in ovarian cancer
cells. Neoplasia. 8:851–861. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Jung TI, Baek WK, Suh SI, Jang BC, Song
DK, Bae JH, Kwon KY, Bae JH, Cha SD, Bae I and Cho CH:
Down-regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
in human cervical carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol. 97:365–373. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Grommes C, Landreth GE and Heneka MT:
Antineoplastic effects of peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor gamma agonists. Lancet Oncol. 5:419–429. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Keshamouni VG, Reddy RC, Arenberg DA, Joel
B, Thannickal VJ, Kalemkerian GP and Standiford TJ: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-gamma activation inhibits tumor
progression in non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncogene. 23:100–108.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Yasui Y, Kim M and Tanaka T: PPAR ligands
for cancer chemoprevention. PPAR Res. 2008:5489192008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Mueller E, Smith M, Sarraf P, Kroll T,
Aiyer A, Kaufman DS, Oh W, Demetri G, Figg WD, Zhou XP, Eng C,
Spiegelman BM and Kantoff PW: Effects of ligand activation of
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in human prostate
cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:10990–10995. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Rumi MA, Ishihara S, Kazumori H, Kadowaki
Y and Kinoshita Y: Can PPAR gamma ligands be used in cancer
therapy? Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 4:465–477. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Lefebvre AM, Chen I, Desreumaux P, Najib
J, Fruchart JC, Geboes K, Briggs M, Heyman R and Auwerx J:
Activation of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
promotes the development of colon tumors in C57BL/6J-APCMin/+ mice.
Nat Med. 4:1053–1057. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Saez E, Tontonoz P, Nelson MC, Alvarez JG,
Ming UT, Baird SM, Thomazy VA and Evans RM: Activators of the
nuclear receptor PPARgamma enhance colon polyp formation. Nat Med.
4:1058–1061. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Saez E, Rosenfeld J, Livolsi A, Olson P,
Lombardo E, Nelson M, Banayo E, Cardiff RD, Izpisua-Belmonte JC and
Evans RM: PPAR gamma signaling exacerbates mammary gland tumor
development. Genes Dev. 18:528–540. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Eibl G: The role of PPAR-gamma and its
interaction with COX-2 in pancreatic cancer. PPAR Res.
2008:3269152008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Kawashima A, Harada T, Imada K, Yano T and
Mizuguchi K: Eicosapentaenoic acid inhibits interleukin-6
production in interleukin-1beta-stimulated C6 glioma cells through
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. Prostaglandins
Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 79:59–65. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42.
|
Allred CD, Talbert DR, Southard RC, Wang X
and Kilgore MW: PPARgamma1 as a molecular target of
eicosapentaenoic acid in human colon cancer (HT-29) cells. J Nutr.
138:250–256. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Straus DS and Glass CK: Cyclopentenone
prostaglandins: new insights on biological activities and cellular
targets. Med Res Rev. 21:185–210. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Matsuoka T and Narumiya S: Prostaglandin
receptor signaling in disease. ScientificWorldJournal. 7:1329–1347.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45.
|
Castellone MD, Teramoto H, Williams BO,
Druey KM and Gutkind JS: Prostaglandin E2 promotes colon cancer
cell growth through a Gs-axin-beta-catenin signaling axis. Science.
310:1504–1510. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Chan TA: Prostaglandins and the colon
cancer connection. Trends Mol Med. 12:240–244. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Scher JU and Pillinger MH: 15d-PGJ2: the
anti-inflammatory prostaglandin? Clin Immunol. 114:100–109. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Shimada T, Kojima K, Yoshiura K, Hiraishi
H and Terano A: Characteristics of the peroxisome proliferator
activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) ligand-induced apoptosis in
colon cancer cells. Gut. 50:658–664. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49.
|
Millan O, Rico D, Peinado H, Zarich N,
Stamatakis K, Pérez-Sala D, Rojas JM, Cano A and Boscá L:
Potentiation of tumor formation by topical administration of
15-deoxy-delta12,14-prostaglandin J2 in a model of skin
carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 27:328–336. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Chinery R, Coffey RJ, Graves-Deal R,
Kirkland SC, Sanchez SC, Zackert WE, Oates JA and Morrow JD:
Prostaglandin J2 and 15-deoxy-delta12,14-prostaglandin J2 induce
proliferation of cyclooxygenase-depleted colorectal cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 59:2739–2746. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51.
|
Reginato MJ, Krakow SL, Bailey ST and
Lazar MA: Prostaglandins promote and block adipogenesis through
opposing effects on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
gamma. J Biol Chem. 273:1855–1858. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52.
|
Padilla J, Kaur K, Cao HJ, Smith TJ and
Phipps RP: Peroxisome proliferator activator receptor-gamma
agonists and 15-deoxy-delta(12,14)(12,14)-PGJ(2) induce apoptosis
in normal and malignant B-lineage cells. J Immunol. 165:6941–6948.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53.
|
Jaradat MS, Wongsud B, Phornchirasilp S,
Rangwala SM, Shams G, Sutton M, Romstedt KJ, Noonan DJ and Feller
DR: Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
isoforms and inhibition of prostaglandin H(2) synthases by
ibuprofen, naproxen and indomethacin. Biochem Pharmacol.
62:1587–1595. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54.
|
Lehmann JM, Lenhard JM, Oliver BB, Ringold
GM and Kliewer SA: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors
alpha and gamma are activated by indomethacin and other
non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J Biol Chem. 272:3406–3410.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55.
|
López-Parra M, Clària J, Titos E,
Planagumà A, Párrizas M, Masferrer JL, Jiménez W, Arroyo V, Rivera
F and Rodés J: The selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor celecoxib
modulates the formation of vasoconstrictor eicosanoids and
activates PPARgamma. Influence of albumin. J Hepatol. 42:75–81.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56.
|
Diamond MP and Saed G: Modulation of the
expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in human
fibroblasts. Fertil Steril. 87:706–709. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57.
|
Shaik MS, Chatterjee A and Singh M: Effect
of a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, nimesulide, on the
growth of lung tumors and their expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. Clin Cancer Res.
10:1521–1529. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58.
|
Yamazaki R, Kusunoki N, Matsuzaki T,
Hashimoto S and Kawai S: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
induce apoptosis in association with activation of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma in rheumatoid synovial cells.
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 302:18–25. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59.
|
Cui W, Yu CH and Hu KQ: In vitro and in
vivo effects and mechanisms of celecoxib-induced growth inhibition
of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res.
11:8213–8221. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60.
|
Nagahara T, Okano J and Murawaki Y:
Mechanisms of anti-proliferative effect of JTE-522, a selective
cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, on human liver cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
18:1281–1290. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61.
|
Meade EA, McIntyre TM, Zimmerman GA and
Prescott SM: Peroxisome proliferators enhance cyclooxygenase-2
expression in epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 274:8328–8334. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62.
|
Pontsler AV, St Hilaire A, Marathe GK,
Zimmerman GA and McIntyre TM: Cyclooxygenase-2 is induced in
monocytes by peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma and
oxidized alkyl phospholipids from oxidized low density lipoprotein.
J Biol Chem. 277:13029–13036. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63.
|
Bishop-Bailey D and Warner TD: PPARgamma
ligands induce prostaglandin production in vascular smooth muscle
cells: indomethacin acts as a peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor-gamma antagonist. FASEB J. 17:1925–1927. 2003.
|
|
64.
|
Kalajdzic T, Faour WH, He QW, Fahmi H,
Martel-Pelletier J, Pelletier JP and Di Battista JA: Nimesulide, a
preferential cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor, suppresses peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor induction of cyclooxygenase 2 gene
expression in human synovial fibroblasts: evidence for receptor
antagonism. Arthritis Rheum. 46:494–506. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65.
|
Lee JH, Yu SM, Yoon EK, Lee WK, Jung JC
and Kim SJ: 15-Deoxy-delta 12,14-prostaglandin J2 regulates
dedifferentiation through peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor-gamma-dependent pathway but not COX-2 expression in
articular chondrocytes. J Korean Med Sci. 22:891–897. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66.
|
Patel KM, Wright KL, Whittaker P,
Chakravarty P, Watson ML and Ward SG: Differential modulation of
COX-2 expression in A549 airway epithelial cells by structurally
distinct PPAR(gamma) agonists: evidence for disparate functional
effects which are independent of NF-(kappa)B and PPAR(gamma). Cell
Signal. 17:1098–1110. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67.
|
Chêne G, Dubourdeau M, Balard P,
Escoubet-Lozach L, Orfila C, Berry A, Bernad J, Aries MF, Charveron
M and Pipy B: n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids induce the
expression of COX-2 via PPARgamma activation in human keratinocyte
HaCaT cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1771:576–589. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68.
|
Pang L, Nie M, Corbett L and Knox AJ:
Cyclooxygenase-2 expression by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
in human airway smooth muscle cells: role of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors. J Immunol. 170:1043–1051. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69.
|
Ulivi V, Cancedda R and Cancedda FD:
15-Deoxy-delta 12,14-prostaglandin J(2) inhibits the synthesis of
the acute phase protein SIP24 in cartilage: involvement of COX-2 in
resolution of inflammation. J Cell Physiol. 217:433–441. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70.
|
Li Z, Jansen M, Ogburn K, Salvatierra L,
Hunter L, Mathew S and Figueiredo-Pereira ME: Neurotoxic
prostaglandin J2 enhances cyclooxygenase-2 expression in neuronal
cells through the p38MAPK pathway: a death wish? J Neurosci Res.
78:824–836. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71.
|
Ulivi V, Giannoni P, Gentili C, Cancedda R
and Descalzi F: p38/NF-κB-dependent expression of COX-2 during
differentiation and inflammatory response of chondrocytes. J Cell
Biochem. 104:1393–1406. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72.
|
Tsatsanis C, Androulidaki A, Venihaki M
and Margioris AN: Signalling networks regulating cyclooxygenase-2.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 38:1654–1661. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73.
|
Paik JH, Ju JH, Lee JY, Boudreau MD and
Hwang DH: Two opposing effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory
drugs on the expression of the inducible cyclooxygenase. Mediation
through different signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 275:28173–28179.
2000.
|
|
74.
|
Boyault S, Simonin MA, Bianchi A, Compe E,
Liagre B, Mainard D, Becuwe P, Dauca M, Netter P, Terlain B and
Bordji K: 15-Deoxy-Δ12;14-PGJ2, but not troglitazone, modulates
IL-1β effects in human chondrocytes by inhibiting NF-κB and AP-1
activation pathways. FEBS Lett. 501:24–30. 2001.
|
|
75.
|
Liu JJ, Liu PQ, Lin DJ, Xiao RZ, Huang M,
Li XD, He Y and Huang RW: Downregulation of cyclooxygenase-2
expression and activation of caspase-3 are involved in peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonists induced apoptosis in
human monocyte leukemia cells in vitro. Ann Hematol. 86:173–183.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76.
|
Hazra S and Dubinett SM: Ciglitazone
mediates COX-2 dependent suppression of PGE2 in human non-small
cell lung cancer cells. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids.
77:51–58. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77.
|
Bren-Mattison Y, Meyer AM, van Putten V,
Li H, Kuhn K, Stearman R, Weiser-Evans M, Winn RA, Heasley LE and
Nemenoff RA: Antitumorigenic effects of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-gamma in non-small cell lung cancer
cells are mediated by suppression of cyclooxygenase-2 via
inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB. Mol Pharmacol. 73:709–717.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78.
|
Delerive P, Gervois P, Fruchart JC and
Staels B: Induction of IkappaBalpha expression as a mechanism
contributing to the anti-inflammatory activities of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-alpha activators. J Biol Chem.
275:36703–36707. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79.
|
Moraes LA, Piqueras L and Bishop-Bailey D:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and inflammation.
Pharmacol Ther. 110:371–385. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80.
|
Wahli W: A gut feeling of the PXR, PPAR
and NF-κB connection. J Intern Med. 263:613–619. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81.
|
Ricote M, Li AC, Willson TM, Kelly CJ and
Glass CK: The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ is a
negative regulator of macrophage activation. Nature. 391:79–82.
1998.
|
|
82.
|
Rossi A, Kapahi P, Natoli G, Takahashi T,
Chen Y, Karin M and Santoro MG: Anti-inflammatory cyclopentenone
prostaglandins are direct inhibitors of IkappaB kinase. Nature.
403:103–108. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83.
|
Ackerman WE, Zhang XL, Rovin BH and Kniss
DA: Modulation of cytokine-induced cyclooxygenase 2 expression by
PPARG ligands through NFκB signal disruption in human WISH and
amnion cells. Biol Reprod. 73:527–535. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84.
|
Straus DS, Pascual G, Li M, Welch JS,
Ricote M, Hsiang CH, Sengchanthalangsy LL, Ghosh G and Glass CK:
15-Deoxy-delta 12,14-prostaglandin J2 inhibits multiple steps in
the NF-κB signaling pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:4844–4849.
2000.
|
|
85.
|
Badawi AF and Badr MZ: Chemoprevention of
breast cancer by targeting cyclooxygenase-2 and peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-γ. Int J Oncol. 20:1109–1122.
2002.
|
|
86.
|
Michael MS, Badr MZ and Badawi AF:
Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 and activation of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-γ synergistically induces apoptosis
and inhibits growth of human breast cancer cells. Int J Mol Med.
11:733–736. 2003.
|
|
87.
|
Badawi AF, Eldeen MB, Liu Y, Ross EA and
Badr MZ: Inhibition of rat mammary gland carcinogenesis by
simultaneous targeting of cyclooxygenase-2 and peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma. Cancer Res. 64:1181–1189.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88.
|
Mustafa A and Kruger WD: Suppression of
tumor formation by a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor and a peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonist in an in vivo mouse
model of spontaneous breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 14:4935–4942.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89.
|
Sun WH, Chen GS, Ou XL, Yang Y, Luo C,
Zhang Y, Shao Y, Xu HC, Xiao B, Xue YP, Zhou SM, Zhao QS and Ding
GX: Inhibition of COX-2 and activation of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma synergistically inhibits
proliferation and induces apoptosis of human pancreatic carcinoma
cells. Cancer Lett. 275:247–255. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90.
|
Narayanan NK, Narayanan BA and Reddy BS: A
combination of docosahexaenoic acid and celecoxib prevents prostate
cancer cell growth in vitro and is associated with
modulation of nuclear factor-κB, and steroid hormone receptors. Int
J Oncol. 26:785–792. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91.
|
Gustafsson A, Hansson E, Kressner U,
Nordgren S, Andersson M, Wang W, Lönnroth C and Lundholm K: EP1-4
subtype, COX and PPAR gamma receptor expression in colorectal
cancer in prediction of disease-specific mortality. Int J Cancer.
121:232–240. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92.
|
Hazra S, Peebles KA, Sharma S, Mao JT and
Dubinett SM: The role of PPARgamma in the cyclooxygenase pathway in
lung cancer. PPAR Res. 2008:7905682008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93.
|
Sasaki H, Tanahashi M, Yukiue H, Moiriyama
S, Kobayashi Y, Nakashima Y, Kaji M, Kiriyama M, Fukai I, Yamakawa
Y and Fujii Y: Decreased peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
gamma gene expression was correlated with poor prognosis in
patients with lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 36:71–76. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|