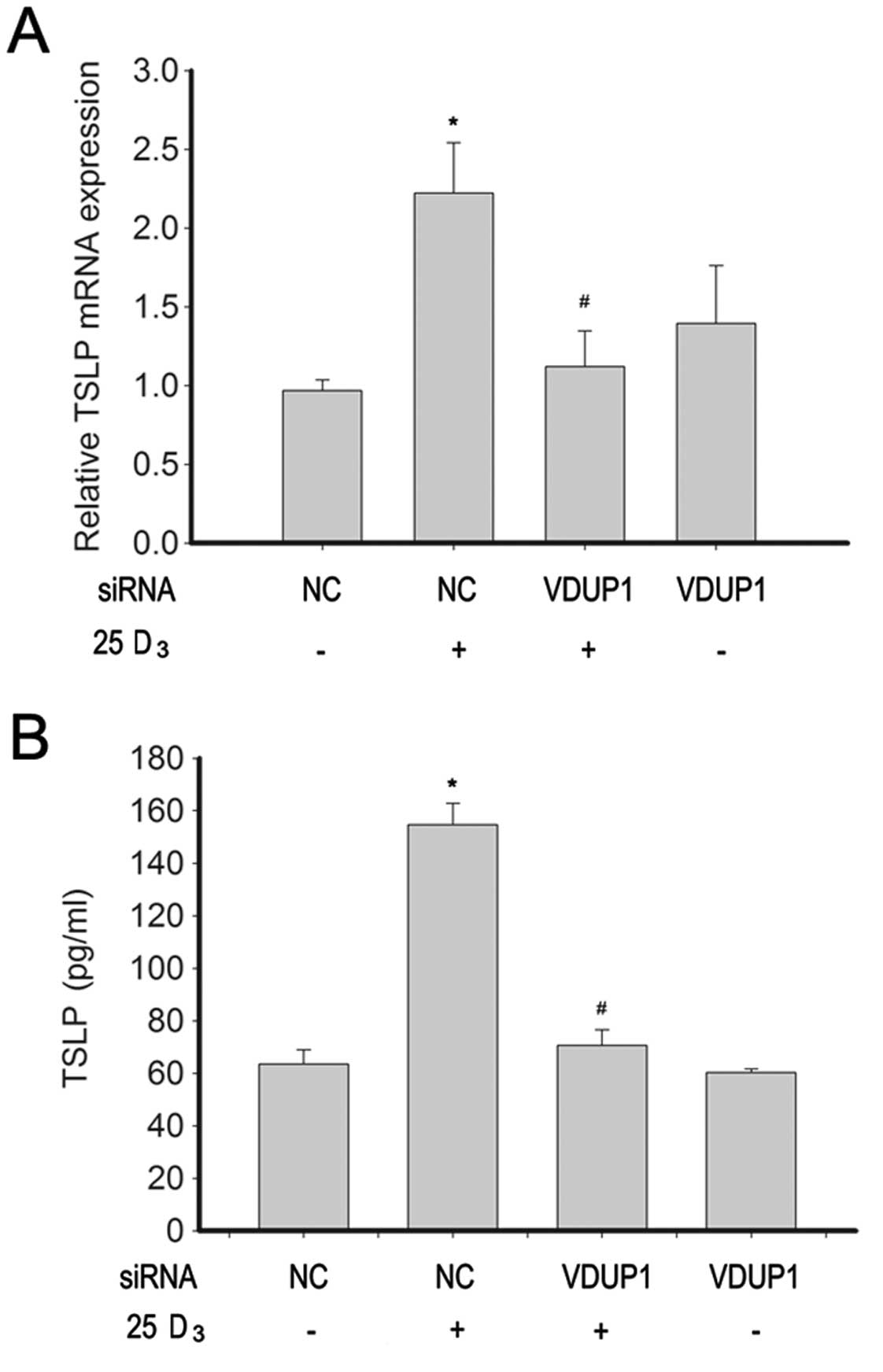
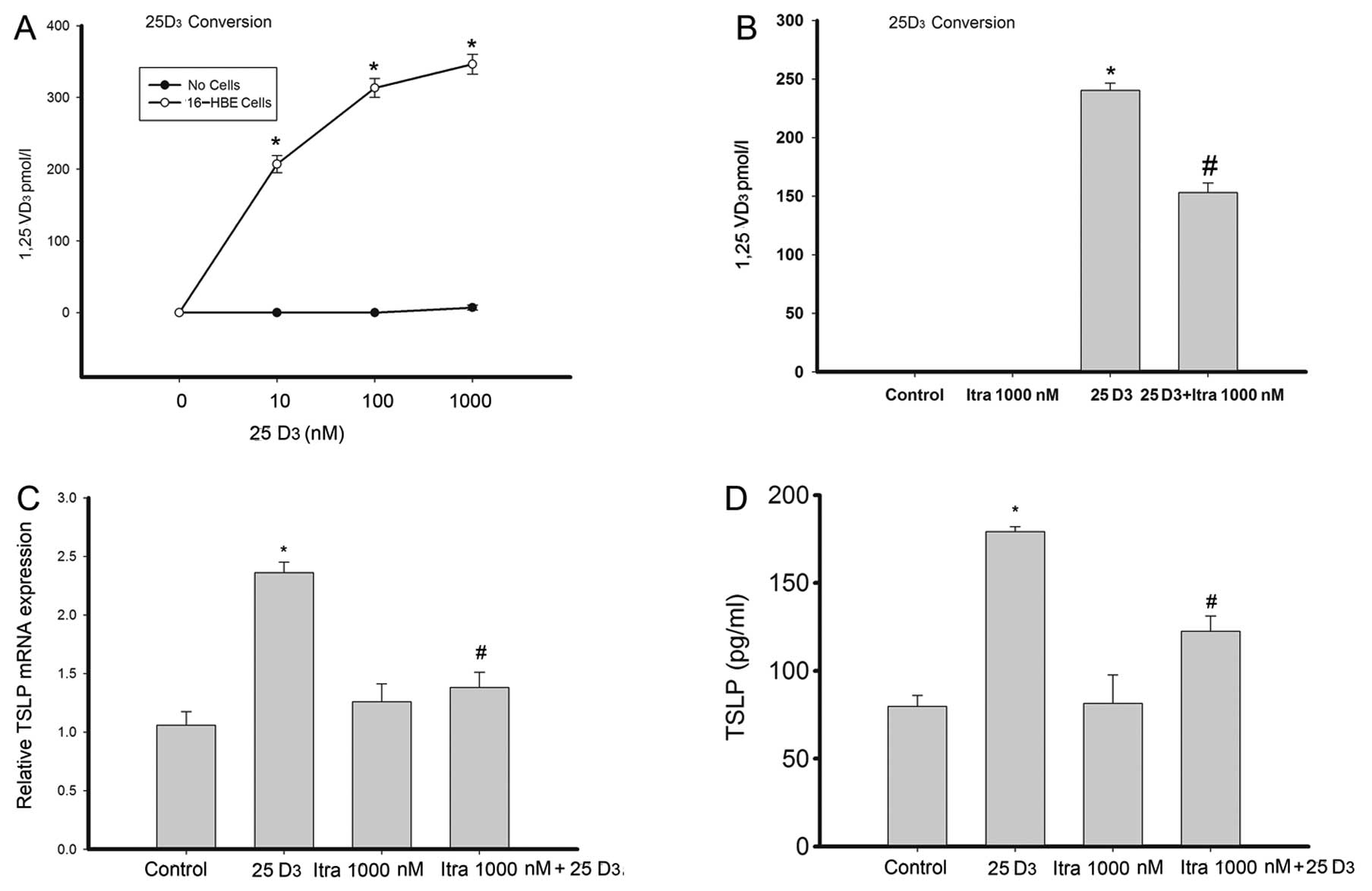
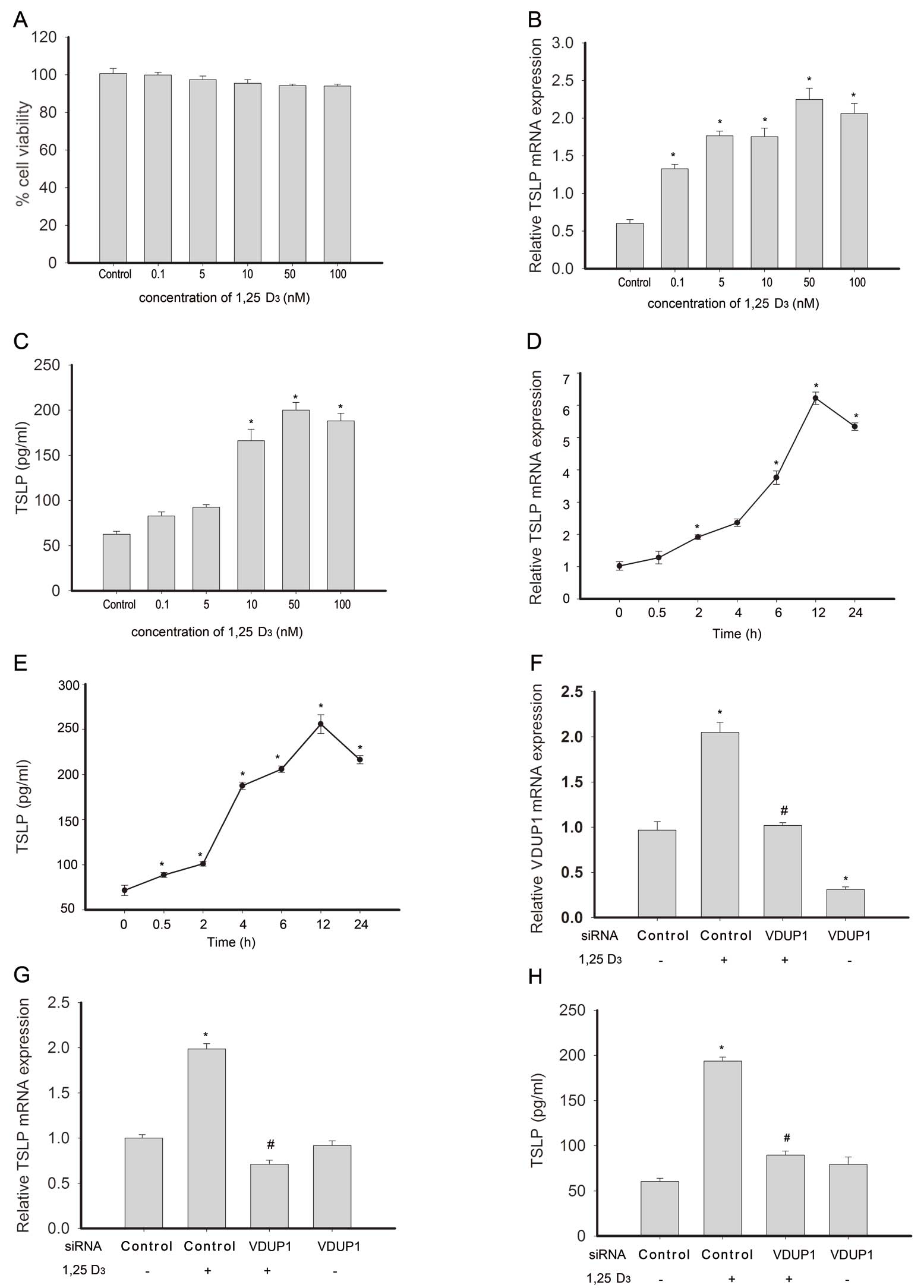
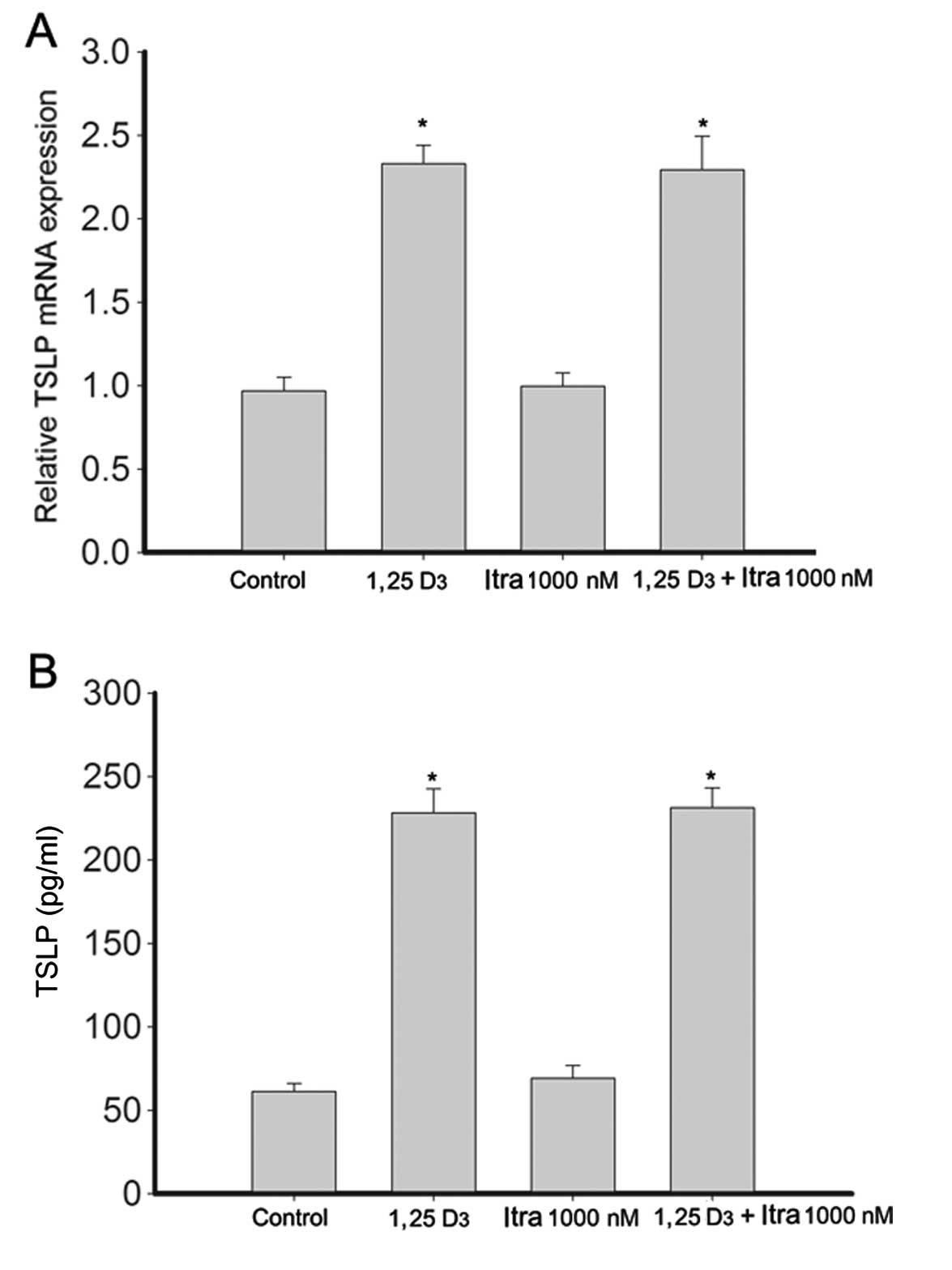
|
1.
|
Pfeffer PE and Hawrylowicz CM: Vitamin D
and lung disease. Thorax. 67:1018–1020. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Brehm JM, Acosta-Pérez E, Klei L, Roeder
K, Barmada M, Boutaoui N, Forno E, Kelly R, Paul K, Sylvia J,
Litonjua AA, Cabana M, Alvarez M, Colón-Semidey A, Canino G and
Celedon C: Vitamin D insufficiency and severe asthma exacerbations
in Puerto Rican children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 186:140–146.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Boonstra A, Barrat FJ, Crain C, Heath VL,
Savelkoul HF and O’Garra A: 1alpha,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 has a
direct effect on naive CD4(+) T cells to enhance the development of
Th2 cells. J Immunol. 167:4974–4980. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Hansdottir S, Monick MM, Hinde SL, Lovan
N, Look DC and Hunninghake GW: Respiratory epithelial cells convert
inactive vitamin D to its active form: potential effects on host
defense. J Immunol. 181:7090–7099. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Zehnder D, Bland R, Walker EA, Bradwell
AR, Howie AJ, Hewison M and Stewart PM: Expression of
25-hydroxyvitamin D3-1alpha-hydroxylase in the human kidney. J Am
Soc Nephrol. 10:2465–2473. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Soumelis V, Reche PA, Kanzler H, Yuan W,
Edward G, Homey B, Gilliet M, Ho S, Antonenko S, Lauerma A, Smith
K, Gorman D, Zurawski S, Abrams J, Menon S, McClanahan T, de
Waal-Malefyt Rd R, Bazan F, Kastelein RA and Liu YJ: Human
epithelial cells trigger dendritic cell mediated allergic
inflammation by producing TSLP. Nat Immunol. 3:673–680.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Zhou B, Comeau MR, De Smedt T, Liggitt HD,
Dahl ME, Lewis DB, Gyarmati D, Aye T, Campbell DJ and Ziegler SF:
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin as a key initiator of allergic airway
inflammation in mice. Nat Immunol. 6:1047–1053. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Wang TT, Tavera-Mendoza LE, Laperriere D,
Libby E, MacLeod NB, Nagai Y, Bourdeau V, Konstorum A, Lallemant B,
Zhang R, Mader S and White JH: Large-scale in silico and
microarray-based identification of direct 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3
target genes. Mol Endocrinol. 19:2685–2695. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Li M, Hener P, Zhang Z, Kato S, Metzger D
and Chambon P: Topical vitamin D3 and low-calcemic analogs induce
thymic stromal lymphopoietin in mouse keratinocytes and trigger an
atopic dermatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:11736–11741. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Chen KS and DeLuca HF: Isolation and
characterization of a novel cDNA from HL-60 cells treated with
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D-3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1219:26–32. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Kim SY, Suh HW, Chung JW, Yoon SR and Choi
I: Diverse functions of VDUP1 in cell proliferation,
differentiation, and diseases. Cell Mol Immunol. 4:345–351.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Junn E, Han SH, Im JY, Yang Y, Cho EW, Um
HD, Kim DK, Lee KW, Han PL, Rhee SG and Choi I: Vitamin D3
up-regulated protein 1 mediates oxidative stress via suppressing
the thioredoxin function. J Immunol. 164:6287–6295. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Perrone L, Devi TS, Hosoya K, Terasaki T
and Singh LP: Thioredoxin interacting protein (TXNIP) induces
inflammation through chromatin modification in retinal capillary
endothelial cells under diabetic conditions. J Cell Physiol.
221:262–272. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14.
|
Zhou R, Tardivel A, Thorens B, Choi I and
Tschopp J: Thioredoxin-interacting protein links oxidative stress
to inflammasome activation. Nat Immunol. 11:136–140. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Kwon HJ, Won YS, Suh HW, Jeon JH, Shao Y,
Yoon SR, Chung JW, Kim TD, Kim HM, Nam KH, Yoon WK, Kim DG, Kim JH,
Kim YS, Kim DY, Kim HC and Choi I: Vitamin D3 upregulated protein 1
suppresses TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB activation in
hepatocarcinogenesis. J Immunol. 185:3980–3989. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Cozens AL, Yezzi MJ, Kunzelmann K, Ohrui
T, Chin L, Eng K, Finkbeiner WE, Widdicombe JH and Gruenert DC:
CFTR expression and chloride secretion in polarized immortal human
bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 10:38–47.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Profita M, Bonanno A, Siena L, Ferraro M,
Montalbano AM, Pompeo F, Riccobono L, Pieper MP and Gjomarkaj M:
Acetylcholine mediates the release of IL-8 in human bronchial
epithelial cells by a NFκB/ERK-dependent mechanism. Eur J
Pharmacol. 582:145–153. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Holick MF: Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J
Med. 357:266–281. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19.
|
Campos LT, Brentani H, Roela RA, Katayama
ML, Lima L, Rolim CF, Milani C, Folgueira MA and Brentani MM:
Differences in transcriptional effects of 1alpha,25
dihydroxyvitamin D3 on fibroblasts associated to breast carcinomas
and from paired normal breast tissues. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol.
133:12–24. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Izban MG, Nowicki BJ and Nowicki S:
1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 promotes a sustained LPS-induced
NF-kappaB-dependent expression of CD55 in human monocytic THP-1
cells. PLoS One. 7:e493182012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Wu AC, Tantisira K, Li L, Fuhlbrigge AL,
Weiss ST and Litonjua A: Effect of vitamin D and inhaled
corticosteroid treatment on lung function in children. Am J Respir
Crit Care Med. 186:508–513. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Xystrakis E, Kusumakar S, Boswell S, Peek
E, Urry Z, Richards DF, Adikibi T, Pridgeon C, Dallman M, Loke TK,
Robinson DS, Barrat FJ, O’Garra A, Lavender P, Lee TH, Corrigan C
and Hawrylowicz CM: Reversing the defective induction of
IL-10-secreting regulatory T cells in glucocorticoid-resistant
asthma patients. J Clin Invest. 116:146–155. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Leyva-Castillo JM, Hener P, Jiang H and Li
M: TSLP produced by keratinocytes promotes allergen sensitization
through skin and thereby triggers atopic march in mice. J Invest
Dermatol. 133:154–163. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24.
|
Back O, Blomquist HK, Hernell O and
Stenberg B: Does vitamin D intake during infancy promote the
development of atopic allergy? Acta Derm Venereol. 89:28–32. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Schauber J and Gallo RL: Vitamin D
deficiency and asthma: not a strong link - yet. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 121:782–783; author reply. 783–784. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Ginde AA and Sutherland ER: Vitamin D in
asthma: panacea or true promise? J Allergy Clin Immunol. 126:59–60.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Sonesson A, Kasetty G, Olin AI, Malmsten
M, Morgelin M, Sorensen OE and Schmidtchen A: Thymic stromal
lymphopoietin exerts antimicrobial activities. Exp Dermatol.
20:1004–1010. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Kamekura R, Kojima T, Koizumi J, Ogasawara
N, Kurose M, Go M, Harimaya A, Murata M, Tanaka S, Chiba H, Himi T
and Sawada N: Thymic stromal lymphopoietin enhances tight-junction
barrier function of human nasal epithelial cells. Cell Tissue Res.
338:283–293. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29.
|
Allakhverdi Z, Comeau MR, Jessup HK, Yoon
BR, Brewer A, Chartier S, Paquette N, Ziegler SF, Sarfati M and
Delespesse G: Thymic stromal lymphopoietin is released by human
epithelial cells in response to microbes, trauma, or inflammation
and potently activates mast cells. J Exp Med. 204:253–258. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Kato A, Favoreto S Jr, Avila PC and
Schleimer RP: TLR3-and Th2 cytokine-dependent production of thymic
stromal lymphopoietin in human airway epithelial cells. J Immunol.
179:1080–1087. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Lee HC and Ziegler SF: Inducible
expression of the proallergic cytokine thymic stromal lymphopoietin
in airway epithelial cells is controlled by NFkappaB. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 104:914–919. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Zhang K, Shan L, Rahman MS, Unruh H,
Halayko AJ and Gounni AS: Constitutive and inducible thymic stromal
lymphopoietin expression in human airway smooth muscle cells: role
in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Physiol Lung Cell
Mol Physiol. 293:L375–L382. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33.
|
Tang H, Cao W, Kasturi SP, Ravindran R,
Nakaya HI, Kundu K, Murthy N, Kepler TB, Malissen B and Pulendran
B: The T helper type 2 response to cysteine proteases requires
dendritic cell-basophil cooperation via ROS-mediated signaling. Nat
Immunol. 11:608–617. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Hansdottir S, Monick MM, Lovan N, Powers
L, Gerke A and Hunninghake GW: Vitamin D decreases respiratory
syncytial virus induction of NF-kappaB-linked chemokines and
cytokines in airway epithelium while maintaining the antiviral
state. J Immunol. 184:965–974. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35.
|
Geldmeyer-Hilt K, Heine G, Hartmann B,
Baumgrass R, Radbruch A and Worm M: 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3)
impairs NF-kappaB activation in human naive B cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 407:699–702. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|