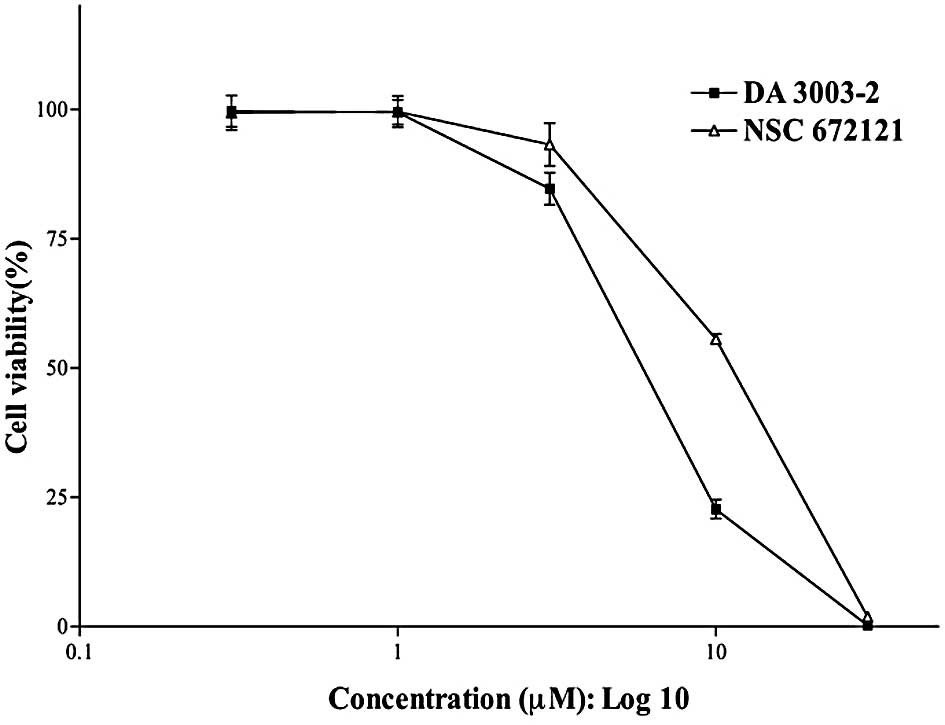
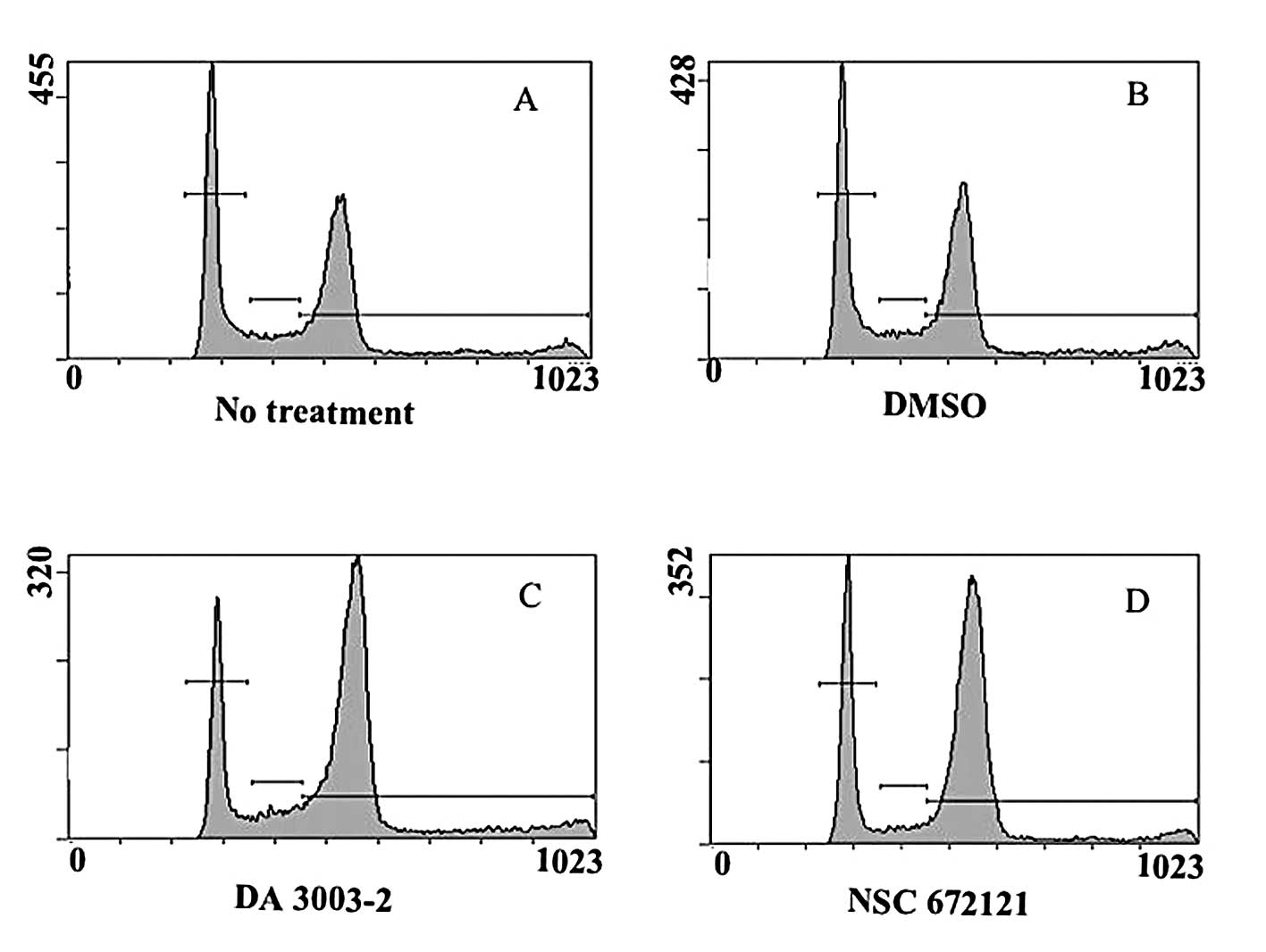
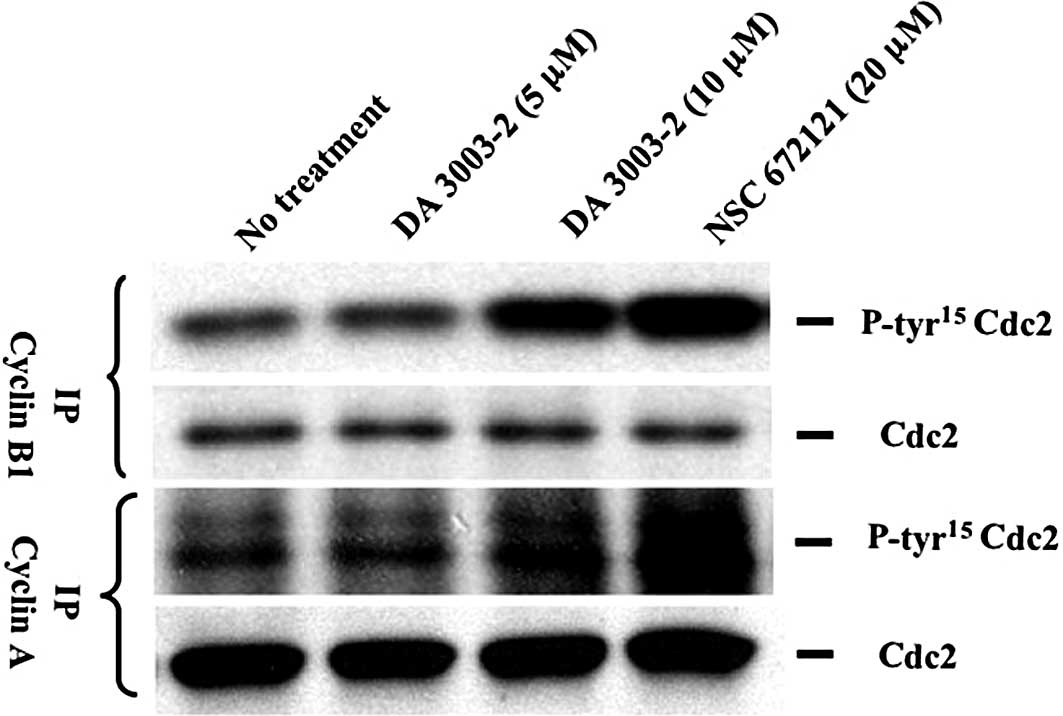
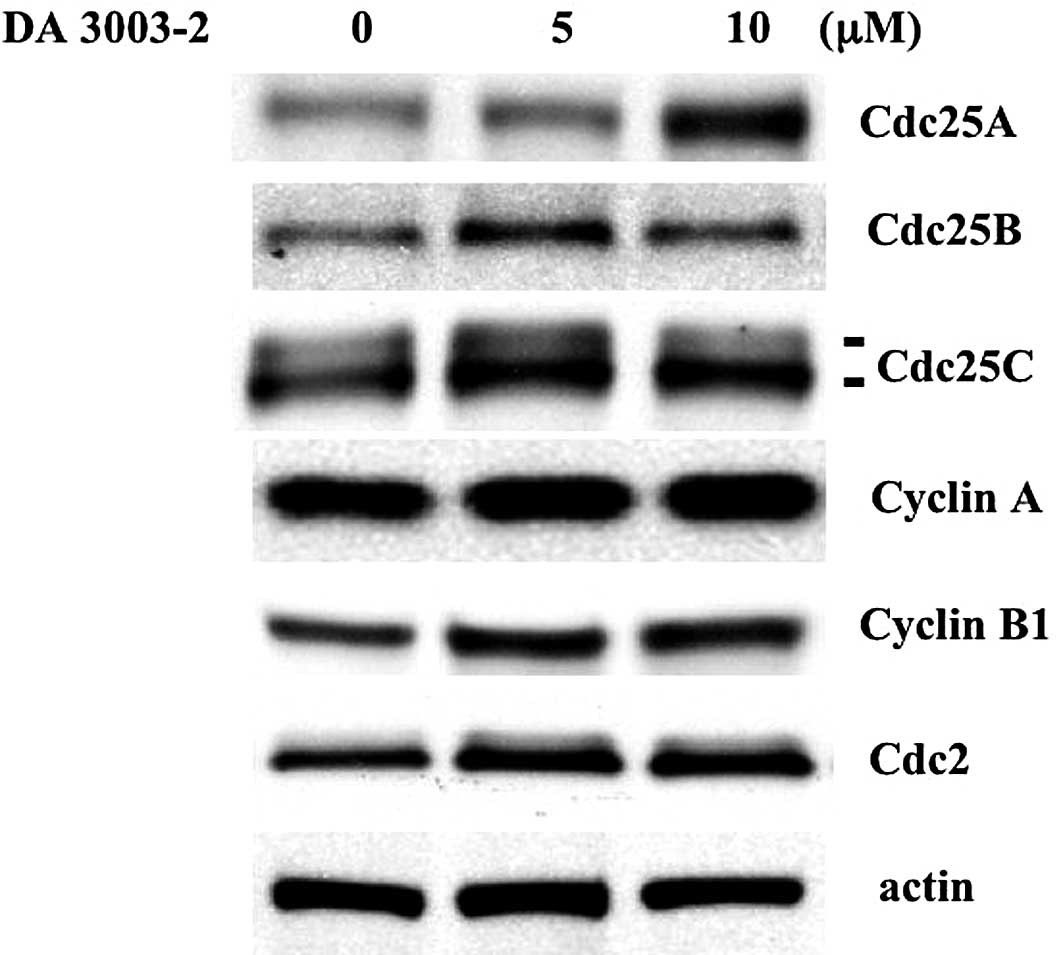
|
1.
|
Kristjánsdóttir K and Rudolph J: Cdc25
phosphatases and cancer. Chem Biol. 11:1043–1045. 2004.
|
|
2.
|
Boutros R, Lobjois V and Ducommun B: CDC25
phosphatases in cancer cells: key players? Good targets? Nat Rev
Cancer. 7:495–507. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Chiu YT, Han HY, Leung SC, Yuen HF, Chau
CW, Guo Z, Qiu Y, Chan KW, Wang X, Wong YC and Ling MT: CDC25A
functions as a novel AR corepressor in prostate cancer cells. J Mol
Biol. 385:446–456. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Ngan ES, Hashimoto Y, Ma ZQ, Tsai MJ and
Tsai SY: Overexpression of Cdc25B, an androgen receptor
coactivator, in prostate cancer. Oncogene. 22:734–739. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Ozen M and Ittmann M: Increased expression
and activity of CDC25C phosphatase and an alternatively spliced
variant in prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 11:4701–4706. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Lazo JS, Aslan DC, Southwick EC, Cooley
KA, Ducruet AP, Joo B, Vogt A and Wipf P: Discovery and biological
evaluation of a new family of potent inhibitors of the dual
specificity protein phosphatase Cdc25. J Med Chem. 44:4042–4049.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Lazo JS, Nemoto K, Pestell KE, Cooley K,
Southwick EC, Mitchell DA, Furey W, Gussio R, Zaharevitz DW, Joo B
and Wipf P: Identification of a potent and selective pharmacophore
for Cdc25 dual specificity phosphatase inhibitors. Mol Pharmacol.
61:720–728. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Lazo JS and Wipf P: Is Cdc25 a druggable
target? Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 8:837–842. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Tamura K, Southwick EC, Kerns J, Rosi K,
Carr BI, Wilcox C and Lazo JS: Cdc25 inhibition and cell cycle
arrest by a synthetic thioalkyl vitamin K analogue. Cancer Res.
60:1317–1325. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Pu L, Amoscato AA, Bier ME and Lazo JS:
Dual G1 and G2 phase inhibition by a novel, selective Cdc25
inhibitor 6-chloro-7 -[corrected]
(2-morpholin-4-ylethylamino)-quinoline-5, 8-dione. J Biol Chem.
277:46877–46885. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Brisson M, Nguyen T, Vogt A, Yalowich J,
Giorgianni A, Tobi D, Bahar I, Stephenson CR, Wipf P and Lazo JS:
Discovery and characterization of novel small molecule inhibitors
of human Cdc25B dual specificity phosphatase. Mol Pharmacol.
66:824–833. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Chmelar R, Buchanan G, Need EF, Tilley W
and Greenberg NM: Androgen receptor coregulators and their
involvement in the development and progression of prostate cancer.
Int J Cancer. 120:719–733. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Balk SP and Knudsen KE: AR, the cell
cycle, and prostate cancer. Nucl Recept Signal. 6:1–12.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Mashal RD, Lester S, Corless C, Richie JP,
Chandra R, Propert KJ and Dutta A: Expression of cell
cycle-regulated proteins in prostate cancer. Cancer Res.
56:4159–4163. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Kallakury BV, Sheehan CE, Ambros RA,
Fisher HA, Kaufman RP Jr, Muraca PJ and Ross JS: Correlation of
p34cdc2 cyclin-dependent kinase overexpression, CD44
downregulation, and HER-2/neu oncogene amplification with
recurrence in prostatic adenocarcinomas. J Clin Oncol.
16:1302–1309. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Maddison LA, Huss WJ, Barrios RM and
Greenberg NM: Differential expression of cell cycle regulatory
molecules and evidence for a ‘cyclin switch’ during progression of
prostate cancer. Prostate. 58:335–344. 2004.
|