|
1
|
Neeper M, Schmidt AM, Brett J, et al:
Cloning and expression of a cell surface receptor for advanced
glycosylation end products of proteins. J Biol Chem.
267:14998–15004. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schmidt AM, Yan SD, Yan SF and Stern DM:
The biology of the receptor for advanced glycation end products and
its ligands. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1498:99–111. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schmidt AM, Mora R, Cao R, et al: The
endothelial cell binding site for advanced glycation end products
consists of a complex: an integral membrane protein and a
lactoferrin-like polypeptide. J Biol Chem. 269:9882–9888.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
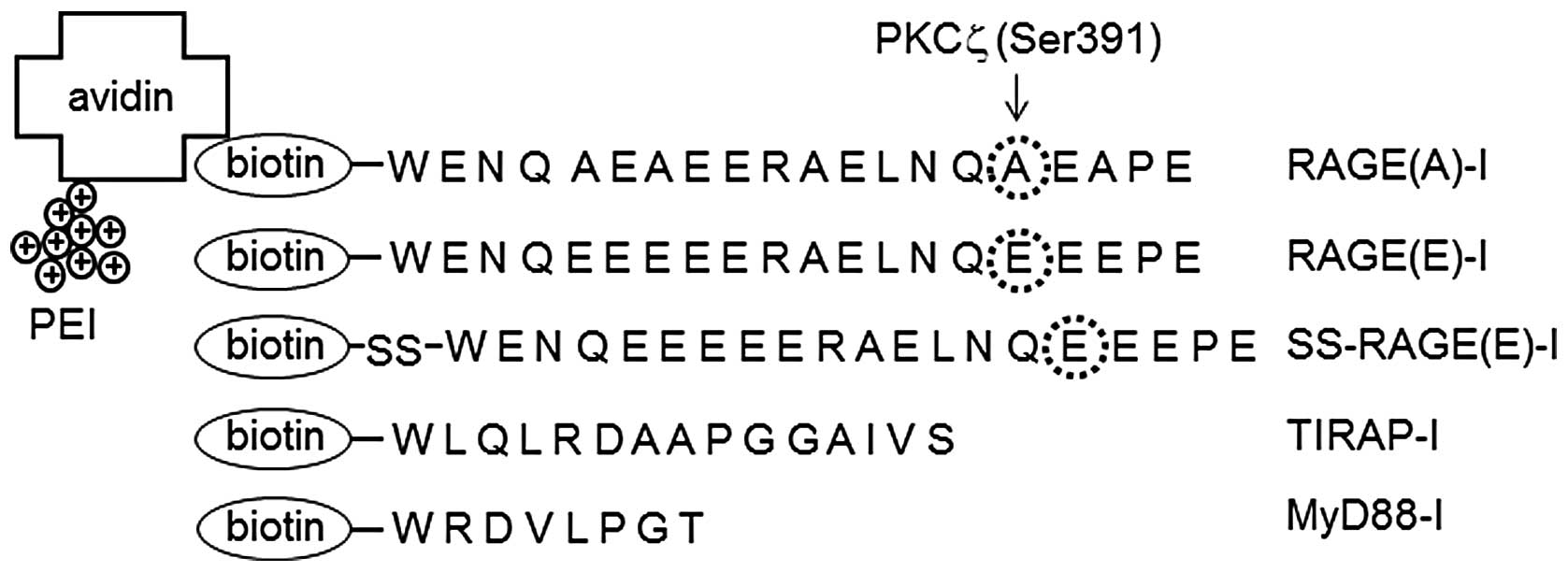
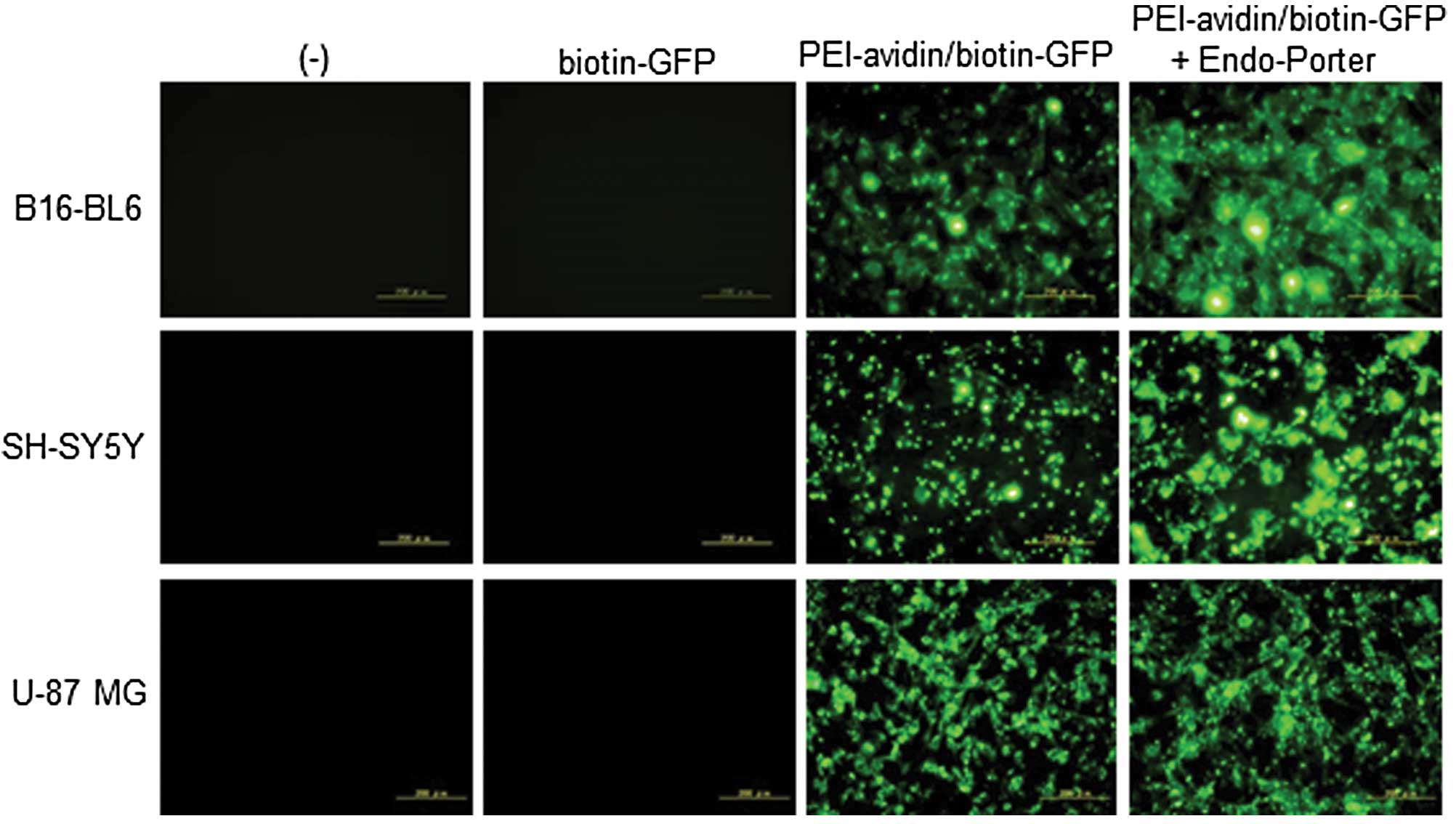
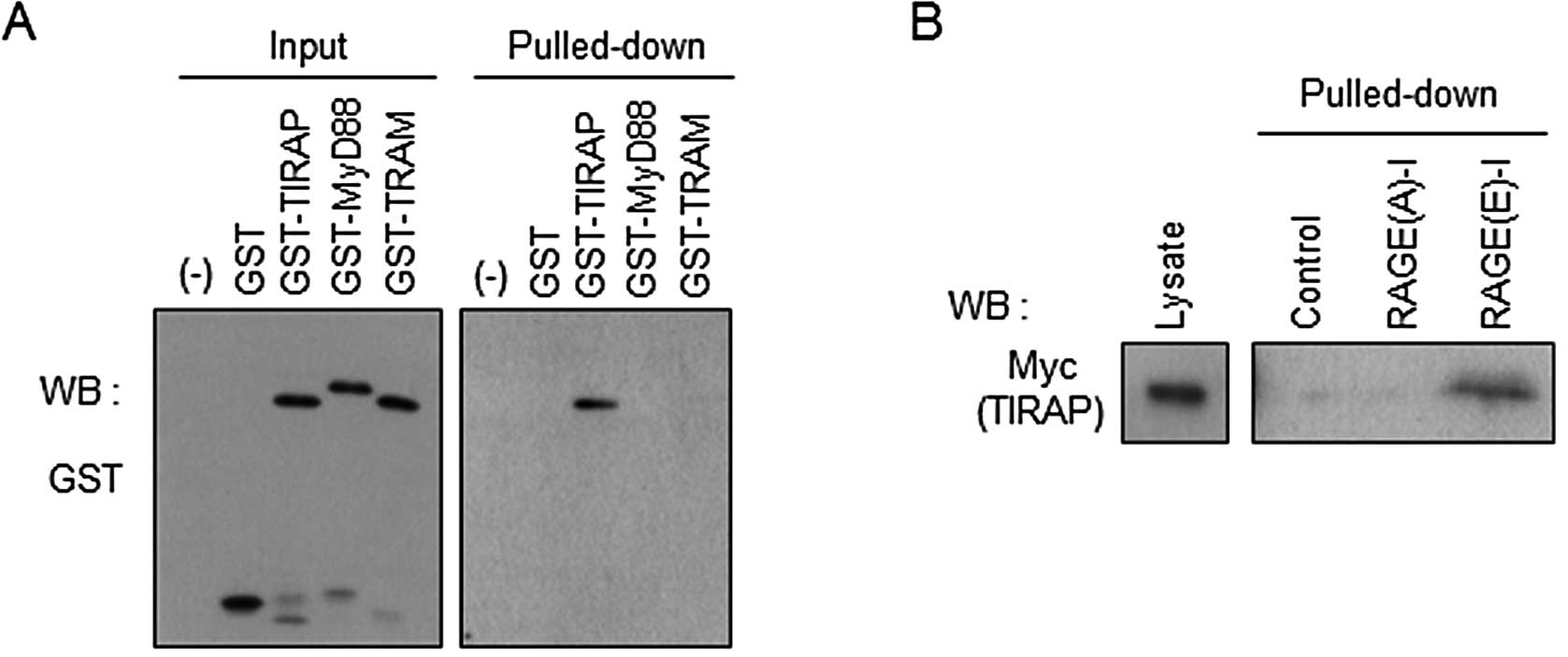
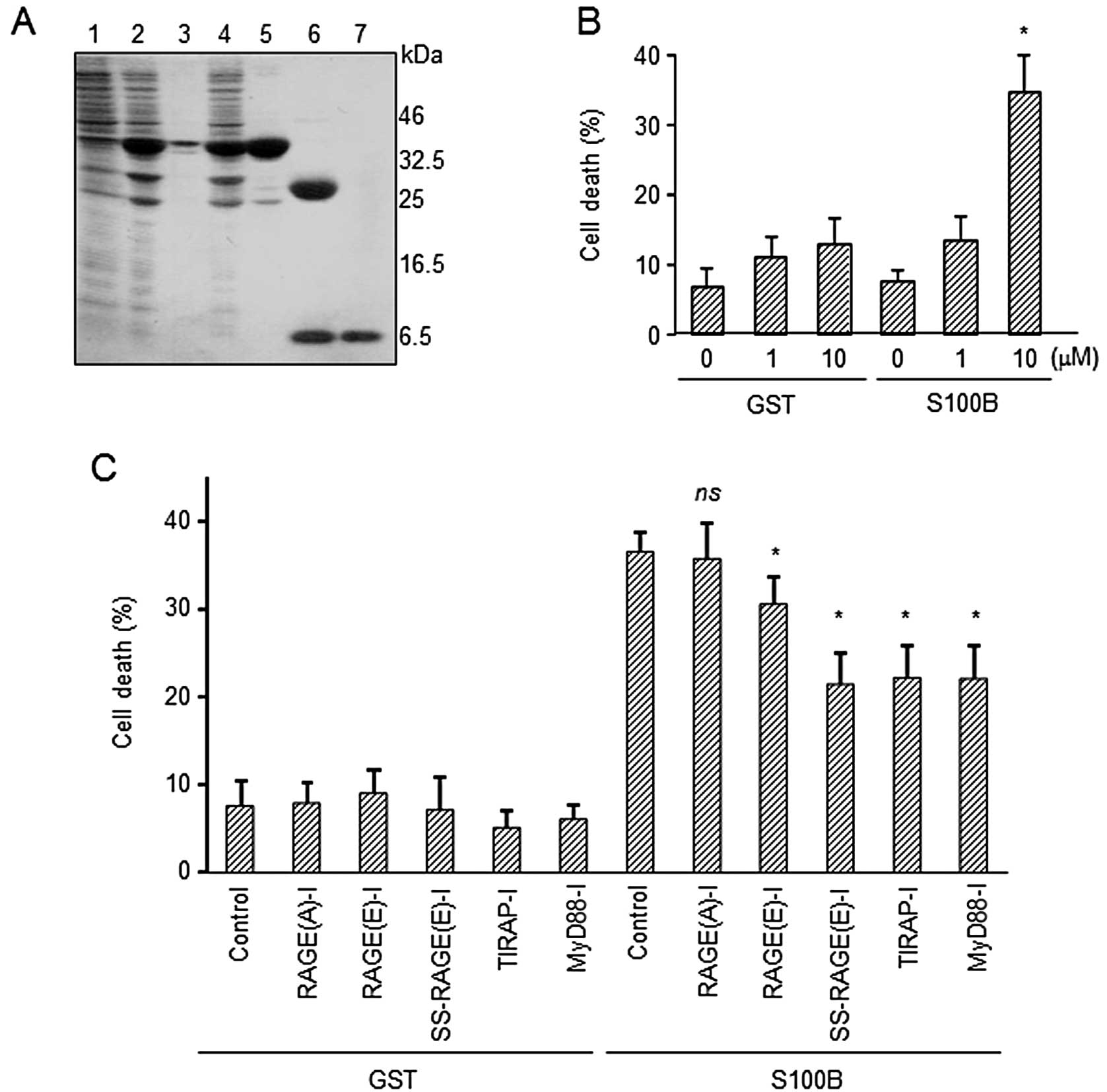
Hofmann MA, Drury S, Fu C, et al: RAGE
mediates a novel proinflammatory axis: a central cell surface
receptor for S100/calgranulin polypeptides. Cell. 97:889–901. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Huttunen HJ, Kuja-Panula J, Sorci G,
Agneletti AL, Donato R and Rauvala H: Coregulation of neurite
outgrowth and cell survival by amphoterin and S100 proteins through
receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) activation. J
Biol Chem. 275:40096–40105. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Leclerc E, Fritz G, Weibel M, Heizmann CW
and Galichet A: S100B and S100A6 differentially modulate cell
survival by interacting with distinct RAGE (receptor for advanced
glycation end products) immunoglobulin domains. J Biol Chem.
282:31317–31331. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Li J, Qu X and Schmidt AM: Sp1-binding
elements in the promoter of RAGE are essential for
amphoterin-mediated gene expression in cultured neuroblastoma
cells. J Biol Chem. 273:30870–30878. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yan SD, Chen X, Fu J, et al: RAGE and
amyloid-beta peptide neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature.
382:685–691. 1996.
|
|
9
|
Huang JS, Guh JY, Chen HC, Hung WC, Lai YH
and Chuang LY: Role of receptor for advanced glycation end-product
(RAGE) and the JAK/STAT-signaling pathway in AGE-induced collagen
production in NRK-49F cells. J Cell Biochem. 81:102–113. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yeh CH, Sturgis L, Haidacher J, et al:
Requirement for p38 and p44/p42 mitogen-activated protein kinases
in RAGE-mediated nuclear factor-kappaB transcriptional activation
and cytokine secretion. Diabetes. 50:1495–1504. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Lander HM, Tauras JM, Ogiste JS, Hori O,
Moss RA and Schmidt AM: Activation of the receptor for advanced
glycation end products triggers a p21(ras)-dependent
mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway regulated by oxidant
stress. J Biol Chem. 272:17810–17814. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Huttunen HJ, Kuja-Panula J and Rauvala H:
Receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) signaling
induces CREB-dependent chromogranin expression during neuronal
differentiation. J Biol Chem. 277:38635–38646. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Brett J, Schmidt AM, Yan SD, et al: Survey
of the distribution of a newly characterized receptor for advanced
glycation end products in tissues. Am J Pathol. 143:1699–1712.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Beccafico S, Riuzzi F, Puglielli C, et al:
Human muscle satellite cells show age-related differential
expression of S100B protein and RAGE. Age. 33:523–541. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Srikanth V, Maczurek A, Phan T, et al:
Advanced glycation endproducts and their receptor RAGE in
Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 32:763–777. 2011.
|
|
16
|
Maczurek A, Shanmugam K and Münch G:
Inflammation and the redox-sensitive AGE-RAGE pathway as a
therapeutic target in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann NY Acad Sci.
1126:147–151. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Koyama H and Nishizawa Y: AGEs/RAGE in
CKD: irreversible metabolic memory road toward CVD? Eur J Clin
Invest. 40:623–635. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Reiniger N, Lau K, McCalla D, et al:
Deletion of the receptor for advanced glycation end products
reduces glomerulosclerosis and preserves renal function in the
diabetic OVE26 mouse. Diabetes. 59:2043–2054. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu L, Ma L, Nicholson LF and Black PN:
Advanced glycation end products and its receptor (RAGE) are
increased in patients with COPD. Respir Med. 105:329–336. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ramasamy R, Yan SF and Schmidt AM:
Receptor for AGE (RAGE): signaling mechanisms in the pathogenesis
of diabetes and its complications. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1243:88–102.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Su XD, Li SS, Tian YQ, Zhang ZY, Zhang GZ
and Wang LX: Elevated serum levels of advanced glycation end
products and their monocyte receptors in patients with type 2
diabetes. Arch Med Res. 42:596–601. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Leclerc E, Heizmann CW and Vetter SW: RAGE
and S100 protein transcription levels are highly variable in human
melanoma tumors and cells. Gen Physiol Biophys. 28:F65–F75.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huttunen HJ, Fages C, Kuja-Panula J,
Ridley AJ and Rauvala H: Receptor for advanced glycation end
products-binding COOH-terminal motif of amphoterin inhibits
invasive migration and metastasis. Cancer Res. 62:4805–4811.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Arumugam T, Ramachandran V, Gomez SB,
Schmidt AM and Logsdon CD: S100P-derived RAGE antagonistic peptide
reduces tumor growth and metastasis. Clin Cancer Res. 18:4356–4364.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Abe R, Shimizu T, Sugawara H, et al:
Regulation of human melanoma growth and metastasis by AGE-AGE
receptor interactions. J Invest Dermatol. 122:461–467. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Arumugam T, Ramachandran V and Logsdon CD:
Effect of cromolyn on S100P interactions with RAGE and pancreatic
cancer growth and invasion in mouse models. J Natl Cancer Inst.
98:1806–1818. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sakaguchi M, Murata H, Yamamoto K, et al:
TIRAP, an adaptor protein for TLR2/4, transduces a signal from RAGE
phosphorylated upon ligand binding. PLoS One. 6:e231322011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kitazoe M, Murata H, Futami J, et al:
Protein transduction assisted by polyethylenimine-cationized
carrier proteins. J Biochem. 137:693–701. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Murata H, Sakaguchi M, Futami J, et al:
Denatured and reversibly cationized p53 readily enters cells and
simultaneously folds to the functional protein in the cells.
Biochemistry. 45:6124–6132. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Futami M, Watanabe Y, Asama T, et al:
Uniformly cationized protein efficiently reaches the cytosol of
mammalian cells. Bioconjug Chem. 23:2025–2031. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schilling D, Thomas K, Nixdorff K, Vogel
SN and Fenton MJ: Toll-like receptor 4 and Toll-IL-1 receptor
domain-containing adapter protein (TIRAP)/myeloid differentiation
protein 88 adapter-like (Mal) contribute to maximal IL-6 expression
in macrophages. J Immunol. 169:5874–5880. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Loiarro M, Sette C, Gallo G, et al:
Peptide-mediated interference of TIR domain dimerization in MyD88
inhibits interleukin-1-dependent activation of NF-{kappa}B. J Biol
Chem. 280:15809–15814. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kaplan IM, Wadia JS and Dowdy SF: Cationic
TAT peptide transduction domain enters cells by macropinocytosis. J
Control Release. 102:247–253. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bassi R, Giussani P, Anelli V, et al:
HMGB1 as an autocrine stimulus in human T98G glioblastoma cells:
role in cell growth and migration. J Neurooncol. 87:23–33. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kataoka K, Ono T, Murata H, et al: S100A7
promotes the migration and invasion of osteosarcoma cells via the
receptor for advanced glycation end products. Oncol Lett.
3:1149–1153. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hudson BI, Kalea AZ, Del Mar Arriero M, et
al: Interaction of the RAGE cytoplasmic domain with diaphanous-1 is
required for ligand-stimulated cellular migration through
activation of Rac1 and Cdc42. J Biol Chem. 283:34457–34468. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yamamoto K, Murata H, Putranto EW, et al:
DOCK7 is a critical regulator of the RAGE-Cdc42 signaling axis that
induces formation of dendritic pseudopodia in human cancer cells.
Oncol Rep. 29:1073–1079. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Deane R, Singh I, Sagare AP, et al: A
multimodal RAGE-specific inhibitor reduces amyloid β-mediated brain
disorder in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J Clin Invest.
122:1377–1392. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Griffin WS, Sheng JG, McKenzie JE, et al:
Life-long overexpression of S100beta in Down’s syndrome:
implications for Alzheimer pathogenesis. Neurobiol Aging.
19:401–405. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mrak RE and Griffinbc WS: The role of
activated astrocytes and of the neurotrophic cytokine S100B in the
pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 22:915–922.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|