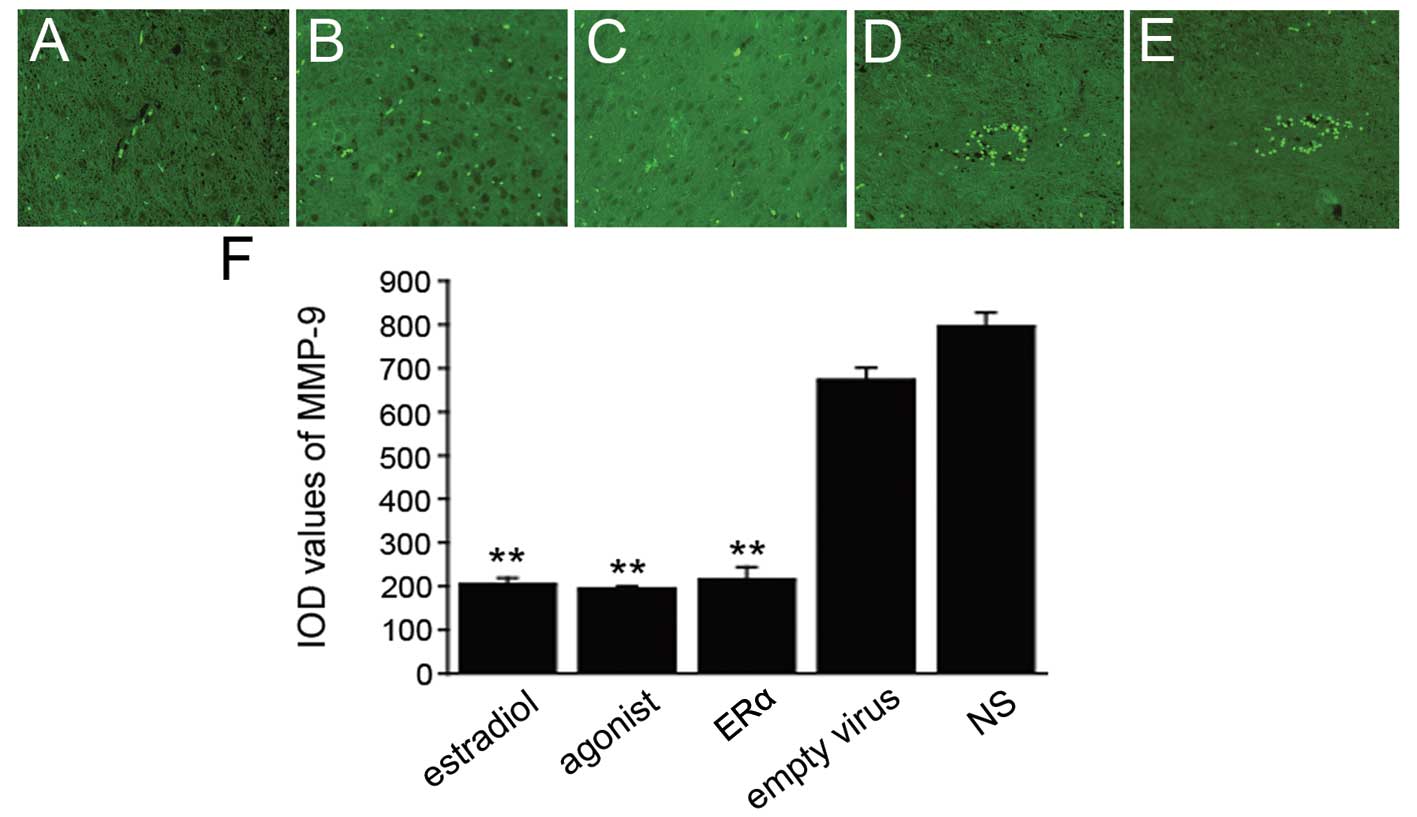
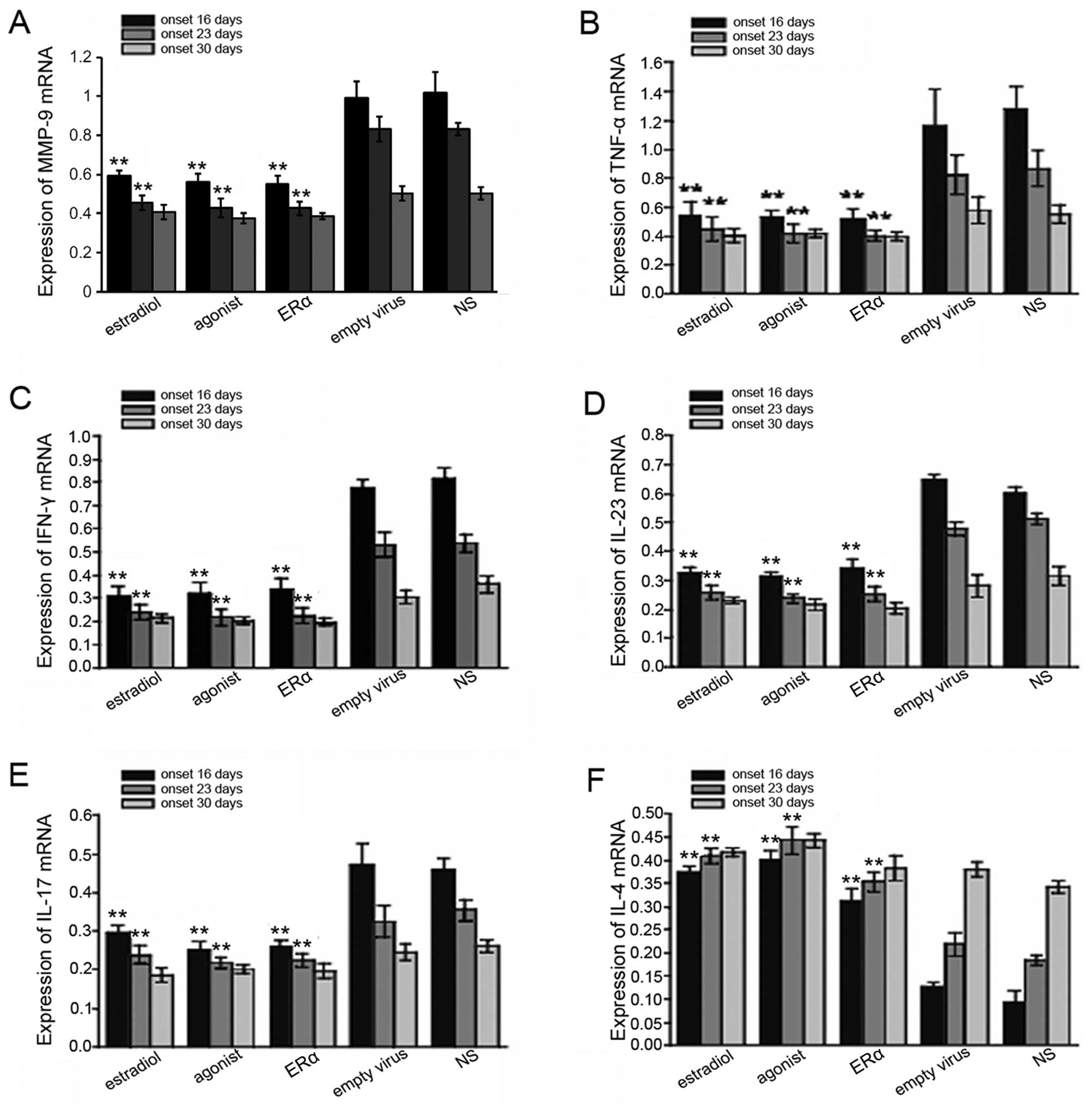
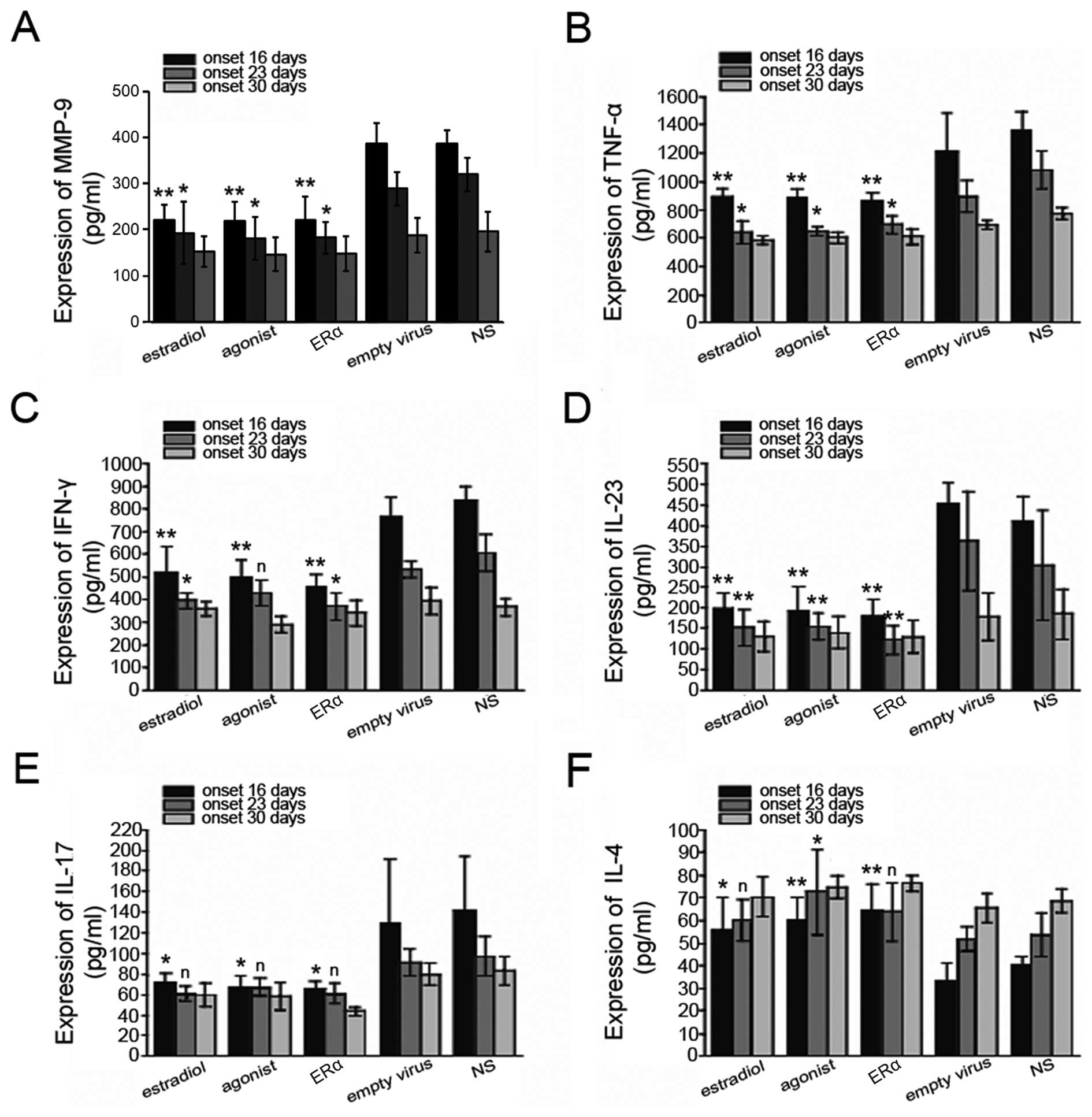
|
1
|
Ouallet J, Baumann N, Marie Y and
Villarroya H: Fas system up-regulation in experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis. J Neurol Sci. 170:96–104. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Barac-Latas V, Muhvic D and
Radosevic-Stabic B: The influence of pregnancy on development and
course of chronic relapsing experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis in rats: implications for multiple sclerosis.
Coll Antropol. 34(Suppl 1): 267–271. 2010.
|
|
3
|
Runmarker B and Andersen O: Pregnancy is
associated with a lower risk of onset and a better prognosis in
multiple sclerosis. Brain. 118:253–261. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Confavreux C, Hutchinson M, Hours MM,
Cortinovis-Tourniaire P and Moreau T: Rate of pregnancy-related
relapse in multiple sclerosis. Pregnancy in Multiple Sclerosis
Group. N Engl J Med. 339:285–291. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Niino M, Hirotani M, Fukazawa T, Kikuchi S
and Sasaki H: Estrogens as potential therapeutic agents in multiple
sclerosis. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 9:87–94. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sicotte NL, Liva SM, Klutch R, et al:
Treatment of multiple sclerosis with the pregnancy hormone estriol.
Ann Neurol. 52:421–428. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Soldan SS, Alvarez Retuerto AI, Sicotte NL
and Voskuhl RR: Immune modulation in multiple sclerosis patients
treated with the pregnancy hormone estriol. J Immunol.
171:6267–6274. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lelu K, Laffont S, Delpy L, et al:
Estrogen receptor alpha signaling in T lymphocytes is required for
estradiol-mediated inhibition of Th1 and Th17 cell differentiation
and protection against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J
Immunol. 187:2386–2393. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wang C, Dehghani B, Li Y, et al: Membrane
estrogen receptor regulates experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis through up-regulation of programmed death 1. J
Immunol. 182:3294–3303. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Bodhankar S, Wang C, Vandenbark AA and
Offner H: Estrogen- induced protection against experimental
autoimmune encephalomyelitis is abrogated in the absence of B
cells. Eur J Immunol. 41:1165–1175. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Subramanian S, Yates M, Vandenbark AA and
Offner H: Oestrogen-mediated protection of experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis in the absence of Foxp3+ regulatory T
cells implicates compensatory pathways including regulatory B
cells. Immunology. 132:340–347. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gold SM and Voskuhl RR: Estrogen treatment
in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci. 286:99–103. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
MacKenzie-Graham AJ, Rinek GA, Avedisian
A, et al: Estrogen treatment prevents gray matter atrophy in
experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neurosci Res.
90:1310–1323. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ziehn MO, Avedisian AA, Dervin SM, O’Dell
TJ and Voskuhl RR: Estriol preserves synaptic transmission in the
hippocampus during autoimmune demyelinating disease. Lab Invest.
92:1234–1245. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Giraud SN, Caron CM, Pham-Dinh D, Kitabgi
P and Nicot AB: Estradiol inhibits ongoing autoimmune
neuroinflammation and NFkappaB-dependent CCL2 expression in
reactive astrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:8416–8421. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bodhankar S and Offner H: Gpr30 forms an
integral part of E2-protective pathway in experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis. Immunol Endocr Metab Agents Med Chem.
11:262–274. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Matejuk A, Bakke AC, Hopke C, Dwyer J,
Vandenbark AA and Offner H: Estrogen treatment induces a novel
population of regulatory cells, which suppresses experimental
autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neurosci Res. 77:119–126. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Tiwari-Woodruff S and Voskuhl RR:
Neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of estrogen receptor
ligand treatment in mice. J Neurol Sci. 286:81–85. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Du S, Sandoval F, Trinh P, Umeda E and
Voskuhl R: Estrogen receptor-beta ligand treatment modulates
dendritic cells in the target organ during autoimmune demyelinating
disease. Eur J Immunol. 41:140–150. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Blasko E, Haskell CA, Leung S, et al:
Beneficial role of the GPR30 agonist G-1 in an animal model of
multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol. 214:67–77. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Subramanian S, Miller LM, Grafe MR,
Vandenbark AA and Offner H: Contribution of GPR30 for 1,25
dihydroxyvitamin D(3) protection in EAE. Metab Brain Dis. 27:29–35.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lelu K, Delpy L, Robert V, et al:
Endogenous estrogens, through estrogen receptor alpha, constrain
autoimmune inflammation in female mice by limiting CD4+
T-cell homing into the CNS. Eur J Immunol. 40:3489–3498. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gold SM, Sasidhar MV, Morales LB, et al:
Estrogen treatment decreases matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 in
autoimmune demyelinating disease through estrogen receptor alpha
(ERalpha). Lab Invest. 89:1076–1083. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Spence RD, Hamby ME, Umeda E, et al:
Neuroprotection mediated through estrogen receptor-alpha in
astrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:8867–8872. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wong LF, Goodhead L, Prat C, Mitrophanous
KA, Kingsman SM and Mazarakis ND: Lentivirus-mediated gene transfer
to the central nervous system: therapeutic and research
applications. Hum Gene Ther. 17:1–9. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Foster TC, Rani A, Kumar A, Cui L and
Semple-Rowland SL: Viral vector-mediated delivery of estrogen
receptor-alpha to the hippocampus improves spatial learning in
estrogen receptor-alpha knockout mice. Mol Ther. 16:1587–1593.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Brewer GJ, Torricelli JR, Evege EK and
Price PJ: Optimized survival of hippocampal neurons in
B27-supplemented Neurobasal, a new serum-free medium combination. J
Neurol Sci. 35:567–576. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hu X, Lei L, Yuan J, Xing W, WJY and Qin
X: Construction of recombinant lentivirus carrying mouse estrogen
receptor α and identification in infected neurons. Acad J Sec Mil
Med Univ. 32:160–166. 2011.
|
|
29
|
Tiwari-Woodruff S, Morales LB, Lee R and
Voskuhl RR: Differential neuroprotective and antiinflammatory
effects of estrogen receptor (ER)alpha and ERbeta ligand treatment.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:14813–14818. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tapia-Gonzalez S, Carrero P, Pernia O,
Garcia-Segura LM and Diz-Chaves Y: Selective Er modulators reduce
microglia reactivity in vivo after peripheral inflammation:
potential role of microglial ERs. J Endocrinol. 198:219–230. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Legge KL, Min B, Bell JJ, et al: Coupling
of peripheral tolerance to endogenous interleukin 10 promotes
effective modulation of myelin-activated T cells and ameliorates
experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Exp Med. 191:2039–2052.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Murphy AC, Lalor SJ, Lynch MA and Mills
KH: Infiltration of Th1 and Th17 cells and activation of microglia
in the CNS during the course of experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis. Brain Behav Immun. 24:641–651. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jacobs EC: Genetic alterations in the
mouse myelin basic proteins result in a range of dysmyelinating
disorders. J Neurol Sci. 228:195–197. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Molineaux SM, Engh H, De Ferra F, Hudson L
and Lazzarini RA: Recombination within the myelin basic protein
gene created the dysmyelinating shiverer mouse mutation. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 83:7542–7546. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fainardi E, Castellazzi M, Bellini T, et
al: Cerebrospinal fluid and serum levels and intrathecal production
of active MMP-9 as markers of disease activity in patients with
multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler. 12:294–301. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kurzepa J, Bartosik-Psujek H,
Suchozebrska-Jesionek D, Rejdak K, Stryjecka-Zimmer M and
Stelmasiak Z: Role of matrix metalloproteinases in the pathogenesis
of multiple sclerosis. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 39:63–67. 2005.(In
Polish).
|
|
37
|
Rubinson DA, Dillon CP, Kwiatkowski AV, et
al: A lentivirus-based system to functionally silence genes in
primary mammalian cells, stem cells and transgenic mice by RNA
interference. Nat Genet. 33:401–406. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Trobridge G and Russell DW: Cell cycle
requirements for transduction by foamy virus vectors compared to
those of oncovirus and lentivirus vectors. J Virol. 78:2327–2335.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yip PK, Wong LF, Pattinson D, et al:
Lentiviral vector expressing retinoic acid receptor beta2 promotes
recovery of function after corticospinal tract injury in the adult
rat spinal cord. Hum Mol Genet. 15:3107–3118. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ambrosino C, Tarallo R, Bamundo A, et al:
Identification of a hormone-regulated dynamic nuclear actin network
associated with estrogen receptor alpha in human breast cancer cell
nuclei. Mol Cell Proteomics. 9:1352–1367. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Vigna E and Naldini L: Lentiviral vectors:
excellent tools for experimental gene transfer and promising
candidates for gene therapy. J Gene Med. 2:308–316. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bruck W: The pathology of multiple
sclerosis is the result of focal inflammatory demyelination with
axonal damage. J Neurol. 252(Suppl 5): v3–v9. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu HY, Buenafe AC, Matejuk A, et al:
Estrogen inhibition of EAE involves effects on dendritic cell
function. J Neurol Sci. 70:238–248. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Baumann N and Pham-Dinh D: Biology of
oligodendrocyte and myelin in the mammalian central nervous system.
Physiol Rev. 81:871–927. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Daigle JL, Hong JH, Chiang CS and McBride
WH: The role of tumor necrosis factor signaling pathways in the
response of murine brain to irradiation. Cancer Res. 61:8859–8865.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Griffiths I, Klugmann M, Anderson T, et
al: Axonal swellings and degeneration in mice lacking the major
proteolipid of myelin. Science. 280:1610–1613. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
De Rosbo NK and Bernard CC: Multiple
sclerosis brain immunoglobulins stimulate myelin basic protein
degradation in human myelin: a new cause of demyelination. J
Neurochem. 53:513–518. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Einstein ER, Csejtey J, Dalal KB, Adams
CW, Bayliss OB and Hallpike JF: Proteolytic activity and basic
protein loss in and around multiple sclerosis plaques: combined
biochemical and histochemical observations. J Neurochem.
19:653–662. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Harauz G, Ishiyama N, Hill CM, Bates IR,
Libich DS and Fares C: Myelin basic protein-diverse conformational
states of an intrinsically unstructured protein and its roles in
myelin assembly and multiple sclerosis. Micron. 35:503–542. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Crawford DK, Mangiardi M, Song B, et al:
Oestrogen receptor beta ligand: a novel treatment to enhance
endogenous functional remyelination. Brain. 133:2999–3016. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Garay L, Gonzalez Deniselle MC, Gierman L,
et al: Steroid protection in the experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis model of multiple sclerosis.
Neuroimmunomodulation. 15:76–83. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Sarkaki A, Amani R, Badavi M, et al:
Pre-treatment effect of different doses of soy isoflavones on
spatial learning and memory in an ovariectomized animal model of
Alzheimer’s disease. Pak J Biol Sci. 11:1114–1119. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sheldahl LC, Marriott LK, Bryant DM,
Shapiro RA and Dorsa DM: Neuroprotective effects of estrogen and
selective estrogen receptor modulators begin at the plasma
membrane. Minerva Endocrinol. 32:87–94. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Riggs BL and Hartmann LC: Selective
estrogen-receptor modulators - mechanisms of action and application
to clinical practice. N Engl J Med. 348:618–629. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Chitnis T and Khoury SJ: Cytokine shifts
and tolerance in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Immunol
Res. 28:223–239. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
McGeachy MJ and Anderton SM: Cytokines in
the induction and resolution of experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis. Cytokine. 32:81–84. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Suryani S and Sutton I: An
interferon-gamma-producing Th1 subset is the major source of IL-17
in experimental autoimmune encephalitis. J Neuroimmunol.
183:96–103. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Butti E, Bergami A, Recchia A, et al: IL4
gene delivery to the CNS recruits regulatory T cells and induces
clinical recovery in mouse models of multiple sclerosis. Gene Ther.
15:504–515. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Bebo BF Jr, Dehghani B, Foster S,
Kurniawan A, Lopez FJ and Sherman LS: Treatment with selective
estrogen receptor modulators regulates myelin specific T-cells and
suppresses experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Glia.
57:777–790. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Juedes AE, Hjelmstrom P, Bergman CM, Neild
AL and Ruddle NH: Kinetics and cellular origin of cytokines in the
central nervous system: insight into mechanisms of myelin
oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-induced experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 164:419–426. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Monteiro de Castro G, Eduarda Zanin M,
Ventura-Oliveira D, Aparecida Vilella C, Ashimine R and De Lima
Zollner R: Th1 and Th2 cytokine immunomodulation by gangliosides in
experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Cytokine. 26:155–163.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Abraham M, Shapiro S, Karni A, Weiner HL
and Miller A: Gelatinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9) are preferentially
expressed by Th1 vs. Th2 cells J Neuroimmunol. 163:157–164. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Correale J and Bassani Molinas Mde L:
Temporal variations of adhesion molecules and matrix
metalloproteinases in the course of MS. J Neuroimmunol.
140:198–209. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Illes Z, Safrany E, Peterfalvi A, et al:
3′UTR C2370A allele of the IL-23 receptor gene is associated with
relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Neurosci Lett. 431:36–38.
2008.
|
|
65
|
Harrington LE, Hatton RD, Mangan PR, et
al: Interleukin 17- producing CD4+ effector T cells
develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2
lineages. Nat Immunol. 6:1123–1132. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Kawanokuchi J, Shimizu K, Nitta A, et al:
Production and functions of IL-17 in microglia. J Neuroimmunol.
194:54–61. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Kolls JK and Linden A: Interleukin-17
family members and inflammation. Immunity. 21:467–476. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Tian AY, Zhang RW, Shi XG and Yu HM:
Alteration of T helper cell subsets in the optic nerve of
experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Int J Mol Med.
25:869–874. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Uyttenhove C, Sommereyns C, Theate I,
Michiels T and van Snick J: Anti-IL-17A autovaccination prevents
clinical and histological manifestations of experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1110:330–336. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|