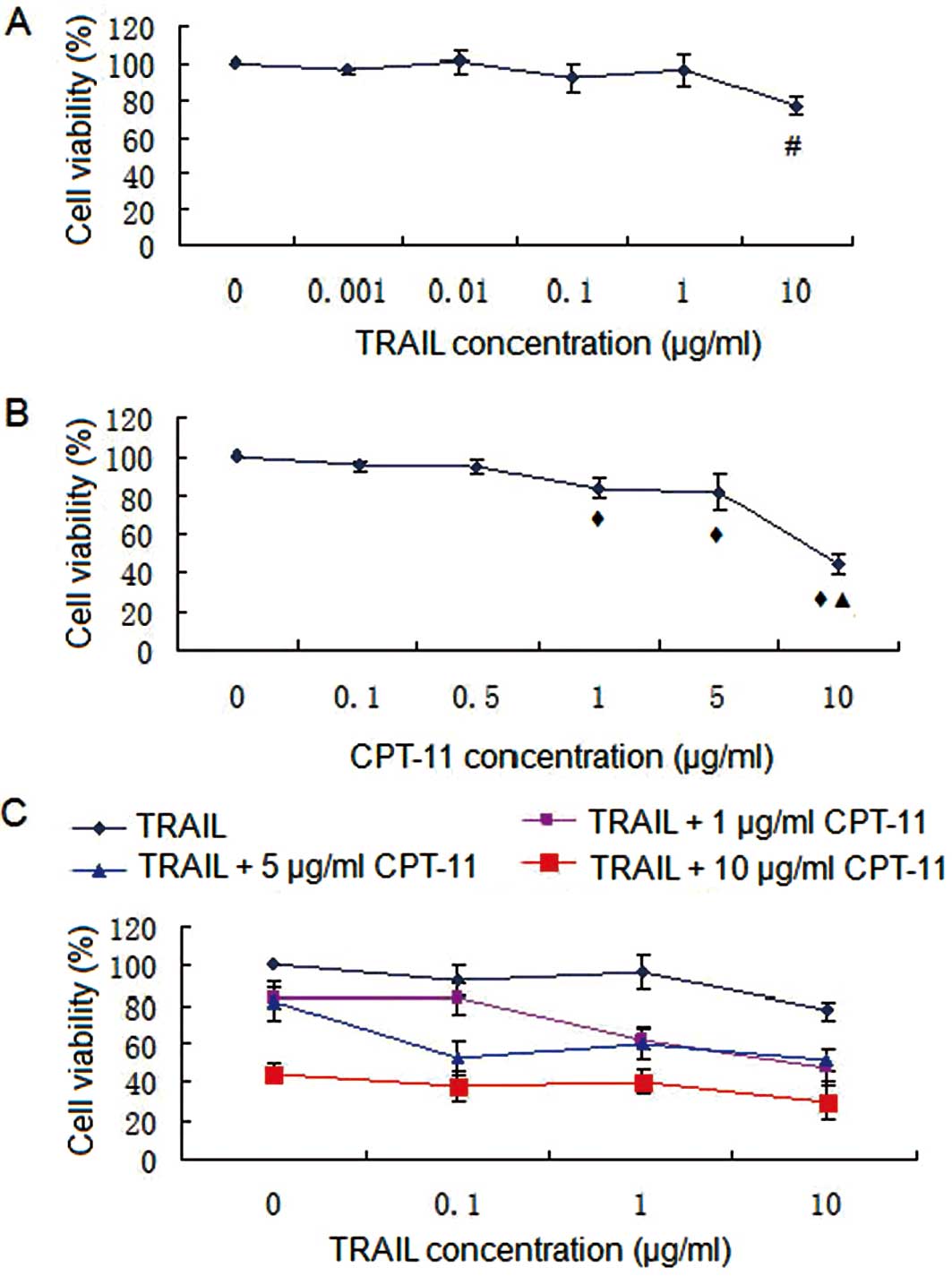
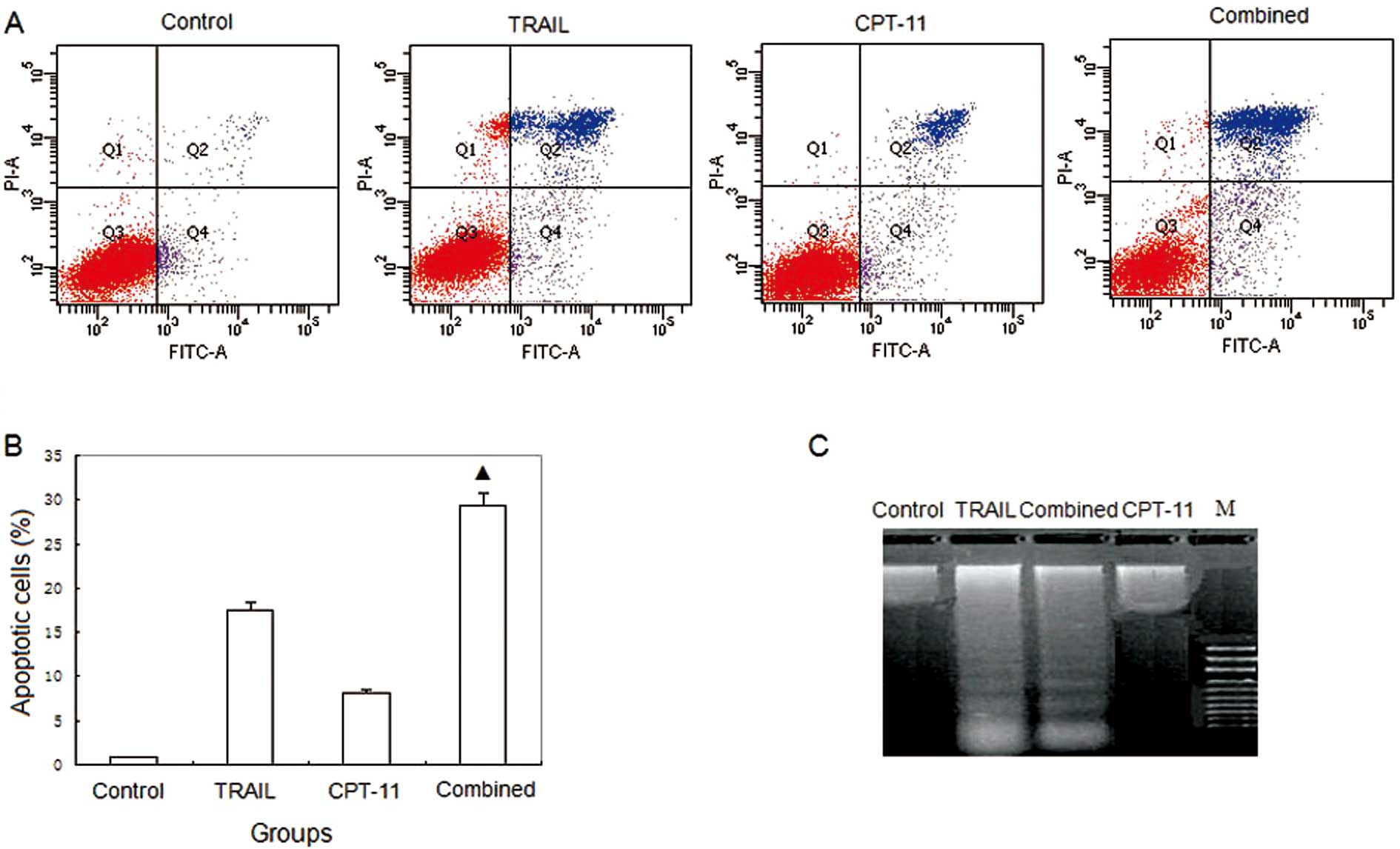
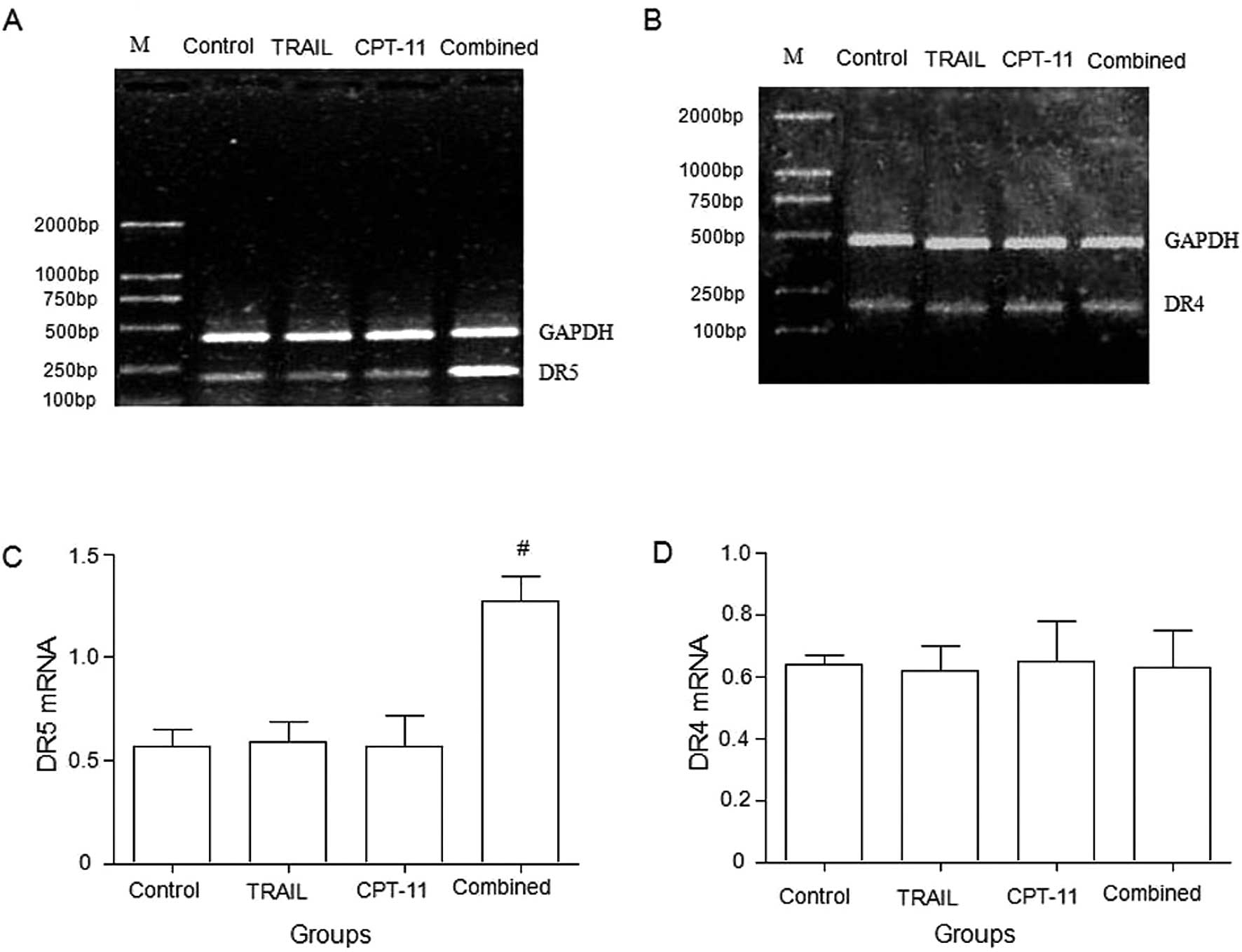
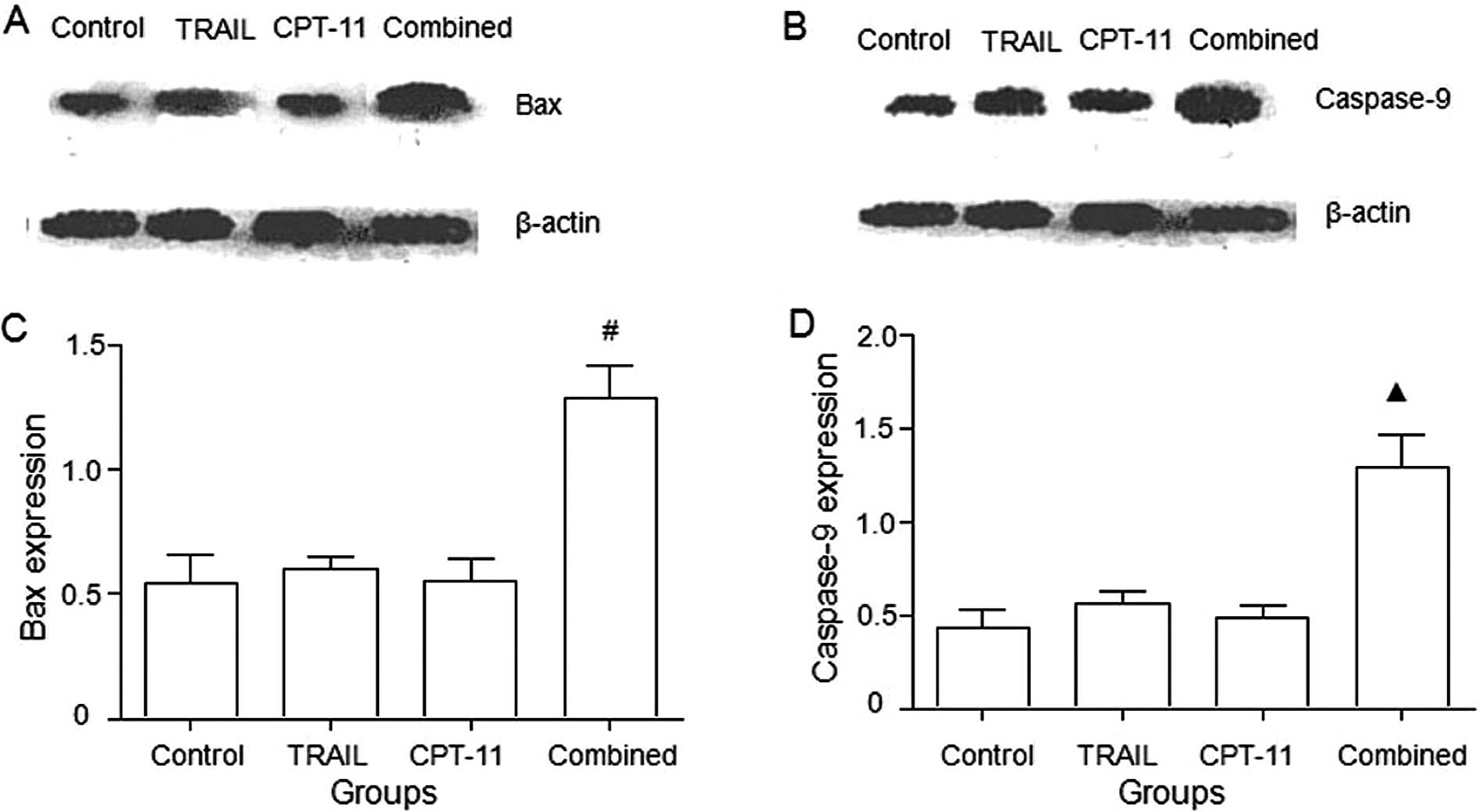
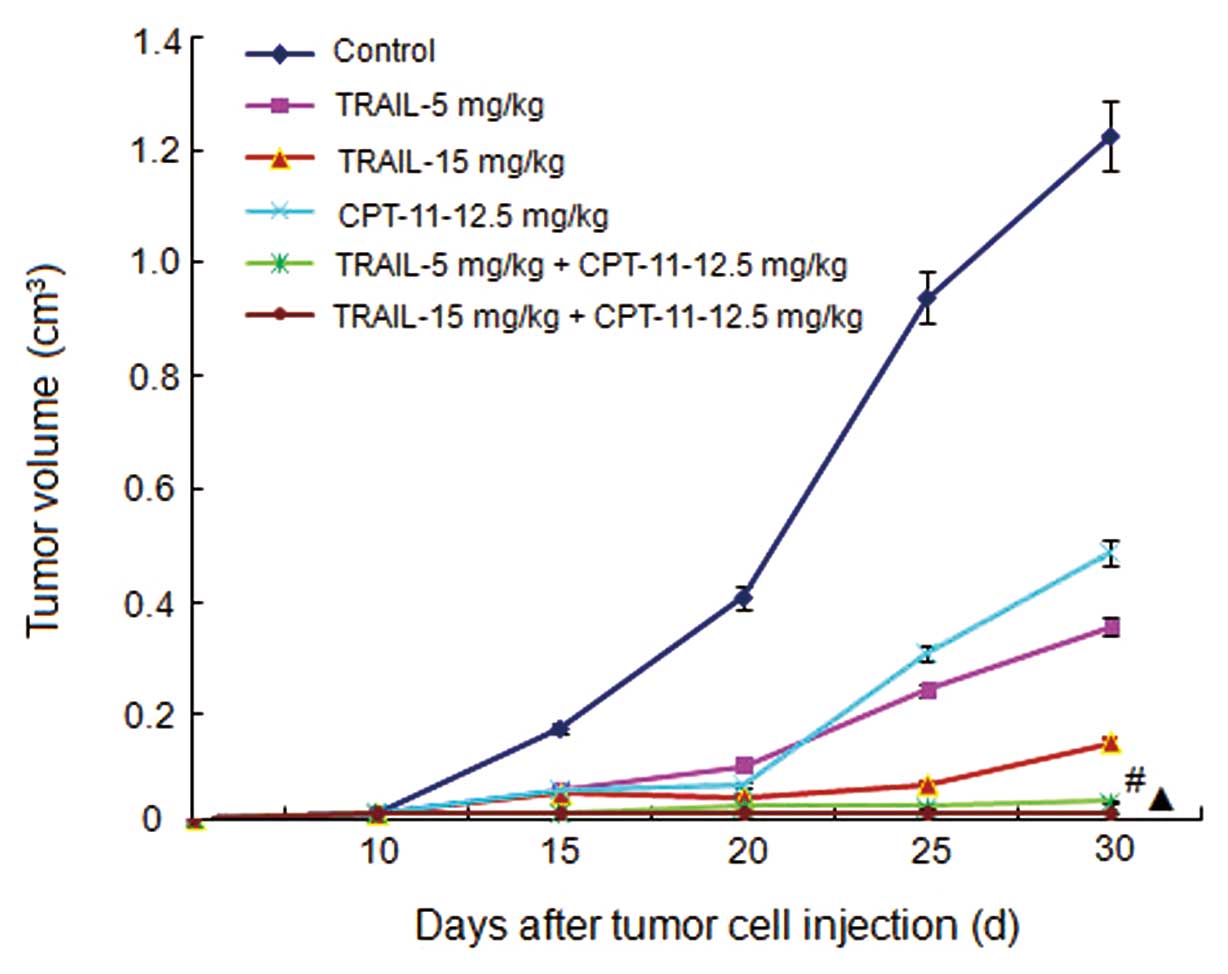
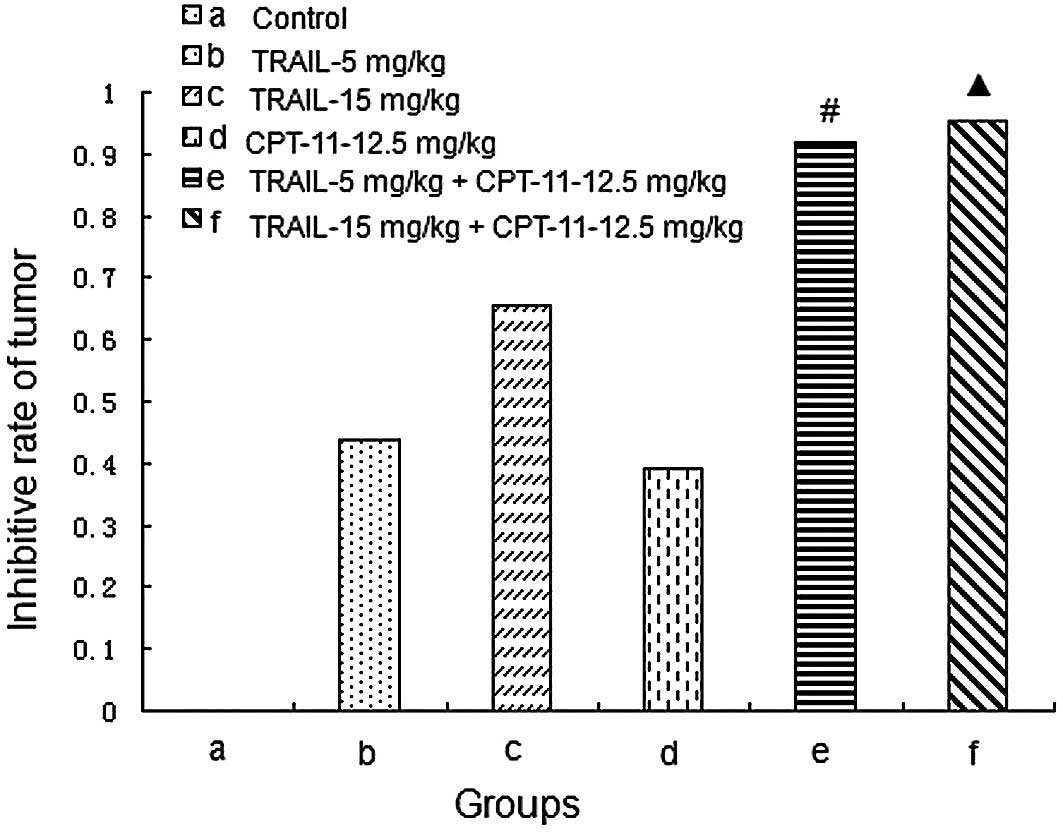
|
1.
|
SJ OosterlingGJ van der BijM BogelsS ten
RaaJA PostGA MeijerRH BeelenM van EgmondAnti-beta1 integrin
antibody reduces surgery-induced adhesion of colon carcinoma cells
to traumatized peritoneal surfacesAnn
Surg2478594200810.1097/SLA.0b013e3181588583
|
|
2.
|
I HennebelleC TerretE ChatelutR BugatP
CanalS GuichardCharacterization of CPT-11 converting
carboxylesterase activity in colon tumor and normal tissues:
comparison with p-nitro-phenylacetate converting carboxylesterase
activityAnticancer
Drugs11465470200010.1097/00001813-200007000-00007
|
|
3.
|
AM SaeternM BrandlWH BakkelundB
SveinbjornssonCytotoxic effect of different camptothecin
formulations on human colon carcinoma in vitroAnticancer
Drugs15899906200410.1097/00001813-200410000-0001115457131
|
|
4.
|
AD SanliogluE DiriceO ElpekAF KorcumM
OzdoganI SuleymanlarMK BalciTS GriffithS SanliogluHigh TRAIL death
receptor 4 and decoy receptor 2 expression correlates with
significant cell death in pancreatic ductal adeno-carcinoma
patientsPancreas38154160200910.1097/MPA.0b013e31818db9e318981952
|
|
5.
|
A AshkenaziP HollandSG
EckhardtLigand-based targeting of apoptosis in cancer: the
potential of recombinant human apoptosis ligand 2/Tumor necrosis
factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (rhApo2L/TRAIL)J Clin
Oncol2636213630200810.1200/JCO.2007.15.7198
|
|
6.
|
J YooSS ParkYJ LeePretreatment of
docetaxel enhances TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in prostate cancer
cellsJ Cell Biochem10416361646200810.1002/jcb.2172918404675
|
|
7.
|
PG OliverAF LoBuglioKR ZinnH KimL NanT
ZhouW WangDJ BuchsbaumTreatment of human colon cancer xenografts
with TRA-8 anti-death receptor 5 antibody alone or in combination
with CPT-11Clin Cancer
Res1421802189200810.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-139218381960
|
|
8.
|
R RaviAJ JainRD SchulickV PhamTS ProuserH
AllenEG MayerH YuDM PardollA AshkenaziA BediElimination of hepatic
metastases of colon cancer cells via p53-independent cross-talk
between irinotecan and Apo2 ligand/TRAILCancer
Res6491059114200410.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-248815604280
|
|
9.
|
K SugamuraJF GibbsA Belicha-VillanuevaC
AndrewsEA RepaskyBL HylanderSynergism of CPT-11 and Apo2L/ TRAIL
against two differentially sensitive human colon tumor
xenograftsOncology74188197200810.1159/00015136618714167
|
|
10.
|
W ZhouJ HuH TangD WangX HuangC HeH
ZhuSmall interfering RNA targeting mcl-1 enhances proteasome
inhibitor-induced apoptosis in various solid malignant tumorsBMC
Cancer11485201110.1186/1471-2407-11-48522078414
|
|
11.
|
DD CuiY HuangSH MaoSC ChenM QiuLL JiC
YiSynergistic antitumor effect of TRAIL and adriamycin on the human
breast cancer cell line MCF-7Braz J Med Biol
Res42854862200919738990
|
|
12.
|
YA YehM HerenyiovaG WeberQuercetin:
synergistic action with carboxyamidotriazole in human breast
carcinoma cellsLife
Sci5712851292199510.1016/0024-3205(95)02085-W7674820
|
|
13.
|
B LiuXC PengXL ZhengJ WangYW QinMiR-126
restoration down-regulate VEGF and inhibit the growth of lung
cancer cell lines in vitro and in vivoLung
Cancer66169175200910.1016/j.lungcan.2009.01.01019223090
|
|
14.
|
A TrunehS SharmaC SilvermanS KhandekarMP
ReddyKC DeenMM McLaughlinSM SrinivasulaGP LiviLA
MarshallTemperature-sensitive differential affinity of TRAIL for
its receptors. DR5 is the highest affinity receptorJ Biol
Chem2752331923325200010.1074/jbc.M91043819910770955
|
|
15.
|
FA KruytTRAIL and cancer therapyCancer
Lett2631425200810.1016/j.canlet.2008.02.00318329793
|
|
16.
|
RW JohnstoneAJ FrewMJ SmythThe TRAIL
apoptotic pathway in cancer onset, progression and therapyNat Rev
Cancer8782798200810.1038/nrc246518813321
|
|
17.
|
R KoschnyH WalczakTM GantenThe promise of
TRAIL-potential and risks of a novel anticancer therapyJ Mol
Med85923935200710.1007/s00109-007-0194-117437073
|
|
18.
|
S LacourA HammannA WotawaL CorcosE
SolaryMT Dimanche-BoitrelAnticancer agents sensitize tumor cells to
tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated
caspase-8 activation and apoptosisCancer Res61164516512001
|
|
19.
|
ES HensonJB JohnstonSB GibsonThe role of
TRAIL death receptors in the treatment of hematological
malignanciesLeuk
Lymphoma492735200810.1080/1042819070171365518203008
|
|
20.
|
RK SrivastavaTRAIL/Apo-2L: mechanisms and
clinical applications in
cancerNeoplasia3535546200110.1038/sj.neo.790020311774036
|
|
21.
|
TR SinghS ShankarX ChenM AsimRK
SrivastavaSynergistic interactions of chemotherapeutic drugs and
tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand/Apo-2
ligand on apoptosis and on regression of breast carcinoma in
vivoCancer Res63539054002003
|
|
22.
|
ER McDonald IIIPC ChuiPF MartelliDT
DickerWS El-DeiryDeath domain mutagenesis of KILLER/DR5 reveals
residues critical for apoptotic signalingJ Biol
Chem2761493914945200110.1074/jbc.M10039920011279061
|
|
23.
|
J WenN RamadeviD NguyenC PerkinsE
WorthingtonK BhallaAntileukemic drugs increase death receptor 5
levels and enhance Apo-2L-induced apoptosis of human acute leukemia
cellsBlood9639003906200011090076
|
|
24.
|
T NakaK SugamuraBL HylanderMB WidmerYM
RustumEA RepaskyEffects of tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand alone and in combination with
chemotherapeutic agents on patients’ colon tumors grown in SCID
miceCancer Res62580058062002
|
|
25.
|
M NaganeG PanJJ WeddleVM DixitWK CaveneeHJ
HuangIncreased death receptor 5 expression by chemotherapeutic
agents in human gliomas causes synergistic cytotoxicity with tumor
necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in vitro and in
vivoCancer Res608478532000
|
|
26.
|
W LiuE BodleJY ChenM GaoGD RosenVC
BroaddusTumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand and
chemotherapy cooperate to induce apoptosis in mesothelioma cell
linesAm J Respir Cell Mol
Biol25111118200110.1165/ajrcmb.25.1.447211472983
|
|
27.
|
T MiyashitaJC ReedTumor suppressor p53 is
a direct transcriptional activator of the human bax
geneCell80293299199510.1016/0092-8674(95)90412-37834749
|
|
28.
|
N ShinouraS SakuraiA AsaiT KirinoH
HamadaCaspase-9 transduction overrides the resistance mechanism
against p53-mediated apoptosis in U-87MG glioma
cellsNeurosurgery491771877200111440440
|
|
29.
|
MS SoengasRM AlarconH YoshidaAJ GiacciaR
HakemTW MakSW LoweApaf-1 and caspase-9 in p53-dependent apoptosis
and tumor
inhibitionScience284156159199910.1126/science.284.5411.15610102818
|
|
30.
|
H LeBlancD LawrenceE VarfolomeevK TotpalJ
MorlanP SchowS FongR SchwallD SinicropiA AshkenaziTumor-cell
resistance to death receptor-induced apoptosis through mutational
inactivation of the proapoptotic Bcl-2 homolog BaxNat
Med8274281200210.1038/nm0302-27411875499
|
|
31.
|
G NunezMA BenedictY HuN InoharaCaspases:
the proteases of the apoptotic
pathwayOncogene1732373245199810.1038/sj.onc.12025819916986
|
|
32.
|
SH KaufmannWC EarnshawInduction of
apoptosis by cancer chemotherapyExp Cell
Res2564249200010.1006/excr.2000.483810739650
|
|
33.
|
R NimmanapalliCL PerkinsM OrlandoE
O’BryanD NguyenKN BhallaPretreatment with paclitaxel enhances apo-2
ligand/tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing
ligand-induced apoptosis of prostate cancer cells by inducing death
receptors 4 and 5 protein levelsCancer Res617597632001
|
|
34.
|
B GliniakT LeTumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand’s antitumor activity in vivo is enhanced
by the chemotherapeutic agent CPT-11Cancer Res59615361581999
|