Introduction
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is a
progressive form of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Unlike simple steatosis, NASH is characterized by hepatocellular
injury accompanied by inflammation and fibrosis (1). Although factors that might forecast
the progression of NAFLD have not been clearly established, many
studies have suggested that initial fibrosis severity might be one
of the most important prognostic factors (2–4).
Therefore, preventing and treating liver fibrosis might be an
optimal treatment goal for NAFLD. NAFLD is generally included as a
component of the metabolic syndrome where insulin resistance plays
a critical role (5–7). A rat model of NASH with insulin
resistance has been reported, by feeding a methionine- and
choline-deficient (MCD) diet to an established animal model of
obese type 2 diabetes (8,9). Although MCD diet alone was reported
to be sufficient to induce severe steatosis and necroinflammation
by generating oxidative stress (10), feeding MCD diet to rats with
generalized insulin resistance accelerated NASH (8). Using this animal model it has been
reported that administration of an antifibrogenic agent improved
NASH (9).
Silymarin, a mixture of flavonoliganans extracted
from the milk thistle (Silibum marianum), has demonstrated
the protective effects in hepatocytes exposed to various chemicals
and toxins (11–14). The mechanism of this protective
effect has not been delineated, although it is often explained by
silymarin action as an antioxidant (15). Silymarin is also reported to
ameliorate carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) induced liver
fibrosis and reduced activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs)
(16).
We hypothesized that silymarin would suppress the
activation of HSCs in MCD diet fed insulin resistant rats, thereby
ameliorating NASH. In order to test this hypothesis, silymarin was
concomitantly administered with MCD diet to insulin-resistant rats,
and an ex vivo study on HSCs performed by isolating HSCs
from these rats.
Materials and methods
Materials
Silymarin was purchased from Sigma Chemicals Co.
(St. Louis, MO, USA). The MCD diet was obtained from Research
Diets, Inc. (New Brunswick, NJ, USA).
Animals and treatment
Male Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) rats,
an established animal model of obese type 2 diabetes (8), were used (Otsuka Pharmaceutical,
Tokushima, Japan). OLETF rats were reported to show obesity and
hyperinsulinemia from 8 weeks of age, and demonstrated the hepatic
accumulation of fat in an age-dependent manner (17,18). As the control animals, Long-Evans
Tokushima Otsuka (LETO) rats, which originated from the same colony
as the OLETF rats by selective mating and did not develop diabetes,
were used. Both OLETF and LETO rats were 4-weeks-old and were
housed in a room under controlled temperature (23°C), humidity, and
lighting (12-h artificial light and dark cycle). Animals were given
free access to the standard laboratory rat chow and tap water. At
24 weeks of age, rats were divided into experimental groups and fed
for 8 weeks. OLETF rats were fed on one of three different diets as
follows: the standard laboratory rat chow (OLETF/vehicle, n=10),
the MCD diet (OLETF/MCD, n=10), and the MCD diet mixed with
silymarin (OLETF/MCD+silymarin, silymarin content 0.5% w/w, n=10).
LETO rats were continued to be fed on the standard laboratory rat
chow (LETO/vehicle, n=10). Although all rats were allowed
unrestricted access to water, OLETF and LETO rats, fed on the
standard chow were pair-fed with either the MCD or with MCD and
silymarin. The body weight and food intake in each group of rats
were recorded every week. All animal procedures were performed in
accordance with the guidelines set by the Institutional Animal Care
and Use Committee at Inha University School of Medicine. After 8
weeks of feeding on experimental diets, rats were sacrificed.
Immunohistological analysis
Sections of liver tissue specimens, fixed in 10%
formalin and embedded in paraffin wax, were stained with H&E
and Masson’s trichrome for histological examination. A blinded
investigator (J.M.K.) evaluated the slides for fatty change,
inflammation existence of hepatocyte ballooning and fibrosis as
described in previous studies with minor modifications (19–22). The degree of steatosis was scored
as the percentage of hepatocytes containing macrovesicular fat
(grade 0, no steatosis; grade 1, <25%; grade 2, 26–50%; grade 3,
51–75%; grade 4, 76–100%). Inflammation was histologically
quantified by counting inflammatory foci in 20 consecutive
high-power fields (40x objective) (average histological grade,
grade 0, no foci; grade 1, <2 foci per high-power field; grade
2, ≥2 foci per high-power field). The individual scores of
steatosis, inflammation and hepatocyte ballooning were added to
produce an overall score, namely NAFLD activity score (NAS) as
previously suggested (21).
Fibrosis scores were as follows: 1, pericellular and perivenular
fibrosis; 2, focal bridging fibrosis; 3, bridging fibrosis with
lobular distortion; and 4, cirrhosis.
Sections of liver tissue specimens were
immunostained with mouse anti-human α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA)
(Dako, Carpinteria, CA, USA). Detection of the primary antibody was
carried out by immunoperoxidase technique using the ABC kit (Vector
Laboratories). Peroxidase activity was identified by reaction with
diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride substrate (DAB). Data are
represented as the number of α-SMA positive cells present in thirty
40x fields (1.3 mm2, approximately 3,000
hepatocytes).
Hepatic stellate cell isolation
It has been previously reported that HSCs could be
isolated from the injured liver using a conventional density
gradient centrifugation method (23). In this study, HSCs were isolated
from the livers of each experimental group by in situ perfusion
using collagenase and pronase (24). The viability and purity of HSC
preparations were consistently found to be >95% as accessed via
trypan blue (Gibco-BRL, Grand Island, NY, USA) exclusion and
autofluorescence, respectively (25,26).
RNA extraction and real-time polymerase
chain reaction (PCR)
Total-RNA was extracted from either frozen whole
liver or isolated HSCs using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad,
CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. RNA samples were
quantified by spectrophotometry. The RNA integrity was assessed
using agarose gel electrophoresis and ethidium bromide staining.
The RNA samples were then diluted in RNase-free water and stored at
−70°C until use.
RNA (5 μg) were reverse-transcribed using the RNA
PCR kit version 1.2 (Takara Bio, Inc., Japan) according to the
manufacturer’s recommendations. Oligonucleotide primers and the
TaqMan probe for α1-procollagen, α-SMA, sterol
regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c), tumor necrosis
factor-α (TNF-α) and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
(GAPDH) internal control were obtained from Perkin-Elmer Applied
Biosystems (Foster City, CA, USA), purchased as a ready-for-use
form in Assays-on-Demand Gene Expression products. The TaqMan probe
was labeled at the 5′ end with the reporter dye FAM and at the 3′
end with the quencher TAMRA. PCR was carried out in triplicate for
each sample on a Bio-Rad iCycler Optical Module (Bio-Rad
Laboratories, Inc., Hercules, CA, USA). Each 20-μl reaction
contained 10 μl of TaqMan Universal PCR Master Mix, 1 μl of
Assays-on-Demand Gene Expression Assay Mix and 9 μl of cDNA diluted
in RNase-free water. All reactions were carried out using the
following cycling parameters: 95°C for 10 min, followed by 40
cycles of 95°C for 15 sec and 60°C for 1 min. mRNA fold changes in
target genes relative to the endogenous GAPDH control were
calculated as suggested in previous studies (27).
Preparation of cytosolic and nuclear
fractions
The cytosolic and nuclear fraction of the protein
was extracted from liver tissue using a protein extraction kit
(Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.) according to the manufacturer’s
instruction. Briefly, 50 mg of liver tissue was added into the
chilled the Dounce homogenizer with 0.75 ml of cytoplasmic protein
extraction buffer (CPEP) and was broken up by stroking. After
incubating Dounce homogenizer containing the homogenate on ice for
2 min, the supernatant was transferred using a pipette. The cell
lysate was centrifuged at 1,000 x g for 10 min at 4°C. Upon
completion of the centrifugation, the supernatant containing
cytoplasmic protein was transferred and centrifuged, and the pellet
containing nuclei was washed using CPEP. The protein concentration
was determined with a Lowry protein assay (Bio-Rad Laboratories,
Inc.).
Western blotting
Whole cell extracts were prepared from HSCs which
were treated as described above by using Triton lysis buffer
containing protease and phosphatase inhibitors as described else
where (9). Total hepatic or whole
cell extract protein was estimated using bovine serum albumin as a
standard (DC protein assay; Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.).
Whole cell protein (50 μg) or cytosolic/nuclear
protein (50 μg) was separated by 10% sodium dodecyl
sulfatepolyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and the resolved proteins
were transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane (Schleicher and
Schuell, Middlesex, UK). The membrane was blocked with 5% skim milk
in 10 mM Tris-HCl containing 150 mM NaCl and 0.5% Tween-20
[Tris-buffered saline (TBS)-T]. After washing with TBS-T, the
membrane was then incubated with 1:1,000 dilution of specific
primary antibodies against phospho-extracellular signal-related
protein kinase (ERK) 1/2 for whole cell protein and nuclear factor
erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) (Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc.,
Santa Cruz, CA, USA) for the cytosolic/nuclear protein. The
membrane was washed and then incubated with a horseradish
peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated secondary antibody (New England
Biolabs, Beverly, MA, USA) diluted 1:2,000. After washing with
TBS-T, the membrane was developed using an enhanced
chemiluminescence detection kit (Amersham, Piscataway, NJ, USA).
Anti β-actin Ab (Cell Signaling Technology, Inc., Danvers, MA, USA)
was used to verify the equal loading of the protein samples.
Statistical analyses
All results are expressed as means or means ±
standard deviation of the mean (SD). Data were analyzed by
nonparametric analysis (Kruskal-Wallis or Mann-Whitney U test) and
P<0.05 was considered statistically significant. All
calculations were performed with SPSS version 12.0 software for
Windows (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
Results
Body and liver weight of the rat
The initial weight of LETO rats, non-diabetic
control animals for OLETF, was significantly lower as expected. The
MCD diet-fed rats had lower final body weight compared to the
standard chow-fed rat groups after 8 weeks despite the pair feeding
as previously reported (8,28,29).
However, the general condition of the MCD-fed rats remained
healthy. Relative liver weight (liver weight/final body weight) of
the MCD-fed rats was significantly higher compared to that of the
standard chow-fed rats. Adding silymarin failed to reverse the
increased relative liver weight (Table I).
 | Table I.Changes in body and liver weight. |
Table I.
Changes in body and liver weight.
| Characteristic | LETO/vehicle
LV | OLETF/vehicle
OV | OLETF/MCD OM | OLETF/MCD+silymarin
OMS |
|---|
| Initial body weight
(g) | 530.23±13.79 |
633.58±30.24a |
595.95±33.82a |
577.29±72.70a |
| Final body weight
(g) | 527.75±16.28 |
588.00±27.44a |
411.57±37.17a,b |
427.80±31.64a,b |
| Liver/final body
weight (%) | 3.67±0.10 | 3.73±0.20 |
4.53±0.16a,b |
4.30±0.26a,b |
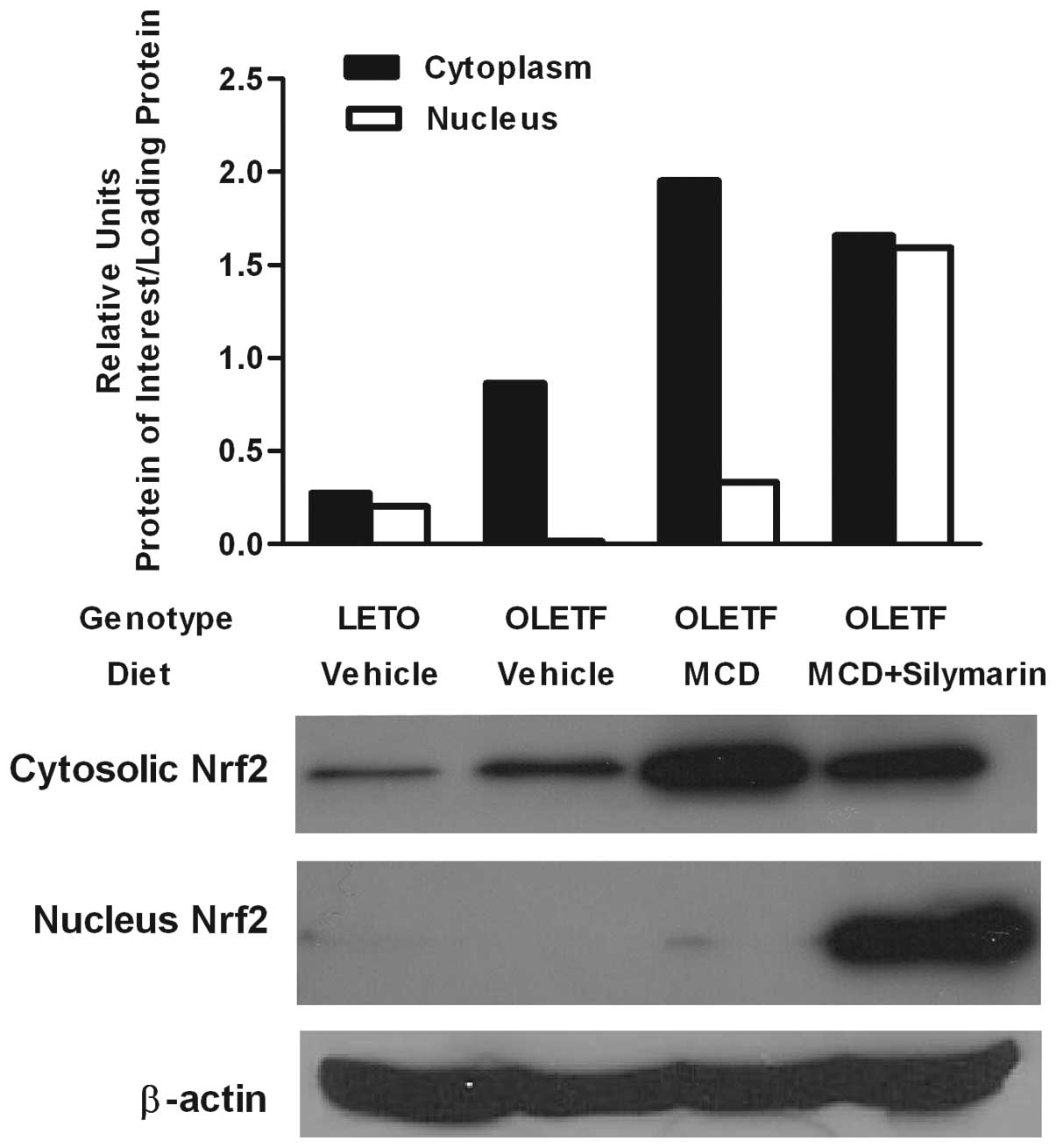
Silymarin enhances translocation of Nrf2
protein
The liver-protective effect of silymarin has been
attributed to its role as an antioxidant (30,31). Since Nrf2 is known to be crucial
for several antioxidant responsive elements, resulting in relief of
the oxidative burden of cells (32,33), nuclear translocation of Nrf2 was
evaluated by western blotting of the cytoplasmic and nuclear
protein. Cytoplasmic Nrf2 protein was increased in both MCD diet
fed rats with or without silymarin. However, nuclear Nrf2 protein
was markedly increased only in the livers of the
OLETF/MCD+silymarin group (Fig.
1).
Silymarin attenuates NAS in the animals
MCD-induced NASH model
Histological analysis of NAFLD was performed as
suggested by other studies (19–22). Fatty change, inflammation, and
existence of hepatocyte ballooning degeneration was assessed and
scored separately. Individual scores were added to produce the
overall NAS. Feeding MCD diet to OLETF rats resulted in probable or
definite NASH as expected. Concomitant administration of silymarin
lowered NAS (Table II).
 | Table II.Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
(NAFLD) activity score (NAS) of each experimental group assessed 8
weeks after the feeding with experimental diets. |
Table II.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
(NAFLD) activity score (NAS) of each experimental group assessed 8
weeks after the feeding with experimental diets.
| Characteristic | LETO/vehicle
LV | OLETF/vehicle
OV | OLETF/MCD OM | OLETF/MCD+Silymarin
OMS |
|---|
| Steatosis | 0.00±0.00 | 0.75±0.50 | 3.00±0.00 | 3.00±0.0 |
| Inflammation | 0.00±0.00 | 0.00±0.00 | 2.13±0.64 | 1.80±0.83 |
| Ballooning | 0.00±0.00 | 0.00±0.00 | 1.88±0.35 | 1.80±0.44 |
| NAS | 0.00±0.00 | 0.75±0.50 |
7.00±0.76a,b |
6.00±0.70a,b |
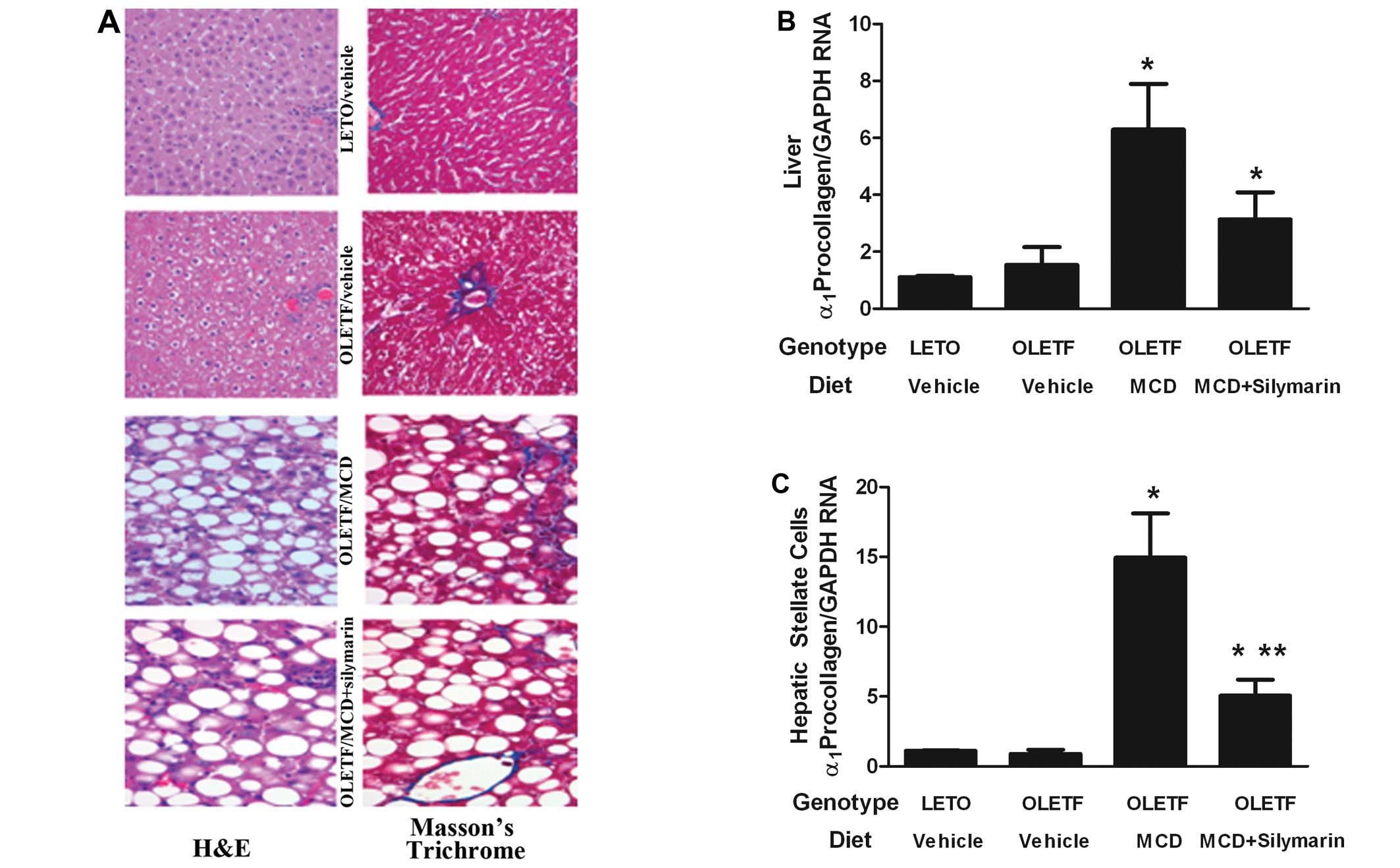
Effects of silymarin on HSCs in MCD fed
insulin-resistant rats
Histological evaluation of liver fibrosis was
performed after H&E and Masson’s trichrome stain. Despite the
significant fatty changes, insulin-resistant OLETF rats with
ordinary diet did not demonstrate liver fibrosis. The MCD diet
induced mild liver fibrosis confined to fibrosis stage 1.
Concomitant administration of silymarin with MCD diet could not
completely block the appearance of liver fibrosis (Fig. 2A). Effect of silymarin on
expression of α1-procollagen mRNA was assessed in the
whole liver.
In accordance with the histological analysis,
α1-procollagen mRNA expression was not enhanced in OLETF
rats without MCD diet when compared with LETO rats. Administration
of the MCD diet significantly increased the expression of
α1-procollagen mRNA in the whole liver lysates, which
decreased after silymarin administration (Fig. 2B).
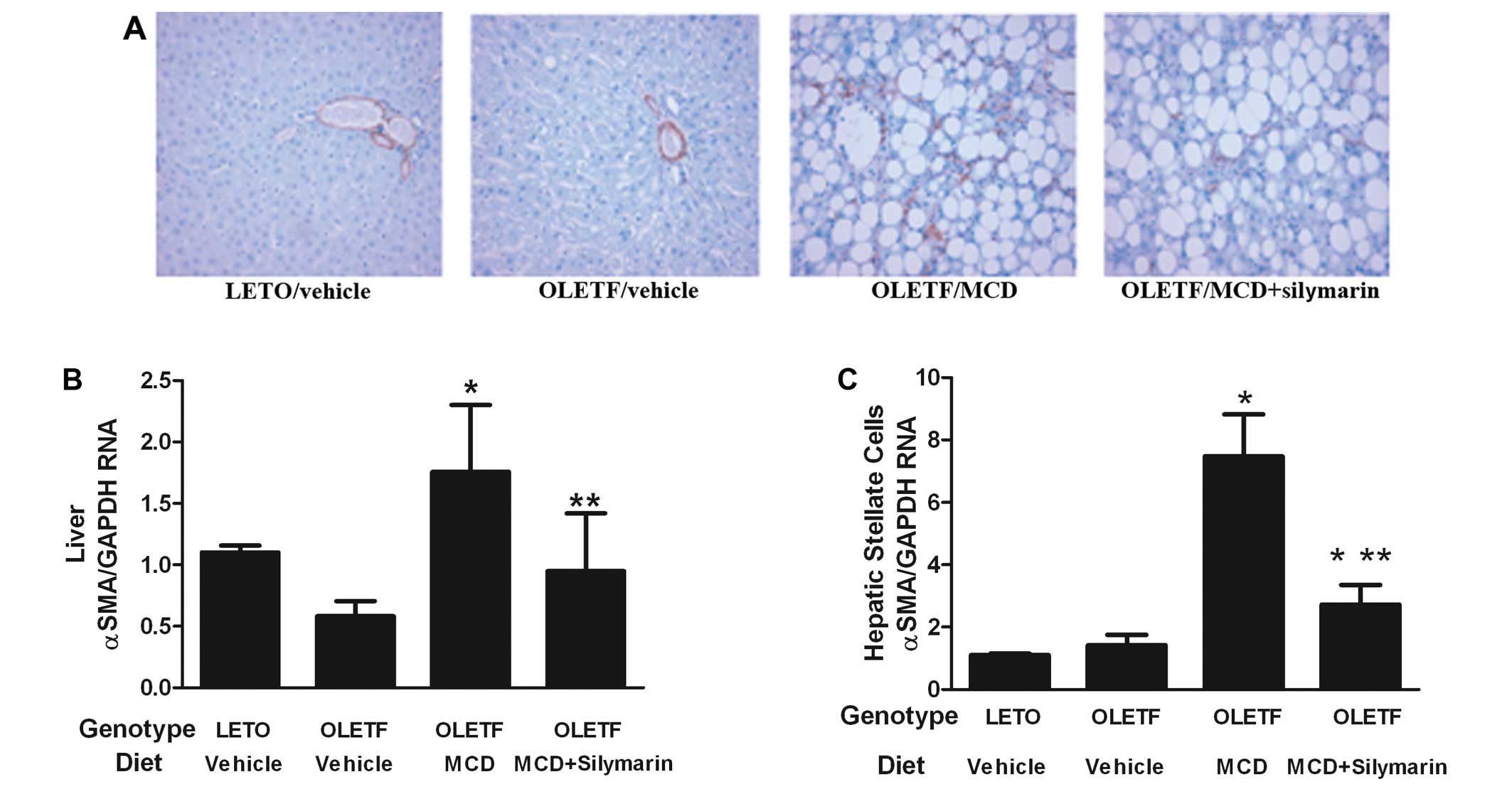
HSC activation was evaluated in the liver by
immunohistochemical analysis and assessment of α-SMA mRNA
expression in the whole liver lysates. Feeding the OLETF rats with
the MCD diet increased α-SMA positive cells in the liver and
concomitant administration of silymarin with the MCD diet
significantly decreased these cells (Fig. 3A). There was no significant
difference in α-SMA positive cells between LETO and OLETF rats fed
with standard diet. Expression of α-SMA mRNA in the liver lysates
correlated with the result of the immunohistochemical study
(Fig. 3B).
In order to investigate the direct effect of
silymarin on HSCs of MCD fed OLETF rats, HSCs were isolated from
the experimental animal. Expression of α-SMA mRNA on HSCs from
OLETF rats without the MCD diet was compatible with that of the
LETO rats. HSCs from MCD fed OLETF rats showed increased α-SMA mRNA
levels which were significantly alleviated by adding silymarin
(Fig. 3C). This result correlated
with the data obtained from the evaluation of the whole liver α-SMA
positive cells and liver lysates.
Expression of α1-procollagen mRNA was
increased in HSCs from MCD fed OLETF rats while no such change was
noticed in both OLETF rats without MCD diet and LETO rats. Giving
silymarin with the MCD diet significantly relieved this increase in
α1-procollagen mRNA expression on HSCs (Fig. 2C).
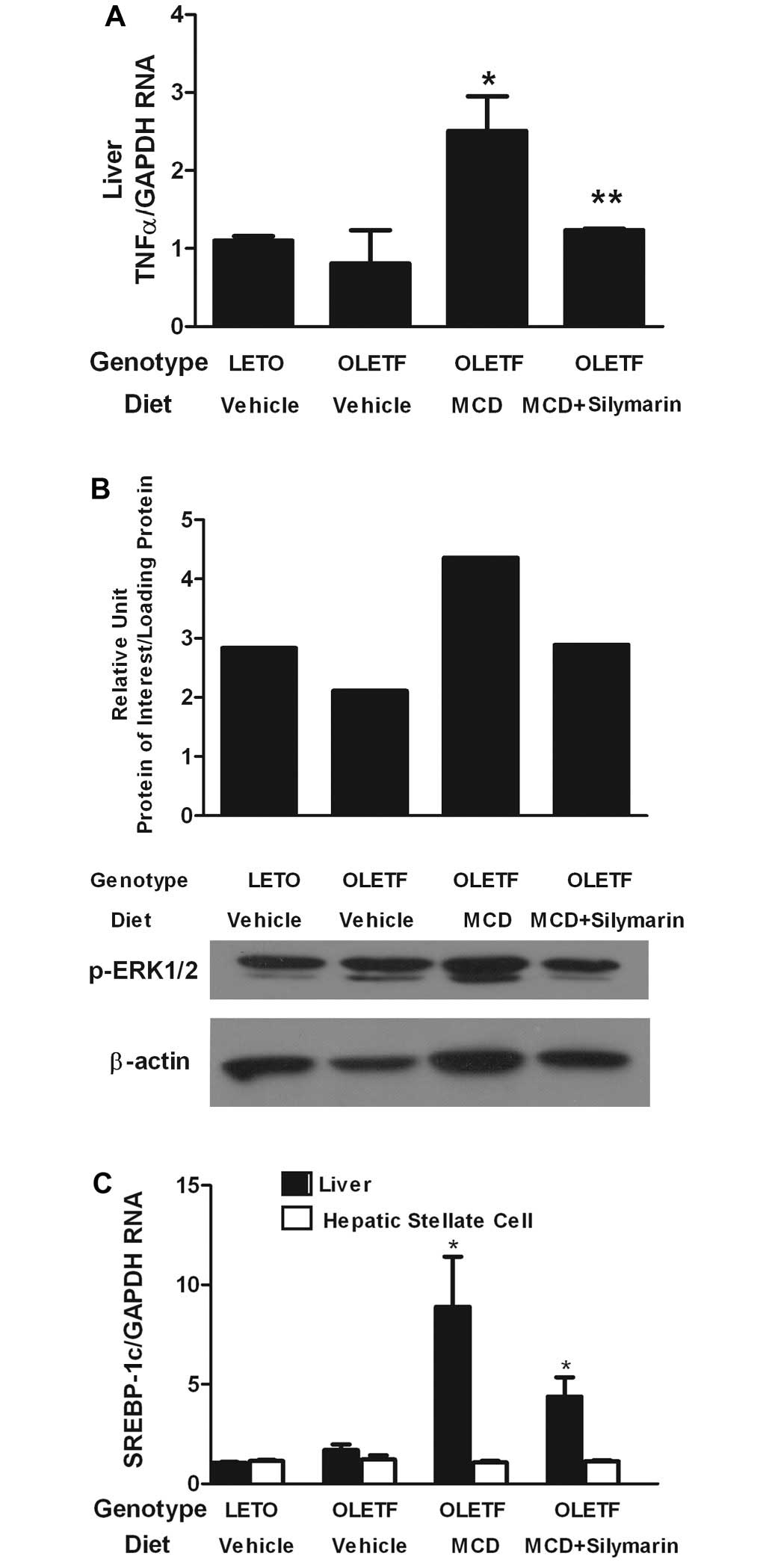
Association of the effects of silymarin
with reduced TNF-α expression on the liver and diminished ERK
activation in HSCs
The role of silymarin on inflammatory cytokine TNF-α
was investigated. Expression of TNF-α mRNA on the whole liver of
MCD diet fed OLETF rats significantly increased and was further
aggravated by the administration of the MCD diet. When silymarin
was administered with the MCD diet, expression of TNF-α mRNA was
markedly reduced in the liver (Fig.
4A). We examined whether a decrease in TNF-α expression in the
liver was accompanied by reduced ERK activation in HSCs.
Phosphorylated ERK1/2 protein expression was increased in HSCs
isolated from MCD-fed OLETF rats. The effect was reversed by
concomitant feeding of silymarin with the MCD diet (Fig. 4B).
The effect of silymarin on SREBP-1c mRNA expression,
a transcriptional factor central to the regulation of lipid
metabolism, was assessed in the whole liver. Expression of SREBP-1c
mRNA was increased in the liver of OLETF rats compared to that of
the LETO. Feeding with the MCD diet further increased the
expression of SREBP-1c mRNA compared to that of OLETF rats with
normal diet. However, concomitant administration of silymarin with
the MCD diet could not reduce the expression of SREBP-1c on the
transcriptional level in the whole liver tissue (Fig. 4C). There was no significant
difference in SREBP-1c mRNA expression on HSCs among four
experimental groups.
Discussion
Concomitant administration of silymarin and the MCD
diet to insulin-resistant rats ameliorated the NASH activity score.
This result coincided with the suppression of HSC activation and
production of α1-procollagen. However, this
anti-fibrogenic effect of silymarin was not prominent enough so as
to be demonstrated under histological analysis. This might be
attributed to our failure to generate moderate to severe fibrosis
in this particular study. Although several investigations reported
that MCD alone would induce NASH with liver fibrosis (34), our preliminary studies all failed
to generate fatty liver with considerable inflammation and fibrosis
when MCD diet alone was given to wild-type rats. When the MCD diet
was fed to rats with systemic insulin resistance, it induced more
severe inflammation as previously reported, but it still did not
generate fibrosis with more advanced grades.
When the evaluation regarding liver fibrosis was
performed in terms of HSC activation, both an in vivo and
ex vivo study showed a significant decrease in activation of
HSCs when silymarin was fed along with the MCD diet, thereby
supporting the antifibrogenic role of silymarin in diet-induced
NASH. We previously reported that HSCs could be isolated from the
injured liver, and these cells provided some interesting
information on HSC function in vivo (23). In the current study, HSC
activation was estimated in the liver by counting α-SMA positive
cells and by quantification of α-SMA mRNA expression in the whole
liver lysates. The results using these two methods were identical,
and they were in accordance with the analysis of HSCs isolated from
the experimental animal groups.
Apart from the role of silymarin on liver fibrosis,
it also seemed to diminish liver inflammation in NASH. Histological
analysis showed attenuated inflammation when silymarin was
administered along with the MCD diet, and the expression of TNF-α
mRNA was also decreased in the liver lysates. It has been reported
that TNF-α treated cultured HSCs demonstrated increased
proliferation and this effect was associated with ERK activation
(34). In accordance with this
report, our study showed that isolated HSCs from MCD diet fed OLETF
rats had increased expression of p-ERK1/2 protein and this was
reversed in rats fed with silymarin and MCD diet.
Nrf2 may upregulate many antioxidant genes. It may
play an important role in the adaptive response against oxidative
stress (35). Nrf2 activity was
reported to increase in cells exposed to oxidative stress, and upon
activation, it would translocate into the nucleus (36). In this study, there was increased
expression of Nrf2 protein in both MCD fed OLETF rats with and
without silymarin administration. However, there seemed to be more
effective nuclear translocation of Nrf2 protein in silymarin-fed
animals which might lead to the enhanced protective effect against
oxidative stress that would accompany NASH.
Our study demonstrates the possible protective
effect of silymarin against diet induced NASH by disturbing the
role of the inflammatory cytokine, TNF-α, and suppressing the
activation of HSCs. Although we used the NASH animal model which is
accompanied by systemic insulin resistance so as to simulate human
NASH, there are still existing undeniable gaps between the animal
model and the actual human disease. Liver fibrosis that is
frequently demonstrated in advanced NASH was not prominent in our
study. The effect of silymarin on NASH-associated liver fibrosis
should be further verified using various animal models.
Acknowledgements
This investigation was supported by a
grant from the National Research Foundation of Korea, grant no.
331-2008-1-E00099.
References
|
1.
|
SG HubscherHistologic assessment of
non-alcoholic fatty liver
diseaseHistopathology49450465200610.1111/j.1365-2559.2006.02416.x17064291
|
|
2.
|
SA HarrisonS TorgersonPH HayashiThe
natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a clinical
histopathological studyAm J
Gastroenterol9820422047200310.1111/j.1572-0241.2003.07659.x14499785
|
|
3.
|
F FassioE AlvarezN DominguezG LandeiraC
LongoNatural history of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a
longitudinal study of repeat liver
biopsiesHepatology40820826200415382171
|
|
4.
|
LA AdamsS SandersonKD LindorP AnguloThe
histological course of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a
longitudinal study of 103 patients with sequential liver biopsiesJ
Hepatol42132138200510.1016/j.jhep.2004.09.012
|
|
5.
|
P MarceauS BironFS HouldLiver pathology
and the metabolic syndrome X in severe obesityJ Clin Endocrinol
Metab8415131517199910.1210/jcem.84.5.566110323371
|
|
6.
|
G MarchesiniM BriziG BianchiNonalcoholic
fatty liver disease: a feature of the metabolic
syndromeDiabetes5018441850200110.2337/diabetes.50.8.184411473047
|
|
7.
|
G MarchesiniE BugianesiG
ForlaniNonalcoholic fatty liver, steatohepatitis, and the metabolic
syndromeHepatology37917923200310.1053/jhep.2003.5016112668987
|
|
8.
|
T OtaT TakamuraS KuritaInsulin resistance
accelerates a dietary rat model of nonalcoholic
steatohepatitisGastroenterology132282293200710.1053/j.gastro.2006.10.01417241878
|
|
9.
|
M UnoS KuritaH MisoTranilast, an
antifibrogenic agent, ameliorates a dietary rat model of
nonalcoholic
steatohepatitisHepatology48109118200810.1002/hep.2233818571789
|
|
10.
|
R CamposA GarridoR GuerraA
ValenzuelaSilybin dihemisuccinate protects against glutathione
depletion and lipid peroxidation induced by acetaminophen on rat
liverPlanta Med55417419198910.1055/s-2006-9620552813577
|
|
11.
|
IA LeclercqGC FarrellC SempouxA dela PenaY
HorsmansCurcumin inhibits NF-kappaB activation and reduces the
severity of experimental steatohepatitis in miceJ
Hepatol41926934200410.1016/j.jhep.2004.08.01015582125
|
|
12.
|
AB HalimO el-AhmadyS Hassab-AllahF
Abdel-GalilY HafezA DarwishBiochemical effect of antioxidants on
lipids and liver function in experimentally-induced liver damageAnn
Clin Biochem34656663199710.1177/0004563297034006109367004
|
|
13.
|
P LetteronG LabbeC DegottMechanism for the
protective effects of silymarin against carbon
tetrachloride-induced lipid peroxidation and hepatotoxicity in
mice. Evidence that silymarin acts both as an inhibitor of
metabolic activation and as a chain-breaking antioxidantBiochem
Pharmacol3920272034199010.1016/0006-2952(90)90625-U
|
|
14.
|
Z SongM SongDY LeeY LiuIV DeaciucCJ
McClainSilymarin prevents palmitate-induced lipotoxicity in HepG2
cells: involvement of maintenance of Akt kinase activationBasic
Clin Pharmacol
Toxicol101262268200710.1111/j.1742-7843.2007.00116.x17845508
|
|
15.
|
M MourelleP MurielL FavariT
FrancoPrevention of CCl4-induced liver cirrhosis by silymarinFundam
Clin
Pharmacol3183191198910.1111/j.1472-8206.1989.tb00449.x2548940
|
|
16.
|
JH TsaiJY LiuTT WuEffects of silymarin on
the resolution of liver fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride in
ratsJ Viral
Hepat15508514200810.1111/j.1365-2893.2008.00971.x18397225
|
|
17.
|
K KawanoT HirashimaS MoriY SaitohM
KurosumiT NatoriSpontaneous long-term hyperglycemic rat with
diabetic complications. Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF)
strainDiabetes4114421428199210.2337/diab.41.11.14221397718
|
|
18.
|
A Dela PeñaIA LeclercqJ FieldJ GeorgeB
JonesG FarrellNF-κB activation, rather than TNF, mediates hepatic
inflammation in a murine dietary model of
steatohepatitisGastroenterology129166316742005
|
|
19.
|
EM BruntNonalcoholic steatohepatitis:
definition and pathologySemin Liver
Dis2136200110.1055/s-2001-1292511296695
|
|
20.
|
R KirschV ClarksonEG WhephardRodent
nutritional model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: species, strain
and sex differences studiesJ Gastroenterol
Hepatol1812721282200310.1046/j.1440-1746.2003.03198.x
|
|
21.
|
DE KleinerEM BruntM Van NattaDesign and
validation of a histological scoring system of nonalcoholic fatty
liver diseaseHepatology4113131321200510.1002/hep.2070115915461
|
|
22.
|
Y YamazakiS KakizakiN HoriguchiThe role of
the nuclear receptor constitutive androstane receptor in the
pathogenesis of non-alcoholic
steatohepatitisGut56565574200710.1136/gut.2006.09326016950832
|
|
23.
|
JI LeeKS LeeYH PaikApoptosis of hepatic
stellate cells in carbon tetrachloride induced acute liver injury
of the rat: analysis of isolated hepatic stellate cellsJ
Hepatol39960966200310.1016/S0168-8278(03)00411-214642612
|
|
24.
|
G Svegliati-BaroniL D’AmbrosioG
FerrettiFibrogenic effect of oxidative stress on rat hepatic
stellate
cellsHepatology27720726199810.1002/hep.5102703139500700
|
|
25.
|
N NietoJA Dominguez-RosalesL FontanaRat
hepatic stellate cells contribute to the acute-phase response with
increased expression of alpha1(I) and alpha1(IV) collagens, tissue
inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 and matrix metalloproteinase-2
messenger RNAsHepatology33597607200110.1053/jhep.2001.22520
|
|
26.
|
RF SchwabeB SchnablYO KweonDA BrennerCD40
activates NF-kappa B and c-Jun N-terminal kinase and enhances
chemokine secretion on activated human hepatic stellate cellsJ
Immunol16668126819200110.4049/jimmunol.166.11.681211359840
|
|
27.
|
KJ LivakTD SchmittgenAnalysis of relative
gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the
2(−Delta Delta C(T)) methodMethods254024082001
|
|
28.
|
IA LeclercqGC FarrellJ FieldDR BellFJ
GonzalezGR RobertsonCYP2E1 and CYP4A as microsomal catalysts of
lipid peroxides in murine nonalcoholic steatohepatitisJ Clin
Invest10510671075200010.1172/JCI881410772651
|
|
29.
|
E IpGC FarrellG RobersonP HallR KirschI
LeclercqCentral role of PPARalpha-dependent hepatic lipid turnover
in dietary steatohepatitis in
miceHepatology38123132200310.1053/jhep.2003.5030712829994
|
|
30.
|
H LigeretA BraultD VallerandY HaddadPS
HaddadAntioxidant and mitochondrial protective effect of silibinin
in cold preservation-warm reperfusion liver injuryJ
Ethnopharmacol115507514200810.1016/j.jep.2007.10.02418061382
|
|
31.
|
MC LinSH KaoPJ ChungKC ChanMY YangCJ
WangImprovement for high fat diet-induced hepatic injuries and
oxidative stress by flavonoid-enriched extract from Nelumbo
nucifera leafJ Agric Food
Chem5759255932200910.1021/jf901058a19499892
|
|
32.
|
M HaqueAJ SanyalThe metabolic
abnormalities associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver diseaseBest
Pract Res Clin
Gastroenterol16709731200210.1053/bega.2002.032512406441
|
|
33.
|
AJ SanyalC Campbell-SargentF
MirshahiNonalcoholic steatohepatitis: association of insulin
resistance and mitochondrial
abnormalitiesGastroenterology12011831192200110.1053/gast.2001.2325611266382
|
|
34.
|
S ZhanDC RockeyTumor necrosis factor α
stimulates endothelin-1 synthesis in rat hepatic stellate cells in
hepatic wound healing through a novel IKK/JKN pathwayExp Cell
Res317104010482011
|
|
35.
|
P GongAI CederbaumNrf2 increased by CYP2E1
in rodent liver and HepG2 cells and protects against oxidative
stress caused by
CYP2E1Hepatology43144153200610.1002/hep.2100416374848
|
|
36.
|
T NguyenPJ SherrattCB PickettRegulatory
mechanisms controlling gene expression medicated by the antioxidant
response elementAnnu Rev Pharmacol
Toxicol43233260200310.1146/annurev.pharmtox.43.100901.14022912359864
|