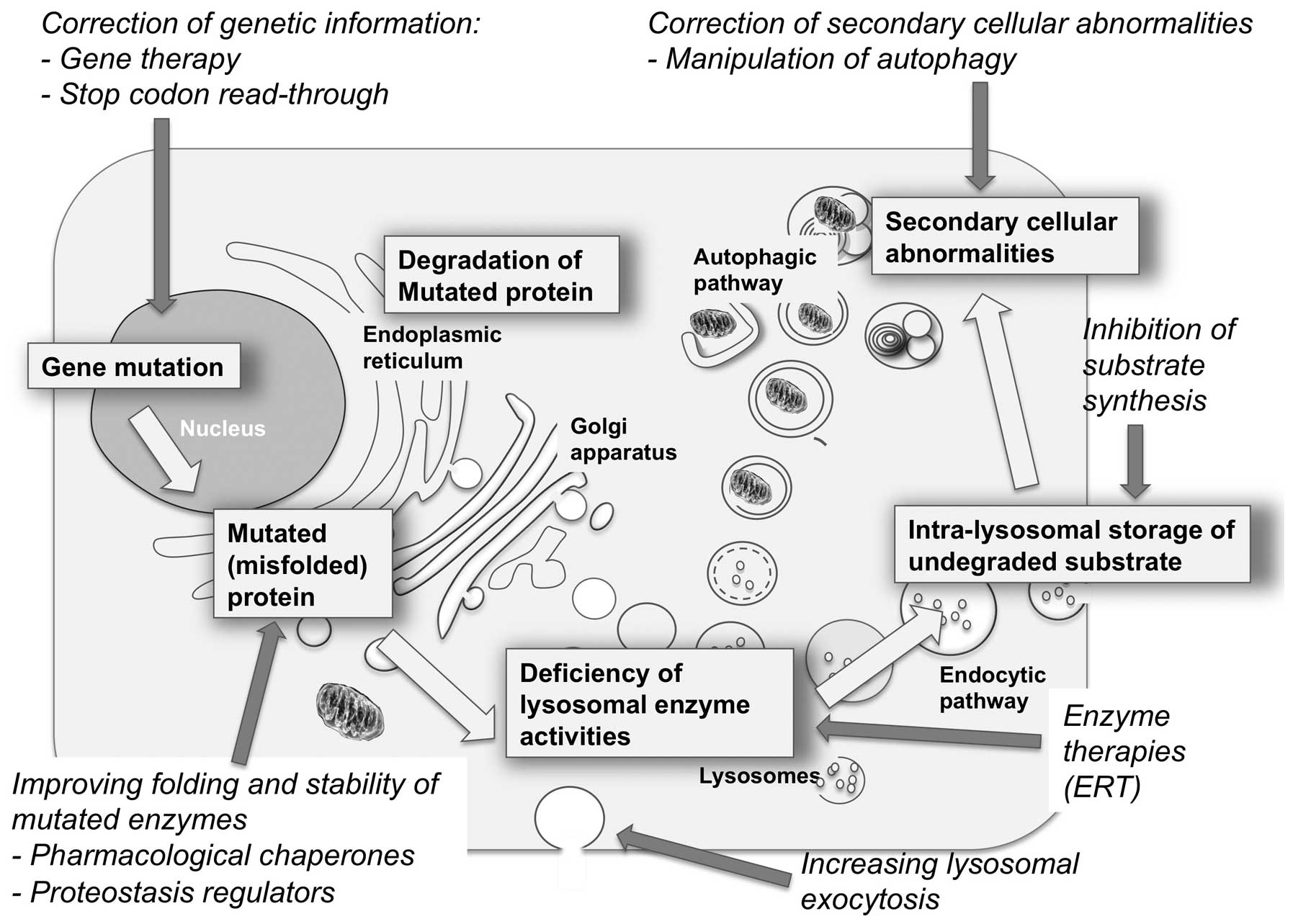
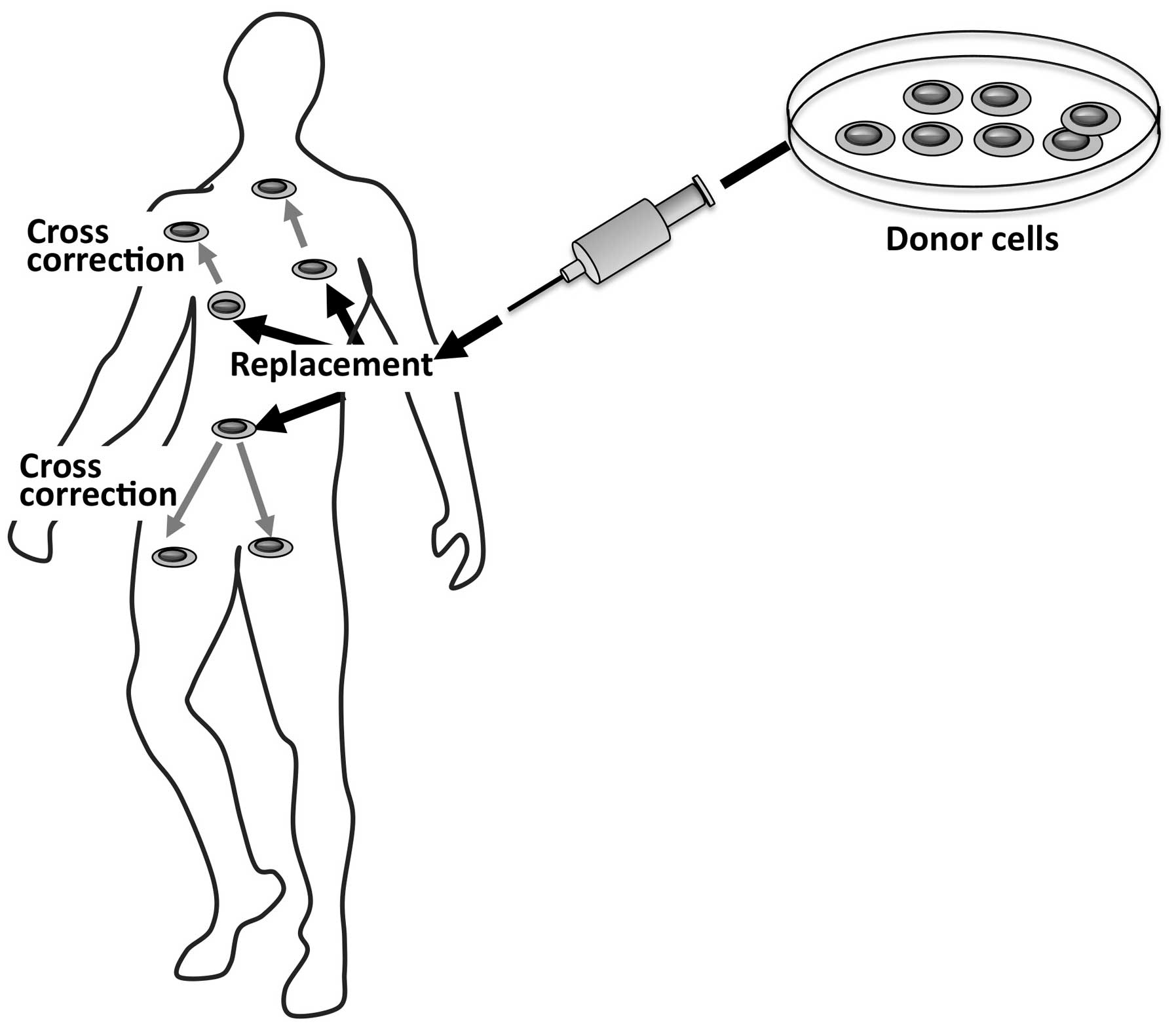
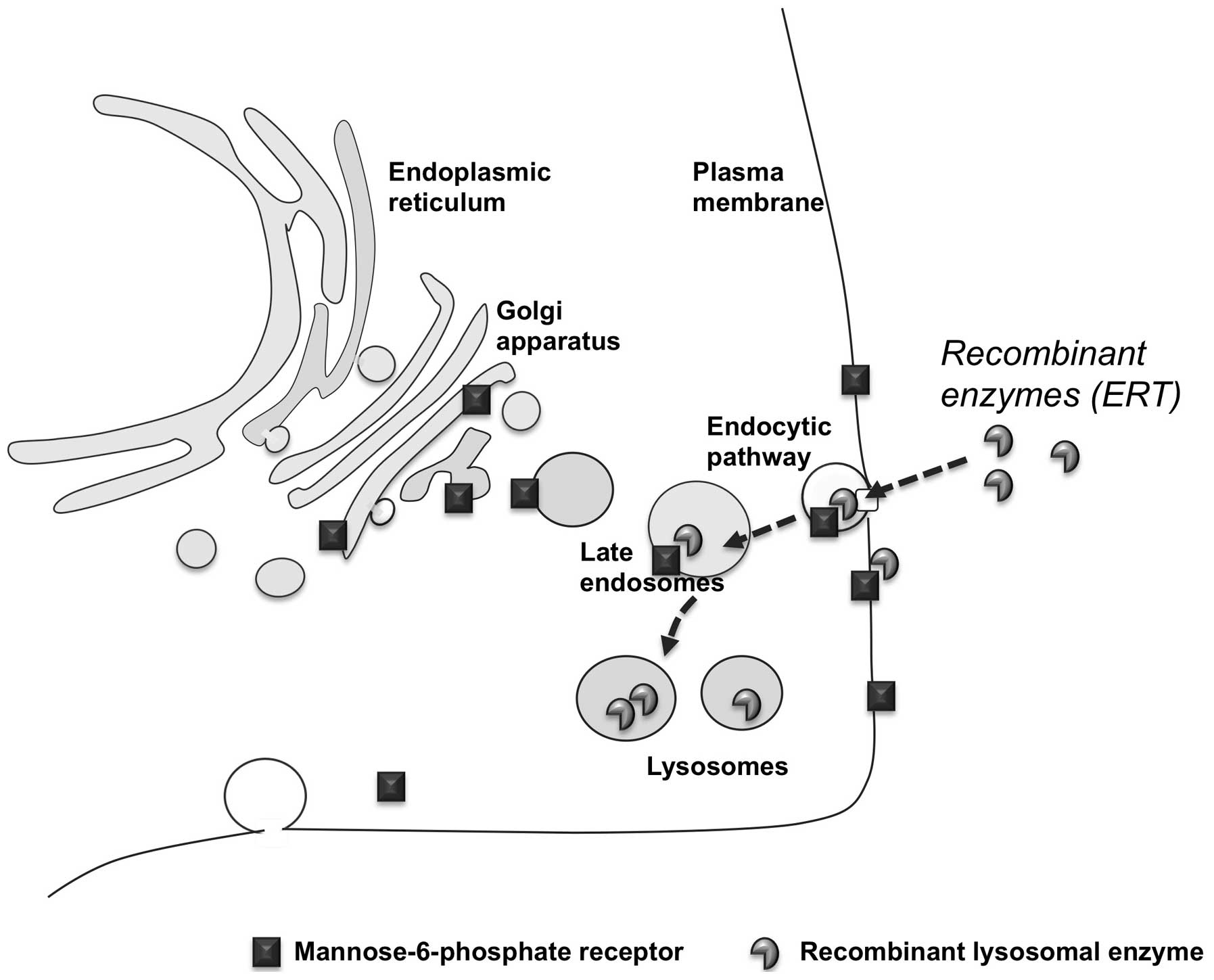
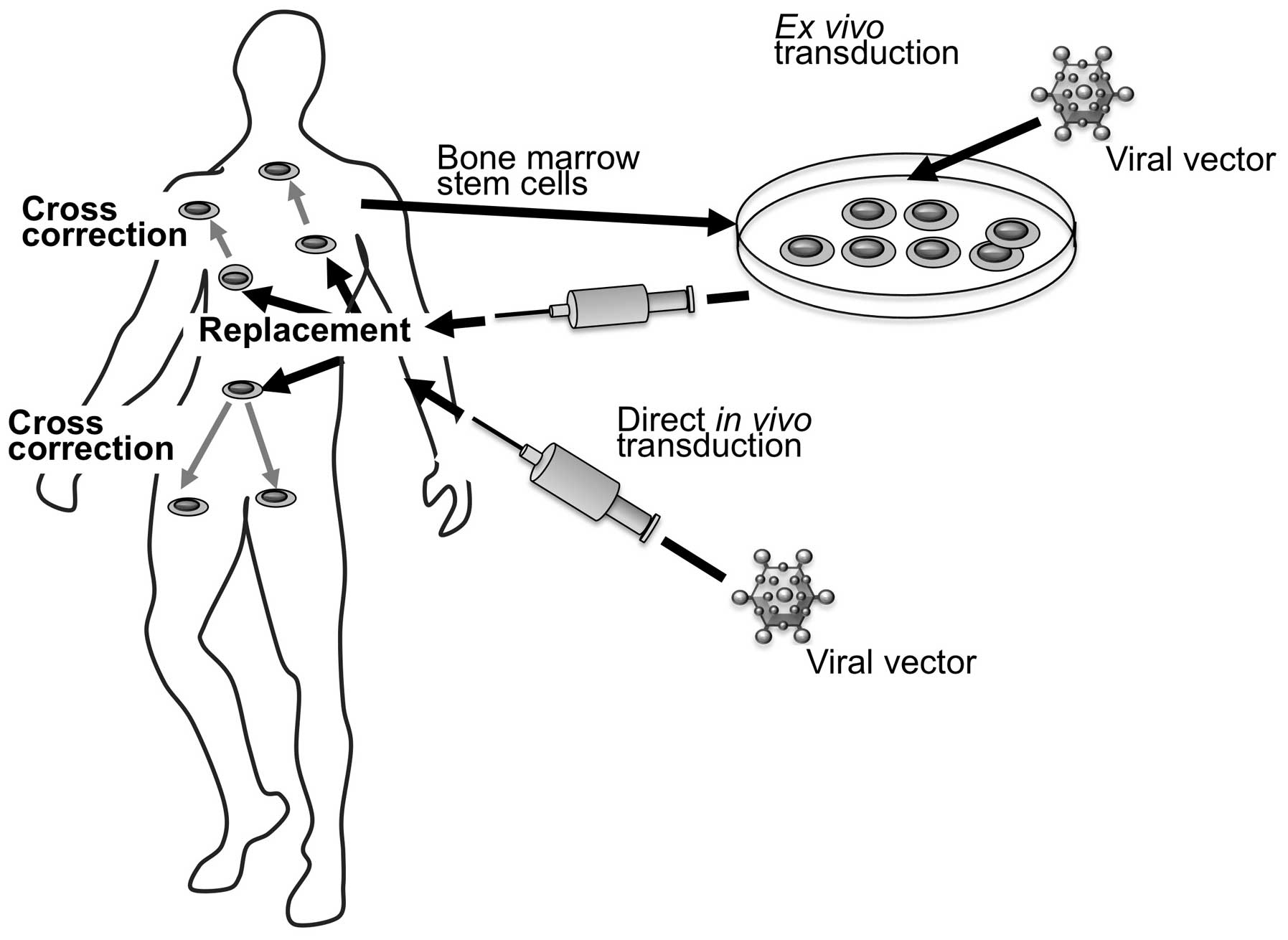
|
1
|
Futerman AH and van Meer G: The cell
biology of lysosomal storage disorders. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
5:554–565. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fuller M, Meikle PJ and Hopwood JJ:
Epidemiology of lysosomal storage diseases: an overview. Fabry
Disease: Perspectives from 5 years of FOS. Mehta A, Beck M and
Sunder-Plassmann G: Oxford PharmaGenesis; Oxford: 2006, PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Beck M: New therapeutic options for
lysosomal storage disorders: enzyme replacement, small molecules
and gene therapy. Hum Genet. 121:1–22. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Beutler E: Lysosomal storage diseases:
natural history and ethical and economic aspects. Mol Genet Metab.
88:208–215. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ballabio A and Gieselmann V: Lysosomal
disorders: from storage to cellular damage. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1793:684–696. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Prasad VK and Kurtzberg J: Transplant
outcomes in mucopolysaccharidoses. Semin Hematol. 47:59–69. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Valayannopoulos V and Wijburg FA: Therapy
for the mucopolysaccharidoses. Rheumatology (Oxford). 50(Suppl 5):
v49–v59. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Orchard PJ, Blazar BR, Wagner J, Charnas
L, Krivit W and Tolar J: Hematopoietic cell therapy for metabolic
disease. J Pediatr. 151:340–346. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
de Ru MH, Boelens JJ, Das AM, Jones SA,
van der Lee JH, Mahlaoui N, Mengel E, Offringa M, O’Meara A, Parini
R, Rovelli A, Sykora KW, Valayannopoulos V, Vellodi A, Wynn RF and
Wijburg FA: Enzyme replacement therapy and/or hematopoietic stem
cell transplantation at diagnosis in patients with
mucopolysaccharidosis type I: results of a European consensus
procedure. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 6:552011.
|
|
10
|
Orchard PJ and Tolar J: Transplant
outcomes in leukodystrophies. Semin Hematol. 47:70–78. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sly WS: Receptor-mediated transport of
acid hydrolases to lysosomes. Curr Top Cell Regul. 26:27–38. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Barton NW, Brady RO, Dambrosia JM, Di
Bisceglie AM, Doppelt SH, Hill SC, Mankin HJ, Murray GJ, Parker RI,
Argoff CE, et al: Replacement therapy for inherited enzyme
deficiency - macrophage-targeted glucocerebrosidase for Gaucher’s
disease. N Engl J Med. 324:1464–1470. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Barton NW, Furbish FS, Murray GJ, Garfield
M and Brady RO: Therapeutic response to intravenous infusions of
glucocerebrosidase in a patient with Gaucher disease. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 87:1913–1916. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mehta A, Beck M, Elliott P, Giugliani R,
Linhart A, Sunder-Plassmann G, Schiffmann R, Barbey F, Ries M and
Clarke JT; Fabry Outcome Survey investigators. Enzyme replacement
therapy with agalsidase alfa in patients with Fabry’s disease: an
analysis of registry data. Lancet. 374:1986–1996. 2009.
|
|
15
|
Lidove O, West ML, Pintos-Morell G, Reisin
R, Nicholls K, Figuera LE, Parini R, Carvalho LR, Kampmann C,
Pastores GM and Mehta A: Effects of enzyme replacement therapy in
Fabry disease - a comprehensive review of the medical literature.
Genet Med. 12:668–679. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Feriozzi S, Torras J, Cybulla M, Nicholls
K, Sunder-Plassmann G and West M; FOS Investigators. The
effectiveness of long-term agalsidase alfa therapy in the treatment
of Fabry nephropathy. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 7:60–69. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
van der Ploeg AT and Reuser AJ: Pompe’s
disease. Lancet. 372:1342–1353. 2008.
|
|
18
|
Strothotte S, Strigl-Pill N, Grunert B,
Kornblum C, Eger K, Wessig C, Deschauer M, Breunig F, Glocker FX,
Vielhaber S, Brejova A, Hilz M, Reiners K, Müller-Felber W, Mengel
E, Spranger M and Schoser B: Enzyme replacement therapy with
alglucosidase alfa in 44 patients with late-onset glycogen storage
disease type 2: 12-month results of an observational clinical
trial. J Neurol. 257:91–97. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
van der Ploeg AT, Clemens PR, Corzo D,
Escolar DM, Florence J, Groeneveld GJ, Herson S, Kishnani PS,
Laforet P, Lake SL, Lange DJ, Leshner RT, Mayhew JE, Morgan C,
Nozaki K, Park DJ, Pestronk A, Rosenbloom B, Skrinar A, van Capelle
CI, van der Beek NA, Wasserstein M and Zivkovic SA: A randomized
study of alglucosidase alfa in late-onset Pompe’s disease. N Engl J
Med. 362:1396–1406. 2010.
|
|
20
|
Parenti G and Andria G: Pompe disease:
from new views on pathophysiology to innovative therapeutic
strategies. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 12:902–915. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Anson DS, McIntyre C and Byers S:
Therapies for neurological disease in the mucopolysaccharidoses.
Curr Gene Ther. 11:132–143. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Begley DJ, Pontikis CC and Scarpa M:
Lysosomal storage diseases and the blood-brain barrier. Curr Pharm
Des. 14:1566–1580. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Grubb JH, Vogler C, Levy B, Galvin N, Tan
Y and Sly WS: Chemically modified beta-glucuronidase crosses
blood-brain barrier and clears neuronal storage in murine
mucopolysaccharidosis VII. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:2616–2621.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Osborn MJ, McElmurry RT, Peacock B, Tolar
J and Blazar BR: Targeting of the CNS in MPS-IH using a nonviral
transferrin-alpha-L-iduronidase fusion gene product. Mol Ther.
16:1459–1466. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Munoz-Rojas MV, Vieira T, Costa R,
Fagondes S, John A, Jardim LB, Vedolin LM, Raymundo M, Dickson PI,
Kakkis E and Giugliani R: Intrathecal enzyme replacement therapy in
a patient with mucopolysaccharidosis type I and symptomatic spinal
cord compression. Am J Med Genet A. 146A:2538–2544. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhu Y, Jiang JL, Gumlaw NK, Zhang J,
Bercury SD, Ziegler RJ, Lee K, Kudo M, Canfield WM, Edmunds T,
Jiang C, Mattaliano RJ and Cheng SH: Glycoengineered acid
alpha-glucosidase with improved efficacy at correcting the
metabolic aberrations and motor function deficits in a mouse model
of Pompe disease. Mol Ther. 17:954–963. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zimran A, Brill-Almon E, Chertkoff R,
Petakov M, Blanco-Favela F, Muñoz ET, Solorio-Meza SE, Amato D,
Duran G, Giona F, Heitner R, Rosenbaum H, Giraldo P, Mehta A, Park
G, Phillips M, Elstein D, Altarescu G, Szleifer M, Hashmueli S and
Aviezer D: Pivotal trial with plant cell-expressed recombinant
glucocerebrosidase, taliglucerase alfa, a novel enzyme replacement
therapy for Gaucher disease. Blood. 118:5767–5773. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Parenti G: Treating lysosomal storage
diseases with pharmacological chaperones: from concept to clinics.
EMBO Mol Med. 1:268–279. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Valenzano KJ, Khanna R, Powe AC, Boyd R,
Lee G, Flanagan JJ and Benjamin ER: Identification and
characterization of pharmacological chaperones to correct enzyme
deficiencies in lysosomal storage disorders. Assay Drug Dev
Technol. 9:213–235. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fan JQ, Ishii S, Asano N and Suzuki Y:
Accelerated transport and maturation of lysosomal
alpha-galactosidase A in Fabry lymphoblasts by an enzyme inhibitor.
Nat Med. 5:112–115. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Germain DP and Fan JQ: Pharmacological
chaperone therapy by active-site-specific chaperones in Fabry
disease: in vitro and preclinical studies. Int J Clin Pharmacol
Ther. 47(Suppl 1): S111–S117. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sawkar AR, Adamski-Werner SL, Cheng WC,
Wong CH, Beutler E, Zimmer KP and Kelly JW: Gaucher
disease-associated glucocerebrosidases show mutation-dependent
chemical chaperoning profiles. Chem Biol. 12:1235–1244. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Parenti G, Zuppaldi A, Gabriela Pittis M,
Rosaria Tuzzi M, Annunziata I, Meroni G, Porto C, Donaudy F, Rossi
B, Rossi M, Filocamo M, Donati A, Bembi B, Ballabio A and Andria G:
Pharmacological enhancement of mutated alpha-glucosidase activity
in fibroblasts from patients with Pompe disease. Mol Ther.
15:508–514. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Okumiya T, Kroos MA, Vliet LV, Takeuchi H,
Van der Ploeg AT and Reuser AJ: Chemical chaperones improve
transport and enhance stability of mutant alpha-glucosidases in
glycogen storage disease type II. Mol Genet Metab. 90:49–57. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Suzuki Y, Ichinomiya S, Kurosawa M,
Matsuda J, Ogawa S, Iida M, Kubo T, Tabe M, Itoh M, Higaki K, Nanba
E and Ohno K: Therapeutic chaperone effect of N-octyl
4-epi-β-valienamine on murine G(M1)-gangliosidosis. Mol Genet
Metab. 106:92–98. 2012.
|
|
36
|
Flanagan JJ, Rossi B, Tang K, Wu X,
Mascioli K, Donaudy F, Tuzzi MR, Fontana F, Cubellis MV, Porto C,
Benjamin E, Lockhart DJ, Valenzano KJ, Andria G, Parenti G and Do
HV: The pharmacological chaperone 1-deoxynojirimycin increases the
activity and lysosomal trafficking of multiple mutant forms of acid
alpha-glucosidase. Hum Mutat. 30:1683–1692. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Porto C, Ferrara MC, Meli M, Acampora E,
Avolio V, Rosa M, Cobucci-Ponzano B, Colombo G, Moracci M, Andria G
and Parenti G: Pharmacological enhancement of alpha-glucosidase by
the allosteric chaperone N-acetylcysteine. Mol Ther. Sep
18–2012.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Urban DJ, Zheng W, Goker-Alpan O, Jadhav
A, Lamarca ME, Inglese J, Sidransky E and Austin CP: Optimization
and validation of two miniaturized glucocerebrosidase enzyme assays
for high throughput screening. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen.
11:817–824. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Marugan JJ, Zheng W, Motabar O, Southall
N, Goldin E, Sidransky E, Aungst RA, Liu K, Sadhukhan SK and Austin
CP: Evaluation of
2-thioxo-2,3,5,6,7,8-hexahydropyrimido(4,5-d)pyrimidin-4(1H)-one
analogues as GAA activators. Eur J Med Chem. 45:1880–1897. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Porto C, Cardone M, Fontana F, Rossi B,
Tuzzi MR, Tarallo A, Barone MV, Andria G and Parenti G: The
pharmacological chaperone N-butyldeoxynojirimycin enhances enzyme
replacement therapy in Pompe disease fibroblasts. Mol Ther.
17:964–971. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Porto C, Pisani A, Rosa M, Acampora E,
Avolio V, Tuzzi MR, Visciano B, Gagliardo C, Materazzi S, la Marca
G, Andria G and Parenti G: Synergy between the pharmacological
chaperone 1-deoxygalactonojirimycin and the human recombinant
alpha-galactosidase A in cultured fibroblasts from patients with
Fabry disease. J Inherit Metab Dis. 35:513–520. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Benjamin ER, Khanna R, Schilling A,
Flanagan JJ, Pellegrino LJ, Brignol N, Lun Y, Guillen D, Ranes BE,
Frascella M, Soska R, Feng J, Dungan L, Young B, Lockhart DJ and
Valenzano KJ: Co-administration with the pharmacological chaperone
AT1001 increases recombinant human α-galactosidase A tissue uptake
and improves substrate reduction in Fabry mice. Mol Ther.
20:717–726. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Khanna R, Flanagan JJ, Feng J, Soska R,
Frascella M, Pellegrino LJ, Lun Y, Guillen D, Lockhart DJ and
Valenzano KJ: The pharmacological chaperone AT2220 increases
recombinant human acid α-glucosidase uptake and glycogen reduction
in a mouse model of pompe disease. PLoS One.
7:e407762012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mu TW, Ong DS, Wang YJ, Balch WE, Yates JR
III, Segatori L and Kelly JW: Chemical and biological approaches
synergize to ameliorate protein-folding diseases. Cell.
134:769–781. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sands MS and Davidson BL: Gene therapy for
lysosomal storage diseases. Mol Ther. 13:839–849. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cardone M: Prospects for gene therapy in
inherited neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Opin Neurol. 20:15–18.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Spampanato C, De Leonibus E, Dama P,
Gargiulo A, Fraldi A, Sorrentino NC, Russo F, Nusco E, Auricchio A,
Surace EM and Ballabio A: Efficacy of a combined intracerebral and
systemic gene delivery approach for the treatment of a severe
lysosomal storage disorder. Mol Ther. 19:860–869. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Platt FM and Jeyakumar M: Substrate
reduction therapy. Acta Paediatr (Suppl). 97:88–93. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Schiffmann R: Therapeutic approaches for
neuronopathic lysosomal storage disorders. J Inherit Metab Dis.
33:373–379. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Giraldo P, Alfonso P, Atutxa K,
Fernández-Galán MA, Barez A, Franco R, Alonso D, Martin A, Latre P
and Pocovi M: Real-world clinical experience with long-term
miglustat maintenance therapy in type 1 Gaucher disease: the ZAGAL
project. Haematologica. 94:1771–1775. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hollak CE, Hughes D, van Schaik IN,
Schwierin B and Bembi B: Miglustat (Zavesca) in type 1 Gaucher
disease: 5-year results of a post-authorisation safety surveillance
programme. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 18:770–777. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lukina E, Watman N, Arreguin EA, Dragosky
M, Iastrebner M, Rosenbaum H, Phillips M, Pastores GM, Kamath RS,
Rosenthal DI, Kaper M, Singh T, Puga AC and Peterschmitt MJ:
Improvement in hematological, visceral, and skeletal manifestations
of Gaucher disease type 1 with oral eliglustat tartrate
(Genz-112638) treatment: 2-year results of a phase 2 study. Blood.
116:4095–4098. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lachmann RH, te Vruchte D, Lloyd-Evans E,
Reinkensmeier G, Sillence DJ, Fernandez-Guillen L, Dwek RA, Butters
TD, Cox TM and Platt FM: Treatment with miglustat reverses the
lipid-trafficking defect in Niemann-Pick disease type C. Neurobiol
Dis. 16:654–658. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Patterson MC, Vecchio D, Prady H, Abel L
and Wraith JE: Miglustat for treatment of Niemann-Pick C disease: a
randomised controlled study. Lancet Neurol. 6:765–772. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wraith JE, Vecchio D, Jacklin E, Abel L,
Chadha-Boreham H, Luzy C, Giorgino R and Patterson MC: Miglustat in
adult and juvenile patients with Niemann-Pick disease type C:
long-term data from a clinical trial. Mol Genet Metab. 99:351–357.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Fecarotta S, Amitrano M, Romano A, Della
Casa R, Bruschini D, Astarita L, Parenti G and Andria G: The
videofluoroscopic swallowing study shows a sustained improvement of
dysphagia in children with Niemann-Pick disease type C after
therapy with miglustat. Am J Med Genet A. 155A:540–547. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Piotrowska E, Jakóbkiewicz-Banecka J,
Barańska S, Tylki-Szymańska A, Czartoryska B, Wegrzyn A and Wegrzyn
G: Genistein-mediated inhibition of glycosaminoglycan synthesis as
a basis for gene expression-targeted isoflavone therapy for
mucopolysaccharidoses. Eur J Hum Genet. 14:846–852. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Roberts AL, Thomas BJ, Wilkinson AS,
Fletcher JM and Byers S: Inhibition of glycosaminoglycan synthesis
using rhodamine B in a mouse model of mucopolysaccharidosis type
IIIA. Pediatr Res. 60:309–314. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Roberts AL, Fletcher JM, Moore L and Byers
S: Trans-generational exposure to low levels of rhodamine B does
not adversely affect litter size or liver function in murine
mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIA. Mol Genet Metab. 101:208–213.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Malinowska M, Wilkinson FL, Langford-Smith
KJ, Langford-Smith A, Brown JR, Crawford BE, Vanier MT, Grynkiewicz
G, Wynn RF, Wraith JE, Wegrzyn G and Bigger BW: Genistein improves
neuropathology and corrects behaviour in a mouse model of
neurodegenerative metabolic disease. PLoS One. 5:e141922010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Piotrowska E, Jakobkiewicz-Banecka J,
Maryniak A, Tylki-Szymanska A, Puk E, Liberek A, Wegrzyn A,
Czartoryska B, Slominska-Wojewodzka M and Wegrzyn G: Two-year
follow-up of Sanfilippo disease patients treated with a
genistein-rich isoflavone extract: assessment of effects on
cognitive functions and general status of patients. Med Sci Monit.
17:196–202. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Ashe KM, Bangari D, Li L, Cabrera-Salazar
MA, Bercury SD, Nietupski JB, Cooper CG, Aerts JM, Lee ER, Copeland
DP, Cheng SH, Scheule RK and Marshall J: Iminosugar-based
inhibitors of glucosylceramide synthase increase brain
glycosphingolipids and survival in a mouse model of Sandhoff
disease. PLoS One. 6:e217582011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Marshall J, Ashe KM, Bangari D, McEachern
K, Chuang WL, Pacheco J, Copeland DP, Desnick RJ, Shayman JA,
Scheule RK and Cheng SH: Substrate reduction augments the efficacy
of enzyme therapy in a mouse model of Fabry disease. PLoS One.
5:e150332010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Douillard-Guilloux G, Raben N, Takikita S,
Batista L, Caillaud C and Richard E: Modulation of glycogen
synthesis by RNA interference: towards a new therapeutic approach
for glycogenosis type II. Hum Mol Genet. 17:3876–3886. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Douillard-Guilloux G, Raben N, Takikita S,
Ferry A, Vignaud A, Guillet-Deniau I, Favier M, Thurberg BL, Roach
PJ, Caillaud C and Richard E: Restoration of muscle functionality
by genetic suppression of glycogen synthesis in a murine model of
Pompe disease. Hum Mol Genet. 19:684–696. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Raben N, Schreiner C, Baum R, Takikita S,
Xu S, Xie T, Myerowitz R, Komatsu M, Van der Meulen JH, Nagaraju K,
Ralston E and Plotz PH: Suppression of autophagy permits successful
enzyme replacement therapy in a lysosomal storage disorder - murine
Pompe disease. Autophagy. 6:1078–1089. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Jones AM and Helm JM: Emerging treatments
in cystic fibrosis. Drugs. 69:1903–1910. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Nelson SF, Crosbie RH, Miceli MC and
Spencer MJ: Emerging genetic therapies to treat Duchenne muscular
dystrophy. Curr Opin Neurol. 22:532–538. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Sermet-Gaudelus I, De Boeck K, Casimir GJ,
Vermeulen F, Leal T, Mogenet A, Roussel D, Fritsch J, Hanssens L,
Hirawat S, Miller NL, Constantine S, Reha A, Ajayi T, Elfring GL
and Miller LL: Ataluren (PTC124) induces CFTR protein expression
and activity in children with nonsense mutation cystic fibrosis. Am
J Respir Crit Care Med. 182:1262–1272. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Finkel RS: Read-through strategies for
suppression of nonsense mutations in Duchenne/Becker muscular
dystrophy: aminoglycosides and ataluren (PTC124). J Child Neurol.
25:1158–1164. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Sarkar C, Zhang Z and Mukherjee AB: Stop
codon read-through with PTC124 induces palmitoyl-protein
thioesterase-1 activity, reduces thioester load and suppresses
apoptosis in cultured cells from INCL patients. Mol Genet Metab.
104:338–345. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Medina DL, Fraldi A, Bouche V, Annunziata
F, Mansueto G, Spampanato C, Puri C, Pignata A, Martina JA,
Sardiello M, Palmieri M, Polishchuk R, Puertollano R and Ballabio
A: Transcriptional activation of lysosomal exocytosis promotes
cellular clearance. Dev Cell. 21:421–430. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Sardiello M, Palmieri M, di Ronza A,
Medina DL, Valenza M, Gennarino VA, Di Malta C, Donaudy F, Embrione
V, Polishchuk RS, Banfi S, Parenti G, Cattaneo E and Ballabio A: A
gene network regulating lysosomal biogenesis and function. Science.
325:473–477. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|