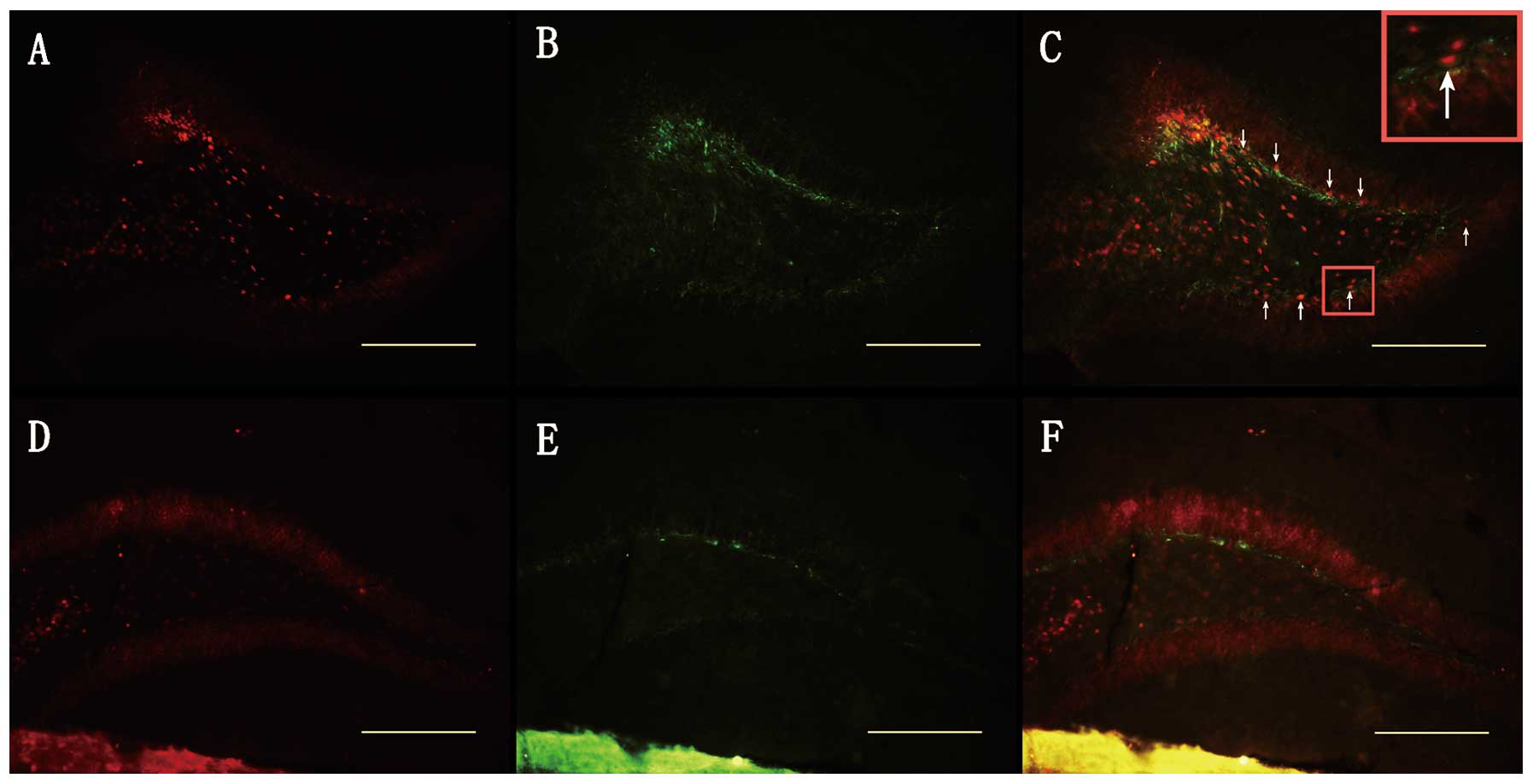
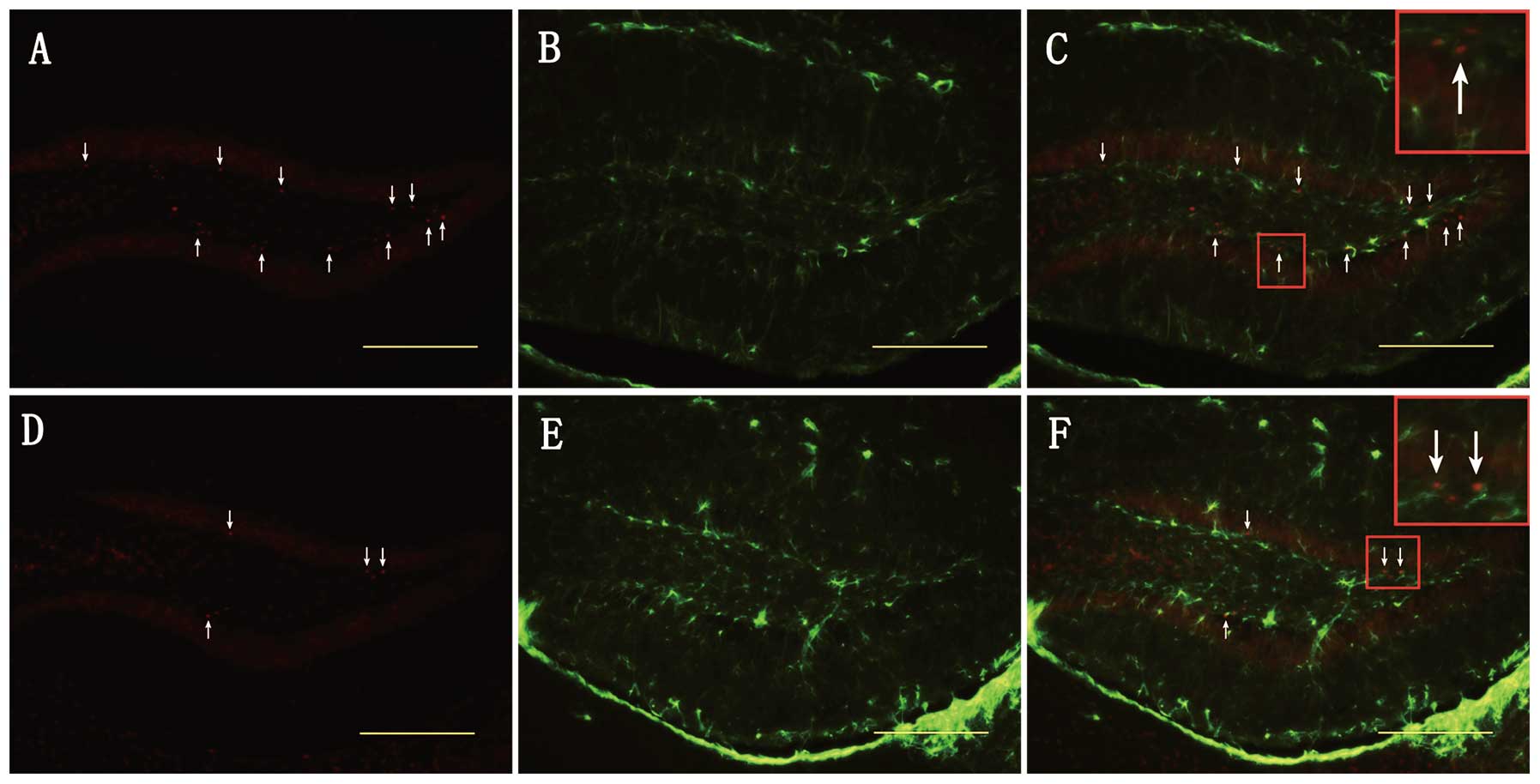
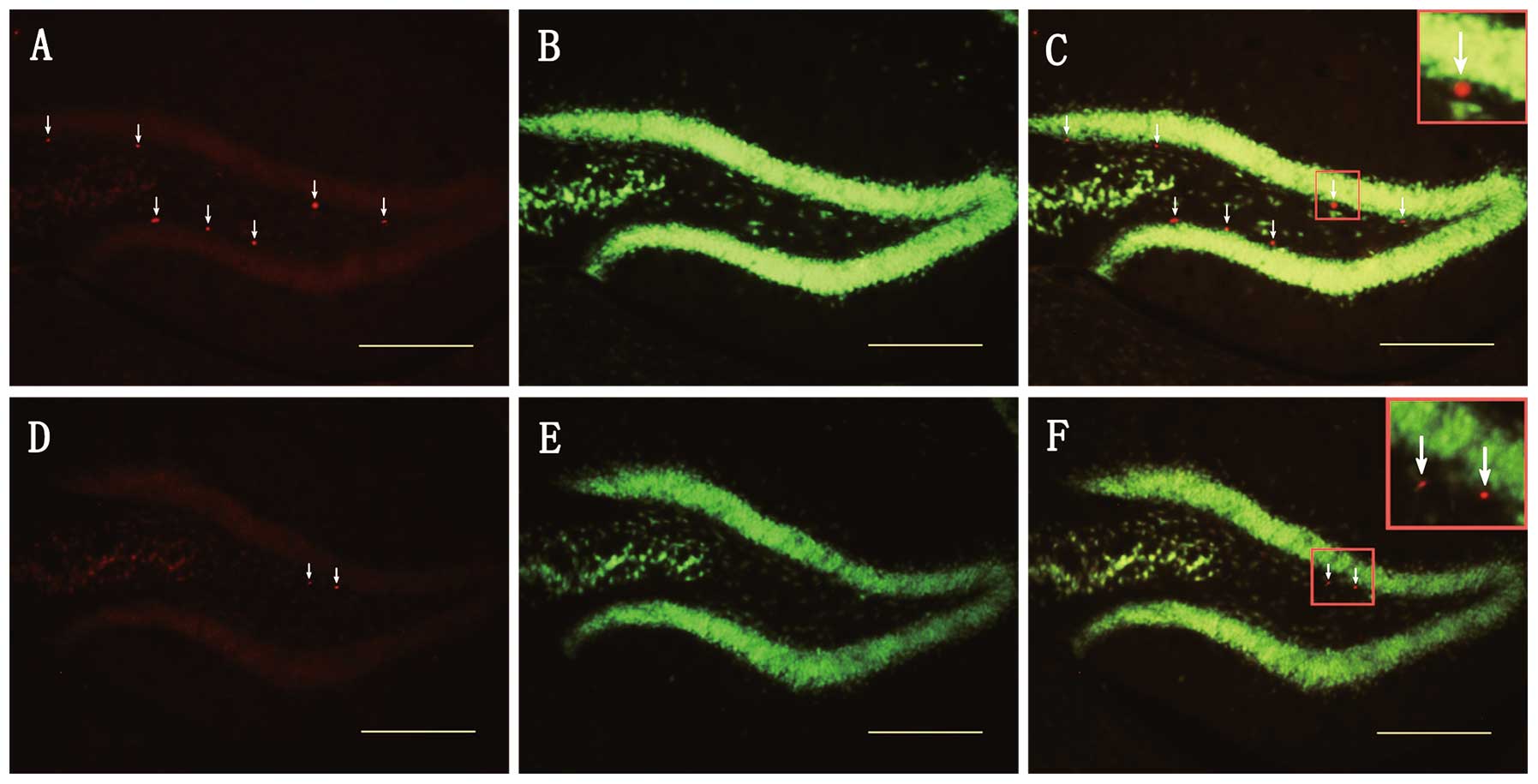
|
1
|
Narayan RK, Michel ME, Ansell B, et al:
Clinical trials in head injury. J Neurotrauma. 19:503–557. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pickard JD and Czosnyka M: Management of
raised intracranial pressure. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry.
56:845–858. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Baratchi S, Kanwar RK and Kanwar JR:
Survivin: a target from brain cancer to neurodegenerative disease.
Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 45:535–554. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Richardson RM, Singh A, Sun D, Fillmore
HL, Dietrich DW III and Bullock MR: Stem cell biology in traumatic
brain injury: effects of injury and strategies for repair. J
Neurosurg. 112:1125–1138. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Alvarez-Buylla A and Lim DA: For the long
run: maintaining germinal niches in the adult brain. Neuron.
41:683–686. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lie DC, Song H, Colamarino SA, Ming GL and
Gage FH: Neurogenesis in the adult brain: new strategies for
central nervous system diseases. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol.
44:399–421. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chirumamilla S, Sun D, Bullock MR and
Colello RJ: Traumatic brain injury induced cell proliferation in
the adult mammalian central nervous system. J Neurotrauma.
19:693–703. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Richardson RM, Sun D and Bullock MR:
Neurogenesis after traumatic brain injury. Neurosurg Clin N Am.
18:169–181. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhao WM, Huan LC, Zhao Y, et al:
Endogenous adult neurogenesis and cognitive function recovery
following traumatic brain injury in the rat hippocampus. Neural
Regen Res. 5:645–650. 2010.
|
|
10
|
Dash PK, Mach SA and Moore AN: Enhanced
neurogenesis in the rodent hippocampus following traumatic brain
injury. J Neurosci Res. 63:313–319. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sun D, Colello RJ, Daugherty WP, Kwon TH,
McGinn MJ, Harvey HB and Bullock MR: Cell proliferation and
neuronal differentiation in the dentate gyrus in juvenile and adult
rats following traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 22:95–105.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gulacsi AA and Anderson SA:
Beta-catenin-mediated Wnt signaling regulates neurogenesis in the
ventral telencephalon. Nat Neurosci. 11:1383–1391. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zechner D, Fujita Y, Hulsken J, et al:
beta-Catenin signals regulate cell growth and the balance between
progenitor cell expansion and differentiation in the nervous
system. Dev Biol. 258:406–418. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang L, Yang X, Yang S and Zhang J: The
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in the adult neurogenesis. Euro
J Neurosci. 33:1–8. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
White BD, Nathe RJ, Maris DO, Nguyen NK,
Goodson JM, Moon RT and Horner PJ: Beta-catenin signaling increases
in proliferating NG2+ progenitors and astrocytes during
post-traumatic gliogenesis in the adult brain. Stem Cells.
28:297–307. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang T, Otevrel T, Gao Z, Ehrlich SM,
Fields JZ and Boman BM: Evidence that APC regulates survivin
expression: a possible mechanism contributing to the stem cell
origin of colon cancer. Cancer Res. 61:8664–8667. 2001.
|
|
17
|
Zhu H, Zhang G, Wang Y, et al: Inhibition
of ErbB2 by Herceptin reduces survivin expression via the
ErbB2-beta-catenin/TCF4-survivin pathway in ErbB2-overexpressed
breast cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 101:1156–1162. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Deveraux QL and Reed JC: IAP family
proteins-suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev. 13:239–252. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li F, Ambrosini G, Chu EY, Plescia J,
Tognin S, Marchisio PC and Altieri DC: Control of apoptosis and
mitotic spindle checkpoint by survivin. Nature. 396:580–584. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hirokawa N: Microtubule organization and
dynamics dependent on microtubule-associated proteins. Curr Opin
Cell Biol. 6:74–81. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Altieri DC: Survivin, versatile modulation
of cell division and apoptosis in cancer. Oncogene. 22:8581–8589.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kobayashi K, Hatano M, Otaki M, Ogasawara
T and Tokuhisa T: Expression of a murine homologue of the inhibitor
of apoptosis protein is related to cell proliferation. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 96:1457–1462. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
O’Connor DS, Schechner JS, Adida C, et al:
Control of apoptosis during angiogenesis by survivin expression in
endothelial cells. Am J Pathol. 156:393–398. 2000.
|
|
24
|
Shin S, Sung BJ, Cho YS, et al: An
anti-apoptotic protein human survivin is a direct inhibitor of
caspase-3 and -7. Biochemistry. 40:1117–1123. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tamm I, Wang Y, Sausville E, Scudiero DA,
Vigna N, Oltersdorf T and Reed JC: IAP-family protein survivin
inhibits caspase activity and apoptosis induced by Fas (CD95), Bax,
caspases and anticancer drugs. Cancer Res. 58:5315–5320.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jiang Y, de Bruin A, Caldas H, et al:
Essential role for survivin in early brain development. J Neurosci.
25:6962–6970. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zwerts F, Lupu F, De Vriese A, et al: Lack
of endothelial cell survivin causes embryonic defects in
angiogenesis, cardiogenesis, and neural tube closure. Blood.
109:4742–4752. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Adida C, Crotty PL, McGrath J, Berrebi D,
Diebold J and Altieri DC: Developmentally regulated expression of
the novel cancer anti-apoptosis gene survivin in human, and mouse
differentiation. Am J Pathol. 152:43–49. 1998.
|
|
29
|
Li F and Brattain MG: Role of the Survivin
gene in pathophysiology. Am J Pathol. 169:1–11. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Johnson EA, Svetlov SI, Wang KK, Hayes RL
and Pineda JA: Cell-specific DNA fragmentation may be attenuated by
a survivin-dependent mechanism after traumatic brain injury in
rats. Exp Brain Res. 167:17–26. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Thompson HJ, Lifshitz J, Marklund N, Grady
MS, Graham DI, Hovda DA and McIntosh TK: Lateral fluid percussion
brain injury: a 15-year review and evaluation. J Neurotrauma.
22:42–75. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wojtowicz JM and Kee N: BrdU assay for
neurogenesis in rodents. Nat Protoc. 1:1399–1405. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Johnson EA, Svetlov SI, Pike BR, et al:
Cell-specific upregulation of survivin after experimental traumatic
brain injury in rats. J Neurotrauma. 21:1183–1195. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ray J, Peterson DA, Schinstine M and Gage
FH: Proliferation, differentiation, and long-term culture of
primary hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 90:3602–3606.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
De Ferrari GV and Inestrosa NC: Wnt
signaling function in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res Brain Res Rev.
33:1–12. 2000.
|
|
36
|
De Ferrari GV, Papassotiropoulos A,
Biechele T, et al: Common genetic variation within the low-density
lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 and late-onset Alzheimer’s
disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:9434–9439. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Inestrosa NC, Alvarez A, Godoy J, Reyes A
and De Ferrari GV: Acetylcholinesterase-amyloid-beta-peptide
interaction and Wnt signaling involvement in Abeta neurotoxicity.
Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 176:53–59. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Lovestone S, Killick R, Di Forti M and
Murray R: Schizophrenia as a GSK-3 dysregulation disorder. Trends
Neurosci. 30:142–149. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
De Ferrari GV and Moon RT: The ups and
downs of Wnt signaling in prevalent neurological disorders.
Oncogene. 25:7545–7553. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wheatley SP, Carvalho A, Vagnarelli P and
Earnshaw WC: INCENP is required for proper targeting of Survivin to
the centromeres and the anaphase spindle during mitosis. Curr Biol.
11:886–890. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Skoufias DA, Mollinari C, Lacroix FB and
Margolis RL: Human survivin is a kinetochore-associated passenger
protein. J Cell Biol. 151:1575–1582. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen J, Jin S, Tahir SK, et al: Survivin
enhances Aurora-B kinase activity and localizes Aurora-B in human
cells. J Biol Chem. 278:486–490. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Coremans V, Ahmed T, Balschun D, et al:
Impaired neurogenesis, learning and memory and low seizure
threshold associated with loss of neural precursor cell survivin.
BMC Neurosci. 11:22010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kernie SG and Parent JM: Forebrain
neurogenesis after focal Ischemic and traumatic brain injury.
Neurobiol Dis. 37:267–274. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ramaswamy S, Goings GE, Soderstrom KE,
Szele FG and Kozlowski DA: Cellular proliferation and migration
following a controlled cortical impact in the mouse. Brain Res.
1053:38–53. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Urrea C, Castellanos DA, Sagen J, Tsoulfas
P, Bramlett HM and Dietrich WD: Widespread cellular proliferation
and focal neurogenesis after traumatic brain injury in the rat.
Restor Neurol Neurosci. 25:65–76. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yu TS, Zhang G, Liebl DJ and Kernie SG:
Traumatic brain injury-induced hippocampal neurogenesis requires
activation of early nestin-expressing progenitors. J Neurosci.
28:12901–12912. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Brown JP, Couillard-Despres S, Cooper-Kuhn
CM, Winkler J, Aigner L and Kuhn HG: Transient expression of
doublecortin during adult neurogenesis. J Comp Neurol. 467:1–10.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Itoh T, Satou T, Nishida S, Hashimoto S
and Ito H: Immature and mature neurons coexist among glial scars
after rat traumatic brain injury. Neurol Res. 29:734–742. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Rola R, Mizumatsu S, Otsuka S, Morhardt
DR, Noble-Haeusslein LJ, et al: Alterations in hippocampal
neurogenesis following traumatic brain injury in mice. Exp Neurol.
202:189–199. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Taupin P: BrdU immunohistochemistry for
studying adult neurogenesis: paradigms, pitfalls, limitations, and
validation. Brain Res Rev. 53:198–214. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Barha CK, Ishrat T, Epp JR, Galea LA and
Stein DG: Progesterone treatment normalizes the levels of cell
proliferation and cell death in the dentate gyrus of the
hippocampus after traumatic brain injury. Exp Neurol. 231:72–81.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Conway EM, Zwerts F, Van Eygen V, DeVriese
A, Nagai N, Luo W and Collen D: Survivin-dependent angiogenesis in
ischemic brain: molecular mechanisms of hypoxia-induced
up-regulation. Am J Pathol. 163:935–946. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lu N, Li XJ, Li CZ, Li DL, Cui PF, Hou YN
and Wang YL: Effect of hypoxic preconditioning on the learning and
memory ability and expressions of survivin and HSP-70 proteins in
rats with focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Nan Fang Yi
Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 27:1856–1859. 2007.(Article in Chinese).
|
|
55
|
Okazaki T, Magaki T, Takeda M, et al:
Intravenous administration of bone marrow stromal cells increases
survivin and Bcl-2 protein expression and improves sensorimotor
function following ischemia in rats. Neurosci Lett. 430:109–114.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Zhang Y, Park TS and Gidday JM: Hypoxic
preconditioning protects human brain endothelium from ischemic
apoptosis by Akt-dependent survivin activation. Am J Physiol Heart
Circ Physiol. 292:H2573–H2581. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|