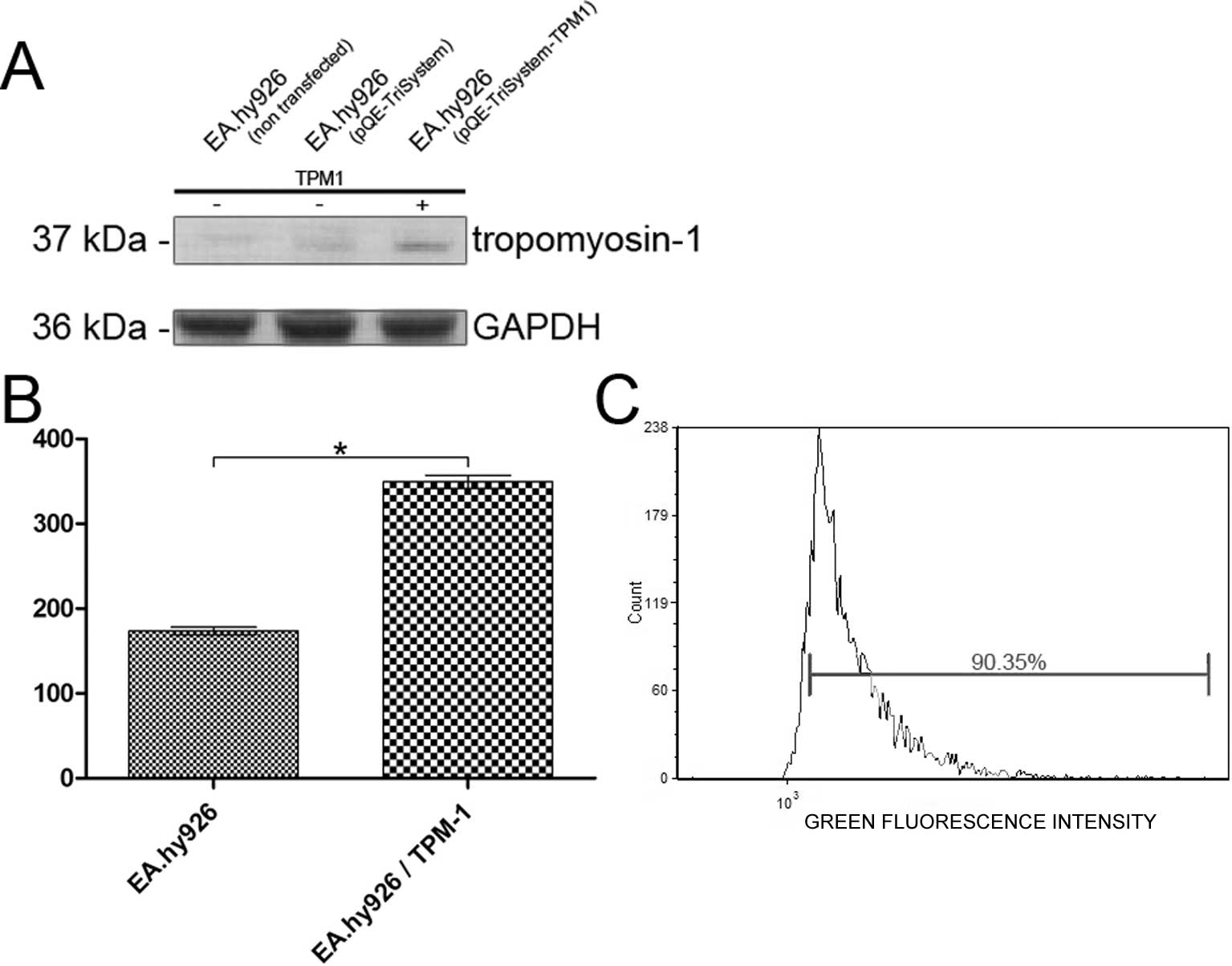
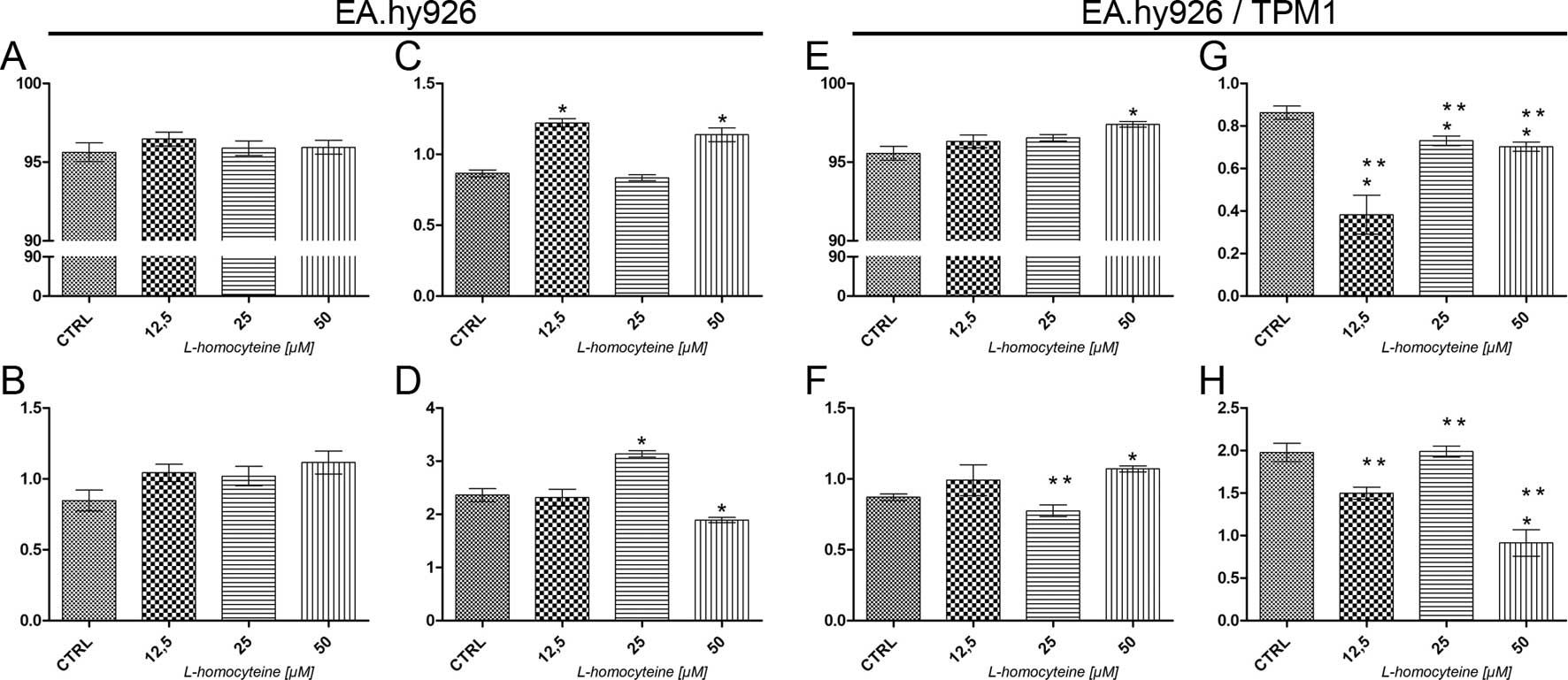
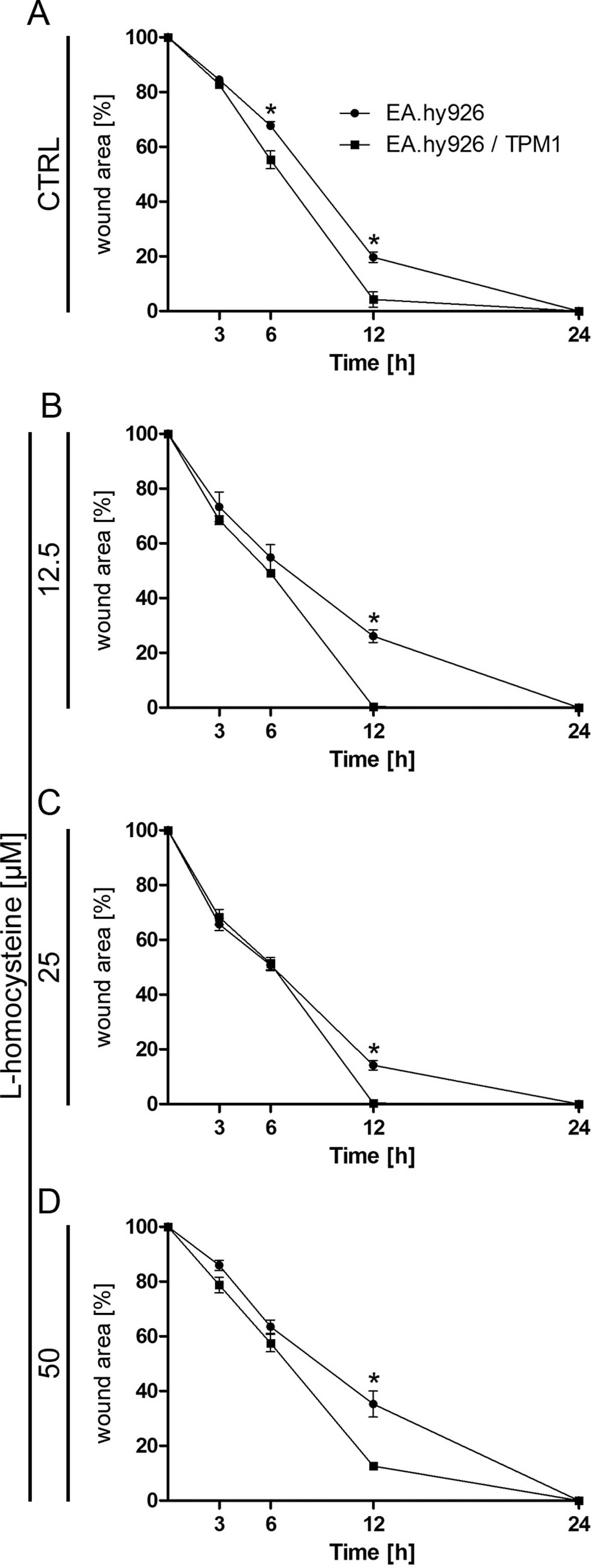
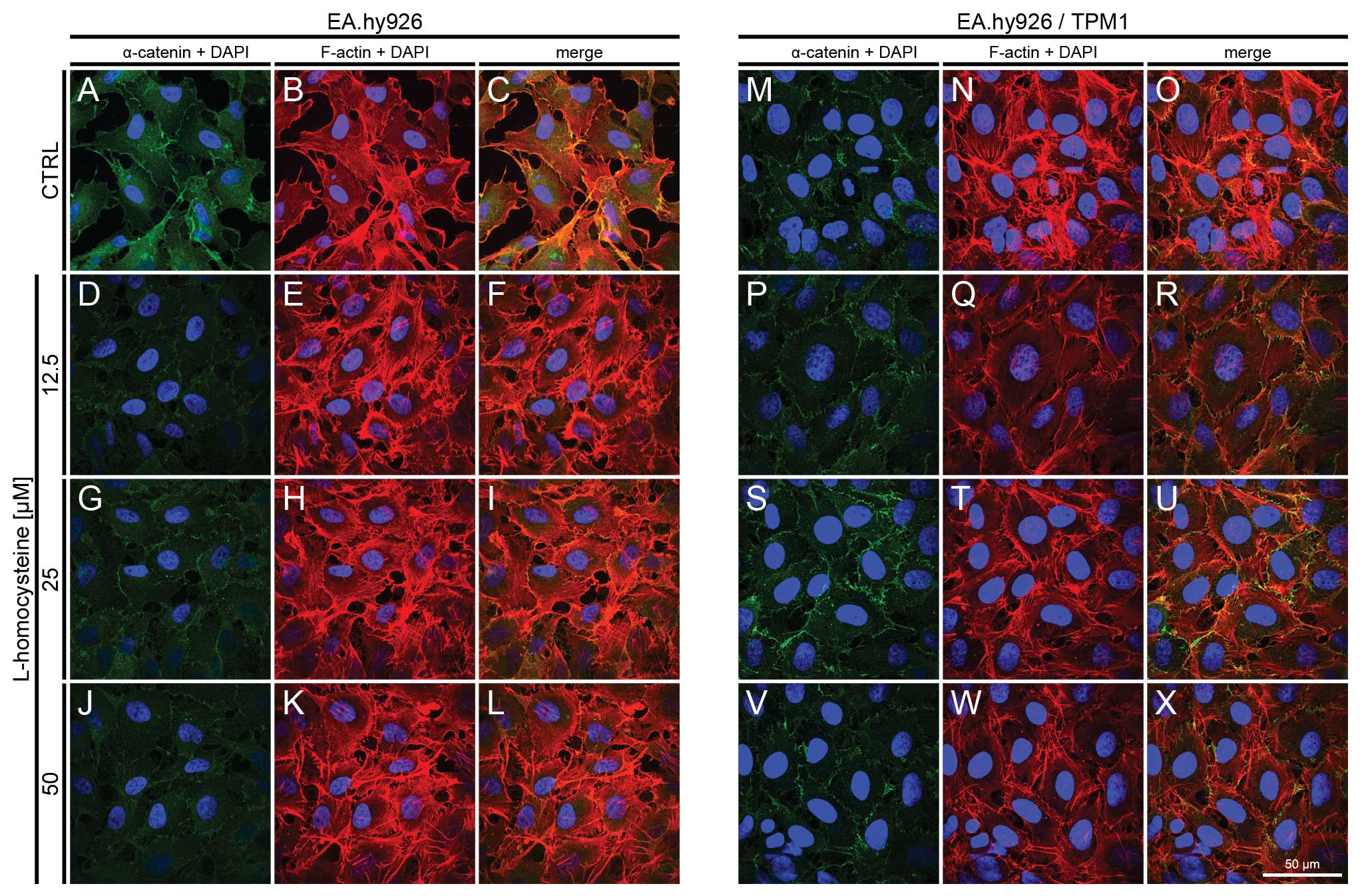
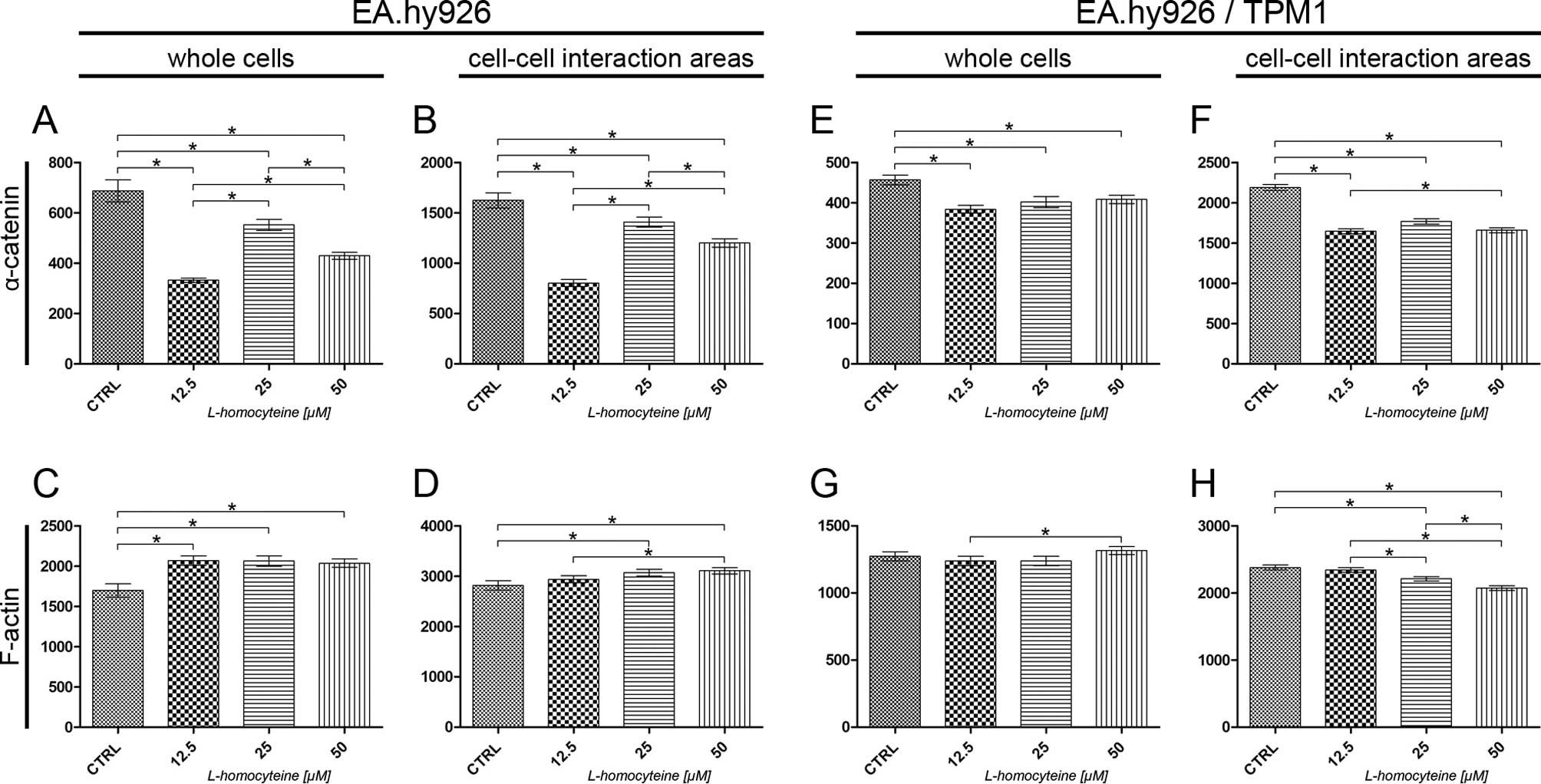
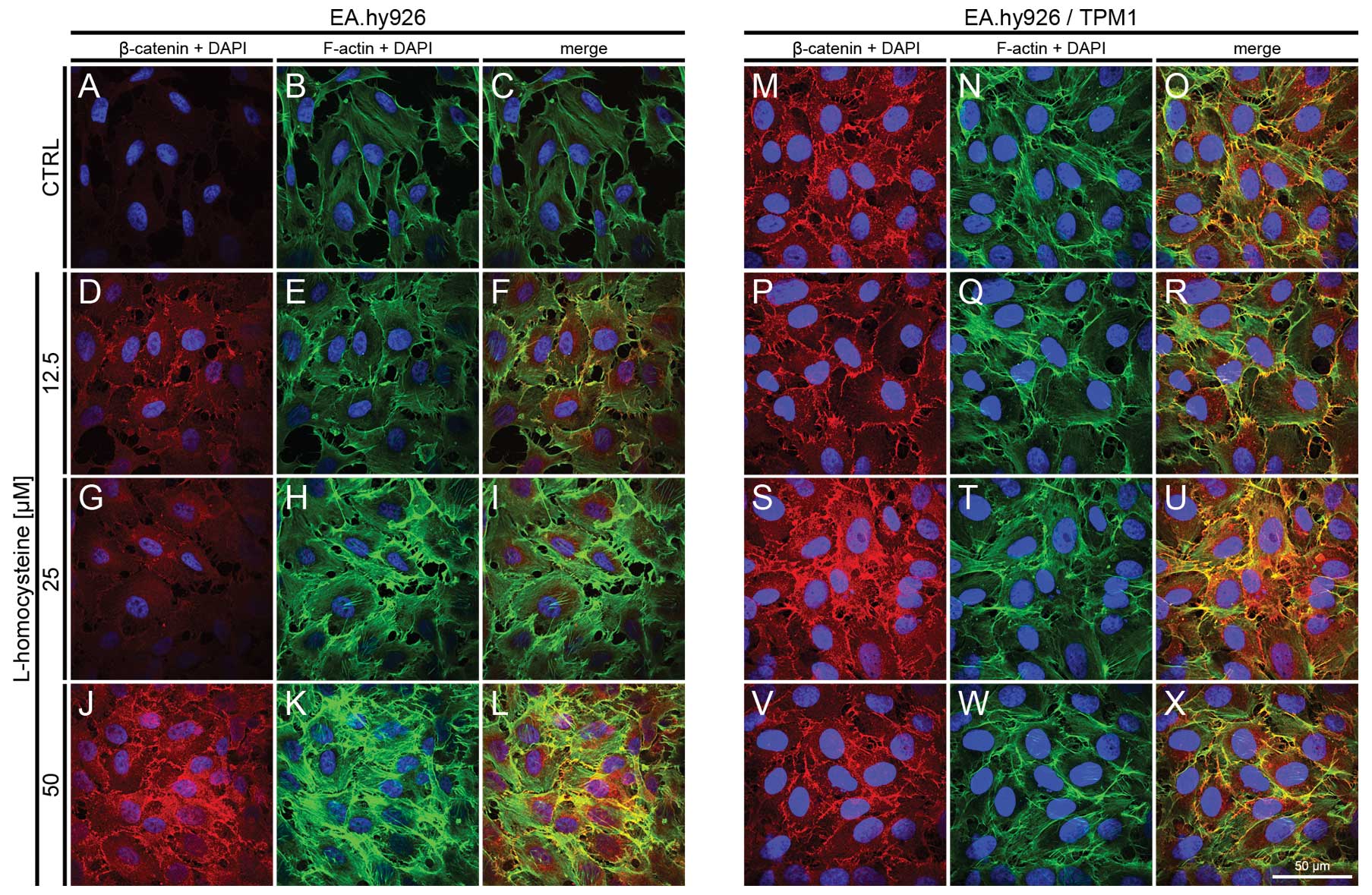
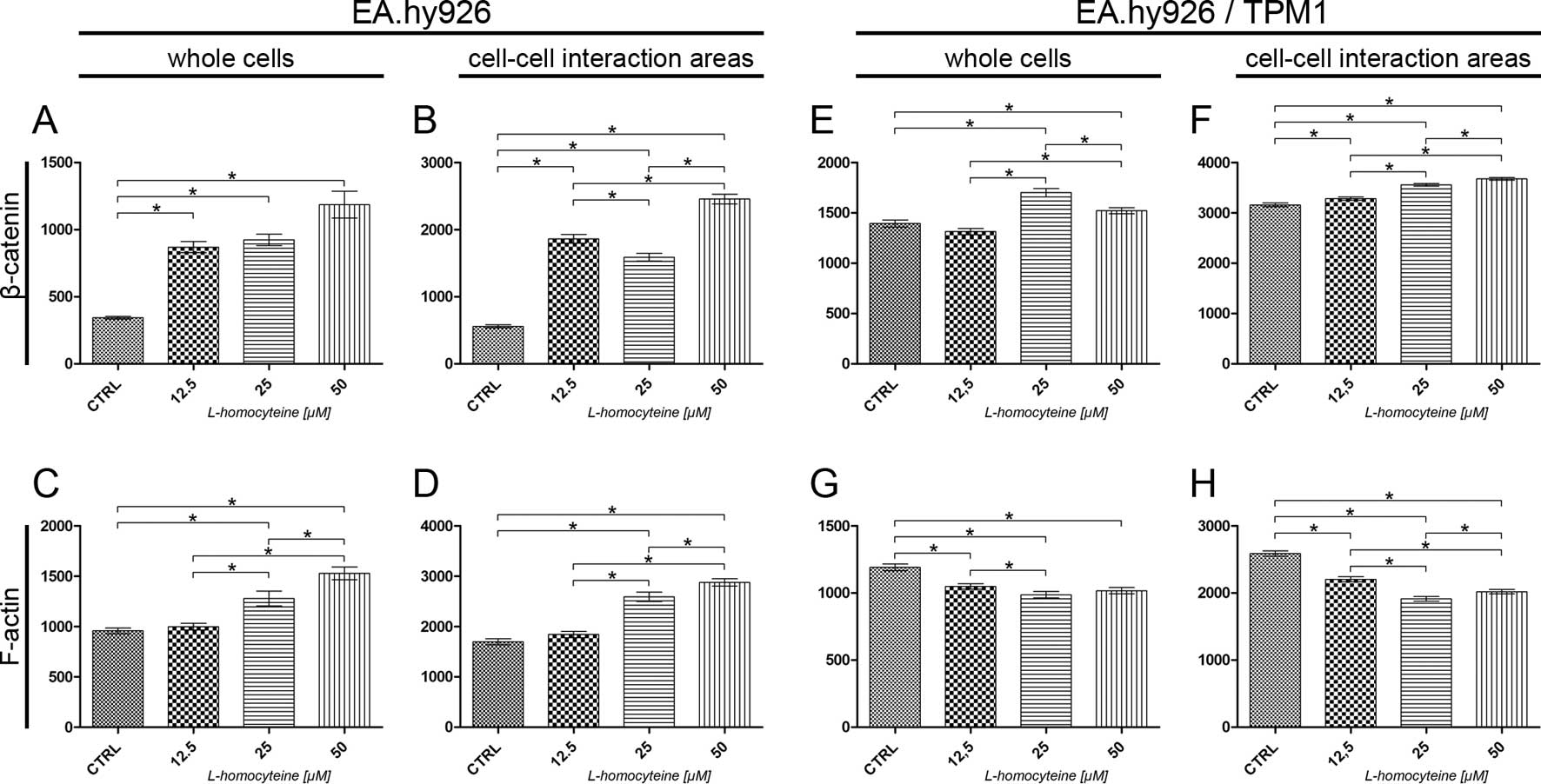
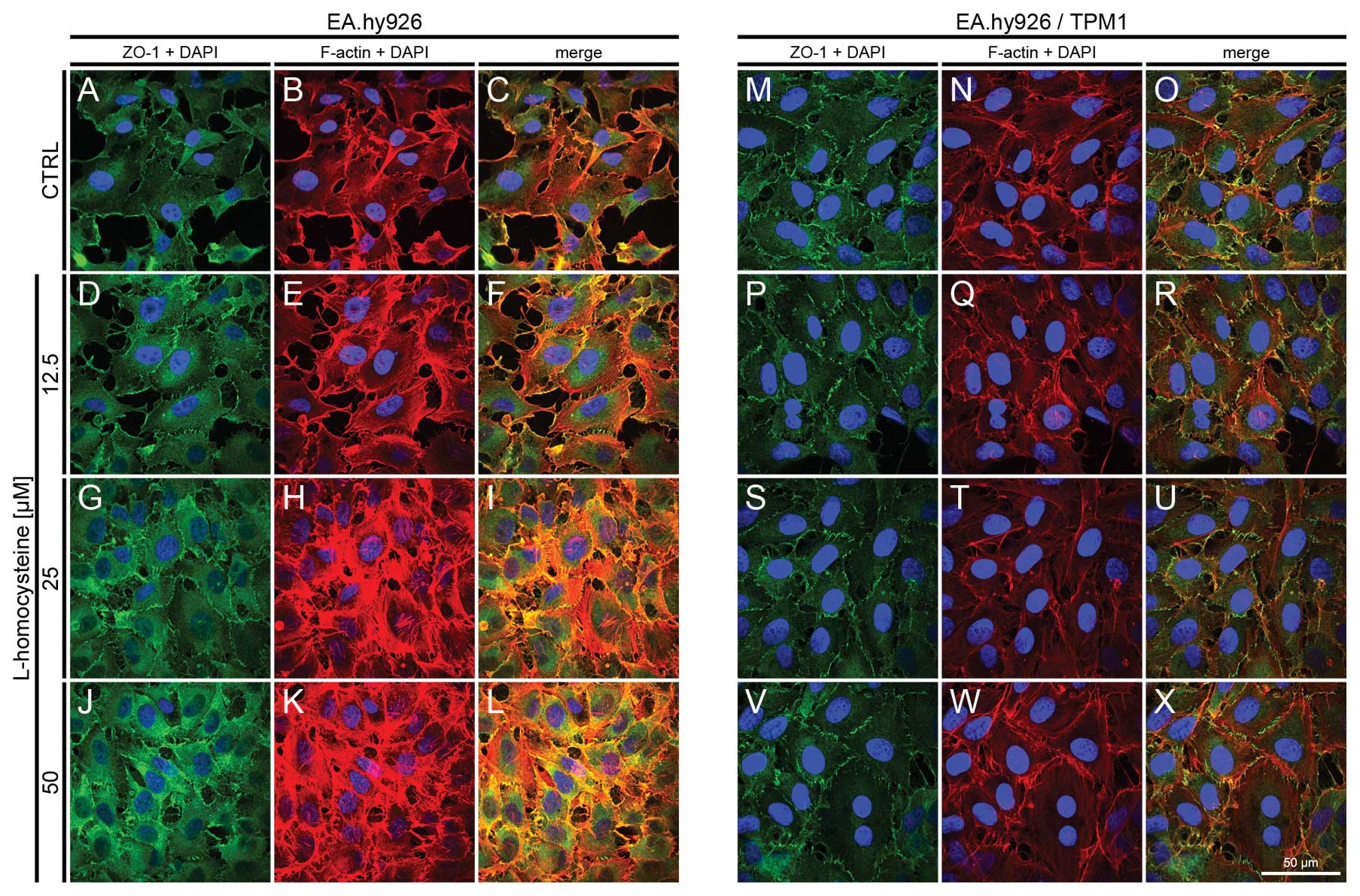
|
1.
|
Pollard TD: Cytoskeletal functions of
cytoplasmic contractile proteins. J Supramol Struct. 5:317–334.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Clarke M and Spudich JA: Nonmuscle
contractile proteins: the role of actin and myosin in cell motility
and shape determination. Annu Rev Biochem. 46:797–822. 1977.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Stossel TP: Contractile proteins in cell
structure and function. Annu Rev Med. 29:427–457. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Stricker J, Falzone T and Gardel ML:
Mechanics of the F-actin cytoskeleton. J Biomech. 43:9–14. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Zhang J, Betson M, Erasmus J, Zeikos K,
Bailly M, Cramer LP and Braga VM: Actin at cell-cell junctions is
composed of two dynamic and functional populations. J Cell Sci.
118:5549–5562. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Homeister JW and Willis MS:
Atherosclerosis: Pathogenesis, Genetics and Experimental Models.
Encyclopedia of Life Sciences 2010. John Wiley & Sons Ltd;
Chichester: 2010, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7.
|
Boushey CJ, Beresford SA, Omenn GS and
Motulsky AG: A quantitative assessment of plasma homocysteine as a
risk factor for vascular disease. Probable benefits of increasing
folic acid intakes. JAMA. 274:1049–1057. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Nygård O, Vollset SE, Refsum H, et al:
Total plasma homocysteine and cardiovascular risk profile. The
Hordaland Homocysteine Study. JAMA. 274:1526–1533. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Ueland PM, Refsum H, Beresford SA and
Vollset SE: The controversy over homocysteine and cardiovascular
risk. Am J Clin Nutr. 72:324–332. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Tehlivets O: Homocysteine as a risk factor
for atherosclerosis: is its conversion to s-adenosyl-L-homocysteine
the key to deregulated lipid metabolism? J Lipids. 2011:7028532011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
McDowell IF and Lang D: Homocysteine and
endothelial dysfunction: a link with cardiovascular disease. J
Nutr. 130:369S–372S. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Heydrick SJ, Weiss N, Thomas SR, Cap AP,
Pimentel DR, Loscalzo J and Keaney JF Jr: L-Homocysteine and
L-homocystine stereospecifically induce endothelial nitric oxide
synthase-dependent lipid peroxidation in endothelial cells. Free
Radic Biol Med. 36:632–640. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13.
|
Dejana E: Endothelial cell-cell junctions:
happy together. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 5:261–270. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Hoelzle MK and Svitkina T: The
cytoskeletal mechanisms of cell-cell junction formation in
endothelial cells. Mol Biol Cell. 23:310–323. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Bazzoni G, Martínez Estrada O and Dejana
E: Molecular structure and functional role of vascular tight
junctions. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 9:147–152. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Braga VM: Cell-cell adhesion and
signalling. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 14:546–556. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Matter K and Balda MS: Signalling to and
from tight junctions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 4:225–236. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Wheelock MJ and Johnson KR:
Cadherin-mediated cellular signaling. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
15:509–514. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Harris ES and Nelson WJ: VE-cadherin: at
the front, center, and sides of endothelial cell organization and
function. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 22:651–658. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Harris TJ and Tepass U: Adherens
junctions: from molecules to morphogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
11:502–514. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Yonemura S: Cadherin-actin interactions at
adherens junctions. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 23:515–522. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Nwariaku FE, Liu Z, Zhu X, et al: NADPH
oxidase mediates vascular endothelial cadherin phosphorylation and
endothelial dysfunction. Blood. 104:3214–3220. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Kinumi T, Ogawa Y, Kimata J, Saito Y,
Yoshida Y and Niki E: Proteomic characterization of oxidative
dysfunction in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC)
induced by exposure to oxidized LDL. Free Radic Res. 39:1335–1344.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Xu Y, Arai H, Murayama T, Kita T and
Yokode M: Hypercholesterolemia contributes to the development of
atherosclerosis and vascular remodeling by recruiting bone
marrow-derived cells in cuff-induced vascular injury. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 363:782–787. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Javanmard SH and Dana N: The effect of
interferon γ on endothelial cell nitric oxide production and
apoptosis. Adv Biomed Res. 1:692012.
|
|
26.
|
Bouïs D, Hospers GA, Meijer C, Molema G
and Mulder NH: Endothelium in vitro: a review of human vascular
endothelial cell lines for blood vessel-related research.
Angiogenesis. 4:91–102. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Edgell CJ, Reisner HM and Graham JB:
Endothelial cell hybrids and the suspension of factor VIII related
antigen expression. Br J Haematol. 46:613–620. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Edgell CJ, Haizlip JE, Bagnell CR,
Packenham JP, Harrison P, Wilbourn B and Madden VJ: Endothelium
specific Weibel-Palade bodies in a continuous human cell line,
EA.hy926. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 26:1167–1172. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Claise C, Chalas J, Edeas M, Abella A,
Khalfoun Y, Laurent D and Lindenbaum A: Comparison of oxidized
low-density lipoprotein toxicity on EA.hy 926 cells and human vein
endothelial cells: influence of antioxidant systems. Cell Mol Life
Sci. 53:156–161. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Vrekoussis T, Stathopoulos EN, De Giorgi
U, et al: Modulation of vascular endothelium by imatinib: a study
on the EA.hy 926 endothelial cell line. J Chemother. 18:56–65.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Rosenkranz AC, Lob H, Breitenbach T,
Berkels R and Roesen R: Endothelial antioxidant actions of
dihydropyridines and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors. Eur
J Pharmacol. 529:55–62. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Pittenger MF, Kazzaz JA and Helfman DM:
Functional properties of non-muscle tropomyosin isoforms. Curr Opin
Cell Biol. 6:96–104. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Perry SV: Vertebrate tropomyosin:
distribution, properties and function. J Muscle Res Cell Motil.
22:5–49. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Cooper JA: Actin dynamics: tropomyosin
provides stability. Curr Biol. 12:R523–R525. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Gunning PW, Schevzov G, Kee AJ and
Hardeman EC: Tropomyosin isoforms: divining rods for actin
cytoskeleton function. Trends Cell Biol. 15:333–341. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Lin JJ, Eppinga RD, Warren KS and McCrae
KR: Human tropomyosin isoforms in the regulation of cytoskeleton
functions. Adv Exp Med Biol. 644:201–222. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Plazar N and Jurdana M:
Hyperhomocysteinemia: relation to cardiovascular disease and venous
thromboembolism. Pathophysiology and Clinical Aspects of Venous
Thromboembolism in Neonates, Renal Disease and Cancer Patients.
Abdelaal MA: InTech; Rijeka: pp. 17–34. 2012
|
|
38.
|
Ridker PM, Manson JE, Buring JE, Shih J,
Matias M and Hennekens CH: Homocysteine and risk of cardiovascular
disease among postmenopausal women. JAMA. 281:1817–1821. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Upchurch GR Jr, Welch GN, Fabian AJ,
Freedman JE, Johnson JL, Keaney JF Jr and Loscalzo J:
Homocyst(e)ine decreases bioavailable nitric oxide by a mechanism
involving glutathione peroxidase. J Biol Chem. 272:17012–17017.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Nagai Y, Tasaki H, Takatsu H, Nihei S,
Yamashita K, Toyokawa T and Nakashima Y: Homocysteine inhibits
angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
281:726–731. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Zhang C, Cai Y, Adachi MT, Oshiro S, Aso
T, Kaufman RJ and Kitajima S: Homocysteine induces programmed cell
death in human vascular endothelial cells through activation of the
unfolded protein response. J Biol Chem. 276:35867–35874. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Lee SJ, Kim KM, Namkoong S, et al: Nitric
oxide inhibition of homocysteine-induced human endothelial cell
apoptosis by down-regulation of p53-dependent Noxa expression
through the formation of S-nitrosohomocysteine. J Biol Chem.
280:5781–5788. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Suhara T, Fukuo K, Yasuda O, et al:
Homocysteine enhances endothelial apoptosis via upregulation of
Fas-mediated pathways. Hypertension. 43:1208–1213. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Mercié P, Garnier O, Lascoste L, et al:
Homocysteine-thiolactone induces caspase-independent vascular
endothelial cell death with apoptotic features. Apoptosis.
5:403–411. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Rodríguez-Nieto S, Chavarría T,
Martínez-Poveda B, Sánchez-Jiménez F, Rodríguez Quesada A and
Medina MA: Anti-angiogenic effects of homocysteine on cultured
endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 293:497–500.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Wejksza K, Rzeski W and Turski WA:
Kynurenic acid protects against the homocysteine-induced impairment
of endothelial cells. Pharmacol Rep. 61:751–756. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Vincent PA, Xiao K, Buckley KM and
Kowalczyk AP: VE-cadherin: adhesion at arm’s length. Am J Physiol
Cell Physiol. 286:C987–C997. 2004.
|
|
48.
|
Drees F, Pokutta S, Yamada S, Nelson WJ
and Weis WI: α-catenin is a molecular switch that binds
E-cadherin-β-catenin and regulates actin-filament assembly. Cell.
123:903–915. 2005.
|
|
49.
|
Yamada S, Pokutta S, Drees F, Weis WI and
Nelson WJ: Deconstructing the cadherin-catenin-actin complex. Cell.
123:889–901. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Millán J, Cain RJ, Reglero-Real N, et al:
Adherens junctions connect stress fibres between adjacent
endothelial cells. BMC Biol. 8:112010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51.
|
Fanning AS, Ma TY and Anderson JM:
Isolation and functional characterization of the actin binding
region in the tight junction protein ZO-1. FASEB. 16:1835–1837.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52.
|
Itoh M, Nagafuchi A, Moroi S and Tsukita
S: Involvement of ZO-1 in cadherin-based cell adhesion through its
direct binding to alpha catenin and actin filaments. J Cell Biol.
138:181–192. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53.
|
Fanning AS, Jameson BJ, Jesaitis LA and
Anderson JM: The tight junction protein ZO-1 establishes a link
between the trans-membrane protein occludin and the actin
cytoskeleton. J Biol Chem. 273:29745–29753. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54.
|
Wittchen ES, Haskins J and Stevenson BR:
Protein interactions at the tight junction. Actin has multiple
binding partners, and ZO-1 forms independent complexes with ZO-2
and ZO-3. J Biol Chem. 274:35179–35185. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55.
|
Van Itallie CM, Fanning AS, Bridges A and
Anderson JM: ZO-1 stabilizes the tight junction solute barrier
through coupling to the perijunctional cytoskeleton. Mol Biol Cell.
20:3930–3940. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56.
|
Chen VC, Li X, Perreault H and Nagy JI:
Interaction of zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) with alpha-actinin-4:
application of functional proteomics for identification of PDZ
domain-associated proteins. J Proteome Res. 5:2123–2134. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57.
|
Etournay R, Zwaenepoel I, Perfettini I,
Legrain P, Petit C and El-Amraoui A: Shroom2, a myosin-VIIa- and
actin-binding protein, directly interacts with ZO-1 at tight
junctions. J Cell Sci. 120:2838–2850. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|