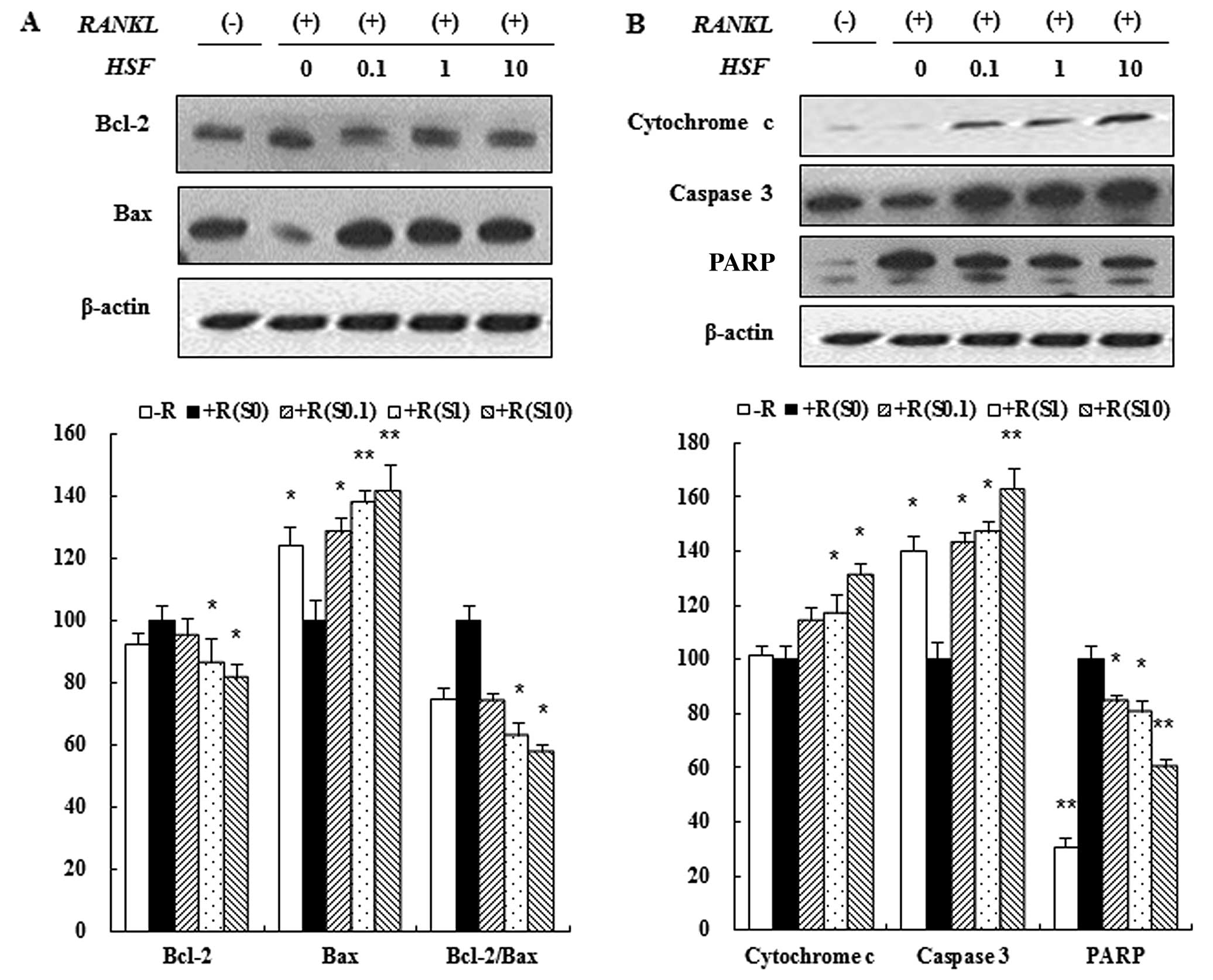
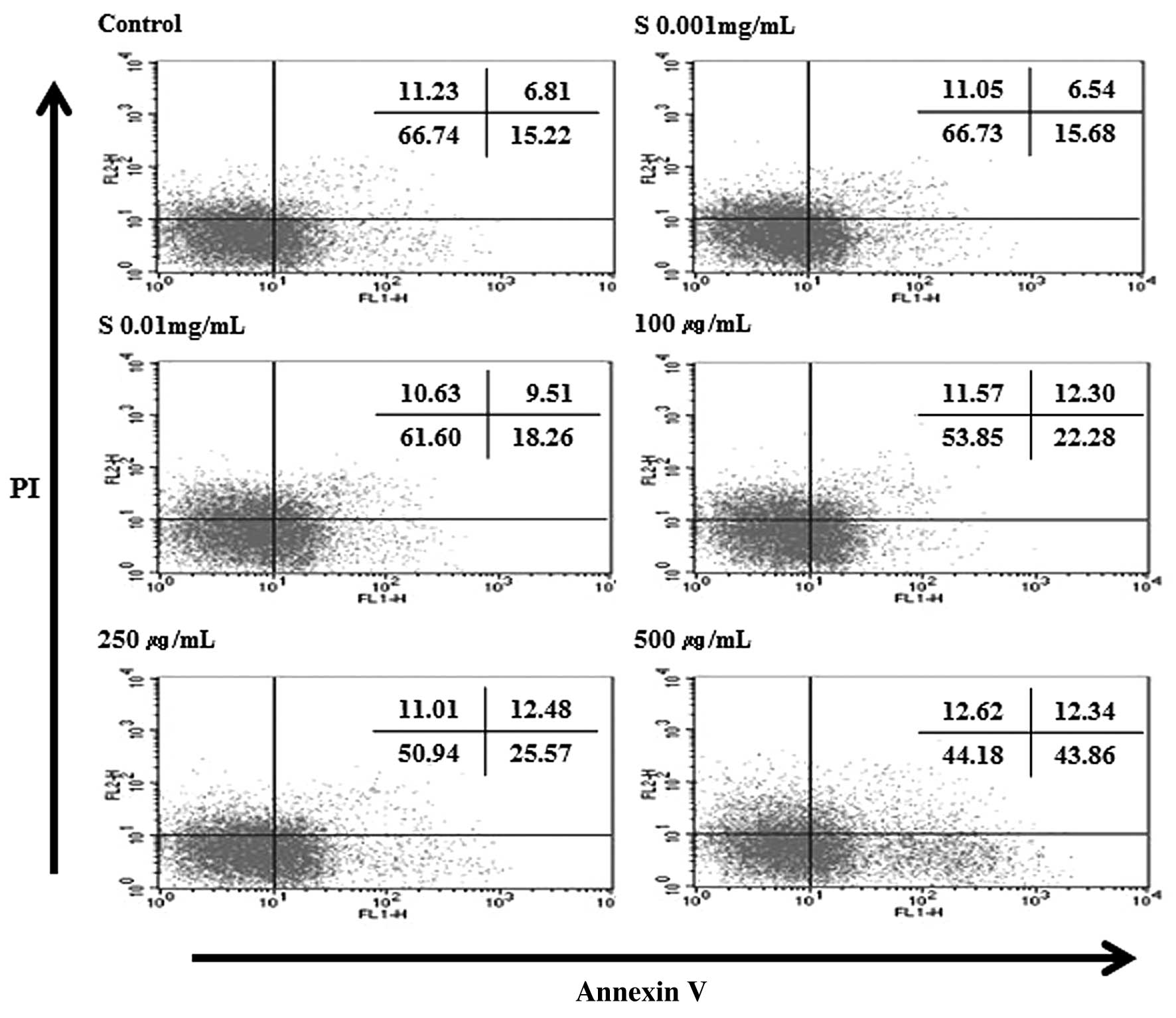
|
1.
|
AM ParfittBone remodeling and bone loss:
Understanding the pathophysiology of osteoporosisClin Obstet
Gynecol30789811198710.1097/00003081-198712000-000043319313
|
|
2.
|
WJ BoyleWS SimonetDL LaceyOsteoclast
differentiation and
activationNature423337342200310.1038/nature0165812748652
|
|
3.
|
K MatsuoN IrieOsteoclast-osteoblast
communicationArch Biochem
Biophys473201209200810.1016/j.abb.2008.03.027
|
|
4.
|
BG DarnayBB AggarwalSignal transduction by
tumour necrosis factor and tumour necrosis factor related ligands
and their receptorsAnn Rheum
Dis5812113199910.1136/ard.58.2008.i210577967
|
|
5.
|
T KogaM InuiK InoueSH KimA SuematsuE
KobayashiT IwataH OhnishiT MatozakiT KodamaCostimulatory signals
mediated by the ITAM motif cooperate with RANKL for bone
homeostasisNature428758763200410.1038/nature0244415085135
|
|
6.
|
O AnusaksathienC LaplaceX LiY RenL PengSR
GoldringDL GalsonTissue-specific and ubiquitous promoters direct
the expression of alternatively spliced transcripts from the
calcitonin receptor geneJ Biol
Chem2762266322674200110.1074/jbc.M00710420011309373
|
|
7.
|
BF BoyceK WrightSV ReddyBA KoopB StoryR
DevlinRJ LeachGD RoodmanJJ WindleTargeting simian virus 40 T
antigen to the osteoclast in transgenic mice causes osteoclast
tumors and transformation and apoptosis of
osteoclastsEndocrinology1365751575919957588333
|
|
8.
|
DE HughesBF BoyceApoptosis in bone
physiology and diseaseMol
Pathol50132137199710.1136/mp.50.3.1329292147
|
|
9.
|
X WuMA McKennaX FengTR NagyJM
McDonaldOsteoclast apoptosis: the role of fas in vivo and in
vitroEndocrinology1445544555552003
|
|
10.
|
L XingBF BoyceRegulation of apoptosis in
osteoclasts and osteoblastic cellsBiochem Biophys Res
Commun328709720200510.1016/j.bbrc.2004.11.07215694405
|
|
11.
|
GA RodanTJ MartinTherapeutic approaches to
bone
diseasesScience28915081514200010.1126/science.289.5484.150810968781
|
|
12.
|
T YamashitaZ YaoF LiQ ZhangIR BadellEM
SchwarzS TakeshitaEF WagnerM NodaK MatsuoNF-kappaB p50 and p52
regulate receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL) and tumor
necrosis factor-induced osteoclast precursor differentiation by
activating c-fos and NFATc1J Biol
Chem2821824518253200710.1074/jbc.M610701200
|
|
13.
|
KH ParkWC JuYH ChoConditioned medium of
soybean extract treated osteoblasts inhibits RANKL induced
differentiation of osteoclastsFASEB J3964702010
|
|
14.
|
JM ShinCK ParkEJ ShinTH ChoIK HwangEffects
of Scutellaria radix extract on osteoblast differentiation
and osteoclast formationKorean J Food Sci Tech406746792008
|
|
15.
|
G WangH YangM LiS LuX ChenX CaiThe use of
silk fibroin/hydroxyapatite composite co-cultured with rabbit
bone-marrow stromal cells in the healing of a segmental bone
defectJ Bone Joint Surg
Br92320325201010.1302/0301-620X.92B2.2260220130332
|
|
16.
|
C ZhouF ConfalonieriM JacquetR PerassoZ
LiJ JaninSilk fibroin: structural implications of a remarkable
amino acid
sequenceProteins44119122200110.1002/prot.107811391774
|
|
17.
|
ED KimT BayaraaEJ ShinCK
HyunFibroin-derived peptides stimulate glucose transport in normal
and insulin-resistant 3T3-L1 adipocytesBiol Pharm
Bull32427433200910.1248/bpb.32.42719252290
|
|
18.
|
M TsukadaG FreddiN MinouraG
AllaraPreparation and application of porous silk fibroin materialsJ
Appl Polym Sci54507514199410.1002/app.1994.070540411
|
|
19.
|
A NishidaM YamadaT KanazawaY TakashimaK
OuchiH OkadaUse of silk protein, sericin, as a sustained-release
material in the form of a gel, sponge and filmChem Pharm
Bull5814801486201010.1248/cpb.58.148021048340
|
|
20.
|
N KatoS SatoA YamanakaH YamadaN FuwaM
NomuraSilk protein, sericin, inhibits lipid peroxidation and
tyrosinase activityBiosci Biotechnol
Biochem62145147199810.1271/bbb.62.1459501526
|
|
21.
|
C AcharyaSK GhoshSC KunduSilk fibroin
protein from mulberry and non-mulberry silkworms: cytotoxicity,
biocompatibility and kinetics of L929 murine fibroblast adhesionJ
Mater Sci Mater
Med1928272836200810.1007/s10856-008-3408-318322779
|
|
22.
|
N MinouraS AibaY GotohM TsukadaY
ImaiAttachment and growth of cultured fibroblast cells on silk
protein matricesJ Biomed Mater
Res2912151221199510.1002/jbm.8202910088557723
|
|
23.
|
S SofiaMB McCarthyG GronowizaDL
KaplanFunctionalized silk-based biomaterials for bone formationJ
Biomed Mater
Res54139148200110.1002/1097-4636(200101)54:1%3C139::AID-JBM17%3E3.0.CO;2-711077413
|
|
24.
|
DH RohSY KangJY KimYB KwonH Young KweonKG
LeeYH ParkRM BaekCY HeoJ ChoeWound healing effect of silk
fibroin/alginate-blended sponge in full thickness skin defect of
ratJ Biomed Mater Res17547552200616691353
|
|
25.
|
T HanawaA WatanabeT TsuchiyaR IkomaM
HidakaM SugiharaNew oral dosage form for elderly patients. II.
Release behavior of benfotiamine from silk fibroin gelChem Pharm
Bull (Tokyo)43872876199510.1248/cpb.43.8727553973
|
|
26.
|
LG GriffithG NaughtonTissue engineering -
current challenges and expanding
opportunitiesScience29510091014200210.1126/science.106921011834815
|
|
27.
|
JH YeoKH ParkWC JuJA LeeGG LeeSO WooSM
HanHY KweonSS KimYH ChoInhibitory effect of conditioned medium of
silk fibroin-treated osteoblasts in osteoclast differentiationJ
Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr37992997200810.3746/jkfn.2008.37.8.992
|
|
28.
|
MM BradfordA rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye bindingAnal
Biochem72248254197610.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3942051
|
|
29.
|
K MatsuzakiN UdagawaN TakahashiK
YamaguchiH YasudaN ShimaT MorinagaY ToyamaY YabeK
HigashioOsteoclast differentiation factor (ODF) induces
osteoclast-like cell formation in human peripheral blood
mononuclear cell culturesBiochem Biophys Res
Commun246199204199810.1006/bbrc.1998.85869600092
|
|
30.
|
E JimiS AkiyamaT TsurukaiN OkahashiK
KobayashiN UdagawaT NishiharaN TakahashiT SudaOsteoclast
differentiation factor acts as a multifunctional regulator in
murine osteoclast differentiation and functionJ
Immunol163434442199910384146
|
|
31.
|
SE LeeKM WooSY KimH KimK KwackZH LeeH
KimThe phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, p38, and extracellular
signal-regulated kinase pathways are involved in osteoclast
differentiationBone307177200210.1016/S8756-3282(01)00657-311792567
|
|
32.
|
GH AltmanF DiazC JakubaT CalabroRL HoranJ
ChenH LuJ RichmondDL KaplanSilk-based
biomaterialsBiomaterials24401416200310.1016/S0142-9612(02)00353-812423595
|
|
33.
|
P ReponenC SahlbergC MunautI ThesleffK
TryggvasonHigh expression of 92-kD type IV collagenase (gelatinase
B) in the osteoclast lineage during mouse developmentJ Cell
Biol12410911102199410.1083/jcb.124.6.10918132709
|
|
34.
|
BD GelbGP ShiHA ChapmanRJ
DesnickPycnodysostosis, a lysosomal disease caused by cathepsin K
deficiencyScience27912361238199610.1126/science.273.5279.12368703060
|
|
35.
|
T IshikawaM KamiyamaN Tani-IshiiH SuzukiY
IchikawaY HamaguchiN MomiyamaH ShimadaInhibition of osteoclast
differentiation and bone resorption by cathepsin K antisense
oligonucleotidesMol Carcinog328491200110.1002/mc.106711746820
|
|
36.
|
K KanazawaA KudoTRAF2 is essential for
TNF-alpha-induced osteoclastogenesisJ Bone Miner
Res20840847200510.1359/JBMR.04122515824857
|
|
37.
|
ZH LeeH KimSignal transduction by receptor
activator of nuclear factor kappa B in osteoclastsBiochem Biophys
Res Commun305211214200310.1016/S0006-291X(03)00695-812745060
|
|
38.
|
H TakayanagiS KimT KogaH NishinaM IsshikiH
YoshidaA SaiuraM IsobeT YokochiJ InoueInduction and activation of
the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2) integrate RANKL signaling
in terminal differentiation of osteoclastsDev
Cell3889901200210.1016/S1534-5807(02)00369-612479813
|
|
39.
|
G KarsentyEF WagnerReaching a genetic and
molecular understanding of skeletal developmentDev
Cell2389406200210.1016/S1534-5807(02)00157-011970890
|
|
40.
|
N IshidaK HayashiM HoshijimaT OgawaS KogaY
MiyatakeM KumegawaT KimuraT TakeyaLarge scale gene expression
analysis of osteoclastogenesis in vitro and elucidation of NFAT2 as
a key regulatorJ Biol
Chem2774114741156200210.1074/jbc.M20506320012171919
|
|
41.
|
K MatsuoDL GalsonC ZhaoL PengC LaplaceKZ
WangMA BachlerH AmanoH AburataniH IshikawaNuclear factor of
activated T-cells (NFAT) rescues osteoclastogenesis in precursors
lacking c-fosJ Biol
Chem2792647526480200410.1074/jbc.M31397320015073183
|
|
42.
|
PH SternAntiresorptive agents and
osteoclast apoptosisJ Cell
Biochem10110871096200710.1002/jcb.2131117407157
|