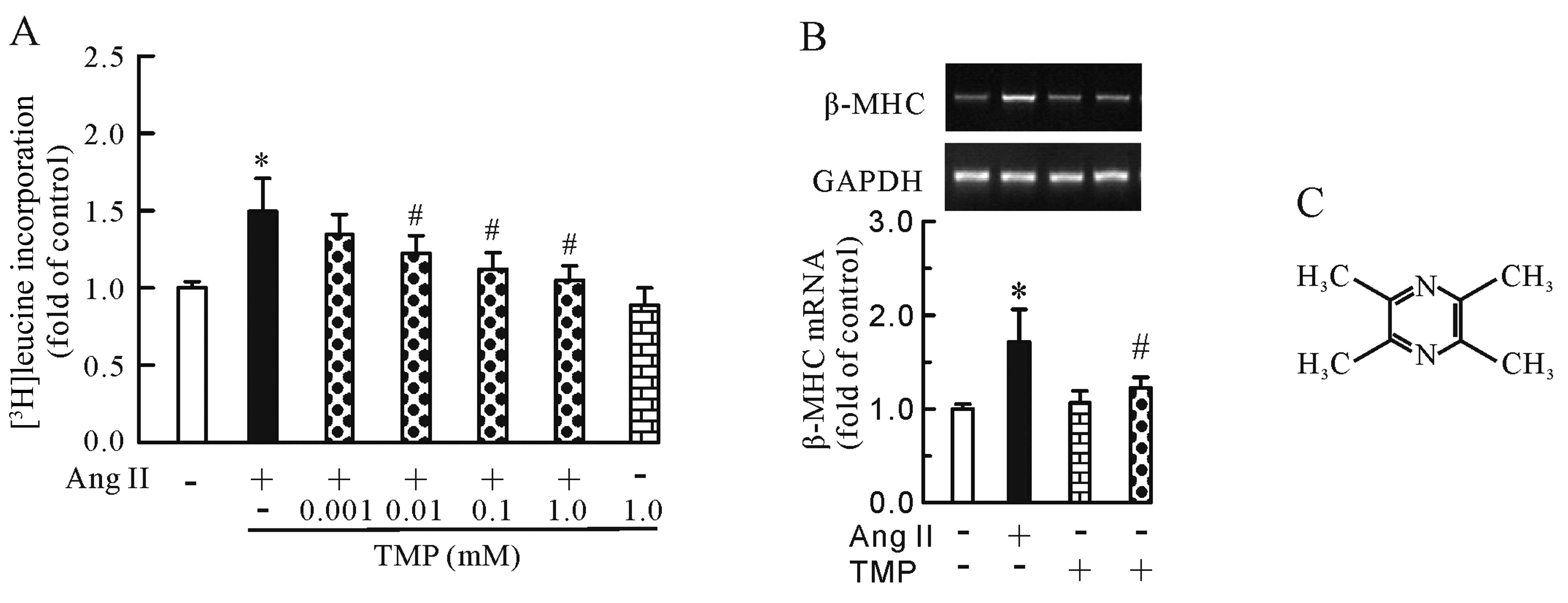
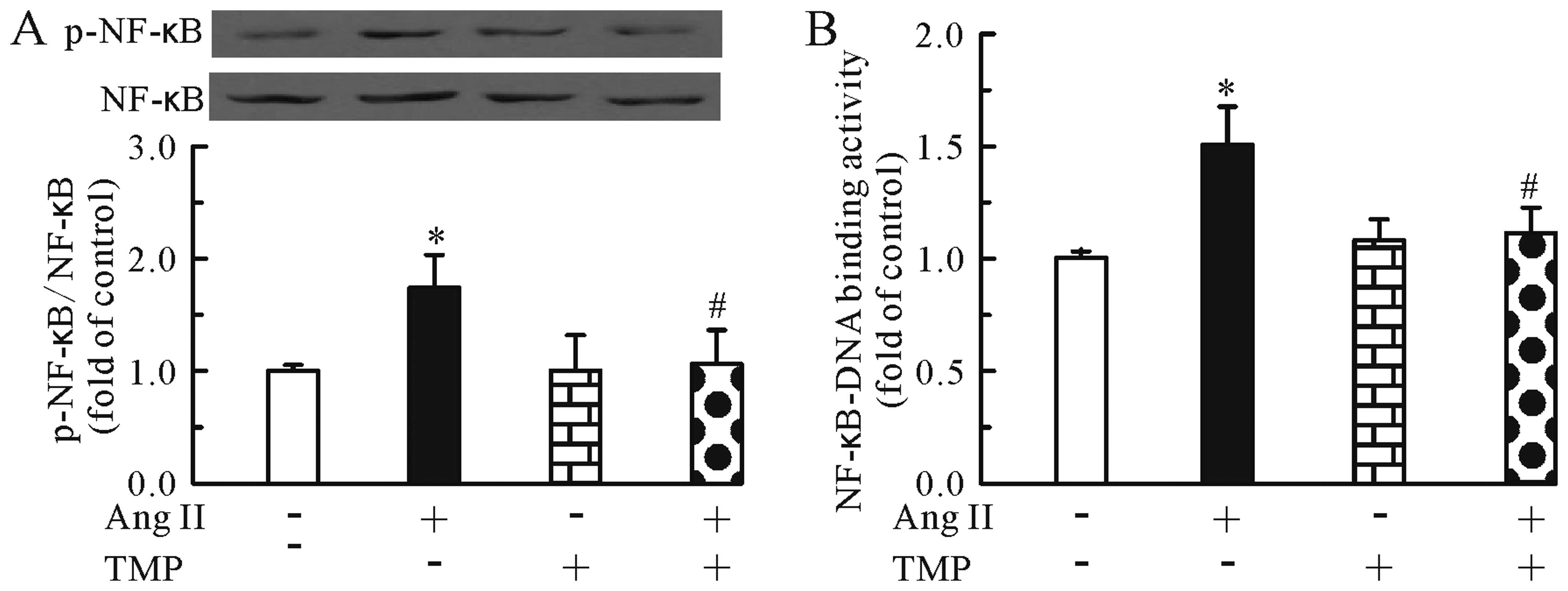
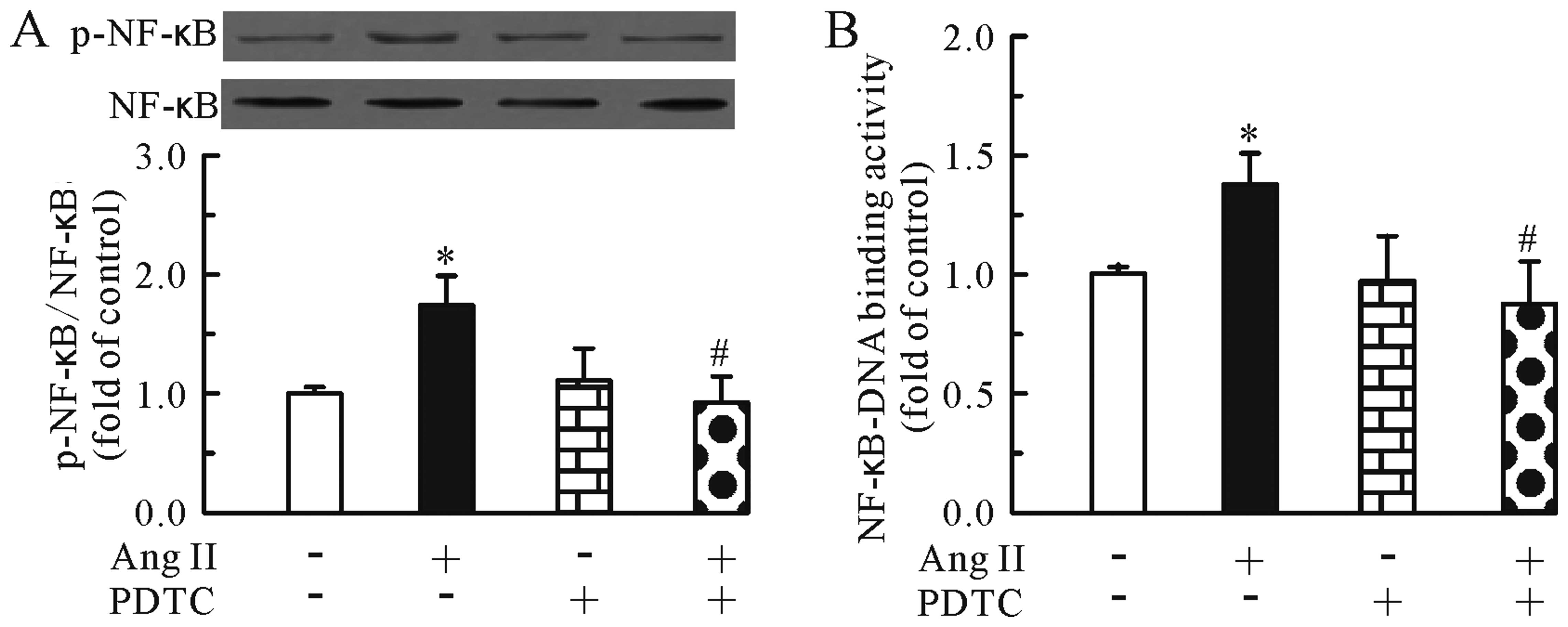
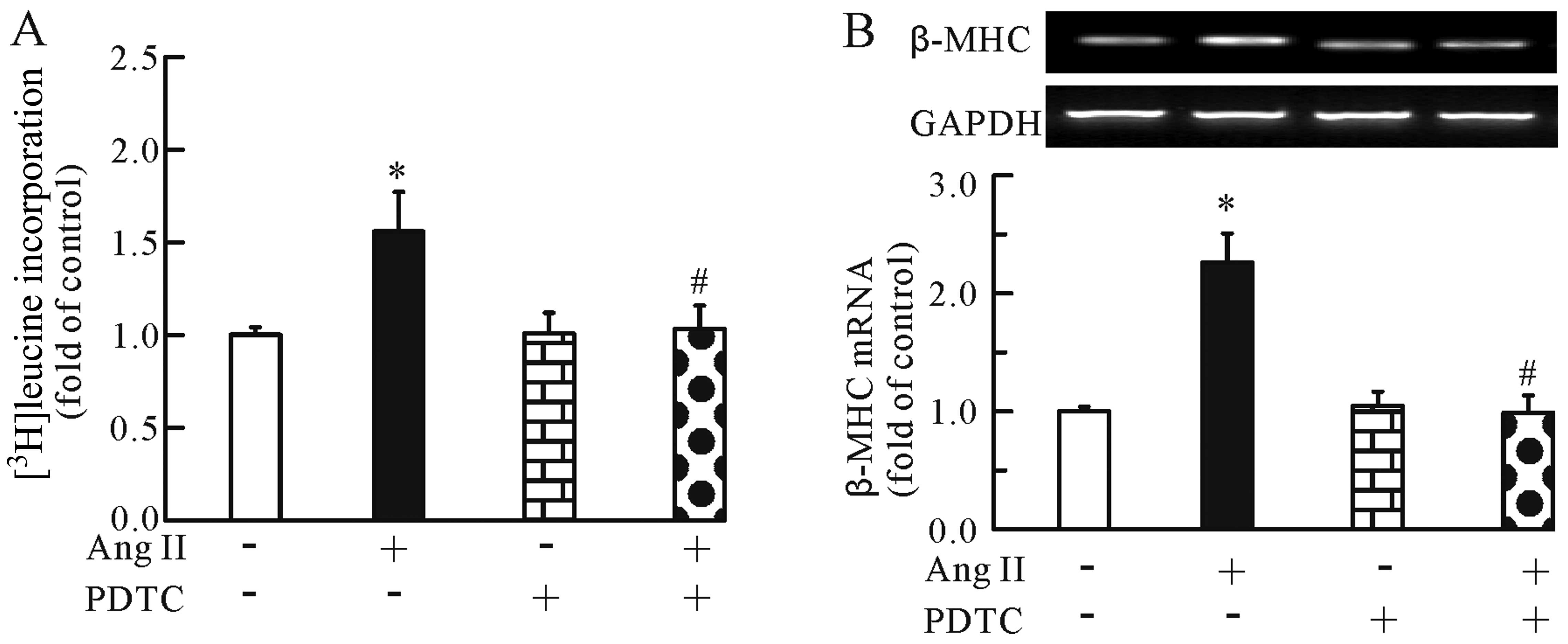
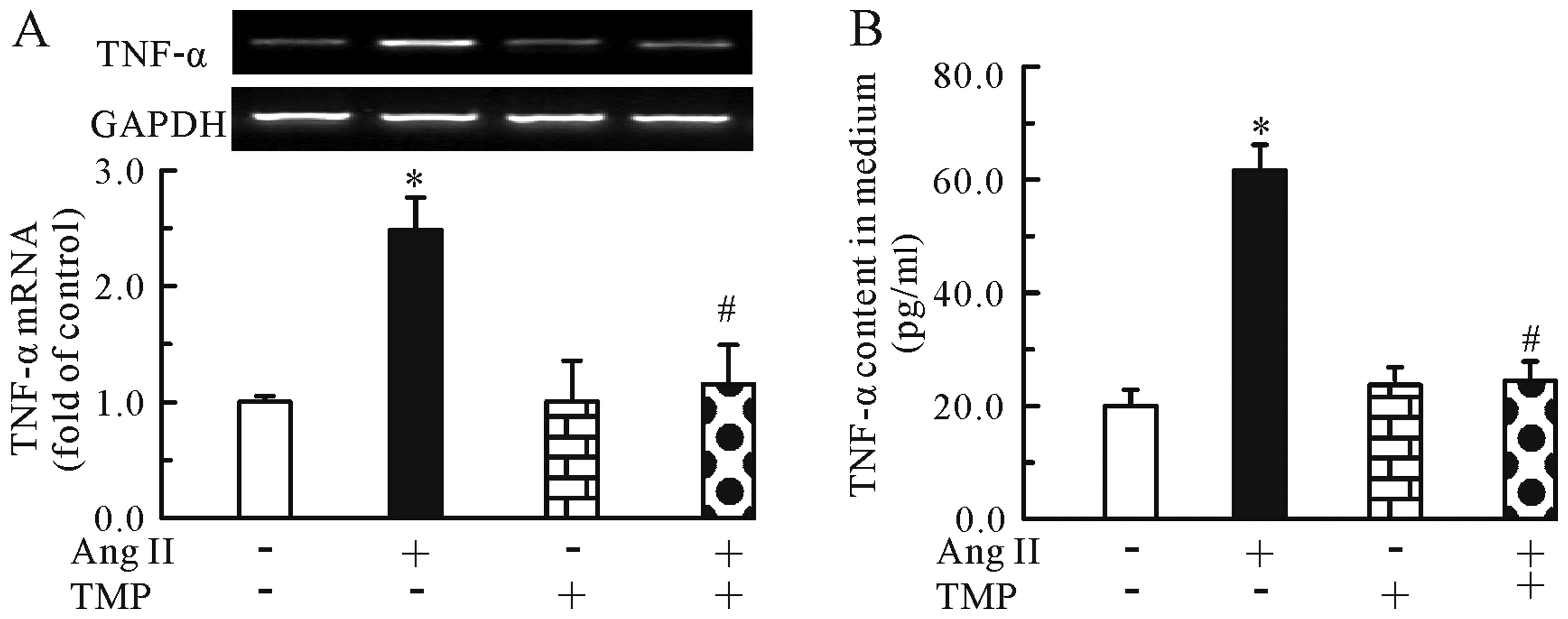
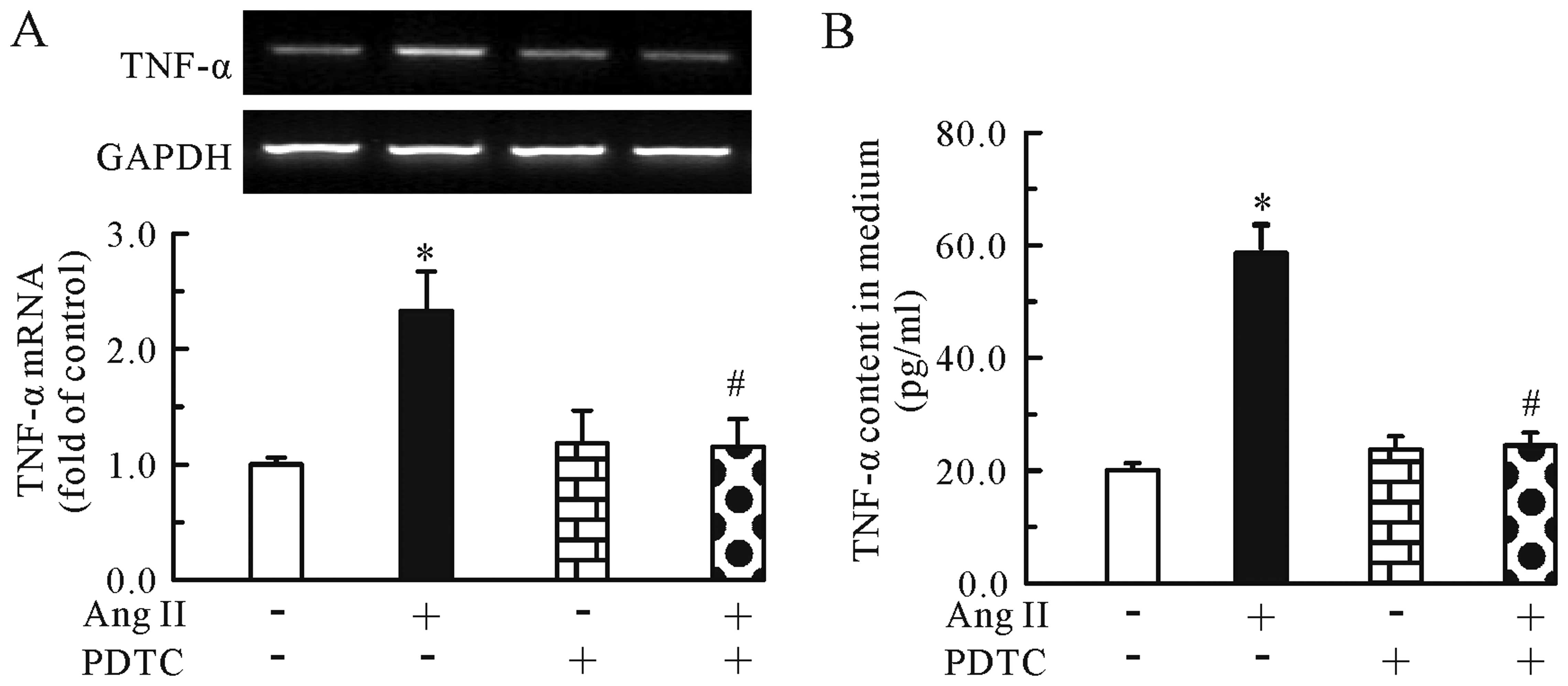
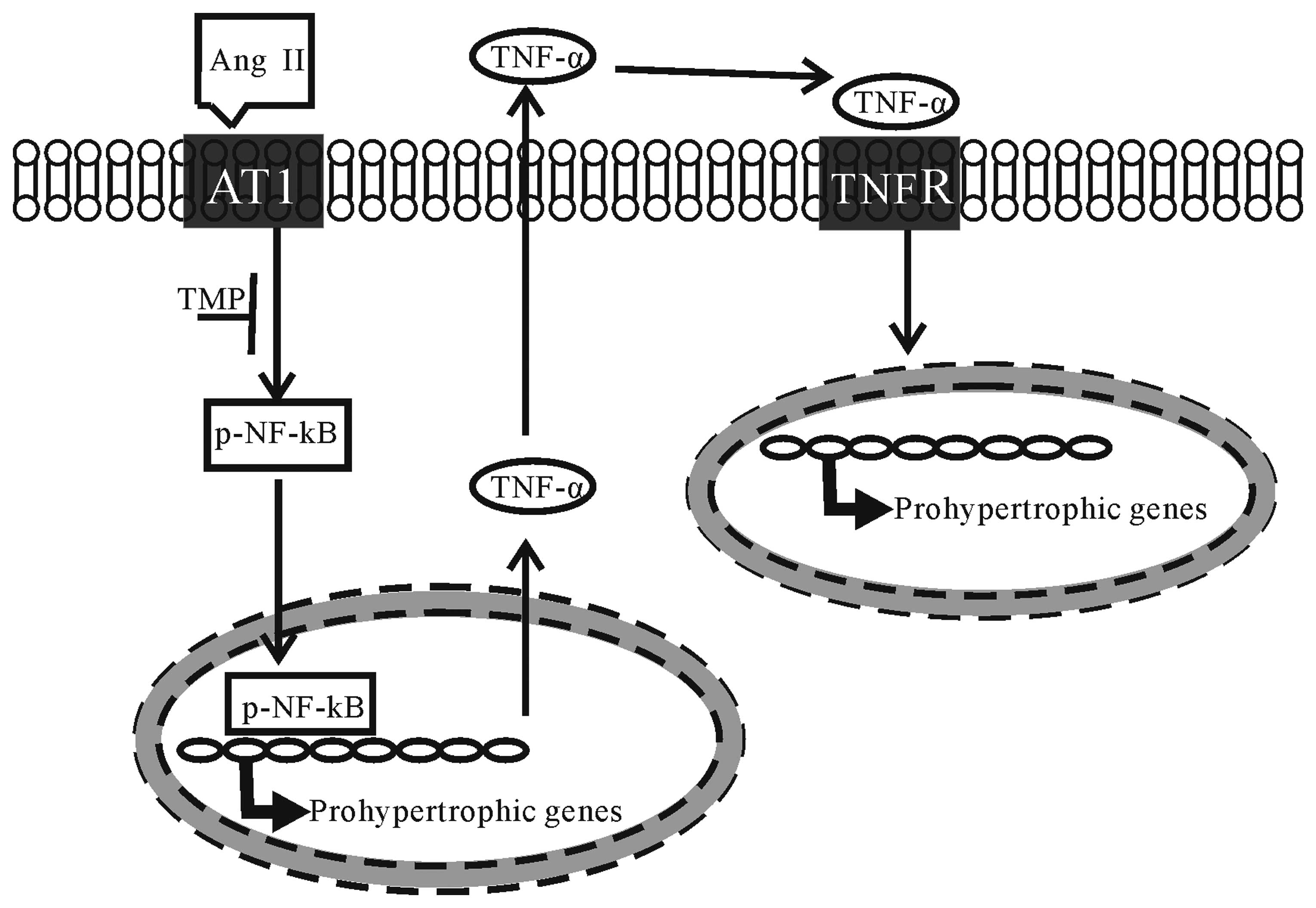
|
1
|
Levy D, Garrison RJ, Savage DD, Kannel WB
and Castelli WP: Prognostic implications of echocardiographically
determined left ventricular mass in the Framingham Heart Study. N
Engl J Med. 322:1561–1566. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sadoshima J and Izumo S: Molecular
characterization of angiotensin II - induced hypertrophy of cardiac
myocytes and hyperplasia of cardiac fibroblasts. Critical role of
the AT1 receptor subtype. Circ Res. 73:413–423. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lee KH, Jang Y and Chung JH: Heat shock
protein 90 regulates IkappaB kinase complex and NF-kappaB
activation in angiotensin II-induced cardiac cell hypertrophy. Exp
Mol Med. 42:703–711. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gupta S, Young D, Maitra RK, et al:
Prevention of cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure by silencing of
NF-kappaB. J Mol Biol. 375:637–649. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen KJ and Chen K: Ischemic stroke
treated with Ligusticum chuanxiong. Chin Med J (Engl).
105:870–873. 1992.
|
|
6
|
Sutter MC and Wang YX: Recent
cardiovascular drugs from Chinese medicinal plants. Cardiovasc Res.
27:1891–1901. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Feng J, Wu G and Tang S: The effects of
tetramethylpyrazine on the incidence of arrhythmias and the release
of PGI2 and TXA2 in the ischemic rat heart. Planta Med. 65:268–270.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fan L, Wang K, Shi Z, Die J, Wang C and
Dang X: Tetramethylpyrazine protects spinal cord and reduces
inflammation in a rat model of spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion
injury. J Vasc Surg. 54:192–200. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu CF, Lin CH, Chen CF, Huang TC and Lin
SC: Antioxidative effects of tetramethylpyrazine on acute
ethanol-induced lipid peroxidation. Am J Chin Med. 33:981–988.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang GJ, Wang HX, Yao YS, Guo LY and Liu
P: The role of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase
II and calcineurin in TNF-alpha-induced myocardial hypertrophy.
Braz J Med Biol Res. 45:1045–1051. 2012.
|
|
11
|
Hu Y, Li T, Wang Y, et al: Tollip
attenuated the hypertrophic response of cardiomyocytes induced by
IL-1beta. Front Biosci. 14:2747–2756. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yokoyama T, Sekiguchi K, Tanaka T, et al:
Angiotensin II and mechanical stretch induce production of tumor
necrosis factor in cardiac fibroblasts. Am J Physiol.
276:H1968–H1976. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang Y, Zhang H, Shao Z, et al:
Suppression of endothelin-1-induced cardiac myocyte hypertrophy by
PPAR agonists: role of diacylglycerol kinase zeta. Cardiovasc Res.
90:267–275. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Feng J, Liu R, Wu G and Tang S: Effects of
tetramethylpyrazine on the release of PGI2 and TXA2 in the hypoxic
isolated rat heart. Mol Cell Biochem. 167:153–158. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zou LY, Hao XM, Zhang GQ, Zhang M, Guo JH
and Liu TF: Effect of tetramethyl pyrazine on L-type calcium
channel in rat ventricular myocytes. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
79:621–626. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gao S, Chen ZW, Zheng H and Chen XL:
Ligustrazine attenuates acute myocardium injury after thermal
trauma. Burns. 33:321–327. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhao HP, Lu D, Zhang W, et al: Protective
action of tetramethylpyrazine phosphate against dilated
cardiomyopathy in cTnT(R141W) transgenic mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
31:281–288. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rajapurohitam V, Kilic A, Javadov S and
Karmazyn M: Role of NF-kappaB and p38 MAPK activation in mediating
angiotensin II and endothelin-1-induced stimulation in leptin
production and cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Mol Cell Biochem.
366:287–297. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu Q, Chen Y, Auger-Messier M and
Molkentin JD: Interaction between NFkappaB and NFAT coordinates
cardiac hypertrophy and pathological remodeling. Circ Res.
110:1077–1086. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Valente AJ, Clark RA, Siddesha JM,
Siebenlist U and Chandrasekar B: CIKS (Act1 or TRAF3IP2) mediates
angiotensin-II-induced Interleukin-18 expression, and
Nox2-dependent cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
53:113–124. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Freund C, Schmidt-Ullrich R, Baurand A, et
al: Requirement of nuclear factor-kappaB in angiotensin II- and
isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy in vivo. Circulation.
111:2319–2325. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang D and Baldwin AS Jr: Activation of
nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent transcription by tumor necrosis
factor-alpha is mediated through phosphorylation of RelA/p65 on
serine 529. J Biol Chem. 273:29411–29416. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Baldwin AS Jr: The NF-kappa B and I kappa
B proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol.
14:649–683. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kawano S, Kubota T, Monden Y, et al:
Blockade of NF-kappaB ameliorates myocardial hypertrophy in
response to chronic infusion of angiotensin II. Cardiovasc Res.
67:689–698. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sun M, Chen M, Dawood F, et al: Tumor
necrosis factor-alpha mediates cardiac remodeling and ventricular
dysfunction after pressure overload state. Circulation.
115:1398–1407. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Janczewski AM, Kadokami T, Lemster B, Frye
CS, McTiernan CF and Feldman AM: Morphological and functional
changes in cardiac myocytes isolated from mice overexpressing
TNF-alpha. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 284:H960–H969. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nakamura K, Fushimi K, Kouchi H, et al:
Inhibitory effects of antioxidants on neonatal rat cardiac myocyte
hypertrophy induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and angiotensin
II. Circulation. 98:794–799. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ock S, Ahn J, Lee SH, et al: Receptor
activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand is a novel inducer of
myocardial inflammation. Cardiovasc Res. 94:105–114. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sriramula S, Haque M, Majid DS and Francis
J: Involvement of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in angiotensin
II-mediated effects on salt appetite, hypertension, and cardiac
hypertrophy. Hypertension. 51:1345–1351. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|