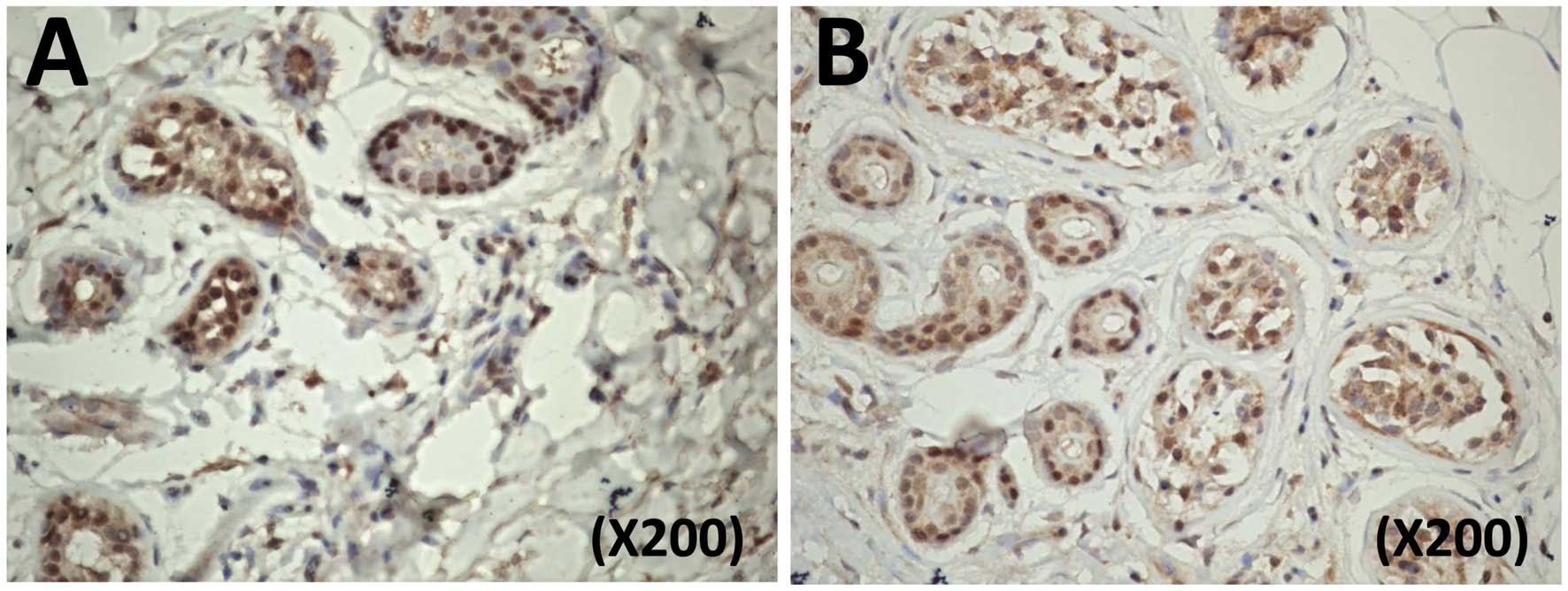
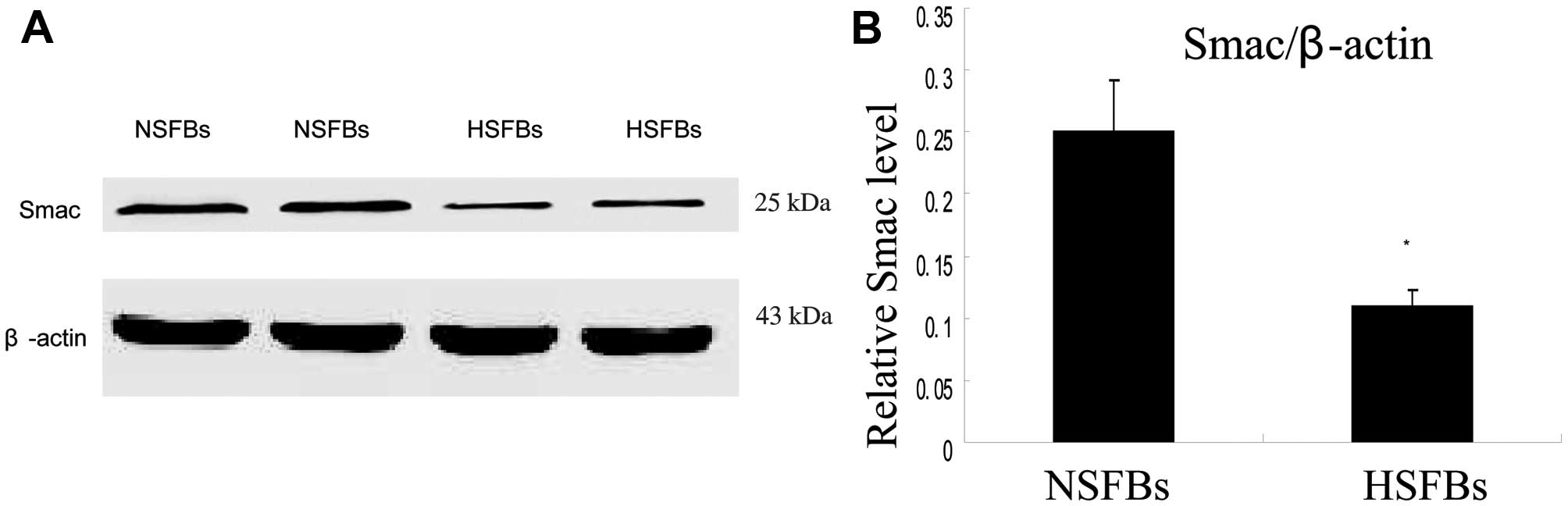
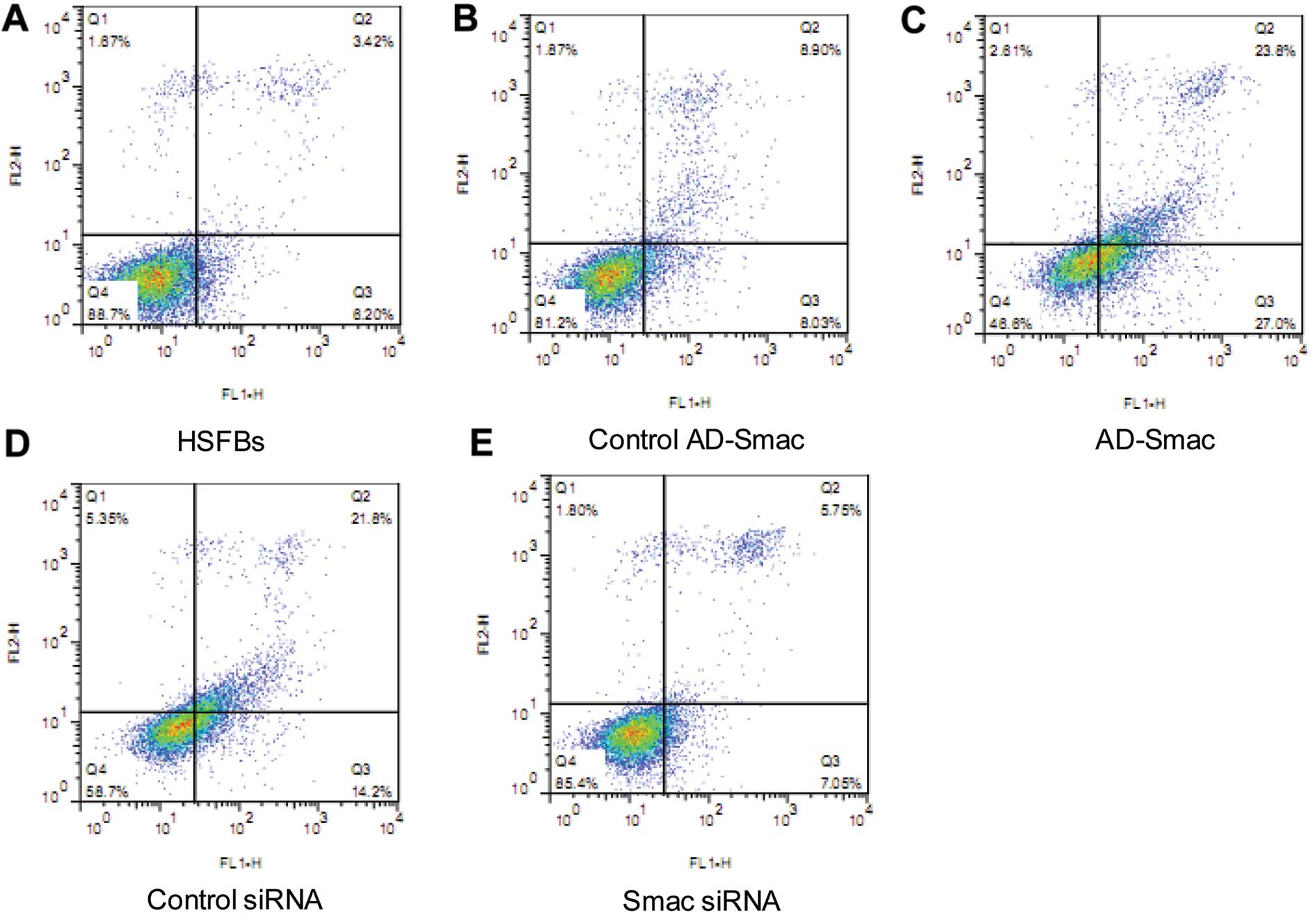
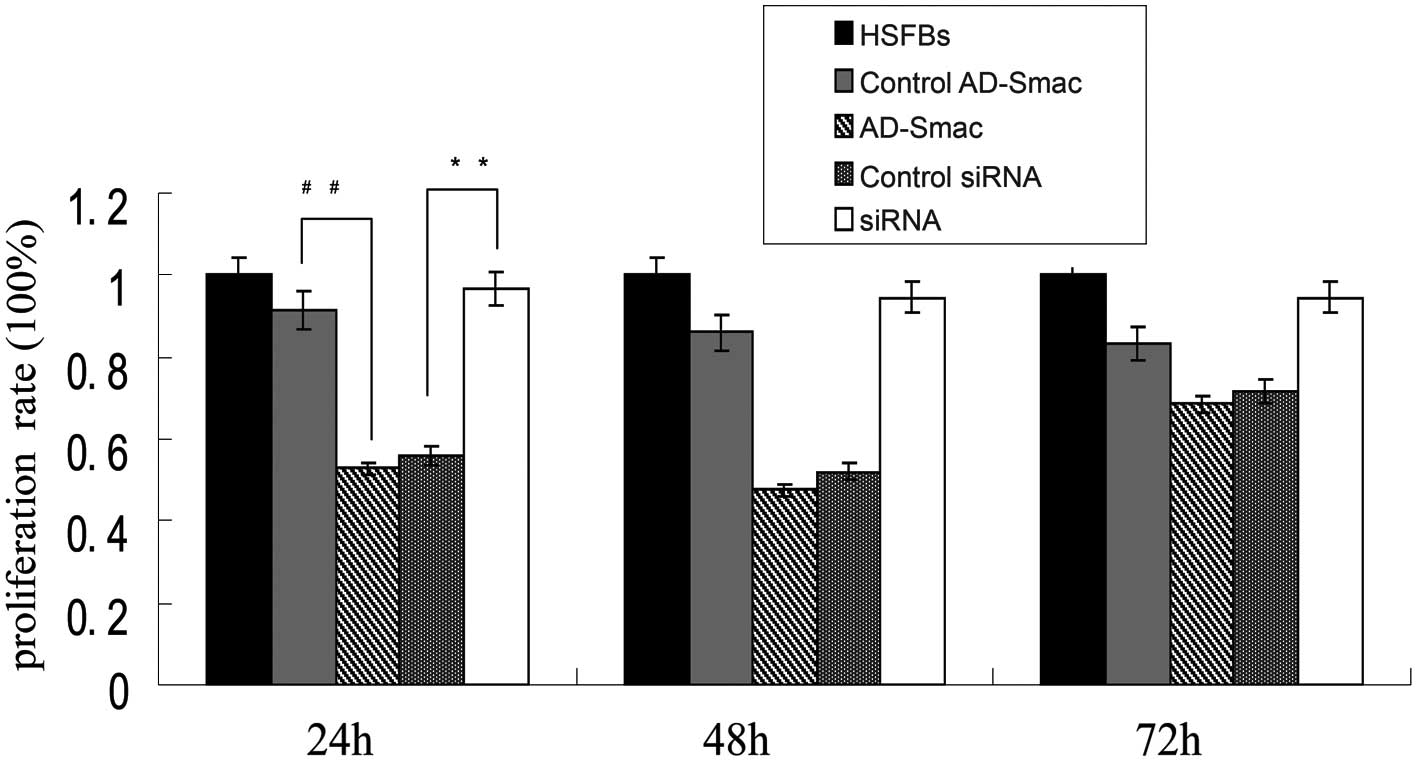
|
1
|
O’Leary R, Wood EJ and Guillou PJ:
Pathological scarring: strategic interventions. Eur J Surg.
168:523–534. 2002.
|
|
2
|
van der Veer WM, Bloemen MC, Ulrich MM, et
al: Potential cellular and molecular causes of hypertrophic scar
formation. Burns. 35:15–29. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
De Felice B, Garbi C, Santoriello M, et
al: Differential apoptosis markers in human keloids and
hypertrophic scars fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biochem. 327:191–201.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Greenhalgh DG: The role of apoptosis in
wound healing. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 30:1019–1030. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
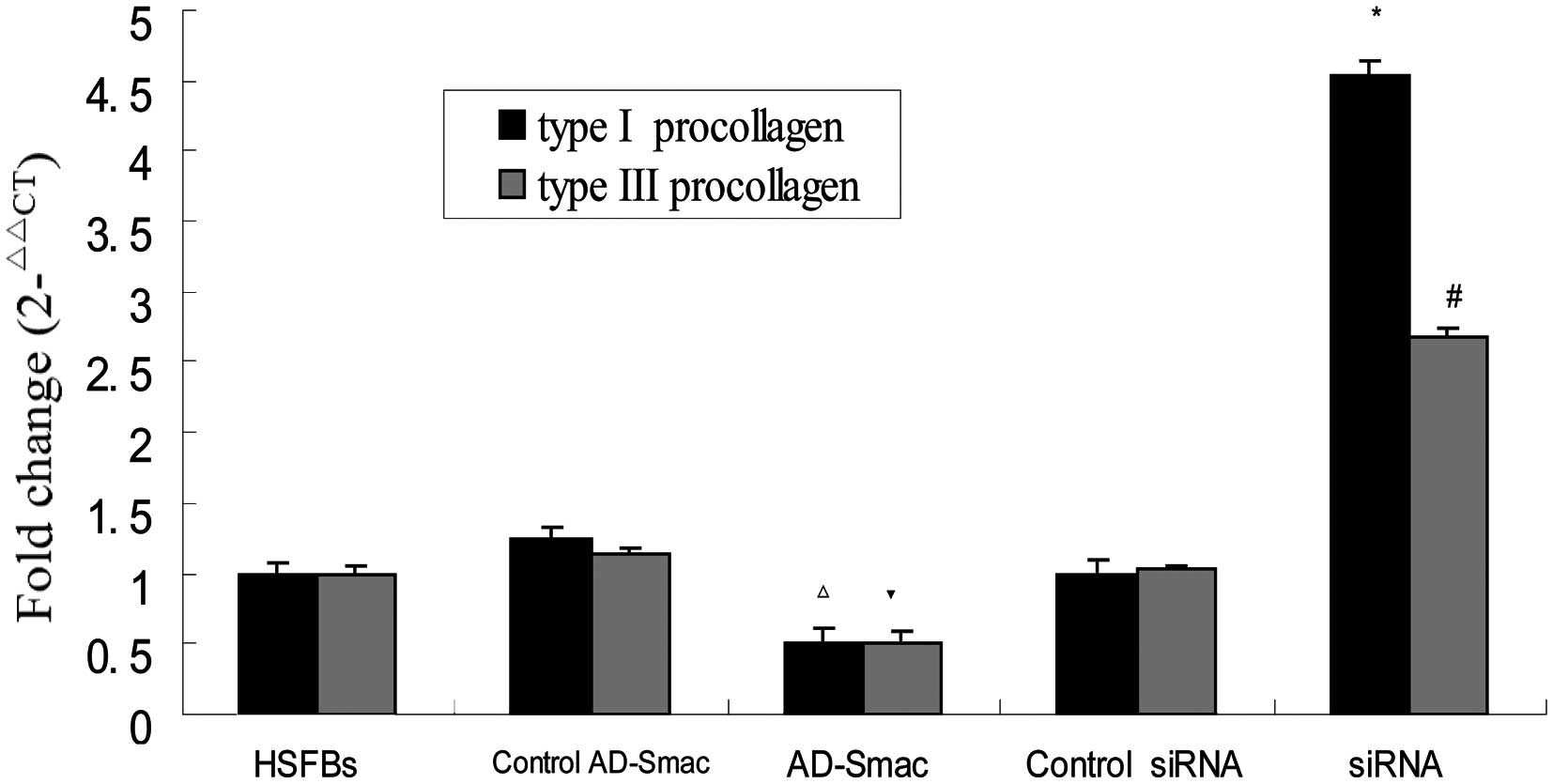
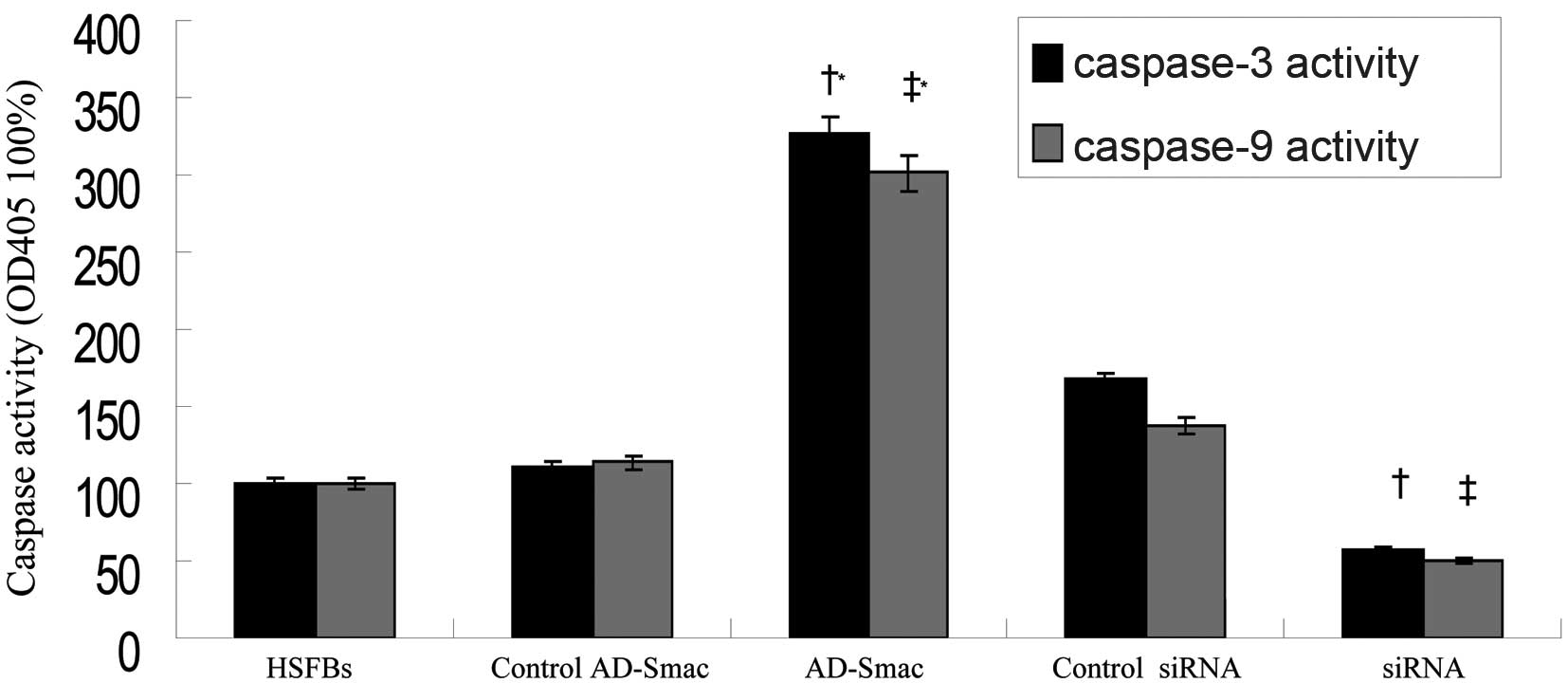
Desmouliere A, Badid C, Bochaton-Piallat
ML and Gabbiani G: Apoptosis during wound healing, fibrocontractive
diseases and vascular wall injury. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
29:19–30. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Linge C, Richardson J, Vigor C, et al:
Hypertrophic scar cells fail to undergo a form of apoptosis
specific to contractile collagen-the role of tissue
transglutaminase. J Invest Dermatol. 125:72–82. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Akasaka Y, Fujita K, Ishikawa Y, et al:
Detection of apoptosis in keloids and a comparative study on
apoptosis between keloids, hypertrophic scars, normal healed flat
scars, and dermatofibroma. Wound Repair Regen. 9:501–506. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tanaka A, Hatoko M, Tada H, et al:
Expression of p53 family in scars. J Dermatol Sci. 34:17–24. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Aarabi S, Bhatt KA, Shi Y, et al:
Mechanical load initiates hypertrophic scar formation through
decreased cellular apoptosis. FASEB J. 21:3250–3261. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Du C, Fang M, Yucheng Li, et al: Smac, a
mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent
caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. Cell. 102:33–42.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Verhagen AM, Ekert PG, Pakusch M, et al:
Identification of DIABLO, a mammalian protein that promotes
apoptosis by binding to and antagonizing IAP proteins. Cell.
102:43–53. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mao HL, Liu PS, Zheng JF, et al:
Transfection of Smac/DIABLO sensitizes drug-resistant tumor cells
to TRAIL or paclitaxel-induced apoptosis in vitro. Pharmacol Res.
56:483–492. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kempkensteffen C, Hinz S, Christoph F, et
al: Expression levels of the mitochondrial IAP antagonists
Smac/DIABLO and Omi/HtrA2 in clear-cell renal cell carcinomas and
their prognostic value. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 134:543–550. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mizutani Y, Nakanishi H, Yamamoto K, et
al: Downregulation of Smac/DIABLO expression in renal cell
carcinoma and its prognostic significance. J Clin Oncol.
23:448–454. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sekimura A, Konishi A, Mizuno K, et al:
Expression of Smac/DIABLO is a novel prognostic marker in lung
cancer. Oncol Rep. 11:797–802. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kempkensteffen C, Jager T, Bub J, et al:
The equilibrium of XIAP and Smac/DIABLO expression is gradually
deranged during the development and progression of testicular germ
cell tumours. Int J Androl. 30:476–483. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bao ST, Gui SQ and Lin MS: Relationship
between expression of Smac and Survivin and apoptosis of primary
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int.
5:580–583. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Martinez-Ruiz G, Maldonado V,
Ceballos-Cancino G, et al: Role of Smac/DIABLO in cancer
progression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 27:482008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sun Z, Li s, Cao C, et al: shRNA targeting
SFRP2 promotes the apoptosis of hypertrophic scar fibroblast. Mol
Cell Biochem. 352:25–33. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Guo L, Chen L, Bi S, et al: PTEN inhibits
proliferation and functions of hypertrophic scar fibroblasts. Mol
Cell Biochem. 361:161–168. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cao C, Li S, Dai X, et al: Genistein
inhibits proliferation and functions of hypertrophic scar
fibroblasts. Burns. 35:89–97. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mahdavian Delavary B, van der Veer WM, van
Egmond M, et al: Macrophages in skin injury and repair.
Immunobiology. 216:753–762. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Honardoust D, Ding J, Varkey M, et al:
Deep dermal fibroblasts refractory to migration and decorin-induced
apoptosis contribute to hypertrophic scarring. J Burn Care Res.
33:668–677. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Akasaka Y, Ono I, Kamiya T, et al: The
mechanisms underlying fibroblast apoptosis regulated by growth
factors during wound healing. J Pathol. 221:285–299. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jiang L, Zhang E, Yang Y, et al:
Effectiveness of apoptotic factors expressed on the wounds of
patients with stage III pressure ulcers. J Wound Ostomy Continence
Nurs. 39:391–396. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jia L, Patwari Y, Kelsey SM, et al: Role
of Smac in human leukaemic cell apoptosis and proliferation.
Oncogene. 22:1589–1599. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen DJ and Huerta S: Smac mimetics as new
cancer therapeutics. Anticancer Drugs. 20:646–658. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chai J, Du C, Wu JW, et al: Structural and
biochemical basis of apoptotic activation by Smac/DIABLO. Nature.
406:855–862. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu G, Chai J, Suber TL, et al: Structural
basis of IAP recognition by Smac/DIABLO. Nature. 408:1008–1012.
2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gao Z, Tian Y, Wang J, et al: A dimeric
Smac/diablo peptide directly relieves caspase-3 inhibition by XIAP.
Dynamic and cooperative regulation of XIAP by Smac/Diablo. J Biol
Chem. 282:30718–30727. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Clark JA, Cheng JC and Leung KS:
Mechanical properties of normal skin and hypertrophic scar. Burns.
22:443–446. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Oliveira GV, Hawkins HK, Chinkes D, et al:
Hypertrophic vs. non hypertrophic scars compared by
immunohistochemistry and laser confocal microscopy: type I and III
collagens. Int Wound J. 6:445–452. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Akita S, Akino K, Tanaka K, et al: A basic
fibroblast growth factor improves lower extremity wound healing
with a porcine-derived skin substitute. J Trauma. 64:809–815. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cho JW, Kang MC and Lee KS: TGF-β1-treated
ADSCs-CM promotes expression of type I collagen and MMP-1,
migration of human skin fibroblasts, and wound healing in
vitro and in vivo. Int J Mol Med. 26:901–906. 2010.
|
|
35
|
Yan G, Sun H, Wang F, et al: Topical
application of hPDGF-A-modified porcine BMSC and keratinocytes
loaded on acellular HAM promotes the healing of combined
radiation-wound skin injury in minipigs. Int J Radiat Biol.
87:591–600. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Weshahy AH and Abdel Hay R: Intralesional
cryosurgery and intralesional steroid injection: a good combination
therapy for treatment of keloids and hypertrophic scars. Dermatol
Ther. 25:273–276. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hayashi T, Furukawa H, Oyama A, et al: A
new uniform protocol of combined corticosteroid injections and
ointment application reduces recurrence rates after surgical
keloid/hypertrophic scar excision. Dermatol Surg. 38:893–897. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Wu JG, Ma L, Zhang SY, et al: Essential
oil from rhizomes of Ligusticum chuanxiong induces apoptosis
in hypertrophic scar fibroblasts. Pharm Biol. 49:86–93. 2010.
|
|
39
|
Morin C, Roumegous A, Carpentier G, et al:
Modulation of inflammation by Cicaderma ointment accelerates skin
wound healing. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 343:115–124. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|