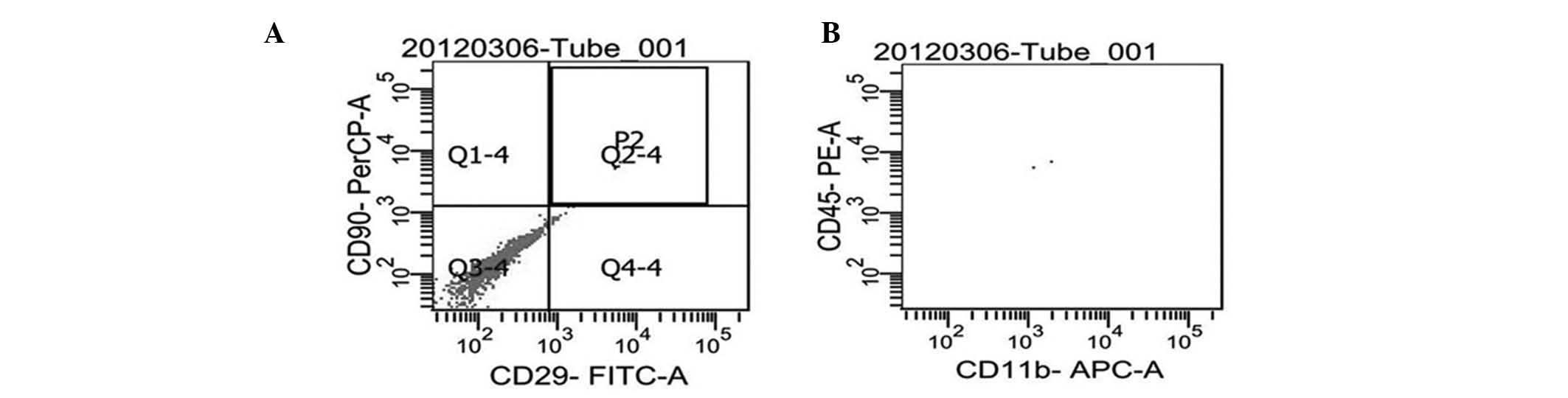
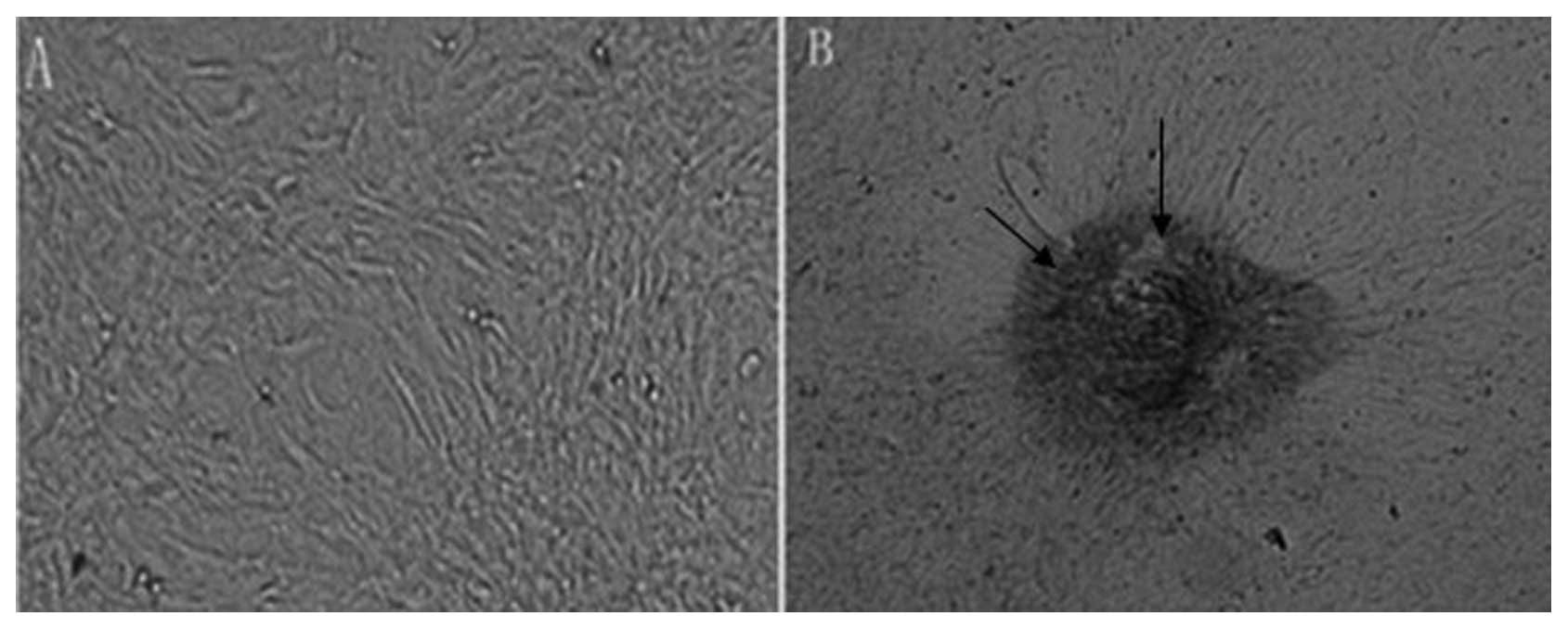
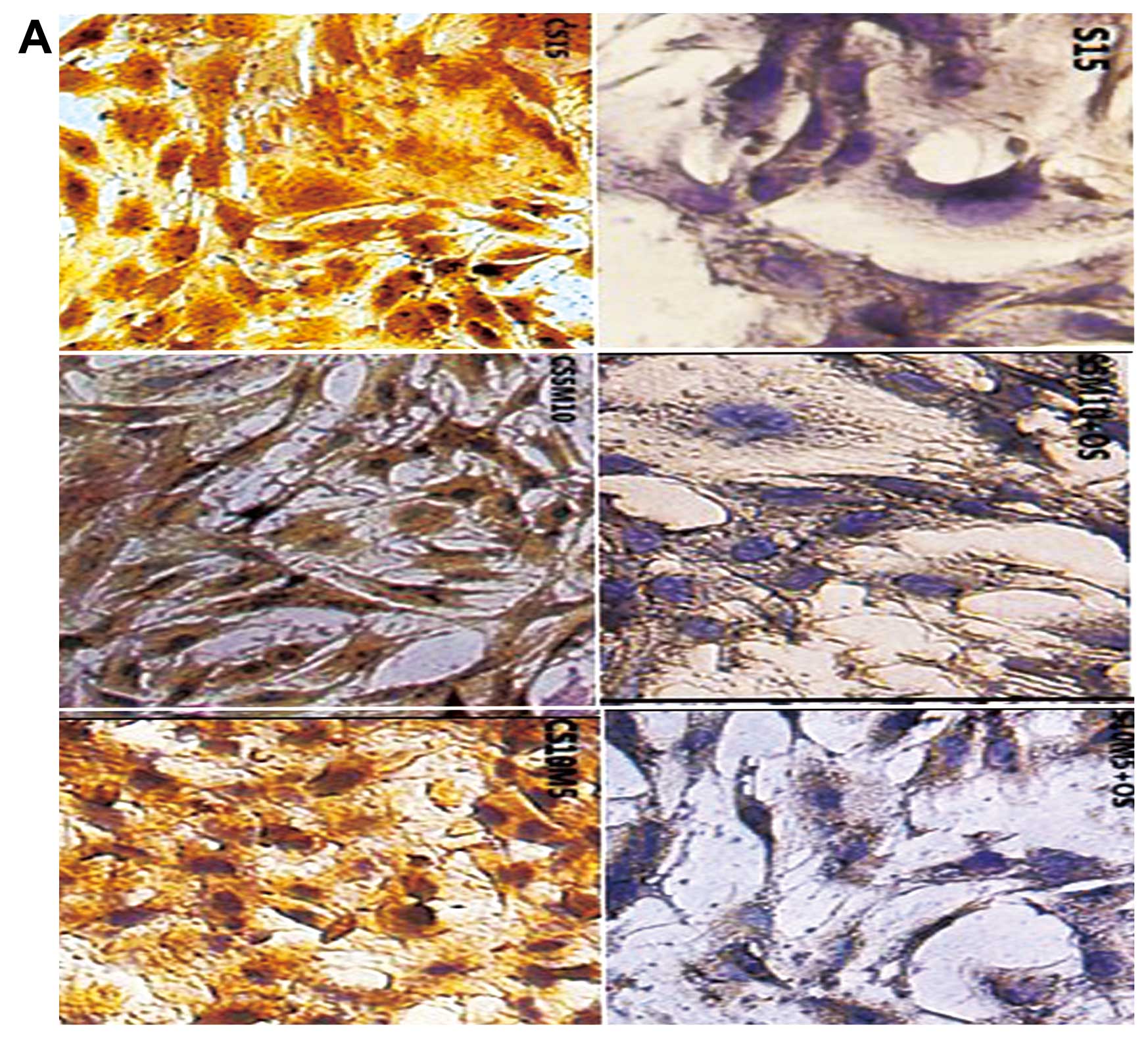
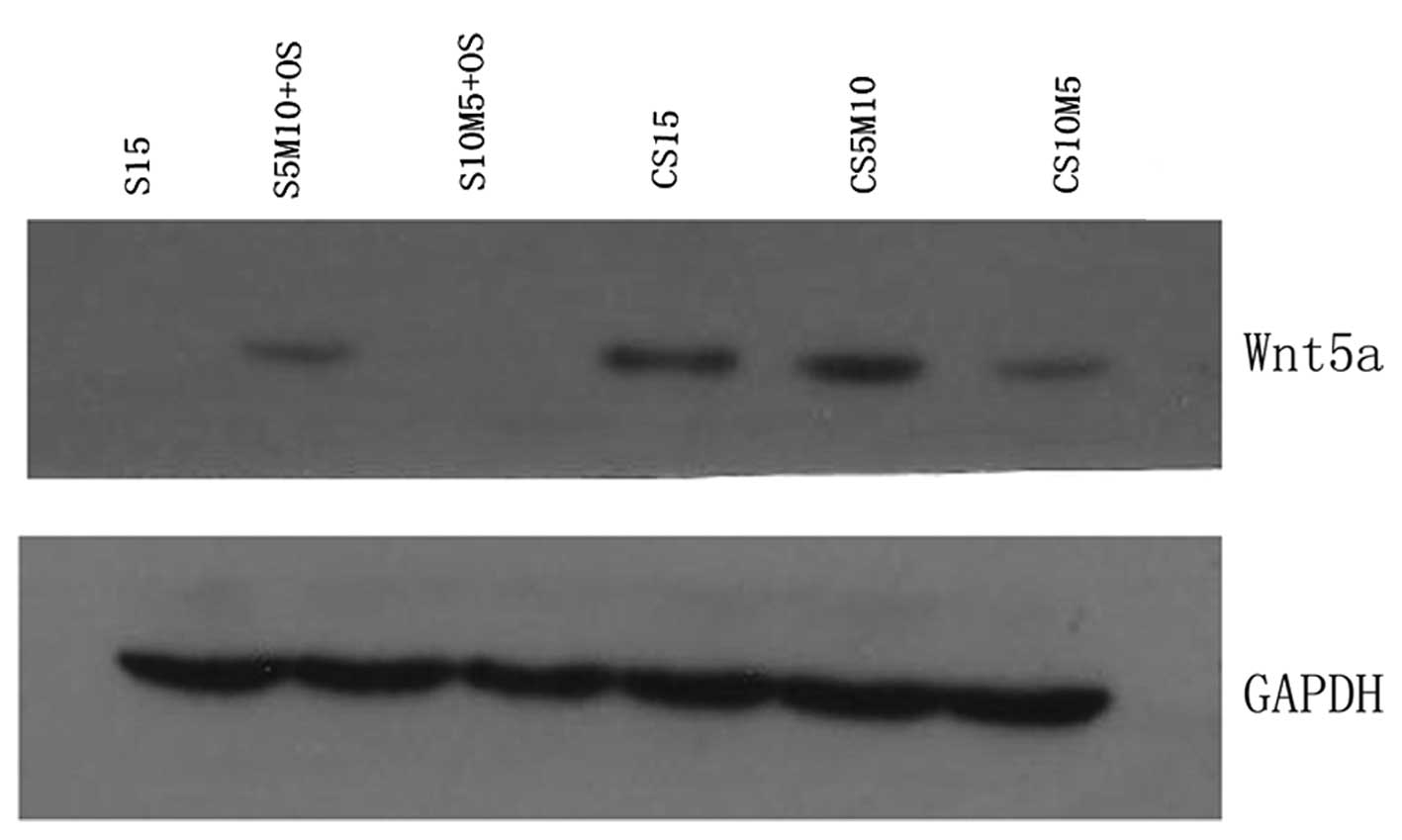
|
1
|
Demer LL and Tintut Y: Vascular
calcification: pathobiology of a multifaceted disease. Circulation.
117:2938–2948. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tanimura A, McGregor DH and Anderson HC:
Matrix vesicles in atherosclerotic calcification. Proc Soc Exp Biol
Med. 172:173–177. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tanimura A, McGregor DH and Anderson HC:
Calcification in atherosclerosis. I Human studies. J Exp Pathol.
2:261–273. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Boström KI, Rajamannan NM and Towler DA:
The regulation of valvular and vascular sclerosis by osteogenic
morphogens. Circ Res. 109:564–577. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Torsney E and Xu Q: Resident vascular
progenitor cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 50:304–311. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hirschi KK and Goodell MA: Hematopoietic,
vascular and cardiac fates of bone marrow-derived stem cells. Gene
Ther. 9:648–652. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Farrington-Rock C, Crofts NJ, Doherty MJ,
et al: Chondrogenic and adipogenic potential of microvascular
pericytes. Circulation. 110:2226–2232. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ball SG, Shuttleworth AC and Kielty CM:
Direct cell contact influences bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell
fate. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 36:714–727. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dufourcq P, Descamps B, Tojais NF, et al:
Secreted frizzled-related protein-1 enhances mesenchymal stem cell
function in angiogenesis and contributes to neovessel maturation.
Stem Cells. 26:2991–3001. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cheung C and Sinha S: Human embryonic stem
cell-derived vascular smooth muscle cells in therapeutic
neovascularisation. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 51:651–664. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao Y, Liu YX, Xie SL, Deng BQ, Wang JF
and Nie RQ: Increased expression of granulocyte colony stimulating
factor mediates mesenchymal stem cells recruitment after vascular
injury. Chin Med J. 124:4286–4292. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Roorda BD, Elst A, Boer TG, Kamps WA and
de Bont ES: Mesenchymal stem cells contribute to tumor cell
proliferation by direct cell-cell contact interactions. Cancer
Invest. 28:526–534. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Abedin M, Tintut Y and Demer LL:
Mesenchymal stem cells and the artery wall. Circ Res. 95:671–676.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kirton JP, Crofts NJ, George SJ, Brennan K
and Canfield AE: Wnt/beta-catenin signaling stimulates chondrogenic
and inhibits adipogenic differentiation of pericytes: potential
relevance to vascular disease? Circ Res. 101:581–589. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Shao JS, Cheng SL, Pingsterhaus JM,
Charlton-Kachigian N, Loewy AP and Towler DA: Msx2 promotes
cardiovascular calcification by activating paracrine Wnt signals. J
Clin Invest. 115:1210–1220. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ishitani T, Kishida S, Hyodo-Miura J, et
al: The TAK1-NLK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade functions
in the Wnt-5a/Ca(2+) pathway to antagonize Wnt/beta-catenin
signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 23:131–139. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun S, Guo Z, Xiao X, et al: Isolation of
mouse marrow mesenchymal progenitors by a novel and reliable
method. Stem Cells. 21:527–535. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Minguell JJ, Erices A and Conget P:
Mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Biol Med. 226:507–520. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Leskela HV, Risteli J, Niskanen S,
Koivunen J, Ivaska KK and Lehenkari P: Osteoblast recruitment from
stem cells does not decrease by age at late adulthood. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 311:1008–1013. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pal SN, Clancy P and Golledge J:
Circulating concentrations of stem-cell-mobilizing cytokines are
associated with levels of osteoprogenitor cells and aortic
calcification severity. Circ J. 75:1227–1234. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Baksh D and Tuan RS: Canonical and
non-canonical Wnts differentially affect the development potential
of primary isolate of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J
Cell Physiol. 212:817–826. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yip CY and Simmons CA: The aortic valve
microenvironment and its role in calcific aortic valve disease.
Cardiovasc Pathol. 20:177–182. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rogers GJ, Hodgkin MN and Squires PE:
E-cadherin and cell adhesion: a role in architecture and function
in the pancreatic islet. Cell Physiol Biochem. 20:987–994. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yue XS, Murakami Y, Tamai T, Nagaoka M,
Cho CS, Ito Y and Akaike T: A fusion protein N-cadherin-Fc as an
artificial extra-cellular matrixm surface for maintenance of stem
cell features. Biomaterials. 31:5287–5296. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cheng CW, Yeh JC, Fan TP, Smith SK and
Charnock-Jones DS: Wnt5a-mediated non-canonical Wnt signalling
regulates human endothelial cell proliferation and migration.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 365:285–290. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bennett CN, Longo KA, Wright WS, et al:
Regulation of osteoblastogenesis and bone mass by Wnt10b. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 102:3324–3329. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gaur T, Lengner CJ, Hovhannisyan H, et al:
Canonical WNT signaling promotes osteogenesis by directly
stimulating Runx2 gene expression. J Biol Chem. 280:33132–33140.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pohjolainen V, Taskinen P, Soini Y, et al:
Noncollagenous bone matrix proteins as a part of calcific aortic
valve disease regulation. Hum Pathol. 39:1695–1701. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Grumolato L, Liu G, Mong P, Mudbhary R, et
al: Canonical and non-canonical Wnts use a common mechanism to
activate completely unrelated coreceptors. Genes Dev. 24:2517–2530.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Qiu W, Chen L and Kassem M: Activation of
non-canonical Wnt/JNK pathway by Wnt3a is associated with
differentiation fate determination of human bone marrow stromal
(mesenchymal) stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 413:98–104.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yuan Y, Niu CC, Deng G, Li ZQ, Pan J, Zhao
C, Yang ZL and Si WK: The Wnt5a/Ror2 noncanonical signaling pathway
inhibits canonical Wnt signaling in K562 cells. Int J Mol Med.
27:63–69. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Niessen K and Karsan A: Notch signaling in
cardiac development. Circ Res. 102:1169–1181. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bhatt PM, Lewi CJ, House DL, et al:
Increased Wnt5a mRNA expression in advanced atherosclerotic
lesions, and oxidized LDL treated human monocyte-derived
macrophages. Open Circ Vasc J. 5:1–7. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mikels A, Minami Y and Nusse R: Ror2
receptor requires tyrosine kinase activity to mediate Wnt5A
signaling. J Biol Chem. 284:30167–30176. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|