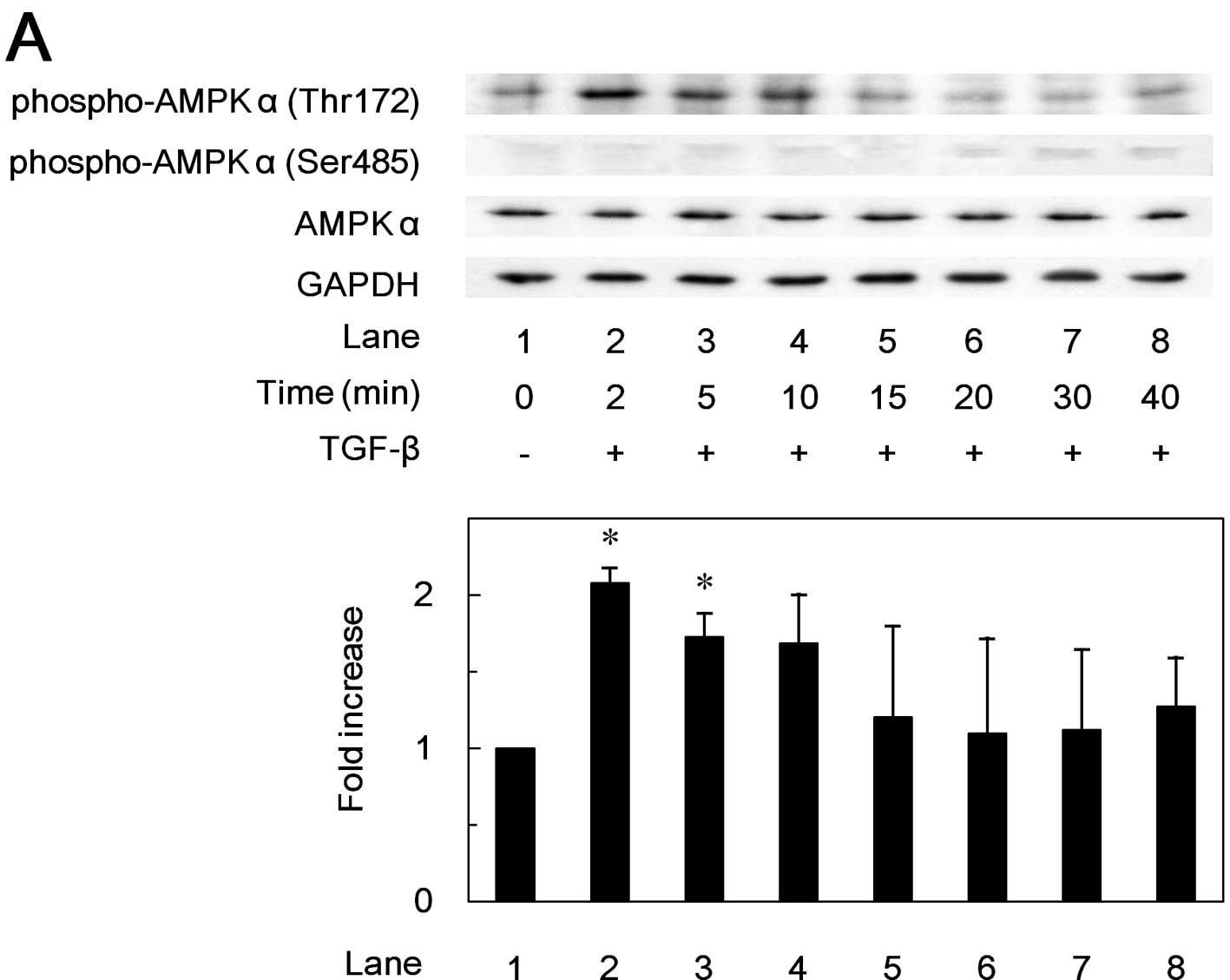
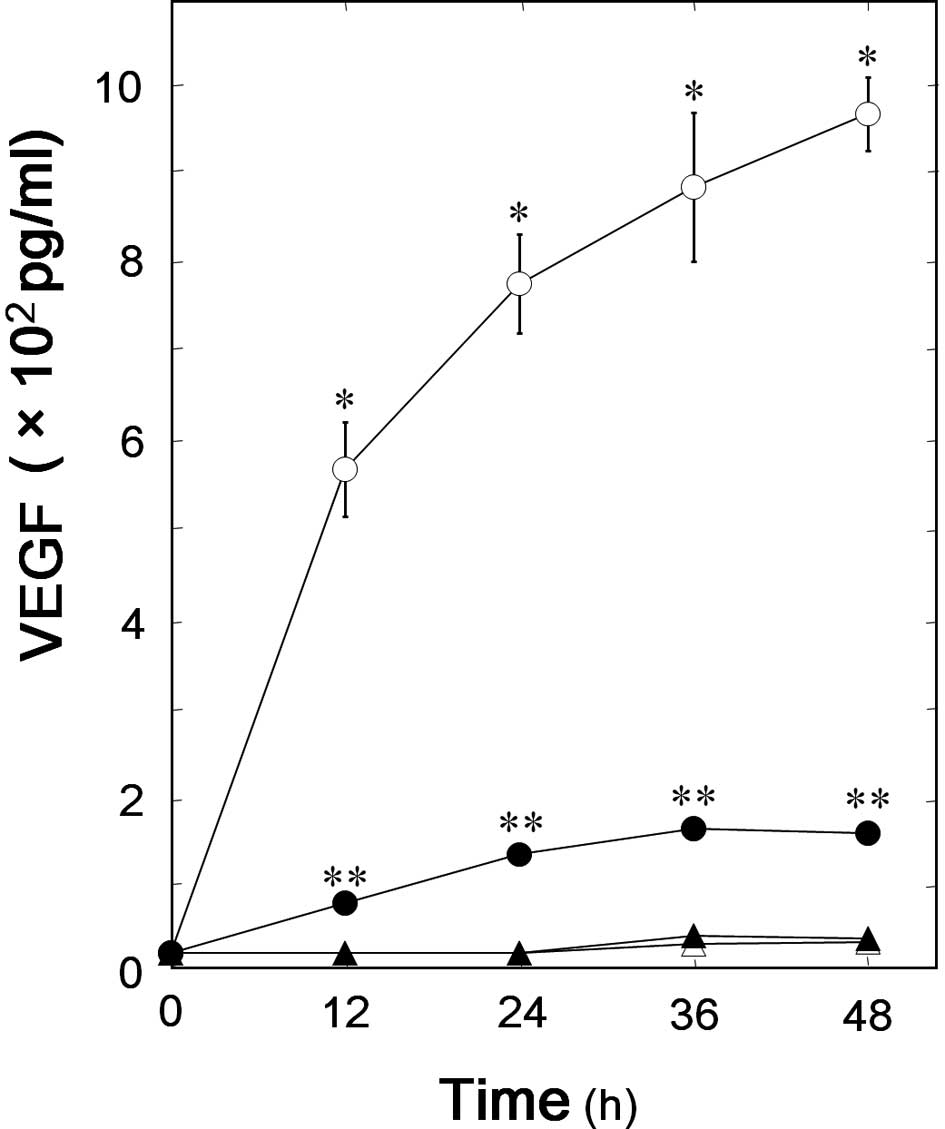
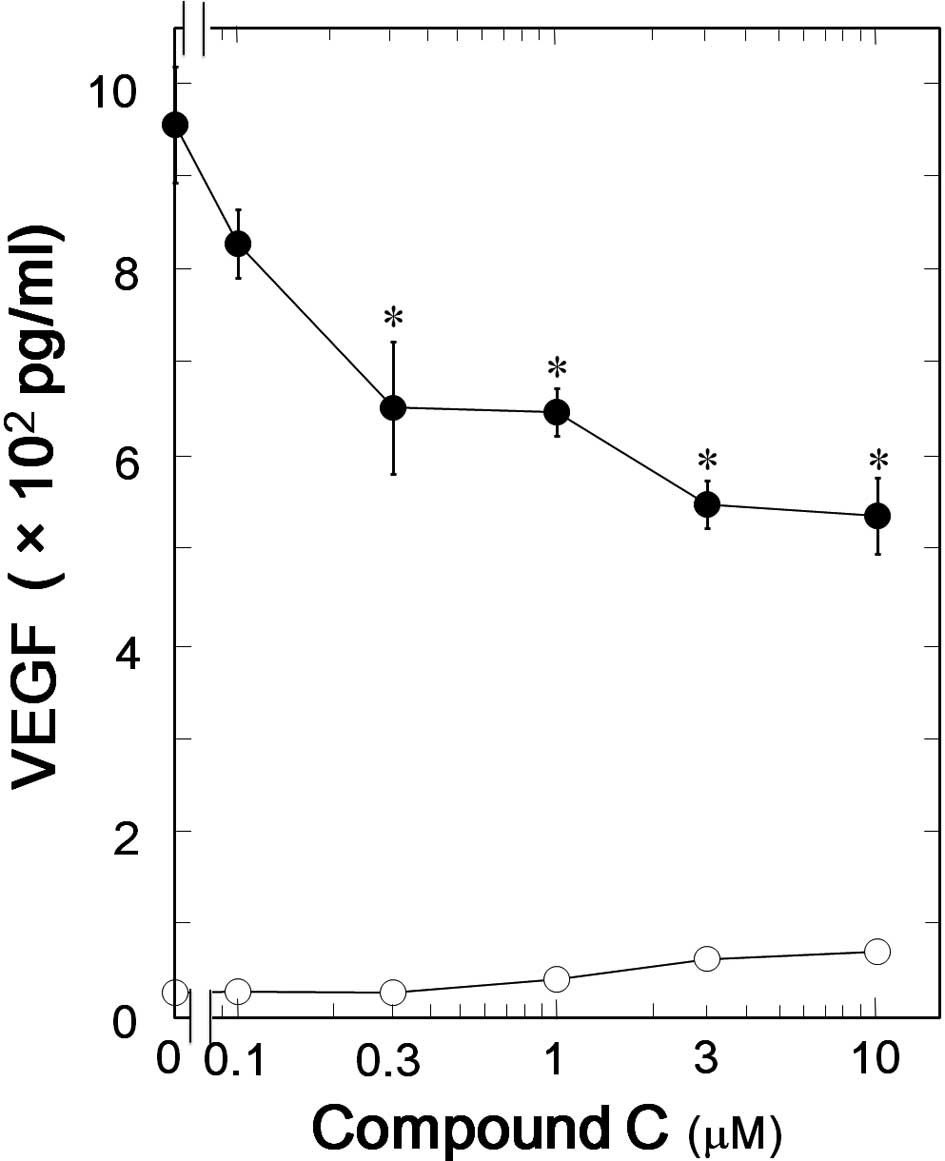
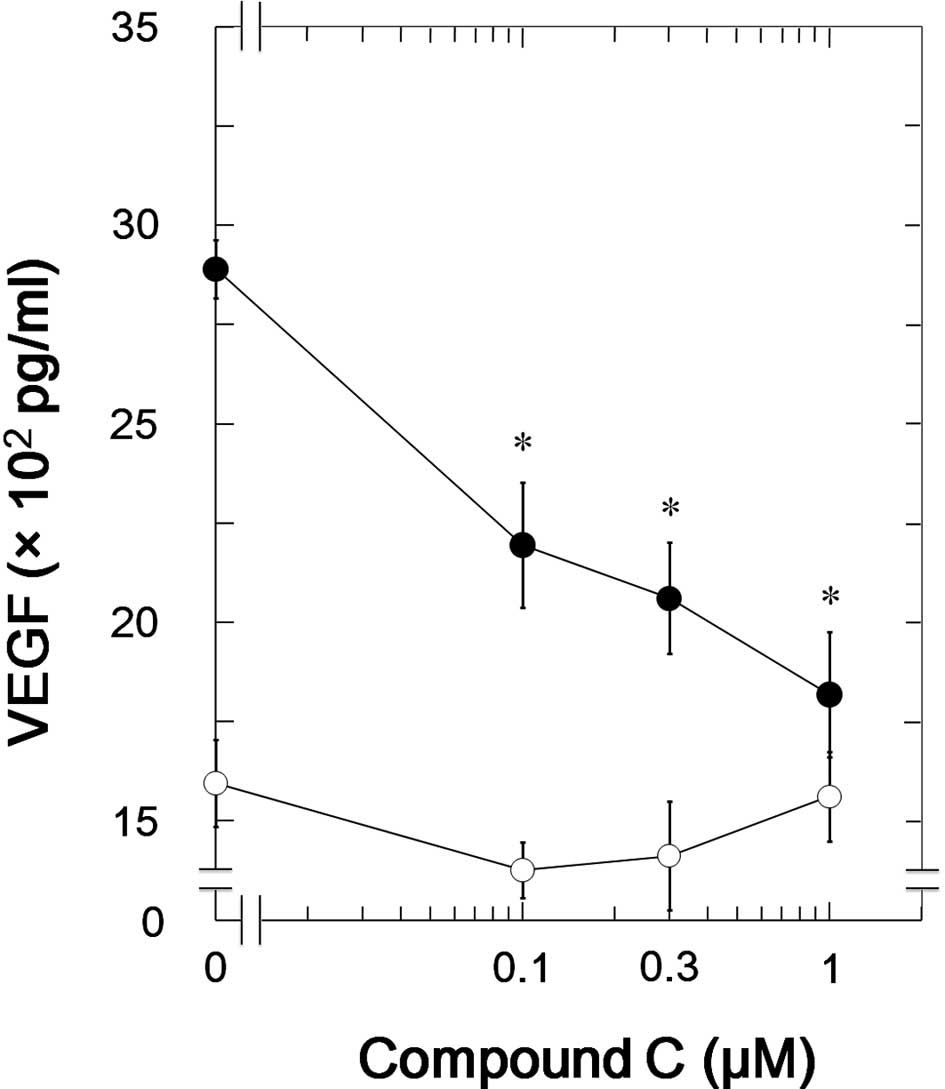
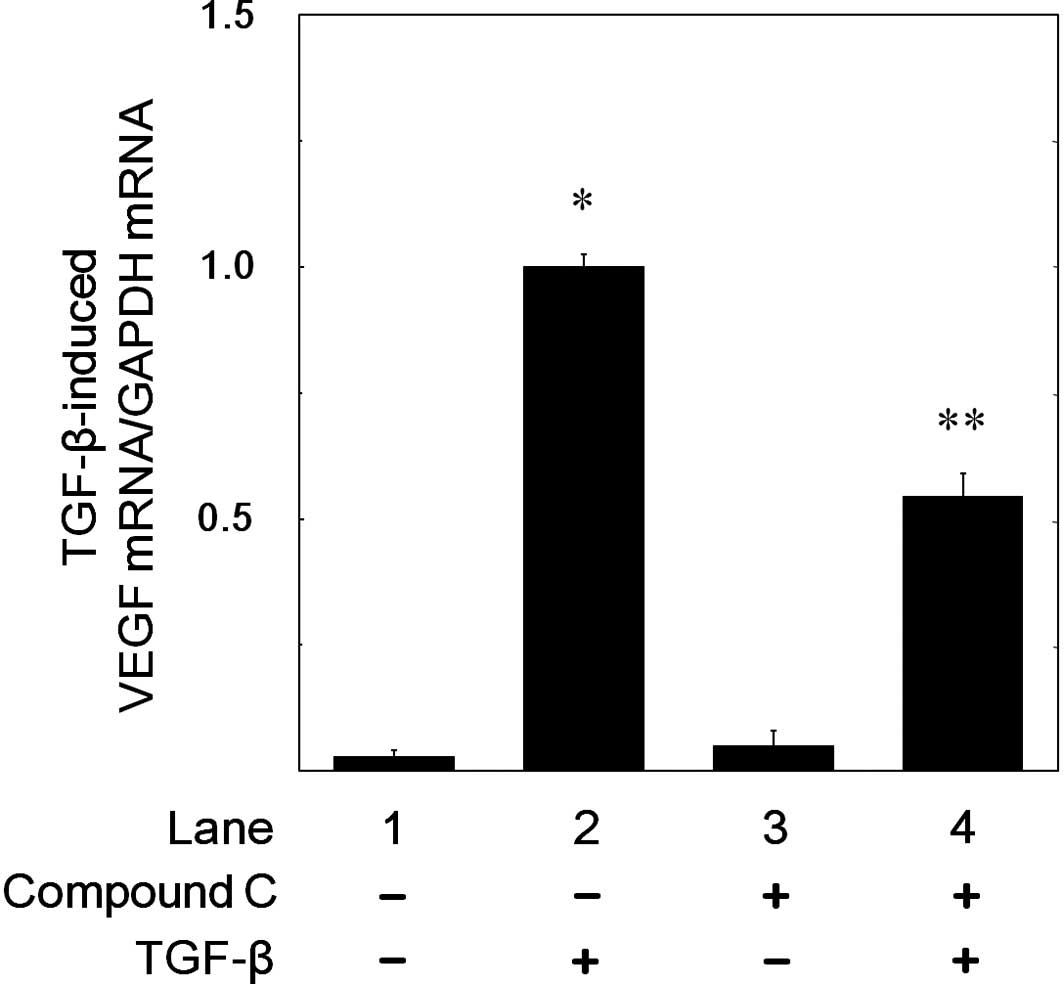
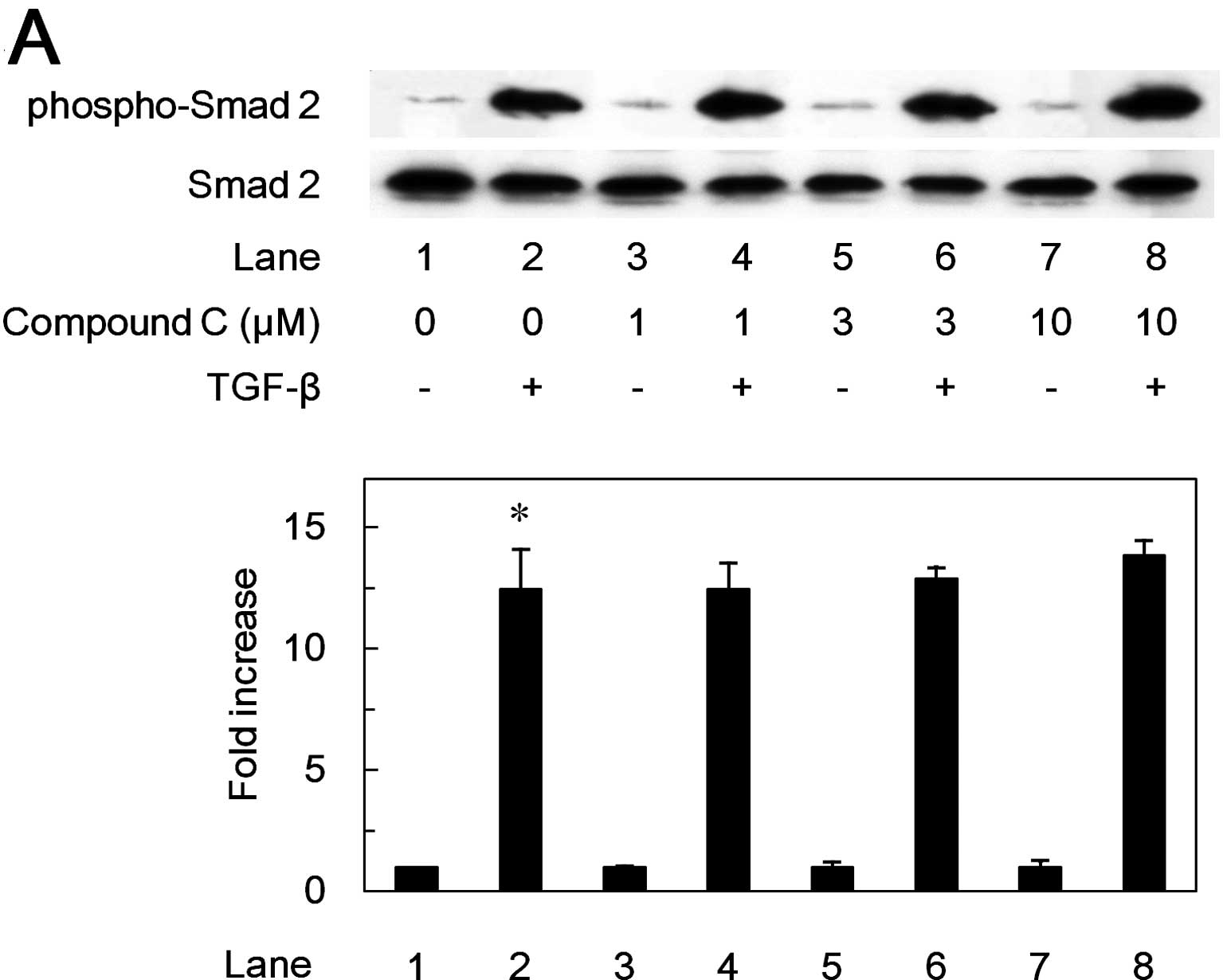
|
1
|
N FerraraVascular endothelial growth
factor: basic science and clinical progressEndocr
Rev25581611200410.1210/er.2003-002715294883
|
|
2
|
G KarsentyEF WagnerReaching a genetic and
molecular understanding of skeletal developmentDev
Cell2389406200210.1016/S1534-5807(02)00157-011970890
|
|
3
|
A ErlebacherEH FilvaroffSE GitelmanR
DerynckToward a molecular understanding of skeletal
developmentCell80371378199510.1016/0092-8674(95)90487-57859279
|
|
4
|
E ZelzerBR OlsenMultiple roles of vascular
endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in skeletal development, growth,
and repairCurr Top Dev
Biol65169187200510.1016/S0070-2153(04)65006-X15642383
|
|
5
|
PB SaadehBJ MehraraDS SteinbrechME
DudziakJA GreenwaldJS LuchsJA SpectorH UenoGK GittesMT
LongakerTransforming growth factor-β1 modulates the expression of
vascular endothelial growth factor by osteoblastsAm J
Physiol277C628C6371999
|
|
6
|
H TokudaD HatakeyamaS AkamatsuK TanabeM
YoshidaT ShibataO KozawaInvolvement of MAP kinases in
TGF-β-stimulated vascular endothelial growth factor synthesis in
osteoblastsArch Biochem Biophys4151171252003
|
|
7
|
Y KannoA IshisakiM YoshidaH TokudaO
NumataO KozawaSAPK/JNK plays a role in transforming growth
factor-β-induced VEGF synthesis in osteoblastsHorm Metab
Res371401452005
|
|
8
|
M KunoS TakaiR Matsushima-NishiwakiC
MinamitaniJ MizutaniT OtsukaA HaradaS AdachiO KozawaH
TokudaRho-kinase inhibitors decrease TGF-β-stimulated VEGF
synthesis through stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun N-terminal
kinase in osteoblastsBiochem Pharmacol771962032009
|
|
9
|
S FogartyDG HardieDevelopment of protein
kinase activators: AMPK as a target in metabolic disorders and
cancerBiochim Biophys
Acta1804581591201010.1016/j.bbapap.2009.09.01219778642
|
|
10
|
LA YehKH LeeKH KimRegulation of rat liver
acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Regulation of phosphorylation and
inactivation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase by the adenylate energy
chargeJ Biol Chem2552308231419806102090
|
|
11
|
DG HardieSA HawleyJW ScottAMP-activated
protein kinase - development of the energy sensor conceptJ
Physiol574715200610.1113/jphysiol.2006.10894416644800
|
|
12
|
R LageC DieguezA Vidal-PuigM LopezAMPK. a
metabolic gauge regulating whole-body energy homeostasisTrends Mol
Med14539549200810.1016/j.molmed.2008.09.00718977694
|
|
13
|
GR SteinbergBE KempAMPK in health and
diseasePhysiol
Rev8910251078200910.1152/physrev.00011.200819584320
|
|
14
|
G ZhouR MyersY LiY ChenX ShenJ
Fenyk-MelodyM WuJ VentreT DoebberN FujiiRole of AMP-activated
protein kinase in mechanism of metformin activaitonJ Clin
Invest10811671174200110.1172/JCI1350511602624
|
|
15
|
EK KimI MillerS AjaJE LandreeM PinnC75, a
fatty acid synthase inhibitor, reduces food intake via hypothalamic
AMP-activated protein kinaseJ Biol
Chem2791997019976200410.1074/jbc.M40216520015028725
|
|
16
|
M NamWH LeeEJ BaeSG KimCompound C inhibits
clonal expansion of preadipocytes by increasing p21 level
irrespectively of AMPK inhibitionArch Biochem
Biophys4797481200810.1016/j.abb.2008.07.02918721791
|
|
17
|
M ShahB KolaA BataveljicTR ArnettB
ViolletL SaxonM KorbonitsC ChenuAMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)
activation regulates in vitro bone formation and bone
massBone47309319201010.1016/j.bone.2010.04.59620399918
|
|
18
|
H SudoHA KodamaY AmagaiS YamamotoS KasaiIn
vitro differentiation and calcification in a new clonal osteogenic
cell line derived from newborn mouse calvariaJ Cell
Biol96191198198310.1083/jcb.96.1.1916826647
|
|
19
|
O KozawaH TokudaM MiwaJ KotoyoriY
OisoCross-talk regulation between cyclic AMP production and
phosphoinositide hydrolysis induced by prostaglandin E2 in
osteoblast-like cellsExp Cell
Res198130134199210.1016/0014-4827(92)90158-51309194
|
|
20
|
H NatsumeH TokudaS AdachiS TakaiR
Matsushima-NishiwakiK KatoC MinamitaniS NiidaJ MizutaniO
KozawaRho-kinase limits FGF-2-stimulated VEGF release in
osteoblastsBone4610681074201010.1016/j.bone.2010.01.37820114091
|
|
21
|
DA SimpsonS FeeneyC BoyleAW StittRetinal
VEGF mRNA measured by SYBR green I fluorescence: a versatile
approach to quantitative PCRMol Vis6178183200011023552
|
|
22
|
K KatoH ItoK HasegawaY InagumaO KozawaT
AsanoModulation of the stress-induced synthesis of hsp27 and
αB-crystallin by cyclic AMP in C6 rat glioma cellsJ
Neurochem669469501996
|
|
23
|
UK LaemmliCleavage of structural proteins
during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage
T4Nature227680685197010.1038/227680a05432063
|
|
24
|
JM KyriakisJ AvruchMammalian
mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways
activated by stress and inflammationPhysiol
Rev81807889200111274345
|
|
25
|
A MoustakasCH HeldinNon-Smad TGF-β
signalsJ Cell Sci118357335842005
|
|
26
|
SA HawleyM DavisonA WoodsSP DaviesRK BeriD
CarlingDG HardieCharacterization of the AMP-activated protein
kinase kinase from rat liver and identification of threonine 172 as
the major site at which it phosphorylates AMP-activated protein
kinaseJ Biol
Chem2712787927887199610.1074/jbc.271.44.278798910387
|
|
27
|
SC SteinA WoodsNA JonesMD DavisonD
CarlingThe regulation of AMP-activated protein kinase by
phosphorylationBiochem
J345437443200010.1042/0264-6021:345043710642499
|
|
28
|
M SuterU RiekR TuerkU SchlattnerT
WallimannD NeumannDissecting the role of 5′-AMP for allosteric
stimulation, activation, and deactivation of AMP-activated protein
kinaseJ Biol Chem28132207322162006
|
|
29
|
KI MitchelhillBJ MichellCM HouseD
StapletonJ DyckJ GambleC UllrichLA WittersBE KempPosttranslational
modifications of the 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase β1 subunitJ
Biol Chem27224475244791997
|
|
30
|
K MiyazawaM ShinozakiT HaraT FuruyaK
MiyazonoTwo major Smad pathways in TGF-β superfamily
signallingGenes Cells7119111042002
|
|
31
|
C WidmannS GibsonMB JarpeGL
JohnsonMitogen-activated protein kinase: conservation of a
three-kinase module from yeast to humanPhysiol
Rev7914318019999922370
|
|
32
|
K YamaguchiK ShirakabeH ShibuyaK IrieI
OishiN UenoT TaniguchiE NishidaK MatsumotoIdentification of a
member of the MAPKKK family as a potential mediator of TGF-β signal
transductionScience2702008201119958533096
|
|
33
|
M MomcilovicSP HongM CarlsonMammalian TAK1
activates Snf1 protein kinase in yeast and phosphorylates
AMP-activated protein kinase in vitroJ Biol
Chem2812533625343200610.1074/jbc.M60439920016835226
|
|
34
|
BM EmerlingB ViolletKV TormosNS
ChandelCompound C inhibits hypoxic activation of HIF-1 independent
of AMPKFEBS
Lett58157275731200710.1016/j.febslet.2007.11.03818036344
|
|
35
|
Y GaoY ZhouA XuD WuEffects of an
AMP-activated protein kinase inhibitor, compound C, on adipogenic
differentiation of 3T3-L1 cellsBiol Pharm
Bull3117161722200810.1248/bpb.31.171618758065
|
|
36
|
DS WangK YamazakiK NohtomiK ShizumeK
OhsumiM ShibuyaH DemuraK SatoIncrease of vascular endothelial
growth factor mRNA expression by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in human
osteoblast-like cellsJ Bone Miner
Res11472479199610.1002/jbmr.56501104088992878
|
|
37
|
HP GerberTH VuAM RyanJ KowalskiZ WerbN
FerraraVEGF couples hypertrophic cartilage remodeling, ossification
and angiogenesis during endochondral bone formationNat
Med5623628199910.1038/946710371499
|
|
38
|
JMW QuinnS TamNA SimsH SalehNE McGregorIJ
PoultonJW ScottMT GillespieBE KempBJW van DenderenGermline deletion
of AMP-activated protein kinase β subunits reduces bone mass
without altering osteoclast differentiation or functionFASEB
J242752852010
|
|
39
|
P DucyM AmlingS TakedaM PriemelAF
SchillingFT BeilJ ShenC VinsonJM RuegerG KarsentyLeptin inhibits
bone formation through a hypothalamic relay: a central control of
bone massCell100197207200010.1016/S0092-8674(00)81558-510660043
|
|
40
|
PA BaldockA SainsburyM CouzensRF
EnriquezGP ThomasEM GardinerH HerzogHypothalamic Y2 receptors
regulate bone formationJ Clin
Invest109915921200210.1172/JCI021458811927618
|
|
41
|
J CornishKE CallonU BavaC LinD NaotBL
HillAB GreyN BroomDE MyersGC NicholsonLeptin directly regulates
bone cell function in vitro and reduces bone fragility in vivoJ
Endocrinol175405415200210.1677/joe.0.175040512429038
|
|
42
|
F ElefteriouJD AhnS TakedaM StarbuckX
YangX LiuH KondoWG RichardsTW BannonM NodaLeptin regulation of bone
resorption by the sympathetic nervous system and
CARTNature434514520200510.1038/nature0339815724149
|
|
43
|
AI IdrisRJ van’t HofIR GreigSA RidgeD
BakerRA RossSH RalstonRegulation of bone mass, bone loss and
osteoclast activity by cannabinoid receptorsNat
Med11774779200510.1038/nm125515908955
|
|
44
|
G MaccarinelliV SibiliaA TorselloF
RaimondoM PittoA GiustinaC NettiD CocchiGhrelin regulates
proliferation and differentiation of osteoblastic cellsJ
Endocrinol184249256200510.1677/joe.1.0583715642801
|
|
45
|
JD AhnB DubernC Lubrano-BerthelierK
ClementG KarsentyCart overexpression is the only identifiable cause
of high bone mass in melanocortin 4 receptor
deficiencyEndocrinology14731963202200610.1210/en.2006-028116614075
|
|
46
|
S SatoR HanadaA KimuraT AbeT MatsumotoM
IwasakiH InoseT IdaM MiedaY TakeuchiCentral control of bone
remodeling by neuromedin UNat
Med1312341240200710.1038/nm164017873881
|
|
47
|
MW HamrickSL FerrariLeptin and the
sympathetic connection of fat to boneOsteoporos
Int19905912200810.1007/s00198-007-0487-917924050
|
|
48
|
LF BonewaldGR MundyRole of transforming
growth factor-β in bone remodelingClin Orthop Relat
Res2612761990
|
|
49
|
K KatoH TokudaS AdachiR
Matsushima-NishiwakiH NatsumeK YamakawaY GuT OtsukaO
KozawaAMP-activated protein kinase positively regulates
FGF-2-stimulated VEGF synthesis in osteoblastsBiochem Biophys Res
Commun400123127201010.1016/j.bbrc.2010.08.02420708602
|