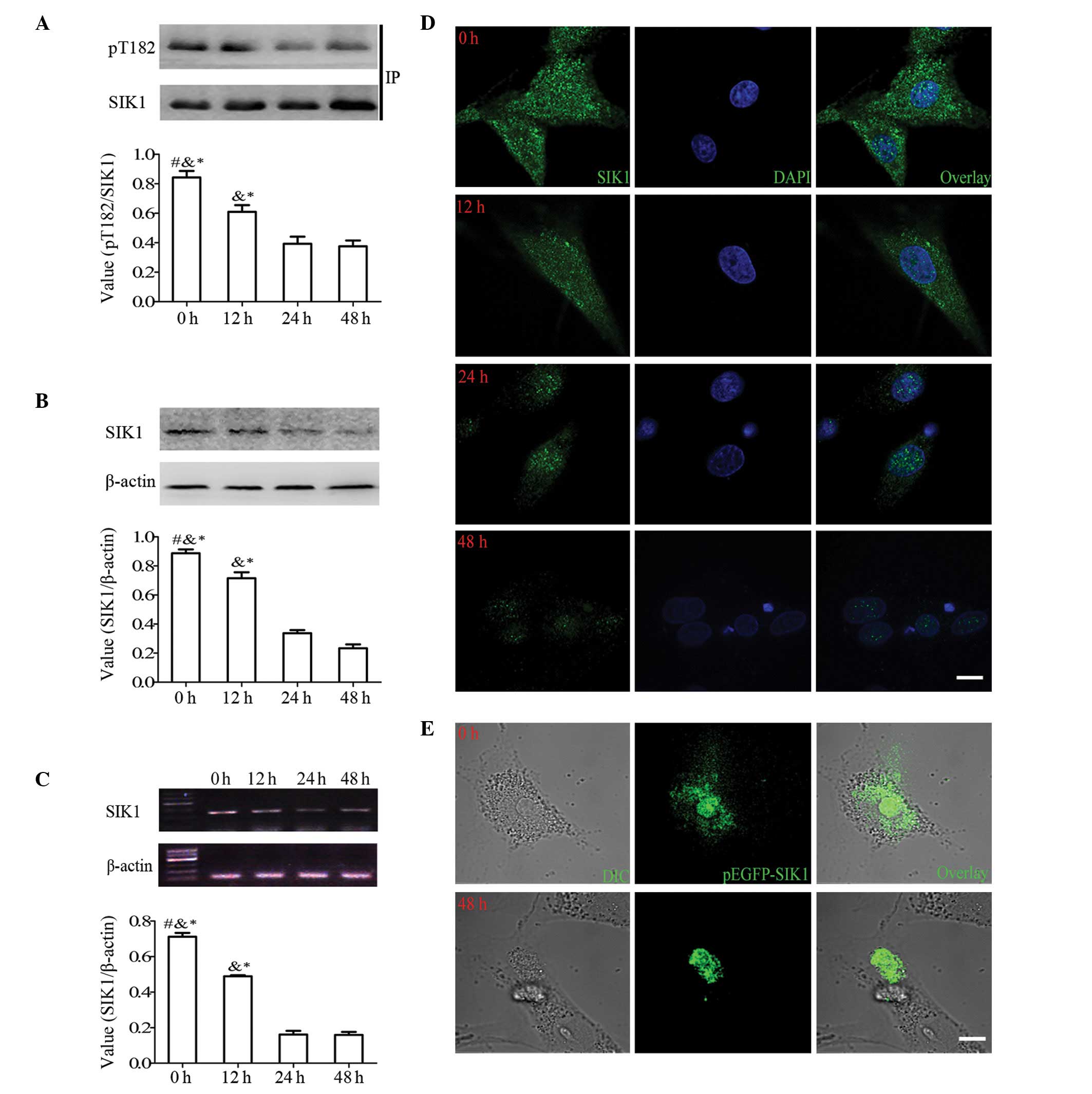
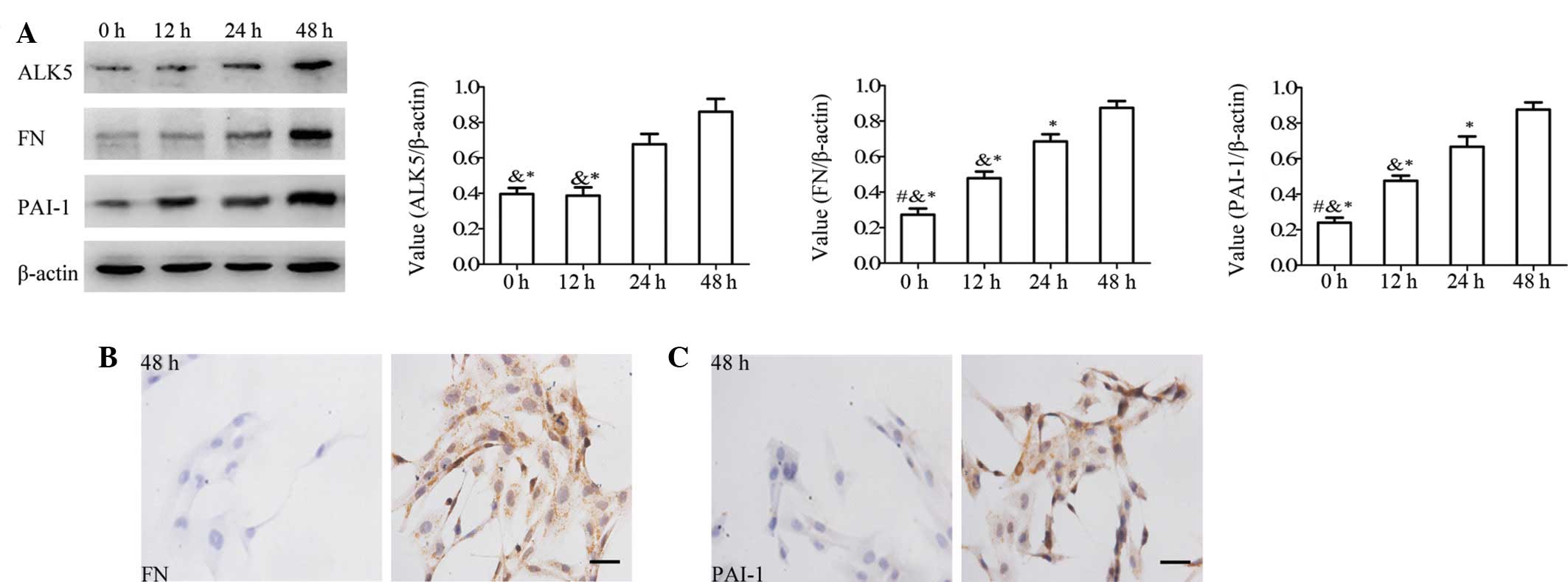
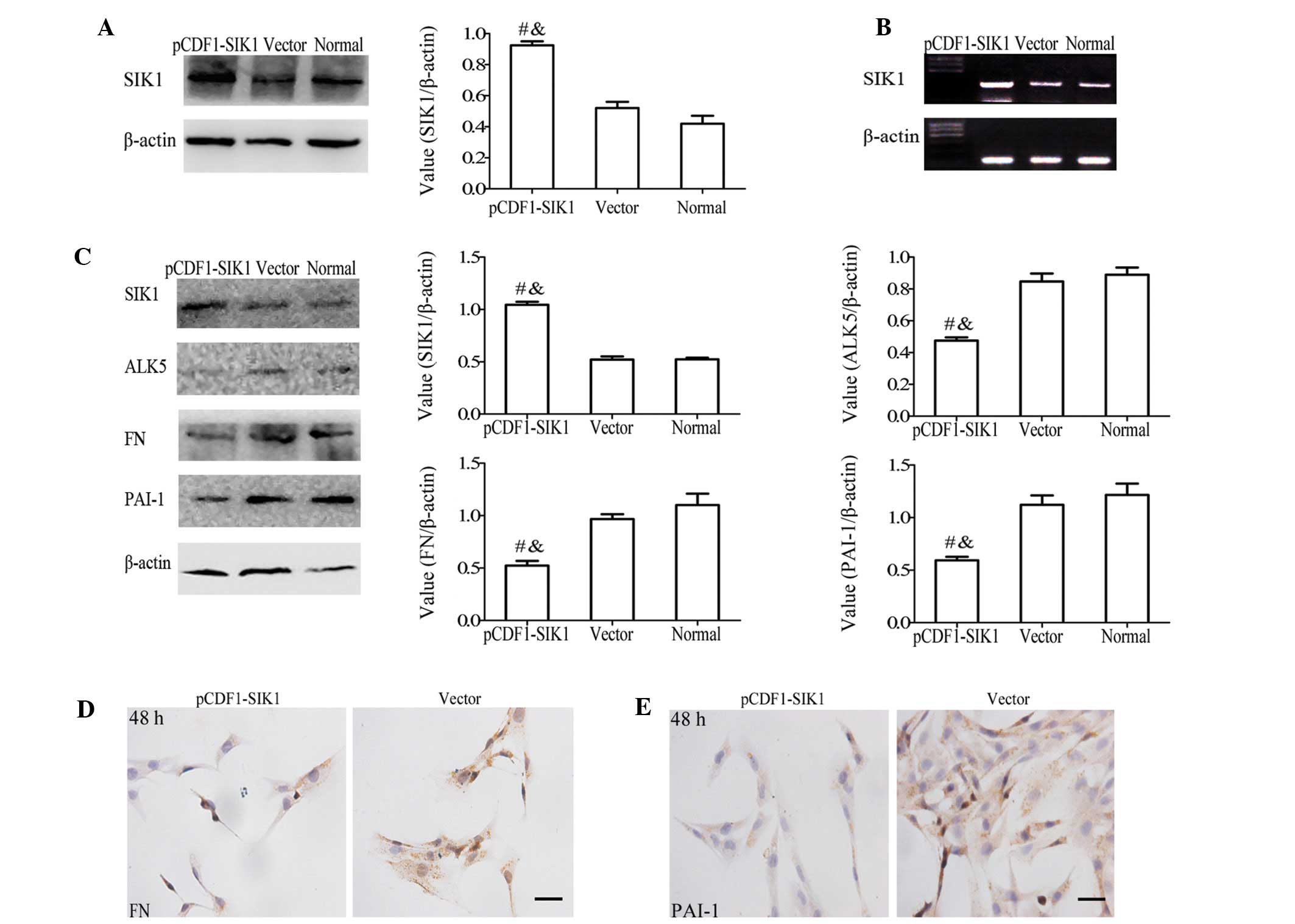
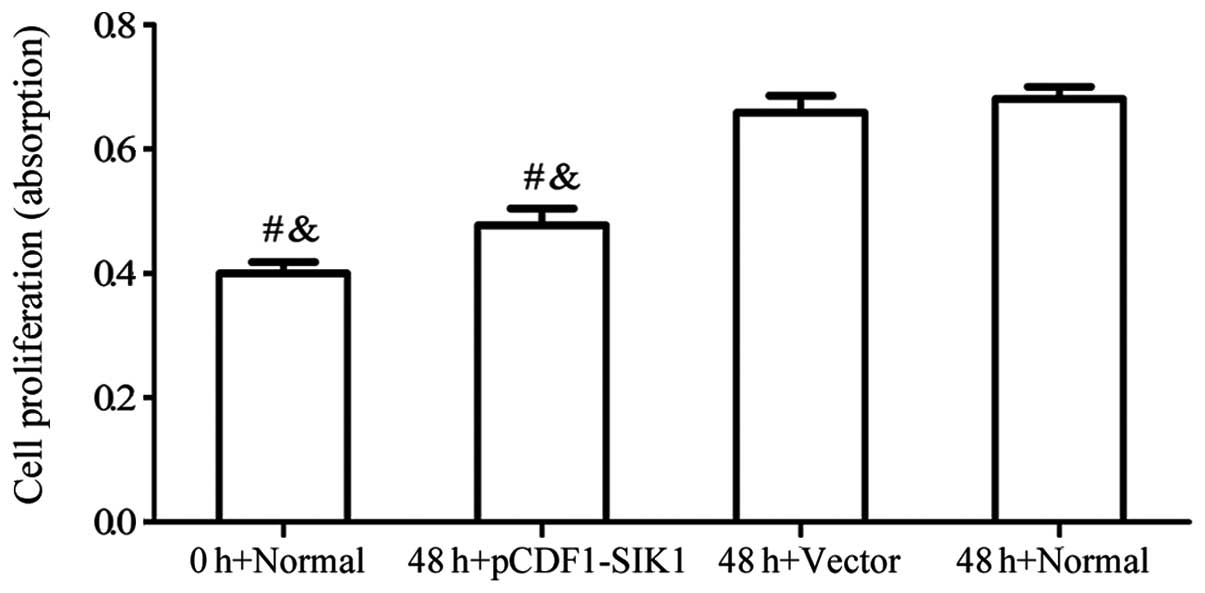
|
1.
|
Border WA and Noble NA: Evidence that
TGF-β should be a therapeutic target in diabetic nephropathy.
Kidney Int. 54:1390–1391. 1998.
|
|
2.
|
Ayo SH, Radnik RA, Glass W, et al:
Increased extracellular matrix synthesis and mRNA in mesangial
cells grown in high-glucose medium. Am J Physiol. 260:F185–F191.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Paradis V, Perlemuter G, Bonvoust F, et
al: High glucose and hyperinsulinemia stimulate connective tissue
growth factor expression: a potential mechanism involved in
progression to fibrosis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
Hepatology. 34:738–744. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4.
|
Schnaper HW, Hayashida T, Hubchak SC and
Poncelet AC: TGF-β signal transduction and mesangial cell
fibrogenesis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 284:F243–F252. 2003.
|
|
5.
|
Lebrin F, Deckers M, Bertolino P and Ten
Dijke P: TGF-β receptor function in the endothelium. Cardiovasc
Res. 65:599–608. 2005.
|
|
6.
|
Moon J, Kim H, Cho I, Sheen Y and Kim D:
IN-1130, a novel transforming growth factor-β type I receptor
kinase (ALK5) inhibitor, suppresses renal fibrosis in obstructive
nephropathy. Kidney Int. 70:1234–1243. 2006.
|
|
7.
|
Laping NJ: ALK5 inhibition in renal
disease. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 3:204–208. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Wang Z, Takemori H, Halder SK, Nonaka Y
and Okamoto M: Cloning of a novel kinase (SIK) of the SNF1/AMPK
family from high salt diet-treated rat adrenal. FEBS Lett.
453:135–139. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Steinberg GR and Kemp BE: AMPK in health
and disease. Physiol Rev. 89:1025–1078. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Takemori H, Katoh Y, Horike N, Doi J and
Okamoto M: ACTH-induced nucleocytoplasmic translocation of
salt-inducible kinase. J Biol Chem. 277:42334–42343. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Hashimoto YK, Satoh T, Okamoto M and
Takemori H: Importance of autophosphorylation at Ser186 in the
A-loop of salt inducible kinase 1 for its sustained kinase
activity. J Cell Biochem. 104:1724–1739. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Al-Hakim AK, Goransson O, Deak M, et al:
14-3-3 cooperates with LKB1 to regulate the activity and
localization of QSK and SIK. J Cell Sci. 118:5661–5673. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Romito A, Lonardo E, Roma G, Minchiotti G,
Ballabio A and Cobellis G: Lack of sik1 in mouse embryonic stem
cells impairs cardiomyogenesis by down-regulating the
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p57kip2. PloS One. 5:e90292010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Berdeaux R, Goebel N, Banaszynski L, et
al: SIK1 is a class II HDAC kinase that promotes survival of
skeletal myocytes. Nat Med. 13:597–603. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Cheng H, Liu P, Wang ZC, et al: SIK1
couples LKB1 to p53-dependent anoikis and suppresses metastasis.
Sci Signal. 2:ra352009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Koo SH, Flechner L, Qi L, et al: The CREB
coactivator TORC2 is a key regulator of fasting glucose metabolism.
Nature. 437:1109–1111. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Yoon YS, Seo WY, Lee MW, Kim ST and Koo
SH: Salt-inducible kinase regulates hepatic lipogenesis by
controlling SREBP-1c phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 284:10446–10452.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Kowanetz M, Lönn P, Vanlandewijck M,
Kowanetz K, Heldin CH and Moustakas A: TGFβ induces SIK to
negatively regulate type I receptor kinase signaling. J Cell Biol.
182:655–662. 2008.
|
|
19.
|
Lönn P, Vanlandewijck M, Raja E, et al:
Transcriptional induction of salt-inducible kinase 1 by
transforming growth factor β leads to negative regulation of type I
receptor signaling in cooperation with the Smurf2 ubiquitin ligase.
J Biol Chem. 287:12867–12878. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Feldman JD, Vician L, Crispino M, Hoe W,
Baudry M and Herschman HR: The Salt-inducible kinase, SIK, is
induced by depolarization in brain. J Neurochem. 74:2227–2238.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Wen X, Zeng Y, Liu L, et al: Zhenqing
recipe alleviates diabetic nephropathy in experimental type 2
diabetic rats through suppression of SREBP-1c. J Ethnopharmacol.
142:144–150. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Huang W, Yu J, Jia X, Xiong L, Li N and
Wen X: Zhenqing recipe improves glucose metabolism and insulin
sensitivity by repressing hepatic FOXO1 in type 2 diabetic rats. Am
J Chin Med. 40:721–733. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Wang S and Hirschberg R: Diabetes-relevant
regulation of cultured blood outgrowth endothelial cells. Microvasc
Res. 78:174–179. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Hills CE, Al-Rasheed N, Willars GB and
Brunskill NJ: C-peptide reverses TGF-β1-induced changes in renal
proximal tubular cells: implications for treatment of diabetic
nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 296:F614–F621.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Du J, Chen Q, Takemori H and Xu H: SIK2
can be activated by deprivation of nutrition and it inhibits
expression of lipogenic genes in adipocytes. Obesity (Silver
Spring). 16:531–538. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Lee MJ, Feliers D, Sataranatarajan K, et
al: Resveratrol ameliorates high glucose-induced protein synthesis
in glomerular epithelial cells. Cell Signal. 22:65–70. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Lin X, Takemori H, Katoh Y, et al:
Salt-inducible kinase is involved in the ACTH/cAMP-dependent
protein kinase signaling in Y1 mouse adrenocortical tumor cells.
Mol Endocrinol. 15:1264–1276. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Katoh Y, Takemori H, Lin X, et al:
Silencing the constitutive active transcription factor CREB by the
LKB1-SIK signaling cascade. FEBS J. 273:2730–2748. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Sasaki T, Takemori H, Yagita Y, et al:
SIK2 is a key regulator for neuronal survival after ischemia via
TORC1-CREB. Neuron. 69:106–119. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Xu J, Wu Y, Song P, Zhang M, Wang S and
Zou MH: Proteasome-dependent degradation of guanosine
5′-triphosphate cyclohydrolase I causes tetrahydrobiopterin
deficiency in diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 116:944–953.
2007.
|
|
31.
|
Trumper A, Trumper K and Horsch D:
Mechanisms of mitogenic and anti-apoptotic signaling by
glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide in beta (INS-1)-cells.
J Endocrinol. 174:233–246. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Wu L and Derynck R: Essential role of
TGF-β signaling in glucose-induced cell hypertrophy. Dev Cell.
17:35–48. 2009.
|
|
33.
|
Gouville AC, Boullay V, Krysa G, et al:
Inhibition of TGF-β signaling by an ALK5 inhibitor protects rats
from dimethylnitrosamine-induced liver fibrosis. Br J Pharmacol.
145:166–177. 2009.
|
|
34.
|
Yata Y, Gotwals P, Koteliansky V and
Rockey DC: Dose-dependent inhibition of hepatic fibrosis in mice by
a TGF-β soluble receptor: implications for antifibrotic therapy.
Hepatology. 35:1022–1030. 2002.
|