|
1.
|
WW KuoCY ChuCH WuJA LinJY LiuYH HsiehKC
UengSD LeeDJ HsiehHH HsuImpaired IGF-I signalling of hypertrophic
hearts in the developmental phase of hypertension in genetically
hypertensive ratsCell Biochem
Funct23325331200510.1002/cbf.124415996002
|
|
2.
|
JA TowbinNE BowlesThe failing
heartNature415227233200210.1038/415227a11805847
|
|
3.
|
D DebloisBS TeaD BeaudryP HametRegulation
of therapeutic apoptosis: a potential target in controlling
hypertensive organ damageCan J Physiol
Pharmacol832941200510.1139/y05-00115759048
|
|
4.
|
SE KjeldsenB DahlofRB DevereuxS JuliusP
AurupJ EdelmanEffects of losartan on cardiovascular morbidity and
mortality in patients with isolated systolic hypertension and left
ventricular hypertrophy: a Losartan Intervention for Endpoint
Reduction (LIFE)
substudyJAMA28814911498200210.1001/jama.288.12.1491
|
|
5.
|
CY HuangLY HaoDE BuetowInsulin-like growth
factor-induced hypertrophy of cultured adult rat cardiomyocytes is
L-type calcium-channel-dependentMol Cell
Biochem2315159200210.1023/A:101443292322011952165
|
|
6.
|
SD LeeCH ChuEJ HuangMC LuJY LiuCJ LiuHH
HsuJA LinWW KuoCY HuangRoles of insulin-like growth factor II in
cardiomyoblast apoptosis and in hypertensive rat heart with
abdominal aorta ligationAm J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab291E306E314200610.1152/ajpendo.00127.200516825605
|
|
7.
|
JD MolkentinJR LuCL AntosA
calcineurin-dependent transcriptional pathway for cardiac
hypertrophyCell93215228199810.1016/S0092-8674(00)81573-19568714
|
|
8.
|
B WilkinsLJ De WindtOF BuenoJC BrazBJ
GlascockTF KimballJD MolkentinTargeted disruption of NFATc3, but
not NFATc4, reveals an intrinsic defect in calcineurin-mediated
cardiac hypertrophy growthMol Cell
Biol2276037613200210.1128/MCB.22.21.7603-7613.200212370307
|
|
9.
|
N KomatsuzakiT NakamuraT KimuraJ
ShimaCharacterization of glutamate decarboxylase from a high
gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-producer, Lactobacillus
paracaseiBiosci Biotechnol
Biochem72278285200810.1271/bbb.7016318256502
|
|
10.
|
H LiY CaoLactic acid bacterial cell
factories for gamma-aminobutyric acidAmino
Acids3911071116201010.1007/s00726-010-0582-720364279
|
|
11.
|
Y UenoK HayakawaS TakahashiK
OdaPurification and characterization of glutamate decarboxylase
from Lactobacillus brevis IFO 12005Biosci Biotechnol
Biochem6111681171199710.1271/bbb.61.11689255981
|
|
12.
|
JY KimMY LeeGE JiYS LeeKT HwangProduction
of gamma-aminobutyric acid in black raspberry juice during
fermentation by Lactobacillus brevis GABA100Int J Food
Microbiol1301216200910.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2008.12.02819167126
|
|
13.
|
LA DennerJY WuTwo forms of rat brain
glutamic acid decarboxylase differ in their dependence on free
pyridoxal phosphateJ
Neurochem44957965198510.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb12910.x3882886
|
|
14.
|
SH OhWG ChoiIT LeeSJ YunCloning and
characterization of a rice cDNA encoding glutamate decarboxylaseJ
Biochem Mol
Biol38595601200510.5483/BMBRep.2005.38.5.59516202241
|
|
15.
|
S YokoyamaJ HiramatsuK HayakawaProduction
of gamma-aminobutyric acid from alcohol distillery lees by
Lactobacillus brevis IFO-12005J Biosci
Bioeng939597200210.1016/S1389-1723(02)80061-516233172
|
|
16.
|
K HayakawaM KimuraK KasahaK MatsumotoH
SansawaY YamoriEffect of a gamma-aminobutyric acid-enriched dairy
product on the blood pressure of spontaneously hypertensive and
normotensive Wistar-Kyoto ratsBr J
Nutr92411417200410.1079/BJN2004122115469644
|
|
17.
|
K InoueT ShiraiH OchiaiM KasaoK HayakawaM
KimuraH SansawaBlood-pressure-lowering effect of a novel fermented
milk containing gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in mild
hypertensivesEur J Clin
Nutr57490495200310.1038/sj.ejcn.160155512627188
|
|
18.
|
J YamakoshiS FukudaT SatohR TsujiM SaitoA
ObataA MatsuyamaM KikuchiT KawasakiAntihypertensive and natriuretic
effects of less-sodium soy sauce containing gamma-aminobutyric acid
in spontaneously hypertensive ratsBiosci Biotechnol
Biochem71165173200710.1271/bbb.6042417213662
|
|
19.
|
M PhilpottCC LimLR FergusonDietary
protection against free radicals: A case for multiple testing to
establish structure-activity relationships for antioxidant
potential of anthocyanic plant speciesInt J Mol
Sci101081103200910.3390/ijms10031081
|
|
20.
|
M PhilpottKS GouldC LimLR FergusonIn situ
and in vitro antioxidant activity of sweetpotato anthocyaninsJ
Agric Food Chem5215111513200410.1021/jf034593j15030203
|
|
21.
|
I Konczak-IslamM YoshimotoDX HouN
TeraharaO YamakawaPotential chemopreventive properties of
anthocyanin-rich aqueous extracts from in vitro produced tissue of
sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.)J Agr Food
Chem5159165922200310.1021/jf030066o13129295
|
|
22.
|
S de Pascual-TeresaDA MorenoC
García-VigueraFlavanols and anthocyanins in cardiovascular health:
A review of current evidenceInt J Mol Sci1116791703201020480037
|
|
23.
|
K NakamuraK FushimiH KouchiK MiharaM
MiyazakiT OheM NambaInhibitory effects of antioxidants on neonatal
rat cardiac myocyte hypertrophy induced by tumor necrosis
factor-alpha and angiotensin
IICirculation98794799199810.1161/01.CIR.98.8.7949727550
|
|
24.
|
HL LiAB WangY HuangDP LiuG LiuCN ZhangC
WeiYQ LiuRT HuiCC LiangIsorhapontigenin, a new resveratrol analog,
attenuates cardiac hypertrophy via blocking signaling transduction
pathwaysFree Radic Biol
Med38243257200510.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.10.02015607907
|
|
25.
|
HL LiY HuangCN ZhangG LiuYS WeiAB WangYQ
LiuRT HuiC WeiGM WilliamsEpigallocathechin-3 gallate inhibits
cardiac hypertrophy through blocking reactive oxidative
species-dependent and -independent signal pathwaysFree Radic Biol
Med4017561775200610.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.01.005
|
|
26.
|
TY WuCC TsaiYT HwangTH ChiuEffect of
antioxidant activity and functional properties of Chingshey purple
sweet potato fermented milk by Lactobacillus acidophilus,
L. delbrueckii subsp lactis, and L gasseri
strainsJ Food
Sci77M2M8201210.1111/j.1750-3841.2011.02507.x22182227
|
|
27.
|
AM DeschampsFG SpinalePathways of matrix
metalloproteinase induction in heart failure: bioactive molecules
and transcriptional regulationCardiovasc
Res69666676200610.1016/j.cardiores.2005.10.00416426590
|
|
28.
|
PM KangS IzumoApoptosis in heart: basic
mechanisms and implications in cardiovascular diseasesTrends Mol
Med9177182200310.1016/S1471-4914(03)00025-X12727144
|
|
29.
|
J HeinekeJD MolkentinRegulation of cardiac
hypertrophy by intracellular signalling pathwaysNat Rev Mol Cell
Biol7589600200610.1038/nrm198316936699
|
|
30.
|
CF LiuYT TungCL WuBH LeeWH HsuTM
PanAntihypertensive effects of Lactobacillus-fermented milk
orally administered to spontaneously hypertensive ratsJ Agric Food
Chem59453745432011
|
|
31.
|
T NishikimiN MaedaH MatsuokaThe role of
natriuretic peptides in cardioprotectionCardiovasc
Res69318328200610.1016/j.cardiores.2005.10.00116289003
|
|
32.
|
CH ChuBS TzangLM ChenCH KuoYC ChengLY
ChenFJ TsaiCH TsaiWW KuoCY HuangIGF-II/mannose-6-phosphate receptor
signaling induced cell hypertrophy and atrial natriuretic
peptide/BNP expression via Gαq interaction and protein kinase
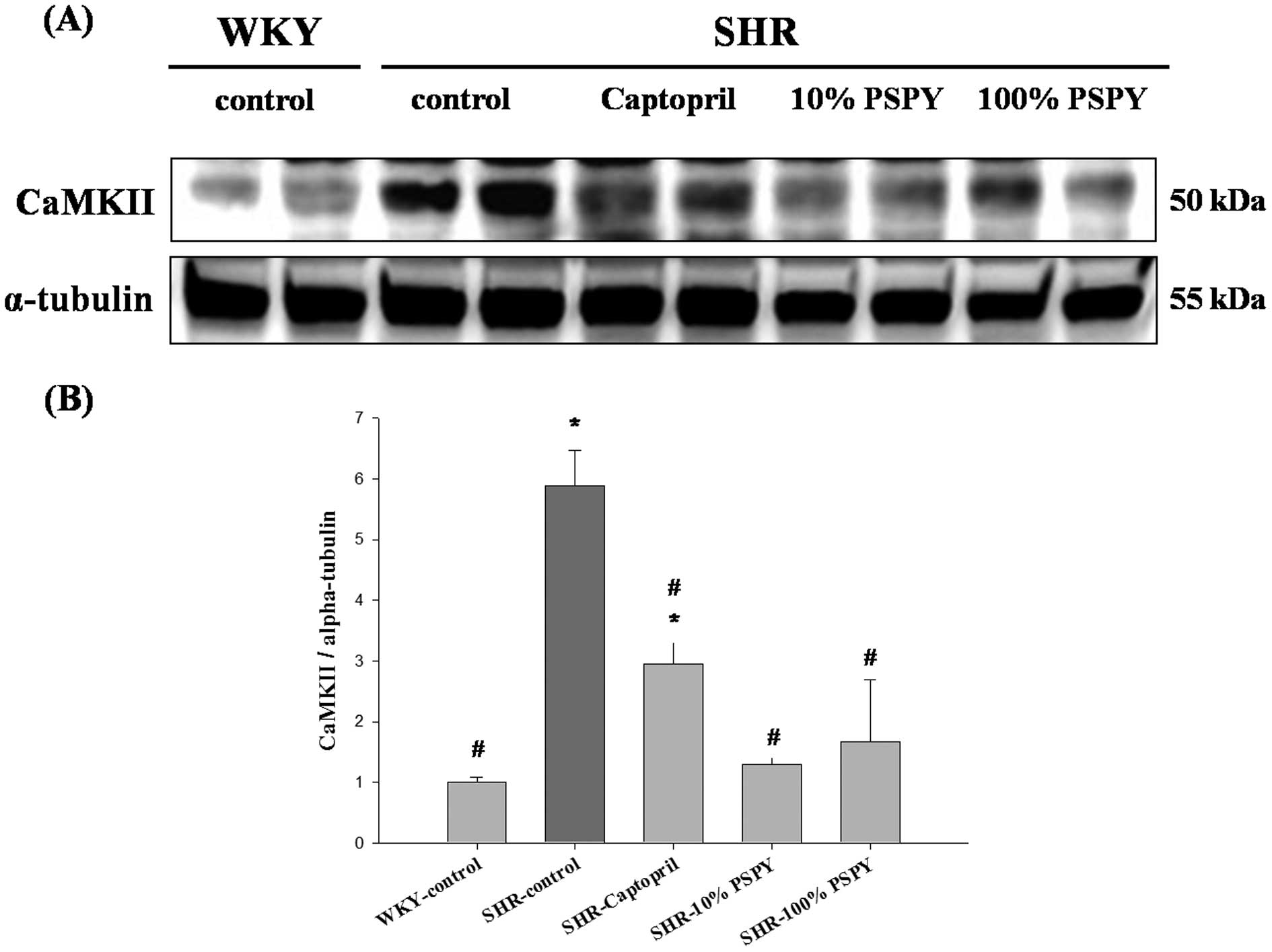
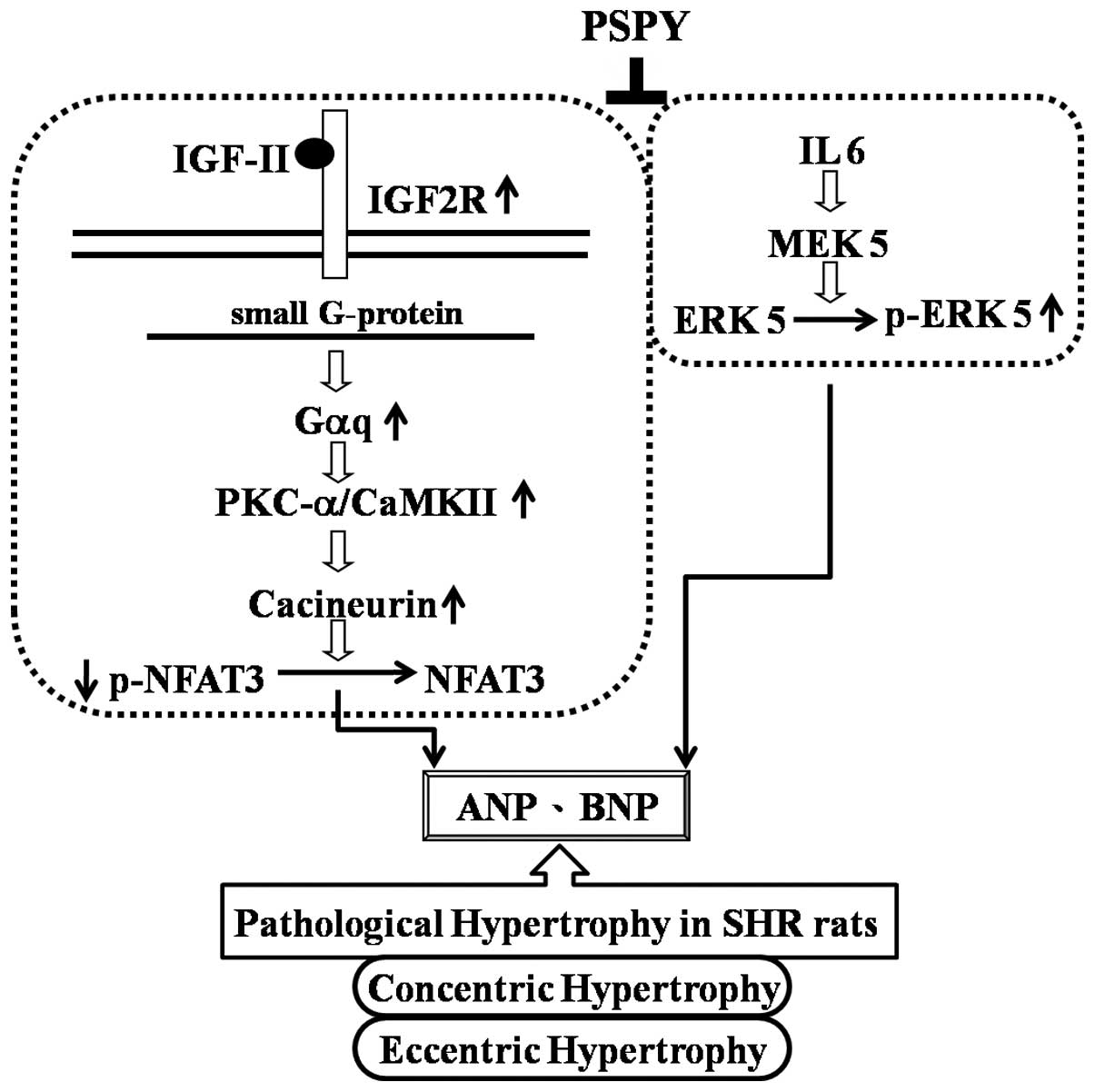
C-α/CaMKII activation in H9c2 cardiomyoblast cellsJ
Endocrinol197381390200818434368
|
|
33.
|
CY HuangLY HaoDE BuetowHypertrophy of
cultured adult rat ventricular cardiomyocytes induced by antibodies
against the insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I or the IGF-I
receptor is IGF-II-dependentMol Cell
Biochem2336572200210.1023/A:101551432432812083381
|
|
34.
|
H OkamuraJ AramburuC
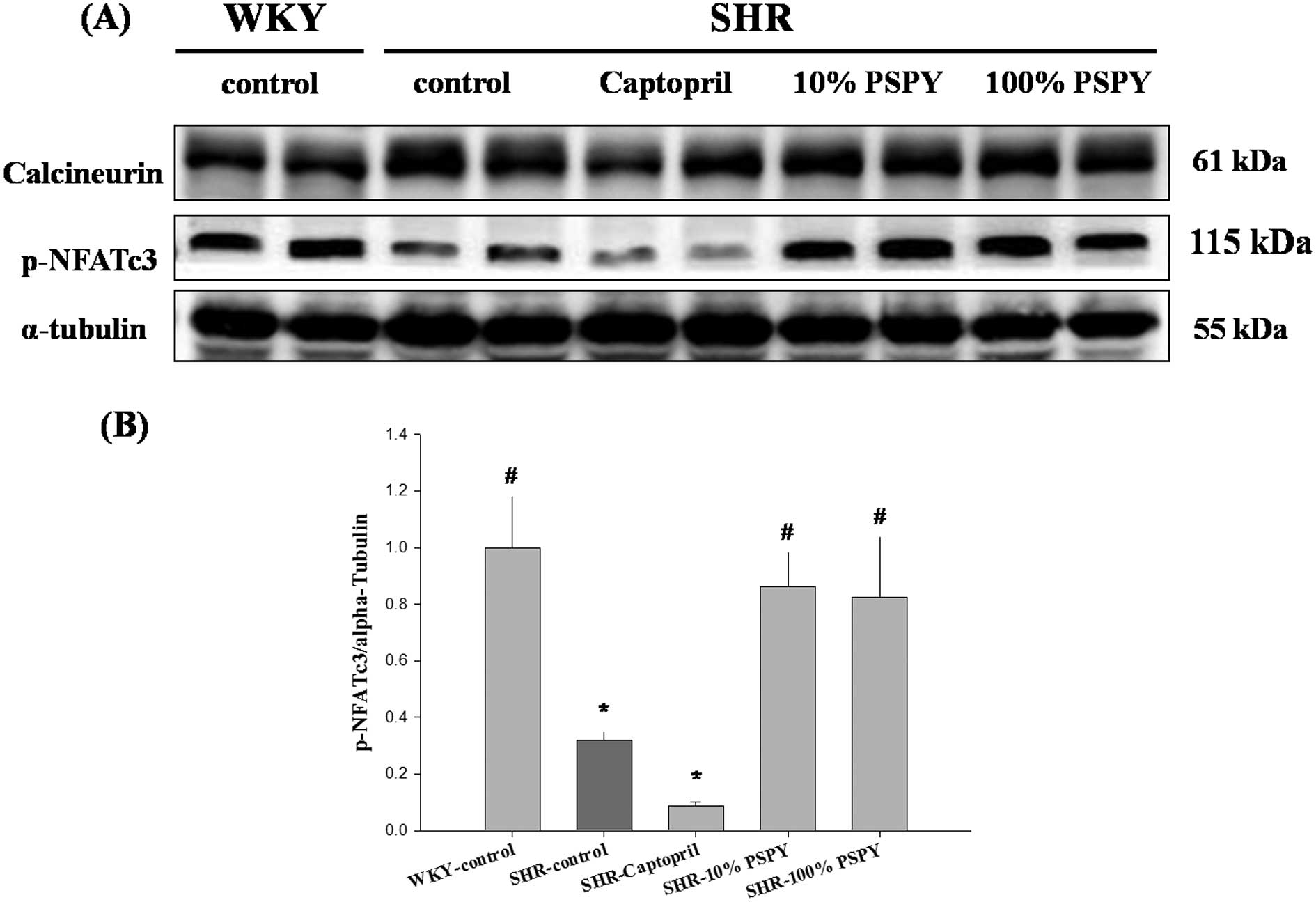
Garcia-RodriguezConcerted dephosphorylation of the transcription
factor NFAT1 induces a conformational switch that regulates
transcriptional activityMol
Cell6539550200010.1016/S1097-2765(00)00053-8
|
|
35.
|
HW LimJD MolkentinCalcineurin and human
heart failureNat Med5246247199910.1038/6430
|
|
36.
|
T KandaT TakahashiInterleukin-6 and
cardiovascular diseasesJpn Heart
J45183193200410.1536/jhj.45.183
|
|
37.
|
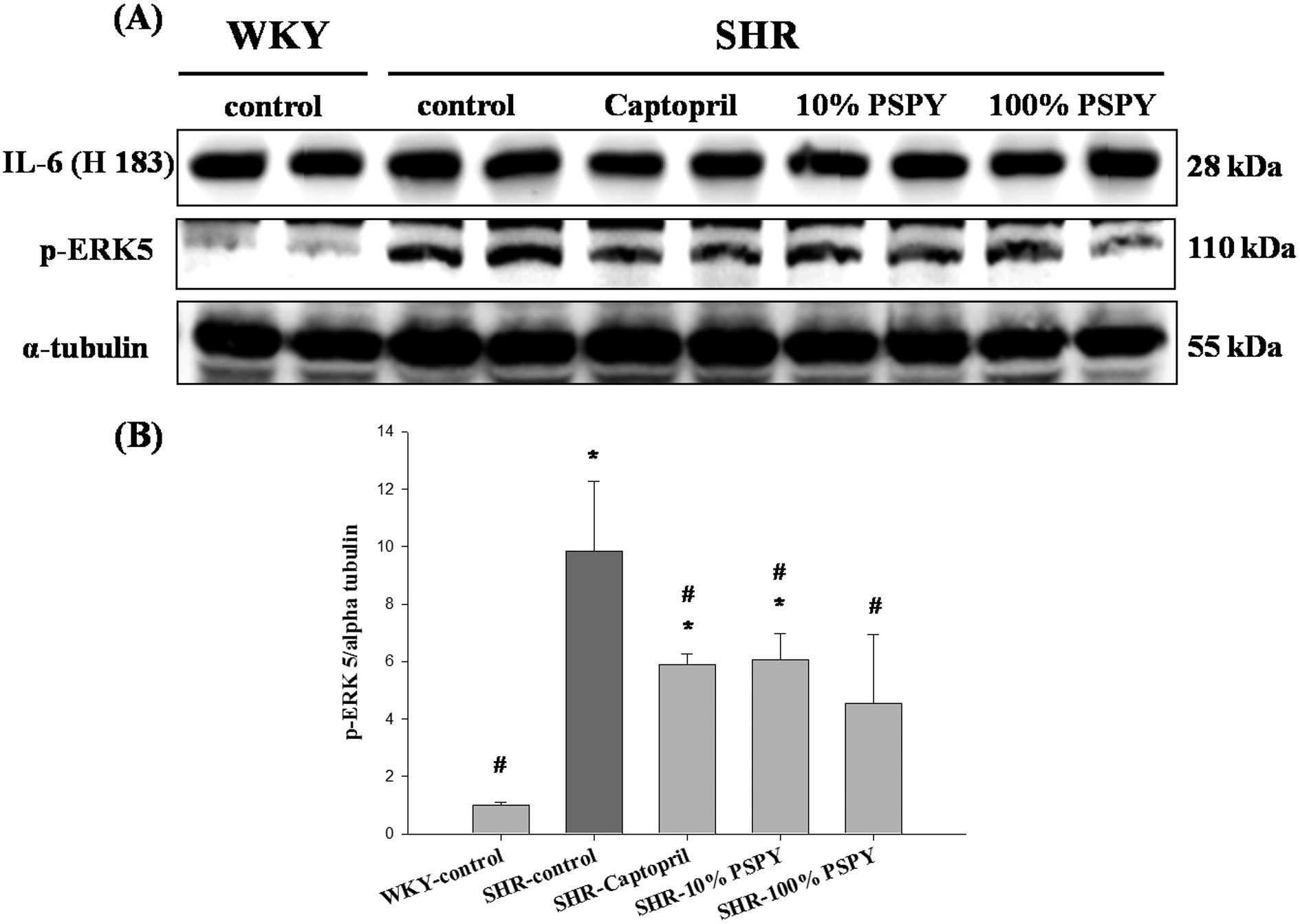
GC MeléndezJL McLartySP LevickY DuJS
JanickiGL BrowerInterleukin 6 mediates myocardial fibrosis,
concentric hypertrophy, and diastolic dysfunction in
ratsHypertension56225231201020606113
|
|
38.
|
T HiranoInterleukin 6 and its receptor:
ten years laterInt Rev Immunol1624928419989505191
|
|
39.
|
H HirotaK YoshidaT KishimotoT
TagaContinuous activation of gp130, a signal-transducing receptor
component for interleukin 6-related cytokines, causes myocardial
hypertrophy in miceProc Natl Acad Sci
USA9248624866199510.1073/pnas.92.11.48627539136
|
|
40.
|
RL NicolN FreyG PearsonM CobbJ
RichardsonEN OlsonActivated MEK5 induces serial assembly of
sarcomeres and eccentric cardiac hypertrophyEMBO
J2027572767200110.1093/emboj/20.11.275711387209
|
|
41.
|
SJ CameronS ItohCP BainesC ZhangS OhtaW
CheM GlassmanJD LeeC YanJ YangJ AbeActivation of big MAP kinase 1
(BMK1/ERK5) inhibits cardiac injury after myocardial ischemia and
reperfusionFEBS
Lett566255260200410.1016/j.febslet.2004.03.12015147905
|
|
42.
|
M KimuraK HayakawaH SansawaInvolvement of
γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) B receptors in the hypotensive effect of
systemically administered GABA in spontaneously hypertensive
ratsJpn J Pharmacol893883942002
|
|
43.
|
MY LinCL YenAntioxidative ability of
lactic acid bacteriaJ Agric Food
Chem4714601466199910.1021/jf981149l10563999
|