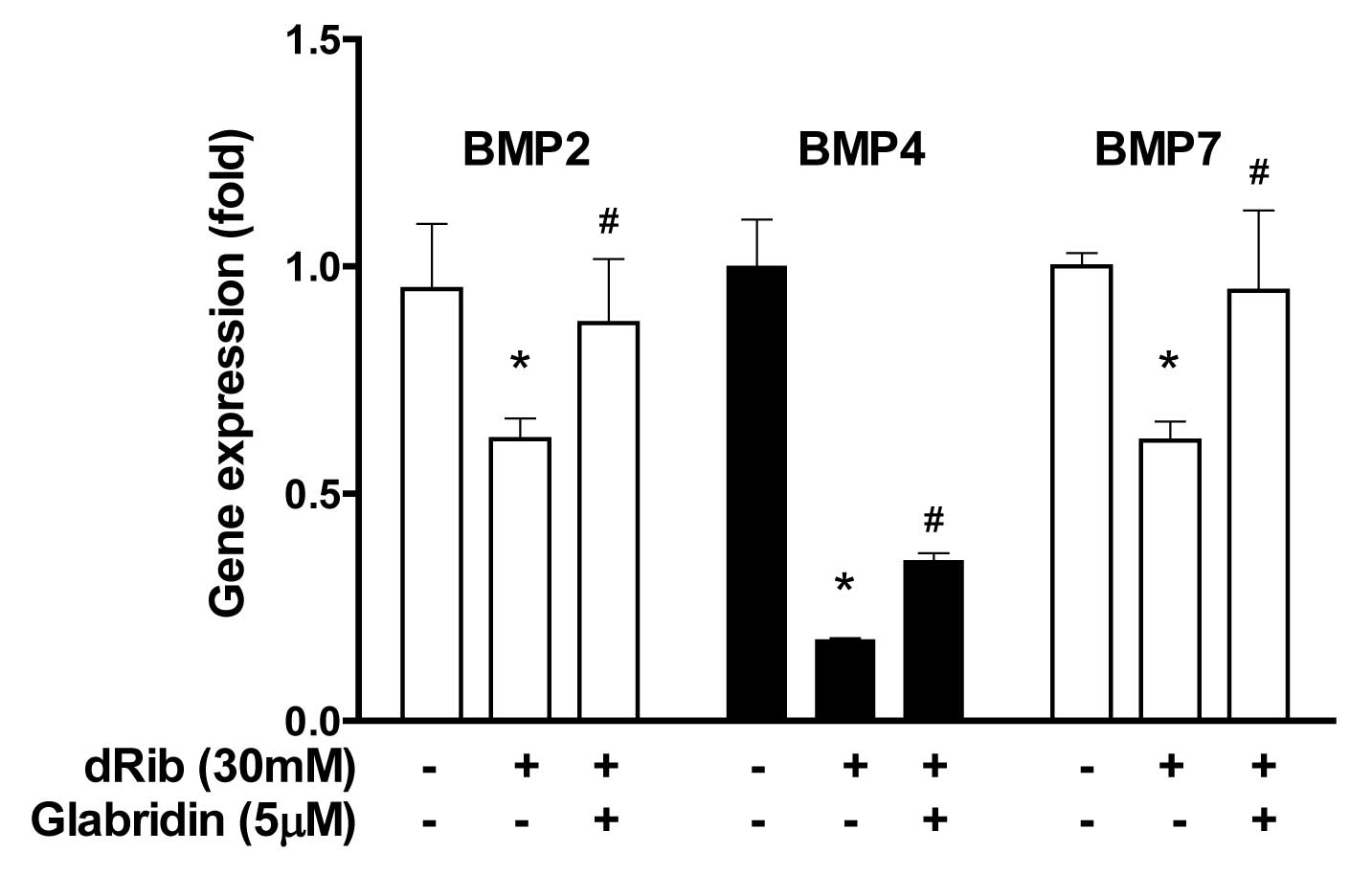
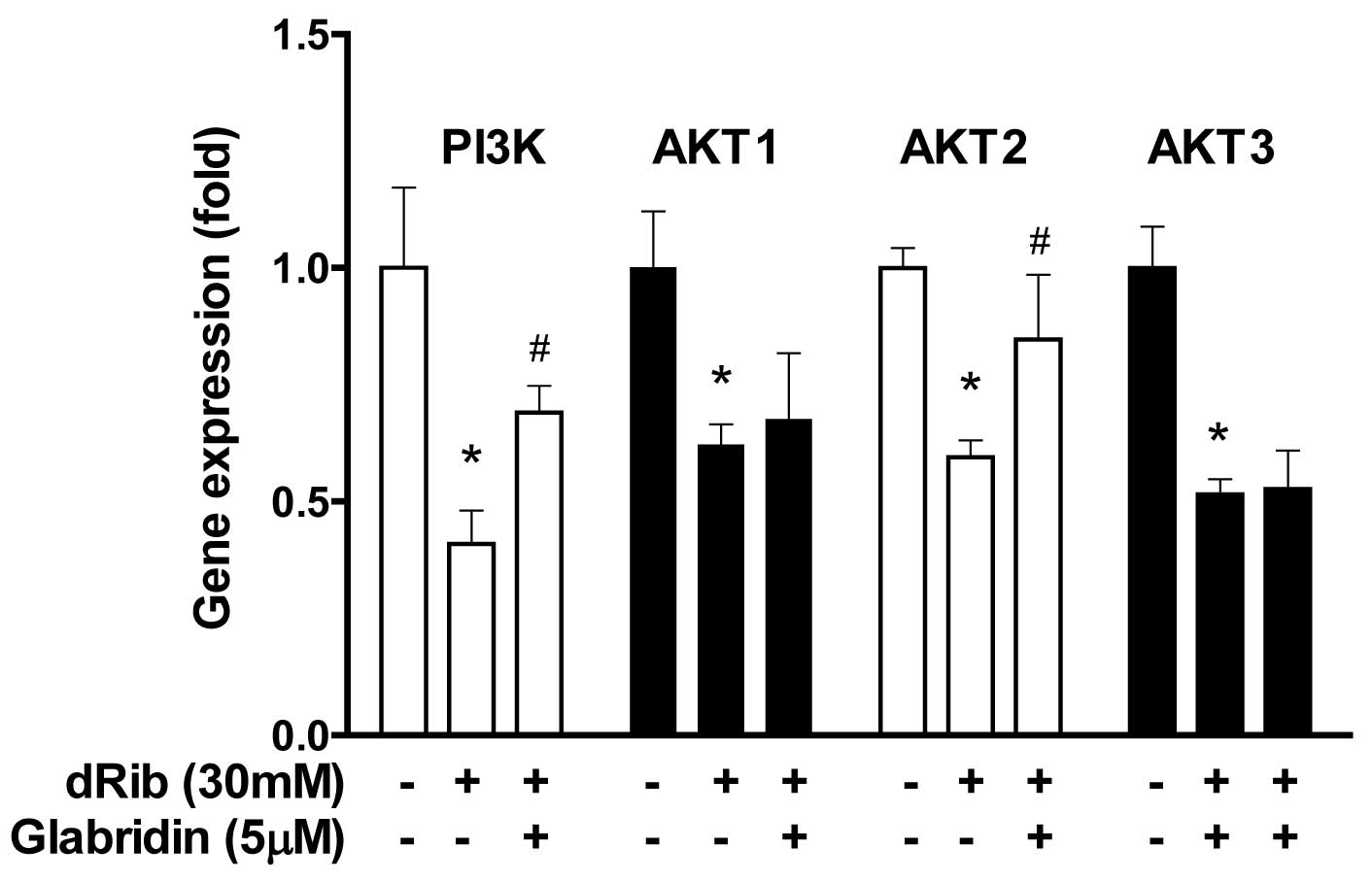
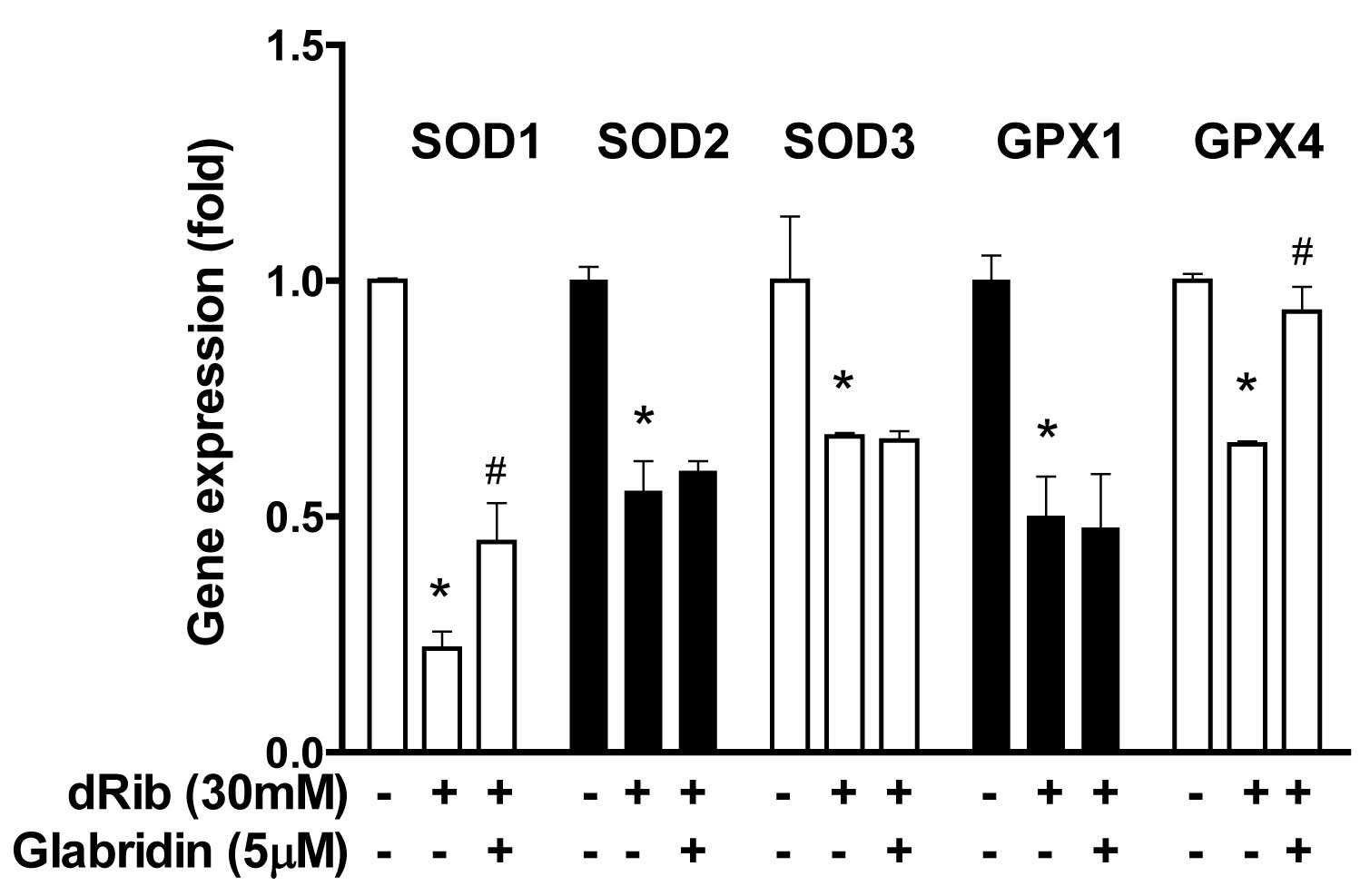
|
1
|
Robertson RP, Harmon J, Tran PO, Tanaka Y
and Takahashi H: Glucose toxicity in beta-cells: type 2 diabetes,
good radicals gone bad, and the glutathione connection. Diabetes.
52:581–587. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Robertson RP: Chronic oxidative stress as
a central mechanism for glucose toxicity in pancreatic islet beta
cells in diabetes. J Biol Chem. 279:42351–42354. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
López-Ibarra PJ, Pastor MM,
Escobar-Jiménez F, Pardo MD, González AG, Luna JD, Requena ME and
Diosdado MA: Bone mineral density at time of clinical diagnosis of
adult-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus. Endocr Pract. 7:346–351.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tuominen JT, Impivaara O, Puukka P and
Ronnemaa T: Bone mineral density in patients with type 1 and type 2
diabetes. Diabetes Care. 22:1196–1200. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Herskind AM, Christensen K,
Nørgaard-Andersen K and Andersen JF: Diabetes mellitus and healing
of closed fractures. Diabetes Metab. 18:63–64. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bai XC, Lu D, Bai J, Zheng H, Ke ZY, Li XM
and Luo SQ: Oxidative stress inhibits osteoblastic differentiation
of bone cells by ERK and NF-kappaB. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
314:197–207. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fatokun AA, Stone TW and Smith RA:
Hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in MC3T3-E1 cells: the
effects of glutamate and protection by purines. Bone. 39:542–551.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Seeman E: Reduced bone formation and
increased bone resorption: rational targets for the treatment of
osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 14(Suppl 3): S2–S8. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Thornalley P, Wolff S, Crabbe J and Stern
A: The autoxidation of glyceraldehyde and other simple
monosaccharides under physiological conditions catalysed by buffer
ions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 797:276–287. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kaneto H, Fujii J, Myint T, Miyazawa N,
Islam KN, Kawasaki Y, Suzuki K, Nakamura M, Tatsumi H, Yamasaki Y
and Taniguchi N: Reducing sugars trigger oxidative modification and
apoptosis in pancreatic beta-cells by provoking oxidative stress
through the glycation reaction. Biochem J. 320:855–863.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bunn HF and Higgins PJ: Reaction of
monosaccharides with proteins: possible evolutionary significance.
Science. 213:222–224. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Koh G, Suh KS, Chon S, Oh S, Woo JT, Kim
SW, Kim JW and Kim YS: Elevated cAMP level attenuates
2-deoxy-d-ribose-induced oxidative damage in pancreatic beta-cells.
Arch Biochem Biophys. 438:70–79. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Koh G, Lee DH and Woo JT: 2-Deoxy-D-ribose
induces cellular damage by increasing oxidative stress and protein
glycation in a pancreatic beta-cell line. Metabolism. 59:325–332.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee YJ, Suh KS, Choi MC, Chon S, Oh S, Woo
JT, Kim SW, Kim JW and Kim YS: Kaempferol protects HIT-T15
pancreatic beta cells from 2-deoxy-D-ribose-induced oxidative
damage. Phytother Res. 24:419–423. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Suh KS, Oh S, Woo JT, Kim SW, Kim JW, Kim
YS and Chon S: Apigenin attenuates 2-deoxy-D-ribose-induced
oxidative cell damage in HIT-T15 pancreatic β-cells. Biol Pharm
Bull. 35:121–126. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Choi EM and Kim YH: Hesperetin attenuates
the highly reducing sugar-triggered inhibition of osteoblast
differentiation. Cell Biol Toxicol. 24:225–231. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee KH and Choi EM: Myricetin, a naturally
occurring flavonoid, prevents 2-deoxy-D-ribose induced dysfunction
and oxidative damage in osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. Eur J
Pharmacol. 591:1–6. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Suh KS, Choi EM, Kwon M, Chon S, Oh S, Woo
JT, Kim SW, Kim JW and Kim YS: Kaempferol attenuates
2-deoxy-d-ribose-induced oxidative cell damage in MC3T3-E1
osteoblastic cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 32:746–749. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chin YW, Jung HA, Liu Y, Su BN, Castoro
JA, Keller WJ, Pereira MA and Kinghorn AD: Anti-oxidant
constituents of the roots and stolons of licorice (Glycyrrhiza
glabra). J Agric Food Chem. 55:4691–4697. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fukai T, Sakagami H, Toguchi M, Takayama
F, Iwakura I, Atsumi T, Ueha T, Nakashima H and Nomura T: Cytotoxic
activity of low molecular weight polyphenols against human oral
tumor cell lines. Anticancer Res. 20:2525–2536. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fukai T, Marumo A, Kaitou K, Kanda T,
Terada S and Nomura T: Anti-Helicobacter pylori flavonoids from
licorice extract. Life Sci. 71:1449–1463. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Haraguchi H, Yoshida N, Ishikawa H, Tamura
Y, Mizutani K and Kinoshita T: Protection of mitochondrial
functions against oxidative stresses by isoflavans from
Glycyrrhiza glabra. J Pharm Pharmacol. 52:219–223. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Choi EM: The licorice root derived
isoflavan glabridin increases the function of osteoblastic MC3T3-E1
cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 70:363–368. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Choi EM: Glabridin protects osteoblastic
MC3T3-E1 cells against antimycin A induced cytotoxicity. Chem Biol
Interact. 193:71–78. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kim HS, Suh KS, Sul D, Kim BJ, Lee SK and
Jung WW: The inhibitory effect and the molecular mechanism of
glabridin on RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cells.
Int J Mol Med. 29:169–177. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kanno S, Anuradha CD and Hirano S:
Localization of zinc after in vitro mineralization in osteoblastic
cells. Biol Trace Elem Res. 83:39–47. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Suh KS, Chon S, Oh S, Kim SW, Kim JW, Kim
YS and Woo JT: Prooxidative effects of green tea polyphenol
(−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate on the HIT-T15 pancreatic beta cell
line. Cell Biol Toxicol. 26:189–199. 2010.
|
|
28
|
Balint E, Szabo P, Marshall CF and Sprague
SM: Glucose-induced inhibition of in vitro bone mineralization.
Bone. 28:21–28. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Terada M, Inaba M, Yano Y, Hasuma T,
Nishizawa Y, Morii H and Otani S: Growth-inhibitory effect of a
high glucose concentration on osteoblast-like cells. Bone.
22:17–23. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Szilágyi G, Simona L, Koska P, Telek G and
Nagy Z: Visualization of mitochondrial membrane potential and
reactive oxygen species via double staining. Neurosci Lett.
399:206–209. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Salido M, Gonzalez JL and Vilches J: Loss
of mitochondrial membrane potential is inhibited by bombesin in
etoposide-induced apoptosis in PC-3 prostate carcinoma cells. Mol
Cancer Ther. 6:1292–1299. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sudo H, Kodama HA, Amagai Y, Yamamoto S
and Kasai S: In vitro differentiation and calcification in a new
clonal osteogenic cell line derived from newborn mouse calvaria. J
Cell Biol. 96:191–198. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bellows CG, Aubin JE and Heersche JN:
Initiation and progression of mineralization of bone nodules formed
in vitro: the role of alkaline phosphatase and organic phosphate.
Bone Miner. 14:27–40. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Domon S, Shimokawa H, Yamaguchi S and Soma
K: Temporal and spatial mRNA expression of bone sialoprotein and
type I collagen during rodent tooth movement. Eur J Orthod.
23:339–348. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen Y, Bal BS and Gorski JP: Calcium and
collagen binding properties of osteopontin, bone sialoprotein, and
bone acidic glycoprotein-75 from bone. J Biol Chem.
267:24871–24878. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Khosla S: Minireview: the OPG/RANKL/RANK
system. Endocrinology. 142:5050–5055. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Price PA and Nishimoto SK:
Radioimmunoassay for the vitamin K-dependent protein of bone and
its discovery in plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 77:2234–2238.
1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Takuwa Y, Ohse C, Wang EA, Wozney JM and
Yamashita K: Bone morphogenetic protein-2 stimulates alkaline
phosphatase activity and collagen synthesis in cultured
osteoblastic cells, MC3T3-E1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
174:96–101. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nakase T, Takaoka K, Masuhara K, Shimizu
K, Yoshikawa H and Ochi T: Interleukin-1β enhances and tumor
necrosis factor-α inhibits bone morphogenetic protein-2-induced
alkaline phosphatase activity in MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells. Bone.
21:17–21. 1997.
|
|
40
|
Vivanco I and Sawyers CL: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:489–501. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yao R and Cooper GM: Requirement for
phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase in the prevention of apoptosis by
nerve growth factor. Science. 267:2003–2006. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Franke TF, Kaplan DR and Cantley LC: PI3K:
downstream AKTion blocks apoptosis. Cell. 88:435–437. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Choi EM: Deoxyactein isolated from
Cimicifuga racemosa protects osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells
against antimycin A-induced cytotoxicity. J Appl Toxicol. Dec
19–2011.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : 2011.
|
|
44
|
Choi EM: Honokiol protects osteoblastic
MC3T3-E1 cells against antimycin A-induced cytotoxicity. Inflamm
Res. 60:1005–1012. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Choi EM and Lee YS: Protective effect of
apocynin on antimycin A-induced cell damage in osteoblastic
MC3T3-E1 cells. J Appl Toxicol. May 2–2011.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar : 2011.
|
|
46
|
Zelko IN, Mariani TJ and Folz RJ:
Superoxide dismutase multigene family: a comparison of the CuZn-SOD
(SOD1), Mn-SOD (SOD2), and EC-SOD (SOD3) gene structures,
evolution, and expression. Free Radic Biol Med. 33:337–349. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Braun KF, Ehnert S, Freude T, Egaña JT,
Schenck TL, Buchholz A, Schmitt A, Siebenlist S, Schyschka L,
Neumaier M, Stöckle U and Nussler AK: Quercetin protects primary
human osteoblasts exposed to cigarette smoke through activation of
the antioxidative enzymes HO-1 and SOD-1. Sci World J.
11:2348–2357. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Sun L, Zhang J, Lu X, Zhang L and Zhang Y:
Evaluation to the antioxidant activity of total flavonoids extract
from persimmon (Diospyros kaki L.) leaves. Food Chem
Toxicol. 49:2689–2696. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yin H, Shi ZG, Yu YS, Hu J, Wang R, Luan
ZP and Guo DH: Protection against osteoporosis by statins is linked
to a reduction of oxidative stress and restoration of nitric oxide
formation in aged and ovariectomized rats. Eur J Pharmacol.
674:200–206. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Nojiri H, Saita Y, Morikawa D, Kobayashi
K, Tsuda C, Miyazaki T, Saito M, Marumo K, Yonezawa I, Kaneko K,
Shirasawa T and Shimizu T: Cytoplasmic superoxide causes bone
fragility owing to low-turnover osteoporosis and impaired collagen
cross-linking. J Bone Miner Res. 26:2682–2694. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Tsai YM, Yang CJ, Hsu YL, Wu LY, Tsai YC,
Hung JY, Lien CT, Huang MS and Kuo PL: Glabridin inhibits
migration, invasion, and angiogenesis of human non-small cell lung
cancer A549 cells by inhibiting the FAK/rho signaling pathway.
Integr Cancer Ther. 10:341–349. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hsu YL, Wu LY, Hou MF, Tsai EM, Lee JN,
Liang HL, Jong YJ, Hung CH and Kuo PL: Glabridin, an isoflavan from
licorice root, inhibits migration, invasion and angiogenesis of
MDA-MB-231 human breast adenocarcinoma cells by inhibiting focal
adhesion kinase/Rho signaling pathway. Mol Nutr Food Res.
55:318–327. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|