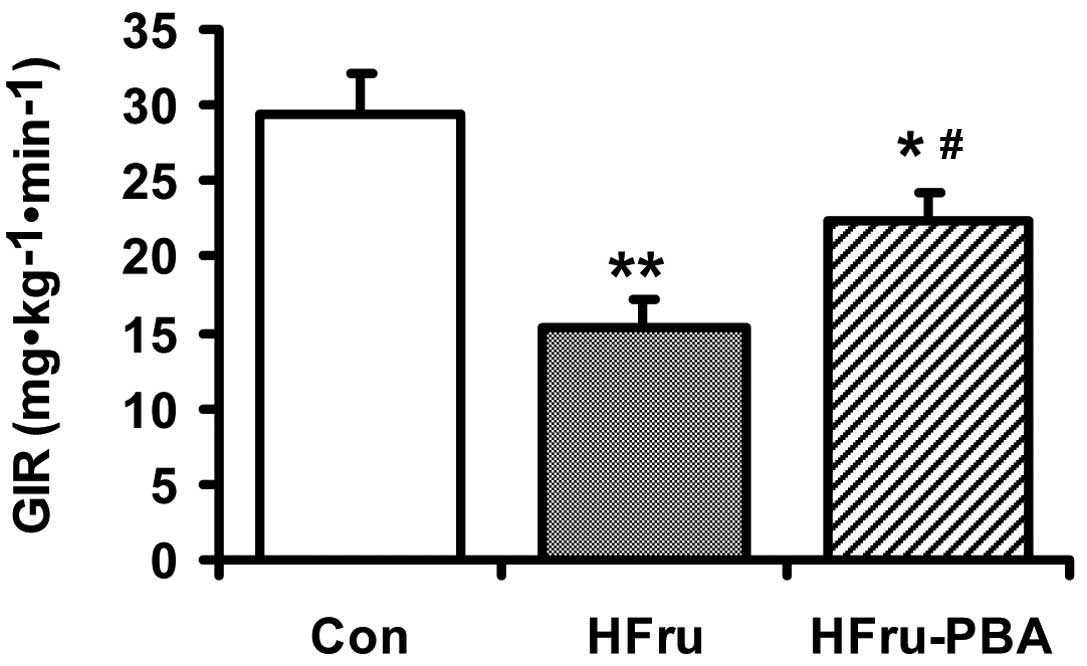
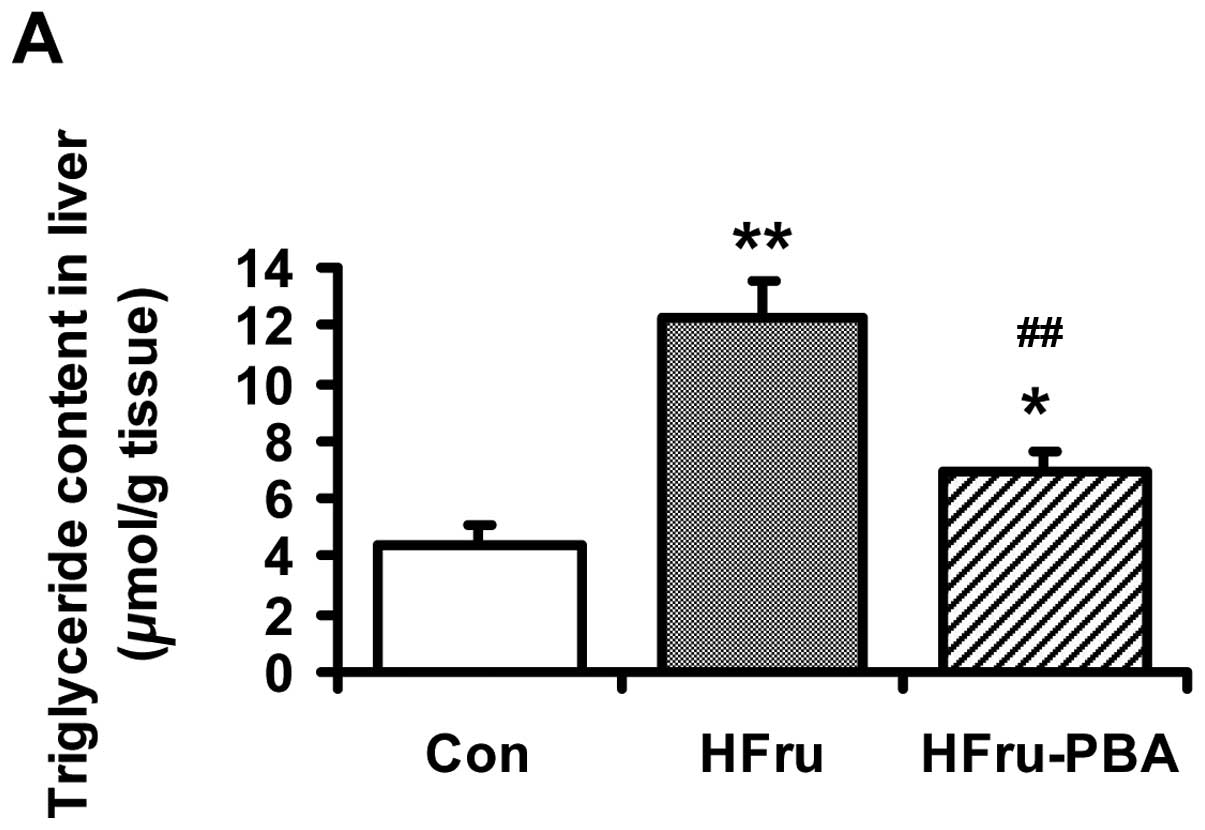
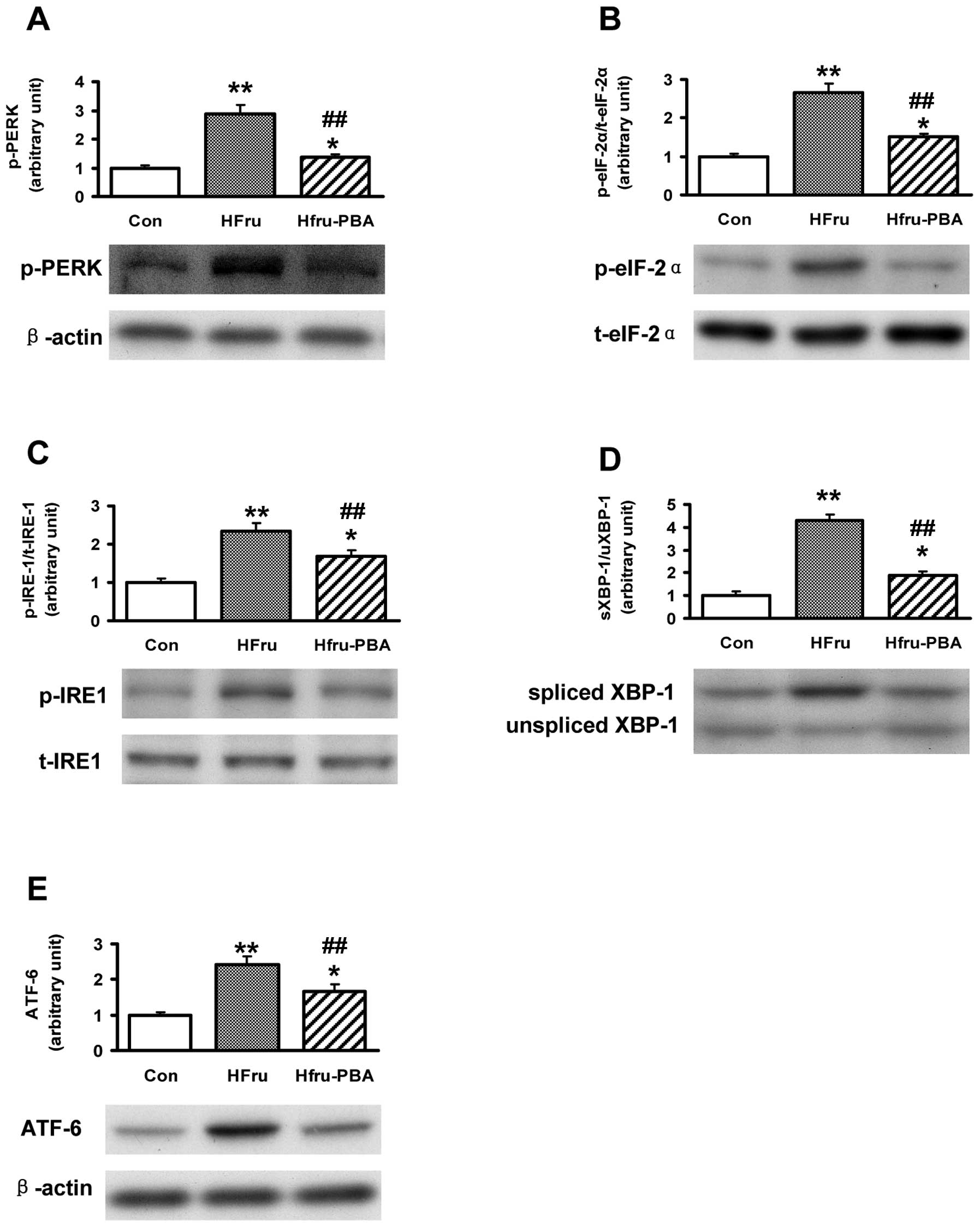
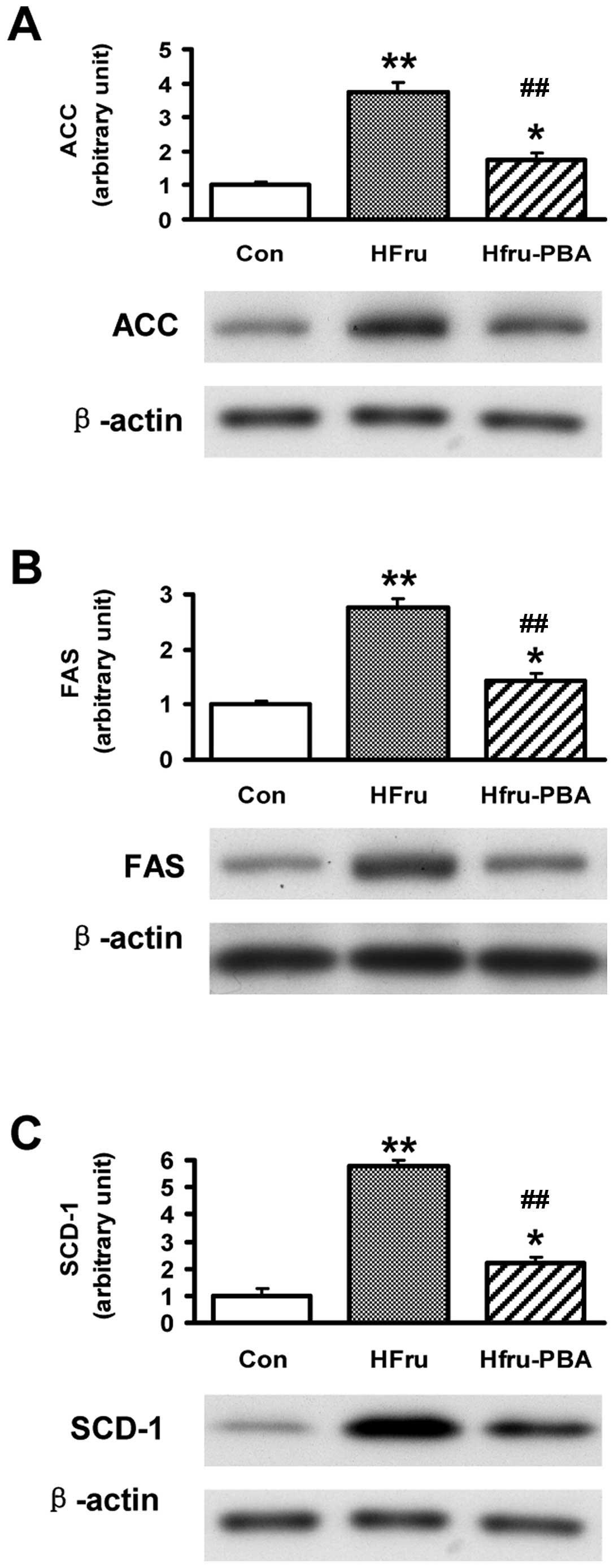
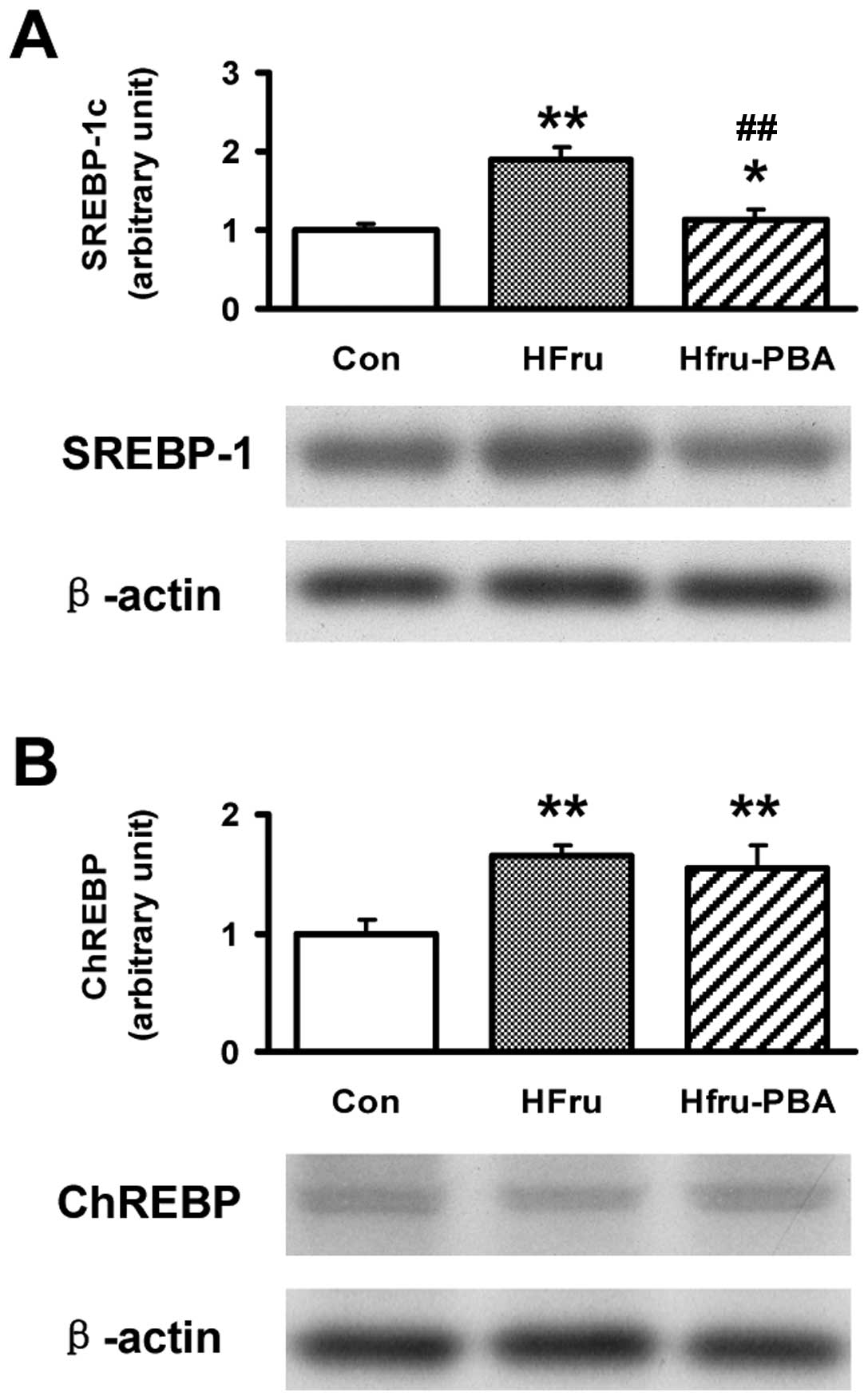
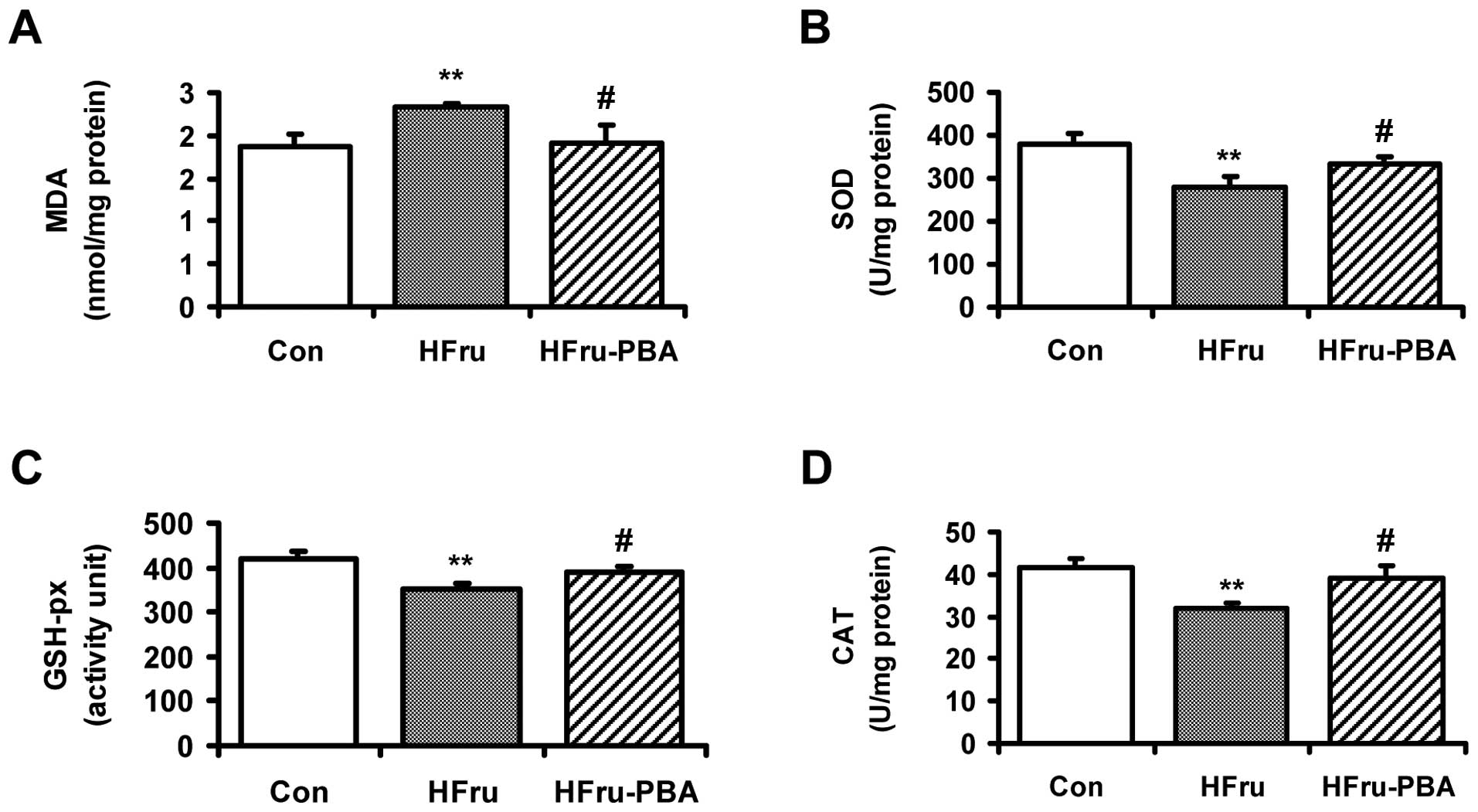
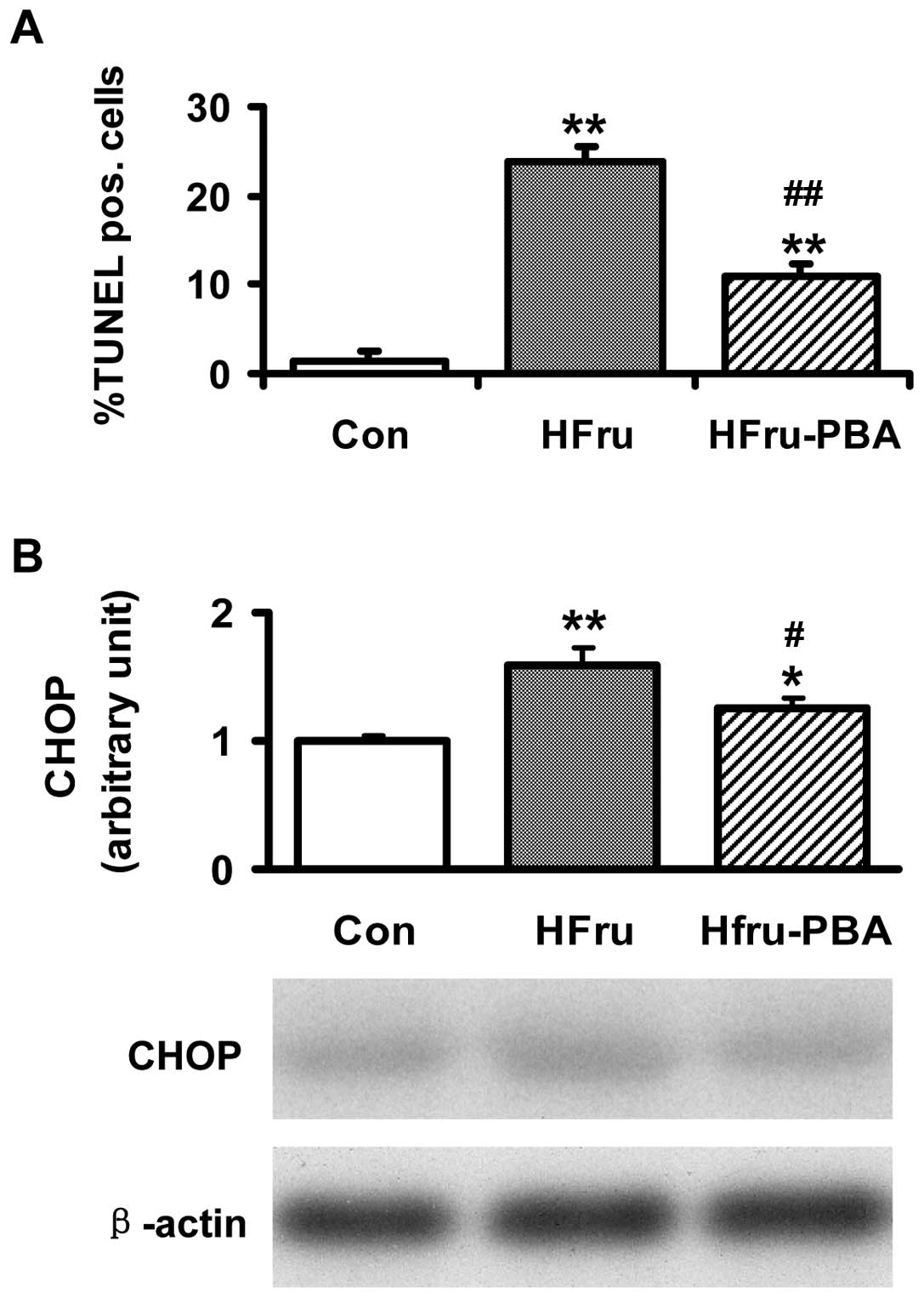
|
1
|
Malavolti M, Battistini NC, Miglioli L, et
al: Influence of lifestyle habits, nutritional status and insulin
resistance in NAFLD. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 4:1015–1023. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cankurtaran M, Tayfur O, Yavuz BB, Geyik
S, Akhan O and Arslan S: Insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome
in patients with NAFLD but without diabetes: effect of a 6 month
regime intervention. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 70:253–259.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Moore JB: Non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease: the hepatic consequence of obesity and the metabolic
syndrome. Proc Nutr Soc. 69:211–220. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Moore JB: Symposium 1: Overnutrition:
consequences and solutions Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: the
hepatic consequence of obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Proc
Nutr Soc. 1–10. 2010.
|
|
5
|
Ouyang X, Cirillo P, Sautin Y, et al:
Fructose consumption as a risk factor for non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease. J Hepatol. 48:993–999. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nomura K and Yamanouchi T: The role of
fructose-enriched diets in mechanisms of nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease. J Nutr Biochem. 23:203–208. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yilmaz Y: Review article: fructose in
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther.
35:1135–1144. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kanuri G, Spruss A, Wagnerberger S,
Bischoff SC and Bergheim I: Role of tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα)
in the onset of fructose-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
in mice. J Nutr Biochem. 22:527–534. 2011.
|
|
9
|
Hsieh PS: Inflammatory change of fatty
liver induced by intraportal low-dose lipopolysaccharide infusion
deteriorates pancreatic insulin secretion in fructose-induced
insulin-resistant rats. Liver Int. 28:1167–1175. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Aragno M, Tomasinelli CE, Vercellinatto I,
et al: SREBP-1c in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease induced by
Western-type high-fat diet plus fructose in rats. Free Radic Biol
Med. 47:1067–1074. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Oyadomari S, Harding HP, Zhang Y,
Oyadomari M and Ron D: Dephosphorylation of translation initiation
factor 2alpha enhances glucose tolerance and attenuates
hepatosteatosis in mice. Cell Metab. 7:520–532. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kammoun HL, Chabanon H, Hainault I, et al:
GRP78 expression inhibits insulin and ER stress-induced SREBP-1c
activation and reduces hepatic steatosis in mice. J Clin Invest.
119:1201–1215. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee AH, Scapa EF, Cohen DE and Glimcher
LH: Regulation of hepatic lipogenesis by the transcription factor
XBP1. Science. 320:1492–1496. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ozcan U, Cao Q, Yilmaz E, et al:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress links obesity, insulin action, and
type 2 diabetes. Science. 306:457–461. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ozcan U, Yilmaz E, Ozcan L, et al:
Chemical chaperones reduce ER stress and restore glucose
homeostasis in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Science.
313:1137–1140. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang JS, Kim JT, Jeon J, et al: Changes in
hepatic gene expression upon oral administration of
taurine-conjugated ursodeoxycholic acid in ob/ob mice. PLoS One.
5:e138582010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ren LP, Chan SM, Zeng XY, et al: Differing
endoplasmic reticulum stress response to excess lipogenesis versus
lipid oversupply in relation to hepatic steatosis and insulin
resistance. PLoS One. 7:e308162012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sewter C, Berger D, Considine RV, et al:
Human obesity and type 2 diabetes are associated with alterations
in SREBP1 isoform expression that are reproduced ex vivo by tumor
necrosis factor-alpha. Diabetes. 51:1035–1041. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ye JM, Doyle PJ, Iglesias MA, Watson DG,
Cooney GJ and Kraegen EW: Peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor (PPAR)-alpha activation lowers muscle lipids and improves
insulin sensitivity in high fat-fed rats: comparison with
PPAR-gamma activation. Diabetes. 50:411–417. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Boncompagni E, Gini E, Ferrigno A, et al:
Decreased apoptosis in fatty livers submitted to subnormothermic
machine-perfusion respect to cold storage. Eur J Histochem.
55:e402011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yu C, Chen Y, Cline GW, et al: Mechanism
by which fatty acids inhibit insulin activation of insulin receptor
substrate-1 (IRS-1)-associated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
activity in muscle. J Biol Chem. 277:50230–50236. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Samuel VT: Fructose induced lipogenesis:
from sugar to fat to insulin resistance. Trends Endocrinol Metab.
22:60–65. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Iizuka K, Bruick RK, Liang G, Horton JD
and Uyeda K: Deficiency of carbohydrate response element-binding
protein (ChREBP) reduces lipogenesis as well as glycolysis. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:7281–7286. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mosbah IB, Zaouali MA, Martel C, et al:
IGL-1 solution reduces endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis
in rat liver transplantation. Cell Death Dis. 3:e2792012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Malhotra JD and Kaufman RJ: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress and oxidative stress: a vicious cycle or a
double-edged sword? Antioxid Redox Signal. 9:2277–2293. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shimizu Y and Hendershot LM: Oxidative
folding: cellular strategies for dealing with the resultant
equimolar production of reactive oxygen species. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 11:2317–2331. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cullinan SB and Diehl JA: Coordination of
ER and oxidative stress signaling: the PERK/Nrf2 signaling pathway.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 38:317–332. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Song B, Scheuner D, Ron D, Pennathur S and
Kaufman RJ: Chop deletion reduces oxidative stress, improves beta
cell function, and promotes cell survival in multiple mouse models
of diabetes. J Clin Invest. 118:3378–3389. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gentile CL, Frye MA and Pagliassotti MJ:
Fatty acids and the endoplasmic reticulum in nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease. Biofactors. 37:8–16. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Back SH, Scheuner D, Han J, et al:
Translation attenuation through eIF2alpha phosphorylation prevents
oxidative stress and maintains the differentiated state in beta
cells. Cell Metab. 10:13–26. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Liu Y, Adachi M, Zhao S, et al: Preventing
oxidative stress: a new role for XBP1. Cell Death Differ.
16:847–857. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cao J, Dai DL, Yao L, et al: Saturated
fatty acid induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis
in human liver cells via the PERK/ATF4/CHOP signaling pathway. Mol
Cell Biochem. 364:115–129. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Alkhouri N, Carter-Kent C and Feldstein
AE: Apoptosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: diagnostic and
therapeutic implications. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
5:201–212. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jin WP, Quan XQ, Meng FP, Cui XD and Piao
HJ: Relationship among hepatocyte apoptosis, P450 2E1 and oxidative
stress in alcoholic liver disease of rats. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing
Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 19:419–421. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
35
|
Haynes CM, Titus EA and Cooper AA:
Degradation of misfolded proteins prevents ER-derived oxidative
stress and cell death. Mol Cell. 15:767–776. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|