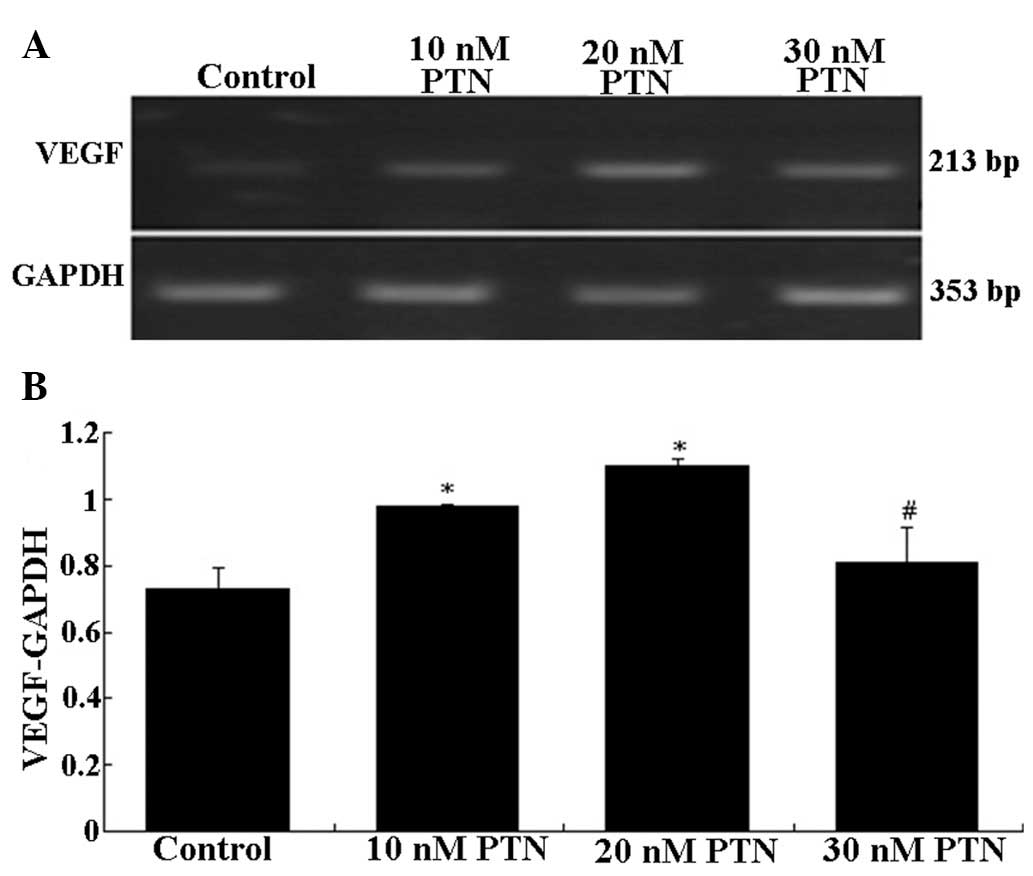
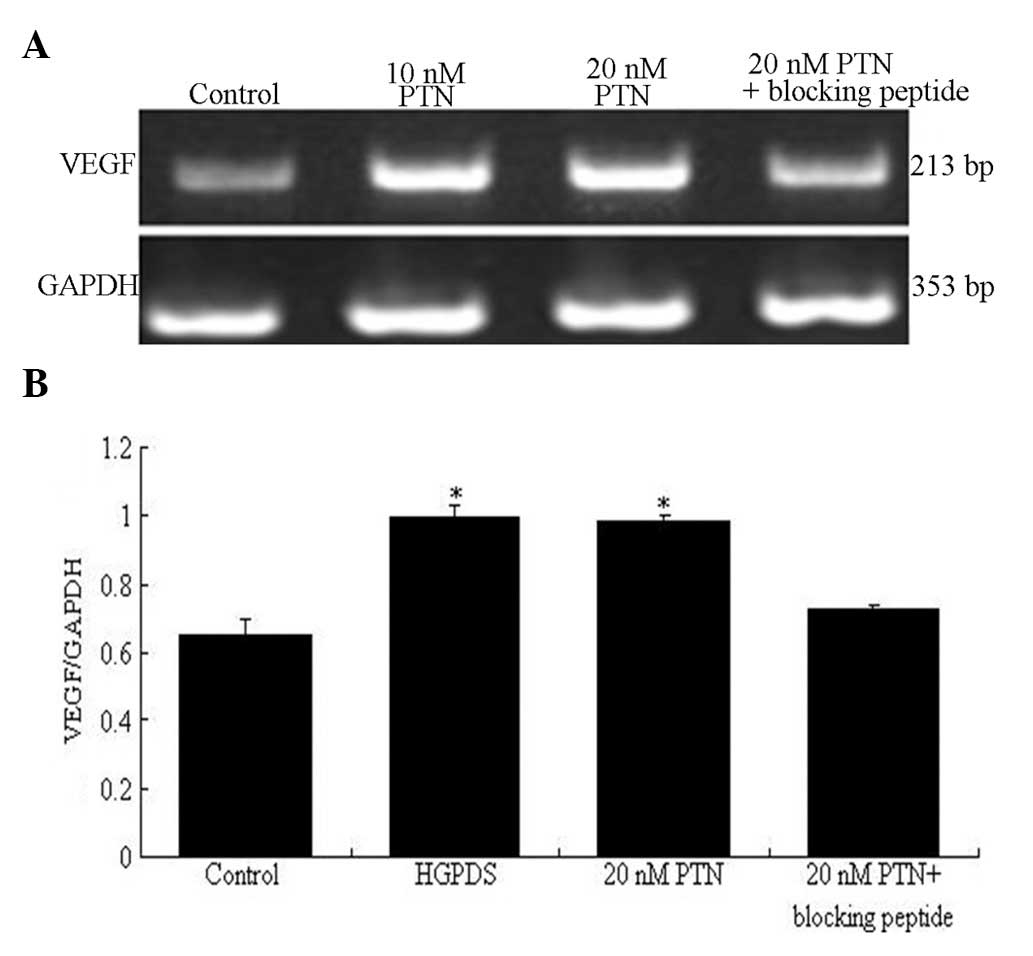
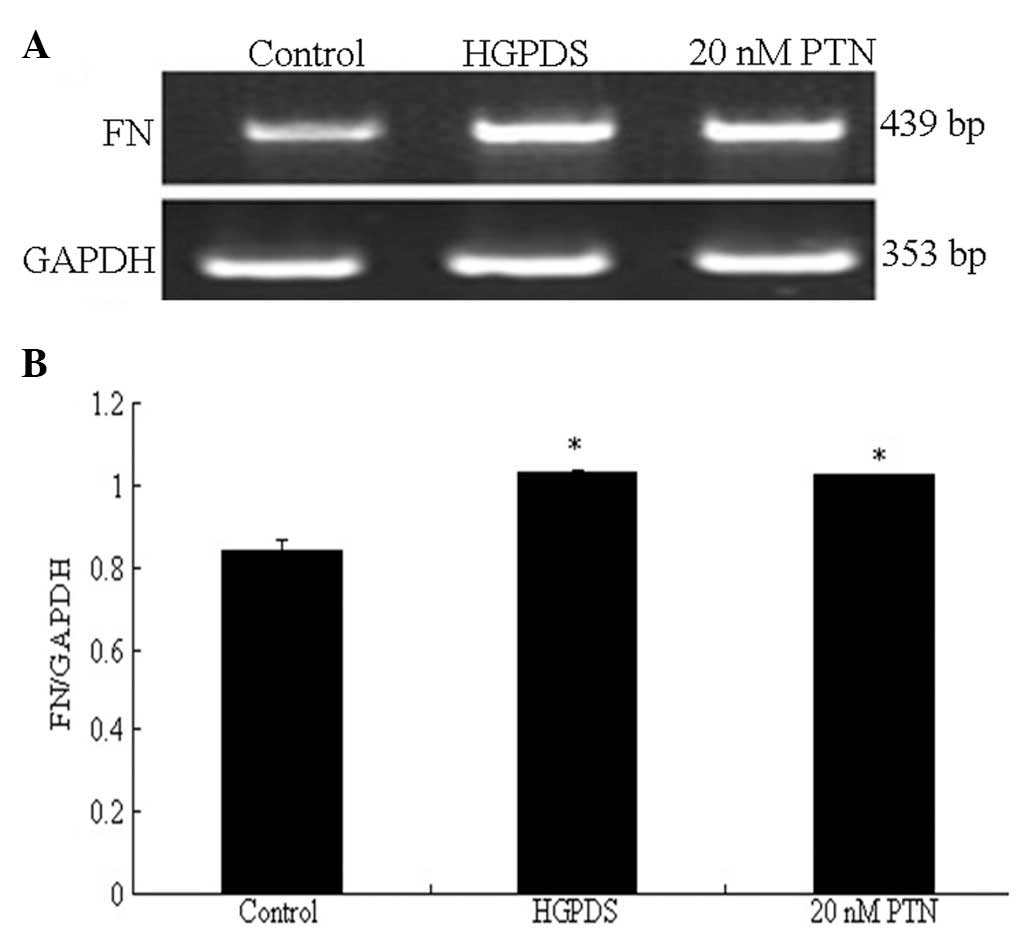
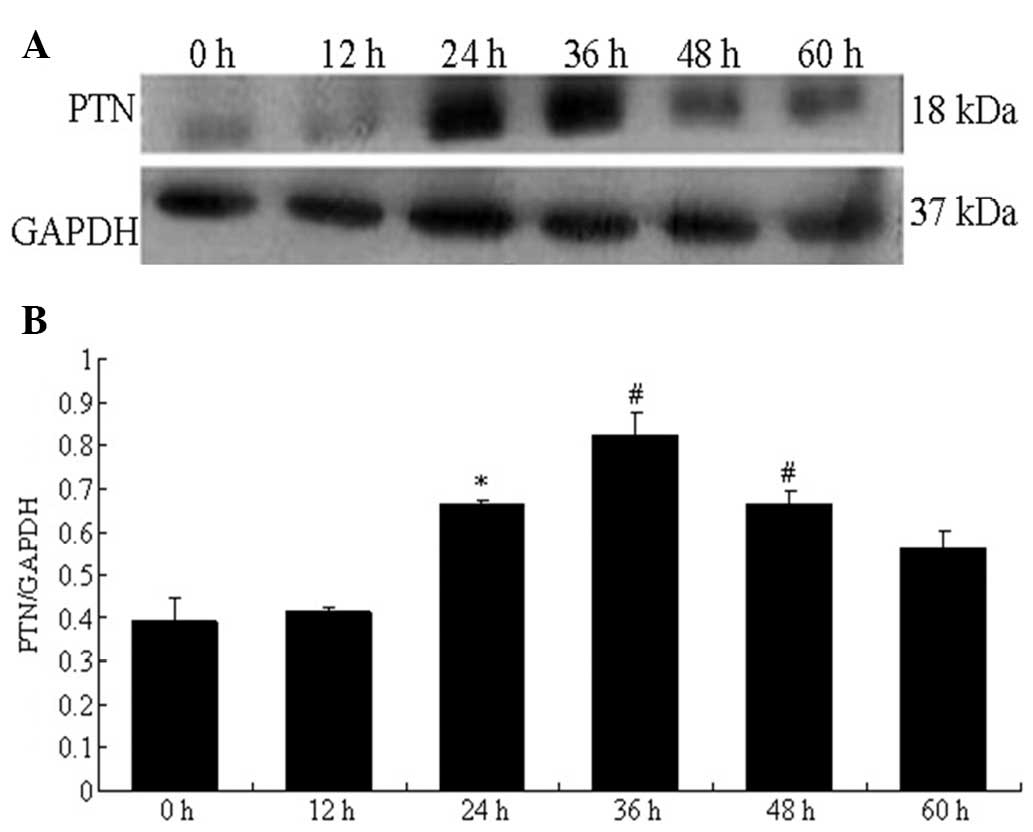
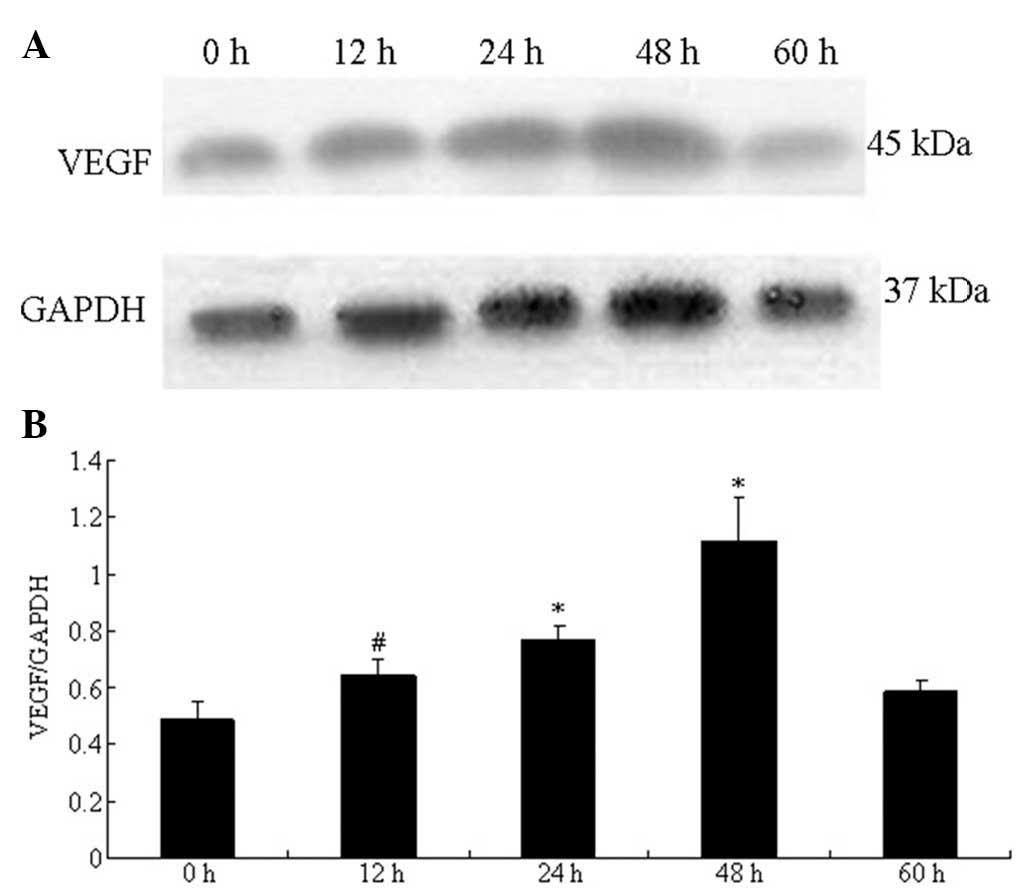
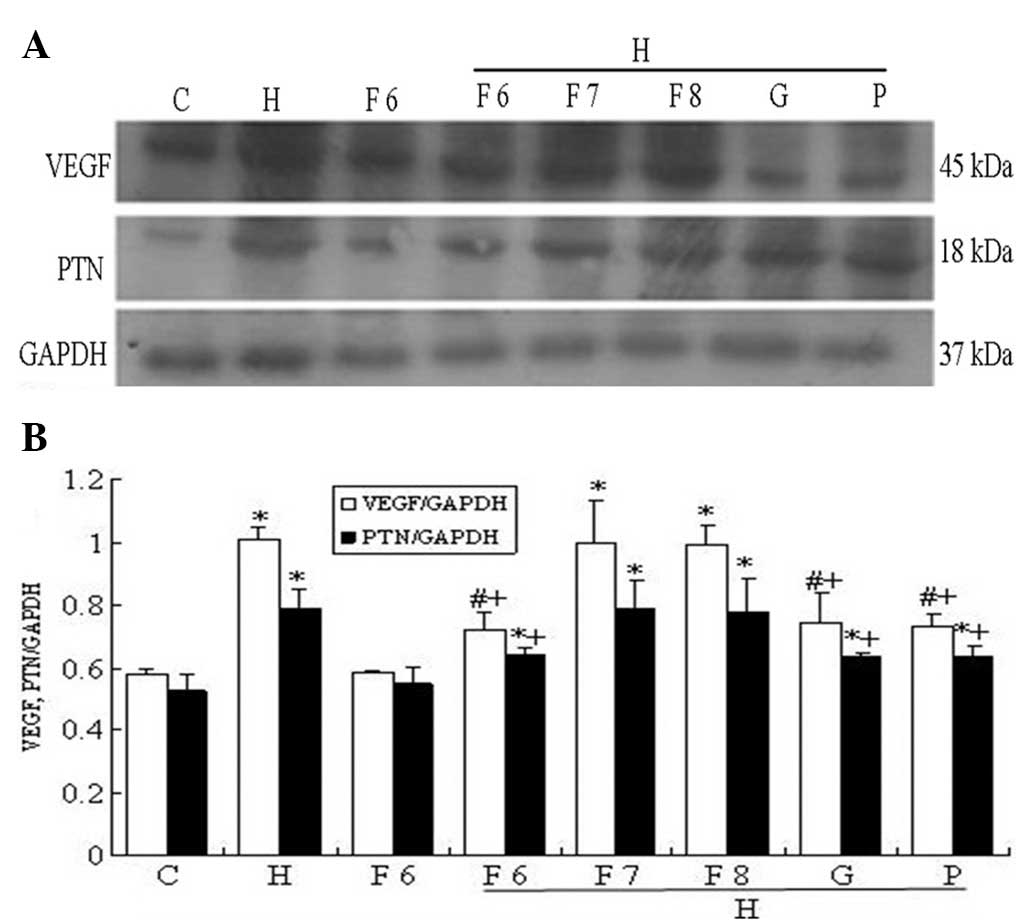
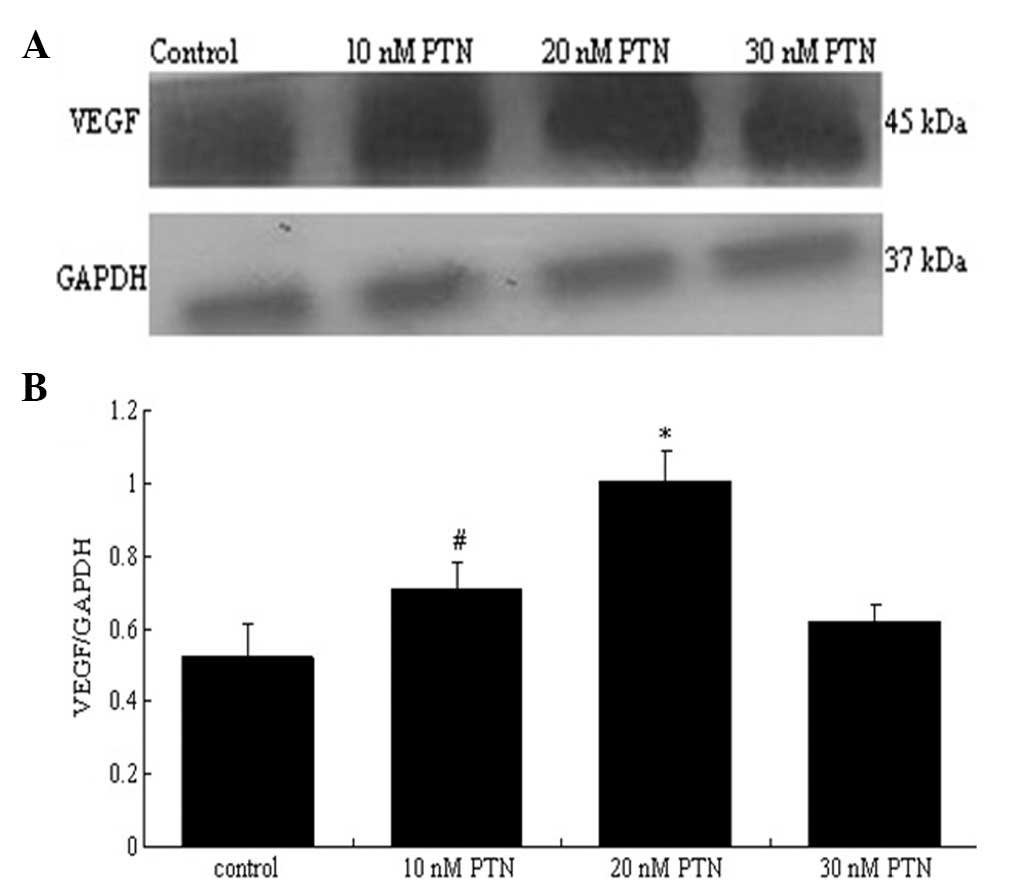
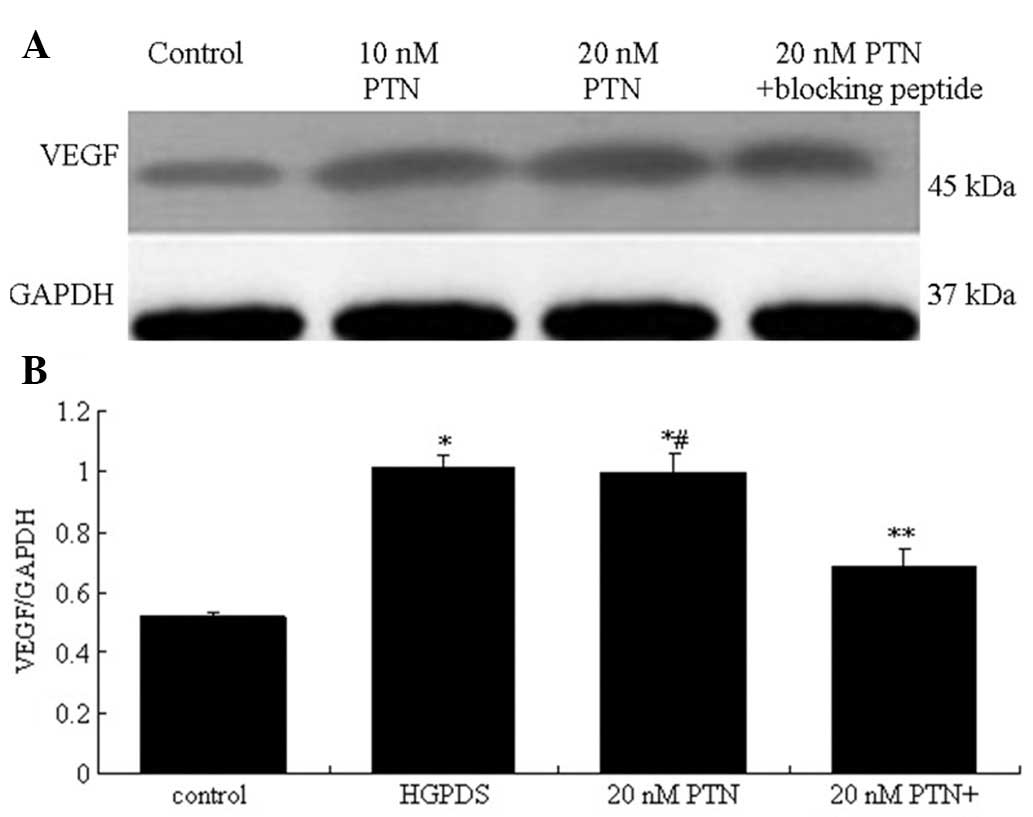
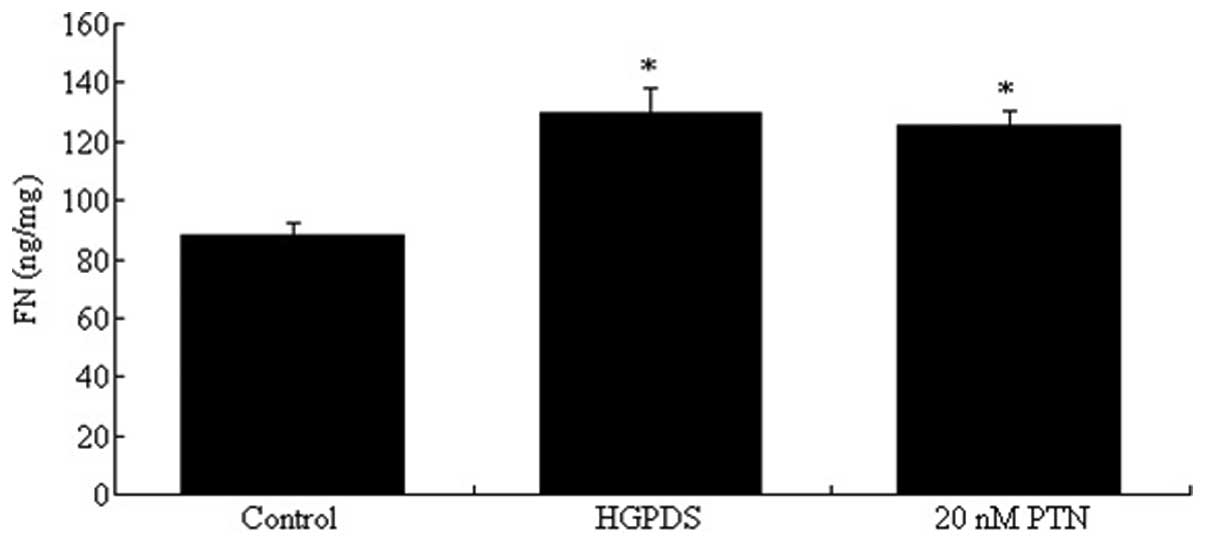
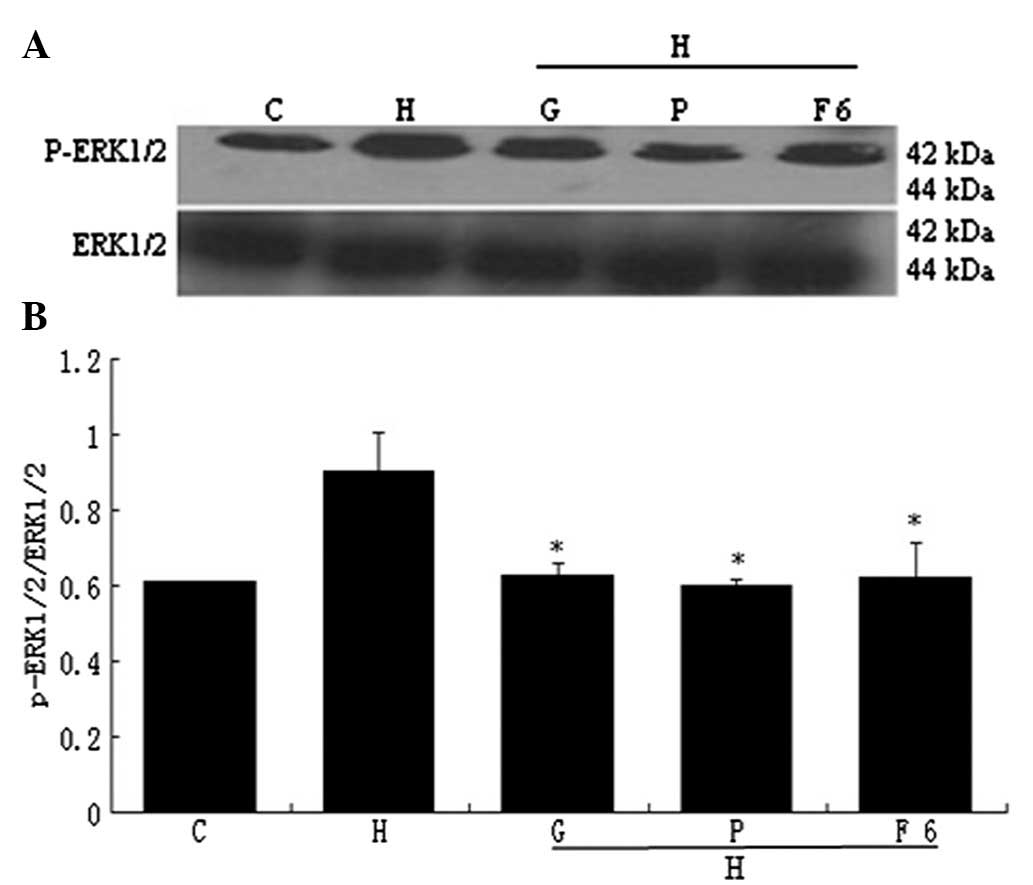
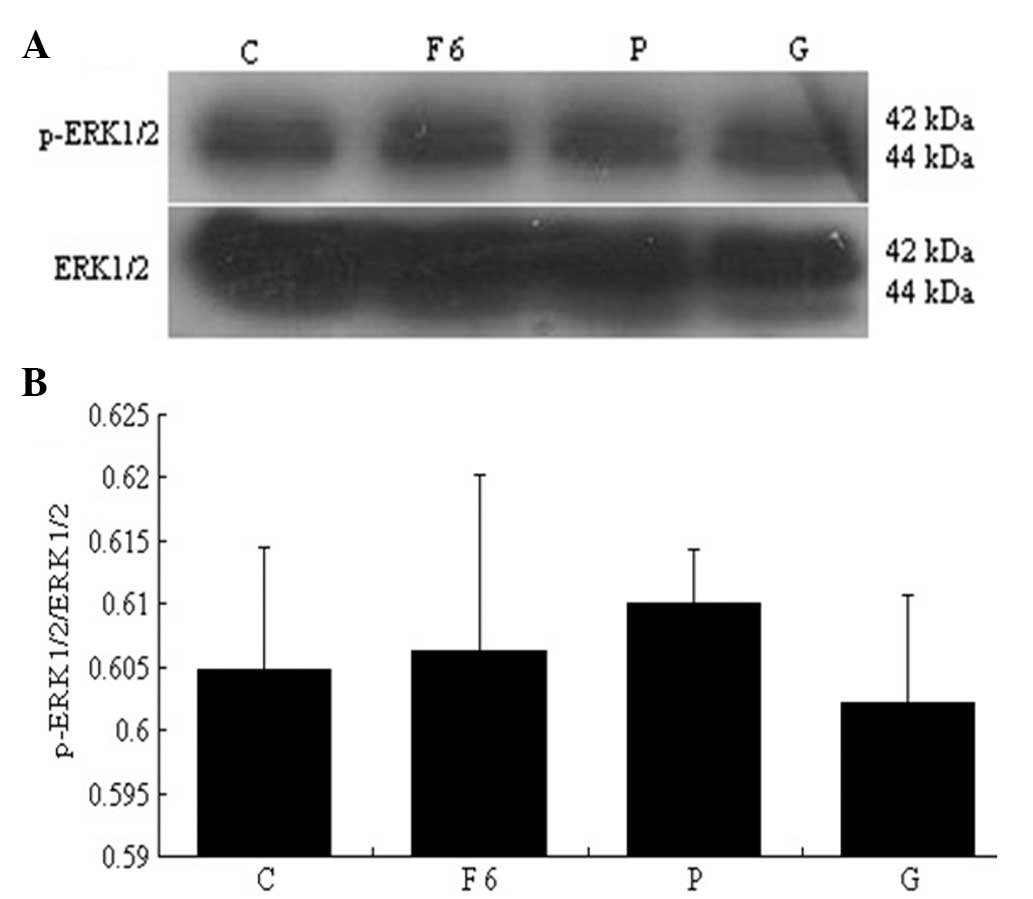
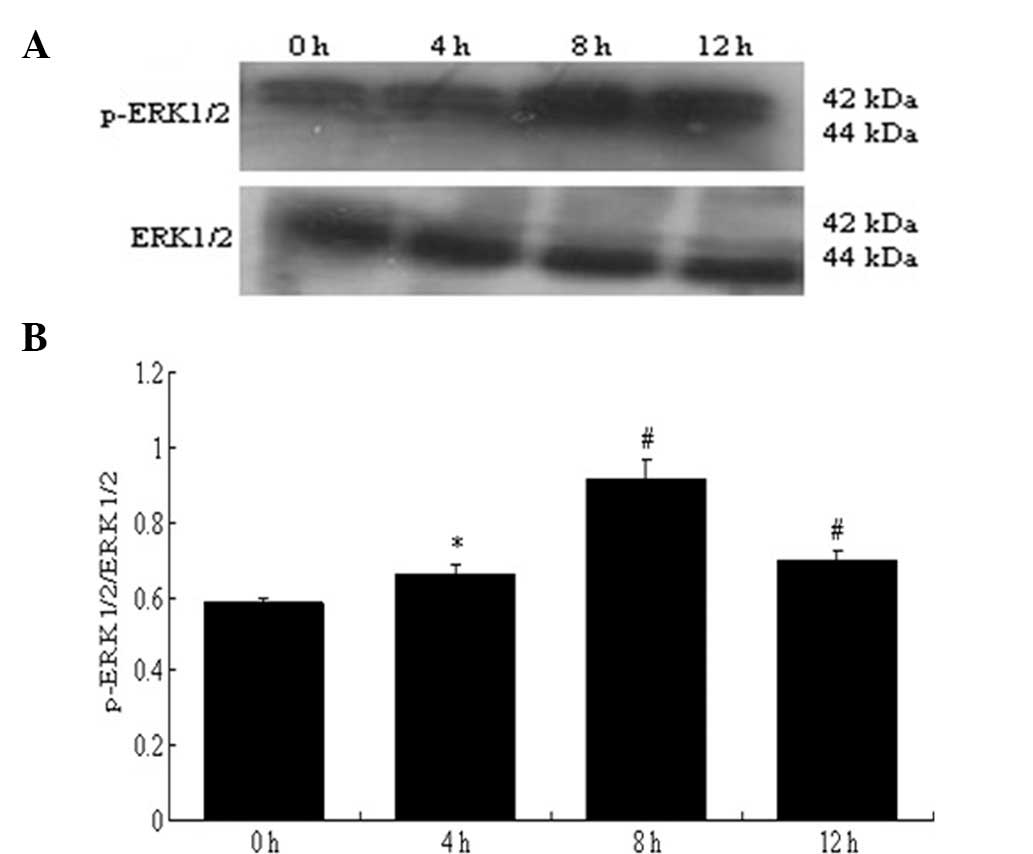
|
1
|
He Z, Potter R, Li X and Flessner M:
Stretch of human mesothelial cells increases cytokine expression.
Adv Perit Dial. 28:2–9. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Loureiro J, Aguilera A, Selgas R, et al:
Blocking TGF-β1 protects the peritoneal membrane from
dialysate-induced damage. J Am Soc Nephrol. 22:1682–1695. 2011.
|
|
3
|
Mizutani M, Ito Y, Mizuno M, et al:
Connective tissue growth factor (CTGF/CCN2) is increased in
peritoneal dialysis patients with high peritoneal solute transport
rate. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 298:F721–F733. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yokoi H, Kasahara M, Mori K, et al:
Peritoneal fibrosis and high transport are induced in mildly
pre-injured peritoneum by 3,4-didexoxyglucosone-3-ene in mice.
Perit Dial Int. 33:143–154. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Heimbürger O, Waniewski J, Werynski A, et
al: Peritoneal transport in CAPD patients with permanent loss of
ultrafiltration capacity. Kidney Int. 38:495–506. 1990.
|
|
6
|
Davies SJ, Phillips L, Naish PF and
Russell GI: Peritoneal glucose exposure and changes in membrane
solute transport with time on peritoneal dialysis. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 12:1046–1051. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Plum J, Hermann S, Fussholler A, et al:
Peritoneal sclerosis in peritoneal dialysis patients related to
dialysis settings and peritoneal transport properties. Kidney Int
Suppl. 78:S42–S47. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zweers MM, de Waart DR, Smit W, et al:
Growth factors VEGF and TGF-beta1 in peritoneal dialysis. J Lab
Clin Med. 134:124–132. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zweers MM, Struijk DG, Smit W and Krediet
RT: Vascular endothelial growth factor in peritoneal dialysis: a
longitudinal follow-up. J Lab Clin Med. 137:125–132. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Milner PG, Li YS, Hoffman RM, et al: A
novel 17 kD heparin-binding growth factor (HBGF-8) in bovine
uterus: purification and N-terminal amino acid sequence. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 165:1096–1103. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rauvala H: An 18-kd heparin-binding
protein of developing brain that is distinct from fibroblast growth
factors. EMBO J. 8:2933–2941. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Deuel TF, Zhang N, Yeh HJ, et al:
Pleiotrophin: a cytokine with diverse functions and a novel
signaling pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys. 397:162–171. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kohashi T, Tateaki Y, Tateno C, et al:
Expression of pleiotrophin in hepatic nonparenchymal cells and
preneoplastic nodules in carbon tetrachloride-induced fibrotic rat
liver. Growth Factors. 20:53–60. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Henger A, Kretzler M, Doran P, et al: Gene
expression fingerprints in human tubulointerstitial inflammation
and fibrosis as prognostic markers of disease progression. Kidney
Int. 65:904–917. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yokoi H, Kasahara M, Mori K, et al:
Pleiotrophin triggers inflammation and increased peritoneal
permeability leading to peritoneal fibrosis. Kidney Int.
81:160–169. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jorres A and Witowski J: PD membrane:
biological responses to different PD fluids. Contrib Nephrol.
150:48–53. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vrtovsnik F, Coester AM, Lopes-Barreto D,
et al: Induction of chronic kidney failure in a long-term
peritoneal exposure model in the rat: effects on functional and
structural peritoneal alterations. Perit Dial Int. 30:558–569.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
De Vriese AS, Mortier S and Lameire NH:
Glucotoxicity of the peritoneal membrane: the case for VEGF.
Nephrol Dial Transplant. 16:2299–2302. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Szeto CC, Wong TY, Lai KB, et al: The role
of vascular endothelial growth factor in peritoneal
hyperpermeability during CAPD-related peritonitis. Perit Dial Int.
22:265–267. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kong Y, Bai PS, Nan KJ, et al:
Pleiotrophin is a potential colorectal cancer prognostic factor
that promotes VEGF expression and induces angiogenesis in
colorectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis. 27:287–298. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Saad S, Stevens VA, Wassef L, et al: High
glucose transactivates the EGF receptor and up-regulates serum
glucocorticoid kinase in the proximal tubule. Kidney Int.
68:985–997. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Waldegger S, Barth P, Raber G and Lang F:
Cloning and characterization of a putative human serine/threonine
protein kinase transcriptionally modified during anisotonic and
isotonic alterations of cell volume. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
94:4440–4445. 1997.
|
|
23
|
Firestone GL, Giampaolo JR and O’Keeffe
BA: Stimulus-dependent regulation of serum and glucocorticoid
inducible protein kinase (SGK) transcription, subcellular
localization and enzymatic activity. Cell Physiol Biochem. 13:1–12.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lang F and Cohen P: Regulation and
physiological roles of serum- and glucocorticoid-induced protein
kinase isoforms. Sci STKE. 2001:re172001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Waerntges S, Klingel K, Weigert C, et al:
Excessive transcription of the human serum- and glucocorticoid
dependent kinase hSGK1 in lung fibrosis. Cell Physiol Biochem.
12:135–142. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fillon S, Klingel K, Warntges S, et al:
Expression of the serine/threonine kinase hSGK1 in chronic viral
hepatitis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 12:47–54. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Roskoski R Jr: ERK1/2 MAP kinases:
structure, function, and regulation. Pharmacol Res. 66:105–143.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhu P, Ren M, Yang C, et al: Involvement
of RAGE, MAPK and NF-κB pathways in AGEs-induced MMP-9 activation
in HaCaT keratinocytes. Exp Dermatol. 21:123–129. 2012.
|
|
29
|
Vasan RS, Sullivan LM, Roubenoff R, et al:
Inflammatory markers and the risk of heart failure in elderly
subjects without prior myocardial infarction: the Framingham heart
study. Circulation. 107:1486–1491. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yokota T, Utsunomiya K, Murakawa Y, et al:
Mechanism of preventive effect of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor on
diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int Suppl. 71:S178–S181. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hayashi M, Tapping RI, Chao TH, et al:
BMK1 mediates growth factor-induced cell proliferation through
direct cellular activation of serum and glucocorticoid-inducible
kinase. J Biol Chem. 276:8631–8634. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mizuno H and Nishida E: The ERK MAP kinase
pathway mediates induction of SGK (serum- and
glucocorticoid-inducible kinase) by growth factors. Genes Cells.
6:261–268. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Meng F, Yamagiwa Y, Taffetani S, et al:
IL-6 activates serum and glucocorticoid kinase via p38alpha
mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 289:C971–C981. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shelly C and Herrera R: Activation of SGK1
by HGF, Rac1 and integrin-mediated cell adhesion in MDCK cells:
PI-3K-dependent and -independent pathways. J Cell Sci.
115:1985–1993. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Prasad N, Topping RS, Zhou D and Decker
SJ: Oxidative stress and vanadate induce tyrosine phosphorylation
of phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1(PDK1). Biochemistry.
39:6929–6935. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|