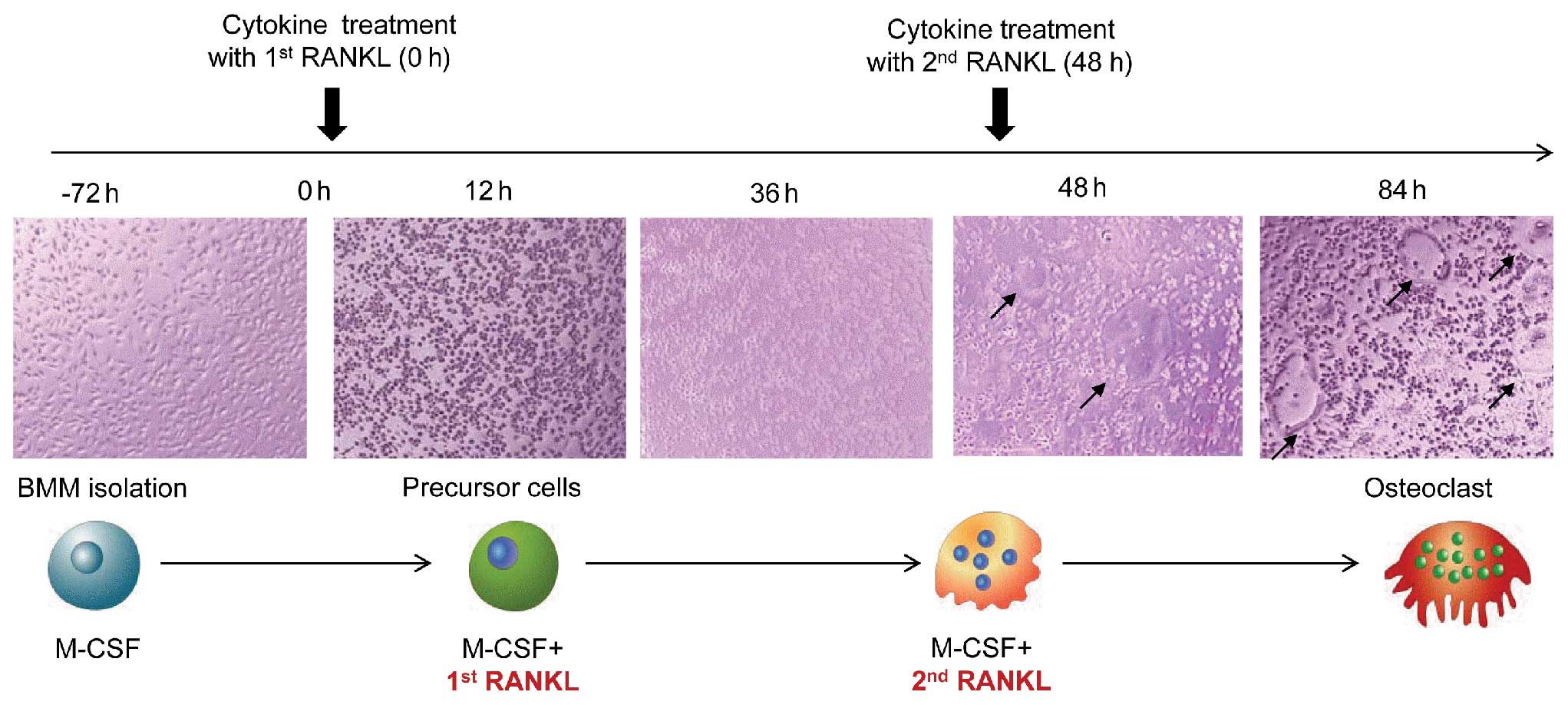
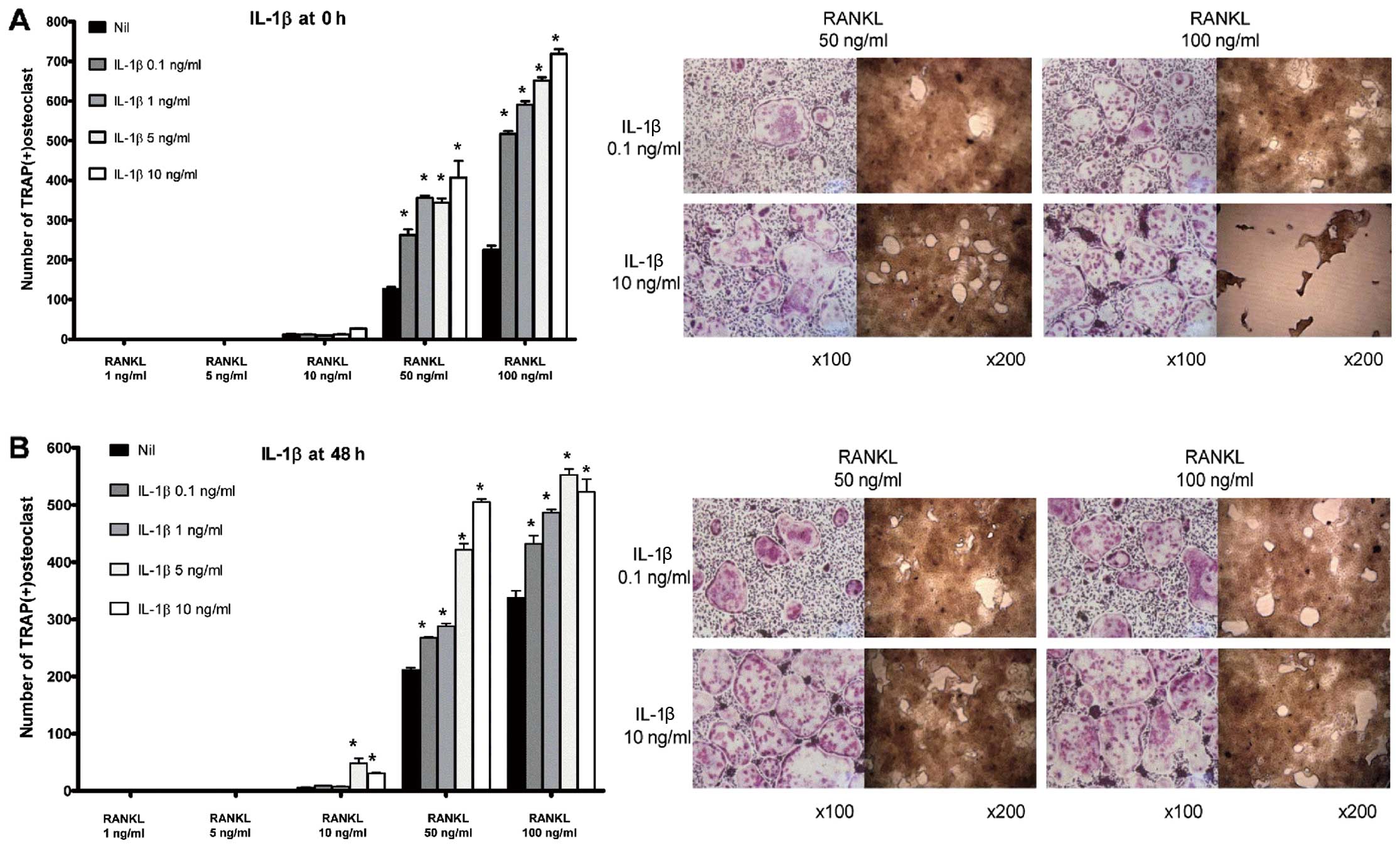
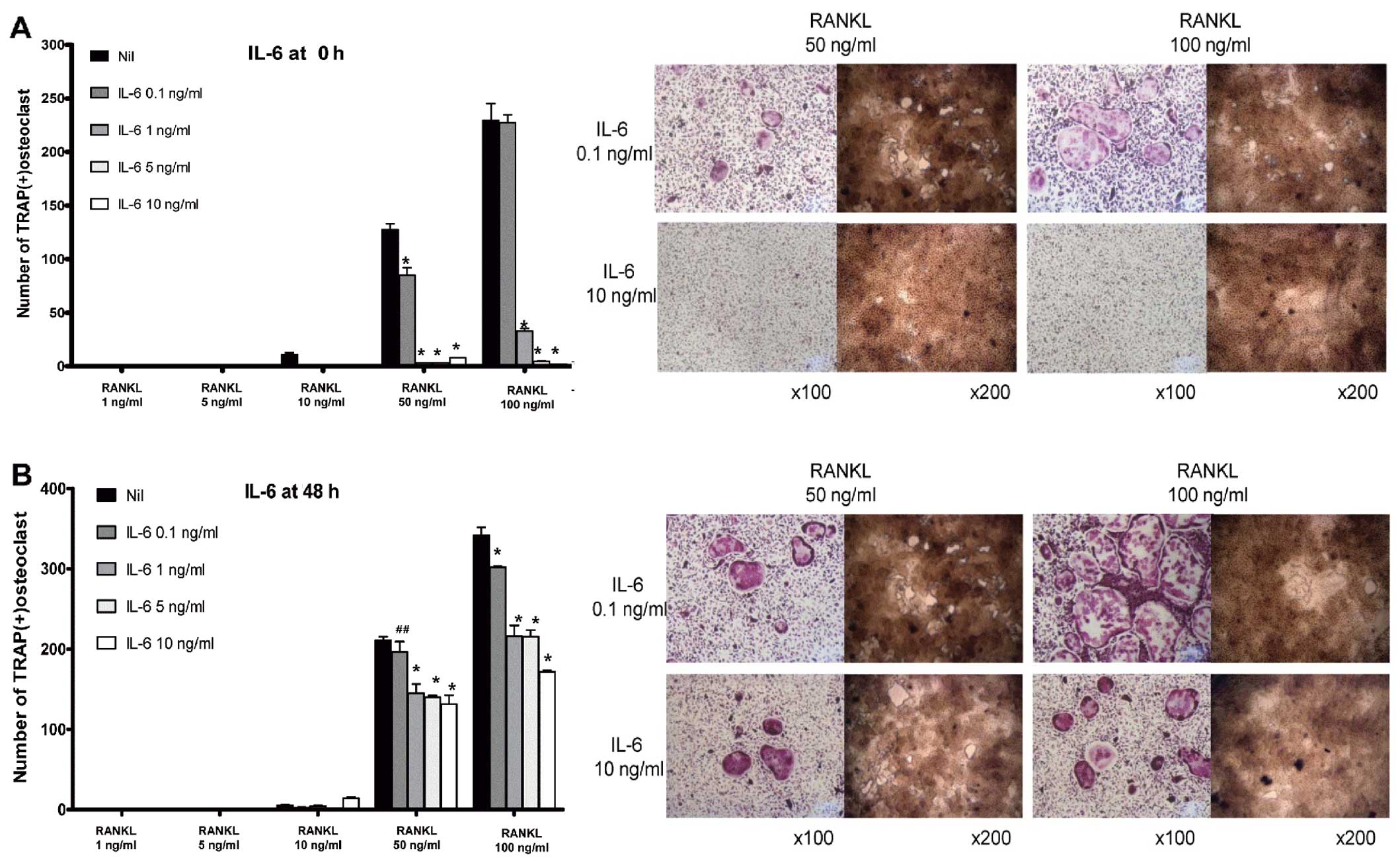
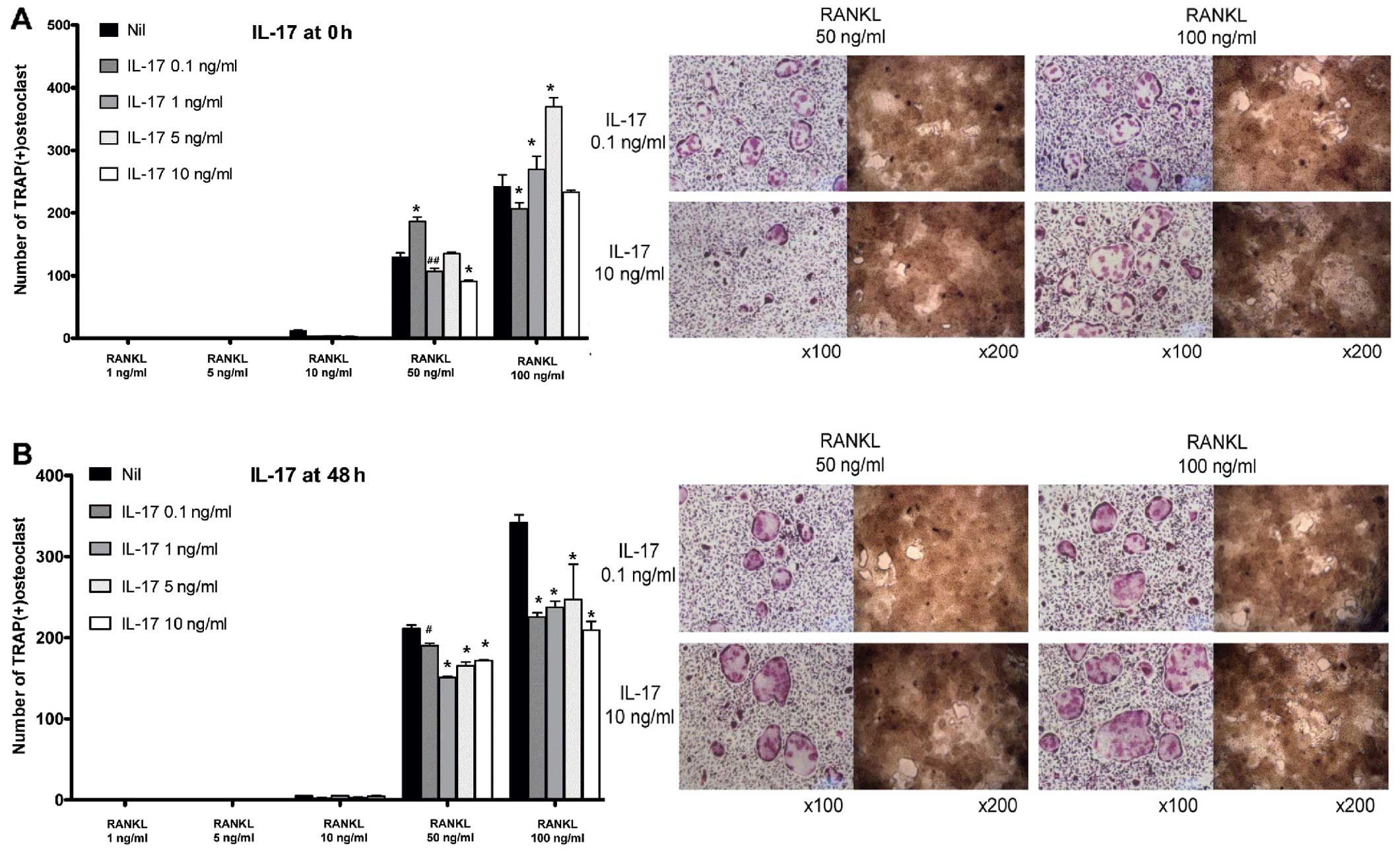
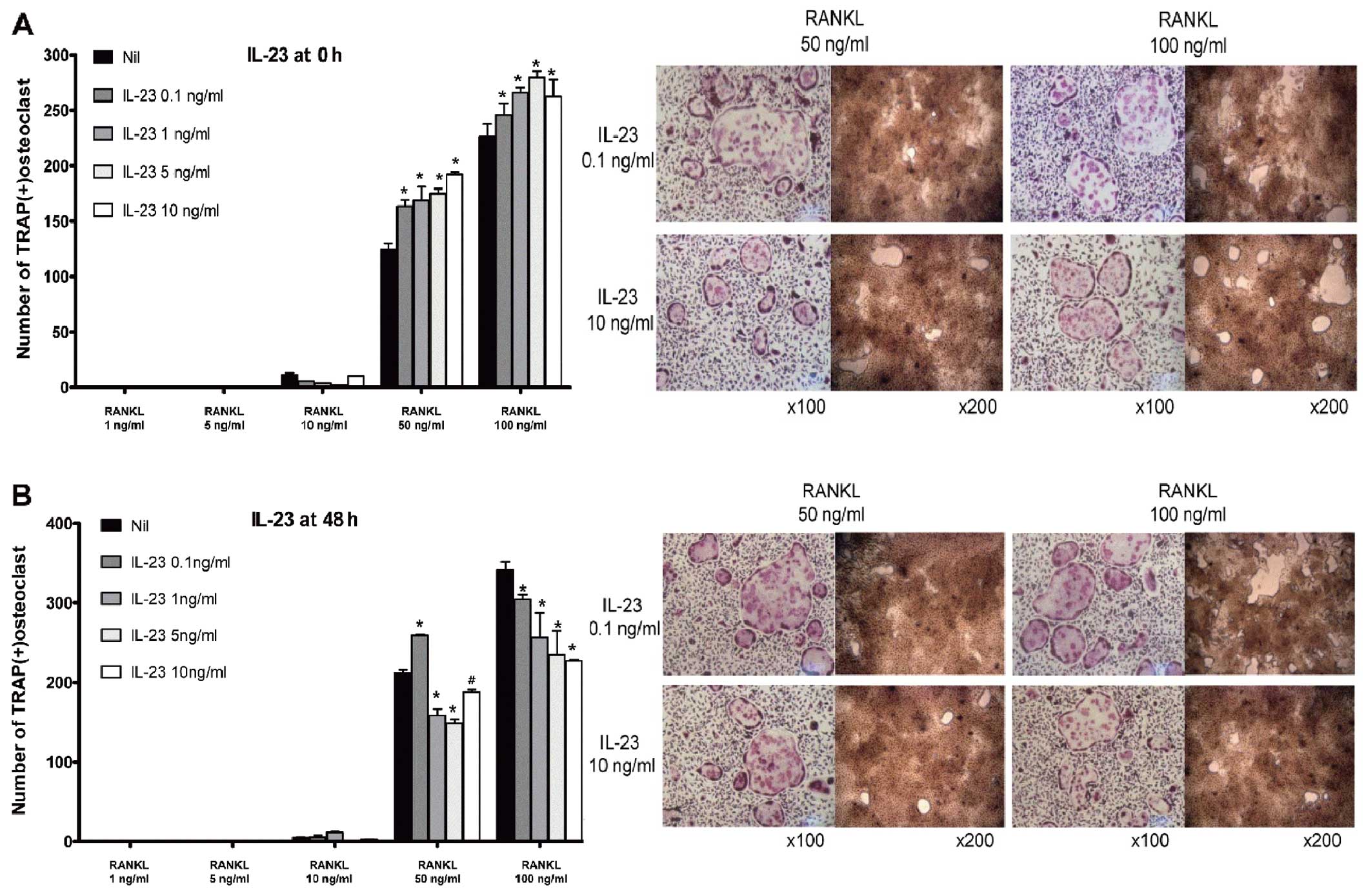
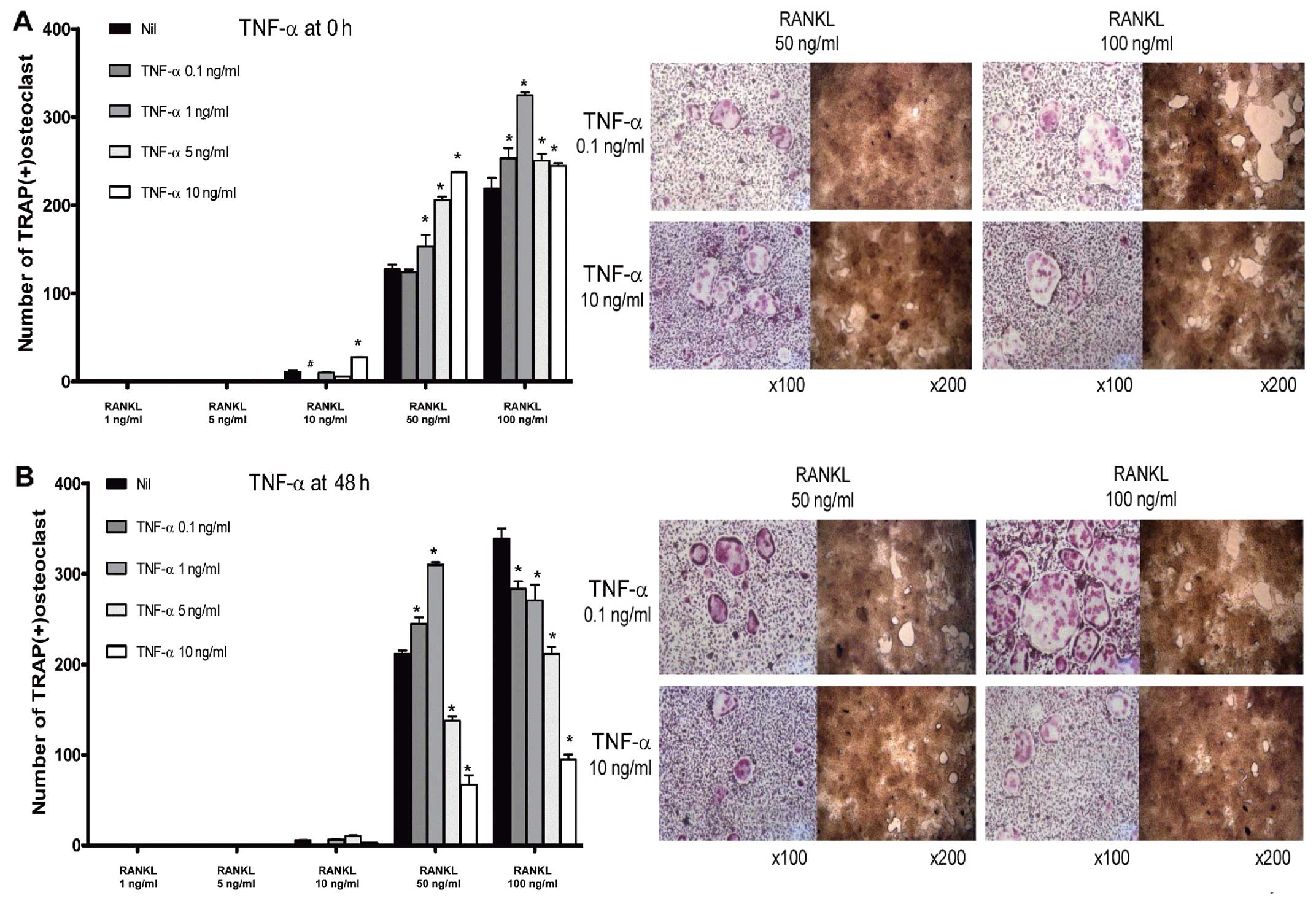
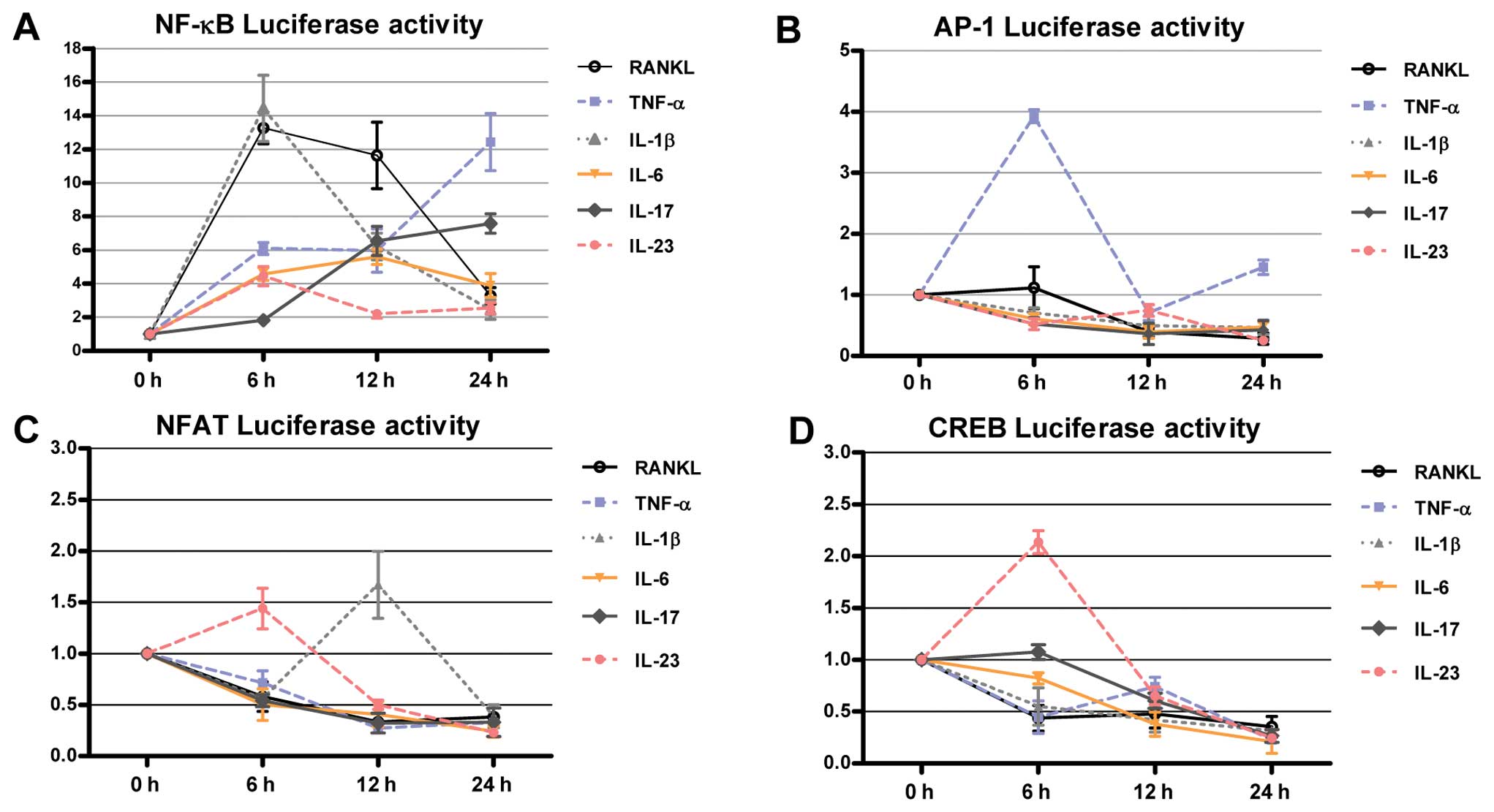
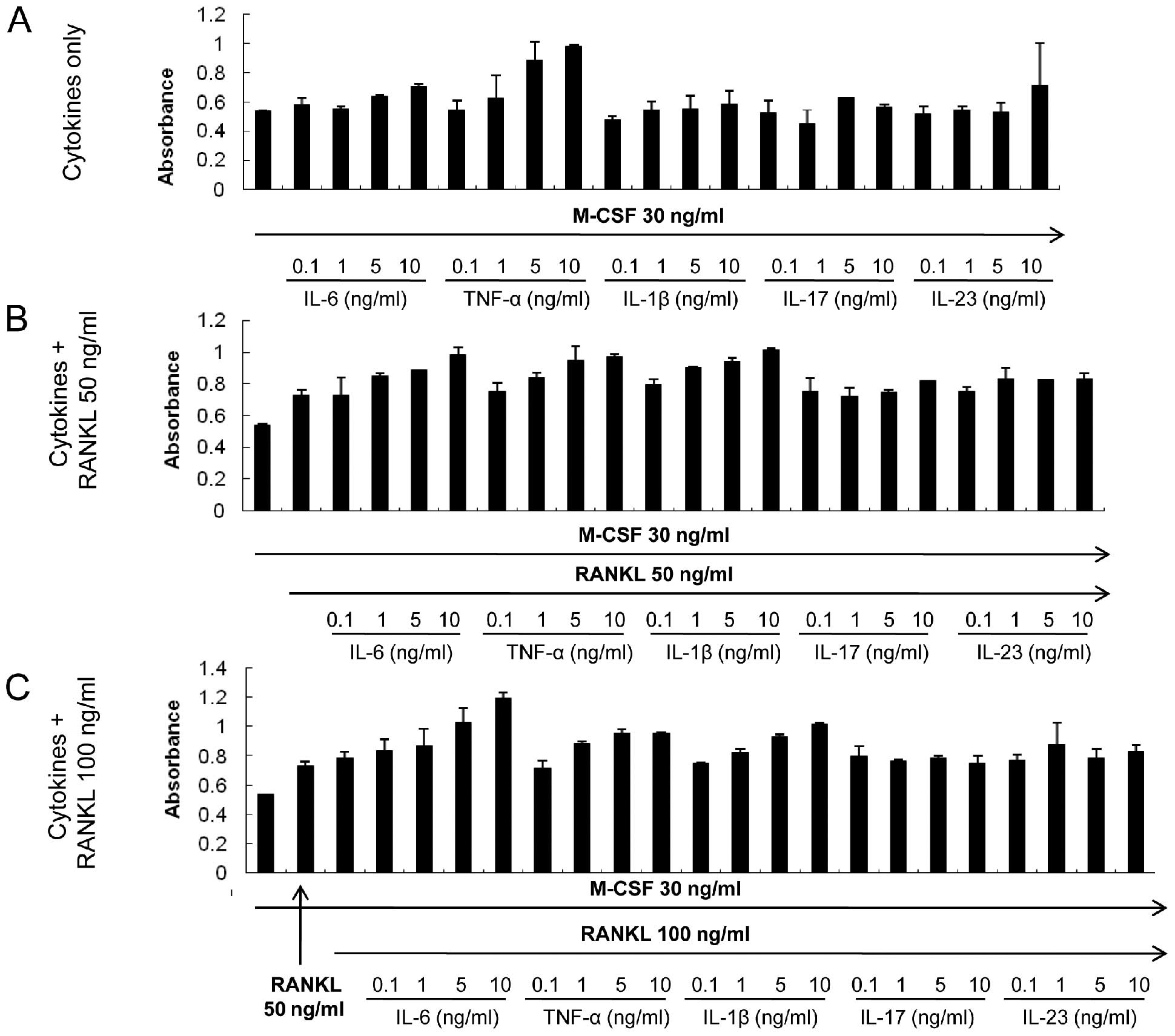
|
1
|
Sato K and Takayanagi H: Osteoclasts,
rheumatoid arthritis, and osteoimmunology. Curr Opin Rheumatol.
18:419–426. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schett G: Osteoimmunology in rheumatic
diseases. Arthritis Res Ther. 11:2102009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gravallese EM, Manning C, Tsay A, Naito A,
Pan C, Amento E and Goldring SR: Synovial tissue in rheumatoid
arthritis is a source of osteoclast differentiation factor.
Arthritis Rheum. 43:250–258. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Martin TJ and Ng KW: Mechanisms by which
cells of the osteoblast lineage control osteoclast formation and
activity. J Cell Biochem. 56:357–366. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Alnaeeli M, Penninger JM and Teng YT:
Immune interactions with CD4+ T cells promote the
development of functional osteoclasts from murine CD11c+
dendritic cells. J Immunol. 177:3314–3326. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Choi Y, Woo KM, Ko SH, Lee YJ, Park SJ,
Kim HM and Kwon BS: Osteoclastogenesis is enhanced by activated B
cells but suppressed by activated CD8(+) T cells. Eur J Immunol.
31:2179–2188. 2001.
|
|
7
|
Xing L, Schwarz EM and Boyce BF:
Osteoclast precursors, RANKL/RANK, and immunology. Immunol Rev.
208:19–29. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cappellen D, Luong-Nguyen NH, Bongiovanni
S, Grenet O, Wanke C and Susa M: Transcriptional program of mouse
osteoclast differentiation governed by the macrophage
colony-stimulating factor and the ligand for the receptor activator
of NFkappa B. J Biol Chem. 277:21971–21982. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kim KW, Cho ML, Lee SH, Oh HJ, Kang CM, Ju
JH, Min SY, Cho YG, Park SH and Kim HY: Human rheumatoid synovial
fibroblasts promote osteoclastogenic activity by activating RANKL
via TLR-2 and TLR-4 activation. Immunol Lett. 110:54–64. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Horwood NJ, Kartsogiannis V, Quinn JM,
Romas E, Martin TJ and Gillespie MT: Activated T lymphocytes
support osteoclast formation in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
265:144–150. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pettit AR, Walsh NC, Manning C, Goldring
SR and Gravallese EM: RANKL protein is expressed at the pannus-bone
interface at sites of articular bone erosion in rheumatoid
arthritis. Rheumatology. 45:1068–1076. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Schett G, Hayer S, Zwerina J, Redlich K
and Smolen JS: Mechanisms of disease: the link between RANKL and
arthritic bone disease. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 1:47–54. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang YH, Heulsmann A, Tondravi MM,
Mukherjee A and Abu-Amer Y: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF)
stimulates RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis via coupling of TNF
type 1 receptor and RANK signaling pathways. J Biol Chem.
276:563–568. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
O’ Gradaigh D, Ireland D, Bord S and
Compston JE: Joint erosion in rheumatoid arthritis: interactions
between tumour necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 1, and receptor
activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand (RANKL) regulate
osteoclasts. Ann Rheum Dis. 63:354–359. 2004.
|
|
15
|
Tamura T, Udagawa N, Takahashi N, Miyaura
C, Tanaka S, Yamada Y, Koishihara Y, Ohsugi Y, Kumaki K, Taga T, et
al: Soluble interleukin-6 receptor triggers osteoclast formation by
interleukin 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 90:11924–11928. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lubberts E, van den Bersselaar L,
Oppers-Walgreen B, Schwarzenberger P, Coenen-de Roo CJ, Kolls JK,
Joosten LA and van den Berg WB: IL-17 promotes bone erosion in
murine collagen-induced arthritis through loss of the receptor
activator of NF-kappa B ligand/osteoprotegerin balance. J Immunol.
170:2655–2662. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ju JH, Cho ML, Moon YM, Oh HJ, Park JS,
Jhun JY, Min SY, Cho YG, Park KS, Yoon CH, Min JK, Park SH, Sung YC
and Kim HY: IL-23 induces receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand
expression on CD4+ T cells and promotes
osteoclastogenesis in an autoimmune arthritis model. J Immunol.
181:1507–1518. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kobayashi K, Takahashi N, Jimi E, Udagawa
N, Takami M, Kotake S, Nakagawa N, Kinosaki M, Yamaguchi K, Shima
N, Yasuda H, Morinaga T, Higashio K, Martin TJ and Suda T: Tumor
necrosis factor alpha stimulates osteoclast differentiation by a
mechanism independent of the ODF/RANKL-RANK interaction. J Exp Med.
191:275–286. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim JH, Jin HM, Kim K, Song I, Youn BU,
Matsuo K and Kim N: The mechanism of osteoclast differentiation
induced by IL-1. J Immunol. 183:1862–1870. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kudo O, Sabokbar A, Pocock A, Itonaga I,
Fujikawa Y and Athanasou NA: Interleukin-6 and interleukin-11
support human osteoclast formation by a RANKL-independent
mechanism. Bone. 32:1–7. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lam J, Takeshita S, Barker JE, Kanagawa O,
Ross FP and Teitelbaum SL: TNF-alpha induces osteoclastogenesis by
direct stimulation of macrophages exposed to permissive levels of
RANK ligand. J Clin Invest. 106:1481–1488. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Akatsu T, Takahashi N, Debari K, Morita I,
Murota S, Nagata N, Takatani O and Suda T: Prostaglandins promote
osteoclastlike cell formation by a mechanism involving cyclic
adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate in mouse bone marrow cell cultures. J
Bone Miner Res. 4:29–35. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Baker-LePain JC, Nakamura MC and Lane NE:
Effects of inflammation on bone: an update. Curr Opin Rheumatol.
23:389–395. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Brennan FM and McInnes IB: Evidence that
cytokines play a role in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest.
118:3537–3545. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Walsh NC, Crotti TN, Goldring SR and
Gravallese EM: Rheumatic diseases: the effects of inflammation on
bone. Immunol Rev. 208:228–251. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tracey D, Klareskog L, Sasso EH, Salfeld
JG and Tak PP: Tumor necrosis factor antagonist mechanisms of
action: a comprehensive review. Pharmacol Ther. 117:244–279. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Furst DE: Anakinra: review of recombinant
human interleukin-I receptor antagonist in the treatment of
rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Ther. 26:1960–1975. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gabay C, Lamacchia C and Palmer G: IL-1
pathways in inflammation and human diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol.
6:232–241. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fonseca JE, Santos MJ, Canhao H and Choy
E: Interleukin-6 as a key player in systemic inflammation and joint
destruction. Autoimmun Rev. 8:538–542. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yago T, Nanke Y, Kawamoto M, Furuya T,
Kobashigawa T, Kamatani N and Kotake S: IL-23 induces human
osteoclastogenesis via IL-17 in vitro, and anti-IL-23 antibody
attenuates collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Arthritis Res Ther.
9:R962007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Koenders MI, Lubberts E, Oppers-Walgreen
B, van den Bersselaar L, Helsen MM, Di Padova FE, Boots AM, Gram H,
Joosten LA and van den Berg WB: Blocking of interleukin-17 during
reactivation of experimental arthritis prevents joint inflammation
and bone erosion by decreasing RANKL and interleukin-1. Am J
Pathol. 167:141–149. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|