Introduction
Periodontal diseases result in damage to periodontal
tissues, including the periodontal ligament (PDL), cementum, and
alveolar bone, and are the main cause of tooth loss in adults.
Periodontal diseases are a health burden worldwide (1). Reconstruction of healthy PDLs is a
major goal in the treatment of periodontal diseases. Human
periodontal ligament stem cells (hPDLSCs) have the potential to
form PDL, cementum, and alveolar bone and are ideal seed cells for
periodontal tissue engineering.
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are a group of
classic bone growth factors that can exert osteogenic effects on a
broad spectrum of cell types. At the same time, BMPs have been
found to be involved in the development of numerous tissues and
organs (2,3), and this nonspecificity of BMPs
usually results in unexpected side effects (4,5).
Thus, it is imperative to identify growth factors with fewer side
effects and favorable specificity as an alternative to BMPs.
NEL-like protein 1 (NELL1) is a secreted protein related to human
craniosynostosis (CS) (6) that
can specifically act on osteochondral lineage. NELL1 has been
demonstrated robust induction of bone in multiple animal models
iXn vivo (7–9). Different from BMP-2, NELL1 cannot
independently induce ectopic osteogenesis in muscle (10). NELL1’s unique role as a novel
osteo-inductive factor makes it an attractive and promising future
in clinical practice. However, few studies have reported the
osteogenic effect of NELL on hPDLSCs.
Studies have confirmed that recombinant NELL1
protein can promote the osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells
(MSCs) and subsequent bone formation (11). However, proteins may spread or be
inactivated and the dose of recombinant proteins is usually large
in clinical practice (12,13),
which then results in unexpected side effects and increases the
cost. Regional gene therapy has been regarded as an effective
strategy to resolve this limitation (14). Adenovirus-mediated NELL1 gene
therapy (AdNELL1) has been indicated to induce bone regeneration in
animal models (7,15). Bone repair is a long-term process
and adenoviruses cannot support lasting expression of target genes
(16). However, lentiviral
vectors can effectively and stably express target genes by
integrating their DNA into the host genome. Recent studies have
also confirmed that lentiviruses expressing BMP-2 are superior to
adenoviruses expressing BMP-2 in gene therapy for bone regeneration
(17). This suggests that
lentivirus expressing NELL1 (Lenti-NELL1) may be a favorable
candidate for bone regeneration.
In the present study, Lenti-NELL1 was constructed
and the feasibility of using virus to infect hPDLSCs was
investigated. In addition, the effect of NELL1 on the osteogenic
differentiation of hPDLSCs following lentivirus infection and the
potential underlying mechanisms were studied. Our results showed
that Lenti-NELL1 infected hPDLSCs could effectively express
bioactive NELL1 over a long period of time and that NELL1 could
further promote the osteogenic differentiation of hPDLSCs in
runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2) independent manner. In
summary, our findings demonstrated that Lenti-NELL1
transfection of hPDLSCs may be a promising strategy for bone and
periodontal tissue engineering.
Materials and methods
Isolation of human PDLSCs
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of
the General Hospital of People’s Liberation Army, and informed
consent was obtained before beginning the study. A total of 40
impacted, caries-free molars were extracted from 28 patients. The
PDL was gently collected and digested in 3 mg/ml type I collagen
(Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) and 4 mg/ml dispase (Roche
Diagnostics GmbH, Mannheim, Germany) for 1 h at 37°C (18). PDL samples from different patients
were pooled, and a single cell suspension was prepared and filtered
through a 200-µm pore size filter. Cells were maintained in
basic medium (α-MEM containing 10% FBS; Gibco-BRL, Grand Island,
NY, USA) at 37°C in 5% CO2. The density of cells in the
logarithmic growth phase was adjusted to 10–15 cells/ml, cells were
then seeded into a 96-well plate (100 μl/well) followed by
incubation for 12 h. The medium was added at a final volume of 200
μl in each well. When cell confluence covered 30–50% of the
bottom of the well, the cells were digested in 0.25% trypsin
(Sigma-Aldrich) and passaging was performed to acquire single
clones and subclones of stable PDLSCs.
Characterization of human PDLSCs
Immunofluorescence staining with STRO-1 was
performed to identify PDLSCs. The purified stem cells were seeded
into plates followed by incubation for 24 h. After washing in PBS,
cells were fixed in 2% p-formaldehyde for 15 min. These cells were
then incubated with mouse anti-human STRO-1 (Millipore, Billerica,
MA, USA) for 12 h and goat anti-mouse IgM (SouthernBiotech,
Birmingham, AL, USA) in the dark for 40 min. To detect the
multipotency, hPDLSCs were incubated in osteogenic and adipogenic
media (Gibco-BRL, Grand Island, NY, USA) for 21 days, alizarin red
staining and oil red O staining were performed to detect the
osteoblast- and adipocyte-like cells, respectively. hPDLSCs
maintained in basic medium served as controls.
Construction of the plasmid expressing
NELL1 (plenti-NELL1-IRES-EGFP)
The ViraPower Lentiviral Expression System
(Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) was employed to synthesize human
NELL1 (NM006157.3) with the whole genome synthetic method. A single
strand oligonucleotide was first synthesized and restriction sites
(BamHI and NheI) were included at both ends. Standard
overlap PCR was performed to ligate the synthesized oligos into a
complete sequence, which was then introduced into pMD-18T vectors
(Takara Bio, Inc., Shiga, Japan). The pMD-18T vectors were used to
transform competent DH5α cells (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA), and
overlap PCR was performed to repair the mutated sites. Restriction
enzymes (BamHI and NheI; Fermentas, Inc., Glen
Burnie, MD, USA) were used to treat the sequence, and the products
were ligated into the target vector plenti-MCS-IRES-EGFP, which was
then transformed into competent Stb13 cells (were from Invitrogen).
Sequencing was performed to determine the inserted sequence and
whether plenti-NELL1-IRES-EGFP could express NELL1.
Viral packing and detection of viral
titer
The plenti-NELL1-IRES-EGFP vectors were mixed with
Packing Mix, Lipofectamine 2000, and Opti-MEM (were from
Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. This
mixture was then added to 293T cells followed by incubation at 37°C
for 6 h. The medium was refreshed with DMEM containing 10% FBS
followed by incubation for 48 h. The supernatant was collected and
centrifuged at 50,000 x g for 2 h at 4°C. The virus particles were
resuspended and stored at −80°C. The virus suspension was serially
diluted, which was then added to HEK293 cells. Fluorescence
microscopy was performed to determine the required titer of the
virus.
Cell transfection
hPDLSCs with favorable growth were seeded into
plates. When cell confluence reached >80%, the cells were
incubated in DMEM containing 5% FBS followed by addition of virus
suspension at multiplicities of infection (MOIs) of 0, 10, 50, 100,
150 and 200. A total of 12 h later, the cells were incubated with
basal medium for 60 h. Then, cells that were positive for green
fluorescence were counted and the cell status was also
observed.
Western blot analysis
Cells were harvested 14 days after lentivirus
transfection. The cell lysate was subjected to SDS-PAGE for protein
separation. The proteins were then transferred onto a PVDF membrane
(Millipore), which was subsequently incubated with 5% non-fat milk
for 1 h. The membrane was then treated with mouse anti-human NELL1
(Sigma-Aldrich) at 4°C overnight and then with a goat anti-mouse
secondary antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Santa Cruz, CA,
USA) for 1 h. GAPDH served as an internal reference (Shanghai
KangCheng Bio-tech, Shanghai, China). Visualization was performed
with ECL (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Rockford, IL, USA). A FluorChem
HD2 gel image system (ProteinSimple, Santa Clara, CA, USA) was
employed to determine the expression of the target protein.
Proliferation assay
Cells were seeded into a 96-well plate
(2×104 cells/well), and an MTS kit (Promega Corporation,
Madison, WI, USA) was employed to detect cell proliferation (OD at
490 nm) (19).
Alkaline phosphatase activity assay
A colorimetric method was used to measure alkaline
phosphate (ALP) activity according to the manufacturer’s
instructions (Nanjing Biotechnology, Nanjing, China) (19). OD was measured at 490 nm.
Alizarin red staining
Samples were fixed in 10% formalin for 15 min and
then in 1% alizarin red for 2 min. Following washing in water,
alizarin red was quantitated. In brief, samples were washed with
10% cetylpyridinium chloride (CPC) to remove the alizarin red and
spectrophotometry was performed to measure the OD at 490 nm
(20). Detection was done in
triplicate and each experiment was performed twice.
Real-time PCR analysis
Total-RNA was extracted with TRIzol reagent
(Invitrogen). BioPhotometer Plus (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany) was
employed to measure the concentration and purity of the RNA. A
RevertAid First Strand cDNA Synthesis kit (Fermentas, Inc.) was
used to synthesize first strand cDNA, and PCR was performed with
SYBR-Green Real-Time PCR Master Mix (Applied Biosystems, Foster
City, CA, USA). The mRNA expression of NELL1, Runx2,
Msx2 and GAPDH was detected using an ABI PRISM 7500
Real-time PCR system (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA).
GAPDH served as an internal reference, and the mRNA expression of
the target genes was normalized to that of GAPDH (14). Specific human genes and primer
sequences are listed in Table
I.
 | Table IPrimer sequences. |
Table I
Primer sequences.
| Human genes
name | Forward primer
sequence (5′→3′) | Reverse primer
sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|
| NELL1 |
GCTTTGGGATGGACCCTGAC |
GAAATAAAAATGCTTTGCTGGC |
| Runx2 |
CTCTACTATGGCACTTCGTCAGG |
GCTTCCATCAGCGTCAACAC |
| Msx2 |
AGATGGAGCGGCGTGGAT |
TGGAGGGCAGCATAGGTTT |
| GAPDH |
GTCTCCTCTGACTTCAACAGCG |
ACCACCCTGTTGCTGTAGCC |
ELISA for osteocalcin
At 7, 14 and 21 days after transfection, ELISA
(Invitrogen) was performed to measure osteocalcin (OCN) in the
supernatant at 490 nm, and the OD value was recorded.
Statistical analysis
Data are presented as the mean with standard
deviation. The comparisons between the 2 groups were tested with
the independent two-sample t-test. P-values <0.05 were
considered statistically significant. Statistical analyses were
performed using SPSS v15.0 statistics software (SPSS, Chicago, IL,
USA).
Results
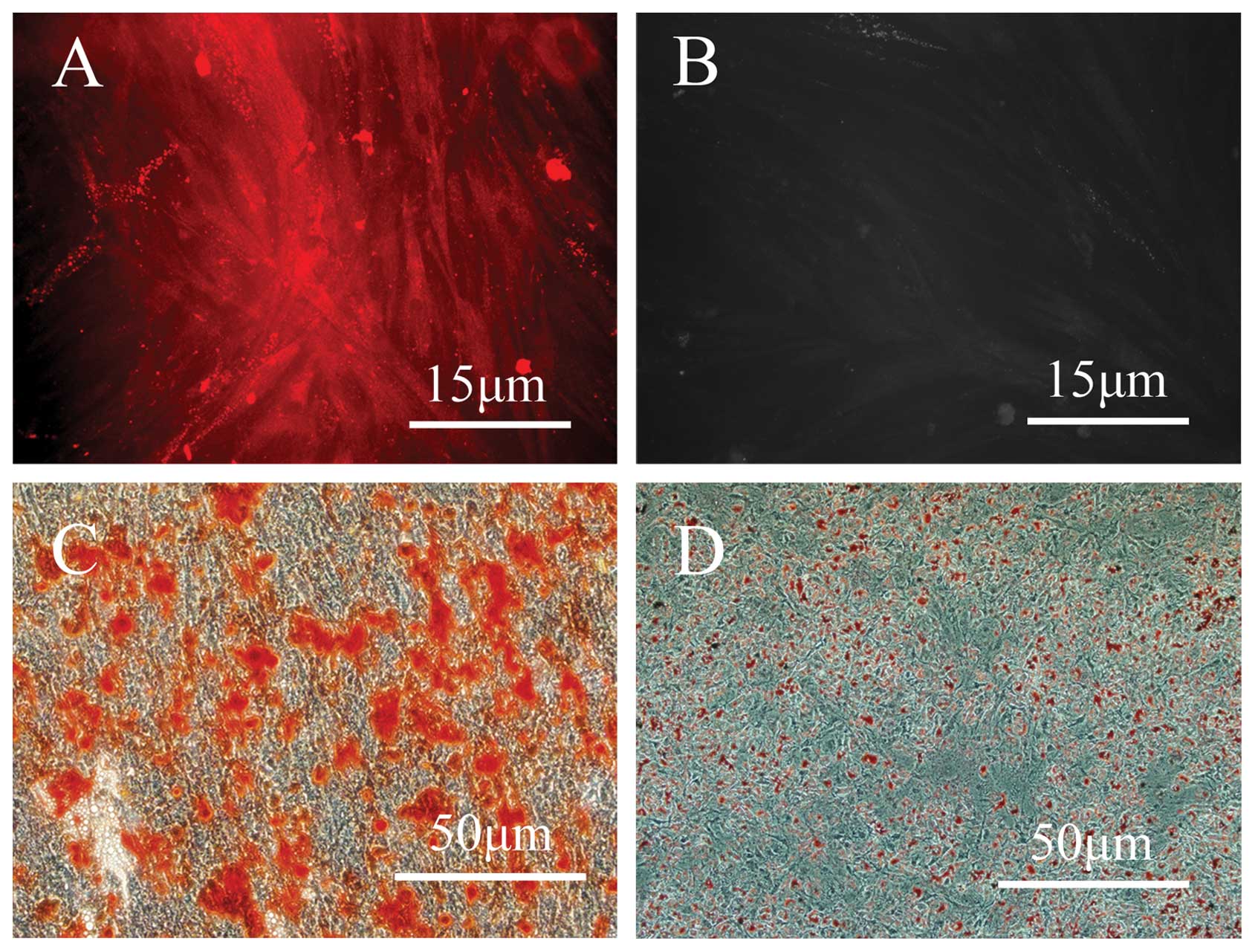
Characterization of human PDLSCs
After digestion with collagenase, hPDLSCs were
successfully collected and >90% of the cells were observed to be
positive for STRO-1 (Fig. 1A and
B). To identify the multipotency of the isolated cells, the
hPDLSCs were cultured in osteogenic and adipogenic media for 21
days, and the differentiation into these lineages was confirmed by
alizarin red and oil red O staining, respectively (Fig. 1C and D).
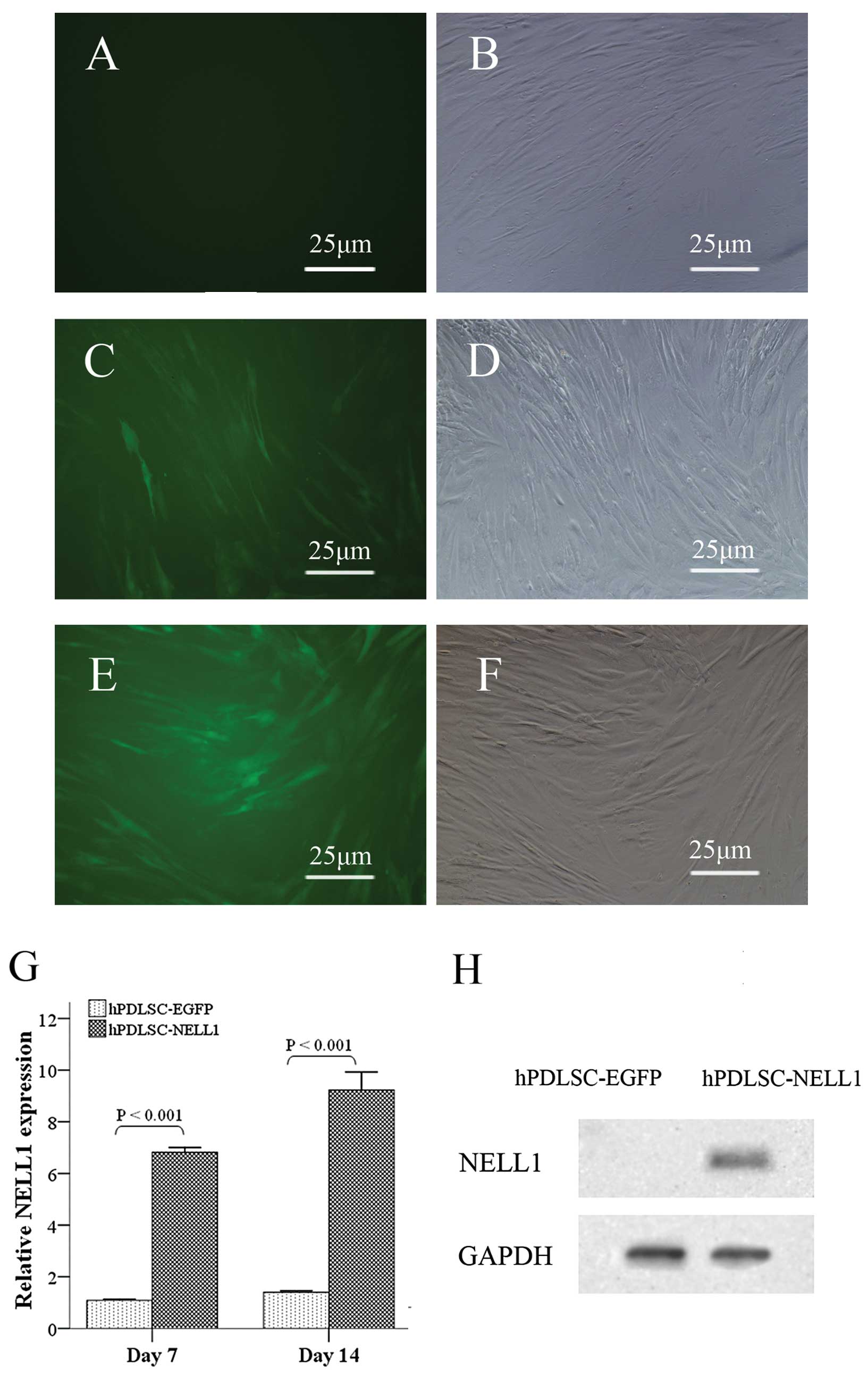
Gene transduction and the effects on cell
proliferation
In order to establish the optimal MOI for high
lentivirus gene transfer efficiency, a series of MOIs were assessed
in this study. A MOI of 100 pfu/cell achieved high transfer
efficiency above 90% 72 h after lenti-EGFP transduction of hPDLSCs
were positive for green fluorescence (Fig. 2C and D). While in the Lenti-NELL1
group, more than 90% of cells were positive for green fluorescence
only when the MOI was 150 pfu/cell (Fig. 2E and F). In addition, the
morphology of the cells in the Lenti-NELL1 group was similar to
that in the Lenti-EGFP group (Fig. 2A
and B). Quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) showed
that the mRNA expression of NELL1 in the Lenti-NELL1 group
at 7 and 14 days after transfection was increased 7.02- and
9.23-fold (P<0.001), respectively, when compared with that in
the Lenti-EGFP group at Day 0 (Fig.
2G). Western blotting assays also demonstrated that cells in
the Lenti-NELL1 group expressed NELL1 (Fig. 2H).
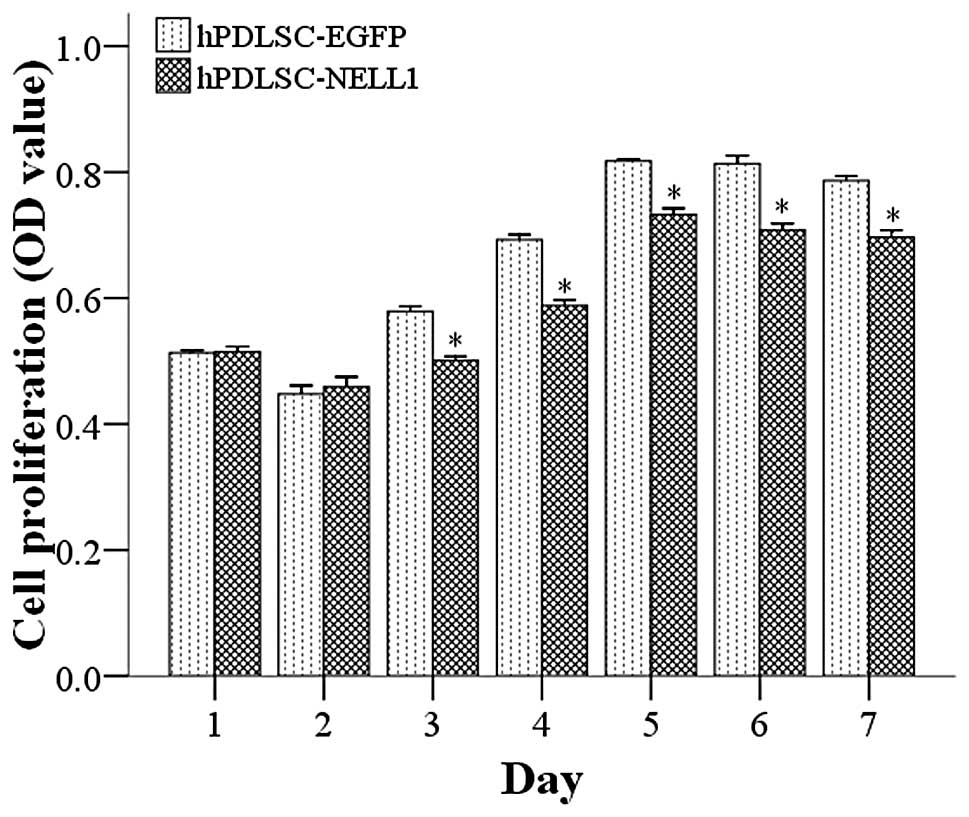
The proliferation and differentiation of stem cells
are 2 opposing processes. Cells with high differentiation usually
have low proliferation and those with high proliferation often
present with low differentiation (21). Thus, theoretically, NELL1 may not
only promote the differentiation of hPDLSCs but also inhibit their
proliferation. A previous study showed that AdNELL1-transfected
goat MSCs inhibited proliferation (7). As expected, 1 and 2 days after
transfection, the proliferation of cells in the Lenti-NELL1 group
was comparable to that in the Lenti-EGFP group. However, 3 days
after transfection, the proliferation of hPDLSCs in the Lenti-NELL1
group was markedly lower than that in the control group (P<0.01)
(Fig. 3).
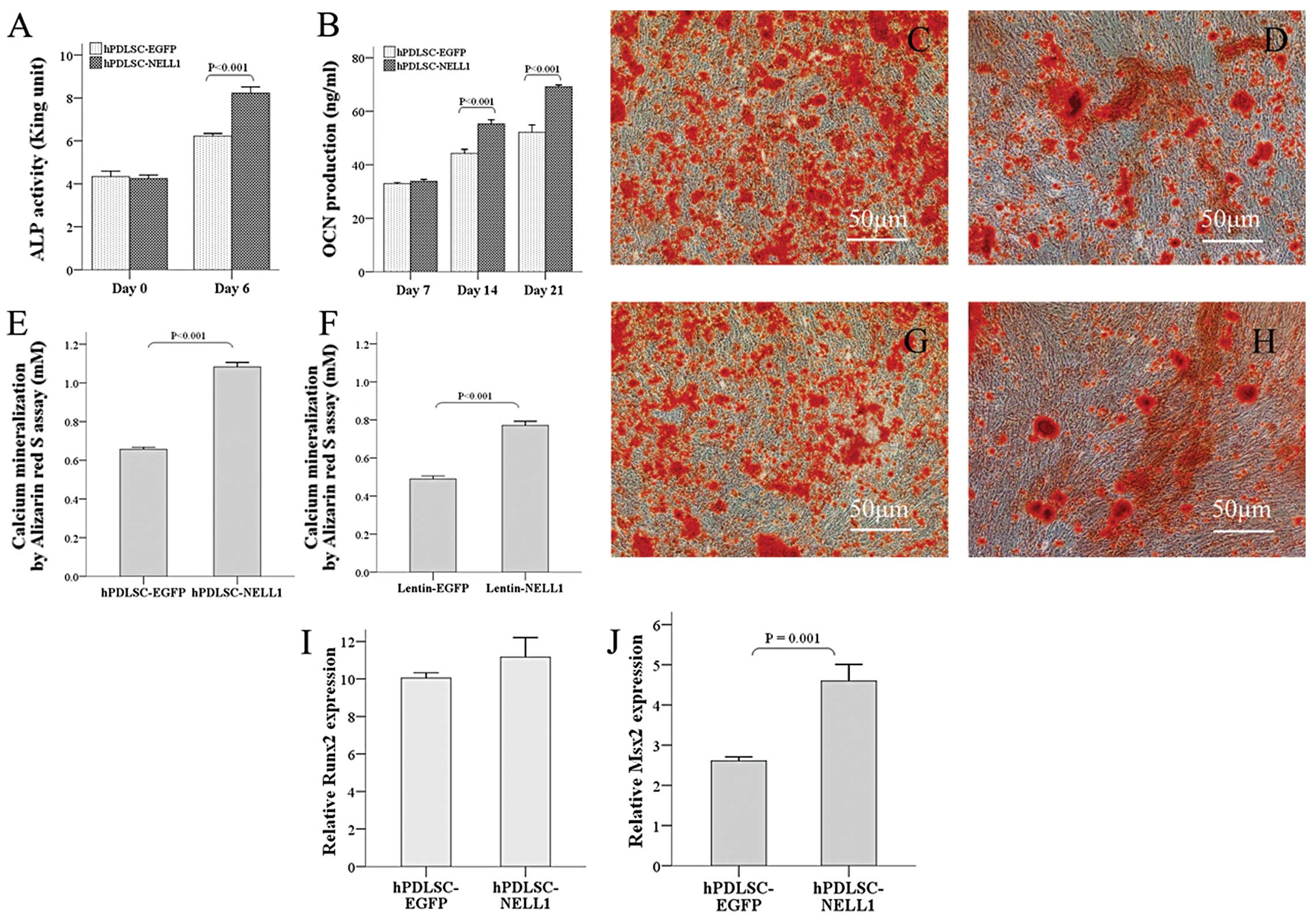
Osteogenic differentiation of hPDLSCs in
vitro after gene transduction
Under appropriate conditions, PDLSCs may
differentiate into multiple cells, including osteoblasts and
adipocytes (18,22). In the present study, cells
transfected with Lenti-EGFP served as controls and the osteogenic
effect of NELL1 was determined. After transfection, these cells
received osteogenic induction. ALP is a marker of early
osteogenesis. The results showed that, as compared to the control
group, cells in the Lenti-NELL1 group had comparable ALP activity
at Day 0 but showed significantly increased ALP activity 6 days
after induction (P<0.001) (Fig.
4A). For the osteogensis late indicator of OCN, their
production was similar to that above. At 7 and 14 days after
induction, OCN levels in the Lenti-NELL1 group were markedly higher
than in the control group (P<0.001) (Fig. 4B). In addition, alizarin red
staining showed that more calcium was found in the Lenti-NELL1
group than in the Lenti-EGFP group (Fig. 4C and D). Quantitative analysis
showed that calcium mineralization was more evident in the
Lenti-NELL1 group than in the control group (P<0.001) (Fig. 4E). On the other hand, NELL1 is a
secreted protein. To further validate whether NELL1 in
Lenti-NELL1-transfected hPDLSCs was biologically active, the
supernatant was mixed with normal osteogenic media made of the
conditional medium at a ratio of 1:1 for osteogenic cultured 21
days. The results showed more calcium deposition in the Lenti-NELL1
than in the control group (P<0.001) (Fig. 4F–H). The above findings indicated
that Lenti-NELL1-transfected hPDLSCs were able to successfully
express bone-inducing active NELL1 protein that could vigorously
facilitate the osteogenic differentiation of hPDLSCs at early and
late stages.
To explore the probable mechanism underlying the
promotion of PDLSCs osteogenic differentiation by NELL1, two
primary transcription factors (Runx2 and Msx2) involved in
osteogenic differentiation were investigated. Studies have
demonstrated that NELL1 is a downstream factor of Runx2 and is
directly regulated by Runx2 (23). As expected, although Runx2 mRNA
expression in the Lenti-NELL1 group at 7 and 14 days after
transfection was increased 11.17 and 10.05-fold when compared with
that in the control group at Day 0, no distinct difference was
noted between the two groups (P>0.01) (Fig. 4I). Msx2 is an important regulator
in osteogenesis, especially in the Runx2 independent signaling
pathway. Interestingly, like NELL1, Msx2 is also highly related to
CS and plays an equally important role in craniofacial development
(24). When compared with the
control group at Day 0, Msx2 mRNA as compared with the control
group at Day 0, the Lenti-NELL1 group at Day 7 was increased by
4.6-fold higher than that in the control group (2.61-fold).
(P<0.001) (Fig. 4J). These
findings implied that NELL1, Runx2 and Msx2 may be involved in
enhancing hPDLSC osteogenic differentiation, although it is
unclear, our study is essential for understanding NELL1’s potent
osteoinduction effect.
Discussion
PDLSC is a neural crest-deried stem cell with the
charactistcs of neural ectoderm and mesoderm differentiation
potential and potent plasticity (22,25,26). Different from other MSCs, PDLSCs
have enomous potential to form PDL, alveolar bone, and cementum and
have been regarded as ideal seed cells in the treatment of
craniofacial bone defects, especially for periodontal
regeneration.
Unlike the gold-standard osteoinductive factors
BMPs, NELL1 can only specifically act on osteochondral lineage and
MSCs (7,9,27),
act as a crucial factor involved in the differentiation of neural
crest cells into osteoblasts (28). For other nonosteochondral lineage,
such as C2C12 myoblasts, NELL1 cannot independently induce
osteogenesis (10). On the other
hand, NELL1 does provide an advantage in the promotion of bone
regeneration. Cowan et al (8) investigated the role of NELL1 in the
suture of distracted palates of 4-week-old male rats. The results
showed that NELL1 and BMP7 could significantly induce bone
formation and newly formed bone in the NELL1 treated group was
superior in mineralization and maturity of chondrocytes to that in
the BMP7 group. To date, few studies have reported the effect of
NELL1 on the osteoblast differentiation of hPDLSCs. In the present
study, our results confirmed that a NELL1-expressing lentivirus
effectively transfected hPDLSCs, which expressed NELL1 over an
extended time period. In addition, NELL1 could potently improve the
osteogenesis of hPDLSCs in vitro.
Currently, it has been demonstrated that recombinant
NELL1 protein can promote bone regeneration in bone-defect animal
models (8,9,11).
When protein is applied, the dose is usually at a high level, which
may induce potential side effects and increase therapeutic cost.
Regional gene therapy may be a preferred stratege for delivering
protein in specific anatomical sites. The selection of optimal
vectors is crucial in regional gene therapy. Although studies have
shown that adenovirus vectors encoding NELL1 can successfully
promote bone regeneration (7,15),
the target gene introduced by an adenovirus is episomal with the
risk of inducing host immune response. Furthermore, adenoviruses
cannot express the target gene lasting adequate time (16,17). Thus, when repair large bone
defects with adenovirus vectors, sufficient amounts and sustained
delivery of NELL1 cannot be assured. Lentiviruses can integrate DNA
into the host genome, resulting in long-term expression of the
target protein (17,29). Previous studies have shown that
NELL1 expression in AdNELL1-transfected MC3T3 cells reached a peak
level 3 days after transfection, but this rapidly decreased at 6
days after transfection (9). In
the present study, Lenti-NELL1-transfected cells presented green
fluorescence under a fluorescence microscope during the entire
study period (6 weeks) (data not shown). Furthermore, qPCR also
verified that at 14 days after transfection, NELL1 mRNA
expression was still at a high level. Safety must be considered
seriously before viral vectors are applied. In our study, the high
efficient packaging system of the third lentivirus was used, which
was less likely to produce replication-competent virus (RCV)
(30,31). Next, we will further validate the
efficacy of Lenti-NELL1 modified hPDLSCs compared with those
obtained by adenovirus for periodontal tissue regeneration in
rodent models.
Although our results demonstrated that NELL1 could
effectively enhance the osteogenic differentiation of hPDLSCs, the
potential mechanism of this process was still unclear. Thus, qPCR
was further applied to measure the mRNA expression of Runx2
and Msx2 in PDLSCs overexpressing NELL1 after osteogenic
induction. Runx2 is a key factor related to osteogenesis, as it can
control the osteogenic differentiation of stromal cells through
temporarily activating or inhibiting the growth and gene expression
of stromal cells (32). The
results showed that, although NELL1 overexpression could improve
the osteogenic differentiation of hPDLSCs, cells overexpressing
NELL1 had comparable Runx2 expression to those in the
control group. This may be attributed to the hierarchical
relationship between NELL1 and Runx2 in the signaling pathway.
Studies have found that NELL1 might be a downstream target of
Runx2. Runx2 can upregulate NELL1 expression by binding to the
osteoblast-specific cis-acting element 2 (OSE2) in its
promoter (23,33). Our study found that overexpssion
of NELL1 in hPDLSCs had no effect to Runx2 expression comparing to
the control group consistent with other findings (23). It implies that Runx2 may exert its
osteogenic effect via regulation of NELL1 expression.
Insterstingly, Msx2 has similar functions to NELL1. Studies have
revealed that Msx2 mutation is related to Boston type CS (24). Currently, roles of Msx2 in
osteogenesis is controversial. Genetic analysis in human diseases
and animal models have shown Msx2’s positive role in improving
osteogenesis (24,34); while in vitro study has
revealed that Msx2 can inhibit osteogenesis (35). There is evidence that NELL1
overexpression-induced craniofacial abnormalities in animal models
are similar to those in animals with Msx2 overexpression (28). In both animal models, cranial
suture overgrowth and increased incidence of exencephaly were
noted. Currently, roles of NELL1 and Msx2 in craniofacial bone
development, CS, and osteogenic differentiation are still unclear.
The results in the present study showed that NELL1 overexpression
could significantly upregulate Msx2 expression. A prior
study showed that the NELL1 promoter contains an Msx2
binding sequence, NELL1 expression is regulated by Msx2, and
Msx2-transfected fetal rat calvarial cells have a reduced
expression of NELL1 (34).
Combined with our findings, it suggested that NELL1 and Msx2 may
intricately interrelate during osteogenesis, and more studies are
required to elucidate their mechanism of enhancing
osteogenisis.
In summary, the above findings suggested
Lenti-NELL1 transfection of hPDLSCs leads to overexpression
of NELL1, which further improved osteogenesis of these cells in
vitro. However, in vivo study was not performed to
validate the above findings. Our group is conducting the
application of NELL1-transfected PDLSCs to repair alveolar
bone defects in animal models. We expect that the findings in this
study will consummate the investigation about NELL1’s
osteoinductive effect on PDLSCs and provide a basis for further
studies on the application of NELL1 as a growth factor and PDLSCs
as seed cells in bone regeneration and periodontal tissue
regeneration.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the
National Natural Science Foundation of China. We thank associate
Professor H. Wang at the Institute of Radiation of Academy of
Military Medical Sciences and the associate Professor S.Y. Si at
the Central Laboratory of the 306th Hospital of PLA for their kind
help.
References
|
1.
|
JR ElterS OffenbacherJF TooleJD
BeckRelationship of periodontal disease and edentulism to
stroke/TIAJ Dent
Res829981001200310.1177/15440591030820121214630902
|
|
2.
|
P DucyG KarsentyThe family of bone
morphogenetic proteinsKidney
Int5722072214200010.1046/j.1523-1755.2000.00081.x10844590
|
|
3.
|
J Rivera-FelicianoCJ TabinBmp2 instructs
cardiac progenitors to form the heart-valve-inducing fieldDev
Biol295580588200610.1016/j.ydbio.2006.03.04316730346
|
|
4.
|
M FranzA BerndtF WehrhanP SchleierJ
ClementP HyckelEctopic bone formation as a complication of surgical
rehabilitation in patients with Moebius’ syndromeJ Craniomaxillofac
Surg35252257200717855104
|
|
5.
|
TE MrozJC WangR HashimotoDC
NorvellComplications related to osteobiologics use in spine
surgery: a systematic reviewSpine (Phila Pa 1976)35Suppl
9S86S104201010.1097/BRS.0b013e3181d81ef220407355
|
|
6.
|
K TingH VastardisJB MullikenHuman NELL-1
expressed in unilateral coronal synostosisJ Bone Miner
Res148089199910.1359/jbmr.1999.14.1.809893069
|
|
7.
|
T AghalooX JiangC SooA study of the role
of nell-1 gene modified goat bone marrow stromal cells in promoting
new bone formationMol
Ther1518721880200710.1038/sj.mt.630027017653100
|
|
8.
|
CM CowanS ChengK TingNell-1 induced bone
formation within the distracted intermaxillary
sutureBone384858200610.1016/j.bone.2005.06.02316243593
|
|
9.
|
T AghalooCM CowanYF ChouNell-1-induced
bone regeneration in calvarial defectsAm J
Pathol169903915200610.2353/ajpath.2006.05121016936265
|
|
10.
|
CM CowanX JiangT HsuSynergistic effects of
Nell-1 and BMP-2 on the osteogenic differentiation of myoblastsJ
Bone Miner Res22918930200710.1359/jbmr.07031217352654
|
|
11.
|
RK SiuSS LuW LiNell-1 protein promotes
bone formation in a sheep spinal fusion modelTissue Eng Part
A1711231135201110.1089/ten.tea.2010.048621128865
|
|
12.
|
J Louis-UgboHS KimSD BodenRetention of
125I-labeled recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 by
biphasic calcium phosphate or a composite sponge in a rabbit
posterolateral spine arthrodesis modelJ Orthop
Res2010501059200210.1016/S0736-0266(02)00011-6
|
|
13.
|
MD KofronCT LaurencinOrthopaedic
applications of gene therapyCurr Gene
Ther53761200510.2174/156652305299748815638710
|
|
14.
|
AW BaltzerJR LiebermanRegional gene
therapy to enhance bone repairGene
Ther11344350200410.1038/sj.gt.330219514724686
|
|
15.
|
SS LuX ZhangC SooThe osteoinductive
properties of Nell-1 in a rat spinal fusion modelSpine
J75060200710.1016/j.spinee.2006.04.02017197333
|
|
16.
|
BT FeeleyAH ConduahO SugiyamaL KrenekIS
ChenJR LiebermanIn vivo molecular imaging of adenoviral versus
lentiviral gene therapy in two bone formation modelsJ Orthop
Res2417091721200610.1002/jor.2022916788987
|
|
17.
|
MS VirkA ConduahSH ParkInfluence of
short-term adenoviral vector and prolonged lentiviral vector
mediated bone morphogenetic protein-2 expression on the quality of
bone repair in a rat femoral defect
modelBone42921931200810.1016/j.bone.2007.12.21618295562
|
|
18.
|
BM SeoM MiuraS GronthosInvestigation of
multipotent postnatal stem cells from human periodontal
ligamentLancet364149155200410.1016/S0140-6736(04)16627-015246727
|
|
19.
|
Q TuP ValverdeJ ChenOsterix enhances
proliferation and osteogenic potential of bone marrow stromal
cellsBiochem Biophys Res
Commun34112571265200610.1016/j.bbrc.2006.01.09216466699
|
|
20.
|
AW JamesA PanM ChiangA new function of
Nell-1 protein in repressing adipogenic differentiationBiochem
Biophys Res
Commun411126131201110.1016/j.bbrc.2011.06.11121723263
|
|
21.
|
SJ LeeSW KangHJ DoEnhancement of bone
regeneration by gene delivery of BMP2/Runx2 bicistronic vector into
adipose-derived stromal
cellsBiomaterials3156525659201010.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.03.01920413153
|
|
22.
|
W TechawattanawisalK NakahamaM KomakiM
AbeY TakagiI MoritaIsolation of multipotent stem cells from adult
rat periodontal ligament by neurosphere-forming culture
systemBiochem Biophys Res
Commun357917923200710.1016/j.bbrc.2007.04.03117459343
|
|
23.
|
T TruongX ZhangD PathmanathanC SooK
TingCraniosynostosis-associated gene nell-1 is regulated by runx2J
Bone Miner Res22718200710.1359/jbmr.06101217042739
|
|
24.
|
AO WilkieZ TangN ElankoFunctional
haploinsufficiency of the human homeobox gene MSX2 causes defects
in skull ossificationNat Genet24387390200010.1038/7422410742103
|
|
25.
|
D WideraWD GrimmJM MoebiusHighly efficient
neural differentiation of human somatic stem cells, isolated by
minimally invasive periodontal surgeryStem Cells
Dev16447460200710.1089/scd.2006.006817610375
|
|
26.
|
GS CouraRC GarcezCB de AguiarM
Alvarez-SilvaRS MaginiAG TrentinHuman periodontal ligament: a niche
of neural crest stem cellsJ Periodontal
Res43531536200810.1111/j.1600-0765.2007.01065.x18624954
|
|
27.
|
X ZhangD CarpenterN BokuiOverexpression of
Nell-1, a craniosynostosis-associated gene, induces apoptosis in
osteoblasts during craniofacial developmentJ Bone Miner
Res1821262134200310.1359/jbmr.2003.18.12.212614672347
|
|
28.
|
X ZhangS KurodaD CarpenterCraniosynostosis
in transgenic mice overexpressing Nell-1J Clin
Invest110861870200210.1172/JCI1537512235118
|
|
29.
|
M MiyazakiO SugiyamaJ ZouComparison of
lentiviral and adenoviral gene therapy for spinal fusion in
ratsSpine (Phila Pa
1976)3314101417200810.1097/BRS.0b013e318176100318475244
|
|
30.
|
L NaldiniU BlomerP GallayIn vivo gene
delivery and stable transduction of nondividing cells by a
lentiviral
vectorScience272263267199610.1126/science.272.5259.2638602510
|
|
31.
|
T KafriU BlomerDA PetersonFH GageIM
VermaSustained expression of genes delivered directly into liver
and muscle by lentiviral vectorsNat
Genet17314317199710.1038/ng1197-3149354796
|
|
32.
|
CA YoshidaT FuruichiT FujitaCore-binding
factor beta interacts with Runx2 and is required for skeletal
developmentNat Genet32633638200210.1038/ng101512434152
|
|
33.
|
X ZhangK TingCM BessetteNell-1, a key
functional mediator of Runx2, partially rescues calvarial defects
in Runx2(+/−) miceJ Bone Miner Res26777791201120939017
|
|
34.
|
YX ZhouX XuL ChenC LiSG BrodieCX DengA
Pro250Arg substitution in mouse Fgfr1 causes increased expression
of Cbfa1 and premature fusion of calvarial suturesHum Mol
Genet920012008200010.1093/hmg/9.13.200110942429
|
|
35.
|
K ShirakabeK TerasawaK MiyamaH ShibuyaE
NishidaRegulation of the activity of the transcription factor Runx2
by two homeobox proteins, Msx2 and Dlx5Genes
Cells6851856200110.1046/j.1365-2443.2001.00466.x11683913
|