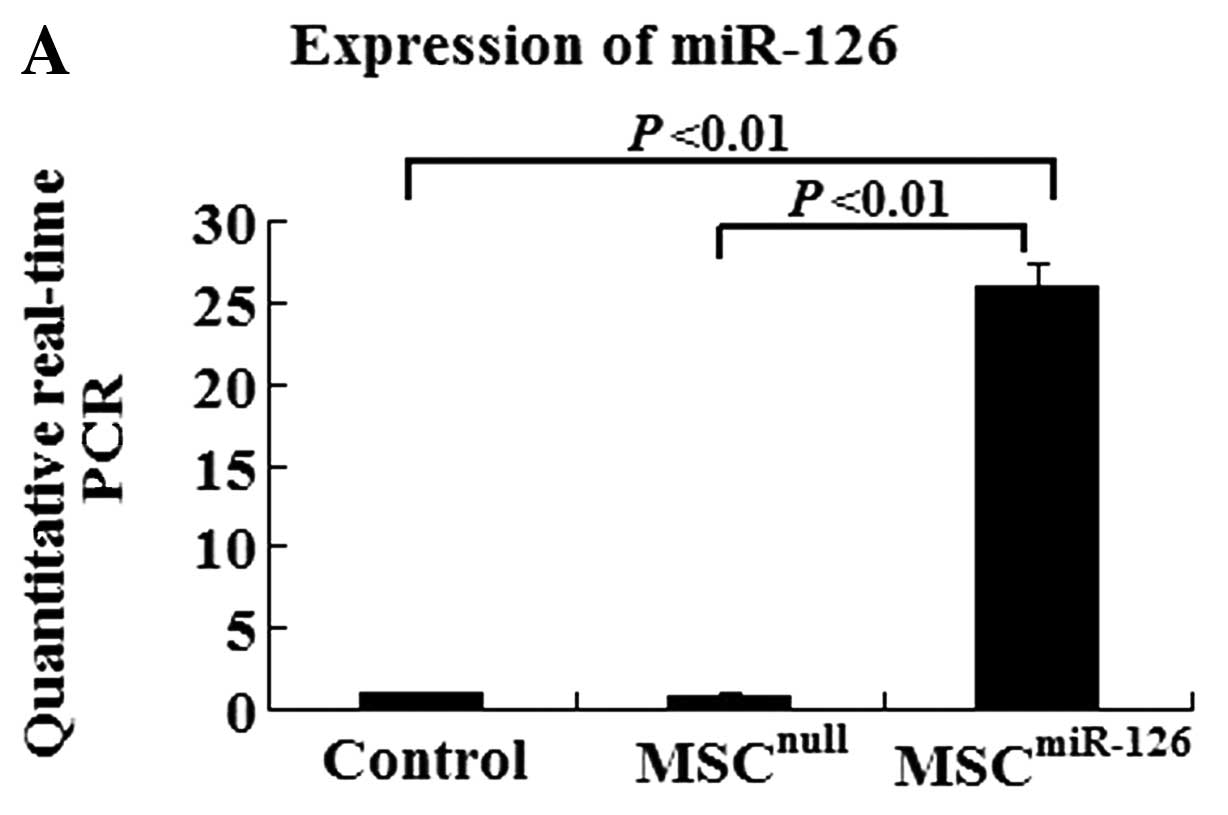
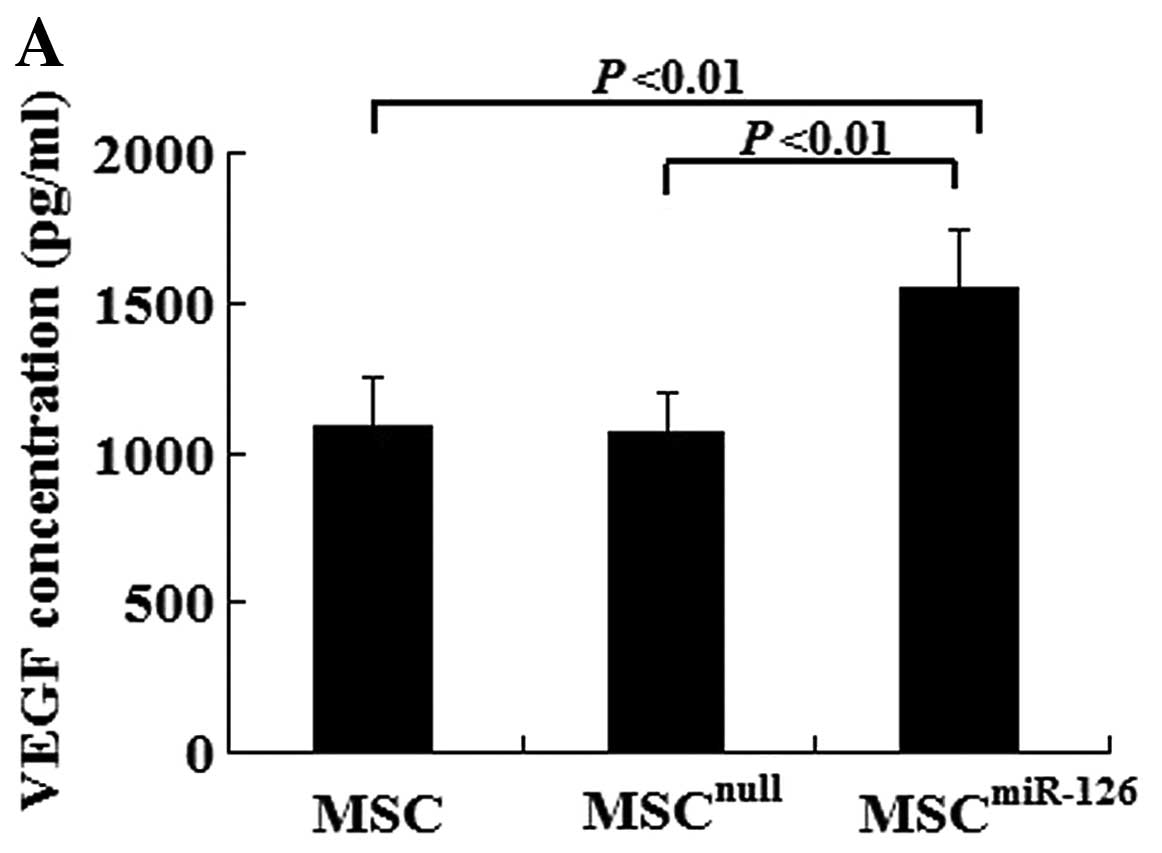
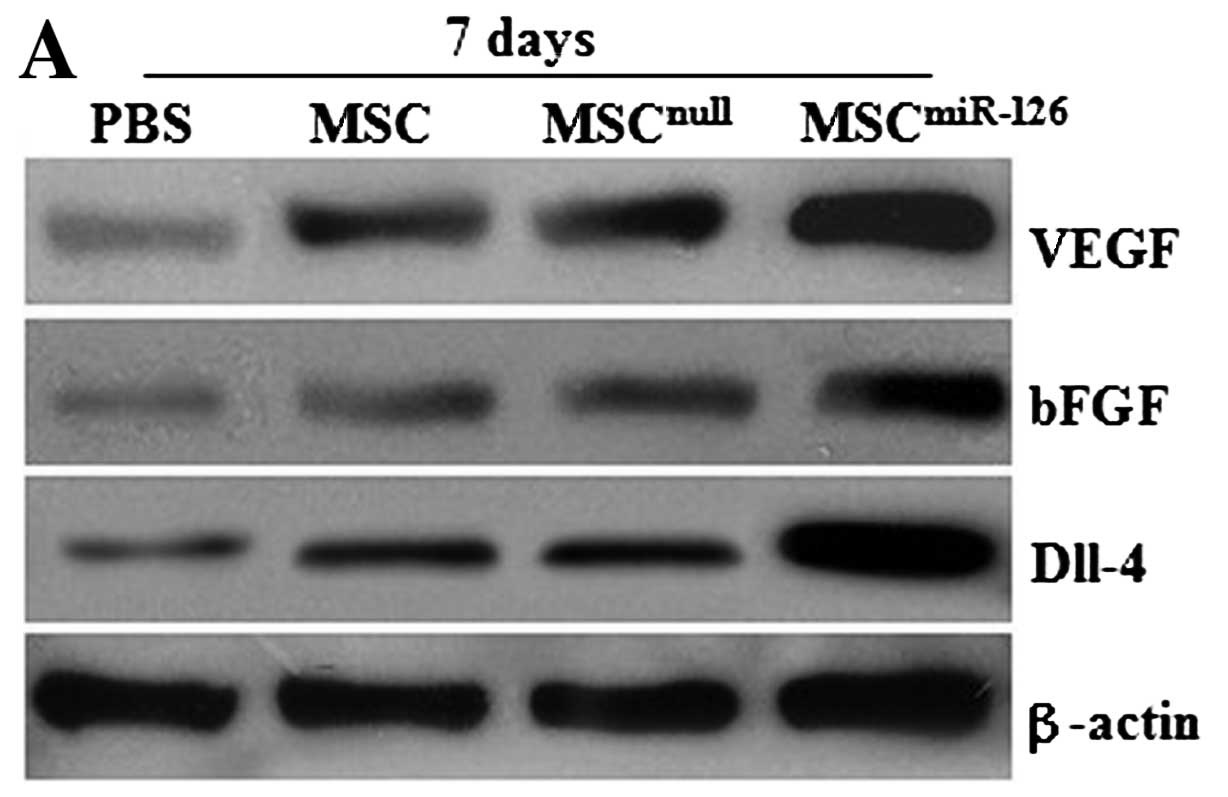
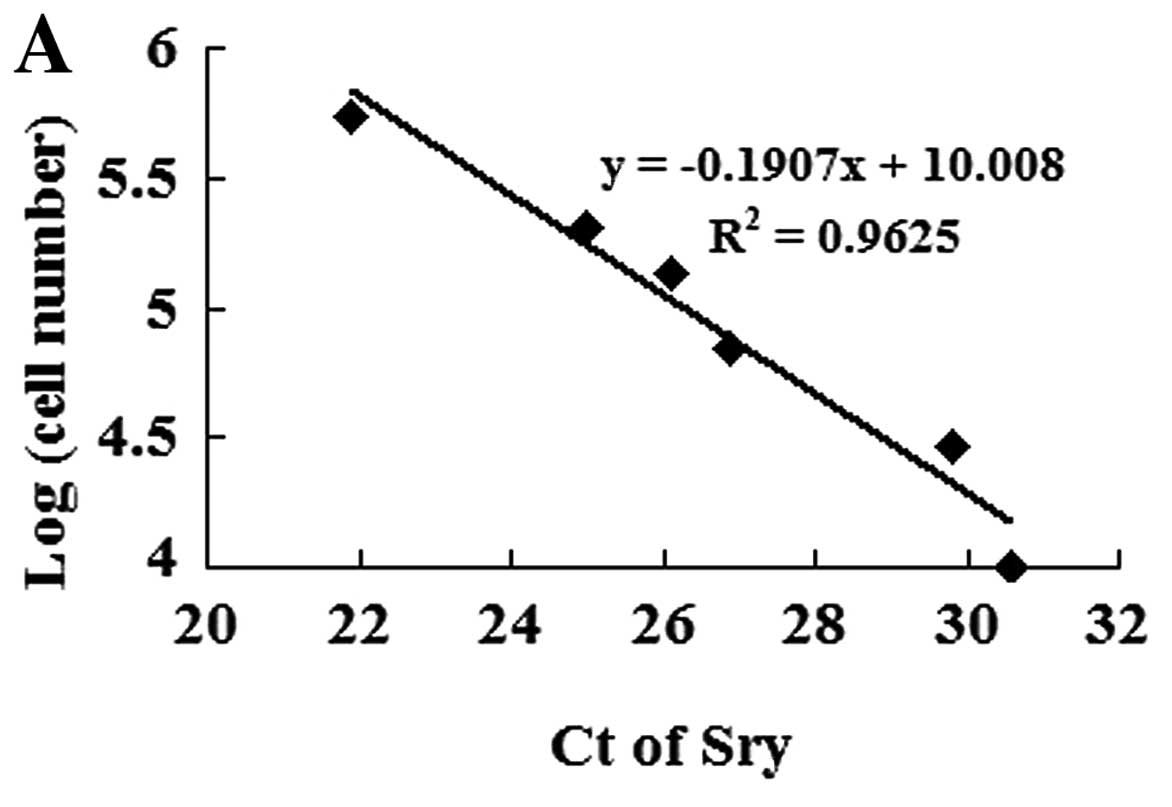
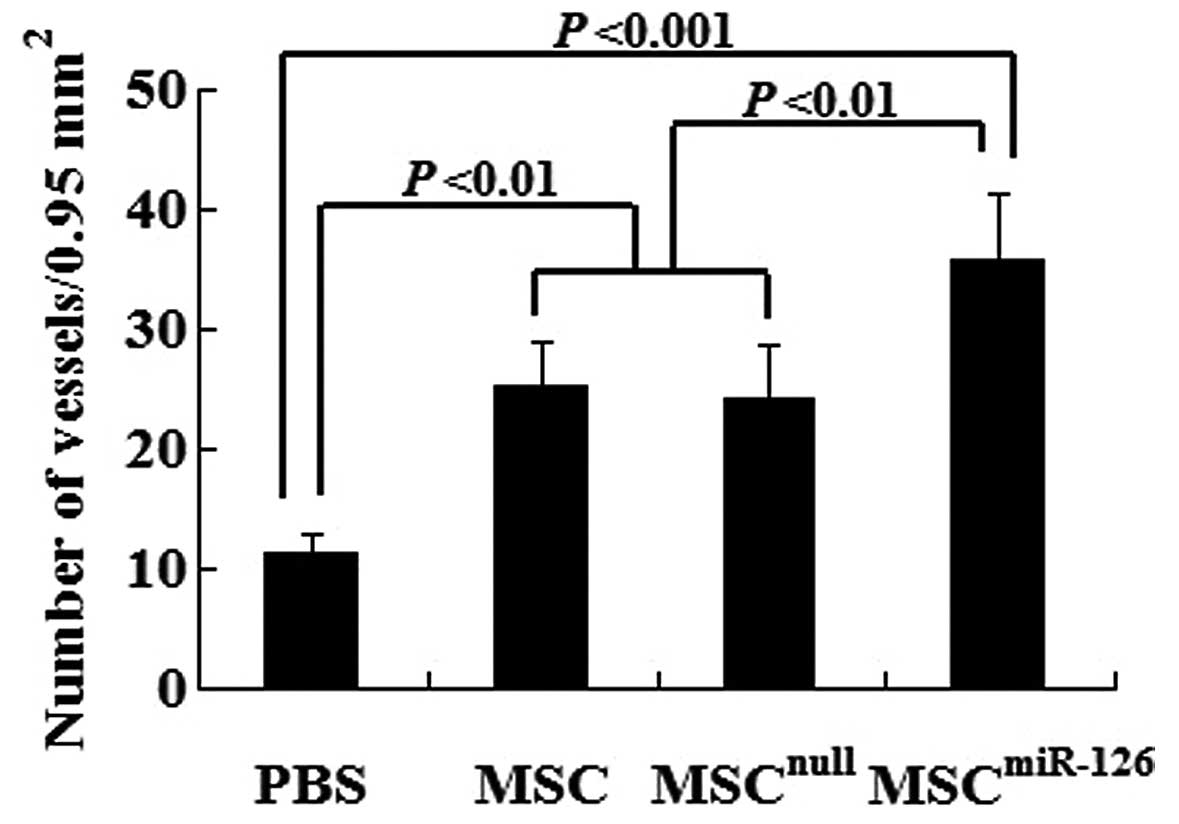
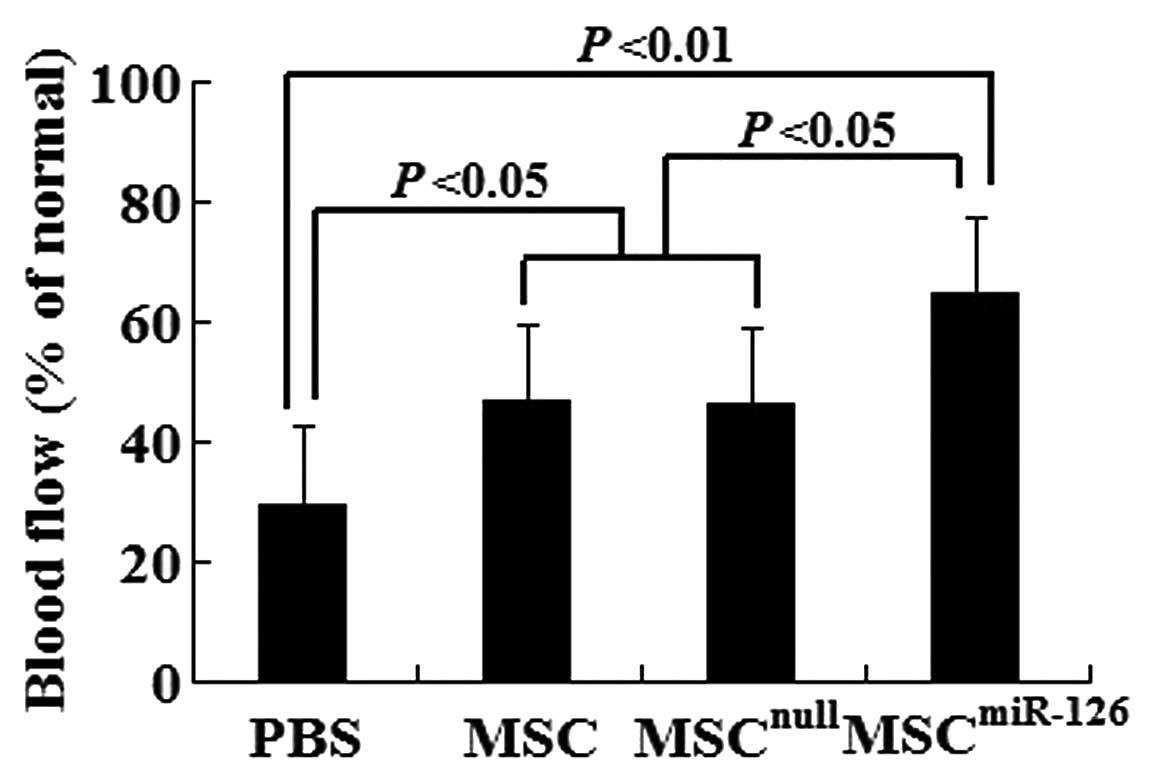
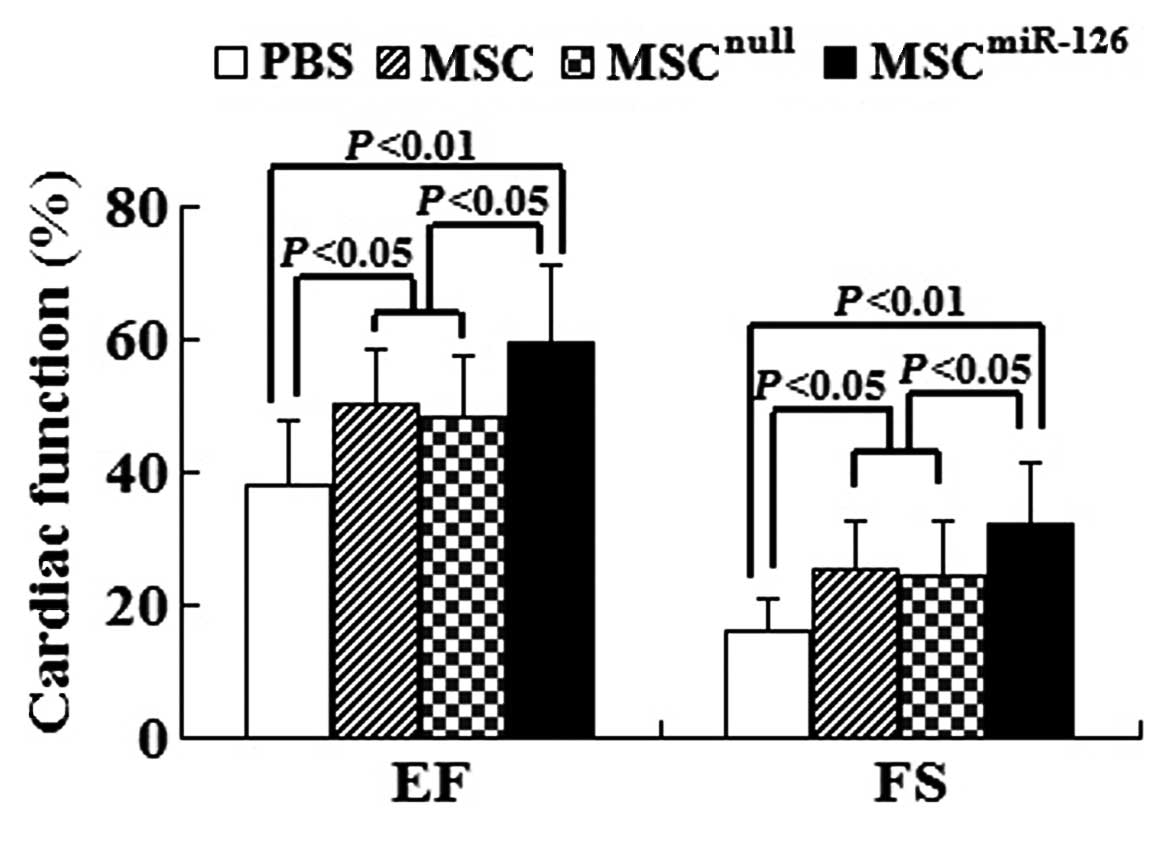
|
1.
|
Feygin J, Mansoor A, Eckman P, Swingen C
and Zhang J: Functional and bioenergetic modulations in the infarct
border zone following autologous mesenchymal stem cell
transplantation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 293:H1772–H1780.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Tang YL, Zhao Q, Qin X, et al: Paracrine
action enhances the effects of autologous mesenchymal stem cell
transplantation on vascular regeneration in rat model of myocardial
infarction. Ann Thorac Surg. 80:229–237. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Stamm C, Westphal B, Kleine HD, et al:
Autologous bone-marrow stem-cell transplantation for myocardial
regeneration. Lancet. 361:45–46. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Kinnaird T, Stabile E, Burnett MS, et al:
Local delivery of marrow-derived stromal cells augments collateral
perfusion through paracrine mechanisms. Circulation. 109:1543–1549.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5.
|
Meyer GP, Wollert KC, Lotz J, et al:
Intracoronary bone marrow cell transfer after myocardial
infarction: eighteen months’ follow-up data from the randomized,
controlled BOOST (Bone marrow transfer to enhance ST-elevation
infarct regeneration) trial. Circulation. 113:1287–1294.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Uemura R, Xu M, Ahmad N and Ashraf M: Bone
marrow stem cells prevent left ventricular remodeling of ischemic
heart through paracrine signaling. Circ Res. 98:1414–1421. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Tang J, Xie Q, Pan G, Wang J and Wang M:
Mesenchymal stem cells participate in angiogenesis and improve
heart function in rat model of myocardial ischemia with
reperfusion. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 30:353–361. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Kinnaird T, Stabile E, Burnett MS, et al:
Marrow-derived stromal cells express genes encoding a broad
spectrum of arteriogenic cytokines and promote in vitro and in vivo
arteriogenesis through paracrine mechanisms. Circ Res. 94:678–685.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Zhao Y, Samal E and Srivastava D: Serum
response factor regulates a muscle-specific microRNA that targets
Hand2 during cardiogenesis. Nature. 436:214–220. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Zhao Y and Srivastava D: A developmental
view of microRNA function. Trends Biochem Sci. 32:189–197. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Kertesz M, Iovino N, Unnerstall U, Gaul U
and Segal E: The role of site accessibility in microRNA target
recognition. Nat Genet. 39:1278–1284. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Wu L and Belasco JG: Let me count the
ways: mechanisms of gene regulation by miRNAs and siRNAs. Mol Cell.
29:1–7. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Wang S, Aurora AB, Johnson BA, et al: The
endothelial-specific microRNA miR-126 governs vascular integrity
and angiogenesis. Dev Cell. 15:261–271. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Fish JE, Santoro MM, Morton SU, et al:
miR-126 regulates angiogenic signaling and vascular integrity. Dev
Cell. 15:272–284. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Nicoli S, Standley C, Walker P, Hurlstone
A, Fogarty KE and Lawson ND: MicroRNA-mediated integration of
haemodynamics and Vegf signalling during angiogenesis. Nature.
464:1196–1200. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Duarte A, Hirashima M, Benedito R, et al:
Dosage-sensitive requirement for mouse Dll4 in artery development.
Genes Dev. 18:2474–2478. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Krebs LT, Xue Y, Norton CR, et al: Notch
signaling is essential for vascular morphogenesis in mice. Genes
Dev. 14:1343–1352. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Roca C and Adams RH: Regulation of
vascular morphogenesis by Notch signaling. Genes Dev. 21:2511–2524.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Phng LK and Gerhardt H: Angiogenesis: a
team effort coordinated by notch. Dev Cell. 16:196–208. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD and Lake RJ:
Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in
development. Science. 284:770–776. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Grajales L, Garcia J, Banach K and Geenen
DL: Delayed enrichment of mesenchymal cells promotes cardiac
lineage and calcium transient development. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
48:735–745. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Krampera M, Pasini A, Rigo A, et al:
HB-EGF/HER-1 signaling in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells:
inducing cell expansion and reversibly preventing multilineage
differentiation. Blood. 106:59–66. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Wang H, Cao F, De A, et al: Trafficking
mesenchymal stem cell engraftment and differentiation in
tumor-bearing mice by bioluminescence imaging. Stem Cells.
27:1548–1558. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Pons J, Huang Y, Takagawa J, et al:
Combining angiogenic gene and stem cell therapies for myocardial
infarction. J Gene Med. 11:743–753. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Li H, Zuo S, He Z, et al: Paracrine
factors released by GATA-4 overexpressed mesenchymal stem cells
increase angiogenesis and cell survival. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 299:H1772–H1781. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Macia E and Boyden PA: Stem cell therapy
is proarrhythmic. Circulation. 119:1814–1823. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Yuasa S and Fukuda K: Cardiac regenerative
medicine. Circ J. 72(Suppl A): A49–A55. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28.
|
Orlic D, Kajstura J, Chimenti S, et al:
Bone marrow cells regenerate infarcted myocardium. Nature.
410:701–705. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Kutryk MJ and Stewart DJ: Angiogenesis of
the heart. Microsc Res Tech. 60:138–158. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30.
|
Sheikh AY, Lin SA, Cao F, et al: Molecular
imaging of bone marrow mononuclear cell homing and engraftment in
ischemic myocardium. Stem Cells. 25:2677–2684. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Terrovitis J, Lautamaki R, Bonios M, et
al: Noninvasive quantification and optimization of acute cell
retention by in vivo positron emission tomography after
intramyocardial cardiac-derived stem cell delivery. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 54:1619–1626. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32.
|
Dresske B, El Mokhtari NE, Ungefroren H,
et al: Multipotent cells of monocytic origin improve damaged heart
function. Am J Transplant. 6:947–958. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Graupera M, Guillermet-Guibert J, Foukas
LC, et al: Angiogenesis selectively requires the p110alpha isoform
of PI3K to control endothelial cell migration. Nature. 453:662–666.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Kerbel RS: Tumor angiogenesis. New Engl J
Med. 358:2039–2049. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Benedito R and Duarte A: Expression of
Dll4 during mouse embryogenesis suggests multiple developmental
roles. Gene Expr Patterns. 5:750–755. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Trindade A, Kumar SR, Scehnet JS, et al:
Overexpression of delta-like 4 induces arterialization and
attenuates vessel formation in developing mouse embryos. Blood.
112:1720–1729. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Williams CK, Li JL, Murga M, Harris AL and
Tosato G: Up-regulation of the Notch ligand Delta-like 4 inhibits
VEGF-induced endothelial cell function. Blood. 107:931–939. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Scehnet JS, Jiang W, Kumar SR, et al:
Inhibition of Dll4-mediated signaling induces proliferation of
immature vessels and results in poor tissue perfusion. Blood.
109:4753–4760. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Noguera-Troise I, Daly C, Papadopoulos NJ,
et al: Blockade of Dll4 inhibits tumour growth by promoting
non-productive angiogenesis. Nature. 444:1032–1037. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Ridgway J, Zhang G, Wu Y, et al:
Inhibition ofDll4 signalling inhibits tumour growth by deregulating
angiogenesis. Nature. 444:1083–1087. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Suchting S, Freitas C, le Noble F, et al:
The Notch ligand Delta-like 4 negatively regulates endothelial tip
cell formation and vessel branching. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:3225–3230. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|