|
1
|
Alzheimer’s Association. Alzheimer’s
disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 4:110–133. 2008.
|
|
2
|
Kukull WA, Higdon R, Bowen JD, McCormick
WC, Teri L, Schellenberg GD, van Belle G, Jolley L and Larson EB:
Dementia and Alzheimer disease incidence: a prospective cohort
study. Arch Neurol. 59:1737–1746. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Querfurth HW and LaFerla FM: Alzheimer’s
disease. N Engl J Med. 362:329–344. 2010.
|
|
4
|
Selkoe DJ, Mandelkow E and Holtzman DM:
The Biology of Alzheimer Disease. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory
Press; Cold Spring Harbor, NY: 2012
|
|
5
|
Choy RW, Cheng Z and Schekman R: Amyloid
precursor protein (APP) traffics from the cell surface via
endosomes for amyloid β (Aβ) production in the trans-Golgi network.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:E2077–E2082. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
LaFerla FM, Green KN and Oddo S:
Intracellular amyloid-beta in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Rev
Neurosci. 8:499–509. 2007.
|
|
7
|
Li S, Shankar GM and Selkoe DJ: How do
soluble oligomers of amyloid beta-protein impair hippocampal
synaptic plasticity? Front Cell Neurosci. 4:52010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Siegenthaler BM and Rajendran L: Retromers
in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurodegener Dis. 10:116–121. 2012.
|
|
9
|
Whitfield JF: The road to LOAD (late-onset
Alzheimer’s disease) and possible ways to block it. Expert Opin
Ther Targets. 11:1257–1260. 2007.
|
|
10
|
Dal Prà I, Chiarini A, Pacchiana R,
Chakravarthy B, Whitfield JF and Armato U: Emerging concepts of how
β-amyloid proteins and pro-inflammatory cytokines might collaborate
to produce an ‘Alzheimer brain’ (Review). Mol Med Rep. 1:173–178.
2008.
|
|
11
|
Hartlage-Rübsamen M, Morawski M, Waniek A,
Jäger C, Zeitschel U, Koch B, Cynis H, Schilling S, Schliebs R,
Demuth HU and Rossner S: Glutaminyl cyclase contributes to the
formation of focal and diffuse pyroglutamate (pGlu)-Aβ deposits in
hippocampus via distinct cellular mechanisms. Acta Neuropathol.
121:705–719. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jawhar S, Wirth O and Bayer TA:
Pyroglutamate amyloid-β (Aβ): a hatchet man in Alzheimer disease. J
Biol Chem. 286:38825–38832. 2011.
|
|
13
|
Nussbaum JM, Schilling S, Cynis H, Silva
A, Swanson E, Wangsanut T, Tayler K, Wiltgen B, Hatami A, Rönicke
R, Reymann K, Hutter-Paier B, Alexandru A, Jagla W, Graubner S,
Glabe CG, Demuth HU and Bloom GS: Prion-like behaviour and
tau-dependent cytotoxicity of pyroglutamylated amyloid-β. Nature.
485:651–655. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Prusiner SB: Cell biology. A unifying role
for prions in neurodegenerative diseases. Science. 336:1511–1513.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Stöhr J, Watts JC, Mensinger ZL, Oehler A,
Grillo SK, DeArmond SJ, Prusiner SB and Giles K: Purified and
synthetic Alzheimer’s amyloid beta (Aβ) prions. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 109:11025–11030. 2012.
|
|
16
|
Yaar M, Zhai S, Pilch PF, Doyle SM,
Eisenhauer PB, Fine RE and Gilchrest BA: Binding of β-amyloid to
the p75 neurotrophin receptor induces apoptosis. A possible
mechanism for Alzheimer’s disease. J Clin Invest. 100:2333–2340.
1997.
|
|
17
|
Yaar M, Zhai S, Fine RE, Eisenhauer PB,
Arbie BL, Stewart KB and Gilchrest BA: Amyloid-β binds trimers as
well as monomers of the 75-kDa neurotrophin receptor and activates
receptor signaling. J Biol Chem. 277:7720–7725. 2001.
|
|
18
|
Kuner P, Schubenel R and Hertel C:
β-amyloid binds to p75NTR and activates NF-kappaB in human
neuroblastoma cells. J Neurosci Res. 54:798–804. 1998.
|
|
19
|
Perini G, Della-Bianca V, Politi V, Della
Valle G, Dal Prà I, Rossi F and Armato U: Role of p75 neurotrophin
receptor in the neurotoxicity by β-amyloid peptides and synergistic
effect of inflammatory cytokines. J Exp Med. 195:907–918. 2002.
|
|
20
|
Chiarini A, Dal Prà I, Whitfield JF and
Armato U: The killing of neurons by beta-amyloid peptides, prions
and pro-inflammatory cytokines. Ital J Anat Embryol. 111:221–246.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Della-Bianca V, Rossi F, Armato U, Dal Prà
I, Costantini C, Perini G, Politi V and Della Valle G: Neurotrophin
p75 receptor is involved in neuronal damage by prion
peptide-(106-126). J Biol Chem. 276:38929–38933. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sotthibundhu A, Li QX, Thangnipon W and
Coulson EJ: Abeta(1–42) stimulates adult SVZ neurogenesis through
the p75 neurotrophin receptor. Neurobiol Aging. 30:1975–1985.
2009.
|
|
23
|
Bai M, Trivedi S and Brown EM:
Dimerization of the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor (CaR) on
the cell surface of CaR-transfected HEK293 cells. J Biol Chem.
273:23605–23610. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chakravarthy B, Gaudet C, Ménard M,
Atkinson T, Brown L, Laferla FM, Armato U and Whitfield J:
Amyloid-beta peptides stimulate the expression of the p75(NTR)
neurotrophin receptor in SHSY5Y human neuroblastoma cells and AD
transgenic mice. J Alzheimers Dis. 19:915–925. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ito S, Ménard M, Atkinson T, Gaudet C,
Brown L, Whitfield J and Chakravarthy B: Involvement of
insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor signaling in the amyloid-β
peptide oligomers-induced p75 neurotrophin receptor protein
expression in mouse hippocampus. J Alzheimers Dis. 31:493–506.
2012.
|
|
26
|
Mufson EJ, Ma SY, Dills J, Cochran EJ,
Leurgans S, Wuu J, Bennett DA, Jaffar S, Gilmor ML, Levey AI and
Kordower JH: Loss of basal forebrain P75 (NTR) immunoreactivity in
subjects with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. J
Comp Neurol. 443:136–153. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chakravarthy B, Gaudet C, Ménard M,
Atkinson T, Chiarini A, Dal Prà I and Whitfield J: The p75
neurotrophin receptor is localized to primary cilia in adult mouse
hippocampal dentate gyrus granule cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 401:458–462. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Woo NH, Teng HK, Siao CJ, Chiaruttini C,
Pang PT, Milner TA, Hempstead BL and Lu B: Activation of p75NTR by
proBDNF facilitates hippocampal long-term depression. Nat Neurosci.
8:1069–1077. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bernabeu RO and Longo FM: The p75
neurotrophin receptor is expressed by adult mouse dentate
progenitor cells and regulates neuronal and non-neuronal cell
genesis. BMC Neurosci. 11:1362010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chakravarthy B, Ménard M, Ito S, Gaudet C,
Dal Prà I, Armato U and Whitfield J: Hippocampal
membrane-associated p75NTR levels are increased in Alzheimer’s
disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 30:675–684. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Brown EM and MacLeod RJ: Extracellular
calcium sensing and extracellular calcium signaling. Physiol Rev.
81:239–297. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Msaouel P, Nixon AM, Bramos AP, Baiba E
and Kentarchos NE: Extracellular calcium-sensing receptor: an
overview of physiology, pathophysiology and clinical perspectives.
In Vivo. 18:739–753. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jensen AA and Bräuner-Osborne H:
Allosteric modulation of the calcium-sensing receptor. Curr
Neuropharmacol. 5:180–186. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Magno AL, Ward BK and Ratajczak T: The
calcium-sensing receptor: a molecular perspective. Endocr Rev.
32:3–30. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hofer AM and Brown EM: Extracellular
calcium sensing and signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 4:530–538.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Pidasheva S, Grant M, Canaff L, Ercan O,
Kumar U and Hendy GN: Calcium-sensing receptor dimerizes in the
endoplasmic reticulum: biochemical and biophysical characterization
of CaSR mutants retained intracellularly. Hum Mol Genet.
15:2200–2209. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Chang W and Shoback D: Extracellular
Ca2+-sensing receptors-an overview. Cell Calcium.
35:183–196. 2004.
|
|
38
|
Ye C, Ho-Pao CL, Kanazirska M, Quinn S,
Rogers K, Seidman CE, Seidman JG, Brown EM and Vassilev PM:
Amyloid-beta proteins activate Ca(2+)-permeable channels through
calcium-sensing receptors. J Neurosci Res. 47:547–554. 1997.
|
|
39
|
Chiarini A, Dal Prà I, Marconi M,
Chakravarthy B, Whitfield JF and Armato U: Calcium-sensing receptor
(CaSR) in human brain’s pathophysiology: roles in late-onset
Alzheimer’s disease (LOAD). Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 10:317–326.
2009.
|
|
40
|
Conley YP, Mukherjee A, Kammerer C,
DeKosky ST, Kamboh MI, Finegold DN and Ferrel RE: Evidence
supporting a role for the calcium-sensing receptor in Alzheimer
disease. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 150B:703–709. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Dal Prà I, Chiarini A, Nemeth EF, Armato U
and Whitfield JF: Roles of Ca2+ and the
Ca2+-sensing receptor (CaSR) in the expression of
inducible NOS (nitric oxide synthase)-2 and its BH4
(tetrahydrobiopterin)-dependent activation in cytokine-stimulated
adult human astrocytes. J Cell Biochem. 96:428–438. 2005.
|
|
42
|
Chiarini A, Dal Prà I, Gottardo R,
Bortolotti F, Whitfield JF and Armato U: The BH4
(tetrahydrobiopterin)-dependent activation, but not the expression,
of inducible NOS (nitric oxide synthase)-2 in proinflammatory
cytokine-stimulated, cultured normal human astrocytes is mediated
by MEK-ERK kinases. J Cell Biochem. 94:731–743. 2005.
|
|
43
|
Chiarini A, Dal Prà I, Menapace L,
Pacchiana R, Whitfield JF and Armato U: Soluble amyloid β-peptide
and myelin basic protein strongly stimulate, alone and in synergism
with combined proinflammatory cytokines, the expression of
functional nitric oxide synthase-2 in normal adult human
astrocytes. Int J Mol Med. 16:801–807. 2005.
|
|
44
|
Chiarini A, Armato U, Pacchiana R and Dal
Prà I: Proteomic analysis of GTP cyclohydrolase 1 multiprotein
complexes in cultured normal adult human astrocytes under both
basal and cytokine-activated conditions. Proteomics. 9:1850–1860.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Chiarini A, Whitfield J, Bonafini C,
Chakravarthy B, Armato U and Dal Prà I: Amyloid-β(25–35), an
amyloid-β(1–42) surrogate, and proinflammatory cytokines stimulate
VEGF-A secretion by cultured, early passage, normoxic adult human
cerebral astrocytes. J Alzheimers Dis. 21:915–926. 2010.
|
|
46
|
Dal Prà I, Whitfileld JF, Pacchiana R,
Bonafini C, Talacchi A, Chakravarthy B, Armato U and Chiarini A:
The amyloid-β42 proxy, amyloid-β25–35, induces normal human
cerebral astrocytes to produce amyloid-β42. J Alzheimers Dis.
24:335–347. 2011.
|
|
47
|
Nedergaard M, Ransom B and Goldman SA: New
roles for astrocytes: redefining the functional architecture of the
brain. Trends Neurosci. 26:523–530. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
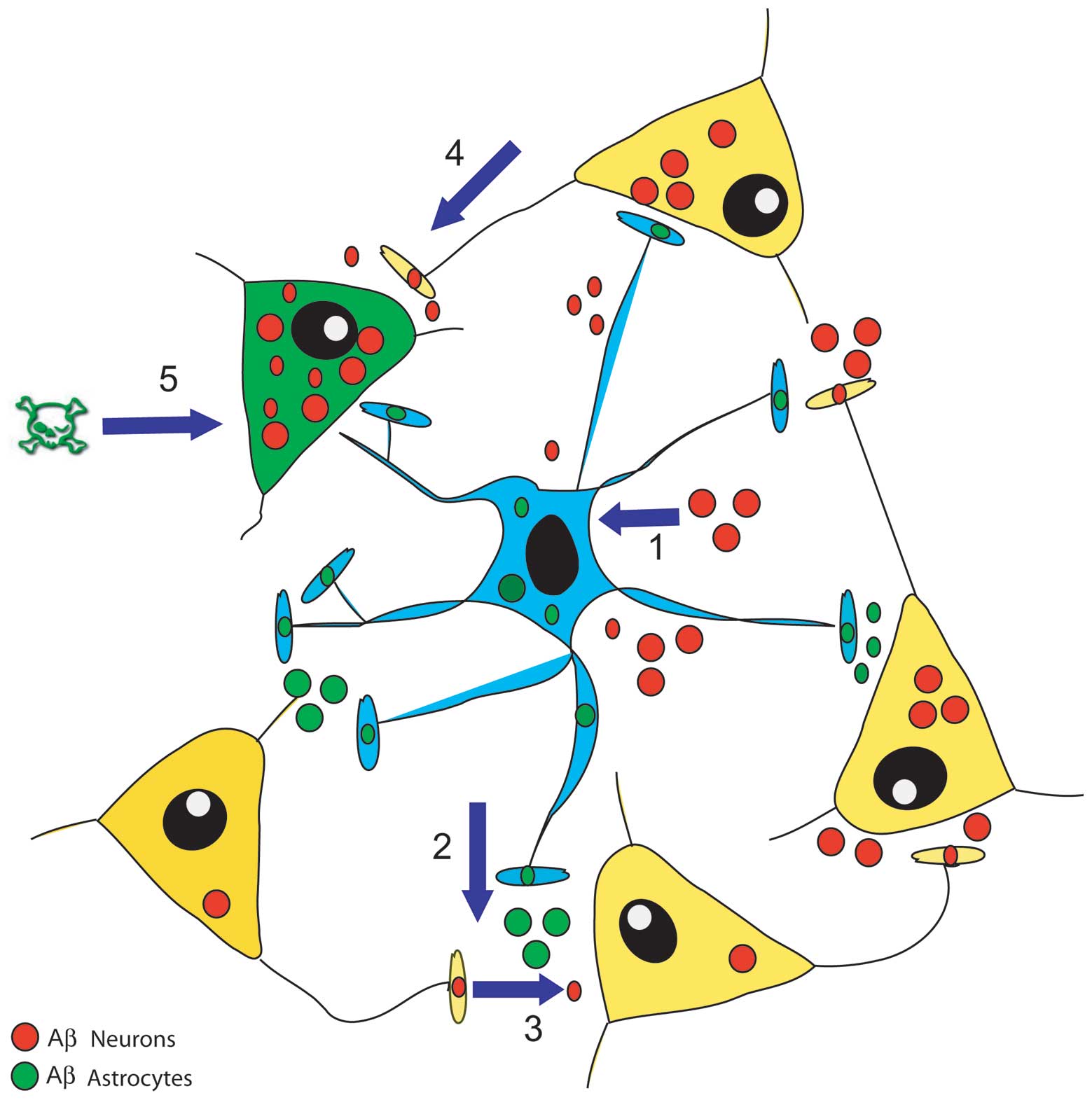
Nagele RG and Wegiel J, Venkataraman V,
Imaki H, Wang KC and Wegiel J: Contribution of glial cells to the
development of amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol
Aging. 25:663–674. 2004.
|
|
49
|
Nedergaard M and Verkhratsky A: Artefact
versus reality-how astrocytes contribute to synaptic events. Glia.
60:1013–1023. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Theodosis DT, Poulain DA and Oliet SH:
Activity-dependent structural and functional plasticity of
astrocyte-neuron interactions. Physiol Rev. 88:983–1008. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
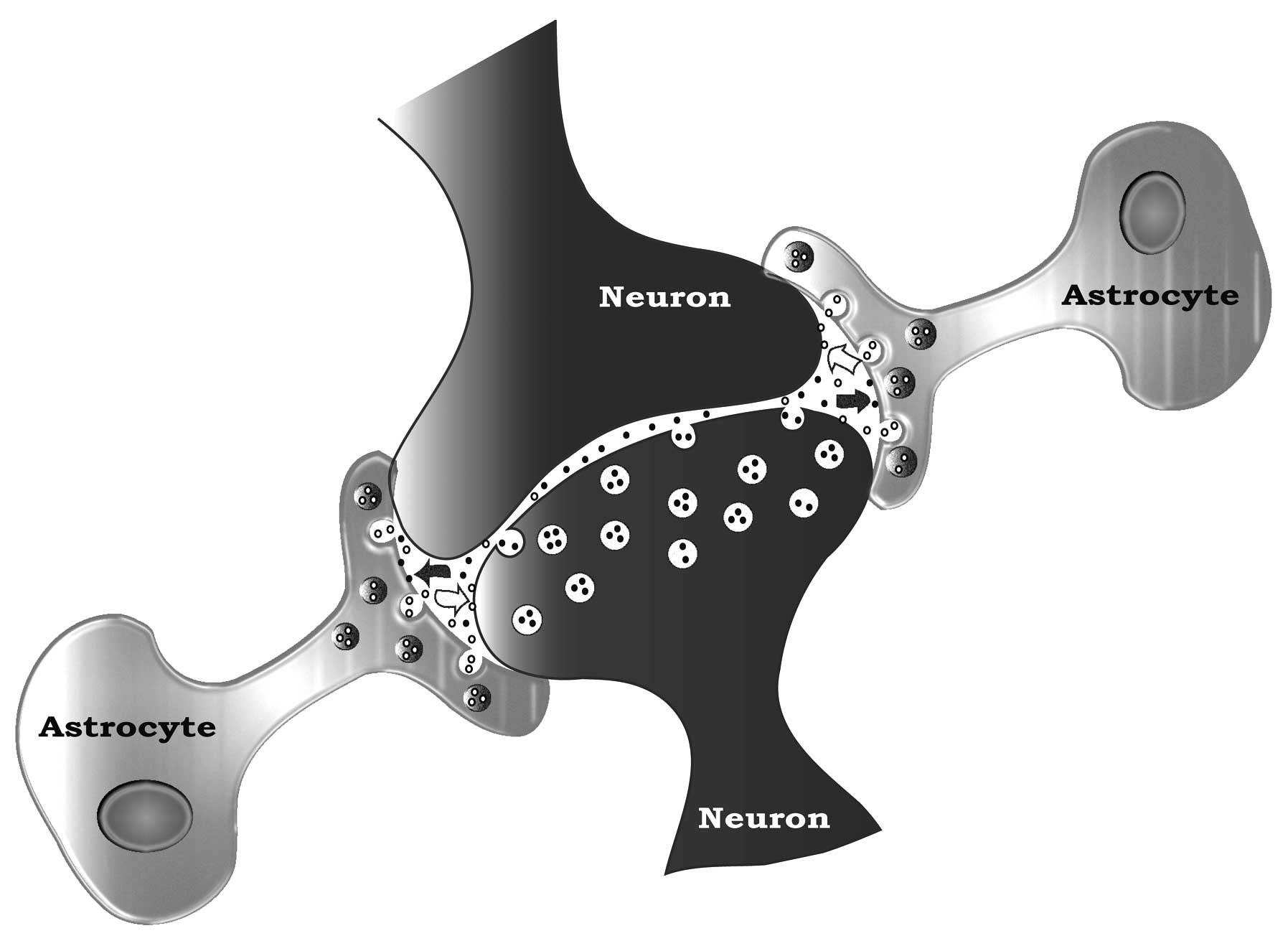
Guenette SY: Astrocytes: a cellular player
in Abeta clearance and degradation. Trends Mol Med. 9:279–280.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
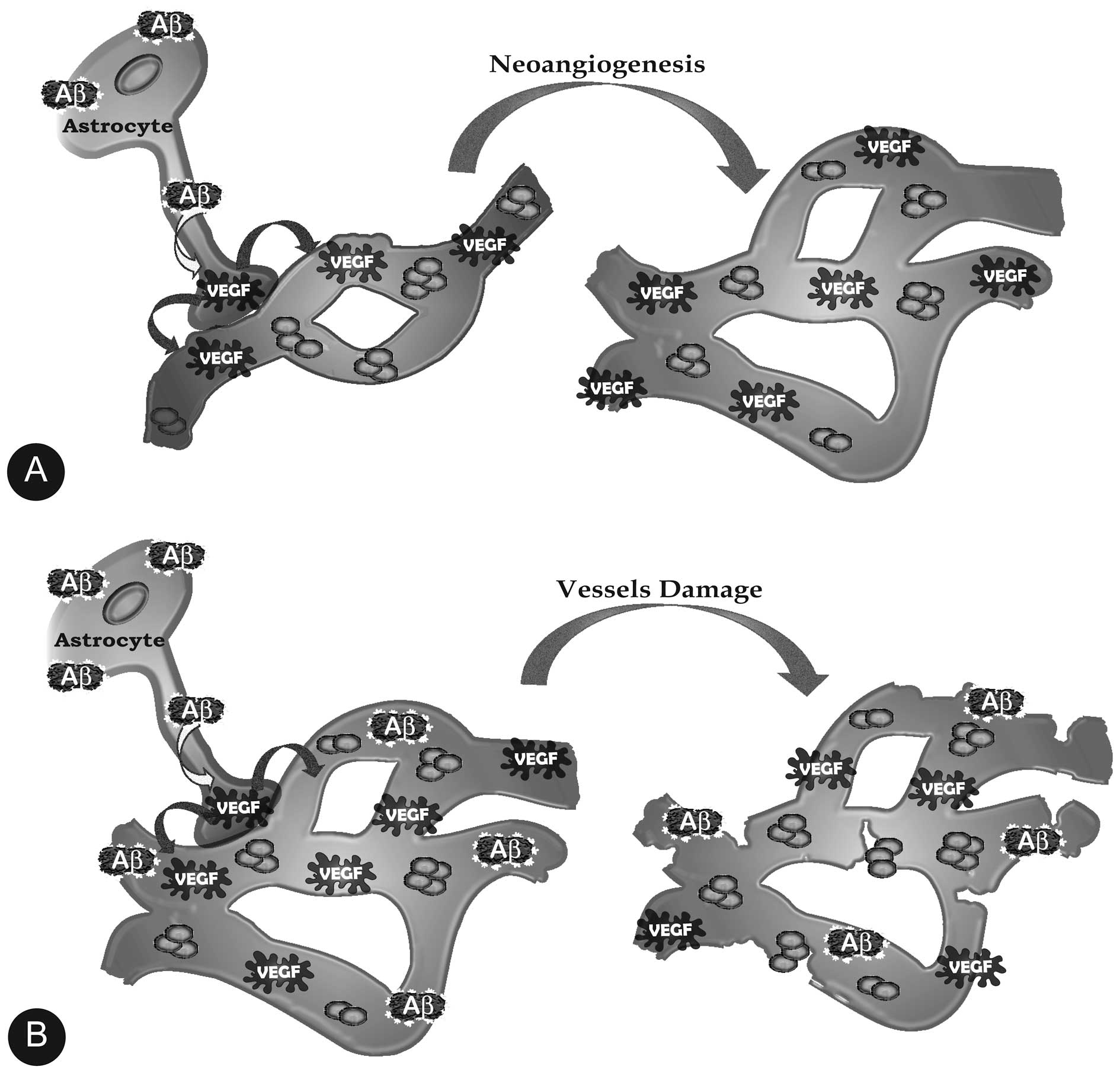
Biron KE, Dickstein DL, Gopaul R and
Jefferies WA: Amyloid triggers extensive cerebral angiogenesis
causing blood brain barrier permeability and hypervascularity in
Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One. 6:e237892011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Pogue AI and Lukiw WJ: Angiogenic
signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroreport. 15:1507–1510.
2004.
|
|
54
|
Zand L, Ryu JK and McLarnon JG: Induction
of angiogenesis in the beta-amyloid peptide-injected rat
hippocampus. Neuroreport. 16:129–132. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Bell RD and Zlokovic BV: Neurovascular
mechanisms and blood-brain barrier disorder in Alzheimer’s disease.
Acta Neuropatol. 118:103–113. 2008.
|
|
56
|
Bakker A, Krauss GL, Albert MS, Speck CL,
Jones LR, Stark CE, Yassa MA, Bassett SS, Shelton AL and Gallagher
M: Reduction of hippocampal hyperactivity improves cognition in
anamnestic mild cognitive impairment. Neuron. 74:467–474. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Putcha D, Brickhouse M, O’Keefe K,
Sullivan C, Rentz D, Marshall G, Dickerson B and Sperling R:
Hippocampal hyperactivation associated with cortical thinning in
Alzheimer’s disease signature regions in non-demented elderly
adults. J Neurosci. 31:17680–17688. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Sperling R: Potential of functional MRI as
a biomarker in early Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 32(Suppl
1): S37–S43. 2011.
|
|
59
|
Yassa MA, Stark SM, Bakker A, Albert MS,
Gallagher M and Stark CE: High-resolution structural and functional
MRI of hippocampal CA3 and dentate gyrus in patients with
anamnestic mild cognitive impairment. Neuroimage. 51:1242–1252.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Jantaratnotai N, Ryu JK, Schwab C, McGeer
PL and McLarnon JG: Comparison of vascular perturbations in an
Aβ-injected animal model and in AD brain. Int J Alzheimers Dis.
2011:9182802011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Meyer-Luehmann M, Spires-Jones TL, Prada
C, Garcia-Alloza M, de Calignon A, Rozkalne A, Koenigsknecht-Talboo
J, Holtzman DM, Bacskai BJ and Hyman BT: Rapid appearance and local
toxicity of amyloid-beta plaques in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s
disease. Nature. 451:720–724. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Altman J and Das GD: Postnatal
neurogenesis in the guinea-pig. Nature. 214:1098–1101. 1967.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Nottebohm F: Testosterone triggers growth
of brain vocal control nuclei in adult female canaries. Brain Res.
189:429–436. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Kempermann G: Adult Neurogenesis. 2.
Oxford University Press; New York: 2011
|
|
65
|
Einstein EB, Patterson CA, Hon BJ, Regan
KA, Reddi J, Melnikoff DE, Mateer MJ, Schulz S, Johnson BN and
Tallent MK: Somatostatin signaling in neuronal cilia is critical
for object recognition memory. J Neurosci. 30:4306–4314. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Burgos-Ramos E, Hervás-Aguilar A,
Aguado-Liera D, Puebla-Jiménez L, Hernández-Pinto AM, Barrios V and
Arilla-Ferreiro E: Somatostatin and Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 286:104–111. 2008.
|
|
67
|
Händel M, Schultz S, Stanarius A, Schreff
M, Erdtmann-Vourliotis M, Schmidt H, Wolf G and Höllt V: Selective
targeting of somatostatin receptor 3 to neuronal cilia.
Neuroscience. 89:909–926. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Stanić D, Malmgren H, He H, Scott L,
Aperia A and Hökfelt T: Developmental changes in frequency of the
ciliary somatostatin receptor 3 protein. Brain Res. 1249:101–112.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Berbari NF, Johnson AD, Lewis JS, Askwith
CC and Mykytyn K: Identification of ciliary localization sequences
within the third intracellular loop of G protein-coupled receptors.
Mol Biol Cell. 19:1540–1547. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Goetz SC, Ocbina PJ and Anderson KV: The
primary cilium as a hedgehog signal transduction machine. Methods
Cell Biol. 94:199–222. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Corbit KC, Aanstad P, Singla V, Norman AR,
Stainier DY and Reiter JF: Vertebrate smoothened functions at the
primary cilium. Nature. 437:1018–1021. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Han YG, Spassky N, Romaguera-Ros M,
Garcia-Verdugo JM, Aguilar A, Schneider-Maunoury S and
Alvarez-Buylla A: Hedgehog signaling and primary cilia are required
for the formation of adult neural stem cells. Nat Neurosci.
11:277–284. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Amador-Arjona A, Elliott J, Miller A,
Ginbey A, Pazour GJ, Enikolopov G, Roberts AJ and Terskikh AV:
Primary cilia regulate proliferation of amplifying progenitors in
adult hippocampus: implications for learning and memory. J
Neurosci. 31:9933–9944. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Schaeffer EL, Novaes BA, Da Silva ER, Skaf
HD and Mendes-Neto AG: Strategies to promote differentiation of
newborn neurons into mature functional cells in Alzheimer brain.
Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 33:1087–1102. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
van Tijn P, Kamphuis W, Marlatt MW, Hol EM
and Lucassen PJ: Presenilin mouse and zebrafish models for
dementia: focus on neurogenesis. Prog Neurobiol. 93:149–164.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Waldau B and Shetty AK: Behavior of neural
stem cells in the Alzheimer brain. Cell Mol Life Sci. 65:2372–2384.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Armato U, Chakravarthy B, Chiarini A, Dal
Prà I and Whitfield JF: Is Alzheimer’s disease at least partly a
ciliopathy? J Alzheimers Dis. 1:101e2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Gaudet C, Ménard M, Brown L, Atkinson T,
LaFerla FM, Ito S, Armato U, Dal Prà I, Whitfield J and
Chakravarthy B: Reduction of the immunostainable length of the
hippocampal dentate granule cells’ primary cilia in 3xAD-transgenic
mice producing human Aβ1–42 and tau. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
September 17–2012.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
79
|
Rodríguez JJ, Jones VC, Tabuchi M, Allan
SM, Knight EM, LaFerla FM, Oddo S and Verkhratsky A: Impaired adult
neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of a triple transgenic mouse
model of Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One. 3:e29352008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Avila J, Insausti R and Del Rio J: Memory
and neurogenesis in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Aging Dis.
1:30–36. 2010.
|
|
81
|
Shetty AK: Reelin signaling, hippocampal
neurogenesis and efficacy of aspirin intake and stem cell
transplantation in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Aging Dis.
1:2–11. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Whitfield JF, Chakravarthy B, Chiarini A
and Dal Prà I: The primary cilium: The tiny driver of dentate gyral
neurogenesis. Neurogenesis Research. Clark GJ and Anderson WT:
Chapter V. Nova Science Publishers Inc; Hauppauge, NY: pp. 137–159.
2012, (In press). ISBN: 9781620817230
|
|
83
|
Fortress AM, Buhusi M, Helke KL and
Granholm AC: Cholinergic degeneration and alterations in the TrkA
and p75NTR balance as a result of pro-NGF injection into aged rats.
J Aging Res. 2011:4605432011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Armato U, Chakravarthy B, Chiarini A, Dal
Prà I and Whitfield JF: A Paradigm-changing surprise from dentate
gyrus granule cells-cilium-localized p75NTR may drive their
progenitor cell proliferation. J Alzheimers Dis. 1:e1042011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Pérez-González R, Antequera D, Vargas T,
Spuch C, Bolos M and Carro E: Leptin induces the proliferation of
neuronal progenitors and neuroprotection in a mouse model of
Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 24:17–25. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Armato U, Chakravarthy B, Chiarini A,
Chioffi F, Dal Prà I and Whitfield JF: Leptin, sonic hedgehogs and
neurogenesis-a primary cilium’s tale. J Alzheimers Dis. 1:e1052012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Bianca VD, Dusi S, Bianchini E, Dal Prà I
and Rossi F: Beta-amyloid activates the O2-forming NADPH
oxidase in microglia, monocytes and neutrophils. A possible
inflammatory mechanism of neuronal damage in Alzheimer’s disease. J
Biol Chem. 274:15493–15499. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Armato U, Bonafini C, Chakravarthy B,
Pacchiana R, Chiarini A, Whitfield JF and Dal Prà I: The
calcium-sensing receptor: A novel Alzheimer’s disease crucial
target? J Neurol Sci. July 27–2012.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|