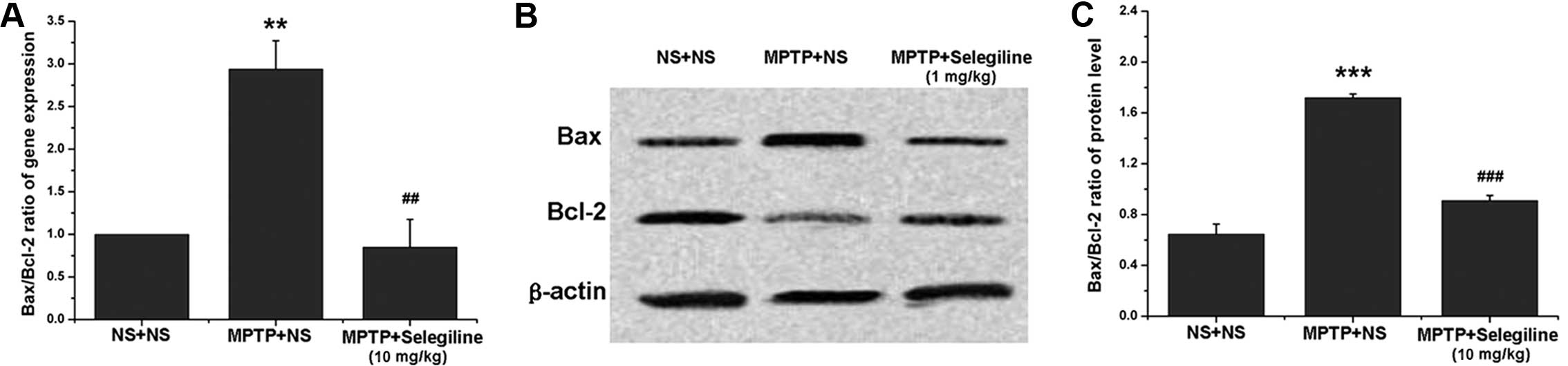
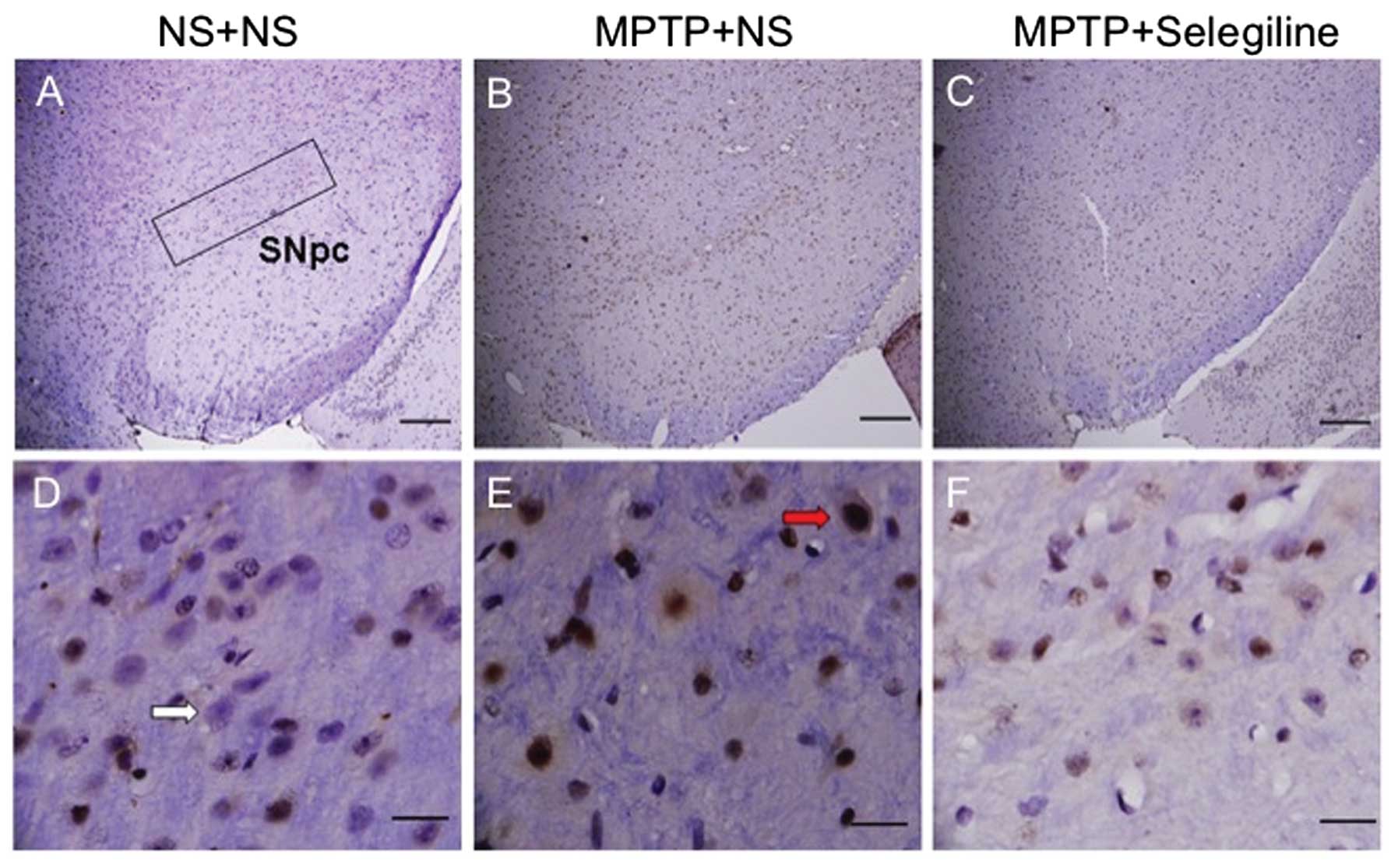
|
1
|
Lees AJ, Hardy J and Revesz T: Parkinson’s
disease. Lancet. 373:2055–2066. 2009.
|
|
2
|
Stocchi F, Vacca L, Grassini P, et al:
Symptom relief in Parkinson disease by safinamide: Biochemical and
clinical evidence of efficacy beyond MAO-B inhibition. Neurology.
67:S24–S29. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bar-Am O, Weinreb O, Amit T and Youdim MB:
The neuroprotective mechanism of 1-(R)-aminoindan, the major
metabolite of the anti-parkinsonian drug rasagiline. J Neurochem.
112:1131–1137. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Olanow CW, Hauser RA, Jankovic J, et al: A
randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, delayed start study
to assess rasagiline as a disease modifying therapy in Parkinson’s
disease (the ADAGIO study): rationale, design, and baseline
characteristics. Mov Disord. 23:2194–2201. 2008.
|
|
5
|
Weinreb O, Mandel S, Bar-Am O, et al:
Multifunctional neuroprotective derivatives of rasagiline as
anti-Alzheimer’s disease drugs. Neurotherapeutics. 6:163–174.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen JJ and Ly AV: Rasagiline: a
second-generation monoamine oxidase type-B inhibitor for the
treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Am J Health Syst Pharm.
63:915–928. 2006.
|
|
7
|
Magyar K, Pálfi M, Jenei V and Szöko E:
Deprenyl: from chemical synthesis to neuroprotection. J Neural
Transm Suppl. 143–156. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Weinreb O, Amit T, Bar-Am O, Sagi Y,
Mandel S and Youdim MB: Involvement of multiple survival signal
transduction pathways in the neuroprotective, neurorescue and APP
processing activity of rasagiline and its propargyl moiety. J
Neural Transm Suppl. 457–465. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Youdim MB, Maruyama W and Naoi M:
Neuropharmacological, neuroprotective and amyloid precursor
processing properties of selective MAO-B inhibitor antiparkinsonian
drug, rasagiline. Drugs Today (Barc). 41:369–391. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Youdim MB and Tipton KF: Rat striatal
monoamine oxidase-B inhibition by l-deprenyl and rasagiline: its
relationship to 2-phenylethylamine-induced stereotypy and
Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 8:247–253.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hara MR, Thomas B, Cascio MB, et al:
Neuroprotection by pharmacologic blockade of the GAPDH death
cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:3887–3889. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Maruyama W, Akao Y, Carrillo MC, Kitani K,
Youdium MB and Naoi M: Neuroprotection by propargylamines in
Parkinson’s disease: suppression of apoptosis and induction of
prosurvival genes. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 24:675–682. 2002.
|
|
13
|
Maruyama W, Nitta A, Shamoto-Nagai M, et
al: N-Propargyl-1 (R)-aminoindan, rasagiline, increases glial cell
line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) in neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y
cells through activation of NF-kappaB transcription factor.
Neurochem Int. 44:393–400. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Weinreb O, Bar-Am O, Amit T,
Chillag-Talmor O and Youdim MB: Neuroprotection via pro-survival
protein kinase C isoforms associated with Bcl-2 family members.
FASEB J. 18:1471–1473. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sagi Y, Mandel S, Amit T and Youdim MB:
Activation of tyrosine kinase receptor signaling pathway by
rasagiline facilitates neurorescue and restoration of nigrostriatal
dopamine neurons in post-MPTP-induced parkinsonism. Neurobiol Dis.
25:35–44. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhu W, Xie W, Pan T, et al: Comparison of
neuroprotective and neurorestorative capabilities of rasagiline and
selegiline against lactacystin-induced nigrostriatal dopaminergic
degeneration. J Neurochem. 105:1970–1978. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Jackson-Lewis V and Przedborski S:
Protocol for the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Nat
Protoc. 2:141–151. 2007.
|
|
18
|
Perier C, Bové J, Wu DC, et al: Two
molecular pathways initiate mitochondria-dependent dopaminergic
neurodegeneration in experimental Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 104:8161–8166. 2007.
|
|
19
|
Fernagut PO, Diguet E, Labattu B and Tison
F: A simple method to measure stride length as an index of
nigrostriatal dysfunction in mice. J Neurosci Methods. 113:123–130.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fleming SM, Salcedo J, Fernagut PO, et al:
Early and progressive sensorimotor anomalies in mice overexpressing
wild-type human alpha-synuclein. J Neurosci. 24:9434–9440. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tillerson JL, Caudle WM, Reverón ME and
Miller GW: Detection of behavioral impairments correlated to
neurochemical deficits in mice treated with moderate doses of
1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine. Exp Neurol.
178:80–90. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Paxinos G and Franklin KBJ: The Mouse
Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. 4th edition. Elsevier Academic
Press; San Diego: 2012
|
|
23
|
He XJ, Yamauchi H, Uetsuka K and Nakayama
H: Neurotoxicity of MPTP to migrating neuroblasts: studies in acute
and subacute mouse models of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotoxicology.
29:413–420. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yokoyama H, Takagi S, Watanabe Y, Kato H
and Araki T: Role of reactive nitrogen and reactive oxygen species
against MPTP neurotoxicity in mice. J Neural Transm. 115:831–842.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kuhn K, Wellen J, Link N, Maskri L,
Lübbert H and Stichel CC: The mouse MPTP model: gene expression
changes in dopaminergic neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 17:1–12. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
West MJ and Gundersen HJ: Unbiased
stereological estimation of the number of neurons in the human
hippocampus. J Comp Neurol. 296:1–22. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu DC, Jackson-Lewis V, Vila M, et al:
Blockade of microglial activation is neuroprotective in the
1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2, 3,6-tetrahydropyridine mouse model of
Parkinson disease. J Neurosci. 22:1763–1771. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
|
|
29
|
Matsunaga W, Isobe K and Shirokawa T:
Involvement of neurotrophic factors in aging of noradrenergic
innervations in hippocampus and frontal cortex. Neurosci Res.
54:313–318. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Novikova L, Garris BL, Garris DR and Lau
YS: Early signs of neuronal apoptosis in the substantia nigra
pars compacta of the progressive neurodegenerative mouse
1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine/probenecid model of
Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience. 140:67–76. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Blin O, Ferrandez AM and Serratrice G:
Quantitative analysis of gait in Parkinson patients: increased
variability of stride length. J Neurol Sci. 98:91–97. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Muller T: Drug therapy in patients with
Parkinson’s disease. Transl Neurodegener. 1:102012.
|
|
33
|
Lewitt PA: MAO-B inhibitor know-how: back
to the pharm. Neurology. 72:1352–1357. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Parkinson Study Group. DATATOP: a
multicenter controlled clinical trial in early Parkinson’s disease.
Arch Neurol. 46:1052–1060. 1989.
|
|
35
|
Parkinson Study Group. A controlled trial
of rasagiline in early Parkinson disease: the TEMPO study. Arch
Neurol. 59:1937–1943. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Olanow CW, Rascol O, Hauser R, Feigin PD,
Jankovic J, Lang A, Langston W, Melamed E, Poewe W, Stocchi F and
Tolosa E; ADAGIO Study Investigators. A double-blind, delayed-start
trial of rasagiline in Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med.
361:1268–1278. 2009.
|
|
37
|
Ansari KS, Yu PH, Kruck TP and Tatton WG:
Rescue of axotomized immature rat facial motoneurons by
R(−)-deprenyl: stereospecificity and independence from monoamine
oxidase inhibition. J Neurosci. 13:4042–4053. 1993.
|
|
38
|
Sharma SK, Carlson EC and Ebadi M:
Neuroprotective actions of Selegiline in inhibiting 1-methyl,
4-phenyl, pyridinium ion (MPP+)-induced apoptosis in
SK-N-SH neurons. J Neurocytol. 32:329–343. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tatton WG, Chalmers-Redman RM, Ju WJ, et
al: Propargylamines induce antiapoptotic new protein synthesis in
serum- and nerve growth factor (NGF)-withdrawn, NGF-differentiated
PC-12 cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 301:753–764. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Holschneider DP, Chen K, Seif I and Shih
JC: Biochemical, behavioral, physiologic, and neurodevelopmental
changes in mice deficient in monoamine oxidase A or B. Brain Res
Bull. 56:453–462. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Weinreb O, Amit T, Bar-Am O and Youdim MB:
Induction of neurotrophic factors GDNF and BDNF associated with the
mechanism of neurorescue action of rasagiline and ladostigil: new
insights and implications for therapy. Ann NY Acad Sci.
1122:155–168. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ebadi M, Sharma S, Shavali S and El Refaey
H: Neuroprotective actions of selegiline. J Neurosci Res.
67:285–289. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Levy OA, Malagelada C and Greene LA: Cell
death pathways in Parkinson’s disease: proximal triggers, distal
effectors, and final steps. Apoptosis. 14:478–500. 2009.
|
|
44
|
Tanaka K, Asanuma M and Ogawa N: Molecular
basis of anti-apoptotic effect of immunophilin ligands on hydrogen
peroxide-induced apoptosis in human glioma cells. Neurochem Res.
29:1529–1536. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Meredith GE and Kang UJ: Behavioral models
of Parkinson’s disease in rodents: a new look at an old problem.
Mov Disord. 21:1595–1606. 2006.
|
|
46
|
Patel M, Mao L, Wu B and Vandevord PJ:
GDNF-chitosan blended nerve guides: a functional study. J Tissue
Eng Regen Med. 1:360–367. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Piquilloud G, Christen T, Pfister LA,
Gander B and Papaloïzos MY: Variations in glial cell line-derived
neurotrophic factor release from biodegradable nerve conduits
modify the rate of functional motor recovery after rat primary
nerve repairs. Eur J Neurosci. 26:1109–1117. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Willson ML, McElnea C, Mariani J, Lohof AM
and Sherrard RM: BDNF increases homotypic olivocerebellar
reinnervation and associated fine motor and cognitive skill. Brain.
131:1099–1112. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Slevin JT, Gerhardt GA, Smith CD, Gash DM,
Kryscio R and Young B: Improvement of bilateral motor functions in
patients with Parkinson disease through the unilateral
intraputaminal infusion of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic
factor. J Neurosurg. 102:216–222. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|