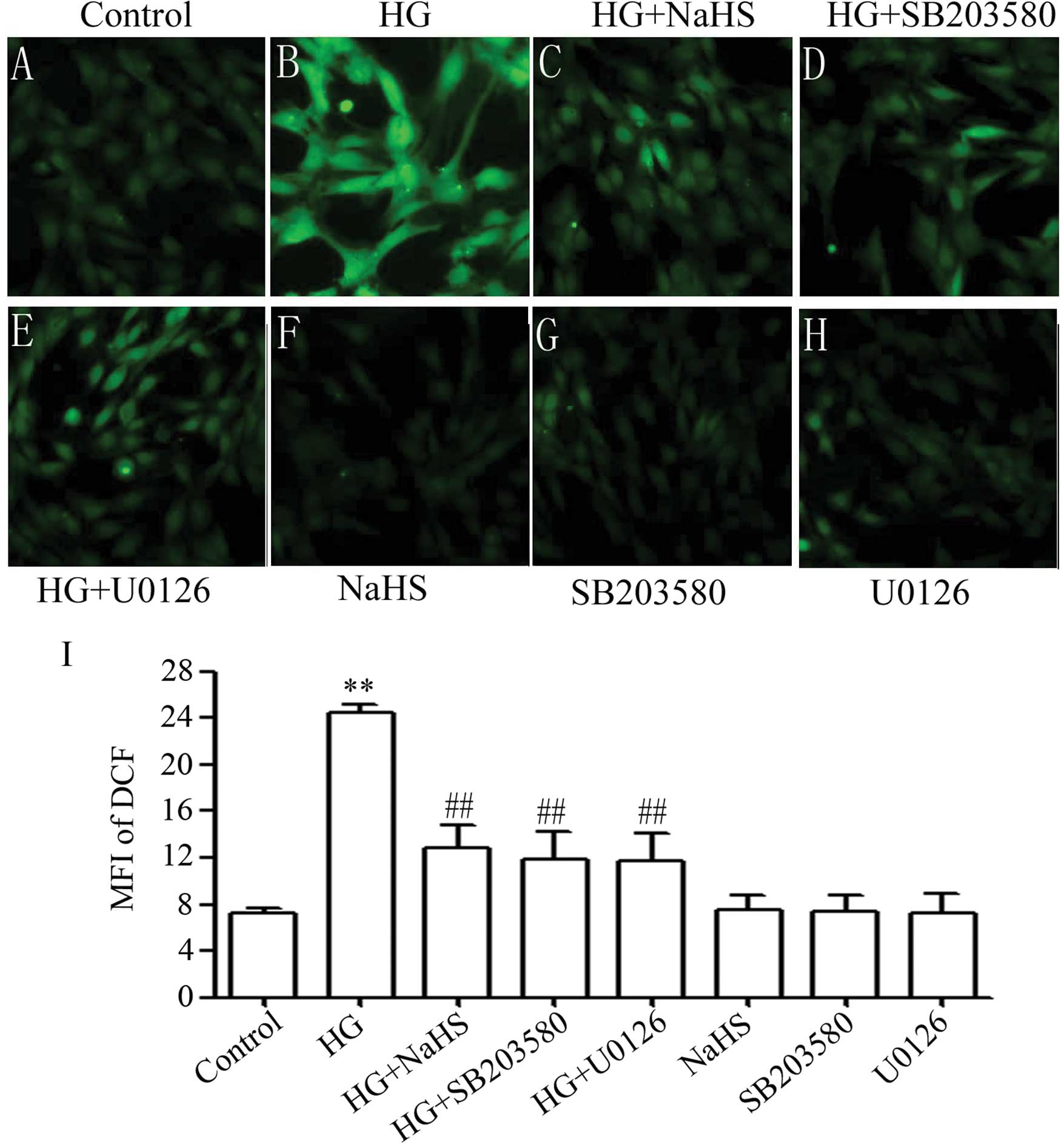
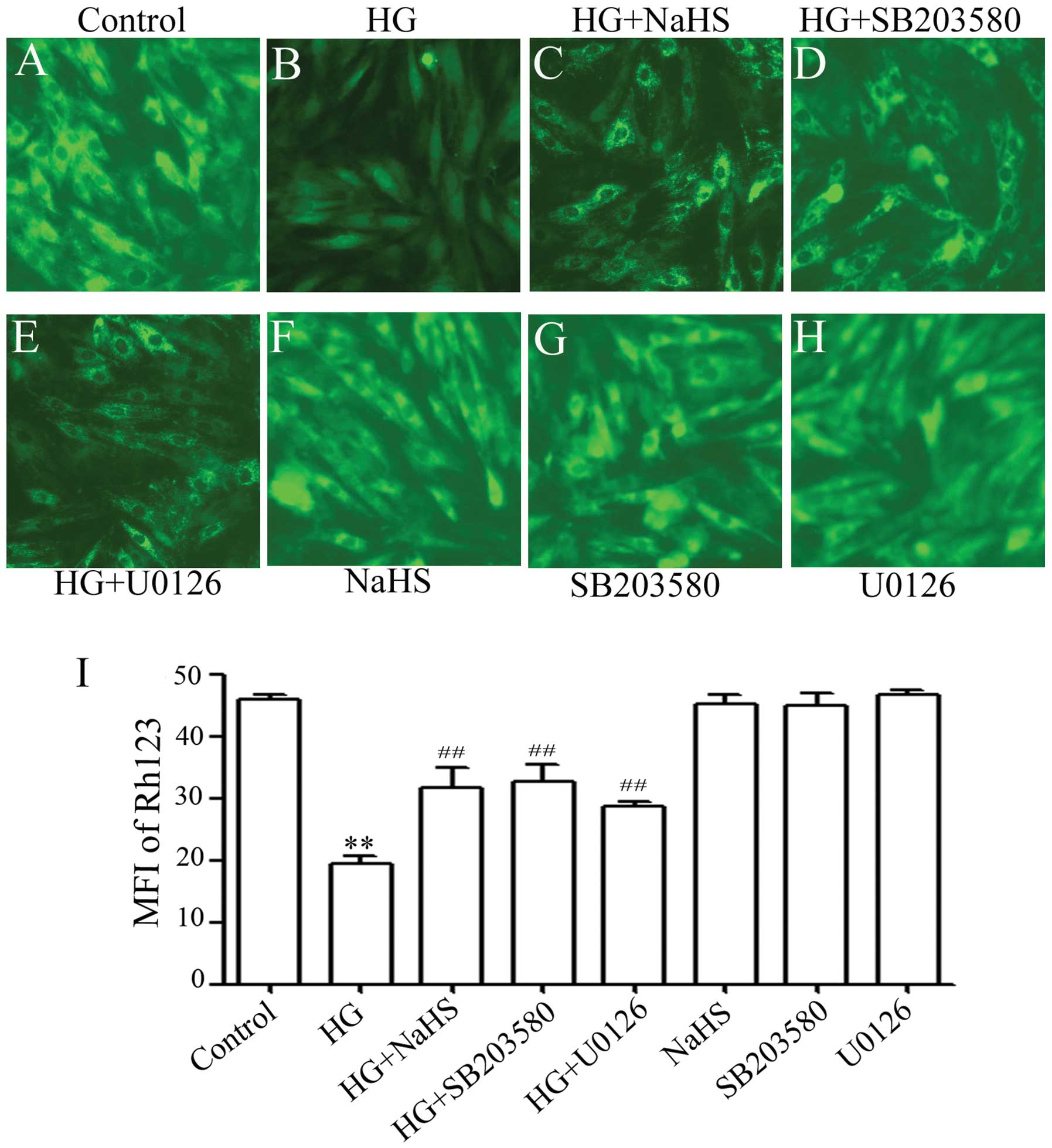
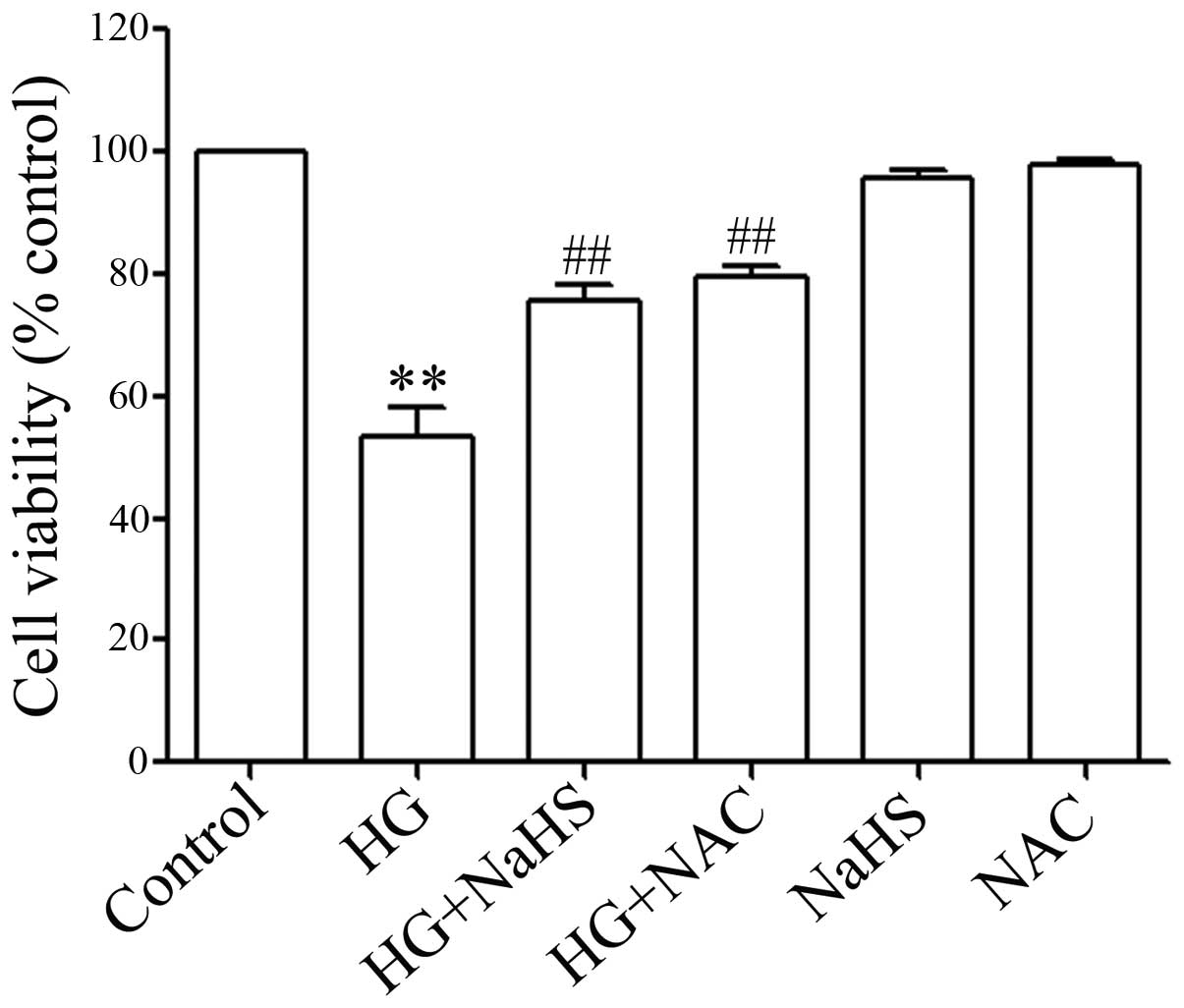
|
1
|
Grundy SM, Benjamin IJ, Burke GL, et al:
Diabetes and cardiovascular disease: a statement for healthcare
professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation.
100:1134–1146. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cai L and Kang YJ: Oxidative stress and
diabetic cardiomyopathy: a brief review. Cardiovasc Toxicol.
1:181–193. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Francis GS: Diabetic cardiomyopathy: fact
or fiction? Heart. 85:247–248. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rodrigues B, Cam MC and McNeill JH:
Metabolic disturbances in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Mol Cell
Biochem. 180:53–57. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Privratsky JR, Wold LE, Sowers JR, Quinn
MT and Ren J: AT1 blockade prevents glucose-induced cardiac
dysfunction in ventricular myocytes: role of the AT1 receptor and
NADPH oxidase. Hypertension. 42:206–212. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ren J and Davidoff AJ: Diabetes rapidly
induces contractile dysfunctions in isolated ventricular myocytes.
Am J Physiol. 272:H148–H158. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rahimi R, Nikfar S, Larijani B and
Abdollahi M: A review on the role of antioxidants in the management
of diabetes and its complications. Biomed Pharmacother. 59:365–373.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cai H and Harrison DG: Endothelial
dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases: the role of oxidant stress.
Circ Res. 87:840–844. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Peake BF, Nicholson CK, Lambert JP, et al:
Hydrogen sulfide preconditions the db/db diabetic mouse heart
against ischemia-reperfusion injury by activating Nrf2 signaling in
an Erk-dependent manner. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
304:H1215–H1224. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Soetikno V, Sari FR, Sukumaran V, et al:
Curcumin prevents diabetic cardiomyopathy in streptozotocin-induced
diabetic rats: possible involvement of PKC-MAPK signaling pathway.
Eur J Pharm Sci. 47:604–614. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Evans JL, Goldfine ID, Maddux BA and
Grodsky GM: Oxidative stress and stress-activated signaling
pathways: a unifying hypothesis of type 2 diabetes. Endocr Rev.
23:599–622. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Igarashi M, Wakasaki H, Takahara N, et al:
Glucose or diabetes activates p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
via different pathways. J Clin Invest. 103:185–195. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yan J, Young ME, Cui L, Lopaschuk GD, Liao
R and Tian R: Increased glucose uptake and oxidation in mouse
hearts prevent high fatty acid oxidation but cause cardiac
dysfunction in diet-induced obesity. Circulation. 119:2818–2828.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Fang S, Jin Y, Zheng H, et al: High
glucose condition upregulated Txnip expression level in rat
mesangial cells through ROS/MEK/MAPK pathway. Mol Cell Biochem.
347:175–182. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Łowicka E and Bełtowski J: Hydrogen
sulfide (H2S) - the third gas of interest for
pharmacologists. Pharmacol Rep. 59:4–24. 2007.
|
|
16
|
Moore PK, Bhatia M and Moochhala S:
Hydrogen sulfide: from the smell of the past to the mediator of the
future? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 24:609–611. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Geng B, Chang L, Pan C, et al: Endogenous
hydrogen sulfide regulation of myocardial injury induced by
isoproterenol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 318:756–763. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Calvert JW, Jha S, Gundewar S, et al:
Hydrogen sulfide mediates cardioprotection through Nrf2 signaling.
Circ Res. 105:365–374. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen SL, Yang CT, Yang ZL, et al: Hydrogen
sulphide protects H9c2 cells against chemical hypoxia-induced
injury. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 37:316–321. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang Z, Yang C, Xiao L, et al: Novel
insights into the role of HSP90 in cytoprotection of H2S
against chemical hypoxia-induced injury in H9c2 cardiac myocytes.
Int J Mol Med. 28:397–403. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nicholson CK and Calvert JW: Hydrogen
sulfide and ischemia-reperfusion injury. Pharmacol Res. 62:289–297.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lan A, Liao X, Mo L, et al: Hydrogen
sulfide protects against chemical hypoxia-induced injury by
inhibiting ROS-activated ERK1/2 and p38MAPK signaling pathways in
PC12 cells. PLoS One. 6:e259212011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dong XB, Yang CT, Zheng DD, et al:
Inhibition of ROS-activated ERK1/2 pathway contributes to the
protection of H2S against chemical hypoxia-induced
injury in H9c2 cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 362:149–157. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Suzuki K, Olah G, Modis K, et al: Hydrogen
sulfide replacement therapy protects the vascular endothelium in
hyperglycemia by preserving mitochondrial function. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 108:13829–13834. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Malhotra A, Vashistha H, Yadav VS, et al:
Inhibition of p66ShcA redox activity in cardiac muscle cells
attenuates hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis. Am
J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 296:H380–H388. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yuan Z, Feng W, Hong J, Zheng Q, Shuai J
and Ge Y: p38MAPK and ERK promote nitric oxide production in
cultured human retinal pigmented epithelial cells induced by high
concentration glucose. Nitric Oxide. 20:9–15. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wilmer WA, Dixon CL and Hebert C: Chronic
exposure of human mesangial cells to high glucose environments
activates the p38 MAPK pathway. Kidney Int. 60:858–871. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sugden PH and Clerk A: ‘Stress-responsive’
mitogen-activated protein kinases (c-Jun N-terminal kinases and p38
mitogen-activated protein kinases) in the myocardium. Circ Res.
83:345–352. 1998.
|
|
29
|
Guo R, Lin J, Xu W, et al: Hydrogen
sulfide attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by inhibition
of the p38 MAPK pathway in H9c2 cells. Int J Mol Med. 31:644–650.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang J, Liu X, Bhalla K, et al: Prevention
of apoptosis by Bcl-2: release of cytochrome c from mitochondria
blocked. Science. 275:1129–1132. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yue TL, Wang C, Gu JL, et al: Inhibition
of extracellular signal-regulated kinase enhances
Ischemia/Reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in cultured cardiac
myocytes and exaggerates reperfusion injury in isolated perfused
heart. Circ Res. 86:692–699. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Strohm C, Barancik T, Brühl ML, Kilian SA
and Schaper W: Inhibition of the ER-kinase cascade by PD98059 and
UO126 counteracts ischemic preconditioning in pig myocardium. J
Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 36:218–229. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Buehler A, Martire A, Strohm C, et al:
Angiogenesis-independent cardioprotection in FGF-1 transgenic mice.
Cardiovasc Res. 55:768–777. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen L, Liu L, Yin J, Luo Y and Huang S:
Hydrogen peroxide-induced neuronal apoptosis is associated with
inhibition of protein phosphatase 2A and 5, leading to activation
of MAPK pathway. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 41:1284–1295. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jain SK, Bull R, Rains JL, et al: Low
levels of hydrogen sulfide in the blood of diabetes patients and
streptozotocin-treated rats causes vascular inflammation? Antioxid
Redox Signal. 12:1333–1337. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yusuf M, Kwong Huat BT, Hsu A, Whiteman M,
Bhatia M and Moore PK: Streptozotocin-induced diabetes in the rat
is associated with enhanced tissue hydrogen sulfide biosynthesis.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 333:1146–1152. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ahmad FU, Sattar MA, Rathore HA, et al:
Exogenous hydrogen sulfide (H2S) reduces blood pressure
and prevents the progression of diabetic nephropathy in
spontaneously hypertensive rats. Ren Fail. 34:203–210.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Whiteman M, Gooding KM, Whatmore JL, et
al: Adiposity is a major determinant of plasma levels of the novel
vasodilator hydrogen sulphide. Diabetologia. 53:1722–1726. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gao Y, Yao X, Zhang Y, et al: The
protective role of hydrogen sulfide in myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion-induced injury in diabetic rats. Int J
Cardiol. 152:177–183. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hu LF, Wong PT, Moore PK and Bian JS:
Hydrogen sulfide attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation
by inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in microglia.
J Neurochem. 100:1121–1128. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Hu LF, Lu M, Wu ZY, Wong PT and Bian JS:
Hydrogen sulfide inhibits rotenone-induced apoptosis via
preservation of mitochondrial function. Mol Pharmacol. 75:27–34.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Adhikari S and Bhatia M:
H2S-induced pancreatic acinar cell apoptosis is mediated
via JNK and p38 MAP kinase. J Cell Mol Med. 12:1374–1383. 2008.
|
|
43
|
Zhi L, Ang AD, Zhang H, Moore PK and
Bhatia M: Hydrogen sulfide induces the synthesis of proinflammatory
cytokines in human monocyte cell line U937 via the ERK-NF-kappaB
pathway. J Leukoc Biol. 81:1322–1332. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mukherjee S, Lekli I, Goswami S and Das
DK: Freshly crushed garlic is a superior cardioprotective agent
than processed garlic. J Agric Food Chem. 57:7137–7144. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hu Y, Chen X, Pan TT, et al:
Cardioprotection induced by hydrogen sulfide preconditioning
involves activation of ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways. Pflugers Arch.
455:607–616. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yang G, Wu L, Bryan S, Khaper N, Mani S
and Wang R: Cystathionine gamma-lyase deficiency and
overproliferation of smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc Res.
86:487–495. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yang G, Yang W, Wu L and Wang R:
H2S, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and apoptosis of
insulin-secreting beta cells. J Biol Chem. 282:16567–16576.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lu M, Hu LF, Hu G and Bian JS: Hydrogen
sulfide protects astrocytes against H(2)O(2)-induced neural injury
via enhancing glutamate uptake. Free Radic Biol Med. 45:1705–1713.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kloesch B, Liszt M and Broell J:
H2S transiently blocks IL-6 expression in rheumatoid
arthritic fibroblast-like synoviocytes and deactivates p44/42
mitogen-activated protein kinase. Cell Biol Int. 34:477–484.
2010.
|
|
50
|
Cai WJ, Wang MJ, Moore PK, Jin HM, Yao T
and Zhu YC: The novel proangiogenic effect of hydrogen sulfide is
dependent on Akt phosphorylation. Cardiovasc Res. 76:29–40. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Bliksøen M, Kaljusto ML, Vaage J and
Stensløkken KO: Effects of hydrogen sulphide on
ischaemia-reperfusion injury and ischaemic preconditioning in the
isolated, perfused rat heart. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 34:344–349.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Marshall CJ: Specificity of receptor
tyrosine kinase signaling: transient versus sustained extracellular
signal-regulated kinase activation. Cell. 80:179–185. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar
|