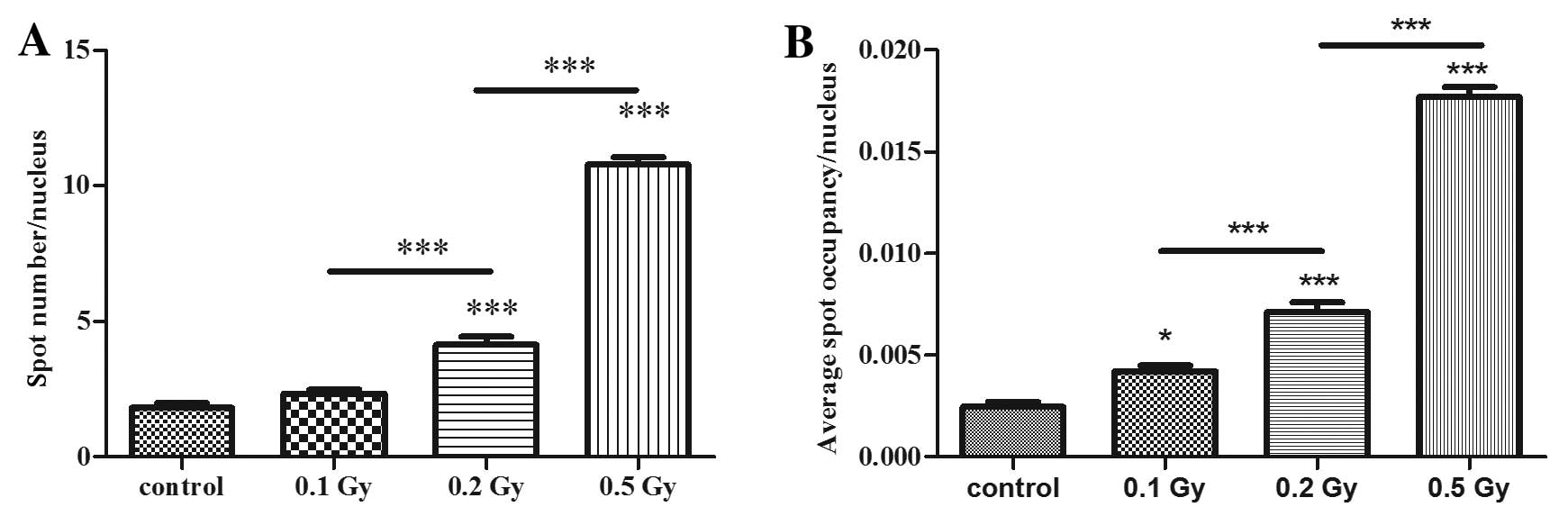
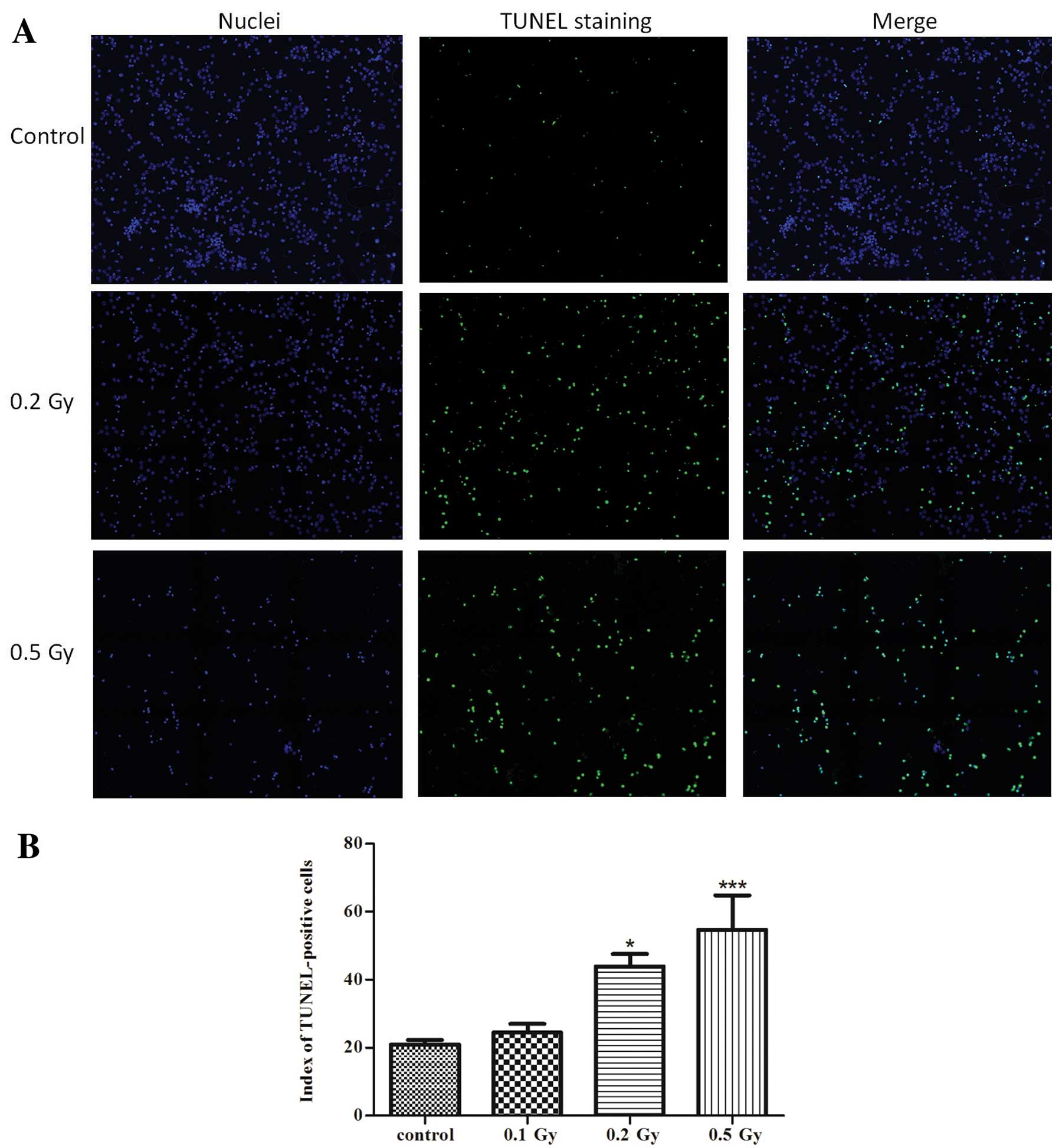
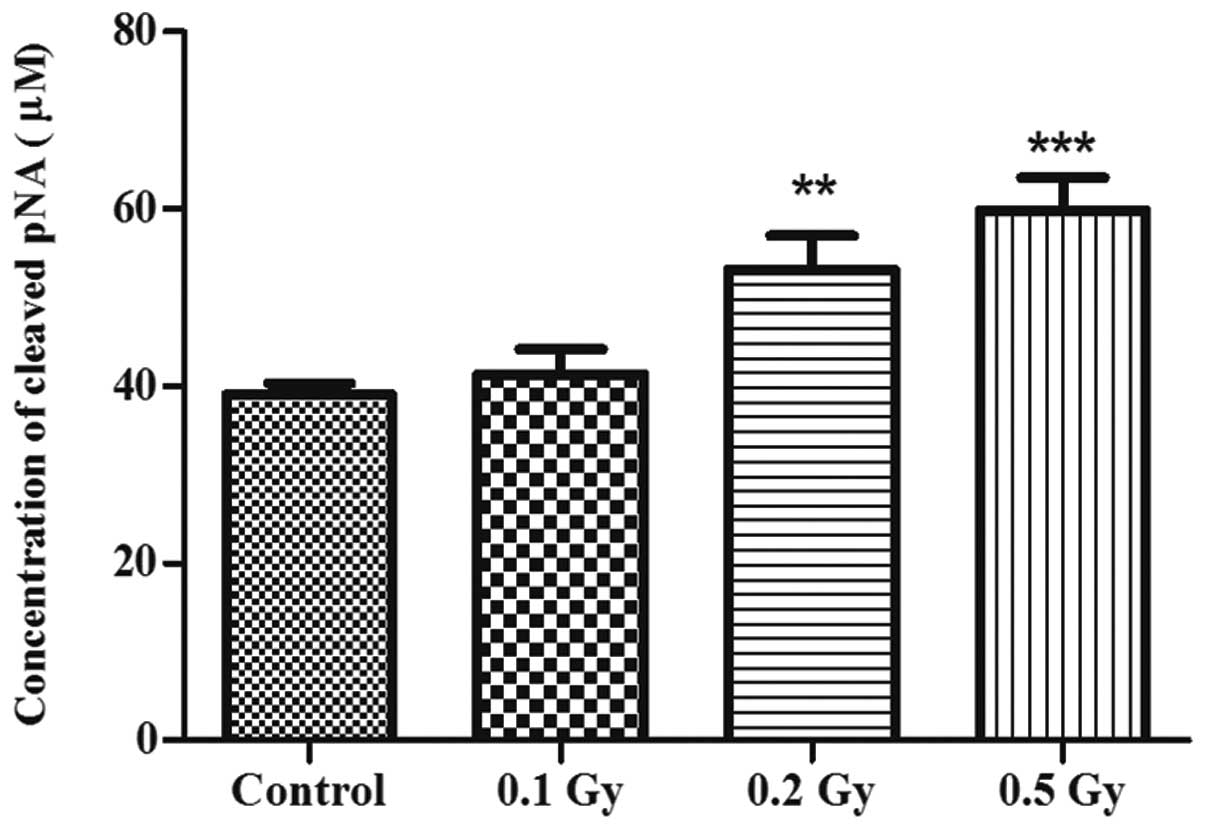
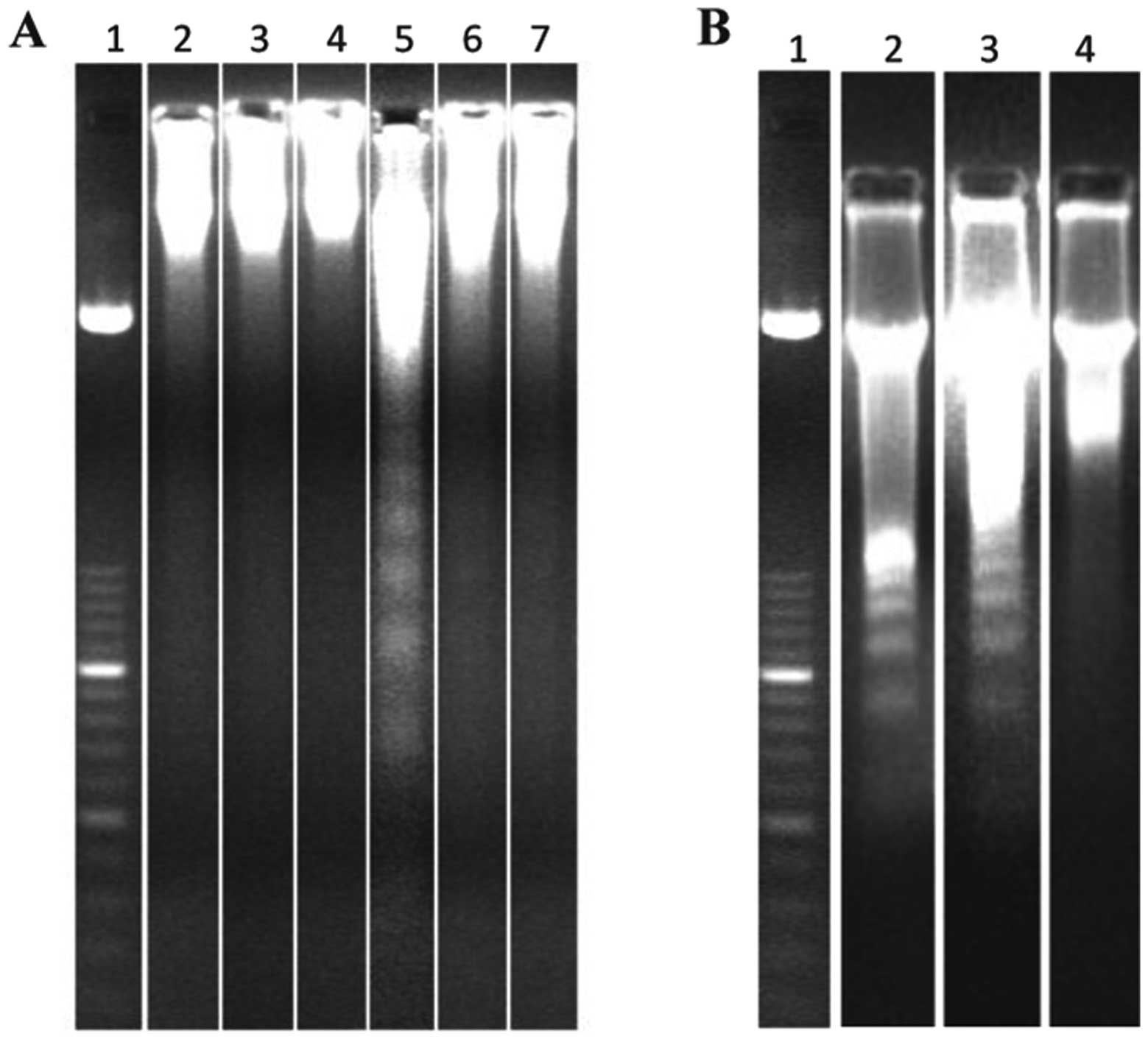
|
1
|
Li YQ, Jay V and Wong CS: Oligodendrocytes
in the adult rat spinal cord undergo radiation-induced apoptosis.
Cancer Res. 56:5417–5422. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Saito S, Aoki I, Sawada K and Suhara T:
Quantitative assessment of central nervous system disorder induced
by prenatal X-ray exposure using diffusion and manganese-enhanced
MRI. NMR Biomed. 25:75–83. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Thabet A, Kalva SP, Liu B, Mueller PR and
Lee SI: Interventional radiology in pregnancy complications:
indications, technique, and methods for minimizing radiation
exposure. Radiographics. 32:255–274. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Otake M and Schull WJ: Radiation-related
brain damage and growth retardation among the prenatally exposed
atomic bomb survivors. Int J Radiat Biol. 74:159–171. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sudhof TC: Neuroligins and neurexins link
synaptic function to cognitive disease. Nature. 455:903–911. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bassell GJ and Warren ST: Fragile X
syndrome: loss of local mRNA regulation alters synaptic development
and function. Neuron. 60:201–214. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Garcia O, Torres M, Helguera P, Coskun P
and Busciglio J: A role for thrombospondin-1 deficits in
astrocyte-mediated spine and synaptic pathology in Down’s syndrome.
PLoS One. 5:e142002010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Luo J: GSK3beta in ethanol neurotoxicity.
Mol Neurobiol. 40:108–121. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zecevic N: Synaptogenesis in layer I of
the human cerebral cortex in the first half of gestation. Cereb
Cortex. 8:245–252. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Balslev Y, Saunders NR and Mollgard K:
Synaptogenesis in the neocortical anlage and early developing
neocortex of rat embryos. Acta Anat (Basel). 156:2–10. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Oppenheim RW: Cell death during
development of the nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 14:453–501.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wolvetang EJ, Wilson TJ, Sanij E, et al:
ETS2 overexpression in transgenic models and in Down syndrome
predisposes to apoptosis via the p53 pathway. Hum Mol Genet.
12:247–255. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Okamoto M, Suzuki Y, Shirai K, et al:
Effect of radiation on the development of immature hippocampal
neurons in vitro. Radiat Res. 172:718–724. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bolaris S, Bozas E, Benekou A, Philippidis
H and Stylianopoulou F: In utero radiation-induced apoptosis and
p53 gene expression in the developing rat brain. Int J Radiat Biol.
77:71–81. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Poulaki V, Benekou A, Bozas E, Bolaris S
and Stylianopoulou F: p53 expression and regulation by NMDA
receptors in the developing rat brain. J Neurosci Res. 56:427–440.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Perez-Otano I and Ehlers MD: Learning from
NMDA receptor trafficking: clues to the development and maturation
of glutamatergic synapses. Neurosignals. 13:175–189. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hynd MR, Scott HL and Dodd PR:
Glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity and neurodegeneration in
Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Int. 45:583–595. 2004.
|
|
18
|
Blandini F: An update on the potential
role of excitotoxicity in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease.
Funct Neurol. 25:65–71. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lipton SA and Rosenberg PA: Excitatory
amino acids as a final common pathway for neurologic disorders. N
Engl J Med. 330:613–622. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Brorson JR, Marcuccilli CJ and Miller RJ:
Delayed antagonism of calpain reduces excitotoxicity in cultured
neurons. Stroke. 26:1259–1267. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Alaoui F, Pratt J, Trocherie S, Court L
and Stutzmann JM: Acute effects of irradiation on the rat brain:
protection by glutamate blockade. Eur J Pharmacol. 276:55–60. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
De Vos WH, Van Neste L, Dieriks B, Joss GH
and Van Oostveldt P: High content image cytometry in the context of
subnuclear organization. Cytometry A. 77:64–75. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Verkhratsky A and Kirchhoff F: NMDA
Receptors in glia. Neuroscientist. 13:28–37. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wallace SS: Enzymatic processing of
radiation-induced free radical damage in DNA. Radiat Res. 150(Suppl
5): S60–S79. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jeggo P and Lavin MF: Cellular
radiosensitivity: how much better do we understand it? Int J Radiat
Biol. 85:1061–1081. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chistiakov DA, Voronova NV and Chistiakov
PA: Genetic variations in DNA repair genes, radiosensitivity to
cancer and susceptibility to acute tissue reactions in
radiotherapy-treated cancer patients. Acta Oncol. 47:809–824. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kurz EU and Lees-Miller SP: DNA
damage-induced activation of ATM and ATM-dependent signaling
pathways. DNA Repair (Amst). 3:889–900. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Harris CC and Hollstein M: Clinical
implications of the p53 tumor-suppressor gene. N Engl J Med.
329:1318–1327. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Verheyde J, de Saint-Georges L, Leyns L
and Benotmane MA: The role of Trp53 in the transcriptional response
to ionizing radiation in the developing brain. DNA Res. 13:65–75.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lai CY, Tsai AC, Chen MC, et al:
Aciculatin induces p53-dependent apoptosis via MDM2 depletion in
human cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 7:e421922012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Laptenko O and Prives C: Transcriptional
regulation by p53: one protein, many possibilities. Cell Death
Differ. 13:951–961. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Koike T, Yang Y, Suzuki K and Zheng X:
Axon and dendrite degeneration: its mechanisms and protective
experimental paradigms. Neurochem Int. 52:751–760. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Vosler PS, Gao Y, Brennan CS, et al:
Ischemia-induced calpain activation causes eukaryotic (translation)
initiation factor 4G1 (eIF4GI) degradation, protein synthesis
inhibition, and neuronal death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:18102–18107. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Arundine M and Tymianski M: Molecular
mechanisms of calcium-dependent neurodegeneration in
excitotoxicity. Cell Calcium. 34:325–337. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Waring P: Redox active calcium ion
channels and cell death. Arch Biochem Biophys. 434:33–42. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wroge CM, Hogins J, Eisenman L and
Mennerick S: Synaptic NMDA receptors mediate hypoxic excitotoxic
death. J Neurosci. 32:6732–6742. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
D’Orsi B, Bonner H, Tuffy LP, et al:
Calpains are downstream effectors of bax-dependent excitotoxic
apoptosis. J Neurosci. 32:1847–1858. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tenneti L and Lipton SA: Involvement of
activated caspase-3-like proteases in N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced
apoptosis in cerebrocortical neurons. J Neurochem. 74:134–142.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Taylor RC, Cullen SP and Martin SJ:
Apoptosis: controlled demolition at the cellular level. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:231–241. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Siman R and Noszek JC: Excitatory amino
acids activate calpain I and induce structural protein breakdown in
vivo. Neuron. 1:279–287. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Czogalla A and Sikorski AF: Spectrin and
calpain: a ‘target’ and a ‘sniper’ in the pathology of neuronal
cells. Cell Mol Life Sci. 62:1913–1924. 2005.
|
|
42
|
Bano D, Young KW, Guerin CJ, et al:
Cleavage of the plasma membrane Na+/Ca2+
exchanger in excitotoxicity. Cell. 120:275–285. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
French JP, Quindry JC, Falk DJ, et al:
Ischemia-reperfusion-induced calpain activation and SERCA2a
degradation are attenuated by exercise training and calpain
inhibition. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 290:H128–H136. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wu HY, Tomizawa K, Oda Y, et al: Critical
role of calpain-mediated cleavage of calcineurin in excitotoxic
neurodegeneration. J Biol Chem. 279:4929–4940. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Saito Y, Nishio K, Ogawa Y, et al:
Molecular mechanisms of 6-hydroxydopamine-induced cytotoxicity in
PC12 cells: involvement of hydrogen peroxide-dependent and
-independent action. Free Radic Biol Med. 42:675–685. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Boehmerle W and Endres M: Salinomycin
induces calpain and cytochrome c-mediated neuronal cell death. Cell
Death Dis. 2:e1682011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Blomgren K, Zhu C, Wang X, et al:
Synergistic activation of caspase-3 by m-calpain after neonatal
hypoxia-ischemia: a mechanism of ‘pathological apoptosis’. J Biol
Chem. 276:10191–10198. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
McGinnis KM, Gnegy ME, Park YH, Mukerjee N
and Wang KK: Procaspase-3 and poly(ADP)ribose polymerase (PARP) are
calpain substrates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 263:94–99. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Komarova EA, Chernov MV, Franks R, et al:
Transgenic mice with p53-responsive lacZ: p53 activity varies
dramatically during normal development and determines radiation and
drug sensitivity in vivo. EMBO J. 16:1391–1400. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Morris EJ, Keramaris E, Rideout HJ, et al:
Cyclin-dependent kinases and P53 pathways are activated
independently and mediate Bax activation in neurons after DNA
damage. J Neurosci. 21:5017–5026. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Djebaili M, Rondouin G, Baille V and
Bockaert J: p53 and Bax implication in NMDA induced-apoptosis in
mouse hippocampus. Neuroreport. 11:2973–2976. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Sedarous M, Keramaris E, O’Hare M, et al:
Calpains mediate p53 activation and neuronal death evoked by DNA
damage. J Biol Chem. 278:26031–26038. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hama Y, Katsuki H, Izumi Y, Kume T and
Akaike A: Excitotoxicity-associated p53 expression in adult rat
retina is mediated by calpain activity but not by Cl−
influx. J Pharmacol Sci. 110:493–496. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|