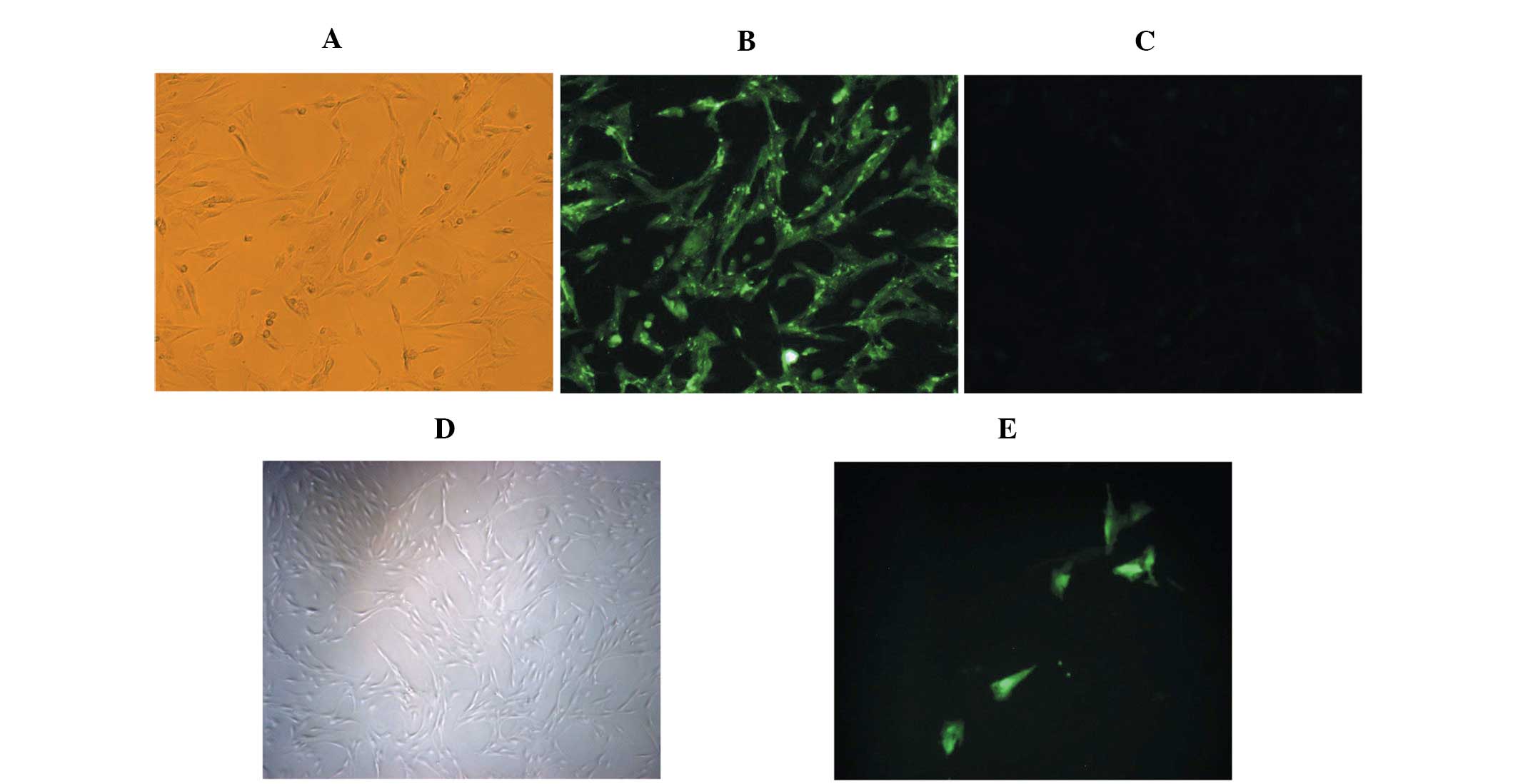
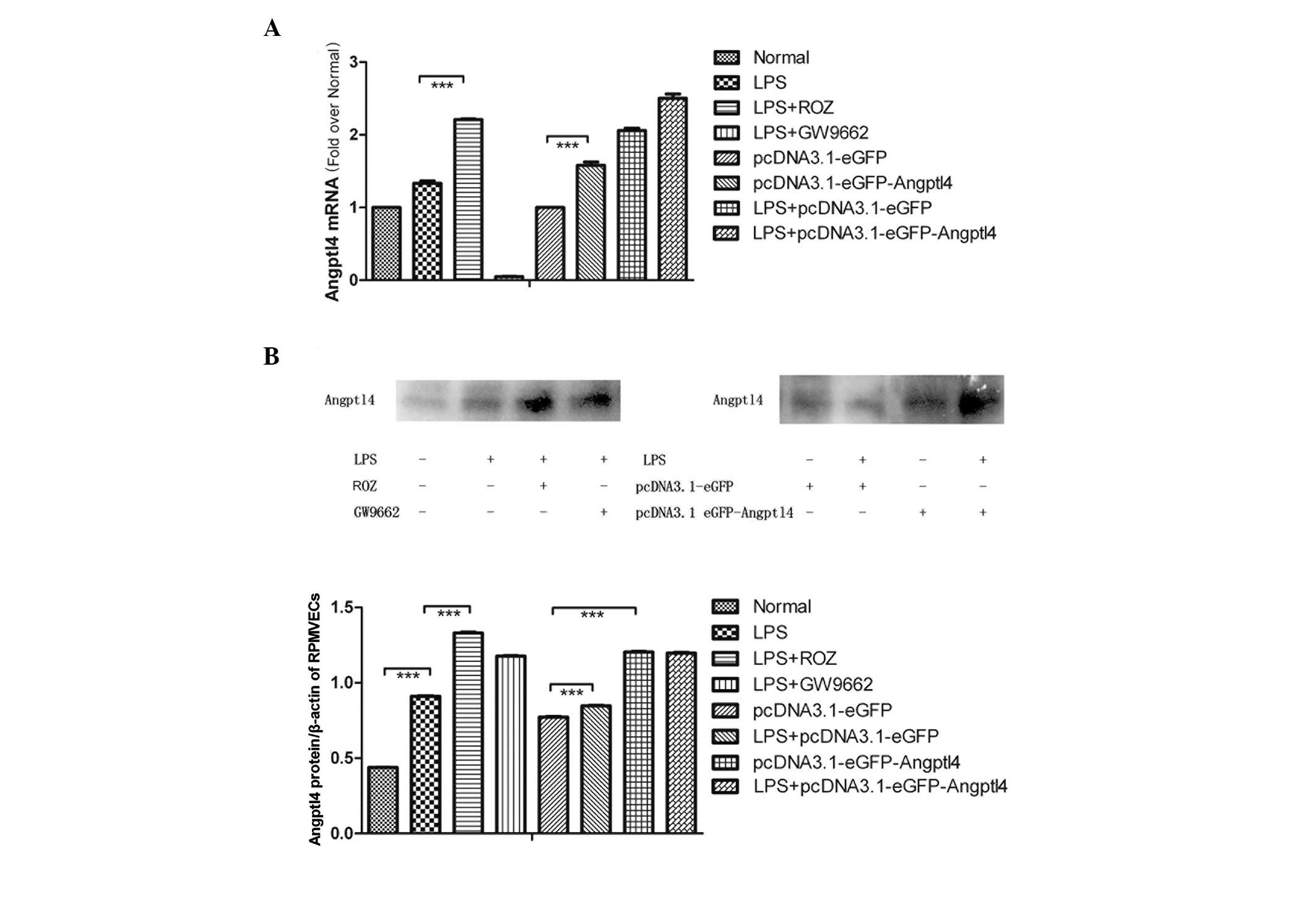
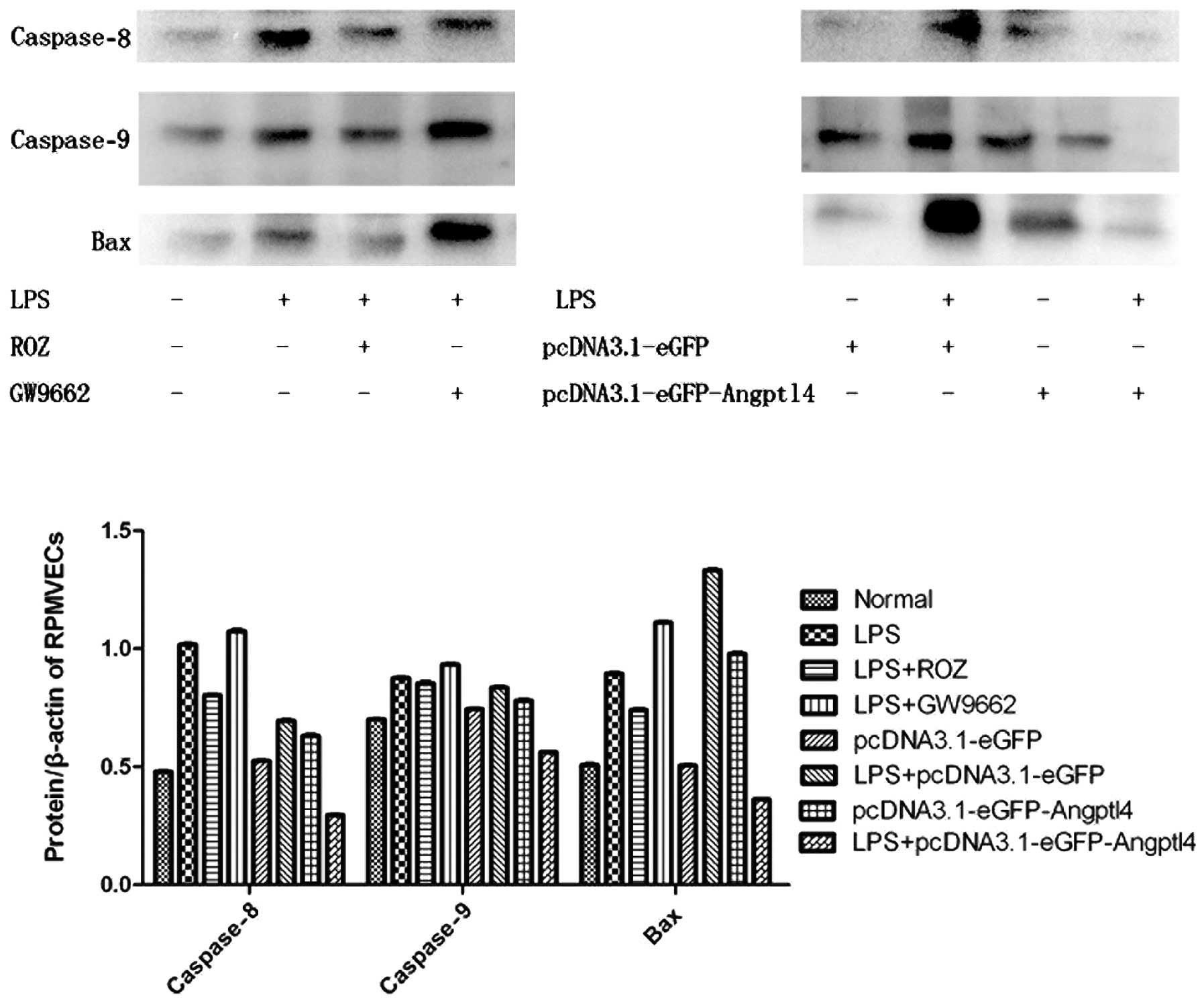
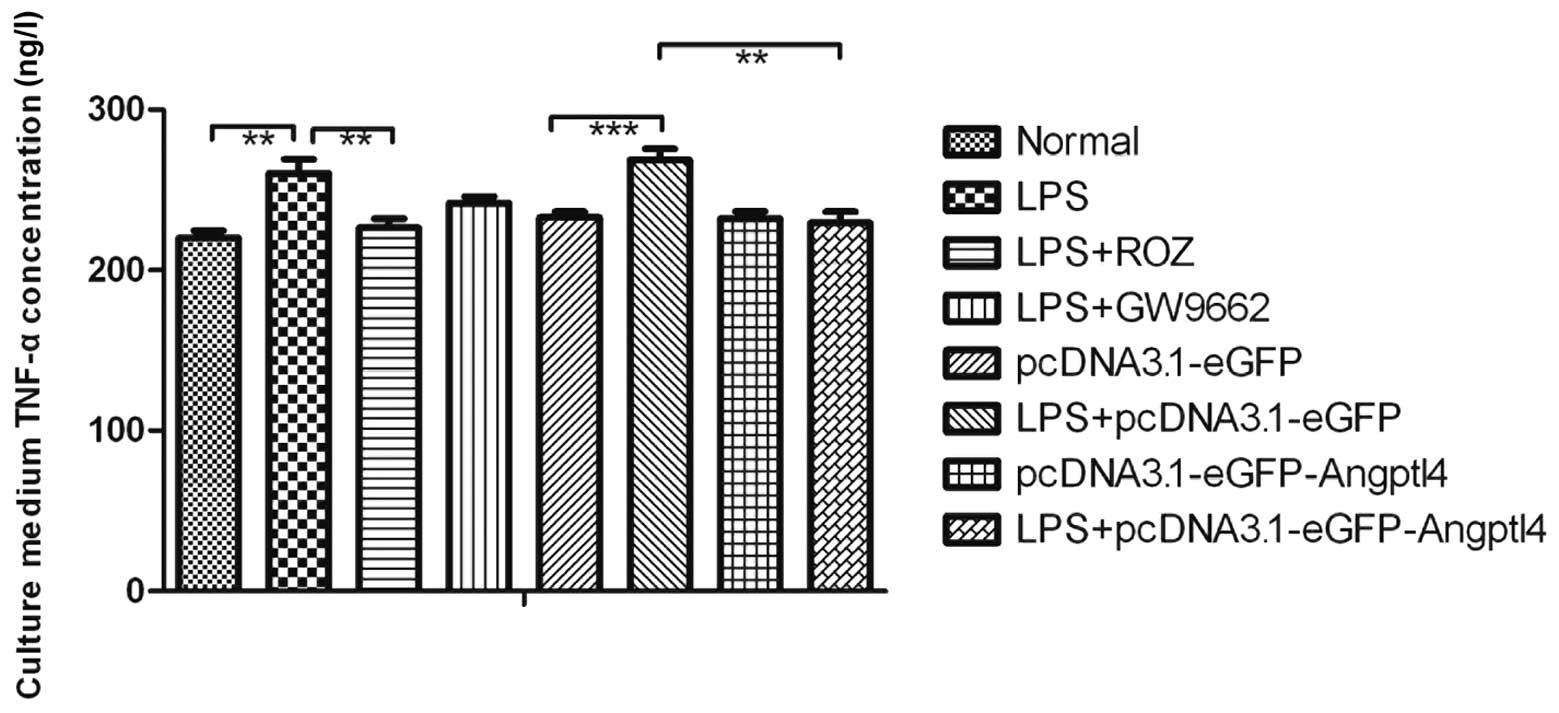
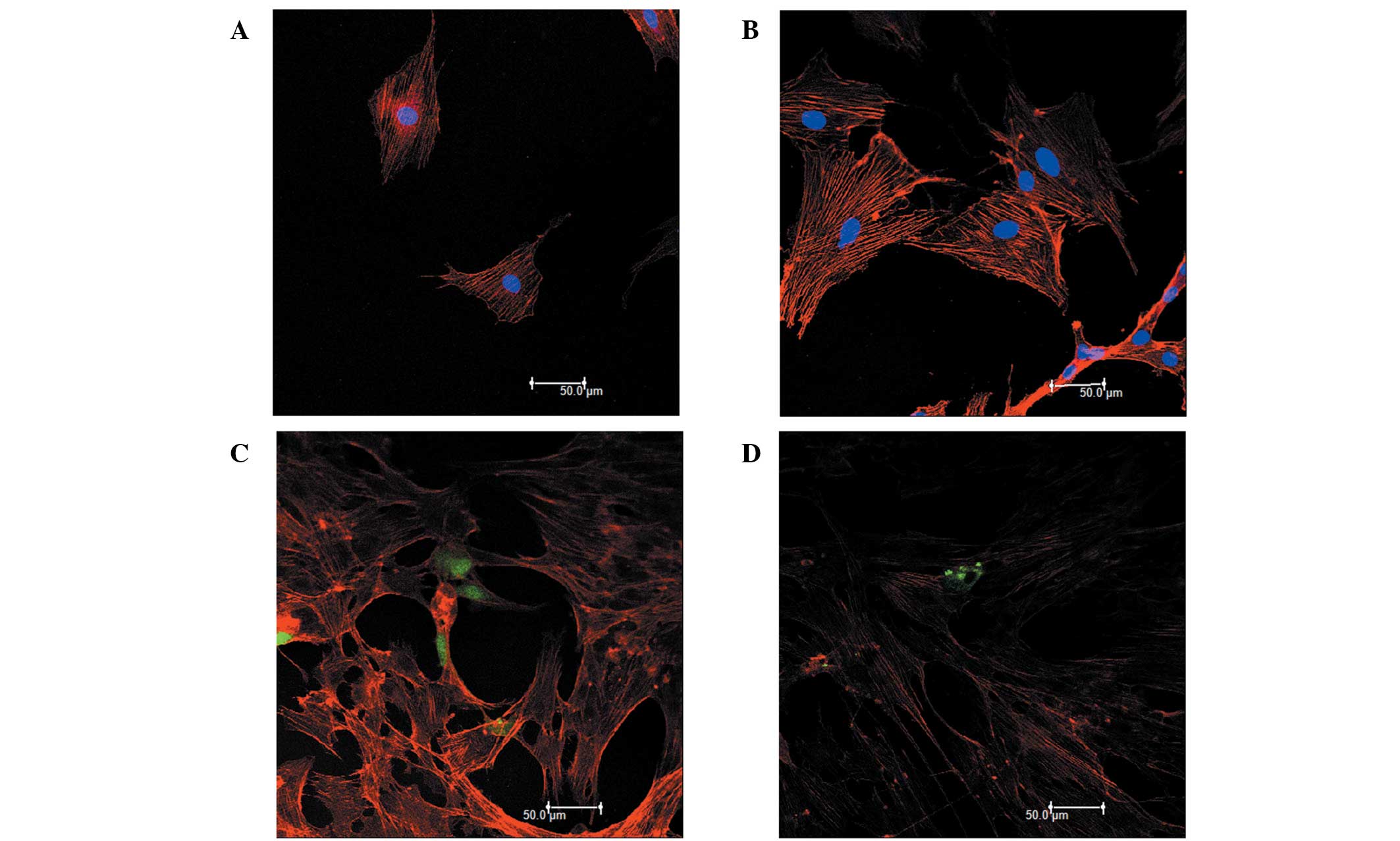
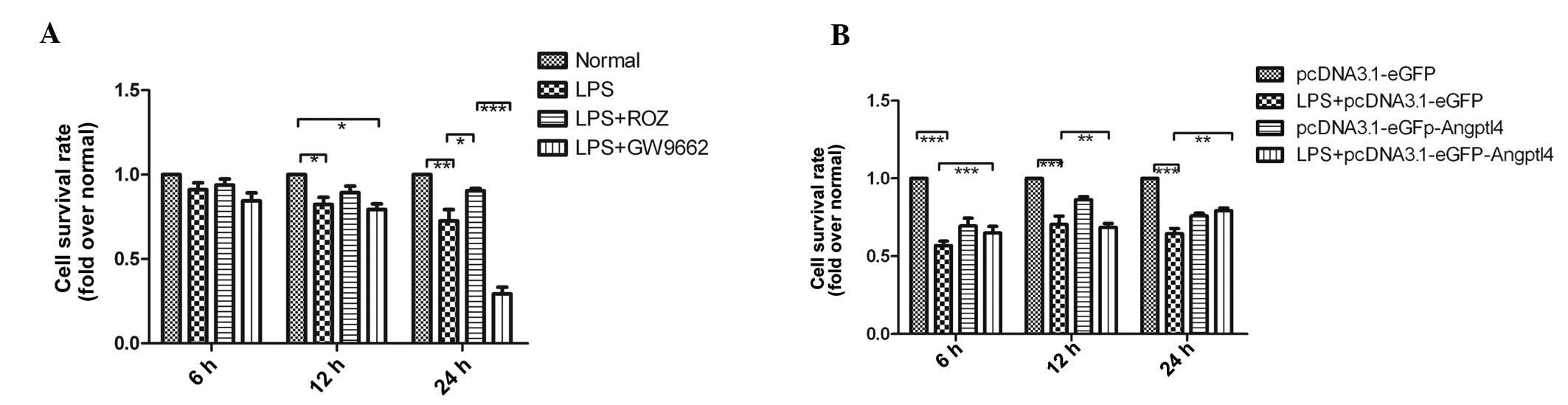
|
1
|
Ge H, Yang G, Yu X, Pourbahrami T and Li
C: Oligomerization state-dependent hyperlipidemic effect of
angiopoietin-like protein 4. J Lipid Res. 45:2071–2079. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xu A, Lam MC, Chan KW, et al:
Angiopoietin-like protein 4 decreases blood glucose and improves
glucose tolerance but induces hyperlipidemia and hepatic steatosis
in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:6086–6091. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sukonina V, Lookene A, Olivecrona T and
Olivecrona G: Angiopoietin-like protein 4 converts lipoprotein
lipase to inactive monomers and modulates lipase activity in
adipose tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:17450–17455. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mandard S, Zandbergen F, van Straten E,
Wahli W, Kuipers F, Muller M and Kersten S: The fasting-induced
adipose factor/angiopoietin-like protein 4 is physically associated
with lipoproteins and governs plasma lipid levels and adiposity. J
Biol Chem. 281:934–944. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhu P, Tan MJ, Huang RL, et al:
Angiopoietin-like 4 protein elevates the prosurvival intracellular
O2(−):H2O2ratio and confers
anoikis resistance to tumors. Cancer Cell. 19:401–415. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kersten S: Regulation of lipid metabolism
via angiopoietin-like proteins. Biochem Soc Trans. 33:1059–1062.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mandard S, Zandbergen F, Tan NS, et al:
The direct peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor target
fasting-induced adipose factor (FIAF/PGAR/ANGPTL4) is present in
blood plasma as a truncated protein that is increased by
fenofibrate treatment. J Biol Chem. 279:34411–34420. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Koliwad SK, Kuo T, Shipp LE, et al:
Angiopoietin-like 4 (ANGPTL4, fasting-induced adipose factor) is a
direct glucocorticoid receptor target and participates in
glucocorticoid-regulated triglyceride metabolism. J Biol Chem.
284:25593–25601. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Padua D, Zhang XH, Wang Q, et al: TGF beta
primes breast tumors for lung metastasis seeding through
angiopoietin-like 4. Cell. 133:66–77. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Belanger AJ, Lu H, Date T, et al: Hypoxia
up-regulates expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor gamma angiopoietin-related gene (PGAR) in cardiomyocytes:
role of hypoxia inducible factor 1alpha. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
34:765–774. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Liu F, Li W, Pauluhn J, Trubel H and Wang
C: Lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats:
comparative assessment of intratracheal instillation and aerosol
inhalation. Toxicology. 304:158–166. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Feingold KR, Shigenaga JK, Cross AS, Moser
A and Grunfeld C: Angiopoietin like protein 4 expression is
decreased in activated macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
421:612–615. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ichikawa H, Naito Y, Takagi T, et al: A
specific peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma
(PPAR-gamma) ligand, pioglitazone, ameliorates gastric mucosal
damage induced by ischemia and reperfusion in rats. Redox Rep.
7:343–346. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Konturek PC, Brzozowski T, Kania J, et al:
Pioglitazone, a specific ligand of the peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma reduces gastric mucosal
injury induced by ischaemia/reperfusion in rat. Scand J
Gastroenterol. 38:468–476. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Villegas I, Martin AR, Toma W and de la
Lastra CA: Rosiglitazone, an agonist of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma, protects against gastric
ischemia-reperfusion damage in rats: role of oxygen free radicals
generation. Eur J Pharmacol. 505:195–203. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wada K, Nakajima A, Takahashi H, et al:
Protective effect of endogenous PPARgamma against acute gastric
mucosal lesions associated with ischemia-reperfusion. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 287:G452–G458. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Takagi T, Naito Y, Ichikawa H, et al: A
PPAR-gamma ligand, 15-deoxy-Delta12,14-prostaglandin J(2),
inhibited gastric mucosal injury induced by ischemia-reperfusion in
rats. Redox Rep. 9:376–381. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Naito Y, Takagi T, Matsuyama K, Yoshida N
and Yoshikawa T: Pioglitazone, a specific PPAR-gamma ligand,
inhibits aspirin-induced gastric mucosal injury in rats. Aliment
Pharmacol Ther. 15:865–873. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Slomiany A, Nishikawa H and Slomiany BL:
Screening and modulation of extracellular signals by mucous
barrier. Serum glycosylphosphatidylinositol phospholipase D
(GPI-PLD) releases protective mucous barrier from oral mucosa. J
Physiol Pharmacol. 53:21–38. 2002.
|
|
20
|
Lappas M, Permezel M and Rice GE:
15-Deoxy-Delta(12,14)-prostaglandin J(2) and troglitazone
regulation of the release of phospholipid metabolites, inflammatory
cytokines and proteases from human gestational tissues. Placenta.
27:1060–1072. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chen SF, Fei X and Li SH: A new simple
method for isolation of microvascular endothelial cells avoiding
both chemical and mechanical injuries. Microvasc Res. 50:119–128.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cheng C, Liu H, Ge H, et al:
Lipopolysaccharide induces expression of SSeCKS in rat lung
microvascular endothelial cell. Mol Cell Biochem. 305:1–8. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang H and Sun GY: LPS induces
permeability injury in lung microvascular endothelium via AT(1)
receptor. Arch Biochem Biophys. 441:75–83. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Adkison JB, Miller GT, Weber DS, et al:
Differential responses of pulmonary endothelial phenotypes to
cyclical stretch. Microvasc Res. 71:175–184. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gao G, Kapushoc ST, Simpson AM, Thiemann
OH and Simpson L: Guide RNAs of the recently isolated LEM125 strain
of Leishmania tarentolae: an unexpected complexity. RNA.
7:1335–1347. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Essler M, Staddon JM, Weber PC and
Aepfelbacher M: Cyclic AMP blocks bacterial
lipopolysaccharide-induced myosin light chain phosphorylation in
endothelial cells through inhibition of Rho/Rho kinase signaling. J
Immunol. 164:6543–6549. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Harhaj NS and Antonetti DA: Regulation of
tight junctions and loss of barrier function in pathophysiology.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 36:1206–1237. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Koishi R, Ando Y, Ono M, et al: Angptl3
regulates lipid metabolism in mice. Nat Genet. 30:151–157. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Oike Y, Yasunaga K, Ito Y, et al:
Angiopoietin-related growth factor (AGF) promotes epidermal
proliferation, remodeling, and regeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 100:9494–9499. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim I, Kim HG, Kim H, et al: Hepatic
expression, synthesis and secretion of a novel
fibrinogen/angiopoietin-related protein that prevents
endothelial-cell apoptosis. Biochem J. 346:603–610. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Brunckhorst MK, Wang H, Lu R, et al:
Angiopoietin-4 promotes glioblastoma progression by enhancing tumor
cell viability and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 70:7283–7293. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lu B, Moser A, Shigenaga JK, Grunfeld C
and Feingold KR: The acute phase response stimulates the expression
of angiopoietin like protein 4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
391:1737–1741. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hermann LM, Pinkerton M, Jennings K, et
al: Angiopoietin-like-4 is a potential angiogenic mediator in
arthritis. Clin Immunol. 115:93–101. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cazes A, Galaup A, Chomel C, et al:
Extracellular matrix-bound angiopoietin-like 4 inhibits endothelial
cell adhesion, migration, and sprouting and alters actin
cytoskeleton. Circ Res. 99:1207–1215. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yang YH, Wang Y, Lam KS, et al:
Suppression of the Raf/MEK/ERK signaling cascade and inhibition of
angiogenesis by the carboxyl terminus of angiopoietin-like protein
4. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 28:835–840. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Galaup A, Cazes A, Le Jan S, et al:
Angiopoietin-like 4 prevents metastasis through inhibition of
vascular permeability and tumor cell motility and invasiveness.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:18721–18726. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li KQ, Li WL, Peng SY, et al: Anti-tumor
effect of recombinant retroviral vector-mediated human ANGPTL4 gene
transfection. Chin Med J (Engl). 117:1364–1369. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dhillon AS and Kolch W: Untying the
regulation of the Raf-1 kinase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 404:3–9.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wu F, Wang H, Li J, Liang J and Ma S:
Homoplantaginin modulates insulin sensitivity in endothelial cells
by inhibiting inflammation. Biol Pharm Bull. 35:1171–1177. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Masamune A, Watanabe T, Kikuta K and
Shimosegawa T: Roles of pancreatic stellate cells in pancreatic
inflammation and fibrosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:S48–S54.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Faulkner A, Rosen S and Norman C: The
right information may matter more than frequency-place alignment:
simulations of frequency-aligned and upward shifting cochlear
implant processors for a shallow electrode array insertion. Ear
Hear. 27:139–152. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|