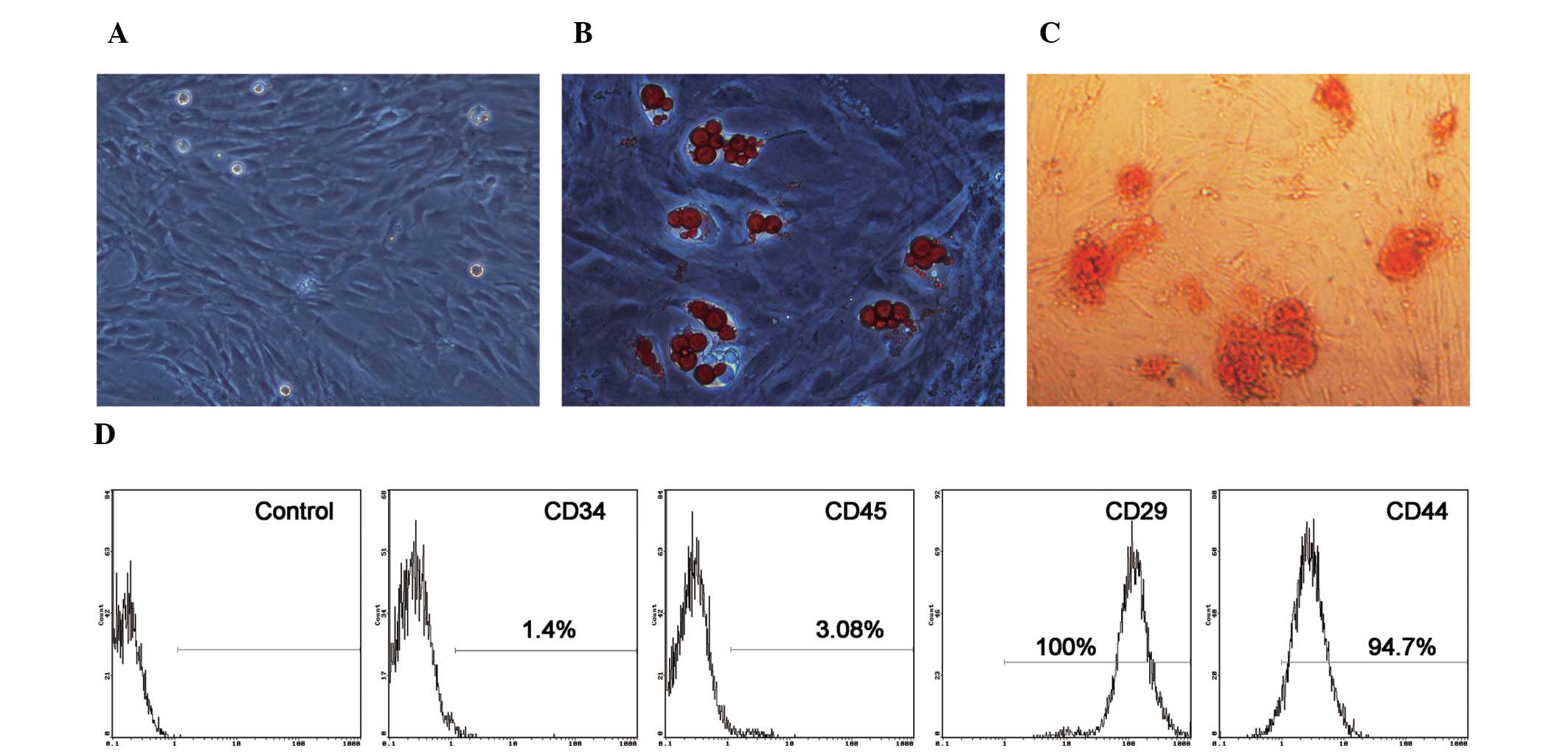
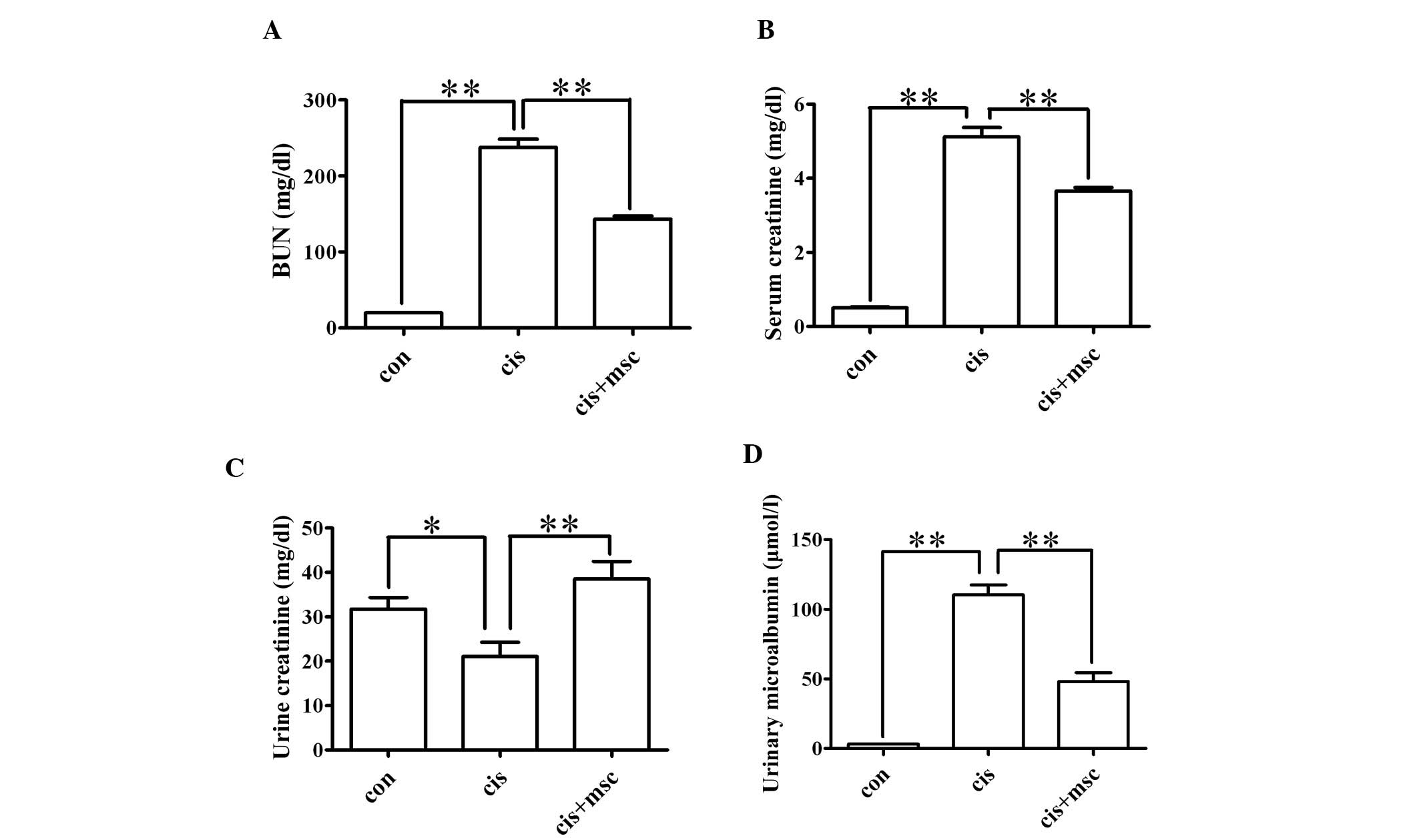
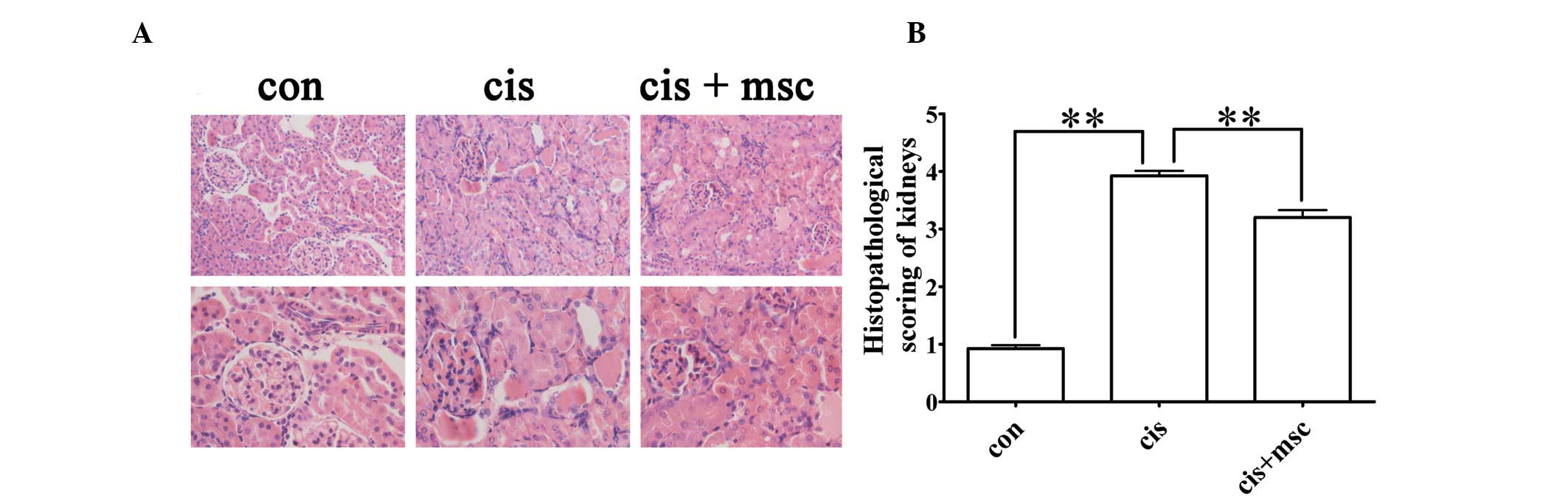
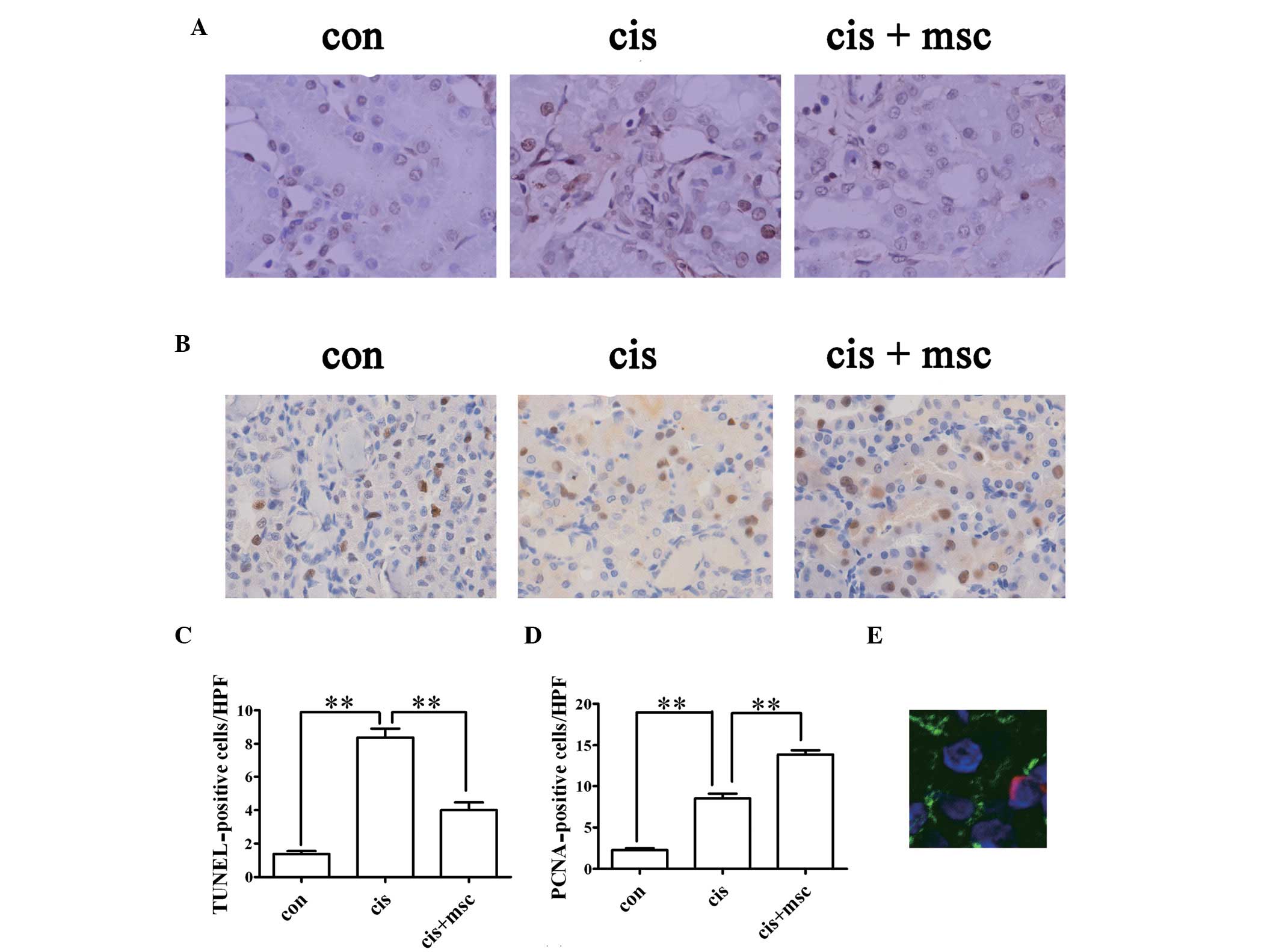
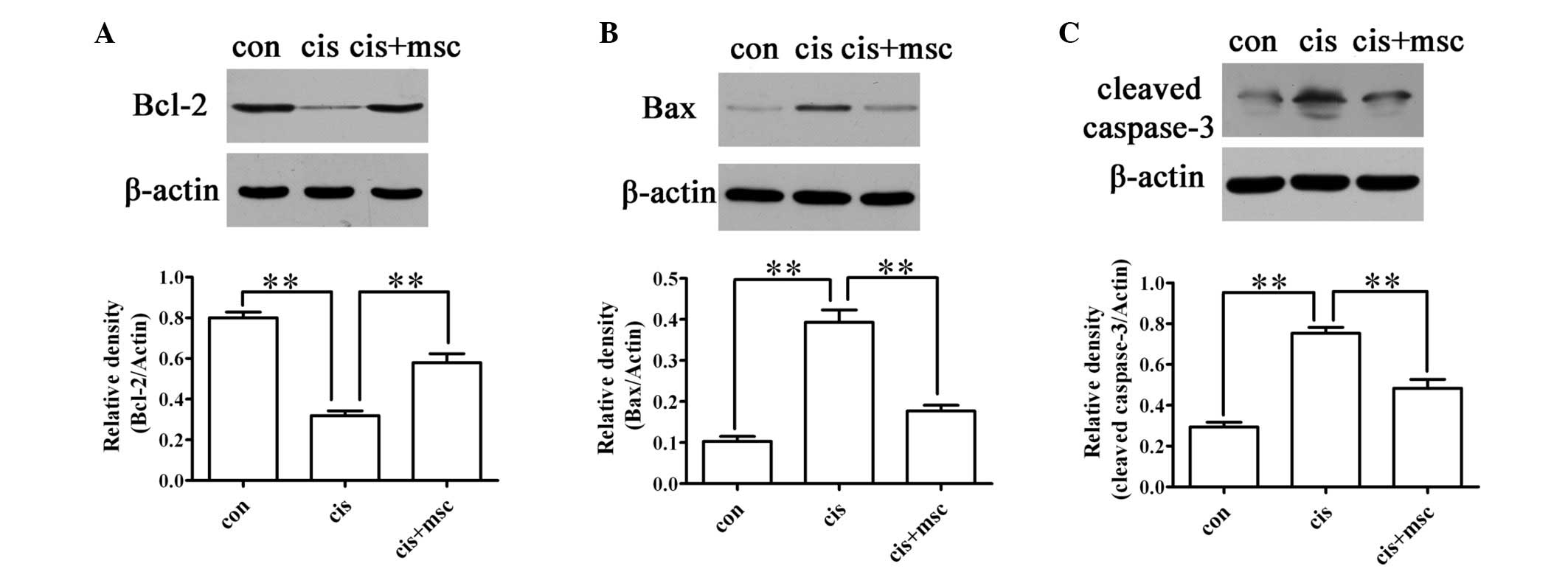
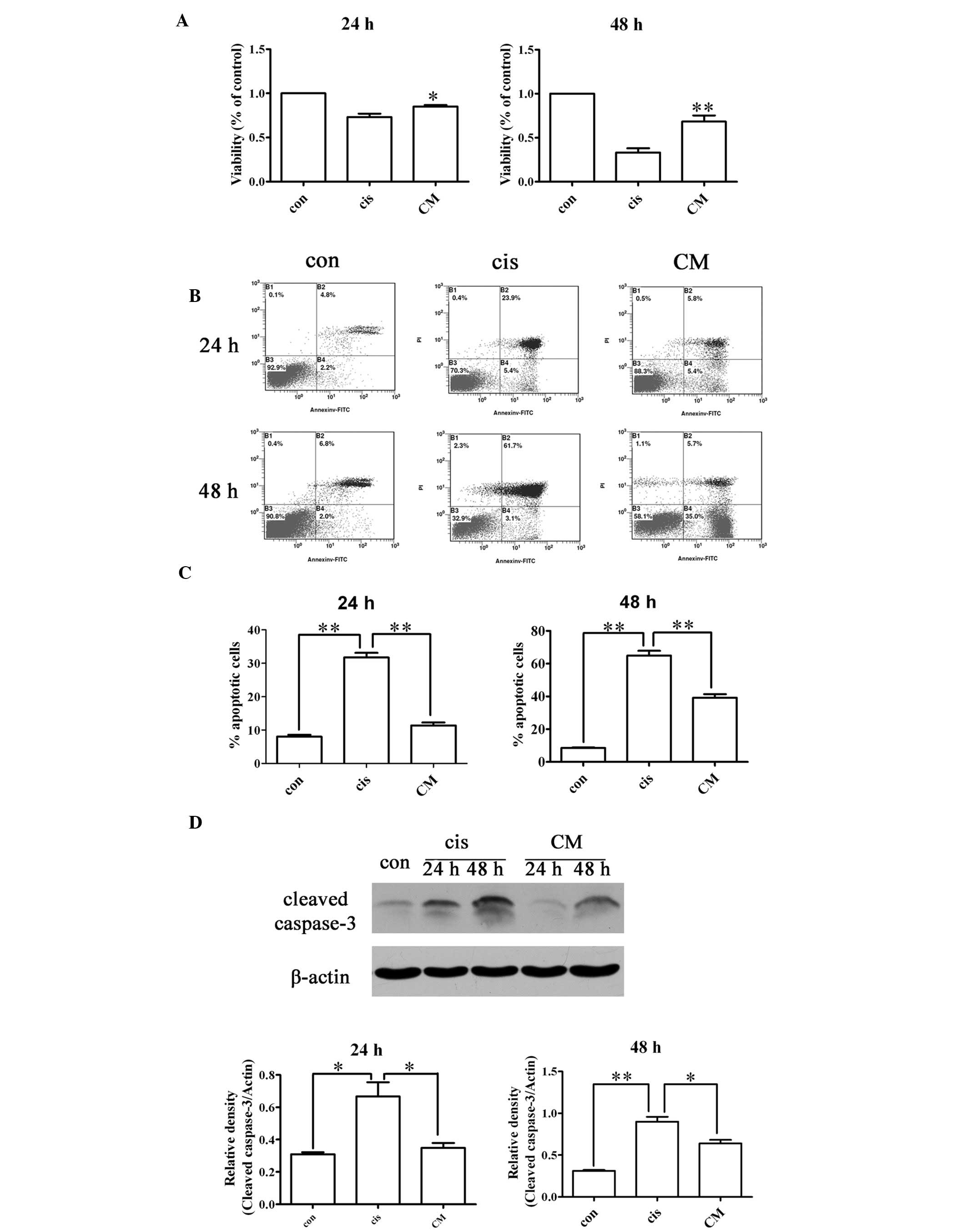
|
1
|
Bagshaw SM: Short- and long-term survival
after acute kidney injury. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 23:2126–2128.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chertow GM, Burdick E, Honour M, Bonventre
JV and Bates DW: Acute kidney injury, mortality, length of stay,
and costs in hospitalized patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 16:3365–3370.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tögel FE and Westenfelder C: Kidney
protection and regeneration following acute injury: progress
through stem cell therapy. Am J Kidney Dis. 60:1012–1022.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Waikar SS, Liu KD and Chertow GM:
Diagnosis, epidemiology and outcomes of acute kidney injury. Clin J
Am Soc Nephrol. 3:844–861. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen YT, Sun CK, Lin YC, et al:
Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell protects kidneys against
ischemia-reperfusion injury through suppressing oxidative stress
and inflammatory reaction. J Transl Med. 9:512011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lange C, Togel F, Ittrich H, et al:
Administered mesenchymal stem cells enhance recovery from
ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute renal failure in rats. Kidney
Int. 68:1613–1617. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tögel F, Hu Z, Weiss K, Isaac J, Lange C
and Westenfelder C: Administered mesenchymal stem cells protect
against ischemic acute renal failure through
differentiation-independent mechanisms. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
289:F31–F42. 2005.
|
|
8
|
Morigi M, Imberti B, Zoja C, et al:
Mesenchymal stem cells are renotropic, helping to repair the kidney
and improve function in acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol.
15:1794–1804. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Morigi M, Introna M, Imberti B, et al:
Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells accelerate recovery of
acute renal injury and prolong survival in mice. Stem Cells.
26:2075–2082. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Morigi M, Rota C, Montemurro T, et al:
Life-sparing effect of human cord blood-mesenchymal stem cells in
experimental acute kidney injury. Stem Cells. 28:513–522.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Herrera MB, Bussolati B, Bruno S, Fonsato
V, Romanazzi GM and Camussi G: Mesenchymal stem cells contribute to
the renal repair of acute tubular epithelial injury. Int J Mol Med.
14:1035–1041. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Herrera MB, Bussolati B, Bruno S, et al:
Exogenous mesenchymal stem cells localize to the kidney by means of
CD44 following acute tubular injury. Kidney Int. 72:430–441. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lazzeri E, Crescioli C, Ronconi E, et al:
Regenerative potential of embryonic renal multipotent progenitors
in acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol. 18:3128–3138. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rota C, Imberti B, Pozzobon M, et al:
Human amniotic fluid stem cell preconditioning improves their
regenerative potential. Stem Cells Dev. 21:1911–1923. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li L, Black R, Ma Z, Yang Q, Wang A and
Lin F: Use of mouse hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells to
treat acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 302:F9–F19.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Horwitz EM, Le Blanc K, Dominici M, et al:
Clarification of the nomenclature for MSC: the international
society for cellular therapy position statement. Cytotherapy.
7:393–395. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jia X, Xie X, Feng G, et al: Bone
marrow-derived cells can acquire renal stem cells properties and
ameliorate ischemia-reperfusion induced acute renal injury. BMC
Nephrology. 13:1052012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yadav N, Rao S, Bhowmik DM and
Mukhopadhyay A: Bone marrow cells contribute to tubular epithelium
regeneration following acute kidney injury induced by mercuric
chloride. Indian J Med Res. 136:211–220. 2012.
|
|
19
|
Bonegio R and Lieberthal W: Role of
apoptosis in the pathogenesis of acute renal failure. Curr Opin
Nephrol Hypertens. 11:301–308. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Havasi A and Borkan SC: Apoptosis and
acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 80:29–40. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yuan L, Wu MJ, Sun HY, et al:
VEGF-modified human embryonic mesenchymal stem cell implantation
enhances protection against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury.
Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 300:F207–F218. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Jo SK, Cho WY, Sung SA, Kim HK and Won NH:
MEK inhibitor, U0126, attenuates cisplatin-induced renal injury by
decreasing inflammation and apoptosis. Kidney Int. 67:458–466.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ramesh G and Reeves WB: p38 MAP kinase
inhibition ameliorates cisplatin nephrotoxicity in mice. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 289:F166–F174. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jiang M, Wei Q, Wang J, et al: Regulation
of PUMA-alpha by p53 in cisplatin-induced renal cell apoptosis.
Oncogene. 25:4056–4066. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wan JX, Zou ZH, You DY, Cui J and Pan YB:
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into
tubular epithelial-like cells in vitro. Cell Biochem Funct.
30:129–138. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bi B, Schmitt R, Israilova M, Nishio H and
Cantley LG: Stromal cells protect against acute tubular injury via
an endocrine effect. J Am Soc Nephrol. 18:2486–2496. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Haynesworth SE, Baber MA and Caplan AI:
Cytokine expression by human marrow-derived mesenchymal progenitor
cells in vitro: effects of dexamethasone and IL-1 alpha. J Cell
Physiol. 166:585–592. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Weimar IS, Miranda N, Muller EJ, et al:
Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor (HGF/SF) is produced by
human bone marrow stromal cells and promotes proliferation,
adhesion and survival of human hematopoietic progenitor cells
(CD34+). Exp Hematol. 26:885–894. 1998.
|
|
29
|
Kim JH, Park DJ, Yun JC, et al: Human
adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells protect kidneys from
cisplatin nephrotoxicity in rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
302:F1141–F1150. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zarjou A, Kim J, Traylor AM, et al:
Paracrine effects of mesenchymal stem cells in cisplatin-induced
renal injury require heme oxygenase-1. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
300:F254–F262. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yasuda H, Kato A, Miyaji T, Zhou H, Togawa
A and Hishida A: Insulin-like growth factor-I increases p21
expression and attenuates cisplatin-induced acute renal injury in
rats. Clin Exp Nephrol. 8:27–35. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nemmar A, Al-Salam S, Zia S, Yasin J, Al
Husseni I and Ali BH: Diesel exhaust particles in the lung
aggravate experimental acute renal failure. Toxicol Sci.
113:267–277. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Du H, Yao W, Fang M and Wu D: ARF triggers
cell G1 arrest by a P53 independent ERK pathway. Mol Cell Biochem.
357:415–422. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tsuruya K, Yotsueda H, Ikeda H, et al:
Involvement of p53-transactivated Puma in cisplatin-induced renal
tubular cell death. Life Sci. 83:550–556. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al:
Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal
cells. The international society for cellular therapy position
statement. Cytotherapy. 8:315–317. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Sheikh-Hamad D, Cacini W, Buckley AR, et
al: Cellular and molecular studies on cisplatin-induced apoptotic
cell death in rat kidney. Arch Toxicol. 78:147–155. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dill T, Schachinger V, Rolf A, et al:
Intracoronary administration of bone marrow-derived progenitor
cells improves left ventricular function in patients at risk for
adverse remodeling after acute ST-segment elevation myocardial
infarction: results of the Reinfusion of Enriched Progenitor cells
And Infarct Remodeling in Acute Myocardial Infarction study
(REPAIR-AMI) cardiac magnetic resonance imaging substudy. Am Heart
J. 157:541–547. 2009.
|
|
38
|
Drexler H, Meyer GP and Wollert KC:
Bone-marrow-derived cell transfer after ST-elevation myocardial
infarction: lessons from the BOOST trial. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc
Med. 3(Suppl 1): S65–S68. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Deng YB, Liu XG, Liu ZG, Liu XL, Liu Y and
Zhou GQ: Implantation of BM mesenchymal stem cells into injured
spinal cord elicits de novo neurogenesis and functional recovery:
evidence from a study in rhesus monkeys. Cytotherapy. 8:210–214.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li Y, Chen J, Zhang CL, et al: Gliosis and
brain remodeling after treatment of stroke in rats with marrow
stromal cells. Glia. 49:407–417. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ezquer F, Ezquer M, Simon V, et al:
Endovenous administration of bone marrow-derived multipotent
mesenchymal stromal cells prevents renal failure in diabetic mice.
Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 15:1354–1365. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Ezquer FE, Ezquer ME, Parrau DB, Carpio D,
Yañez AJ and Conget PA: Systemic administration of multipotent
mesenchymal stromal cells reverts hyperglycemia and prevents
nephropathy in type 1 diabetic mice. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant.
14:631–640. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lieberthal W, Triaca V and Levine J:
Mechanisms of death induced by cisplatin in proximal tubular
epithelial cells: apoptosis vs. necrosis. Am J Physiol.
270:F700–F708. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ramesh G and Reeves WB: TNFR2-mediated
apoptosis and necrosis in cisplatin-induced acute renal failure. Am
J Physiol Renal Physiol. 285:F610–F618. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liu H and Baliga R: Cytochrome P450 2E1
null mice provide novel protection against cisplatin-induced
nephrotoxicity and apoptosis. Kidney Int. 63:1687–1696. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hamar P, Song E, Kokeny G, Chen A, Ouyang
N and Lieberman J: Small interfering RNA targeting Fas protects
mice against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 101:14883–14888. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Price PM, Safirstein RL and Megyesi J:
Protection of renal cells from cisplatin toxicity by cell cycle
inhibitors. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 286:F378–F384. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Santos NA, Bezerra CS, Martins NM, Curti
C, Bianchi ML and Santos AC: Hydroxyl radical scavenger ameliorates
cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by preventing oxidative stress,
redox state unbalance, impairment of energetic metabolism and
apoptosis in rat kidney mitochondria. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
61:145–155. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Owens DM and Keyse SM: Differential
regulation of MAP kinase signalling by dual-specificity protein
phosphatases. Oncogene. 26:3203–3213. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Dhillon AS, Hagan S, Rath O and Kolch W:
MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene. 26:3279–3290.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Rodriguez-Garcia ME, Quiroga AG, Castro J,
Ortiz A, Aller P and Mata F: Inhibition of p38-MAPK potentiates
cisplatin-induced apoptosis via GSH depletion and increases
intracellular drug accumulation in growth-arrested kidney tubular
epithelial cells. Toxicol Sci. 111:413–423. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Sohn SI, Rim HK, Kim YH, et al: The
ameliorative effect of 23-hydroxytormentic acid isolated from
Rubus coreanus on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats.
Biol Pharm Bull. 34:1508–1513. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wei Q, Dong G, Franklin J and Dong Z: The
pathological role of Bax in cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Kidney Int.
72:53–62. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yokoo T, Ohashi T, Shen JS, et al: Human
mesenchymal stem cells in rodent whole-embryo culture are
reprogrammed to contribute to kidney tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 102:3296–3300. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Duffield JS and Bonventre JV: Kidney
tubular epithelium is restored without replacement with bone
marrow-derived cells during repair after ischemic injury. Kidney
Int. 68:1956–1961. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Duffield JS, Park KM, Hsiao LL, et al:
Restoration of tubular epithelial cells during repair of the
postischemic kidney occurs independently of bone marrow-derived
stem cells. J Clin Invest. 115:1743–1755. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|