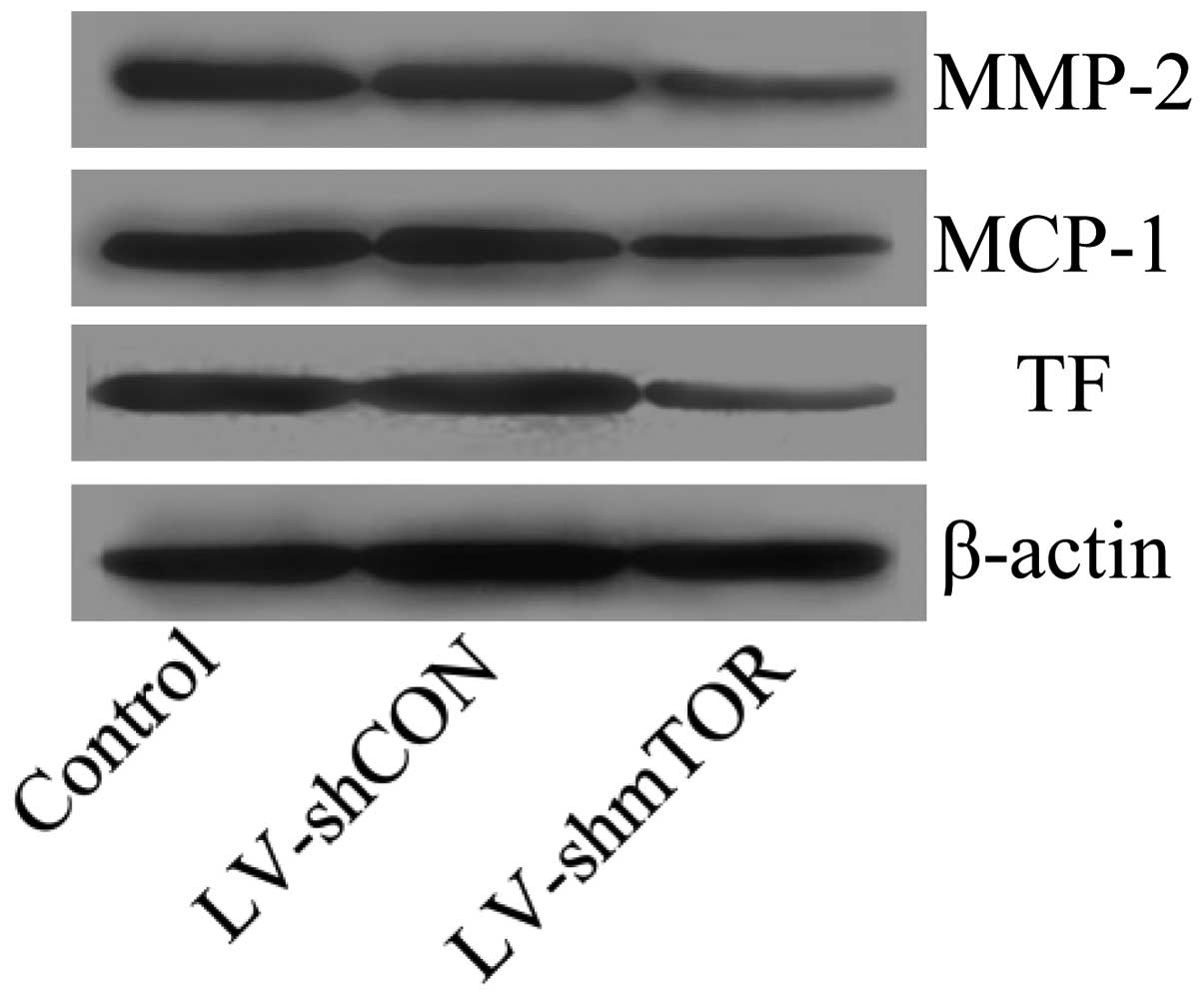
|
1
|
Davies MJ and Thomas AC: Plaque fissuring
- the cause of acute myocardial infarction, sudden ischaemic death,
and crescendo angina. Br Heart J. 53:363–373. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Falk E, Shah PK and Fuster V: Coronary
plaque disruption. Circulation. 92:657–671. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Davies MJ, Richardson PD, Woolf N, Katz DR
and Mann J: Risk of thrombosis in human atherosclerotic plaques:
role of extracellular lipid, macrophage, and smooth muscle cell
content. Br Heart J. 69:377–381. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Virmani R, Burke AP, Farb A and Kolodgie
FD: Pathology of the vulnerable plaque. J Am Coll Cardiol.
47:C13–C18. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mizuno Y, Jacob RF and Mason R:
Inflammation and the development of atherosclerosis. J Atheroscler
Thromb. 18:351–358. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Libby P, Ridker PM and Maseri A:
Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation. 105:1135–1143. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shah PK, Falk E, Badimon JJ, et al: Human
monocyte-derived macrophages induce collagen breakdown in fibrous
caps of atherosclerotic plaques. Potential role of matrix-degrading
metalloproteinases and implications for plaque rupture.
Circulation. 92:1565–1569. 1995.
|
|
8
|
Niu J and Kolattukudy PE: Role of MCP-1 in
cardiovascular disease: molecular mechanisms and clinical
implications. Clin Sci (Lond). 117:95–109. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lwaleed BA, Cooper AJ, Voegeli D and
Getliffe K: Tissue factor: a critical role in inflammation and
cancer. Biol Res Nurs. 9:97–107. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Boyle JJ: Macrophage activation in
atherosclerosis: pathogenesis and pharmacology of plaque rupture.
Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 3:63–68. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Verheye S, Martinet W, Kockx MM, et al:
Selective clearance of macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques by
autophagy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 49:706–715. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Thomas G and Hall MN: TOR signalling and
control of cell growth. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 9:782–787. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dennis PB, Fumagalli S and Thomas G:
Target of rapamycin (TOR): balancing the opposing forces of protein
synthesis and degradation. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 9:49–54. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Easton JB and Houghton PJ: Therapeutic
potential of target of rapamycin inhibitors. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 8:551–564. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Woltman AM, van der Kooij SW, Coffer PJ,
et al: Rapamycin specifically interferes with GM-CSF signaling in
human dendritic cells, leading to apoptosis via increased p27KIP1
expression. Blood. 101:1439–1445. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang S, Shu L, Dilling MB, et al:
Sustained activation of the JNK cascade and rapamycin-induced
apoptosis are suppressed by p53/p21(Cip1). Mol Cell. 11:1491–1501.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ravikumar B, Vacher C, Berger Z, et al:
Inhibition of mTOR induces autophagy and reduces toxicity of
polyglutamine expansions in fly and mouse models of Huntington
disease. Nat Genet. 36:585–595. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Noda T and Ohsumi Y: Tor, a
phosphatidylinositol kinase homologue, controls autophagy in yeast.
J Biol Chem. 273:3963–3966. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Abraham RT and Gibbons JJ: The mammalian
target of rapamycin signaling pathway: twists and turns in the road
to cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 13:3109–3114. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Suzuki T, Kopia G, Hayashi S, et al:
Stent-based delivery of sirolimus reduces neointimal formation in a
porcine coronary model. Circulation. 104:1188–1193. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Elloso MM, Azrolan N, Sehgal SN, et al:
Protective effect of the immunosuppressant sirolimus against aortic
atherosclerosis in apo E-deficient mice. Am J Transplant.
3:562–569. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mizushima N and Komatsu M: Autophagy:
renovation of cells and tissues. Cell. 147:728–741. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang Z and Klionsky DJ: Eaten alive: a
history of macroautophagy. Nat Cell Biol. 12:814–822. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen Y, Lin MC, Yao H, et al:
Lentivirus-mediated RNA interference targeting enhancer of zeste
homolog 2 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth through
down-regulation of stathmin. Hepatology. 46:200–208. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Jiang L, Lai YK, Zhang J, et al: Targeting
S100P inhibits colon cancer growth and metastasis by
lentivirus-mediated RNA interference and proteomic analysis. Mol
Med. 17:709–716. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
von der Thusen JH, van Berkel TJ and
Biessen EA: Induction of rapid atherogenesis by perivascular
carotid collar placement in apolipoprotein E-deficient and
low-density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice. Circulation.
103:1164–1170. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−(Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
|
|
28
|
Levine B and Klionsky DJ: Development by
self-digestion: molecular mechanisms and biological functions of
autophagy. Dev Cell. 6:463–477. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mizushima N: Methods for monitoring
autophagy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 36:2491–2502. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Toth PP: High-density lipoprotein as a
therapeutic target: clinical evidence and treatment strategies. Am
J Cardiol. 96:50K–58K. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ma KL, Ruan XZ, Powis SH, Moorhead JF and
Varghese Z: Anti-atherosclerotic effects of sirolimus on human
vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
292:H2721–H2728. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ma KL, Varghese Z, Ku Y, et al: Sirolimus
inhibits endogenous cholesterol synthesis induced by inflammatory
stress in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Heart
Circ Physiol. 298:H1646–H1651. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Mathis AS, Jin S, Friedman GS, et al: The
pharmacodynamic effects of sirolimus and sirolimus-calcineurin
inhibitor combinations on macrophage scavenger and nuclear hormone
receptors. J Pharm Sci. 96:209–222. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Croons V, Martinet W, Herman AG,
Timmermans JP and De Meyer GR: Selective clearance of macrophages
in atherosclerotic plaques by the protein synthesis inhibitor
cycloheximide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 320:986–993. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Martinet W, Verheye S, De Meyer I, et al:
Everolimus triggers cytokine release by macrophages: rationale for
stents eluting everolimus and a glucocorticoid. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 32:1228–1235. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Huang WP, Scott SV, Kim J and Klionsky DJ:
The itinerary of a vesicle component, Aut7p/Cvt5p, terminates in
the yeast vacuole via the autophagy/Cvt pathways. J Biol Chem.
275:5845–5851. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chan TF, Bertram PG, Ai W and Zheng XF:
Regulation of APG14 expression by the GATA-type transcription
factor Gln3p. J Biol Chem. 276:6463–6467. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Crouzet J, Faucher JF, Toubin M, Hoen B
and Estavoyer JM: Serum C-reactive protein (CRP) and procalcitonin
(PCT) levels and kinetics in patients with leptospirosis. Eur J
Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 30:299–302. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bea F, Blessing E, Bennett B, et al:
Simvastatin promotes atherosclerotic plaque stability in
apoE-deficient mice independently of lipid lowering. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 22:1832–1837. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zaman AG, Helft G, Worthley SG and Badimon
JJ: The role of plaque rupture and thrombosis in coronary artery
disease. Atherosclerosis. 149:251–266. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Morancho A, Rosell A, García-Bonilla L and
Montaner J: Metalloproteinase and stroke infarct size: role for
anti-inflammatory treatment? Ann NY Acad Sci. 1207:123–133. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Deshmane SL, Kremlev S, Amini S and Sawaya
BE: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1): an overview. J
Interferon Cytokine Res. 29:313–326. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Rull A, Beltrán-Debón R, Aragonès G, et
al: Expression of cytokine genes in the aorta is altered by the
deficiency in MCP-1: effect of a high-fat, high-cholesterol diet.
Cytokine. 50:121–128. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu XL, Zhang PF, Ding SF, et al: Local
gene silencing of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 prevents
vulnerable plaque disruption in apolipoprotein E-knockout mice.
PLoS One. 7:e334972012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Jude B, Zawadzki C, Susen S and Corseaux
D: Relevance of tissue factor in cardiovascular disease. Arch Mal
Coeur Vaiss. 98:667–671. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kume N: Molecular mechanisms of coronary
atherosclerotic plaque formation and rupture. Nihon Rinsho.
68:637–641. 2010.(In Japanese).
|
|
47
|
Song E, Lee SK, Wang J, et al: RNA
interference targeting Fas protects mice from fulminant hepatitis.
Nat Med. 9:347–351. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Paroo Z and Corey DR: Challenges for RNAi
in vivo. Trends Biotechnol. 22:390–394. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|