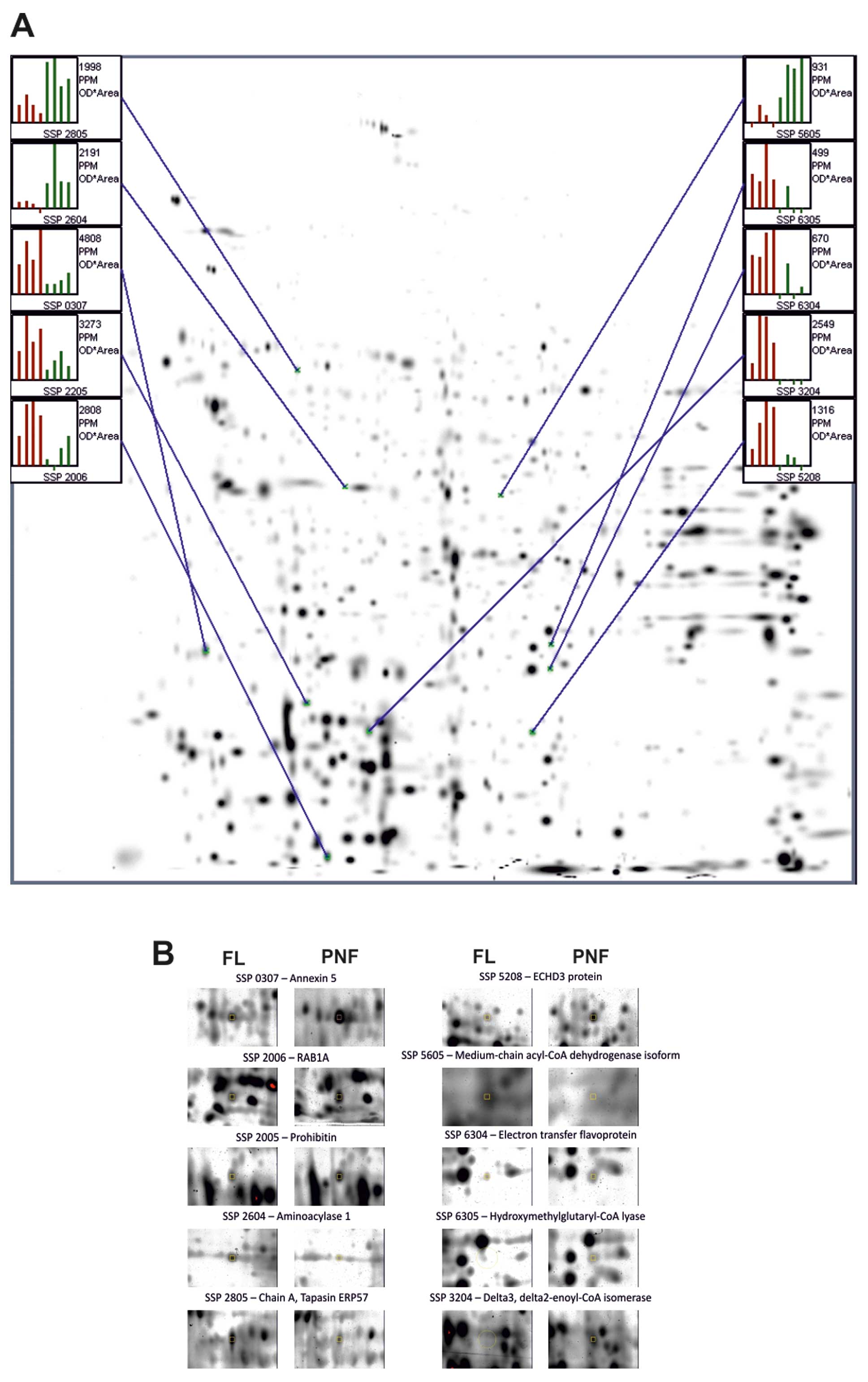
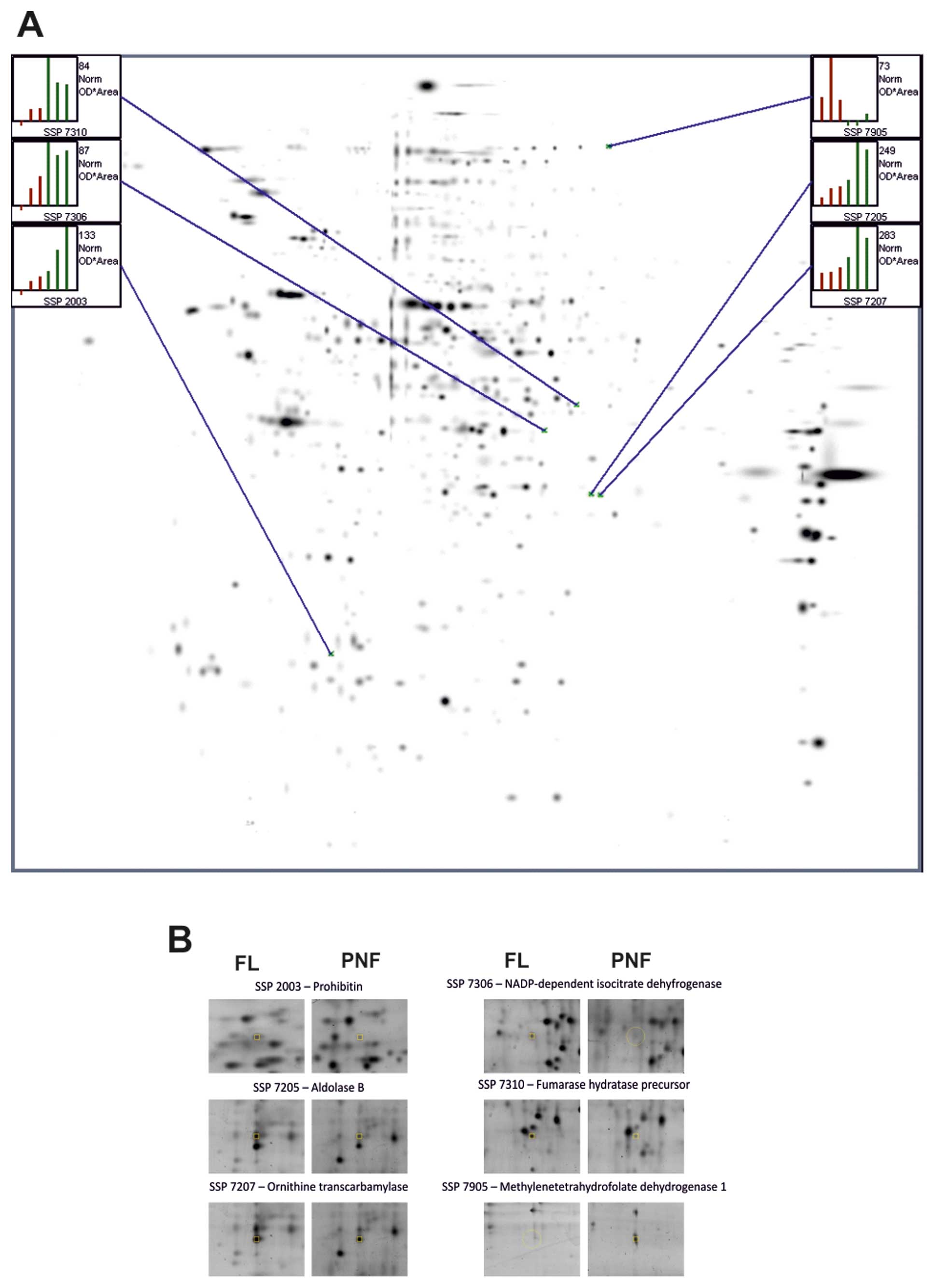
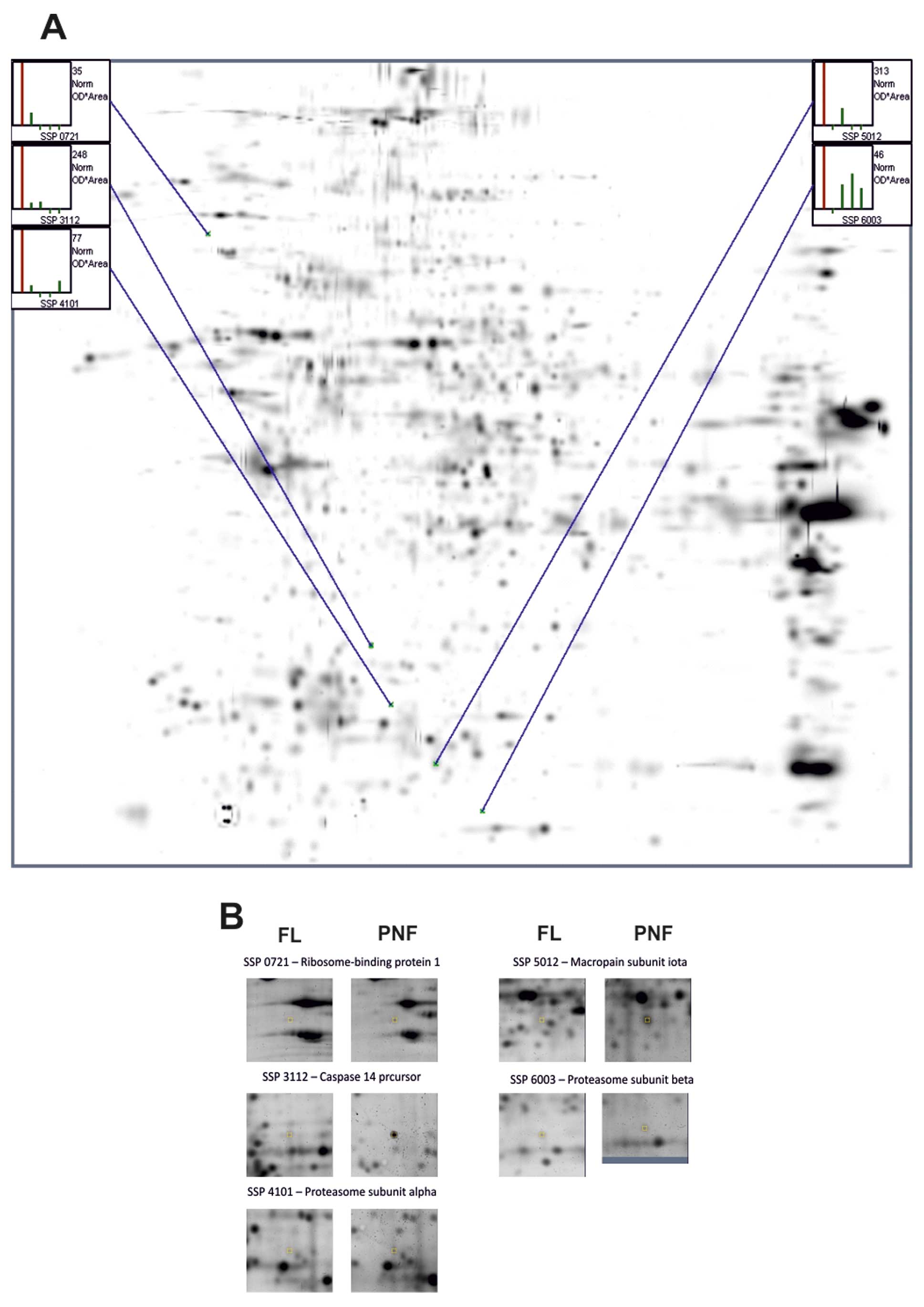
|
1.
|
RJ PloegAM D’AlessandroSJ KnechtleRisk
factors for primary dysfunction after liver transplantation-a
multivariate
analysisTransplantation55807813199310.1097/00007890-199304000-000248475556
|
|
2.
|
HY YooA MaheshwariPJ
ThuluvathRetransplantation of liver: primary graft nonfunction and
hepatitis C virus are associated with worse outcomeLiver
Transpl9897904200310.1053/jlts.2003.5017612942450
|
|
3.
|
T UemuraHB RandallEQ SanchezLiver
retransplantation for primary nonfunction: analysis of a 20-year
single-center experienceLiver Transpl13227233200717256780
|
|
4.
|
BW Shaw JrRD GordonS IwatsukiTE
StarzlRetransplantation of the liverSemin Liver
Dis5394401198510.1055/s-2008-1040638
|
|
5.
|
GR SilberhumerH PokornyH HetzCombination
of extended donor criteria and changes in the Model for End-Stage
Liver Disease score predict patient survival and primary
dysfunction in liver transplantation: a retrospective
analysisTransplantation83588592200710.1097/01.tp.0000255319.07499.b7
|
|
6.
|
MG AminMP WolfJA TenBrook JrExpanded
criteria donor grafts for deceased donor liver transplantation
under the MELD system: a decision analysisLiver
Transpl1014681475200410.1002/lt.20304
|
|
7.
|
N KemmerM SecicV ZachariasT KaiserGW
NeffLong-term analysis of primary nonfunction in liver transplant
recipientsTransplant
Proc3914771480200710.1016/j.transproceed.2006.11.01217580166
|
|
8.
|
AK BurroughsCA SabinK Rolles3-month and
12-month mortality after first liver transplant in adults in
Europe: predictive models for
outcomeLancet367225232200610.1016/S0140-6736(06)68033-116427491
|
|
9.
|
R AdamP McMasterJG O’GradyEvolution of
liver transplantation in Europe: report of the European Liver
Transplant RegistryLiver
Transpl912311243200310.1016/j.lts.2003.09.01814625822
|
|
10.
|
J PitreO SoubraneB DoussetHow valid is
emergency liver transplantation for acute liver necrosis in
patients with multiple-organ failure?Liver Transpl
Surg217199610.1002/lt.5000201029346621
|
|
11.
|
HR DoyleF MorelliJ McMichaelHepatic
retransplantation - an analysis of risk factors associated with
outcomeTransplantation6114991505199610.1097/00007890-199605270-000168633379
|
|
12.
|
KJ OldhaferA BornscheuerNR FrühaufRescue
hepatectomy for initial graft non-function after liver
transplantationTransplantation6710241028199910.1097/00007890-199904150-0001510221488
|
|
13.
|
SK SoJA BarteauGA PerdrizetJW
MarshSuccessful retransplantation after a 48-hour anhepatic
stateTransplant Proc251962196319938385827
|
|
14.
|
H ChenCH PengBY ShenMulti-factor analysis
of initial poor graft function after orthotopic liver
transplantationHepatobiliary Pancreat Dis
Int6141146200717374571
|
|
15.
|
JR LakeJS ShorrBJ SteffenAH ChuRD GordonRH
WiesnerDifferential effects of donor age in liver transplant
recipients infected with hepatitis B, hepatitis C and without viral
hepatitisAm J
Transplant5549557200510.1111/j.1600-6143.2005.00741.x15707410
|
|
16.
|
S FengNP GoodrichJL
Bragg-GreshamCharacteristics associated with liver graft failure:
the concept of a donor risk indexAm J
Transplant6783790200610.1111/j.1600-6143.2006.01242.x16539636
|
|
17.
|
PA ClavienM SelznerHA RüdigerA prospective
randomized study in 100 consecutive patients undergoing major liver
resection with versus without ischemic preconditioningAnn
Surg238843852200310.1097/01.sla.0000098620.27623.7d
|
|
18.
|
SM StrasbergTK HowardEP MolmentiM
HertlSelecting the donor liver: risk factors for poor function
after orthotopic liver
transplantationHepatology20829838199410.1002/hep.18402004107927223
|
|
19.
|
E TotsukaF DodsonA UrakamiInfluence of
high donor serum sodium levels on early postoperative graft
function in human liver transplantation: effect of correction of
donor hypernatremiaLiver Transpl
Surg5421428199910.1002/lt.500050510
|
|
20.
|
H YersizA ShakedK OlthoffCorrelation
between donor age and the pattern of liver graft recovery after
transplantationTransplantation60790794199510.1097/00007890-199510270-000057482736
|
|
21.
|
AM CameronRM GhobrialH YersizOptimal
utilization of donor grafts with extended criteria: a single-center
experience in over 1000 liver transplantsAnn
Surg243748755200610.1097/01.sla.0000219669.84192.b316772778
|
|
22.
|
SR JohnsonS AlexopoulosM CurryDW
HantoPrimary nonfunction (PNF) in the MELD era: An SRTR database
analysisAm J
Transplant710031009200710.1111/j.1600-6143.2006.01702.x17286618
|
|
23.
|
J BusquetsX XiolJ FiguerasThe impact of
donor age on liver transplantation: influence of donor age on early
liver function and on subsequent patient and graft
survivalTransplantation7117651771200110.1097/00007890-200106270-0001111455256
|
|
24.
|
WK WashburnLB JohnsonWD LewisRL
JenkinsGraft function and outcome of older (> or = 60 years)
donor liversTransplantation61106210661996
|
|
25.
|
H PokornyT GruenbergerT SolimanS
RockenschaubF LängleR SteiningerOrgan survival after primary
dysfunction of liver grafts in clinical orthotopic liver
transplantationTranspl Int13Suppl
1S154S157200010.1007/s00147005031011111986
|
|
26.
|
B MüllhauptD DimitroulisJT GerlachPA
ClavienHot topics in liver transplantation: organ allocation -
extended criteria donor - living donor liver transplantationJ
Hepatol48Suppl 1S58S67200818308415
|
|
27.
|
HY ChungSC ChanCM LoST FanStrategies for
widening liver donor poolAsian J
Surg336369201010.1016/S1015-9584(10)60011-521029941
|
|
28.
|
RW BusuttilK TanakaThe utility of marginal
donors in liver transplantationLiver
Transpl9651663200310.1053/jlts.2003.5010512827549
|
|
29.
|
M GastacaExtended criteria donors in liver
transplantation: adapting donor quality and recipientTransplant
Proc41975979200910.1016/j.transproceed.2009.02.01619376402
|
|
30.
|
K HatsugaiN OhkohchiT FukumoriY AkamatsuS
SatomiMechanism of primary graft non-function in a rat model for
fatty liver transplantationTranspl Int13Suppl
1S583S590200010.1007/s00147005040811112079
|
|
31.
|
D AzoulayMM LinharesE HuguetDecision for
retransplantation of the liver: an experience- and cost-based
analysisAnn
Surg236713721200210.1097/00000658-200212000-0000312454509
|
|
32.
|
C VascottoL CesarattoC D’AmbrosioProteomic
analysis of liver tissues subjected to early ischemia/reperfusion
injury during human orthotopic liver
transplantationProteomics634553465200610.1002/pmic.200500770
|
|
33.
|
M ChevalletS LucheT RabilloudSilver
staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gelsNat
Protoc118521858200610.1038/nprot.2006.28817487168
|