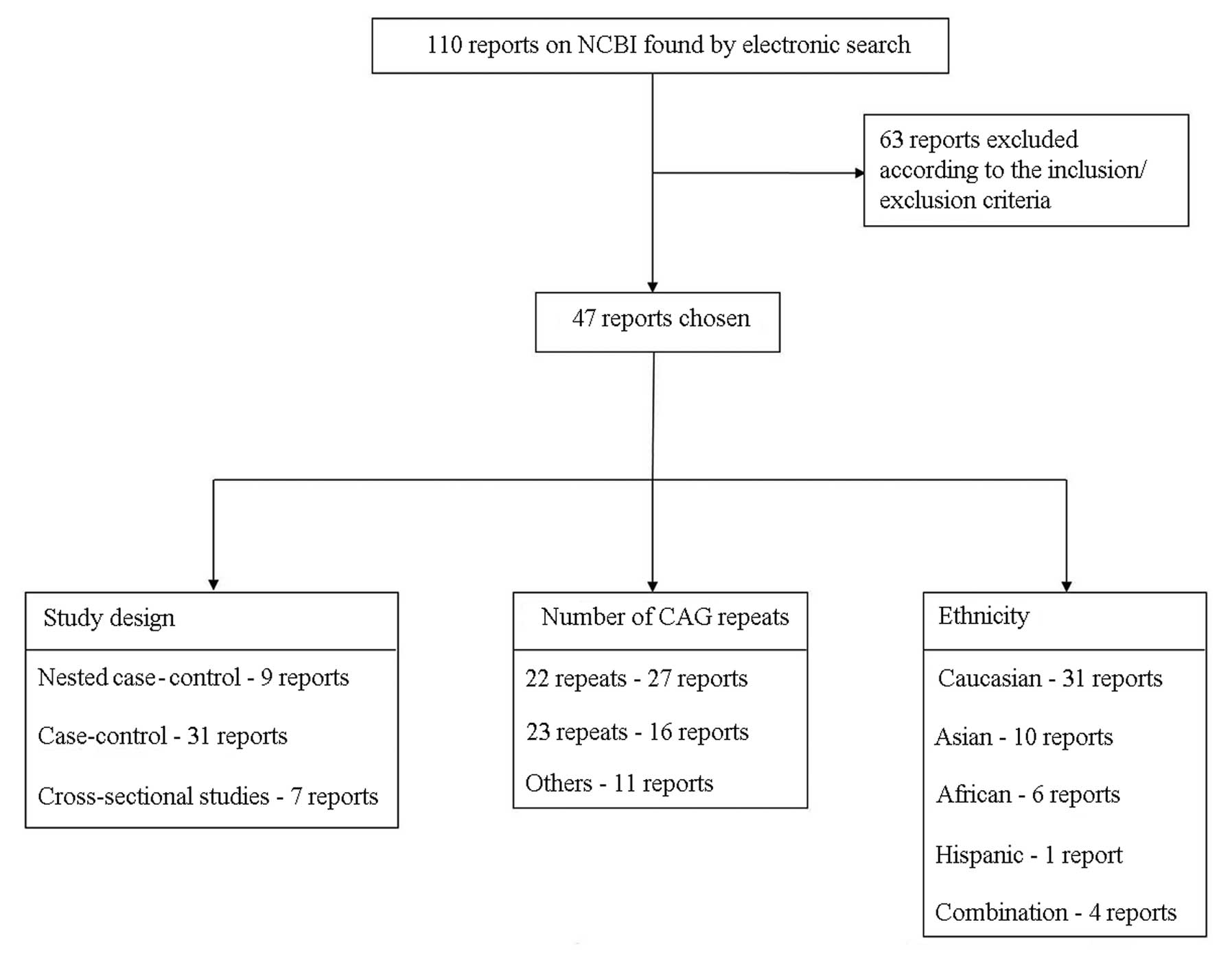
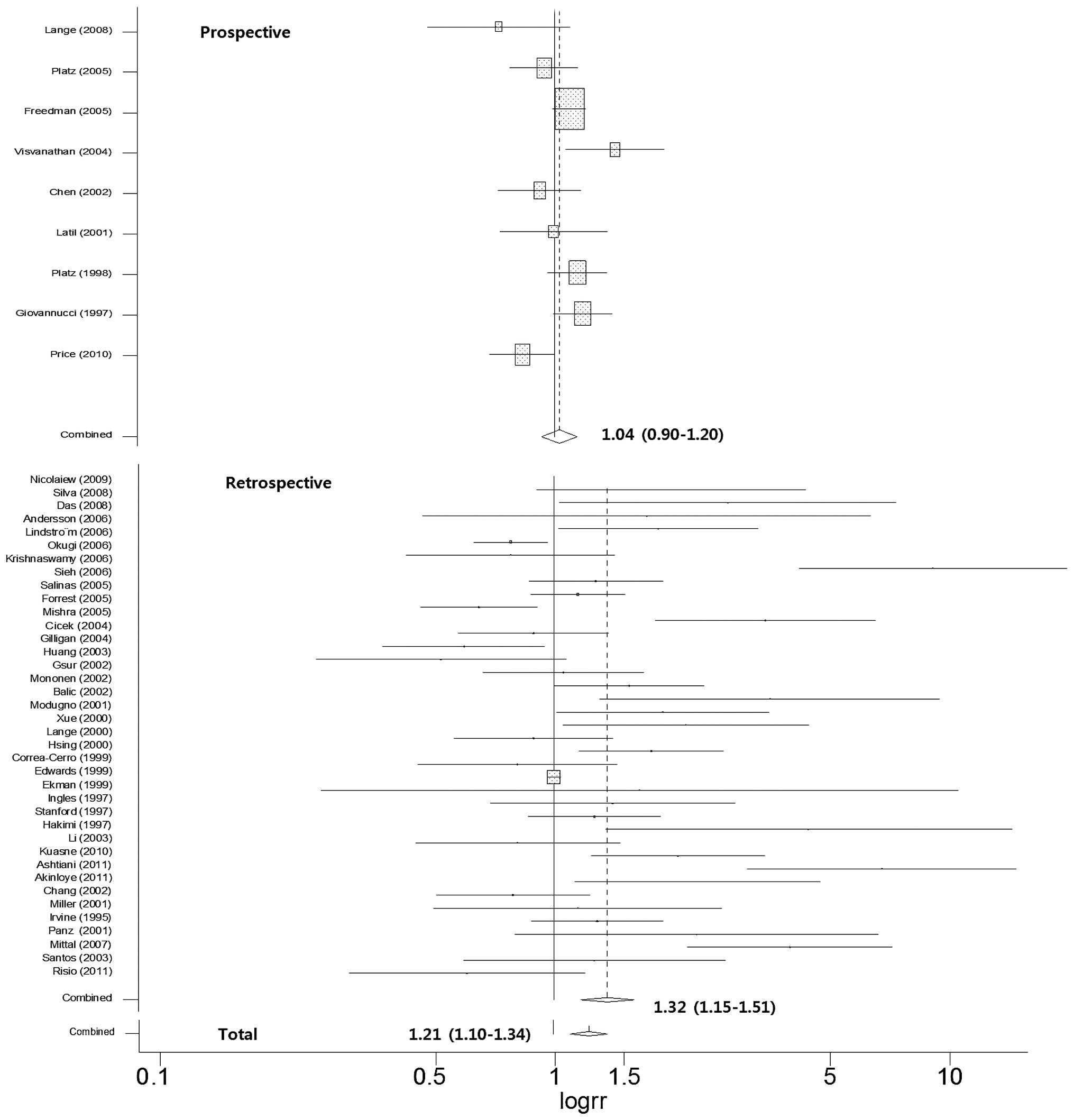
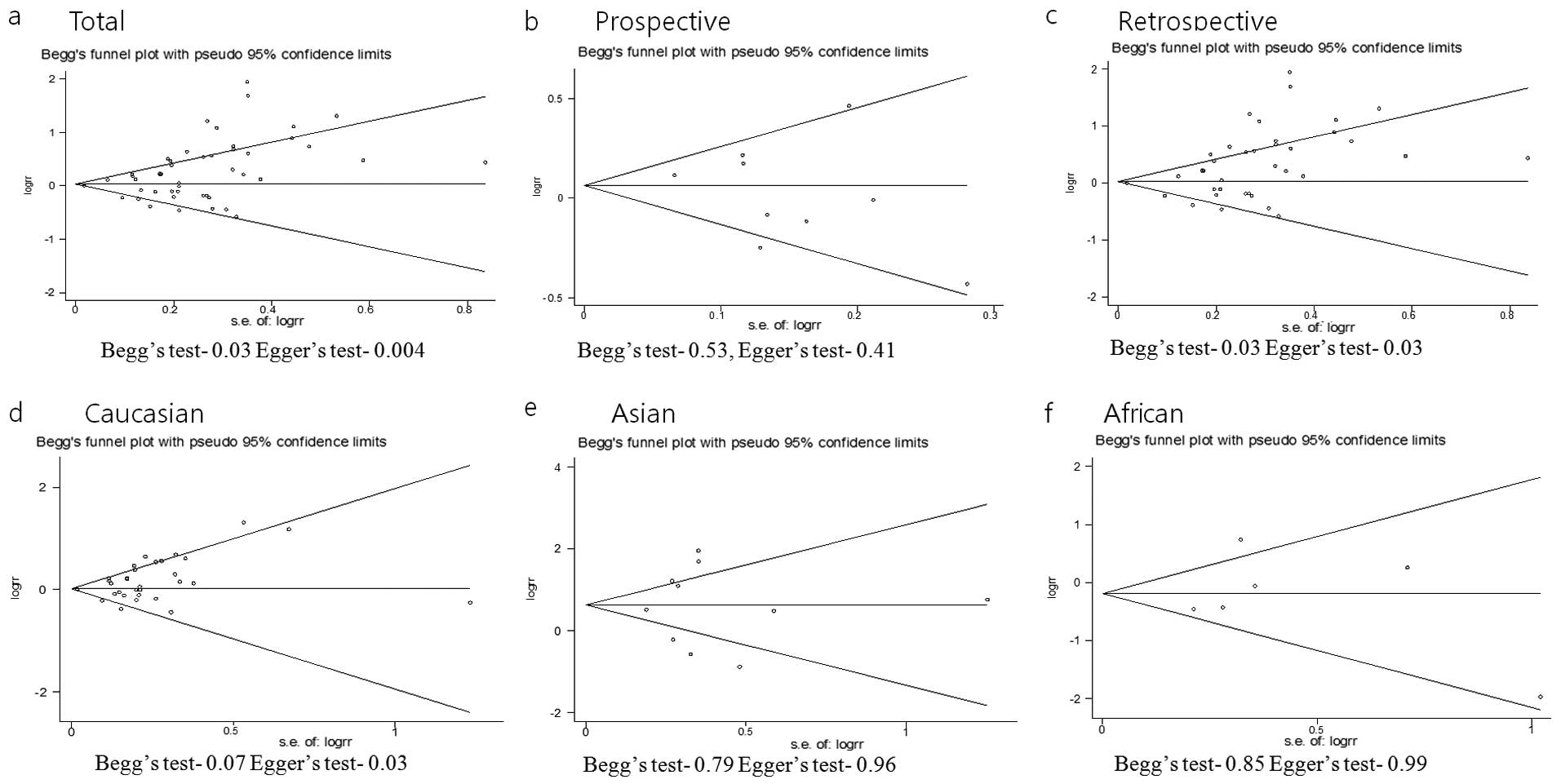
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J,
Smigal C and Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin.
56:106–130. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Parkin DM, Whelan SL, Ferlay J, Raymond
and Young J: Cancer incidence in five continents. VIIIARC Sci Publ;
(143): pp. i–xxxiv. pp. 1–1240. Lyon: 1997
|
|
3
|
Ross RK, Pike MC, Coetzee GA, Reichardt
JK, Yu MC, Feigelson H, et al: Androgen metabolism and prostate
cancer: establishing a model of genetic susceptibility. Cancer Res.
58:4497–4504. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zeegers MP, Jellema A and Ostrer H:
Empiric risk of prostate carcinoma for relatives of patients with
prostate carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Cancer. 97:1894–1903. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
|
|
6
|
Nelson KA and Witte JS: Androgen receptor
CAG repeats and prostate cancer. Am J Epidemiol. 155:883–890. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wilding G: The importance of steroid
hormones in prostate cancer. Cancer Surv. 14:113–130.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Crawford ED: Understanding the
epidemiology, natural history, and key pathways involved in
prostate cancer. Urology. 73(Suppl 5): S4–S10. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Montgomery JS, Price DK and Figg WD: The
androgen receptor gene and its influence on the development and
progression of prostate cancer. J Pathol. 195:138–146. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chamberlain NL, Driver ED and Miesfeld RL:
The length and location of CAG trinucleotide repeats in the
androgen receptor N-terminal domain affect transactivation
function. Nucleic Acids Res. 22:3181–3186. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Buchanan G, Yang M, Cheong A, Harris JM,
Irvine RA, Lambert PF, et al: Structural and functional
consequences of glutamine tract variation in the androgen receptor.
Hum Mol Genet. 13:1677–1692. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Risio M, Venesio T, Kolomoets E, Armaroli
P, Gallo F, Balsamo A, et al: Genetic polymorphisms of CYP17A1,
vitamin D receptor and androgen receptor in Italian heredo-familial
and sporadic prostate cancers. Cancer Epidemiol. 35:e18–e24. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zeegers MP, Kiemeney LA, Nieder AM and
Ostrer H: How strong is the association between CAG and GGN repeat
length polymorphisms in the androgen receptor gene and prostate
cancer risk? Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 13:1765–1771.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gu M, Dong X, Zhang X and Niu W: The CAG
repeat polymorphism of androgen receptor gene and prostate cancer:
a meta-analysis. Mol Biol Rep. 39:2615–2624. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lindstrom S, Ma J, Altshuler D,
Giovannucci E, Riboli E, Albanes D, et al: A large study of
androgen receptor germline variants and their relation to sex
hormone levels and prostate cancer risk. Results from the National
Cancer Institute Breast and Prostate Cancer Cohort Consortium. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 95:E121–E127. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ahluwalia B, Jackson MA, Jones GW,
Williams AO, Rao MS and Rajguru S: Blood hormone profiles in
prostate cancer patients in high-risk and low-risk populations.
Cancer. 48:2267–2273. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kazemi-Esfarjani P, Trifiro MA and Pinsky
L: Evidence for a repressive function of the long polyglutamine
tract in the human androgen receptor: possible pathogenetic
relevance for the (CAG)n-expanded neuronopathies. Hum Mol Genet.
4:523–527. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Giovannucci E, Stampfer MJ, Krithivas K,
Brown M, Dahl D, Brufsky A, et al: The CAG repeat within the
androgen receptor gene and its relationship to prostate cancer.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:3320–3323. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hakimi JM, Schoenberg MP, Rondinelli RH,
Piantadosi S and Barrack ER: Androgen receptor variants with short
glutamine or glycine repeats may identify unique subpopulations of
men with prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 3:1599–1608.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yoshida KI, Yano M, Chiba K, Honda M and
Kitahara S: CAG repeat length in the androgen receptor gene is
enhanced in patients with idiopathic azoospermia. Urology.
54:1078–1081. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sawaya ME and Shalita AR: Androgen
receptor polymorphisms (CAG repeat lengths) in androgenetic
alopecia, hirsutism, and acne. J Cutan Med Surg. 3:9–15.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mitsumori K, Terai A, Oka H, Segawa T,
Ogura K, Yoshida O and Ogawa O: Androgen receptor CAG repeat length
polymorphism in benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH): correlation
with adenoma growth. Prostate. 41:253–257. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shibata A, Stamey TA, McNeal JE, Cheng I
and Peehl DM: Genetic polymorphisms in the androgen receptor and
type II 5 alpha-reductase genes in prostate enlargement. J Urol.
166:1560–1564. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Andersson P, Varenhorst E and Soderkvist
P: Androgen receptor and vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and
prostate cancer risk. Eur J Cancer. 42:2833–2837. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sartor O, Zheng Q and Eastham JA: Androgen
receptor gene CAG repeat length varies in a race-specific fashion
in men without prostate cancer. Urology. 53:378–380. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lange EM, Sarma AV, Ray A, Wang Y, Ho LA,
Anderson SA, et al: The androgen receptor CAG and GGN repeat
polymorphisms and prostate cancer susceptibility in
African-American men: results from the Flint Men's Health Study. J
Hum Genet. 53:220–226. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Platz EA, Leitzmann MF, Rifai N, Kantoff
PW, Chen YC, Stampfer MJ, et al: Sex steroid hormones and the
androgen receptor gene CAG repeat and subsequent risk of prostate
cancer in the prostate-specific antigen era. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 14:1262–1269. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Freedman ML, Pearce CL, Penney KL,
Hirschhorn JN, Kolonel LN, Henderson BE and Altshuler D: Systematic
evaluation of genetic variation at the androgen receptor locus and
risk of prostate cancer in a multiethnic cohort study. Am J Hum
Genet. 76:82–90. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Visvanathan K, Helzlsouer KJ, Boorman DW,
Strickland PT, Hoffman SC, Comstock GW, et al: Association among an
ornithine decarboxylase polymorphism, androgen receptor gene (CAG)
repeat length and prostate cancer risk. J Urol. 171:652–655. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen C, Lamharzi N, Weiss NS, Etzioni R,
Dightman DA, Barnett M, et al: Androgen receptor polymorphisms and
the incidence of prostate cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
11:1033–1040. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Latil AG, Azzouzi R, Cancel GS, Guillaume
EC, Cochan-Priollet B, Berthon PL and Cussenot O: Prostate
carcinoma risk and allelic variants of genes involved in androgen
biosynthesis and metabolism pathways. Cancer. 92:1130–1137. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Platz EA, Giovannucci E, Dahl DM,
Krithivas K, Hennekens CH, Brown M, et al: The androgen receptor
gene GGN microsatellite and prostate cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 7:379–384. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Price DK, Chau CH, Till C, Goodman PJ,
Baum CE, Ockers SB, et al: Androgen receptor CAG repeat length and
association with prostate cancer risk: results from the prostate
cancer prevention trial. J Urol. 184:2297–2302. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nicolaiew N, Cancel-Tassin G, Azzouzi AR,
Grand BL, Mangin P, Cormier L, et al: Association between estrogen
and androgen receptor genes and prostate cancer risk. Eur J
Endocrinol. 160:101–106. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Silva Neto B, Koff WJ, Biolchi V, Brenner
C, Biolo KD, Spritzer PM and Brum IS: Polymorphic CAG and GGC
repeat lengths in the androgen receptor gene and prostate cancer
risk: analysis of a Brazilian population. Cancer Invest. 26:74–80.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Das K, Cheah PY, Lim PL, Zain YB,
Stephanie FC, Zhao Y, et al: Shorter CAG repeats in androgen
receptor and non-GG genotypes in prostate-specific antigen loci are
associated with decreased risk of benign prostatic hyperplasia and
prostate cancer. Cancer Lett. 268:340–347. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lindström S, Zheng SL, Wiklund F, Jonsson
BA, Adami HO, Balter KA, et al: Systematic replication study of
reported genetic associations in prostate cancer: Strong support
for genetic variation in the androgen pathway. Prostate.
66:1729–1743. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Okugi H, Nakazato H, Matsui H, Ohtake N,
Nakata S and Suzuki K: Association of the polymorphisms of genes
involved in androgen metabolism and signaling pathways with
familial prostate cancer risk in a Japanese population. Cancer
Detect Prev. 30:262–268. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Krishnaswamy V, Kumarasamy T, Venkatesan
V, Shroff S, Jayanth VR and Paul SF: South Indian men with reduced
CAG repeat length in the androgen receptor gene have an increased
risk of prostate cancer. J Hum Genet. 51:254–257. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sieh W, Edwards KL, Fitzpatrick AL,
Srinouanprachanh SL, Farin FM, Monks SA, et al: Prostate-specific
antigen and its interaction with the androgen receptor (United
States). Cancer Causes Control. 17:187–197. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Salinas CA, Austin MA, Ostrander EO and
Stanford JL: Polymorphisms in the androgen receptor and the
prostate-specific antigen genes and prostate cancer risk. Prostate.
65:58–65. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Forrest MS, Edwards SM, Houlston R,
Kote-Jarai Z, Key T, Allen N, et al: Association between hormonal
genetic polymorphisms and early-onset prostate cancer. Prostate
Cancer Prostatic Dis. 8:95–102. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mishra D, Thangaraj K, Mandhani A, Kumar A
and Mittal R: Is reduced CAG repeat length in androgen receptor
gene associated with risk of prostate cancer in Indian population?
Clin Genet. 68:55–60. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Cicek MS, Conti DV, Curran A, Neville PJ,
Paris PL, Casey G and Witte JS: Association of prostate cancer risk
and aggressiveness to androgen pathway genes: SRD5A2, CYP17, and
the AR. Prostate. 59:69–76. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gilligan T, Manola J, Sartor O, Weinrich
SP, Moul JW and Kantoff PW: Absence of a correlation of androgen
receptor gene CAG repeat length and prostate cancer risk in an
African-American population. Clin Prostate Cancer. 3:98–103. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Huang SP, Chou YH, Chang WS, Wu MT, Yu CC,
Wu T, et al: Androgen receptor gene polymorphism and prostate
cancer in Taiwan. J Formos Med Assoc. 102:680–686. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Gsur A, Preyer M, Haidinger G, Zidek T,
Madersbacher S, Schatzl G, et al: Polymorphic CAG repeats in the
androgen receptor gene, prostate-specific antigen polymorphism and
prostate cancer risk. Carcinogenesis. 23:1647–1651. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Mononen N, Ikonen T, Autio V, Rokman A,
Matikainen MP, Tammela TL, et al: Androgen receptor CAG
polymorphism and prostate cancer risk. Hum Genet. 111:166–171.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Balic I, Graham ST, Troyer DA, Higgins BA,
Pollock BH, Johnson-Pais TL, et al: Androgen receptor length
polymorphism associated with prostate cancer risk in Hispanic men.
J Urol. 168:2245–2248. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Modugno F, Weissfeld JL, Trump DL, Zmuda
JM, Shea P, Cauley JA and Ferrell RE: Allelic variants of aromatase
and the androgen and estrogen receptors: toward a multigenic model
of prostate cancer risk. Clin Cancer Res. 7:3092–3096.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Xue W, Irvine RA, Yu MC, Ross RK, Coetzee
GA and Ingles SA: Susceptibility to prostate cancer: interaction
between genotypes at the androgen receptor and prostate-specific
antigen loci. Cancer Res. 60:839–841. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lange EM, Chen H, Brierley K, Livermore H,
Wojno KJ, Langefeld CD, et al: The polymorphic exon 1 androgen
receptor CAG repeat in men with a potential inherited
predisposition to prostate cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 9:439–442. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hsing AW, Gao YT, Wu G, Wang X, Deng J,
Chen YL, et al: Polymorphic CAG and GGN repeat lengths in the
androgen receptor gene and prostate cancer risk: a population-based
case-control study in China. Cancer Res. 60:5111–5116. 2000.
|
|
54
|
Correa-Cerro L, Wohr G, Haussler J,
Berthon P, Drelon E, Mangin P, et al: (CAG)nCAA and GGN repeats in
the human androgen receptor gene are not associated with prostate
cancer in a French-German population. Eur J Hum Genet. 7:357–362.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Edwards SM, Badzioch MD, Minter R, Hamoudi
R, Collins N, Ardern-Jones A, et al: Androgen receptor
polymorphisms: association with prostate cancer risk, relapse and
overall survival. Int J Cancer. 84:458–465. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ekman P, Gronberg H, Matsuyama H, Kivineva
M, Bergerheim US and Li C: Links between genetic and environmental
factors and prostate cancer risk. Prostate. 39:262–268. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ingles SA, Ross RK, Yu MC, Irvine RA, La
Pera G, Haile RW and Coetzee GA: Association of prostate cancer
risk with genetic polymorphisms in vitamin D receptor and androgen
receptor. J Natl Cancer Inst. 89:166–170. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Stanford JL, Just JJ, Gibbs M, Wicklund
KG, Neal CL, Blumenstein BA and Ostrander EA: Polymorphic repeats
in the androgen receptor gene: molecular markers of prostate cancer
risk. Cancer Res. 57:1194–1198. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Li C, Gronberg H, Matsuyama H, Weber G,
Nordenskjold M, Naito K, et al: Difference between Swedish and
Japanese men in the association between AR CAG repeats and prostate
cancer suggesting a susceptibility-modifying locus overlapping the
androgen receptor gene. Int J Mol Med. 11:529–533. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kuasne H, Rodrigues IS, Fuganti PE,
Losi-Guembarovski R, Ito K, Kishima MO, et al: Polymorphisms in the
AR and PSA genes as markers of susceptibility and aggressiveness in
prostate cancer. Cancer Invest. 28:917–924. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Ashtiani ZO, Hasheminasab SM, Ayati M,
Goulian BS and Modarressi MH: Are GSTM1, GSTT1 and CAG repeat
length of androgen receptor gene polymorphisms associated with risk
of prostate cancer in Iranian patients? Pathol Oncol Res.
17:269–275. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Akinloye O, Gromoll J and Simoni M:
Variation in CAG and GGN repeat lengths and CAG/GGN haplotype in
androgen receptor gene polymorphism and prostate carcinoma in
Nigerians. Br J Biomed Sci. 68:138–142. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Chang BL, Zheng SL, Hawkins GA, Isaacs SD,
Wiley KE, Turner A, et al: Polymorphic GGC repeats in the androgen
receptor gene are associated with hereditary and sporadic prostate
cancer risk. Hum Genet. 110:122–129. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Miller EA, Stanford JL, Hsu L, Noonan E
and Ostrander EA: Polymorphic repeats in the androgen receptor gene
in high-risk sibships. Prostate. 48:200–205. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Irvine RA, Yu MC, Ross RK and Coetzee GA:
The CAG and GGC microsatellites of the androgen receptor gene are
in linkage disequilibrium in men with prostate cancer. Cancer Res.
55:1937–1940. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Panz VR, Joffe BI, Spitz I, Lindenberg T,
Farkas A and Haffejee M: Tandem CAG repeats of the androgen
receptor gene and prostate cancer risk in black and white men.
Endocrine. 15:213–216. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Mittal RD, Mishra DK, Thangaraj K, Singh R
and Mandhani A: Is there an inter-relationship between prostate
specific antigen, kallikrein-2 and androgen receptor gene
polymorphisms with risk of prostate cancer in north Indian
population? Steroids. 72:335–341. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Santos ML, Sarkis AS, Nishimoto IN and
Nagai MA: Androgen receptor CAG repeat polymorphism in prostate
cancer from a Brazilian population. Cancer Detect Prev. 27:321–326.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M and
Minder C: Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical
test. BMJ. 315:629–634. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Begg CB and Mazumdar M: Operating
characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias.
Biometrics. 50:1088–1101. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Duval S and Tweedie R: Trim and fill: A
simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for
publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics. 56:455–463. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|