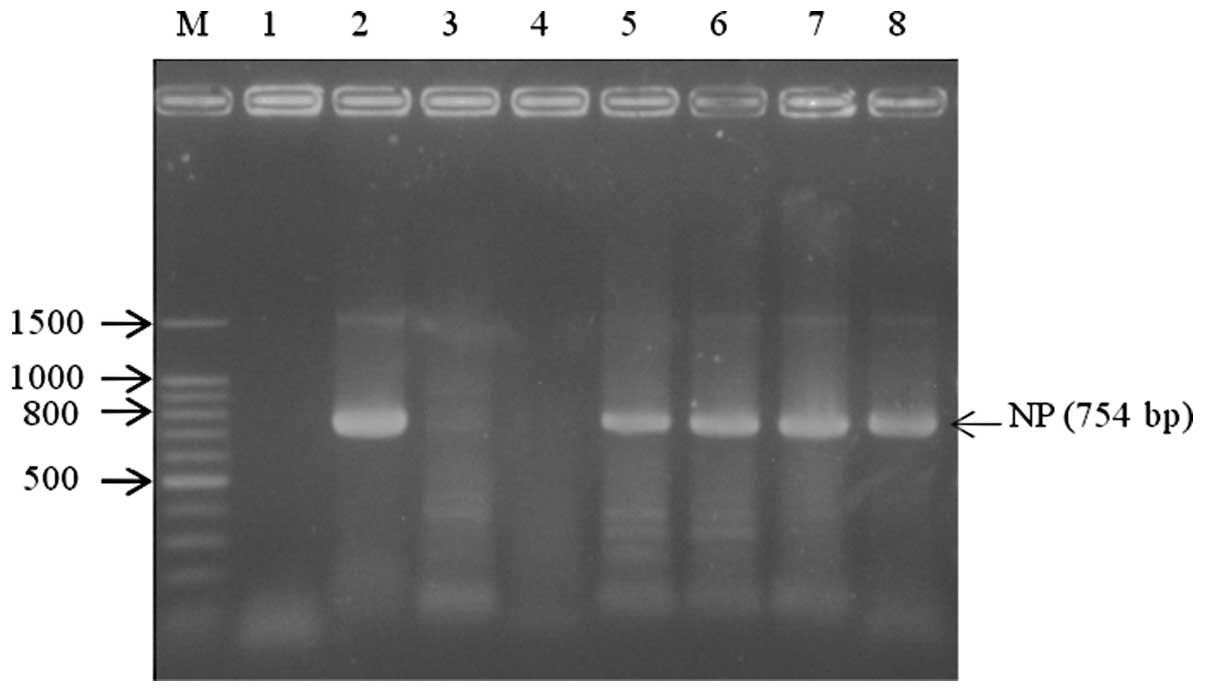
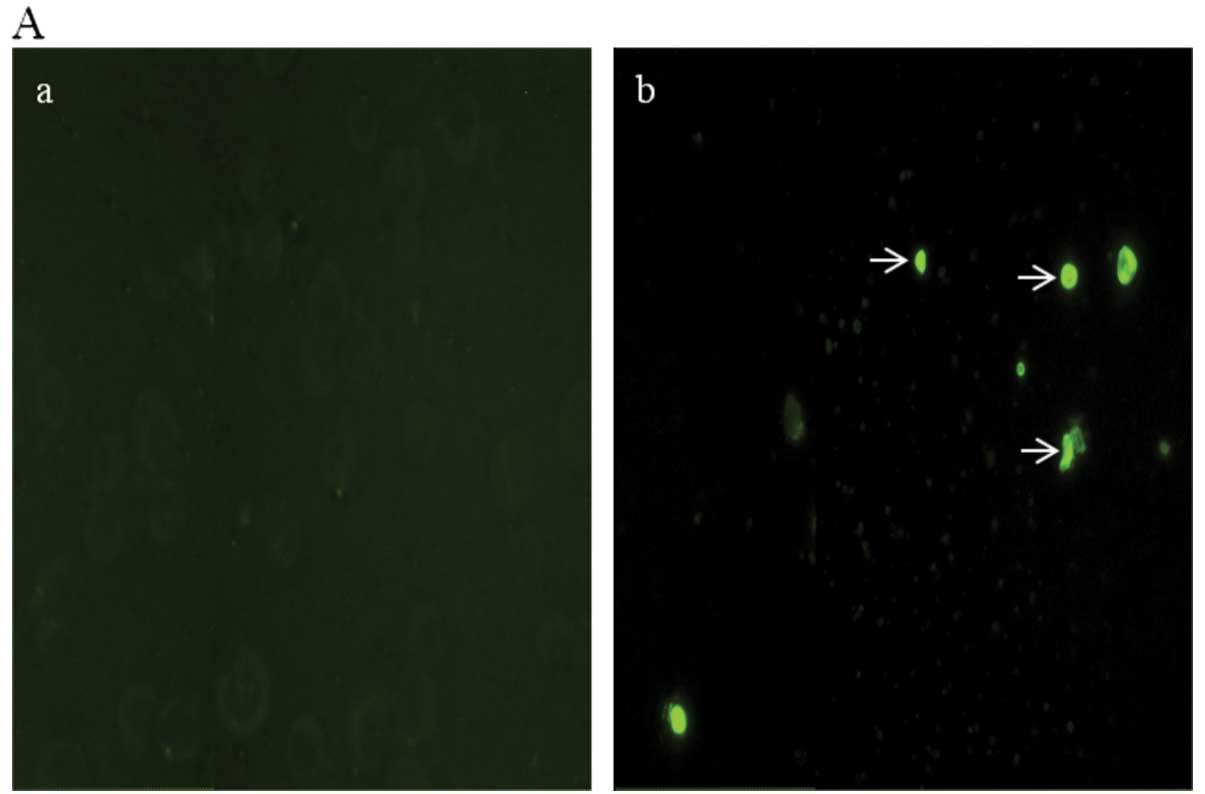
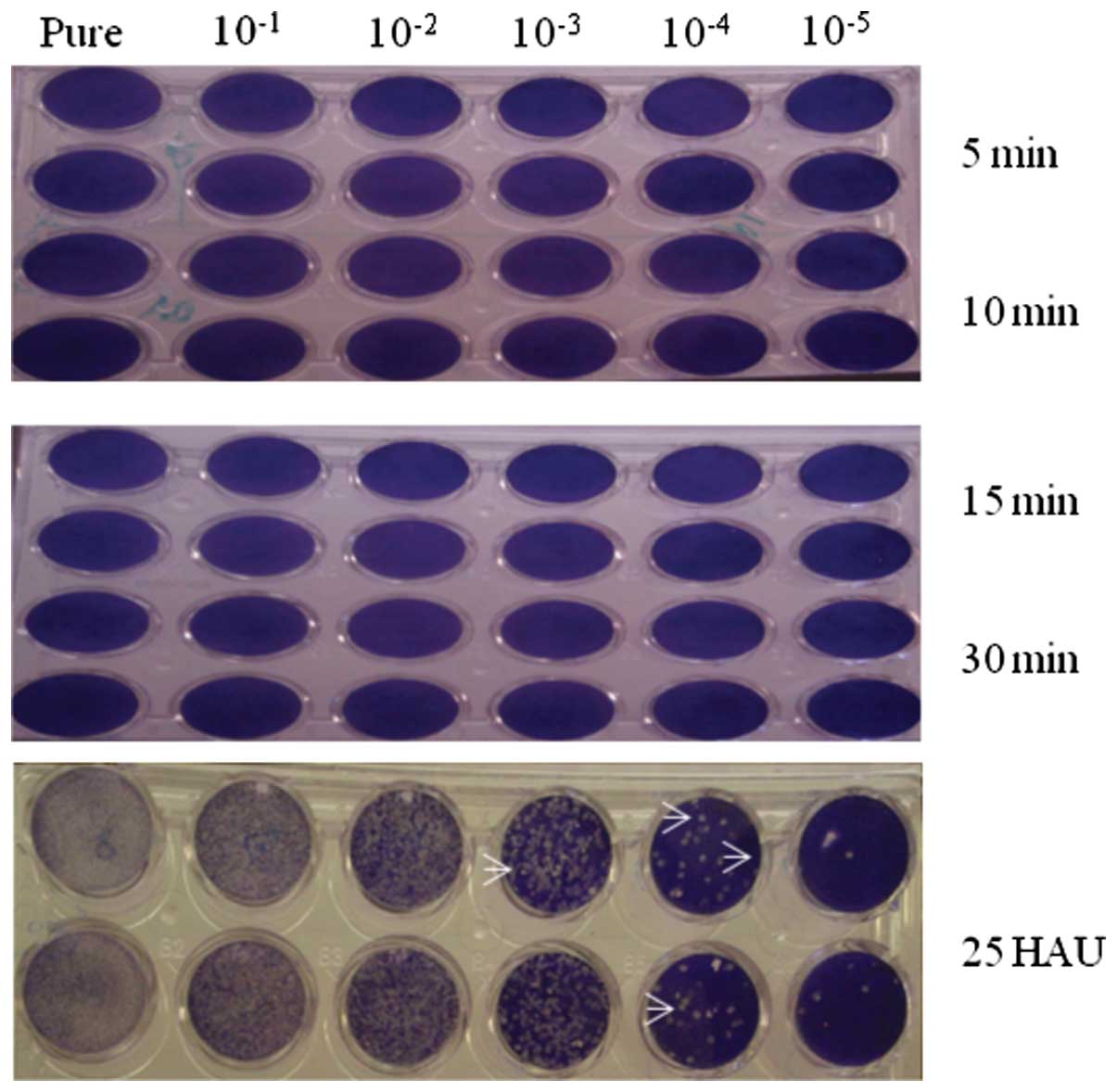
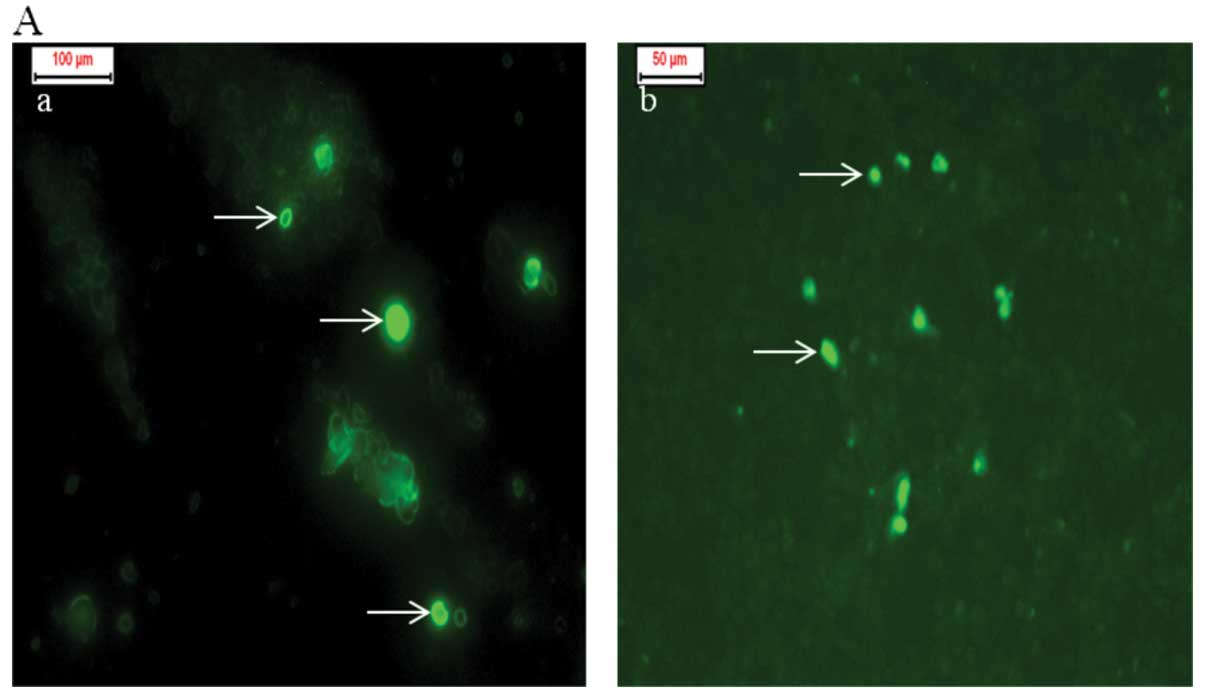
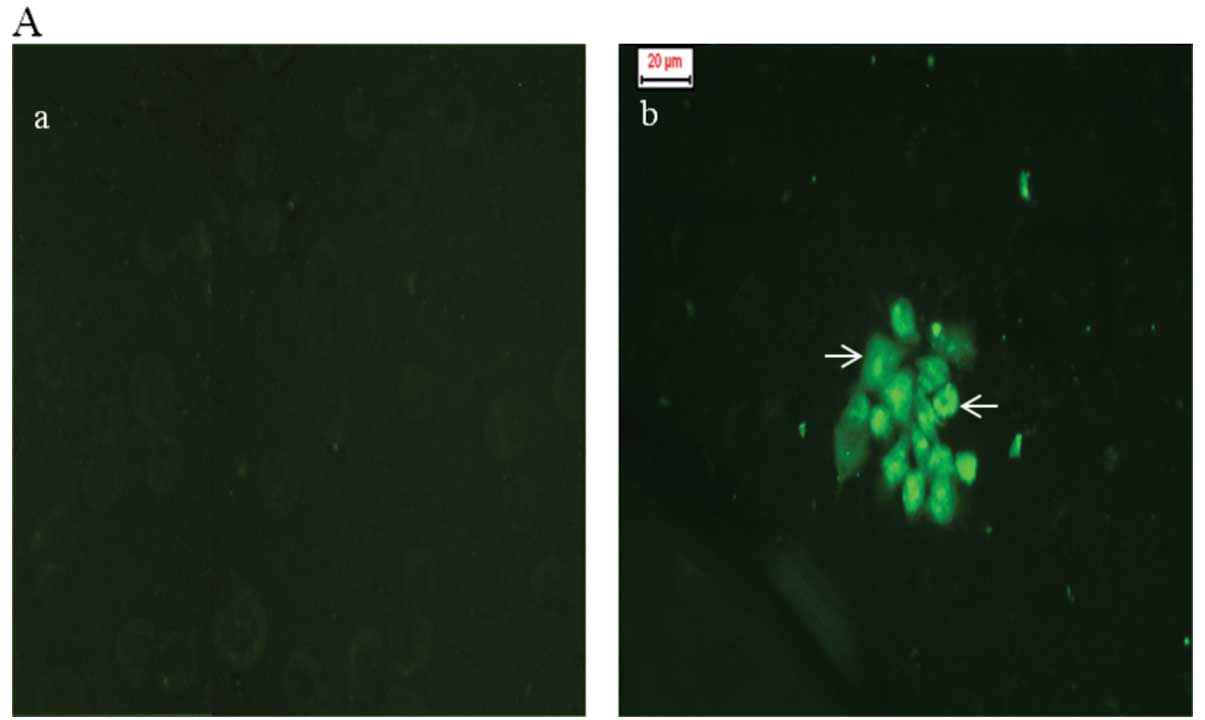
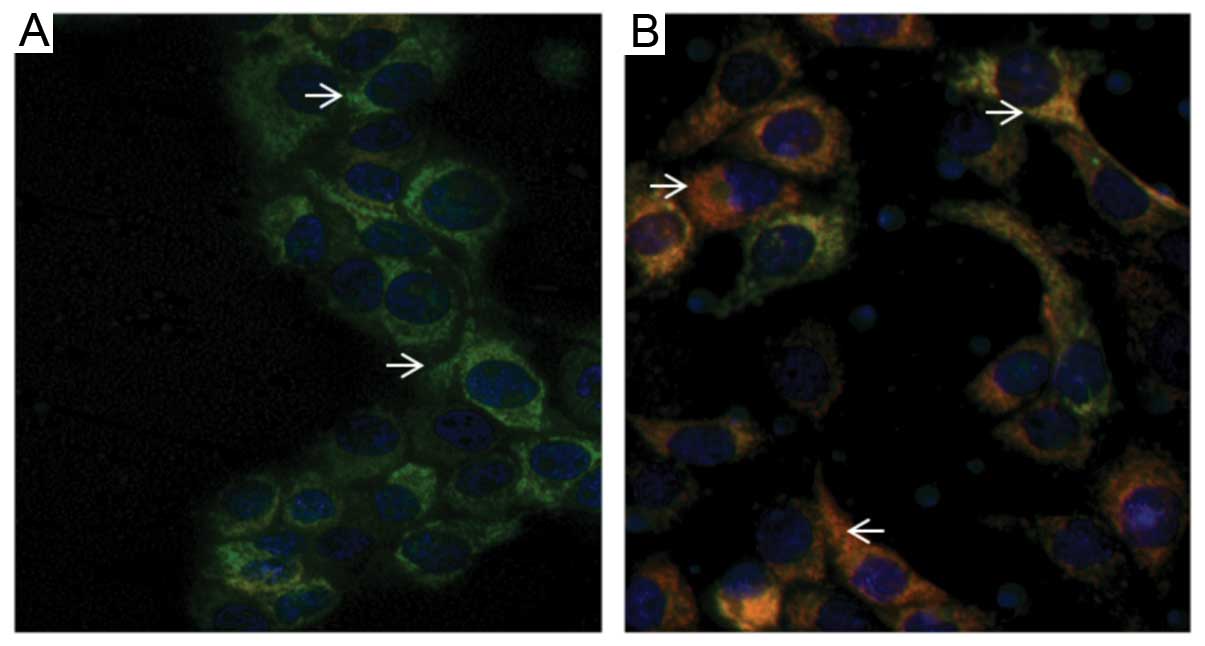
|
1
|
Mayo M: A summary of taxonomic changes
recently approved by ICTV. Arch Virol. 147:1655–1656. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Seal BS, King DJ and Sellers HS: The avian
response to Newcastle disease virus. Dev Comp Immunol. 24:257–268.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
De Leeuw O and Peeters B: Complete
nucleotide sequence of Newcastle disease virus: evidence for the
existence of a new genus within the subfamily
Paramyxovirinae. J Gen Virol. 80:131–136. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Krishnamurthy S and Samal SK: Nucleotide
sequences of the trailer, nucleocapsid protein gene and intergenic
regions of Newcastle disease virus strain Beaudette C and
completion of the entire genome sequence. J Gen Virol.
79:2419–2424. 1998.
|
|
5
|
El Zowalaty ME, Chander Y, Redig PT, El
Latif HKA, et al: Selective isolation of avian influenza virus
(AIV) from cloacal samples containing AIV and Newcastle disease
virus. J Vet Diagn Invest. 23:330–332. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hanson R and Brandly C: Identification of
vaccine strains of Newcastle disease virus. Science. 122:156–157.
1955.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Alexander DJ: Newcastle disease, other
avian paramyxoviruses, and pneumovirus infections. Diseases of
Poultry. Saif JM, Barnes HJ, Glisson JR, Fadly AM, McDougald LR and
Swayne DE: 11th edition. Iowa State University Press; Ames, Iowa,
USA: pp. 63–99. 2003
|
|
8
|
Alabsi AM, Ali R, Ideris A, Omar AR, et
al: Anti-leukemic activity of Newcastle disease virus strains
AF2240 and V4-UPM in murine myelomonocytic leukemia in vivo. Leuk
Res. 36:634–645. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lam HY, Yeap SK, Rasoli M, Omar AR, Yusoff
K, Suraini AA and Alitheen NB: Safety and clinical usage of
Newcastle disease virus in cancer therapy. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2011:7187102011.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
10
|
Sinkovics JG and Horvath JC: Newcastle
disease virus (NDV): Brief history of its oncolytic strains. J Clin
Virol. 16:1–15. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lam K, Vasconcelos A and Bickford A:
Apoptosis as a cause of death in chicken embryos inoculated with
Newcastle disease virus. Microb Pathog. 19:169–174. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Washburn B and Schirrmacher V: Human tumor
cell infection by Newcastle disease virus leads to upregulation of
HLA and cell adhesion molecules and to induction of interferons,
chemokines and finally apoptosis. Int J Oncol. 21:85–93.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fawthrop DJ, Boobis AR and Davies DS:
Mechanisms of cell death. Arch Toxicol. 65:437–444. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Green DR: Apoptotic pathways: paper wraps
stone blunts scissors. Cell. 102:1–4. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Budihardjo I, Oliver H, Lutter M, Luo X
and Wang X: Biochemical pathways of caspase activation during
apoptosis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 15:269–290. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hengartner MO: The biochemistry of
apoptosis. Nature. 407:770–776. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Igney FH and Krammer PH: Death and
anti-death: tumour resistance to apoptosis. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:277–288. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hu S, Vincenz C, Buller M and Dixit VM: A
novel family of viral death effector domain-containing molecules
that inhibit both CD-95-and tumor necrosis factor
receptor-1-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 272:9621–9624. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zamzami N, Marchetti P, Castedo M, Zanin
C, et al: Reduction in mitochondrial potential constitutes an early
irreversible step of programmed lymphocyte death in vivo. J Exp
Med. 181:1661–1672. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Reichard KW, Lorence RM, Cascino CJ,
Peeples ME, et al: Newcastle disease virus selectively kills human
tumor cells. J Surg Res. 52:448–453. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Csatary L, Eckhardt S, Bukosza I, Czegledi
F, et al: Attenuated veterinary virus vaccine for the treatment of
cancer. Cancer Detect Prev. 17:619–627. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Csatary LK and Bakács T: Use of Newcastle
disease virus vaccine (MTH-68/H) in a patient with high-grade
glioblastoma. JAMA. 281:1588–1589. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Schirrmacher V and Fournier P: Newcastle
disease virus: A promising vector for viral therapy, immune
therapy, and gene therapy of cancer. Methods Mol Biol. 542:565–605.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fábián Z, Töröcsik B, Kiss K, Csatary LK,
et al: Induction of apoptosis by a Newcastle disease virus vaccine
(MTH68/H) in PC12 rat phaeochromocytoma cells. Anticancer Res.
21:125–135. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Washburn B, Weigand MA, Grosse-Wilde A,
Janke M, et al: Tnf-related apoptosis-inducing ligand mediates
tumoricidal activity of human monocytes stimulated by Newcastle
disease virus. J Immunol. 170:1814–1821. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Elankumaran S, Rockemann D and Samal SK:
Newcastle disease virus exerts oncolysis by both intrinsic and
extrinsic caspase-dependent pathways of cell death. J Virol.
80:7522–7534. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Molouki A, Hsu YT, Jahanshiri F, Rosli R
and Yusoff K: Newcastle disease virus infection promotes Bax
redistribution to mitochondria and cell death in HeLa cells.
Intervirology. 53:87–94. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
CEC: Council Directive 92/66/EC of 14 July
1992 introducing community measures for the control of Newcastle
disease. Off J Eur Comm. L260:1–20. 1992.
|
|
29
|
Ramanujam P, Tan W, Nathan S and Yusoff K:
Novel peptides that inhibit the propagation of Newcastle disease
virus. Arch Virol. 147:981–993. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nicoletti I, Migliorati G, Pagliacci M,
Grignani F and Riccardi C: A rapid and simple method for measuring
thymocyte apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow
cytometry. J Immunol Methods. 139:271–279. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nagai Y, Hamaguchi M and Toyoda T:
Molecular biology of Newcastle disease virus. Prog Vet Microbiol
Immunol. 5:16–64. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wilde A and Morrison T: Structural and
functional characterization of Newcastle disease virus
polycistronic RNA species. J Virol. 51:71–76. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ravindra P, Tiwari AK, Ratta B, Chaturvedi
U, et al: Newcastle disease virus-induced cytopathic effect in
infected cells is caused by apoptosis. Virus Res. 141:13–20. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ravindra P, Tiwari AK, Ratta B, Chaturvedi
U, Palia SK, Subudhi PK, Kumar R, Sharma B, Rai A and Chauhan R:
Induction of apoptosis in Vero cells by Newcastle disease virus
requires viral replication, de-novo protein synthesis and caspase
activation. Virus Res. 133:285–290. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tyler KL, Squier M, Rodgers SE, Schneider
BE, et al: Differences in the capacity of reovirus strains to
induce apoptosis are determined by the viral attachment protein
sigma 1. J Virol. 69:6972–6979. 1995.
|
|
36
|
Schirrmacher V, Haas C, Bonifer R and
Ertel C: Virus potentiation of tumor vaccine T-cell stimulatory
capacity requires cell surface binding but not infection. Clin
Cancer Res. 3:1135–1148. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zeng J, Fournier P and Schirrmacher V:
Induction of interferon-alpha and tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand in human blood mononuclear cells by
hemagglutininneuraminidase but not F protein of Newcastle disease
virus. Virology. 297:19–30. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Jan JT and Griffin DE: Induction of
apoptosis by sindbis virus occurs at cell entry and does not
require virus replication. J Virol. 73:10296–10302. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ramsey-Ewing A and Moss B: Apoptosis
induced by a post-binding step of vaccinia virus entry into Chinese
hamster ovary cells. Virology. 242:138–149. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Carrascosa AL, Bustos MJ, Nogal ML,
González de Buitrago G and Revilla Y: Apoptosis induced in an early
step of African swine fever virus entry into Vero cells does not
require virus replication. Virology. 294:372–382. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hightower LE and Bratt MA: Protein
synthesis in Newcastle disease virus-infected chicken embryo cells.
J Virol. 13:788–800. 1974.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lam K and Vasconcelos A: Newcastle disease
virus-induced apoptosis in chicken peripheral blood lymphocytes.
Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 44:45–56. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Crompton M: The mitochondrial permeability
transition pore and its role in cell death. Biochem J. 341:233–249.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Revillard JP, Adorini L, Goldman M,
Kabelitz D and Waldmann H: Apoptosis: potential for disease
therapies. Immunol Today. 19:291–293. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Thornberry NA and Lazebnik Y: Caspases:
enemies within. Science. 281:1312–1316. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ravindra P, Tiwari AK, Ratta B, Bais MV,
et al: Time course of Newcastle disease virus-induced apoptotic
pathways. Virus Res. 144:350–354. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Collins PL and Hightower LE: Newcastle
disease virus stimulates the cellular accumulation of stress (heat
shock) mRNAs and proteins. J Virol. 44:703–707. 1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kasibhatla S, Brunner T, Genestier L,
Echeverri F, et al: DNA damaging agents induce expression of Fas
ligand and subsequent apoptosis in T lymphocytes via the activation
of NF-kappa B and AP-1. Mol Cell. 1:543–551. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|