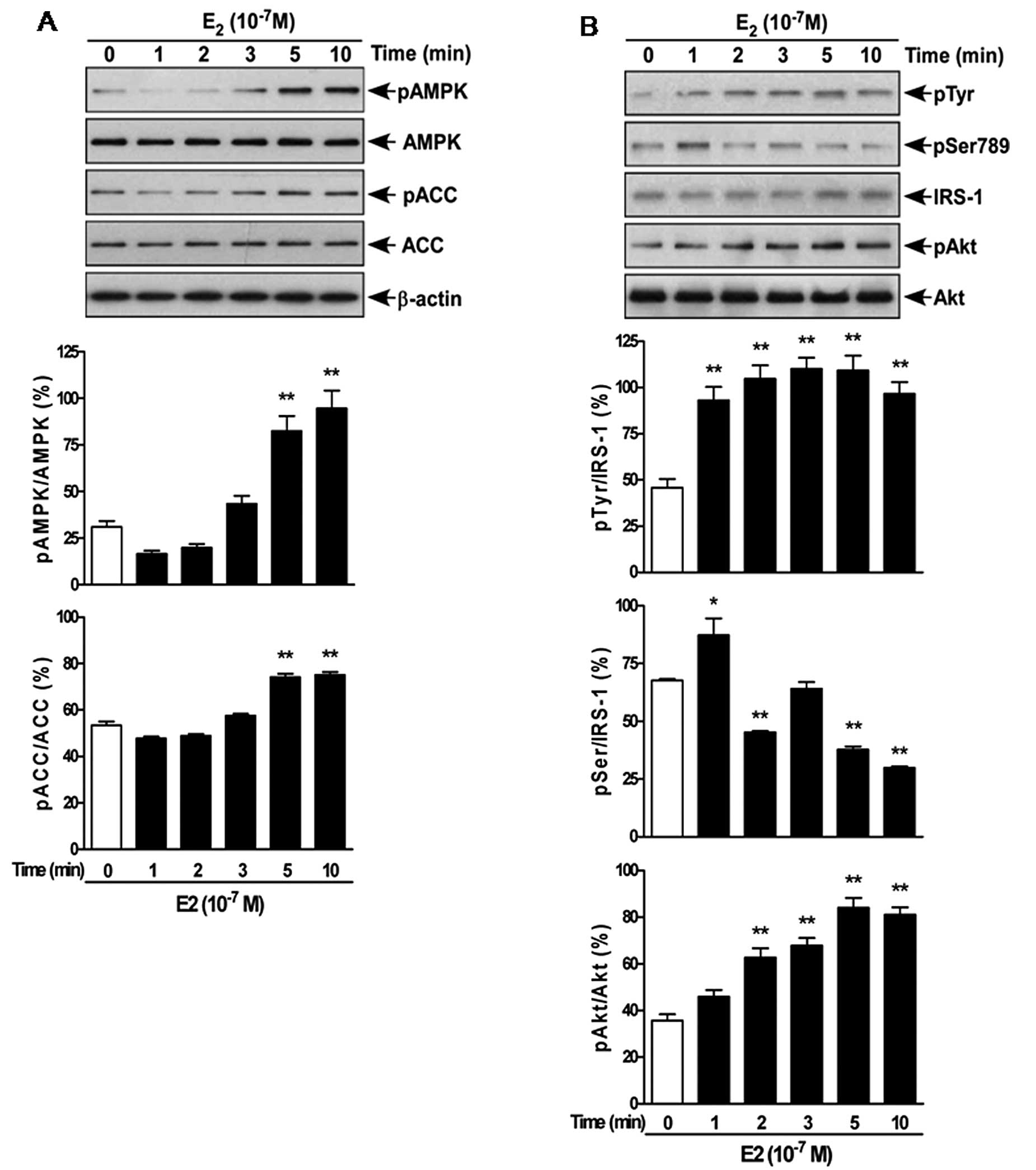
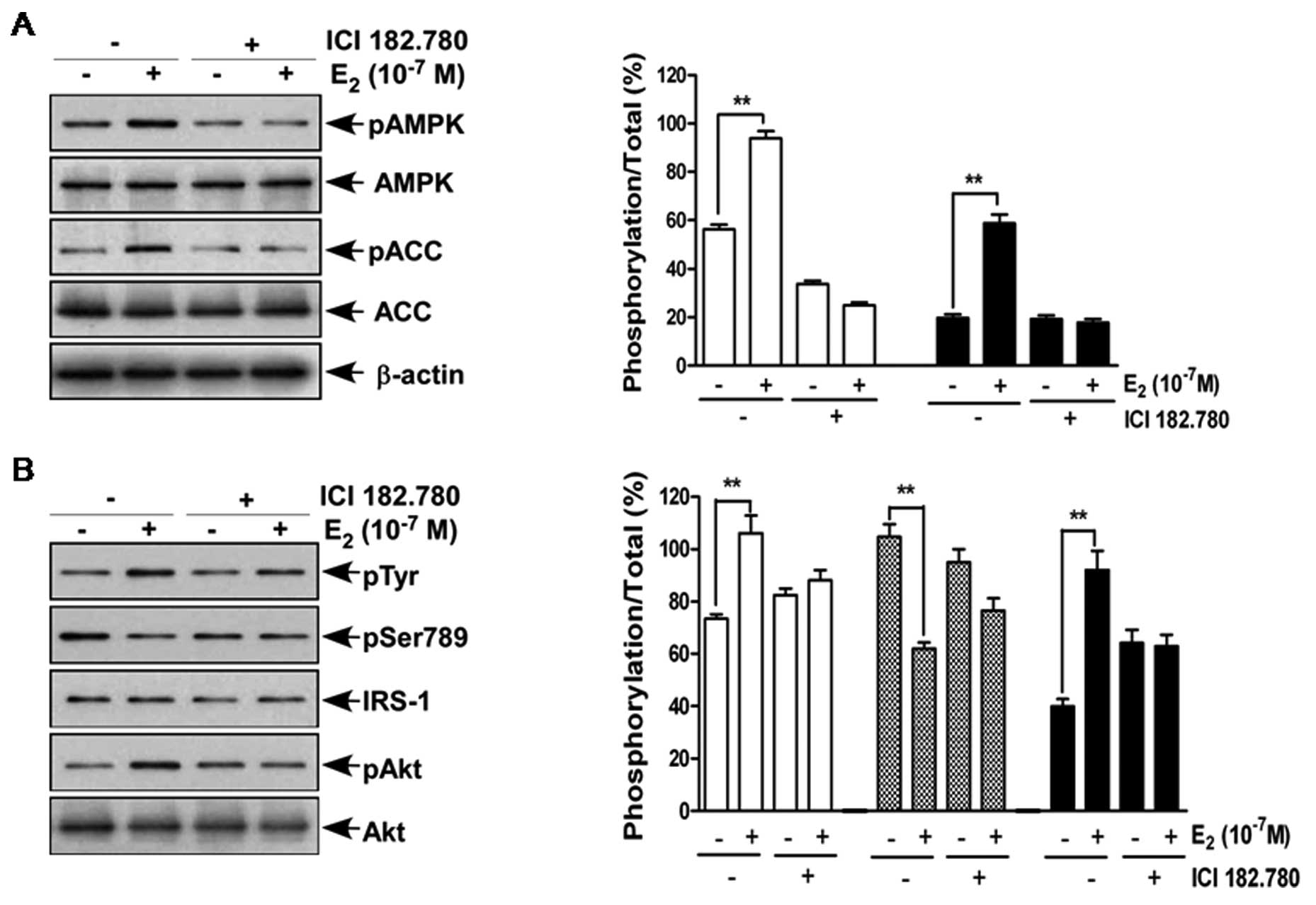
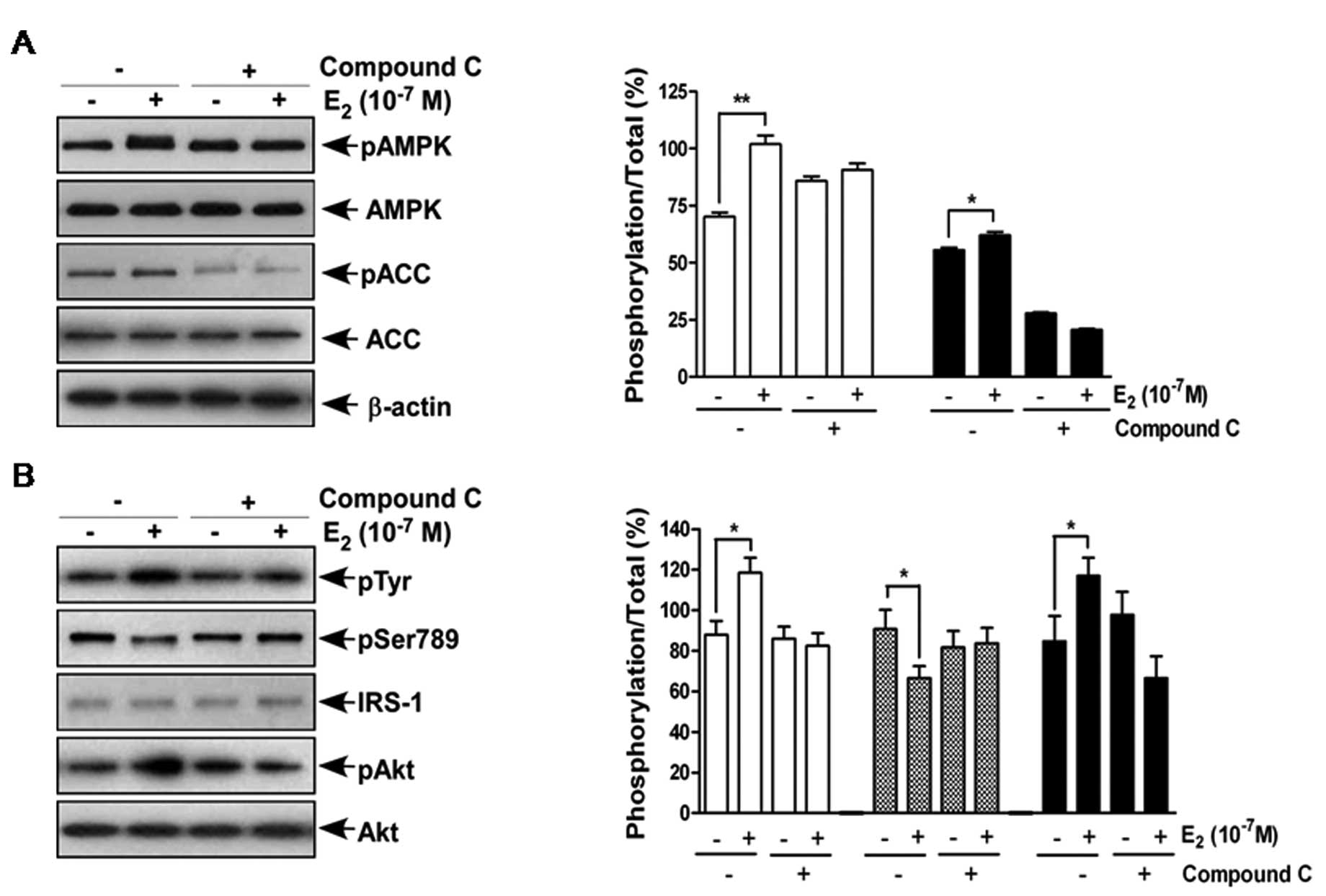
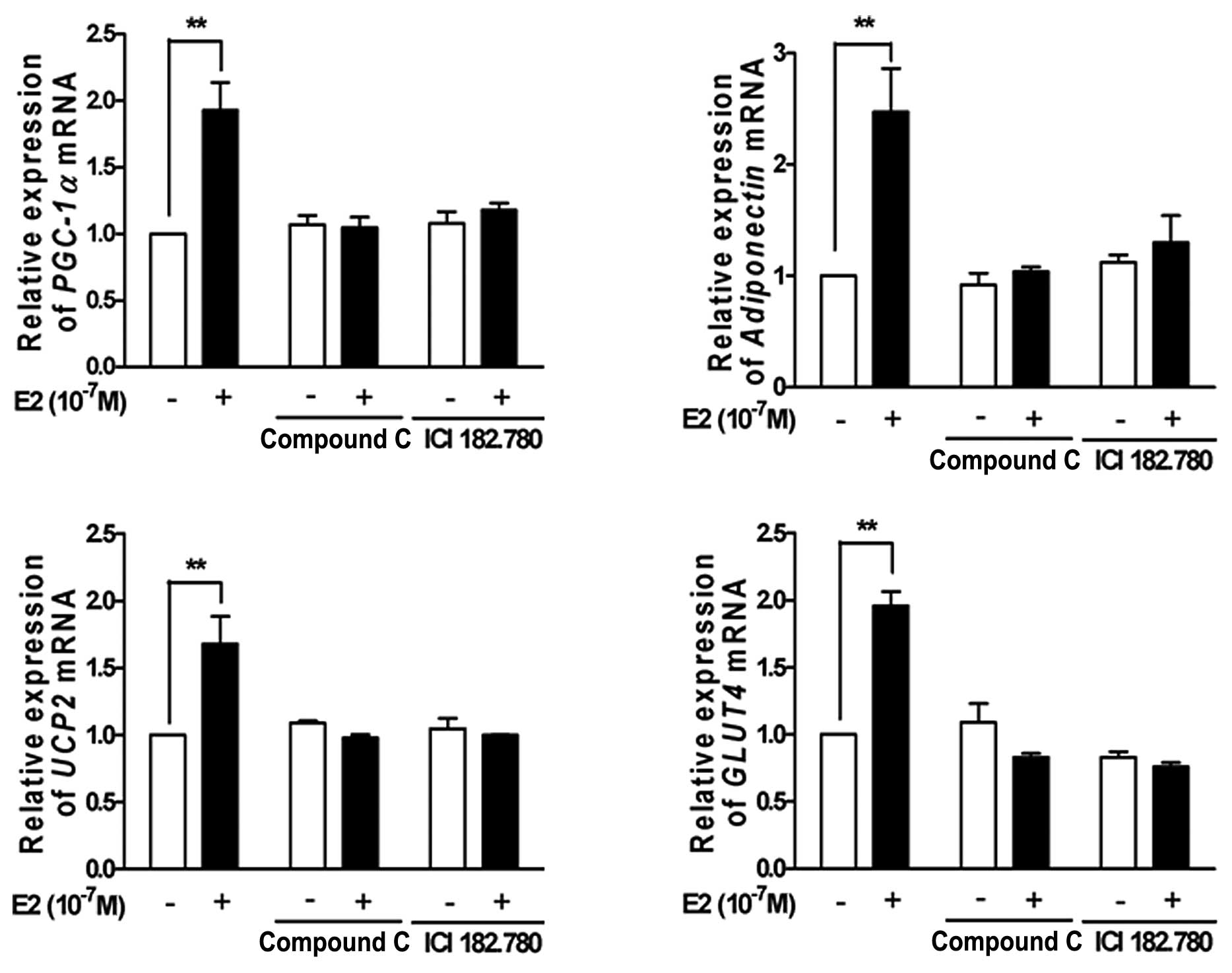
|
1.
|
S LiuF Mauvais-JarvisMinireview:
estrogenic protection of β-cell failure in metabolic
diseasesEndocrinology151859864201019966178
|
|
2.
|
JG SchneiderC TompkinsRS BlumenthalS
MoraThe metabolic syndrome in womenCardiol
Rev14286291200610.1097/01.crd.0000233757.15181.6717053375
|
|
3.
|
YW ParkS ZhuL PalaniappanS HeshkaMR
CarnethonSB HeymsfieldThe metabolic syndrome: prevalence and
associated risk factor findings in the US population from the Third
National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988–1994Arch
Intern Med1634274362003
|
|
4.
|
K PenttiMT TuppurainenR HonkanenL SandiniH
KrögerE AlhavaS SaarikoskiHormone therapy protects from diabetes:
the Kuopio osteoporosis risk factor and prevention studyEur J
Endocrinol160979983200910.1530/EJE-09-015119321660
|
|
5.
|
L RichardsDiabetes: Postmenopausal hormone
therapy prevents diabetesNat Rev
Endocrinol5352200910.1038/nrendo.2009.92
|
|
6.
|
YQ LiangM AkishitaS KimJ AkoM HashimotoK
IijimaY OhikeT WatanabeN SudohK TobaEstrogen receptor beta is
involved in the anorectic action of estrogenInt J Obes Relat Metab
Disord2611031109200210.1038/sj.ijo.080205412119576
|
|
7.
|
ML LiuX XuWQ RangYJ LiHP SongInfluence of
ovariectomy and 17beta-estradiol treatment on insulin sensitivity,
lipid metabolism and post-ischemic cardiac functionInt J
Cardiol97485493200410.1016/j.ijcard.2003.11.04615561337
|
|
8.
|
A PaquetteM ShinodaR Rabasa LhoretD
Prud’hommeJM LavoieTime course of liver lipid infiltration in
ovariectomized rats: impact of a high-fat
dietMaturitas58182190200710.1016/j.maturitas.2007.08.00217889461
|
|
9.
|
V SaengsirisuwanS PongseedaM PrasannarongK
VichaiwongC ToskulkaoModulation of insulin resistance in
ovariectomized rats by endurance exercise training and estrogen
replacementMetabolism583847200910.1016/j.metabol.2008.08.00419059529
|
|
10.
|
E RiantA WagetH CogoJF ArnalR BurcelinP
GourdyEstrogens protect against high-fat diet-induced insulin
resistance and glucose intolerance in
miceEndocrinology15021092117200910.1210/en.2008-097119164473
|
|
11.
|
SC HewittJC HarrellKS KorachLessons in
estrogen biology from knockout and transgenic animalsAnnu Rev
Physiol67285308200510.1146/annurev.physiol.67.040403.11591415709960
|
|
12.
|
ER LevinRapid signaling by steroid
receptorsAm J Physiol Regul Integr Comp
Physiol295R1425R1430200810.1152/ajpregu.90605.200818784332
|
|
13.
|
ER ProssnitzJB ArterburnHO SmithTI OpreaLA
SklarHJ HathawayEstrogen signaling through the transmembrane G
protein-coupled receptor GPR30Annu Rev
Physiol70165190200810.1146/annurev.physiol.70.113006.10051818271749
|
|
14.
|
PA HeineJA TaylorGA IwamotoDB LubahnPS
CookeIncreased adipose tissue in male and female estrogen
receptor-α knockout miceProc Natl Acad Sci USA9712729127342000
|
|
15.
|
C OhlssonN HellbergP PariniO VidalM
Bohlooly-YM RudlingMK LindbergM WarnerB AngelinJA GustafssonObesity
and disturbed lipoprotein profile in estrogen
receptor-alpha-deficient male miceBiochem Biophys Res
Commun278640645200010.1006/bbrc.2000.382711095962
|
|
16.
|
R LageC DiéguezA Vidal-PuigM LópezAMPK: a
metabolic gauge regulating whole-body energy homeostasisTrends Mol
Med14539549200810.1016/j.molmed.2008.09.00718977694
|
|
17.
|
AR SaltielCR KahnInsulin signaling and the
regulation of glucose and lipid
metabolismNature414799806200110.1038/414799a11742412
|
|
18.
|
N HorikeH TakemoriY KatohJ DoiL MinT
AsanoXJ SunH YamamotoS KasayamaM MuraokaAdipose-specific
expression, phosphorylation of Ser794 in insulin receptor
substrate-1, and activation in diabetic animals of salt-inducible
kinase-2J Biol
Chem2871844018447200310.1074/jbc.M21177020012624099
|
|
19.
|
TM D’EonSC SouzaM AronovitzMS ObinSK
FriedAS GreenbergEstrogen regulation of adiposity and fuel
partitioning. Evidence of genomic and non-genomic regulation of
lipogenic and oxidative pathwaysJ Biol
Chem2803598335991200516109719
|
|
20.
|
NH RogersCA WitczakMF HirshmanLJ
GoodyearAS GreenbergEstradiol stimulates Akt, AMP-activated protein
kinase (AMPK) and TBC1D1/4, but not glucose uptake in rat
soleusBiochem Biophys Res
Commun382646650200910.1016/j.bbrc.2009.02.15419265681
|
|
21.
|
TM D’EonNH RogersZS StanchevaAS
GreenbergEstradiol and the estradiol metabolite,
2-hydroxyestradiol, activate AMP-activated protein kinase in C2C12
myotubesObesity (Silver Spring)1612841288200818421261
|
|
22.
|
YR LeeJ ParkHN YuJS KimHJ YounSH
JungUp-regulation of PI3K/Akt signaling by 17beta-estradiol through
activation of estrogen receptor-alpha, but not estrogen
receptor-beta, and stimulates cell growth in breast cancer
cellsBiochem Biophys Res
Commun33612211226200510.1016/j.bbrc.2005.08.25616169518
|
|
23.
|
BK GorresGL BomhoffJK MorrisPC GeigerIn
vivo stimulation of oestrogen receptor α increases
insulin-stimulated skeletal muscle glucose uptakeJ
Physiol589204120542011
|
|
24.
|
N OuchiH KobayashiS KiharaM KumadaK SatoT
InoueT FunahashiK WalshAdiponectin stimulates angiogenesis by
promoting cross-talk between AMP-activated protein kinase and Akt
signaling in endothelial cellsJ Biol
Chem27913041309200410.1074/jbc.M31038920014557259
|
|
25.
|
MH ZouSS KirkpatrickBJ DavisJS NelsonWG
Wiles IVU SchlattnerD NeumannM BrownleeMB FreemanMH
GoldmanActivation of the AMP-activated protein kinase by the
anti-diabetic drug metformin in vivo. Role of mitochondrial
reactive nitrogen speciesJ Biol
Chem2794394043951200410.1074/jbc.M40442120015265871
|
|
26.
|
K MurakiS OkuyaY TanizawaEstrogen receptor
alpha regulates insulin sensitivity through IRS-1 tyrosine
phosphorylation in mature 3T3-L1 adipocytesEndocr
J53841851200610.1507/endocrj.K06-00517001108
|
|
27.
|
A NaazM ZakroczymskiP HeineJ TaylorP
SaundersD LubahnPS CookeEffect of ovariectomy on adipose tissue of
mice in the absence of estrogen receptor alpha (ER alpha): a
potential role for estrogen receptor beta (ER beta)Horm Metab
Res34758763200210.1055/s-2002-3825912660895
|
|
28.
|
G SharmaER ProssnitzMechanisms of
estradiol-induced insulin secretion by the G protein-coupled
estrogen receptor GPR30/GPER in pancreatic
beta-cellsEndocrinology15230303039201110.1210/en.2011-009121673097
|
|
29.
|
E FilardoJ QuinnY PangC GraeberS ShawJ
DongP ThomasActivation of the novel estrogen receptor G
protein-coupled receptor 30 (GPR30) at the plasma
membraneEndocrinology14832363245200710.1210/en.2006-160517379646
|
|
30.
|
P PuigserverBM SpiegelmanPeroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1 alpha (PGC-1
alpha): transcriptional coactivator and metabolic regulatorEndocr
Rev247890200310.1210/er.2002-0012
|
|
31.
|
D KnuttiA KralliPGC-1, a versatile
coactivatorTrends Endocrinol
Metab12360365200110.1016/S1043-2760(01)00457-X11551810
|
|
32.
|
S DianoTL HorvathMitochondrial uncoupling
protein 2 (UCP2) in glucose and lipid metabolismTrends Mol
Med185258201210.1016/j.molmed.2011.08.00321917523
|
|
33.
|
MC SalehMB WheelerCB ChanUncoupling
protein-2: evidence for its function as a metabolic
regulatorDiabetologia45174187200210.1007/s00125-001-0737-x
|
|
34.
|
C PecqueurE CouplanF BouillaudD
RicquierGenetic and physiological analysis of the role of
uncoupling proteins in human energy homeostasisJ Mol Med
(Berl)794856200110.1007/s00109000015011327103
|
|
35.
|
JW RyderM GilbertJR ZierathSkeletal muscle
and insulin sensitivity: pathophysiological alterationsFront
Biosci6D154D163200110.2741/Ryder11171554
|
|
36.
|
GI BellKS PolonskyDiabetes mellitus and
genetically programmed defects in beta-cell
functionNature414788791200110.1038/414788a11742410
|
|
37.
|
T YamauchiJ KamonH WakiY TerauchiN KubotaK
HaraY MoriT IdeK MurakamiN Tsuboyama-KasaokaThe fat-derived hormone
adiponectin reverses insulin resistance associated with both
lipoatrophy and obesityNat Med7941946200110.1038/9098411479627
|