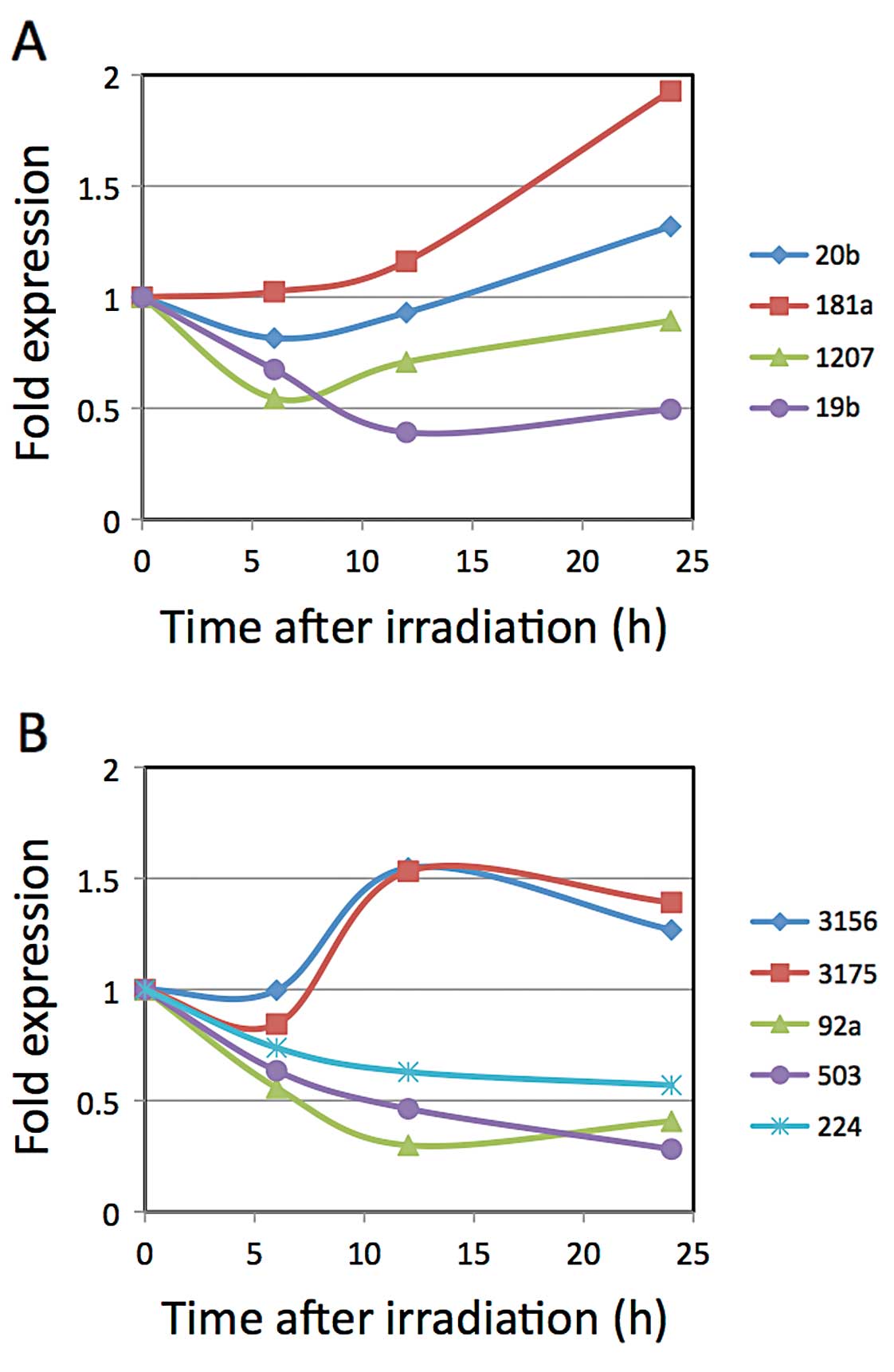
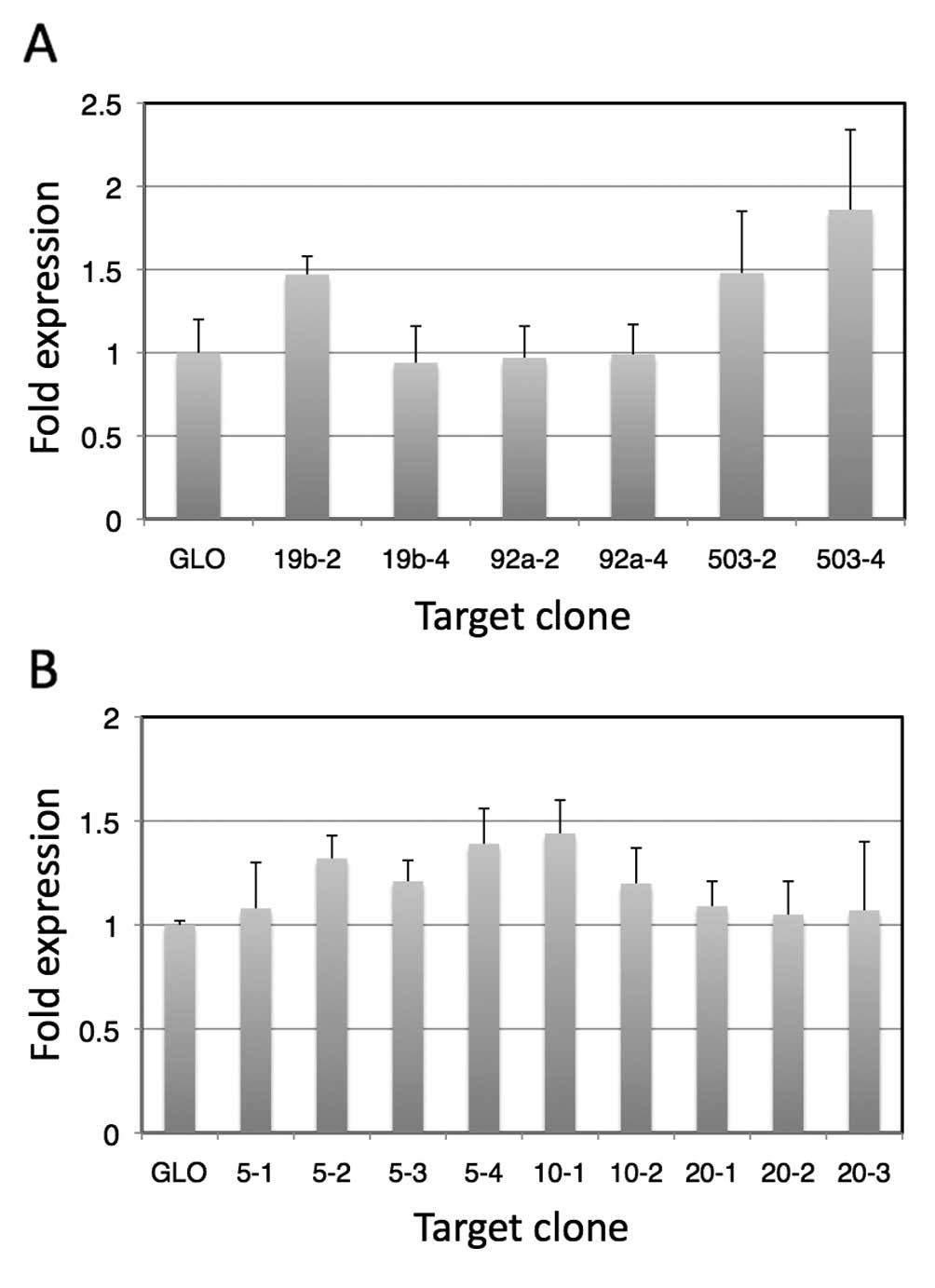
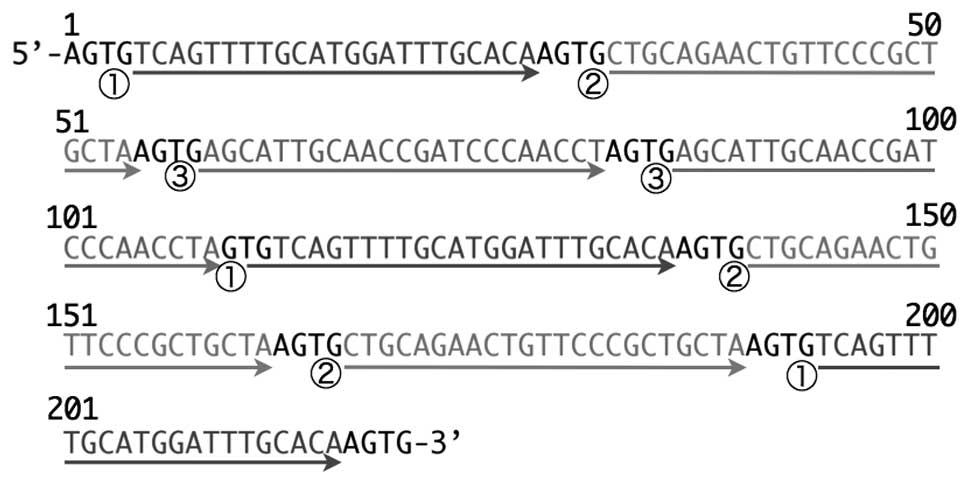
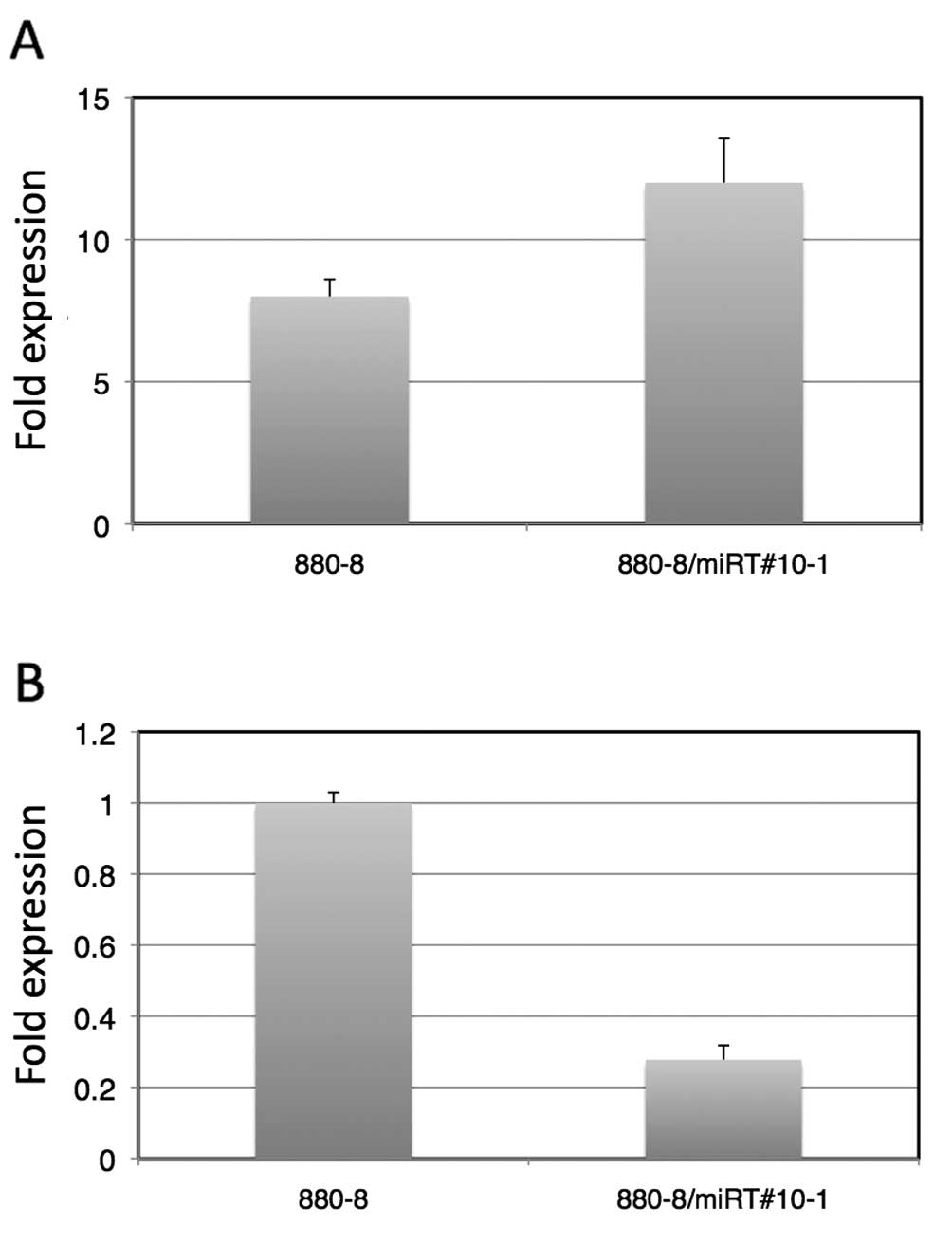
|
1.
|
Steiner MS and Gungrich JR: Gene therapy
for prostate cancer: where are we now? J Urol. 164:1121–1136. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Mauceri HJ, Hanna NN, Staba MJ, Beckett
MA, Kufe DW and Weichselbaum RR: Radiation-inducible gene therapy.
CR Acad Sci III. 322:225–228. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Ogawa R, Lee SI, Kagiya G, Hirano H,
Fukuda S, Kondo T and Kodaki T: Construction of X-ray-inducible
promoters through cis-acting element elongation and
error-prone polymerase chain reaction. J Gene Med. 10:316–324.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Morii A, Ogawa R, Watanabe A, Kakutani S,
Zhao QL, Kume K, et al: Regulation of gene expression in prostate
cancer cells with an artificially constructed promoter responsive
to radiation. Gene Ther. 19:219–227. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ: Oncomirs
- microRNA with a role of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:259–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6.
|
Josson S, Sung SY, Lao K, Cung LW and
Johnstone PA: Radiation modulation of microRNA in prostate cancer
cell lines. Prostate. 68:1599–1606. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Shin S, Cha HJ, Lee EM, Lee SJ, Seo SK,
Jin HO, Park IC, Jin YW and An S: Alteration of miRNA profiles by
ionizing radiation in A549 human small-cell lung cancer cells. Int
J Oncol. 35:81–86. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Chaudhry MA, Sachdeva H and Omaruddin RA:
Radiation-induced microRNA modulation in glioblastoma cells
differing in DNA-repair pathways. DNA Cell Biol. 29:553–561. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Oh JS, Kim JJ, Byun JY, et al: Lin28-let7
modulates radiosensitivity of human cancer cells with activation of
K-Ras. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 76:5–8. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Ogawa R, Morii A and Watanabe A:
Ultrasound stimulation induces microRNA expression changes that
could be involved in sonication-induced apoptosis. J Med
Ultrasonics. 39:207–216. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11.
|
Fornari F, Gramantieri L, Giovannini C, et
al: miR-122/cyclin G1 interaction modulates p53 activity and
affects doxorubicin sensitivity of human hepatocarcinoma cells.
Cancer Res. 69:5761–5767. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Wilmink GJ, Roth CL, Ibey BL, et al:
Identification of microRNAs associated with hyperthermia-induced
cellular stress response. Cell Stress Chaperones. 15:1027–1038.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Kulshreshtha R, Ferracin M, Wojcik SE, et
al: A microRNA signature of hypoxia. Mol Cell Biol. 27:1859–1867.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14.
|
Brown BD, Venneri MA, Zingale A, Sergi
Sergi L and Naldini L: Endogenous microRNA regulation suppresses
transgene expression in hematopoietic lineages and enables stable
gene transfer. Nat Med. 12:585–591. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Brown BD, Gentner B, Cantore A, Colleoni
S, Amendola M, Zingale A, Baccarini A, Lazzari G, Galli C and
Naldini L: Endogenous microRNA can be broadly exploited to regulate
transgene expression according to tissue, lineage and
differentiation state. Nat Biotechnol. 25:1457–1467. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Wu C, Lin J, Hong M, Choudhury Y, Balani
P, Leung D, Dang LH, Zhao Y, Zeng J and Wang S: Combinatorial
control of suicide gene expression by tissue-specific promoter and
microRNA regulation for cancer therapy. Mol Ther. 17:2058–2066.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Xie J, Xie Q, Zhang H, Ameres SL, Hung JH,
Su Q, He R, Mu X, Ahmed S, Park S, Kato H, Li C, Mueller C, Weng Z,
Flotte TR, Zamore PD and Gao G: MicroRNA-regulated, systemically
delivered rAVV9: a step closer to CNS-restricted transgene
expression. Mol Ther. 19:526–535. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Sambrook J and Russell DW: Molecular
Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. 3rd edition. Cold Spring Harbor
Laboratory Press; New York: 2001
|
|
19.
|
Li B, Shi XB, Nori D, Chao CK, Chen AM,
Valicenti R and White Rde V: Down-regulation of microRNA106b is
involved in p21-mediated cell cycle arrest in response to radiation
in prostate cancer cells. Prostate. 71:567–574. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Simone NL, Soule BP, Ly D, et al: Ionizing
radiation-induced oxidative stress alters miRNA expression. PLoS
One. 4:e63772009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|